The Causal Association between Alcohol, Smoking, Coffee Consumption, and the Risk of Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
2.1.1. Data Sources
2.1.2. Selection of Instrumental Variables
2.1.3. Statistical Analysis Methods
2.2. Study Search and Inclusion Criteria
- Any studies using the MR method to investigate causality between risk factors and osteoarthritis/rheumatoid arthritis or related phenotypes.
- Any studies on gender, age, cohort, and race.
- Any studies that include MR as part of their analysis.
- Any case reports, narrative reviews, or other non-research-based studies.
- Any studies that did not include alcohol/smoking/coffee consumption in the exposures or OA/RA in the outcomes.
- Any studies of non-European origin cohorts.
- Any studies for which the complete English manuscript is not available.
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
3.2. Study Characteristics and Literature Inclusion
3.3. Results of Meta-Analysis
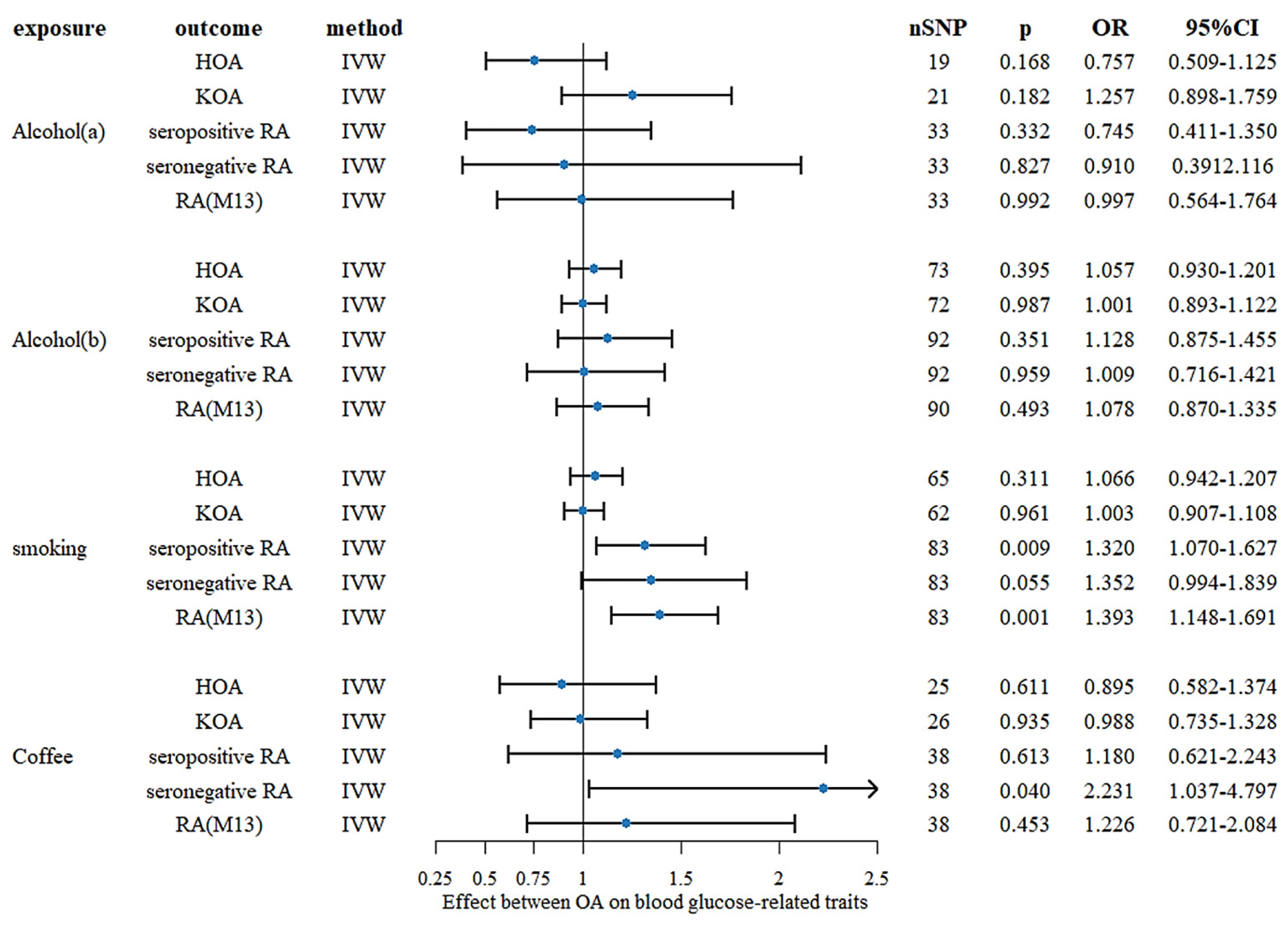
3.3.1. Alcohol Intake
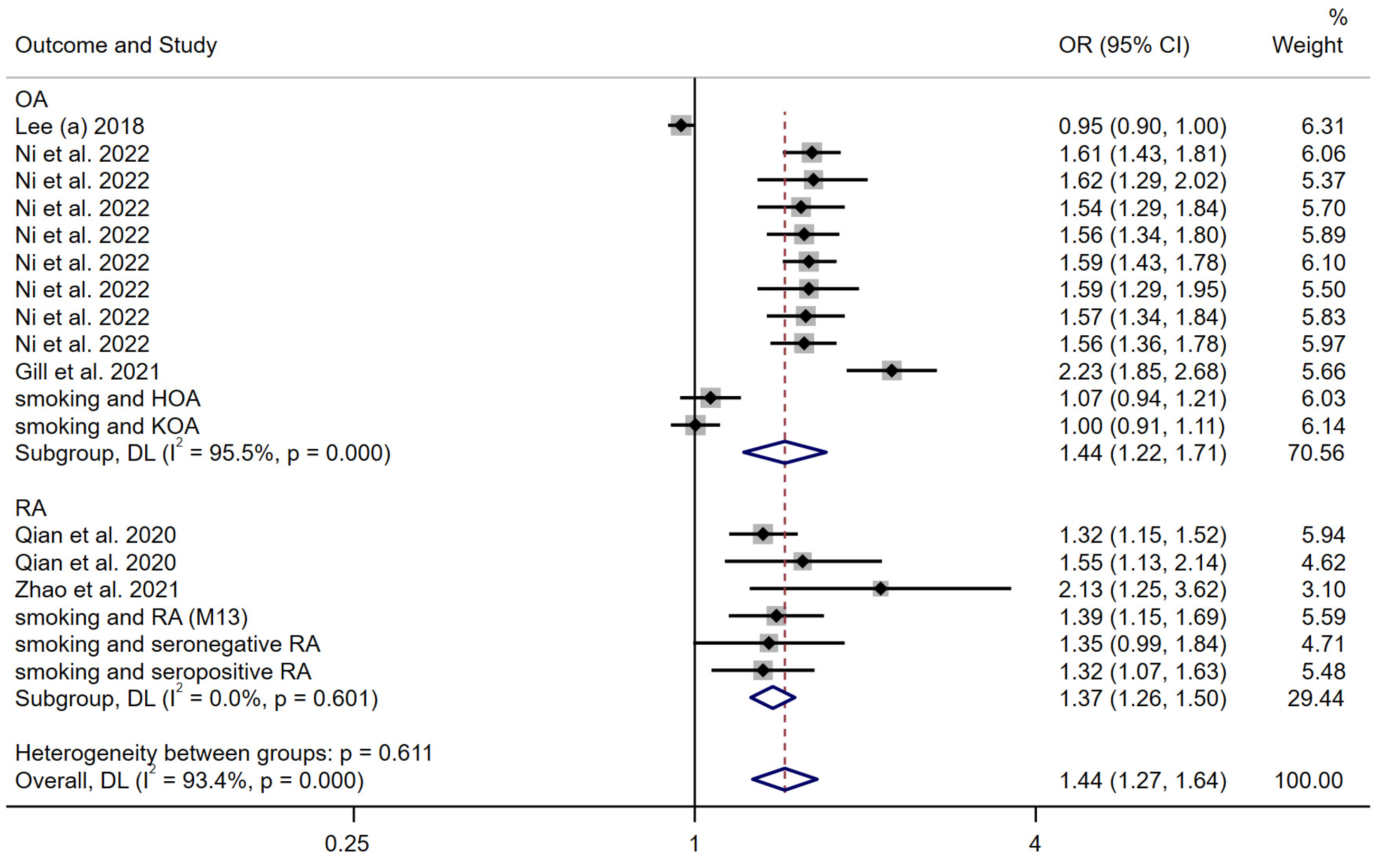
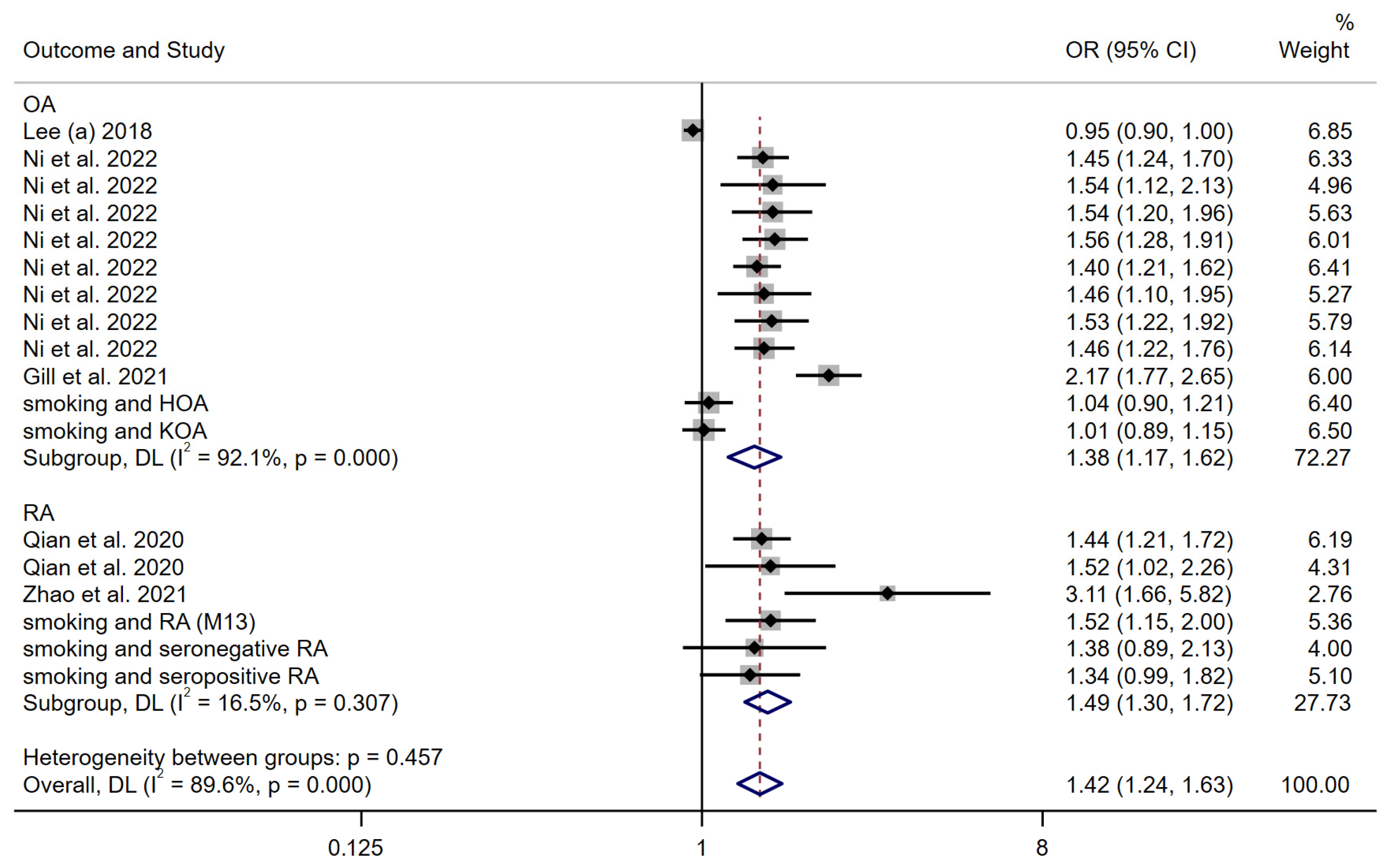
3.3.2. Smoking Behavior
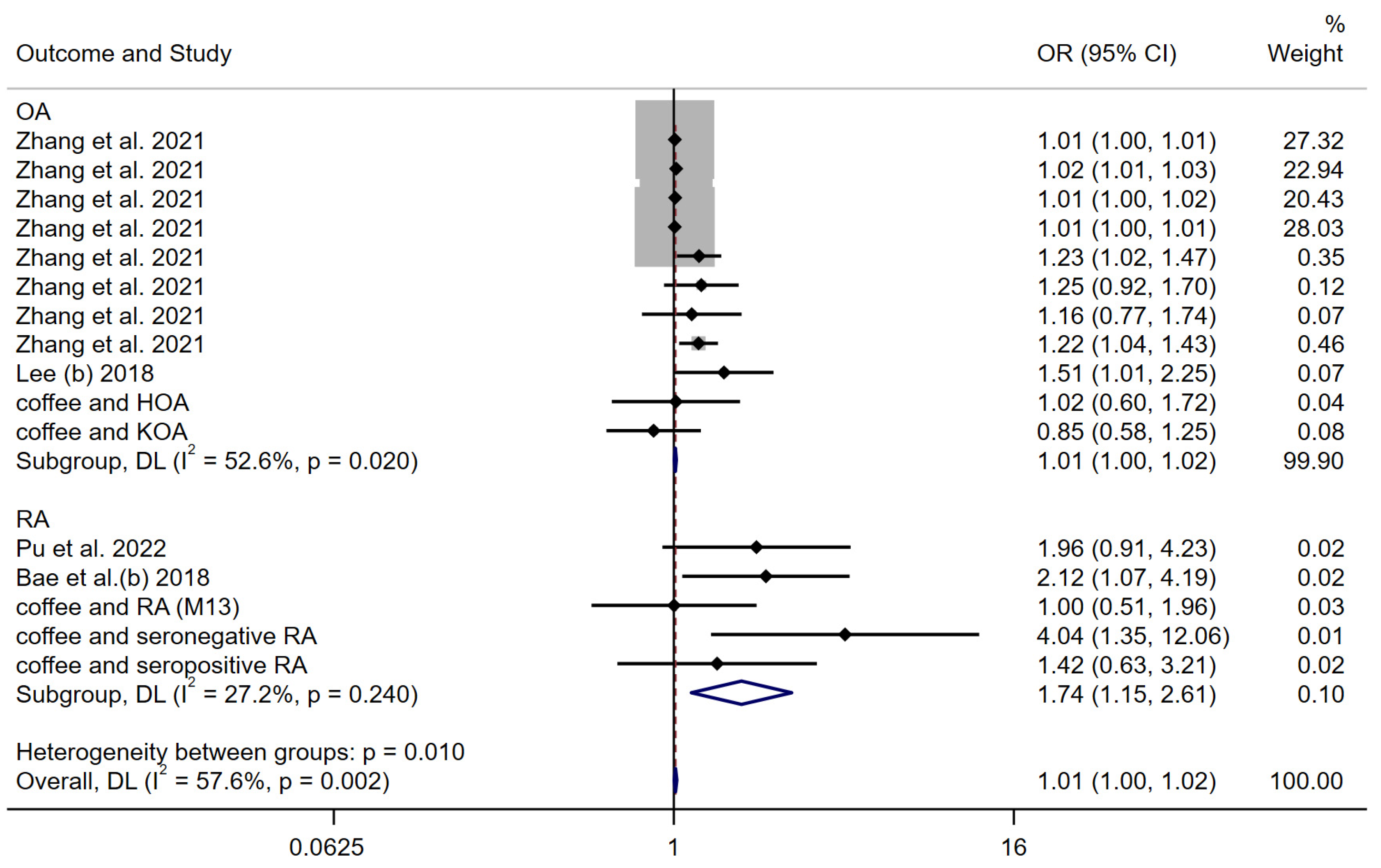
3.3.3. Coffee Consumption
4. Discussion
4.1. Alcohol Intake
4.2. Smoking Behavior
4.3. Coffee Consumption
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
4.5. Clinical Implications
4.6. Further Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Study | Year | Ethnicity | Cohort | Design of MR Study | Genetic Instrument | Exposure | Outcome | Sample Size | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bae et al. (a) [17] | 2018 | European descent | UK Biobank | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 24 SNPs associated with alcohol intake frequency as the IVs | Alcohol consumption | Rheumatoid arthritis | 5539 autoantibody-positive individuals with RA and 20,169 controls | Results do not support a causal association between alcohol intake and RA risk |
| Jiang et al. [18] | 2021 | European descent | European ancestries | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 99 genome-wide significant variants associated with drink | Alcohol consumption | Rheumatoid arthritis | 29,880 RA cases and 73,758 controls | No evidence of a causal relationship was identified for RA |
| Lee (a) [19] | 2018 | European descent | arcOGEN | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 4 SNPs associated with smoking behavior were selected as IVs | Smoking behavior | Osteoarthritis | 7410 cases and 11,009 controls | MR analysis suggested the inverse association between smoking behavior and osteoarthritis |
| Ni et al. [20] | 2022 | European descent | UK Biobank | Two-sample univariable MR analysis and multivariable MR (MVMR). | 298 independent SNPs were included as IVs for smoking initiation | Smoking initiation | Osteoarthritis | N = 327,918 | The findings support an independent deleterious causal effect for smoking upon OA risk |
