Cholesterol Exacerbates the Pathophysiology of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Upregulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Modulating Microcirculatory Dysfunction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Procedures
2.2. Fasting Blood Glucose
2.3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
2.4. Quantification of Insulin
2.5. Insulin Resistance Index (HOMA-IR)
2.6. Biochemical Parameters
2.7. Histopathology
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Total and Differential Counts of White Blood Cells
2.10. Quantification of Hepatic Myeloperoxidase
2.11. Flow Cytometry
2.12. RT-PCR
2.13. Microcirculation Parameters
2.13.1. Intravital Microscopy
2.13.2. Blood Flow Measurement by Laser Speckle
2.14. Statistical Analyzes
3. Results
3.1. Cholesterol Affects Metabolic and Hepatic Parameters in Mice on the HFHC Diet
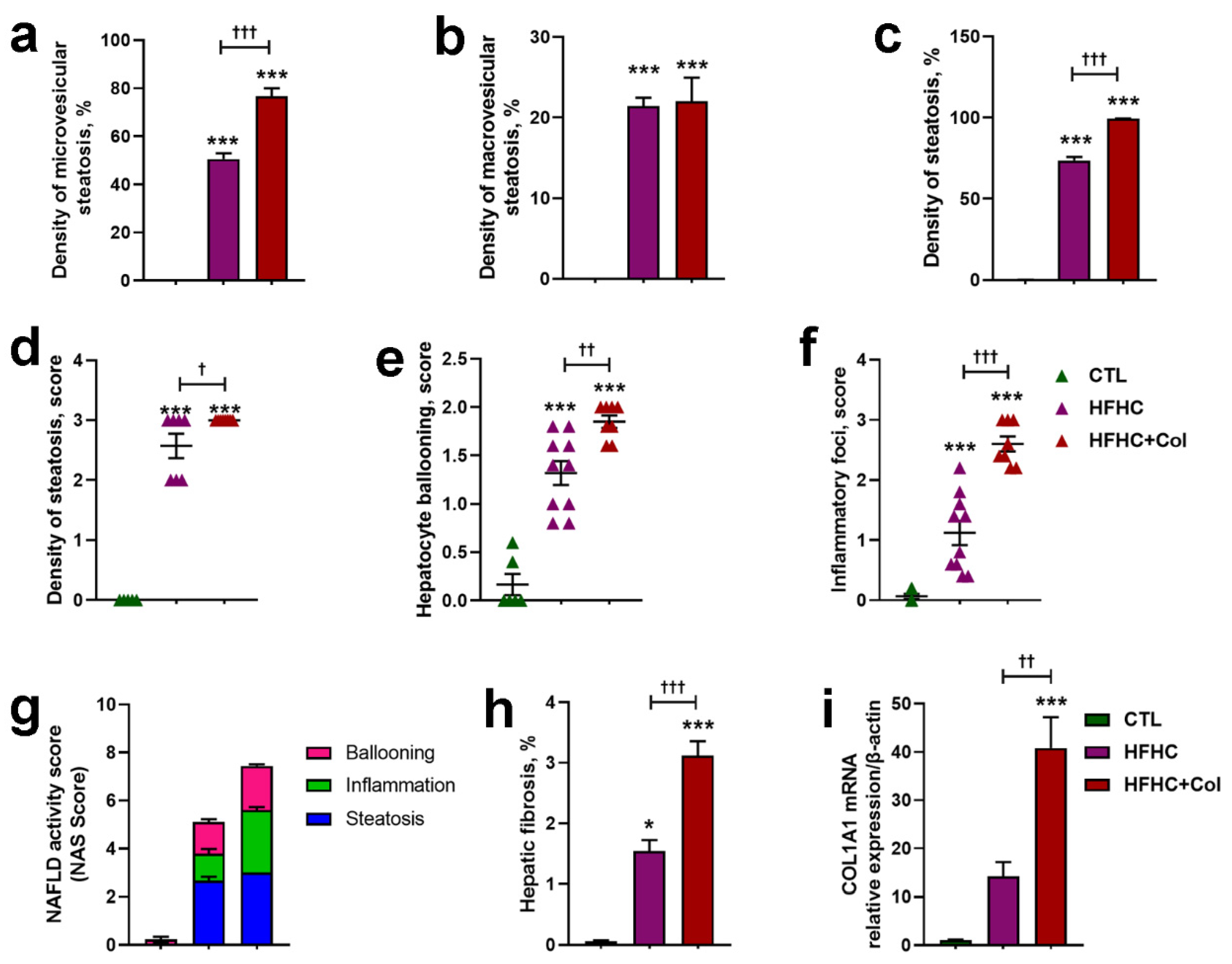
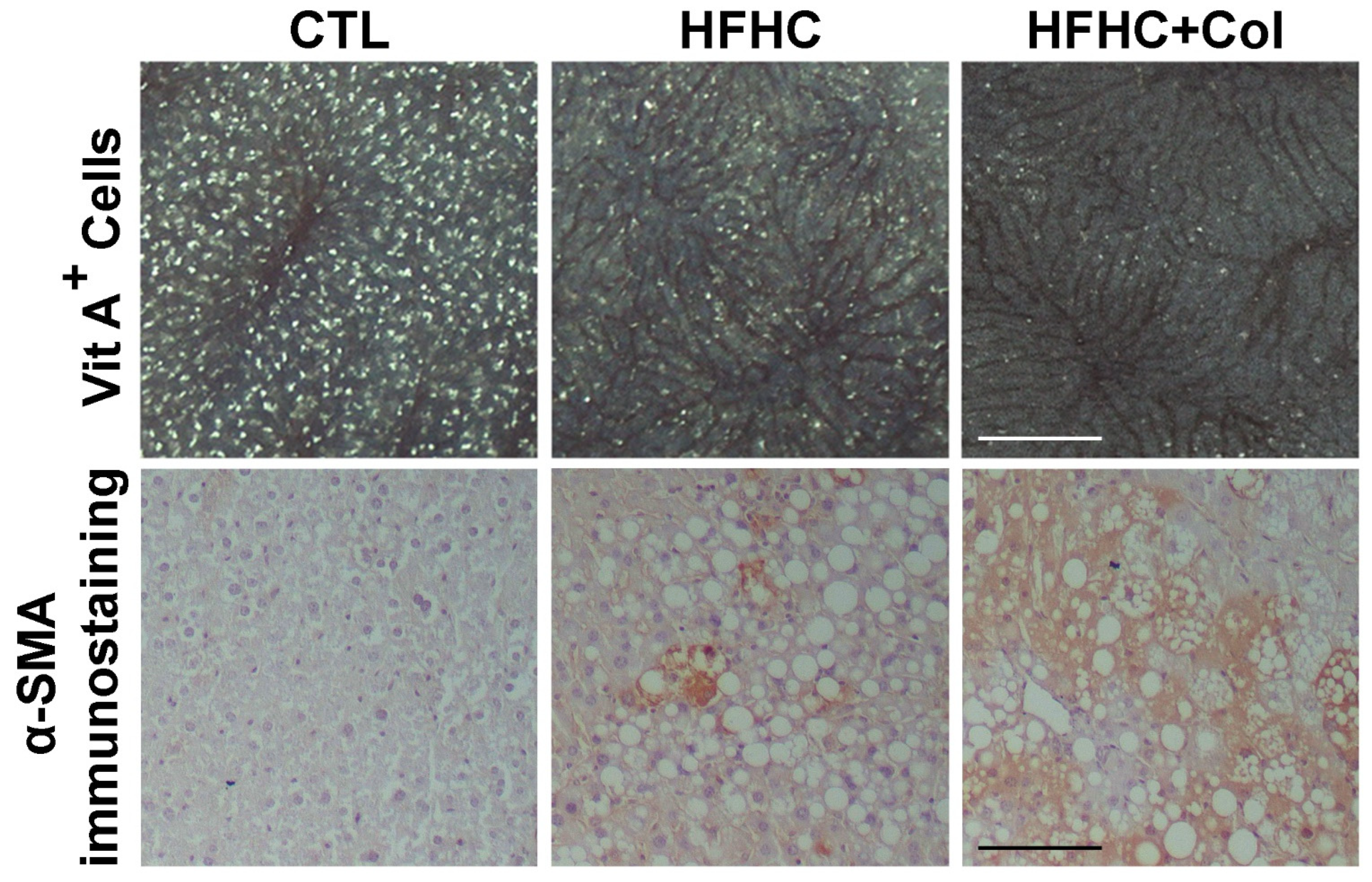
3.2. Cholesterol Worsens Histological Features of NASH
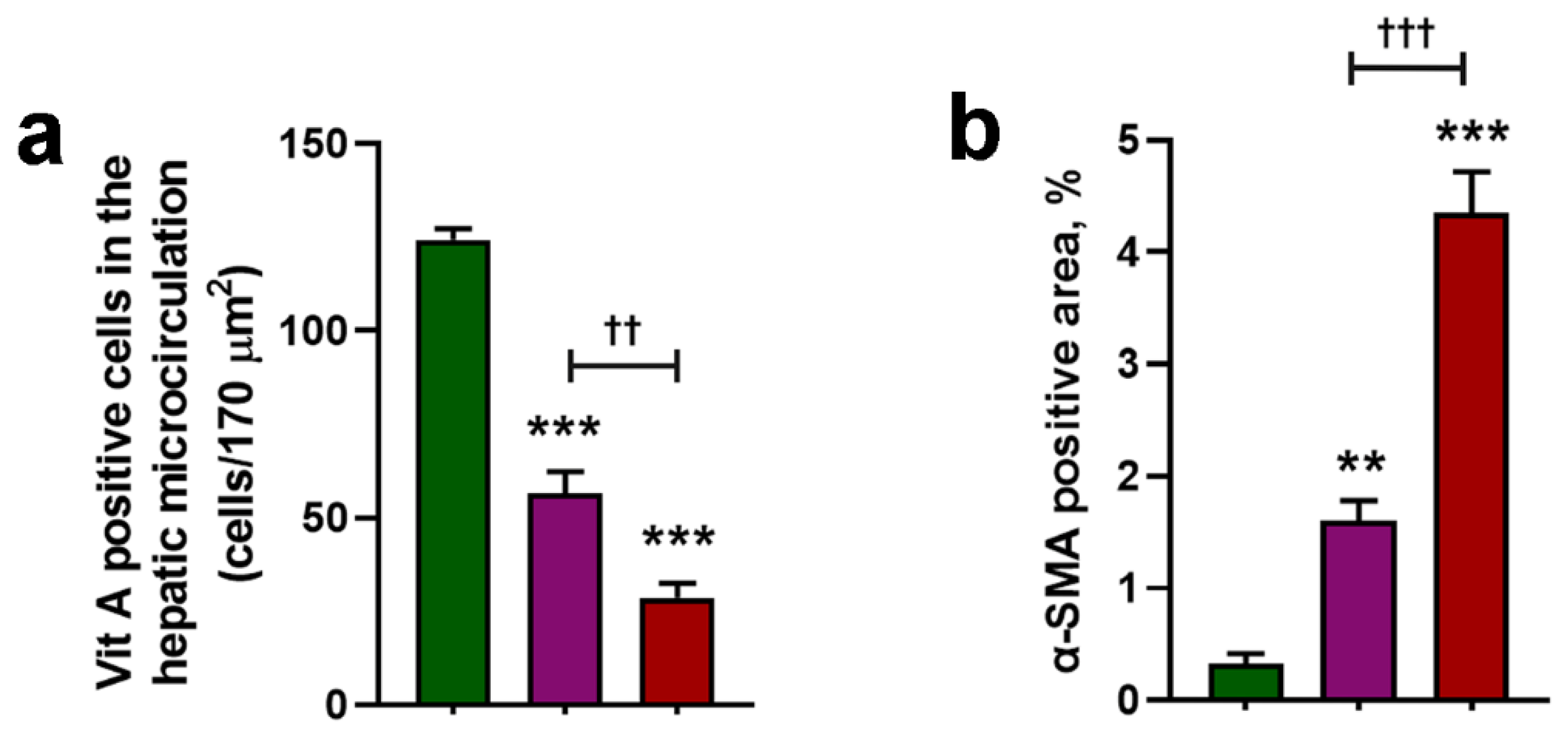
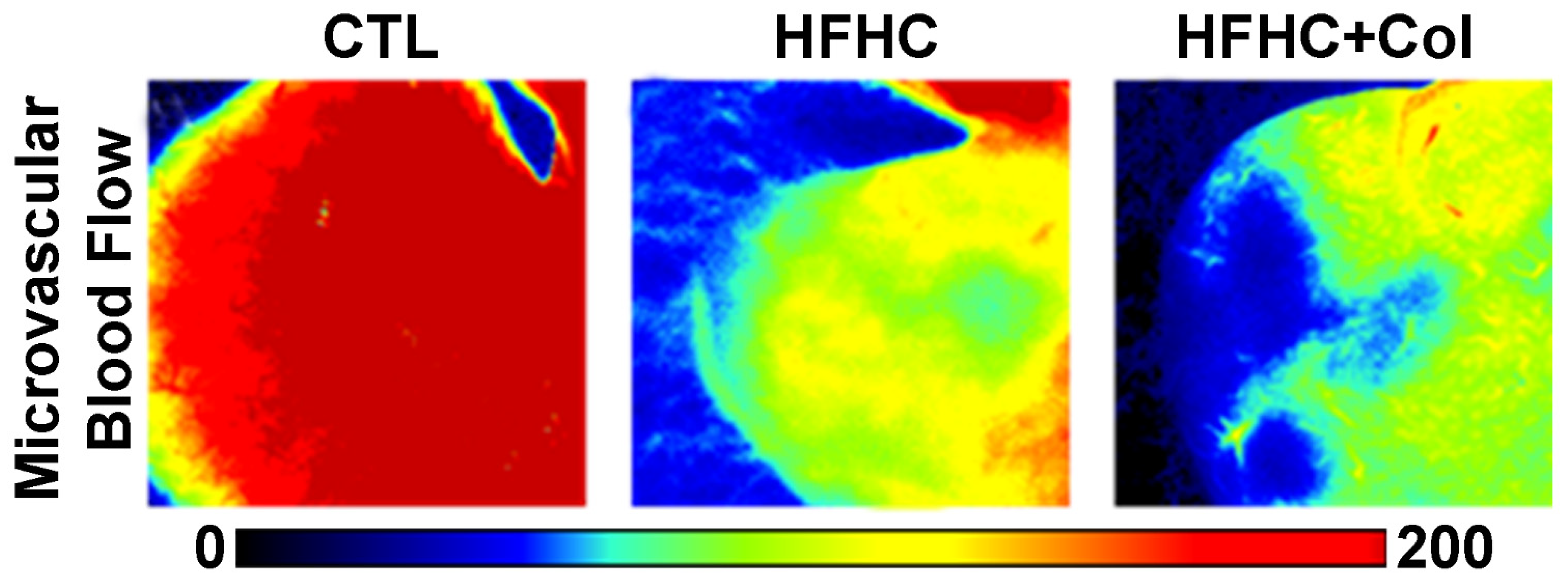
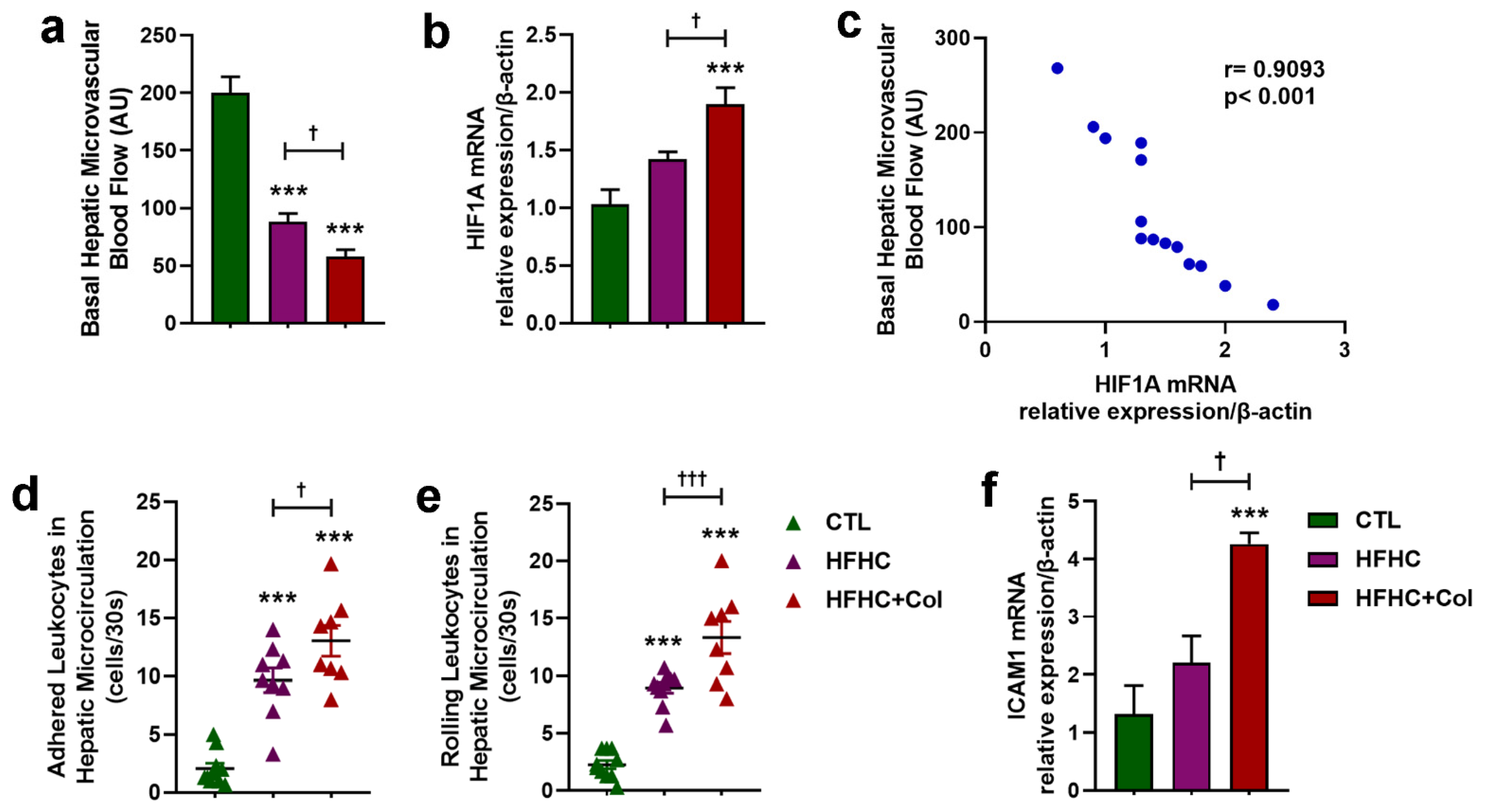
3.3. Cholesterol Exacerbates Microcirculatory Dysfunction and Increases HIF1A
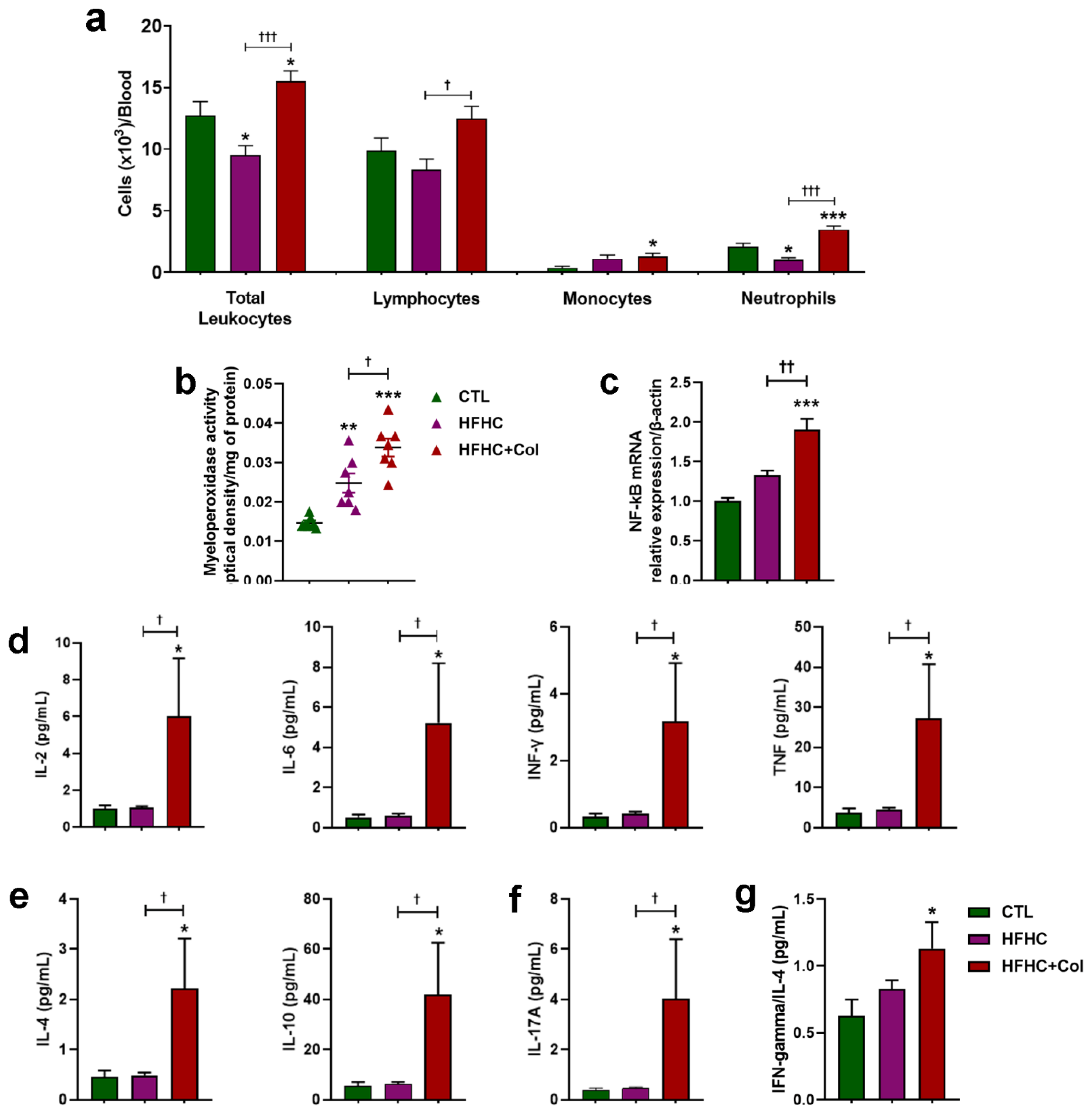
3.4. Cholesterol—Increased Systemic and Hepatic Pro-Inflammatory Status
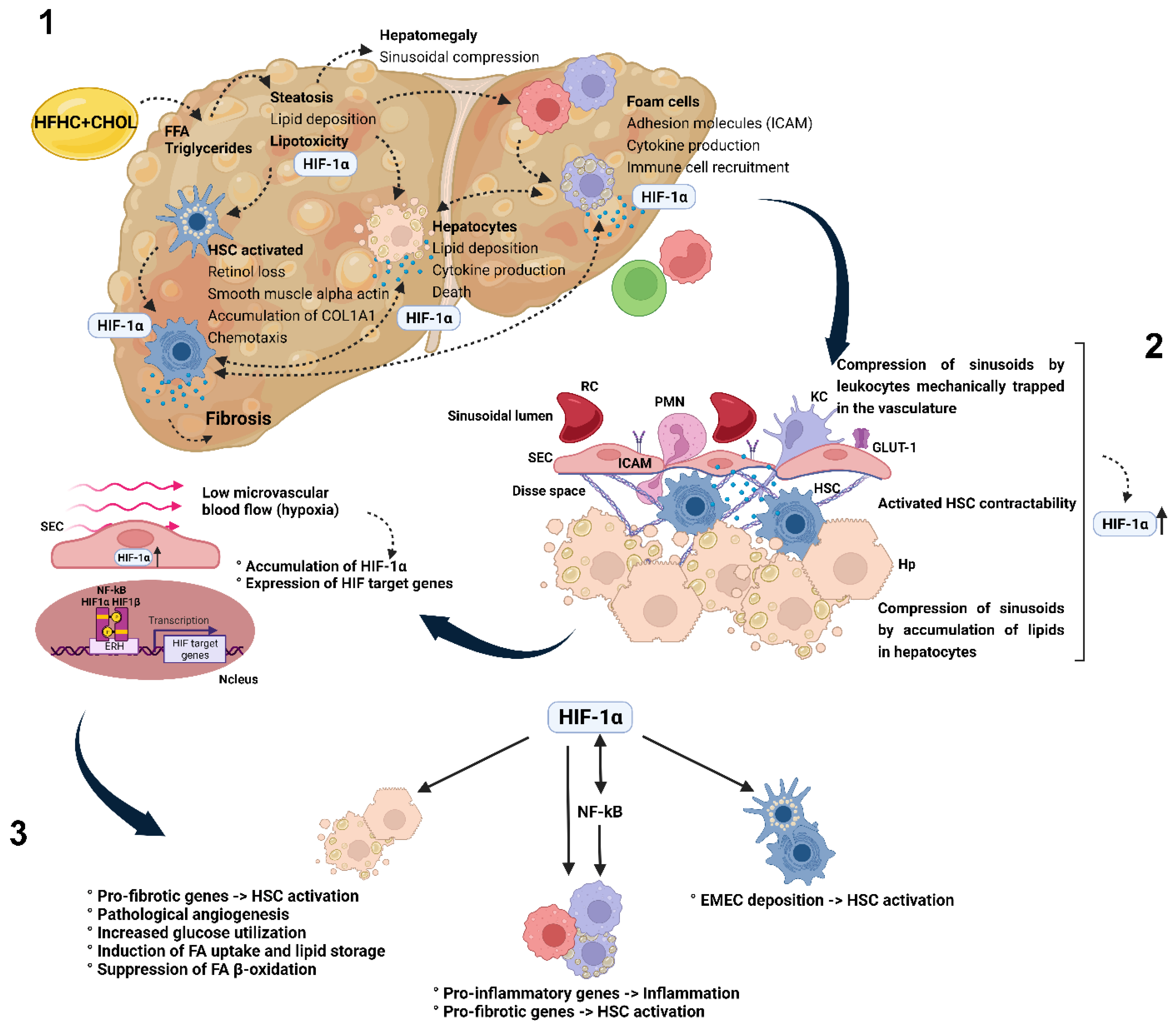
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Byass, P. The global burden of liver disease: A challenge for methods and for public health. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, J.; Weyler, J.; Dirinck, E.; Vonghia, L.; Kwanten, W.J.; Mortelmans, L.; Peleman, C.; Chotkoe, S.; Spinhoven, M.; Vanhevel, F.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for NAFLD in people with type 1 diabetes. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1592–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multi-society Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Moschen, A.R. Multiple Parallel Hits Hypothesis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Revisited after a Decade. Hepatology 2021, 73, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N. The Role of Cholesterol in the Pathogenesis of NASH. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, C.L.; Morales, A.L.; Savard, C.; Farrell, G.C.; Ioannou, G.N. Role of Cholesterol-Associated Steatohepatitis in the Development of NASH. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Q.; Teoh, N.; Xu, L.; Pok, S.; Li, X.; Chu, E.S.H.; Chiu, J.; Dong, L.; Arfianti, E.; Haigh, W.G.; et al. Dietary cholesterol promotes steatohepatitis related hepatocellular carcinoma through dysregulated metabolism and calcium signaling. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.M.; Estall, J.L. Diet-Induced Models of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Food for Thought on Sugar, Fat, and Cholesterol. Cells 2021, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology 2010, 52, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Araujo, B.P.; Rodrigues, K.L.; Silvares, R.R.; Martins, C.S.M.; Flores, E.E.I.; Fernandes-Santos, C.; Daliry, A. Simvastatin Improves Microcirculatory Function in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Downregulates Oxidative and ALE-RAGE Stress. Nutrients 2022, 14, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.; Silvares, R.R.; Rodrigues, K.L.; Flores, E.E.I.; Daliry, A. Pyridoxamine and Caloric Restriction Improve Metabolic and Microcirculatory Abnormalities in Rats with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Vasc. Res. 2021, 58, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, S.; Yang, W.; Winslet, M.C.; Seifalian, A.M. The role of nitric oxide in the modulation of hepatic