Active Hexose-Correlated Compound Shows Direct and Indirect Effects against Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Other Reagents
2.2. Tissue Culture
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. Testing of AHCC In Vivo
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
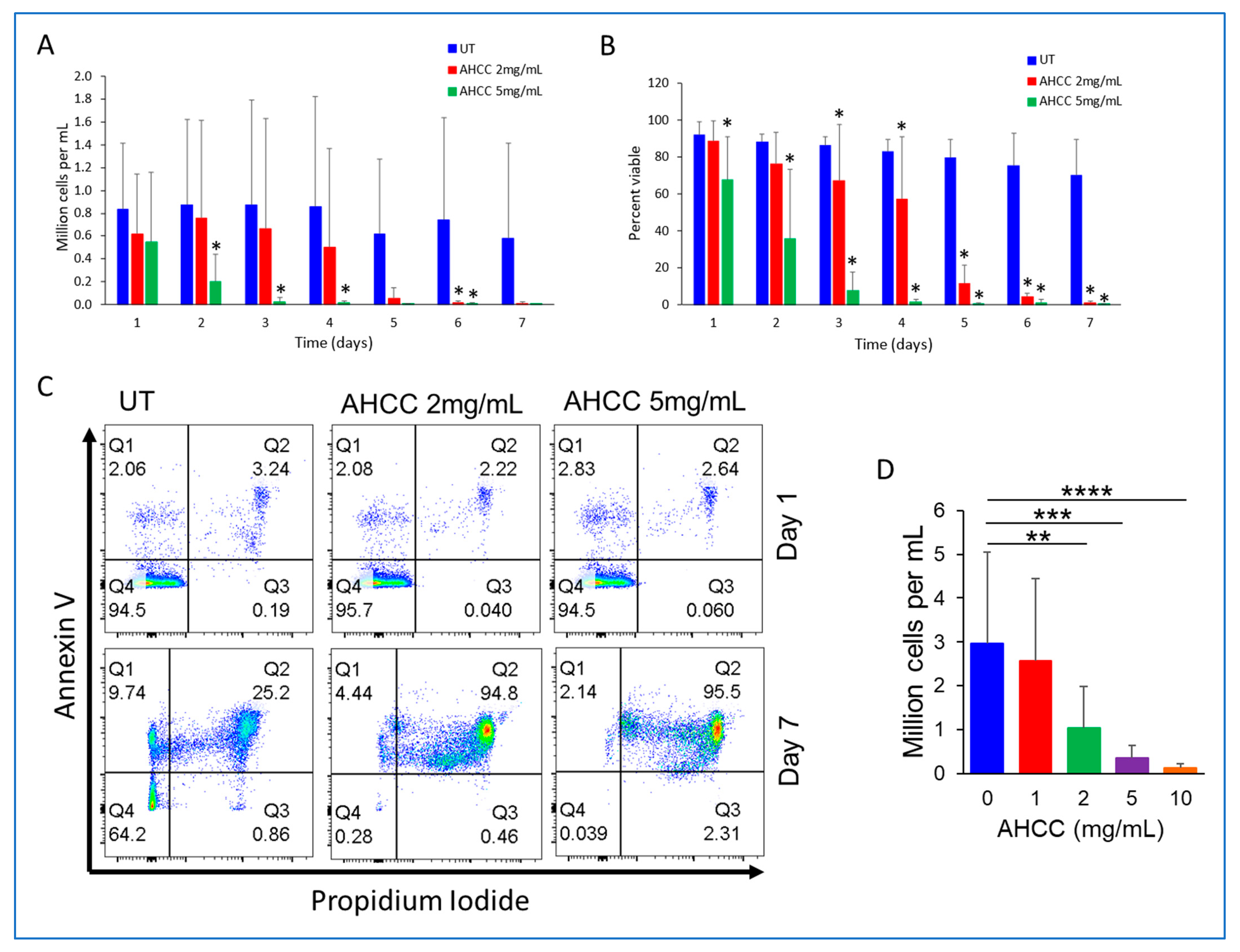
3.1. AHCC Reduces the Viability of CLL Cells
3.2. AHCC Reduces NLC Numbers and Alters Their Phenotype
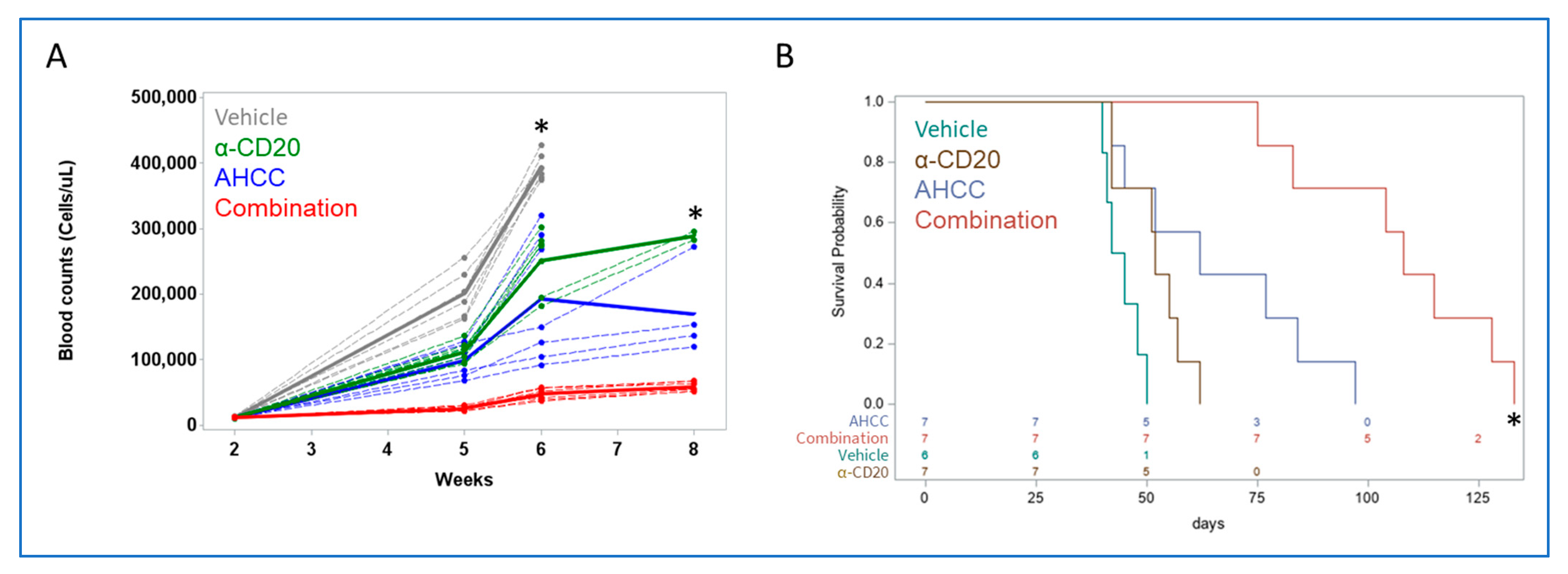
3.3. AHCC Reduces Leukemic Load While Extending Survival in a Mouse Model of CLL
3.4. AHCC Enhances Antibody Effect to Reduce Leukemic Load and Extend Survival In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Scheffold, A.; Stilgenbauer, S. Revolution of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Therapy: The Chemo-Free Treatment Paradigm. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Leukemia—Chronic Lymphocytic—CLL: Statistics. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/leukemia-chronic-lymphocytic-cll/statistics#:~:text=CLL%20makes%20up%2025%25%20of,will%20be%20diagnosed%20with%20CLL (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Bosch, F.; Dalla-Favera, R. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: From genetics to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Rai, K.R. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment: So many choices, such great options. Cancer 2019, 125, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samhouri, Y.; Shah, R.; Khan, C. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Rapidly Changing Treatment Landscape. In Advances in Hematologic Malignancies; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.A.; Tsukada, N.; Burger, M.; Zvaifler, N.J.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Kipps, T.J. Blood-derived nurse-like cells protect chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from spontaneous apoptosis through stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 2000, 96, 2655–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarobkiewicz, M.K.; Bojarska-Junak, A.A. The Mysterious Actor-γδ T Lymphocytes in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL). Cells 2022, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukada, N.; Burger, J.A.; Zvaifler, N.J.; Kipps, T.J. Distinctive features of “nurselike” cells that differentiate in the context of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002, 99, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissard, F.; Laurent, C.; Ramsay, A.G.; Quillet-Mary, A.; Fournie, J.J.; Poupot, M.; Ysebaert, L. Nurse-like cells impact on disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, A.A.; Cisel, B.; Koczkodaj, D.; Wasik-Szczepanek, E.; Piersiak, T.; Dmoszynska, A. Circulating microenvironment of CLL: Are nurse-like cells related to tumor-associated macrophages? Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2013, 50, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissard, F.; Fournie, J.J.; Quillet-Mary, A.; Ysebaert, L.; Poupot, M. Nurse-like cells mediate ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, A.A.; Cisel, B.; Wasik-Szczepanek, E. Guilty bystanders: Nurse-like cells as a model of microenvironmental support for leukemic lymphocytes. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaglio, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Bergui, L.; Bonello, L.; Horenstein, A.L.; Tamagnone, L.; Boumsell, L.; Malavasi, F. CD38 and CD100 lead a network of surface receptors relaying positive signals for B-CLL growth and survival. Blood 2005, 105, 3042–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, M.; Endo, T.; Tsukada, N.; Ohata, J.; Kitada, S.; Reed, J.C.; Zvaifler, N.J.; Kipps, T.J. Nurselike cells express BAFF and APRIL, which can promote survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via a paracrine pathway distinct from that of SDF-1alpha. Blood 2005, 106, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissard, F.; Tosolini, M.; Ligat, L.; Quillet-Mary, A.; Lopez, F.; Fournie, J.J.; Ysebaert, L.; Poupot, M. Nurse-like cells promote CLL survival through LFA-3/CD2 interactions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52225–52236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.A.; Grillo-Lopez, A.J.; White, C.A.; McLaughlin, P.; Czuczman, M.S.; Link, B.K.; Maloney, D.G.; Weaver, R.L.; Rosenberg, J.; Levy, R. Rituximab anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Safety and efficacy of re-treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3135–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, B.S.; Rautela, J.; Hertzog, P.J. Antitumour actions of interferons: Implications for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchar, J.P.; Mehta, P.; Justiniano, S.E.; Guenterberg, K.D.; Kondadasula, S.V.; Mo, X.; Chemudupati, M.; Kanneganti, T.D.; Amer, A.; Muthusamy, N.; et al. Reciprocal regulation of activating and inhibitory Fc{gamma} receptors by TLR7/8 activation: Implications for tumor immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Fatehchand, K.; Patel, H.; Fang, H.; Justiniano, S.E.; Mo, X.; Jarjoura, D.; Tridandapani, S.; Butchar, J.P. Toll-like receptor 2 ligands regulate monocyte Fcgamma receptor expression and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12345–12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basmadjian, C.; Zhao, Q.; Bentouhami, E.; Djehal, A.; Nebigil, C.G.; Johnson, R.A.; Serova, M.; de Gramont, A.; Faivre, S.; Raymond, E.; et al. Cancer wars: Natural products strike back. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddaoua, A.; Martinez-Plata, E.; Ortega-Gonzalez, M.; Ocon, B.; Aranda, C.J.; Zarzuelo, A.; Suarez, M.D.; de Medina, F.S.; Martinez-Augustin, O. The nutritional supplement Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC) has direct immunomodulatory actions on intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages involving TLR/MyD88 and NF-kappaB/MAPK activation. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, B.; Fujii, H.; Kosuna, K.; Yin, Z. Active hexose correlated compound enhances tumor surveillance through regulating both innate and adaptive immune responses. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2006, 55, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Uhara, J.; Satoi, S.; Kaibori, M.; Yamada, H.; Kitade, H.; Imamura, A.; Takai, S.