| Gill et al. [21] | 2021 | European descent | UK Biobank | Two-sample univariable MR analysis and multivariable MR (MVMR). | 24 SNPs associated with smoking as the IVs | Smoking behavior | Osteoarthritis | 60,800 OA cases and 328,251 controls | There was evidence of an unfavorable effect of genetically predicted smoking on OA risk in the main IVW MR analyses |
| Qian et al. [22] | 2020 | European descent | European ancestries | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 367 SNPs were used as IVs for smoking initiation | Smoking behavior | Rheumatoid arthritis | 14,361 cases and 43,923 controls | Results provide support for a causal association between smoking and increased risk of RA |
| Zhao et al. [23] | 2021 | European descent | European ancestries | Two sample. Univariable and multivariable MR methods | 124 SNPs were used as IVs for Lifetime smoking | Lifetime smoking | Rheumatoid arthritis | 14,361 cases, 43,923 controls | Each S.D. increase in smoking exposure led to a higher risk of RA |
| Zhang et al. [24] | 2021 | European descent | UK Biobank | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 11 and 8 independent SNPs with moderate LD were selected as genetic instruments for coffee consumption | Coffee consumption | Osteoarthritis | primary outcome, N = 50,508 (10,083 with cases and 40,425 controls) secondary outcomes, knee OA (4462 cases and 17,885 controls) and hip OA (12,625 cases and 50,898 controls), and self-reported OA (12,658 cases and 50,898 controls) | Coffee consumption was associated with an increased risk of overall OA, knee OA, self-reported OA, but not hip OA, using primary genetic instruments |
| Lee (b) [25] | 2018 | European descent | arcOGEN | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 4 SNPs from coffee consumption GWASs were selected as IVs | Coffee consumption | Osteoarthritis | 7410 cases and 11,009 controls | Coffee consumption is causally associated with an increased risk of osteoarthritis |
| Pu et al. [26] | 2022 | European descent | UK Biobank | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 27 SNPs related to coffee intake were selected | Coffee consumption | Rheumatoid arthritis | 14,361 cases and 43,923 controls | Study did not support a causal association between coffee intake and RA risk |
| Bae et al. (b) [27] | 2018 | European descent | European ancestries | Two-sample univariable MR analysis | 4 SNPs were selected as IVs | Coffee consumption | Rheumatoid arthritis | N = 41,282 | Results do not support causal associations between coffee consumption and the development of RA |
| Study | Title and Abstract | Background | Objectives | Study Design and Data Sources | Statistical Methods and Main Analysis | Assessment of Assumptions | Software and Pre-Registration | Descriptive Data | Main Results | Sensitivity and Additional Analyses | Key Results | Limitations | Interpretation | Generalizability | Total Score | % Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bae et al. (a) [17] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Jiang et al. [18] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Lee (a) [19] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Ni et al. [20] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 100 |