microcirculation and tissue oxygenation in an experimental model of hepatic steatosis. Microvasc. Res. 2005, 70, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Bowden, N.; Fragiadaki, M.; Souilhol, C.; Hsiao, S.; Mahmoud, M.; Allen, S.; Pirri, D.; Ayllon, B.T.; Akhtar, S.; et al. Mechanical Activation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1alpha Drives Endothelial Dysfunction at Atheroprone Sites. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 2087–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhang, F.; Mo, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B.; Ding, X.; Guo, H.; Li, F.; Guo, C. Involvement of HIF1 stabilization and VEGF signaling modulated by Grx-1 in murine model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Cell Biol. Int. 2023, 47, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, M.W.; Kwiecien, S.; Pajdo, R.; Ptak-Belowska, A.; Brzozowski, B.; Krzysiek-Maczka, G.; Strzalka, M.; Konturek, S.J.; Brzozowski, T. Esophagoprotective activity of angiotensin-(1-7) in experimental model of acute reflux esophagitis. Evidence for the role of nitric oxide, sensory nerves, hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and proinflammatory cytokines. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 65, 809–822. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewska, M.; Sikora, M.; Stec, A.; Zaremba, M.; Maciejewski, C.; Pawlik, K.; Rudnicka, L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) as a Biomarker for Changes in Microcirculation in Individuals with Systemic Sclerosis. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino Rodrigues, K.; Vieira Dias Da Silva, V.; Nunes Goulart da Silva Pereira, E.; Rangel Silvares, R.; Peres de Araujo, B.; Eduardo Ilaquita Flores, E.; Ramos, I.P.; Pereira Borges, J.; Fernandes-Santos, C.; Daliry, A. Aerobic Exercise Training Improves