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kwon, A.H.; et al. Improved prognosis of postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma patients when treated with functional foods: A prospective cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2002, 37, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, K.; Kuramitsu, Y.; Ohiro, Y.; Obara, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Li, Y.Q.; Hosokawa, M. Combination therapy of active hexose correlated compound plus UFT significantly reduces the metastasis of rat mammary adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Drugs 1998, 9, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Nishioka, N.; Simon, R.R.; Kaur, R.; Lynch, B.; Roberts, A. Genotoxicity and subchronic toxicity evaluation of Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 59, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowawintaweewat, S.; Manoromana, S.; Sriplung, H.; Khuhaprema, T.; Tongtawe, P.; Tapchaisri, P.; Chaicumpa, W. Prognostic improvement of patients with advanced liver cancer after active hexose correlated compound (AHCC) treatment. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 24, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parida, D.K.; Wakame, K.; Nomura, T. Integrating Complimentary and Alternative Medicine in Form of Active Hexose Co-Related Compound (AHCC) in the Management of Head & Neck Cancer Patients. Int. J. Clin. Med. 2011, 2, 588–592. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka, R.; Fujii, H.; Miura, T.; Fukuchi, Y.; Tajima, K. Personalized cancer therapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer: Combined use of active hexose correlated compound and genistein concentrated polysaccharide. Pers. Med. Universe 2012, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, E.L.; Fujii, H.; Sun, B.; Walshe, T. A Phase I study of the safety of the nutritional supplement, active hexose correlated compound, AHCC, in healthy volunteers. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2007, 53, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacio, R.M.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, H.M.; Qi, X.F.; Kim, S.K. Therapeutic effect of Active Hexose-Correlated Compound (AHCC) combined with CpG-ODN (oligodeoxynucleotide) in B16 melanoma murine model. Cytokine 2015, 76, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetvicka, V.; Vetvickova, J. Immune-enhancing effects of Maitake (Grifola frondosa) and Shiitake (Lentinula edodes) extracts. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Belay, T.; Fu, C.L.; Woart, A. Active Hexose Correlated Compound Activates Immune Function to Decrease Chlamydia trachomatis Shedding in a Murine Stress Model. J. Nutr. Med. Diet. Care 2015, 1, JNMDC-1-006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.W.; Lee, N.; Fujii, H.; Kang, I. Active Hexose Correlated Compound promotes T helper (Th) 17 and 1 cell responses via inducing IL-1beta production from monocytes in humans. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 275, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Fujii, H.; Walshe, T. Effects of active hexose correlated compound on frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells producing interferon-gamma and/or tumor necrosis factor-alpha in healthy adults. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takanari, J.; Hirayama, Y.; Homma, K.; Miura, T.; Nishioka, H.; Maeda, T. Effects of active hexose correlated compound on the seasonal variations of immune competence in healthy subjects. J. Evid.-Based Integr. Med. 2015, 20, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terakawa, N.; Matsui, Y.; Satoi, S.; Yanagimoto, H.; Takahashi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamao, J.; Takai, S.; Kwon, A.H.; Kamiyama, Y. Immunological effect of active hexose correlated compound (AHCC) in healthy volunteers: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suknikhom, W.; Lertkhachonsuk, R.; Manchana, T. The Effects of Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC) on Levels of CD4+ and CD8+ in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer or Peritoneal Cancer Receiving Platinum Based Chemotherapy. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aviles, H.; O’Donnell, P.; Orshal, J.; Fujii, H.; Sun, B.; Sonnenfeld, G. Active hexose correlated compound activates immune function to decrease bacterial load in a murine model of intramuscular infection. Am. J. Surg. 2008, 195, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, B.W.; Nogusa, S.; Ackerman, E.A.; Gardner, E.M. Supplementation with active hexose correlated compound increases the innate immune response of young mice to primary influenza infection. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2868–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehchand, K.; Santhanam, R.; Shen, B.; Erickson, E.L.; Gautam, S.; Elavazhagan, S.; Mo, X.; Belay, T.; Tridandapani, S.; Butchar, J.P. Active hexose-correlated compound enhances extrinsic-pathway-mediated apoptosis of Acute Myeloid Leukemic cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Fatehchand, K.; Elavazhagan, S.; Reader, B.F.; Ren, L.; Mo, X.; Byrd, J.C.; Tridandapani, S.; Butchar, J.P. Reprogramming Nurse-like Cells with Interferon γ to Interrupt Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cell Survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 14356–14362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buteyn, N.J.; Santhanam, R.; Merchand-Reyes, G.; Murugesan, R.A.; Dettorre, G.M.; Byrd, J.C.; Sarkar, A.; Vasu, S.; Mundy-Bosse, B.L.; Butchar, J.P.; et al. Activation of the Intracellular Pattern Recognition Receptor NOD2 Promotes Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cell Apoptosis and Provides a Survival Advantage in an Animal Model of AML. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorko, N.A.; Bernot, K.M.; Whitman, S.P.; Siebenaler, R.F.; Ahmed, E.H.; Marcucci, G.G.; Yanes, D.A.; McConnell, K.K.; Mao, C.; Kalu, C.; et al. Mll partial tandem duplication and Flt3 internal tandem duplication in a double knock-in mouse recapitulates features of counterpart human acute myeloid leukemias. Blood 2012, 120, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernot, K.M.; Nemer, J.S.; Santhanam, R.; Liu, S.; Zorko, N.A.; Whitman, S.P.; Dickerson, K.E.