| Gill et al. [21] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 100 |
| Qian et al. [22] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 100 |
| Zhao et al. [23] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 92.9 |
| Zhang et al. [24] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 13 | 92.9 |
| Lee (b) [25] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 12 | 85.7 |
| Pu et al. [26] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 100 |
| Bae et al. (b) [27] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 12.5 | 89.3 |
References
- Ma, L.; Cranney, A.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.M. Acute Monoarthritis: What Is the Cause of My Patient’s Painful Swollen Joint? CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. = J. L’association Med. Can. 2009, 180, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; March, L.; Chew, M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: A Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 1711–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.N.; Arant, K.R.; Loeser, R.F. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, J.A. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, ITC1–ITC16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otón, T.; Carmona, L. The Epidemiology of Established Rheumatoid Arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 33, 101477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyn-Jones, S.; Palmer, A.J.R.; Agricola, R.; Price, A.J.; Vincent, T.L.; Weinans, H.; Carr, A.J. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2015, 386, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finckh, A.; Gilbert, B.; Hodkinson, B.; Bae, S.-C.; Thomas, R.; Deane, K.D.; Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Lauper, K. Global Epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedström, A.K.; Stawiarz, L.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L. Smoking and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in a Swedish population-based case-control study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, L.; Meng, F.; Cao, J.; Shen, Y. Association between Smoking and Risk of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Xiang, C.; Cai, Q.; Wei, X.; He, J. Alcohol Consumption as a Preventive Factor for Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asoudeh, F.; Dashti, F.; Jayedi, A.; Hemmati, A.; Fadel, A.; Mohammadi, H. Caffeine, Coffee, Tea and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 822557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, C.H.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, S.J.; Song, G.G.; Jung, J.H. Is Knee Osteoarthritis Related to Coffee Drinking? A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekula, P.; Del Greco, M.F.; Pattaro, C.; Köttgen, A. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3253–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Walia, G.K.; Sachdeva, M.P. “Mendelian Randomization”: An Approach for Exploring Causal Relations in Epidemiology. Public Health 2017, 145, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C. Mendelian Randomization as a Tool for Causal Inference in Human Nutrition and Metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2021, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.-C.; Lee, Y.H. Alcohol Intake and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Z. Rheumatol. 2019, 78, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Manouchehrinia, A.; Olsson, T.; Alfredsson, L.; Kockum, I. Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Common Autoimmune Inflammatory Diseases—Evidence From a Large-Scale Genetic Analysis Totaling 1 Million Individuals. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 687745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H. Causal Association between Smoking Behavior and the Decreased Risk of Osteoarthritis: A Mendelian Randomization. Z. Rheumatol. 2019, 78, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Wang, P.; Yin, K.-J.; Huang, J.-X.; Tian, T.; Cen, H.; Sui, C.; Xu, Z.; Pan, H.-F. Does Smoking Protect against Developing Osteoarthritis? Evidence from a Genetically Informed Perspective. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 55, 152013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.; Karhunen, V.; Malik, R.; Dichgans, M.; Sofat, N. Cardiometabolic Traits Mediating the Effect of Education on Osteoarthritis Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.J.H.; Xie, Z.; Wen, C.; Mao, Y. Genetic Predisposition to Smoking Is Associated with Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.S.; Holmes, M.V.; Zheng, J.; Sanderson, E.; Carter, A.R. The Impact of Education Inequality on Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Is Mediated by Smoking and Body Mass Index: Mendelian Randomization Study. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, T.; Shen, S.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Lu, Y.; Lei, X. Causal Association of Coffee Consumption and Total, Knee, Hip and Self-Reported Osteoarthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 768529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H. Investigating the Possible Causal Association of Coffee Consumption with Osteoarthritis Risk Using a Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 3133–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, B.; Gu, P.; Zheng, C.; Ma, L.; Zheng, X.; Zeng, Z. Self-Reported and Genetically Predicted Effects of Coffee Intake on Rheumatoid Arthritis: Epidemiological Studies and Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 926190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.-C.; Lee, Y.H. Coffee Consumption and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2875–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wedow, R.; Li, Y.; Brazel, D.M.; Chen, F.; Datta, G.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; McGuire, D.; Tian, C.; et al. Association Studies of up to 1.2 Million Individuals Yield New Insights into the Genetic Etiology of Tobacco and Alcohol Use. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, C.G.; Hatzikotoulas, K.; Southam, L.; Stefánsdóttir, L.; Zhang, Y.; Coutinho de Almeida, R.; Wu, T.T.; Zheng, J.; Hartley, A.; Teder-Laving, M.; et al. Deciphering Osteoarthritis Genetics across 826,690 Individuals from 9 Populations. Cell 2021, 184, 4784–4818.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration Avoiding Bias from Weak Instruments in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Yang, F.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Hong, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, G.; Wang, W.; Yan, S. A Mendelian Randomization Study on the Role of Serum Parathyroid Hormone and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of Widespread Horizontal Pleiotropy in Causal Relationships Inferred from Mendelian Randomization between Complex Traits and Diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base Platform Supports Systematic Causal Inference across the Human Phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dimou, N.; Egger, M.; Gallo, V.; Golub, R.; Higgins, J.P.; Langenberg, C.; Loder, E.W.; Richards, J.B.; et al. STROBE-MR: Guidelines for Strengthening the Reporting of Mendelian Randomization Studies. PeerJ, 2019; preprints. [Google Scholar]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Davey Smith, G. Reading Mendelian Randomisation Studies: A Guide, Glossary, and Checklist for Clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Bae, J.; Choe, J.-Y. The Relationship between Alcohol Consumption and Knee Osteoarthritis in Korean Population over 50 Years-Old: Results from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Medicine 2021, 100, e24746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuri, S.G.; Zhang, W.; Maciewicz, R.A.; Muir, K.; Doherty, M. Beer and Wine Consumption and Risk of Knee or Hip Osteoarthritis: A Case Control Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, N.E.; Hu, Y.; Song, M.; Rosner, B.A.; Karlson, E.W.; Ratzlaff, C.; Lu, B.; Liang, M.H.; Willett, W.C. Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Total Hip Replacement Due to Hip Osteoarthritis in Women. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.; Mak, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Filbay, S.; Khan, W. The Association between Alcohol Consumption and Osteoarthritis: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Observational Studies. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucca, C.B.; Scotti, L.; Cappellano, G.; Barone-Adesi, F.; Chiocchetti, A. Nutrition and Rheumatoid Arthritis Onset: A Prospective Analysis Using the UK Biobank. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giuseppe, D.; Alfredsson, L.; Bottai, M.; Askling, J.; Wolk, A. Long Term Alcohol Intake and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Women: A Population Based Cohort Study. BMJ 2012, 345, e4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.F.; England, B.R.; Mikuls, T.R.; Hsu, J.Y.; George, M.D.; Pedro, S.; Sayles, H.; Michaud, K. Changes in Alcohol Use and Associations with Disease Activity, Health Status, and Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanEvery, H.; Yang, W.; Olsen, N.; Bao, L.; Lu, B.; Wu, S.; Cui, L.; Gao, X. Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis among Chinese Adults: A Prospective Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, G.; Stamatakis, E.; Hamer, M. Associations between Alcohol and Obesity in More than 100 000 Adults in England and Scotland. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Huang, C.; Momma, H.; Sugiyama, S.; Niu, K.; Nagatomi, R. The Longitudinal Association between Alcohol Consumption and Muscle Strength: A Population-Based Prospective Study. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2019, 19, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.-C.; Hung, L.-F.; Wu, W.-L.; Chang, D.-M.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lai, J.-H.; Ho, L.-J. Chondroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Resveratrol in Advanced Glycation End Products-Stimulated Chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizov, A.; Zaiss, Z. Alcohol Consumption in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Path through the Immune System. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, G.; Mirijello, A.; Ferrulli, A.; Antonelli, M.; Landolfi, R.; Gasbarrini, A.; Addolorato, G. Review Article: Alcohol and Gut Microbiota—The Possible Role of Gut Microbiota Modulation in the Treatment of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caslin, B.; Mohler, K.; Thiagarajan, S.; Melamed, E. Alcohol as Friend or Foe in Autoimmune Diseases: A Role for Gut Microbiome? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1916278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, S.; Pahor, M.; Ferrucci, L.; Simonsick, E.M.; Guralnik, J.M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Fellin, R.; Harris, T.B. Relationship of Alcohol Intake with Inflammatory Markers and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Well-Functioning Older Adults: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Circulation 2004, 109, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Törmälehto, S.; Aarnio, E.; Mononen, M.E.; Arokoski, J.P.A.; Korhonen, R.K.; Martikainen, J.A. Eight-Year Trajectories of Changes in Health-Related Quality of Life in Knee Osteoarthritis: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, B.J.; Weyand, J.A.; Liu, B.; Smith, J.F.; Perez, B.R.; Clark, J.C.; Goodman, M.; Hirschi Budge, K.M.; Eggett, D.L.; Arroyo, J.A.; et al. Exposure to Second-Hand Cigarette Smoke Exacerbates the Progression of Osteoarthritis in a Surgical Induced Murine Model. Histol. Histopathol. 