Microvascular Function and Oxidative Stress Parameters in Diet-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 2991–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Silvares, R.R.; Flores, E.E.I.; Rodrigues, K.L.; Daliry, A. Pyridoxamine improves metabolic and microcirculatory complications associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Microcirculation 2020, 27, e12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, H.; Hennig, A.; Schwartz, D.E. Stereology: Applications to biomedical research. Physiol. Rev. 1971, 51, 158–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimbeni, F.; Bedossa, P.; Fedchuk, L.; Pais, R.; Charlotte, F.; Lebray, P.; Poynard, T.; Ratziu, V.; Group, L.S. Clinical validation of the FLIP algorithm and the SAF score in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contos, M.J.; Sanyal, A.J. The clinicopathologic spectrum and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2002, 9, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.P.T.; Guimaraes, F.V.; Sa, Y.; da Silva Ribeiro, N.B.; de Arantes, A.C.S.; de Frias Carvalho, V.; Sousa, L.P.; Perretti, M.; Martins, M.A.; PMR, E.S. Annexin-A1-Derived Peptide Ac2-26 Suppresses Allergic Airway Inflammation and Remodelling in Mice. Cells 2022, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzetti, M.; da Costa, C.A.; Nesi, R.T.; Barroso, M.V.; Martins, V.; Victoni, T.; Lagente, V.; Pires, K.M.; e Silva, P.M.; Resende, A.C.; et al. Oxidative stress and nitrosative stress are involved in different stages of proteolytic pulmonary emphysema. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.E. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.T.; Van Rooyen, D.M.; Koina, M.E.; McCuskey, R.S.; Teoh, N.C.; Farrell, G.C. Hepatocyte free cholesterol lipotoxicity results from JNK1-mediated mitochondrial injury and is HMGB1 and TLR4-dependent. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Canbay, A.; Angulo, P.; Taniai, M.; Burgart, L.J.; Lindor, K.D.; Gores, G.J. Hepatocyte apoptosis and fas expression are prominent features of human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzaugarat, M.E.; Ferreyra Solari, N.E.; Billordo, L.A.; Abecasis, R.; Gadano, A.C.; Chernavsky, A.C. Altered phenotype and functionality of circulating immune cells characterize adult patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Ahmad, M.F.; Nagy, L.E.; Tsukamoto, H. Inflammatory pathways in alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieseck, R.L., 3rd; Wilson, M.S.; Wynn, T.A. Type 2 immunity in tissue repair and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Espinoza, L.; Huch, M. The balancing act of the liver: Tissue regeneration versus fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Wang, K.; Aoyama, T.; Grivennikov, S.I.; Paik, Y.; Scholten, D.; Cong, M.; Iwaisako, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Interleukin-17 signaling in inflammatory, Kupffer cells, and hepatic stellate cells exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 765–776.e763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Qian, X.; Jiang, R.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Ryffel, B.; Sun, B. IL-17A plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis through hepatic stellate cell activation. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Li, W.Y.; Zheng, M.H.; Chen, Y.P. T-helper 17 cell: A distinctive cell in liver diseases. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, Q.; Han, X.