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; McConnell, K.K.; et al. Eradicating acute myeloid leukemia in a Mll(PTD/wt):Flt3(ITD/wt) murine model: A path to novel therapeutic approaches for human disease. Blood 2013, 122, 3778–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichi, R.; Shinton, S.A.; Martin, E.S.; Koval, A.; Calin, G.A.; Cesari, R.; Russo, G.; Hardy, R.R.; Croce, C.M. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted TCL1 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6955–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubna, A.K. Imiquimod—Its role in the treatment of cutaneous malignancies. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzio, M.; Fonte, E.; Caligaris-Cappio, F. Toll-like Receptors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 4, e2012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.A.; Mahajan, S.; Ritz, J. B lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia contain signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3 constitutively phosphorylated on serine residues. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 3140–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severin, F.; Frezzato, F.; Visentin, A.; Martini, V.; Trimarco, V.; Carraro, S.; Tibaldi, E.; Brunati, A.M.; Piazza, F.; Semenzato, G.; et al. In Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Is Constitutively Activated and Its Inhibition Leads to CLL Cell Death Unaffected by the Protective Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Yun, S.M.; Suh, D.H.; Kim, K.; No, J.H.; Jeong, E.H.; Kim, Y.B. Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC) Inhibits the Proliferation of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Suppressing Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Activation. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Walker, S.R.; Heppler, L.N.; Tyekucheva, S.; Nelson, E.A.; Klitgaard, J.; Nicolais, M.; Kroll, Y.; Xiang, M.; Yeh, J.E.; et al. Targeting constitutively active STAT3 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A clinical trial of the STAT3 inhibitor pyrimethamine with pharmacodynamic analyses. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, E95–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarubin, T.; Han, J. Activation and signaling of the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulavin, D.V.; Saito, S.; Hollander, M.C.; Sakaguchi, K.; Anderson, C.W.; Appella, E.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Phosphorylation of human p53 by p38 kinase coordinates N-terminal phosphorylation and apoptosis in response to UV radiation. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 6845–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skytthe, M.K.; Graversen, J.H.; Moestrup, S.K. Targeting of CD163+ Macrophages in Inflammatory and Malignant Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagala, M.; Ysebaert, L.; Ligat, L.; Lopez, F.; Fournie, J.J.; Laurent, C.; Poupot, M. IL-10 Rescues CLL Survival through Repolarization of Inflammatory Nurse-like Cells. Cancers 2021, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Jiang, L.; Ye, C.; Qin, G.; Luo, Z.; Mo, Y.; Chen, J. The Ratio of CD86+/CD163+ Macrophages Predicts Postoperative Recurrence in Stage II-III Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 724429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfroi, B.; De Grandis, M.; Moreaux, J.; Tabruyn, S.; Mayol, J.F.; Quintero, M.; Righini, C.; Sturm, N.