2021, 36, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, M.; Vie, G.; Winsvold, B.; Bjørngaard, J.; Åsvold, B.; Gabrielsen, M.; Pedersen, L.; Hellevik, A.; Langhammer, A.; Furnes, O.; et al. The Causal Role of Smoking on the Risk of Hip or Knee Replacement Due to Primary Osteoarthritis: A Mendelian Randomisation Analysis of the HUNT Study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Omar, M.; Feng, X.; Neunaber, C.; Jagodzinski, M. Impact of Smoking on the Incidence and Post-Operative Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 22, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Crowson, C.S. Where There’s Smoke, There’s a Joint: Passive Smoking and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 2161–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Y.; Salliot, C.; Gelot, A.; Mariette, X.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Seror, R. Passive Smoking in Childhood and Adulthood and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Women: Results from the French E3N Cohort Study. RMD Open 2022, 8, e001980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seror, R.; Henry, J.; Gusto, G.; Aubin, H.-J.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Mariette, X. Passive Smoking in Childhood Increases the Risk of Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, J.A.; Chang, S.-C.; Nguyen, U.-S.D.T.; Barbhaiya, M.; Tedeschi, S.K.; Lu, B.; Costenbader, K.H.; Zhang, Y.; Choi, H.K.; Karlson, E.W. Smoking Behavior Changes in the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Period and Risk of Mortality During Thirty-Six Years of Prospective Followup. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolove, J.; Wagner, C.A.; Lahey, L.J.; Sayles, H.; Duryee, M.J.; Reimold, A.M.; Kerr, G.; Robinson, W.H.; Cannon, G.W.; Thiele, G.M.; et al. Increased Inflammation and Disease Activity among Current Cigarette Smokers with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of US Veterans. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ehnert, S.; Tendulkar, G.; Zhu, S.; Arnscheidt, C.; Aspera-Werz, R.H.; Nussler, A.K. Primary Human Chondrocytes Affected by Cigarette Smoke-Therapeutic Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Gao, L.; Cucchiarini, M.; Madry, H. Association of Nicotine with Osteochondrogenesis and Osteoarthritis Development: The State of the Art of Preclinical Research. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, F.; Maurits, M.P.; van Boheemen, L.; Verstappen, M.; Mankia, K.; Matthijssen, X.M.E.; Dorjée, A.L.; Emery, P.; Knevel, R.; van Schaardenburg, D.; et al. Determining in Which Pre-Arthritis Stage HLA-Shared Epitope Alleles and Smoking Exert Their Effect on the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, J.; Peres, R.S.; Pinto, L.G.; Oliveira, R.D.R.; Lima, K.A.; Donate, P.B.; Silva, J.R.; Ryffel, B.; Cunha, T.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; et al. Smoking-Induced Aggravation of Experimental Arthritis Is Dependent of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Th17 Cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, S.; Barde, F.; Artaud, F.; Nguyen, Y.; Macdonald, C.; Mariette, X.