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Shen, L.; et al. Interleukin-17 exacerbates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Geng, Y.; Sepulveda, R.; Solis, N.; Torres, J.; Arab, J.P.; Barrera, F.; Cabrera, D.; Moshage, H.; Arrese, M. Chemical hypoxia induces pro-inflammatory signals in fat-laden hepatocytes and contributes to cellular crosstalk with Kupffer cells through extracellular vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthiaume, F.; Barbe, L.; Mokuno, Y.; MacDonald, A.D.; Jindal, R.; Yarmush, M.L. Steatosis reversibly increases hepatocyte sensitivity to hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 152, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.; Wang, G.L.; Roe, R.; Semenza, G.L. Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17771–17778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.A.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5510–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravenna, L.; Principessa, L.; Verdina, A.; Salvatori, L.; Russo, M.A.; Petrangeli, E. Distinct phenotypes of human prostate cancer cells associate with different adaptation to hypoxia and pro-inflammatory gene expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Q.; Nozaki, Y.; Sakoe, K.; Komatsu, N.; Kirito, K. NF-kB mediates aberrant activation of HIF-1 in malignant lymphoma. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 38, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Uden, P.; Kenneth, N.S.; Rocha, S. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by NF-kB. Biochem. J. 2008, 412, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaiba, R.S.; Bonello, S.; Zahringer, C.; Schmidt, S.; Hess, J.; Kietzmann, T.; Gorlach, A. Hypoxia up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha transcription by involving phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and nuclear factor kappaB in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 4691–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius, J.; Guma, M.; Schachtrup, C.; Akassoglou, K.