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Huard, B. The microenvironment of DLBCL is characterized by noncanonical macrophages recruited by tumor-derived CCL5. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4338–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchand-Reyes, G.; Santhanam, R.; Robledo-Avila, F.H.; Weigel, C.; Ruiz-Rosado, J.D.; Mo, X.; Partida-Sánchez, S.; Woyach, J.A.; Oakes, C.C.; Tridandapani, S.; et al. Disruption of Nurse-like Cell Differentiation as a Therapeutic Strategy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirosawa, M.; Nakahara, M.; Otosaka, R.; Imoto, A.; Okazaki, T.; Takahashi, S. The p38 pathway inhibitor SB202190 activates MEK/MAPK to stimulate the growth of leukemia cells. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hofmann, P.A. Protein phosphatase 2A-mediated cross-talk between p38 MAPK and ERK in apoptosis of cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 286, H2204–H2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fey, D.; Croucher, D.R.; Kolch, W.; Kholodenko, B.N. Crosstalk and signaling switches in mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, B.S.; McClanahan, F.; Yazdanparast, H.; Zaborsky, N.; Kalter, V.; Rossner, P.M.; Benner, A.; Durr, C.; Egle, A.; Gribben, J.G.; et al. Depletion of CLL-associated patrolling monocytes and macrophages controls disease development and repairs immune dysfunction in vivo. Leukemia 2016, 30, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Brown, J.R. Targeting Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase in CLL. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 687458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merchand-Reyes, G.; Santhanam, R.; Valencia-Pena, M.L.; Kumar, K.; Mo, X.; Belay, T.; Woyach, J.A.; Mundy-Bosse, B.; Tridandapani, S.; Butchar, J.P. Active Hexose-Correlated Compound Shows Direct and Indirect Effects against Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245138
Merchand-Reyes G, Santhanam R, Valencia-Pena ML, Kumar K, Mo X, Belay T, Woyach JA, Mundy-Bosse B, Tridandapani S, Butchar JP. Active Hexose-Correlated Compound Shows Direct and Indirect Effects against Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Nutrients. 2023; 15(24):5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245138
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerchand-Reyes, Giovanna, Ramasamy Santhanam, Maria L. Valencia-Pena, Krishan Kumar, Xiaokui Mo, Tesfaye Belay, Jennifer A. Woyach, Bethany Mundy-Bosse, Susheela Tridandapani, and Jonathan P. Butchar. 2023. "Active Hexose-Correlated Compound Shows Direct and Indirect Effects against Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" Nutrients 15, no. 24: 5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245138
APA StyleMerchand-Reyes, G., Santhanam, R., Valencia-Pena, M. L., Kumar, K., Mo, X., Belay, T., Woyach, J. A., Mundy-Bosse, B., Tridandapani, S., & Butchar, J. P. (2023). Active Hexose-Correlated Compound Shows Direct and Indirect Effects against Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Nutrients, 15(24), 5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245138