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Salliot, C.; Seror, R. Association between Beverage Consumption and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Study from the French E3N Cohort. Rheumatology 2022, 81, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Han, Y.; Zhao, H.; Han, X.; Yin, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X. Association between Coffee Consumption, Caffeine Intake, and Metabolic Syndrome Severity in Patients with Self-Reported Rheumatoid Arthritis: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2018. Nutrients 2022, 15, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukup, T.; Hloch, K.; Doseděl, M.; Tebbens, J.D.; Nekvindová, J.; Šembera, Š.; Veleta, T.; Pávek, P.; Barvík, I. The Influence of Coffee Intake and Genetics on Adenosine Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 21, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloyer, L.; Golumba-Nagy, V.; Meyer, A.; Yan, S.; Schiller, J.; Breuninger, M.; Jochimsen, D.; Kofler, D.M. Adenosine Receptor A2a Blockade by Caffeine Increases IFN-Gamma Production in Th1 Cells from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 51, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heliövaara, M.; Aho, K.; Knekt, P.; Impivaara, O.; Reunanen, A.; Aromaa, A. Coffee Consumption, Rheumatoid Factor, and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiphorou, E.; Santos, E.J.F.; Marques, A.; Böhm, P.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Daien, C.I.; Esbensen, B.A.; Ferreira, R.J.O.; Fragoulis, G.E.; Holmes, P.; et al. 2021 EULAR Recommendations for the Implementation of Self-Management Strategies in Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwinnutt, J.M.; Wieczorek, M.; Balanescu, A.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Boonen, A.; Cavalli, G.; de Souza, S.; de Thurah, A.; Dorner, T.E.; Moe, R.H.; et al. 2021 EULAR Recommendations Regarding Lifestyle Behaviours and Work Participation to Prevent Progression of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Peng, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, K.; Xu, P. The Causal Association between Alcohol, Smoking, Coffee Consumption, and the Risk of Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5009. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15235009
Wang J, Zhang B, Peng L, Wang J, Xu K, Xu P. The Causal Association between Alcohol, Smoking, Coffee Consumption, and the Risk of Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):5009. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15235009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junxiang, Binfei Zhang, Leixuan Peng, Jiachen Wang, Ke Xu, and Peng Xu. 2023. "The Causal Association between Alcohol, Smoking, Coffee Consumption, and the Risk of Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 5009. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15235009
APA StyleWang, J., Zhang, B., Peng, L., Wang, J., Xu, K., & Xu, P. (2023). The Causal Association between Alcohol, Smoking, Coffee Consumption, and the Risk of Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. Nutrients, 15(23), 5009. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15235009