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Nizet, V.; Johnson, R.S.; Haddad, G.G.; Karin, M. NF-kB links innate immunity to the hypoxic response through transcriptional regulation of HIF-1alpha. Nature 2008, 453, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Pore, N.; Behrooz, A.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Maity, A. Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9519–9525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Sakata, M.; Takeda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Sawada, K.; Kimura, A.; Minekawa, R.; Tahara, M.; Tasaka, K.; et al. Induction of glucose transporter 1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha under hypoxic conditions in trophoblast-derived cells. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 183, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Léveillé, M.; Courty, E.; Gunes, A.; Nguyen, B.N.; Estall, J.L. Differences in metabolic and liver pathobiology induced by two dietary mouse models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E863–E876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, C.R. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 88, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermani, S.K.; Khatony, A.; Jalali, R.; Rezaei, M.; Abdi, A. Accuracy and Precision of Measured Blood Sugar Values by Three Glucometers Compared to the Standard Technique. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, OC05–OC08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, A.; Canbay, A. Why Bile Acids Are So Important in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Progression. Cells 2019, 8, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolites in NAFLD Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Valenti, L.; Romeo, S. Genetics and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: Clinical impact. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, E.N.G.d.S.; Araujo, B.P.d.; Rodrigues, K.L.; Silvares, R.R.; Guimarães, F.V.; Martins, C.S.M.; Flores, E.E.I.; Silva, P.M.R.e.; Daliry, A. Cholesterol Exacerbates the Pathophysiology of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Upregulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Modulating Microcirculatory Dysfunction. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245034
Pereira ENGdS, Araujo BPd, Rodrigues KL, Silvares RR, Guimarães FV, Martins CSM, Flores EEI, Silva PMRe, Daliry A. Cholesterol Exacerbates the Pathophysiology of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Upregulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Modulating Microcirculatory Dysfunction. Nutrients. 2023; 15(24):5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245034
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Evelyn Nunes Goulart da Silva, Beatriz Peres de Araujo, Karine Lino Rodrigues, Raquel Rangel Silvares, Fernanda Verdini Guimarães, Carolina Souza Machado Martins, Edgar Eduardo Ilaquita Flores, Patrícia Machado Rodrigues e Silva, and Anissa Daliry. 2023. "Cholesterol Exacerbates the Pathophysiology of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Upregulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Modulating Microcirculatory Dysfunction" Nutrients 15, no. 24: 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245034
APA StylePereira, E. N. G. d. S., Araujo, B. P. d., Rodrigues, K. L., Silvares, R. R., Guimarães, F. V., Martins, C. S. M., Flores, E. E. I., Silva, P. M. R. e., & Daliry, A. (2023). Cholesterol Exacerbates the Pathophysiology of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Upregulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Modulating Microcirculatory Dysfunction. Nutrients, 15(24), 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245034





