Association of the Protective Dietary Pattern for Blood Pressure with Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 6–17 Years Old: Data from China Nutrition and Health Surveillance (2015–2017)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Basic Information Collection
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Definitions of Blood Pressure Outcomes
2.5. Dietary Assessment
2.6. Dietary Pattern Analysis
2.7. Covariates
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protective Dietary Pattern for Children and Adolescents Blood Pressure
3.2. Characteristics of Study Participants
3.3. Food and Nutrients Daily Intake According to Quintiles of PDP Scores for Children’s and Adolescents’ Blood Pressure
3.4. Association of PDP and DASH Scores with Blood Pressure Outcomes
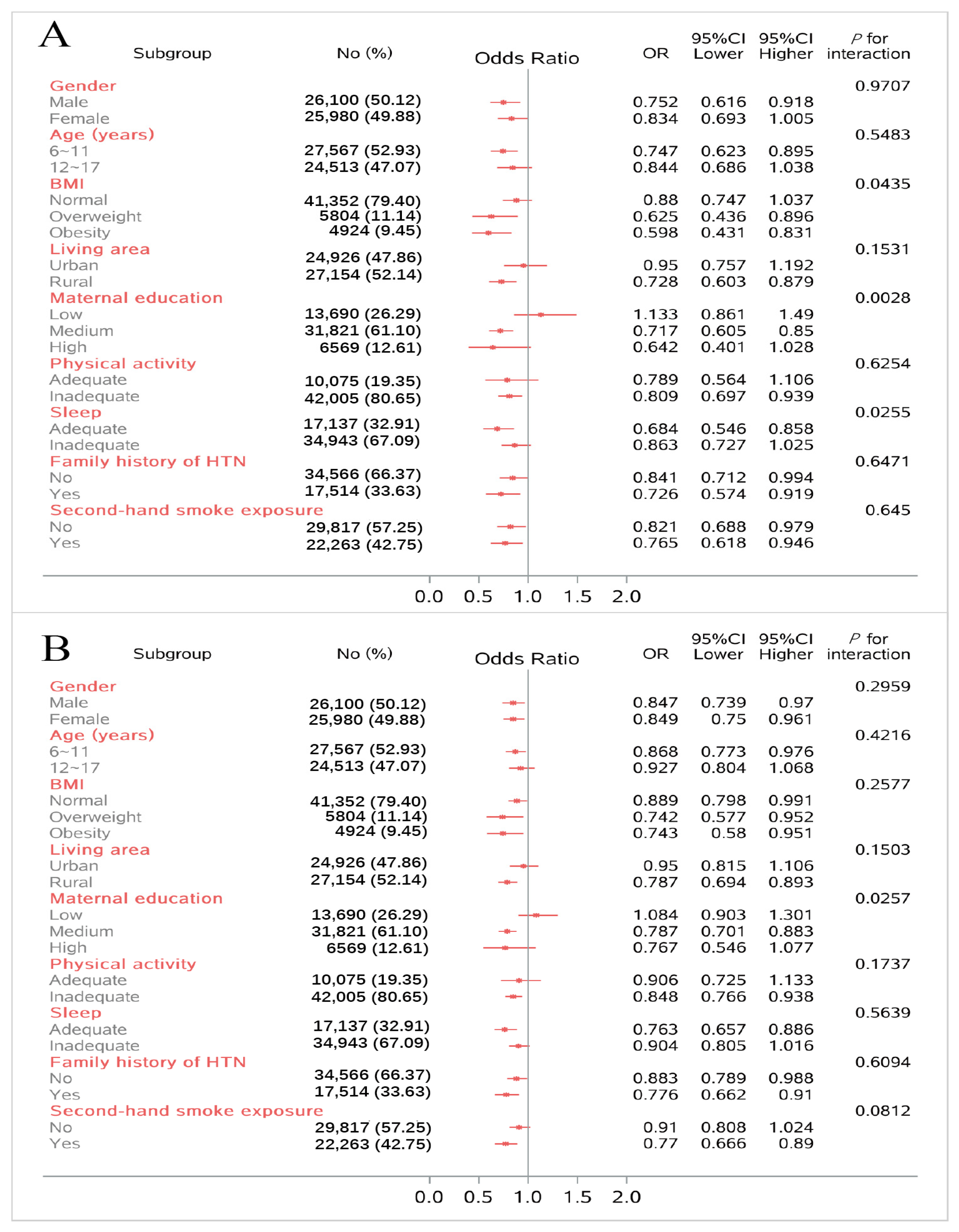
3.5. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Joseph, P.; Hu, B.; Yin, L.; Tse, L.A.; Rangarajan, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Islam, S.; et al. Modifiable risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease and mortality in China: A PURE substudy. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2852–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Danaei, G.; Riley, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Stevens, G.A.; Gregg, E.W.; Bennett, J.E.; Solomon, B.; Singleton, R.K.; et al. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation 2008, 117, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, E.M.; Khoury, P.R.; Bazzano, L.; Burns, T.L.; Daniels, S.; Dwyer, T.; Hu, T.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Juonala, M.; Prineas, R.; et al. Relation of Blood Pressure in Childhood to Self-Reported Hypertension in Adulthood. Hypertension 2019, 73, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Magnussen, C.G.; Yang, L.; Bovet, P.; Xi, B. Elevated Blood Pressure in Childhood or Adolescence and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Adulthood: A Systematic Review. Hypertension 2020, 75, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Robinson, C.H.; Yu, A.; Bamhraz, A.A.; Ewusie, J.E.; Sanger, S.; Mitsnefes, M.; Parekh, R.S.; Raina, R.; Thabane, L.; et al. Risk of Target Organ Damage in Children With Primary Ambulatory Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hypertension 2023, 80, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din-Dzietham, R.; Liu, Y.; Bielo, M.V.; Shamsa, F. High blood pressure trends in children and adolescents in national surveys, 1963 to 2002. Circulation 2007, 116, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, B.; Gidding, S.S.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Brady, T.M.; Flynn, J.T.; Malle, L.M.; South, A.M.; Tran, A.H.; Urbina, E.M.; Hypertens, A.H.A.C.; et al. Pediatric Primary Hypertension: An Underrecognized Condition: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2023, 80, E101–E111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, M.; Xi, B. Changing trends in the levels of blood pressure and prevalence of hypertension among Chinese children and adolescents from 1991 to 2015. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2020, 41, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, M.; Urbina, E.M. Hypertension in adolescents: Diagnosis, treatment, and implications. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, H.J.; Liu, H.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Du, J.; Liu, J. Dietary factors associated with hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, S.C.; Saelens, B.E.; Khoury, P.R.; Dart, K.B.; Hinn, K.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Daniels, S.R.; Urbina, E.M. Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Dietary Intervention Improves Blood Pressure and Vascular Health in Youth With Elevated Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2021, 77, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, S.C.; Saelens, B.E.; Levin, L.; Dart, K.; Falciglia, G.; Daniels, S.R. The efficacy of a clinic-based behavioral nutrition intervention emphasizing a DASH-type diet for adolescents with elevated blood pressure. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojhabrimanesh, A.; Akhlaghi, M.; Rahmani, E.; Amanat, S.; Atefi, M.; Najafi, M.; Hashemzadeh, M.; Salehi, S.; Faghih, S. A Western dietary pattern is associated with higher blood pressure in Iranian adolescents. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Schulze, M.B.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Nöthlings, U.; Boeing, H. Application of a New Statistical Method to Derive Dietary Patterns in Nutritional Epidemiology. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 159, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batis, C.; Mendez, M.A.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Adair, L.; Popkin, B. Using both principal component analysis and reduced rank regression to study dietary patterns and diabetes in Chinese adults. Public. Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarova, S.V.; Jessri, M. Associations between dietary patterns and cardiovascular disease risk in Canadian adults: A comparison of partial least squares, reduced rank regression, and the simplified dietary pattern technique. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naja, F.; Itani, L.; Hwalla, N.; Sibai, A.M.; Kharroubi, S.A. Identification of dietary patterns associated with elevated blood pressure among Lebanese men: A comparison of principal component analysis with reduced rank regression and partial least square methods. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, D.; Piao, W.; Huang, K.; Zhao, L. Nutrient-Derived Beneficial for Blood Pressure Dietary Pattern Associated with Hypertension Prevention and Control: Based on China Nutrition and Health Surveillance 2015-2017. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongmei, Y.; Liyun, Z.; Jian, Z.; Zhenyu, Y.; Lichen, Y.; Jian, H.; Hongyun, F.; Qiya, G.; Xiaoli, X.; Lahong, J.; et al. China Nutrition and Health Surveys (1982−2017). China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons-Morton, D.G.; Hunsberger, S.A.; Van Horn, L.; Barton, B.A.; Robson, A.M.; McMahon, R.P.; Muhonen, L.E.; Kwiterovich, P.O.; Lasser, N.L.; Kimm, S.Y.; et al. Nutrient intake and blood pressure in the Dietary Intervention Study in Children. Hypertension 1997, 29, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, B. Does Potassium Deficiency Contribute to Hypertension in Children and Adolescents? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, P.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Qin, X. Inverse association between dietary vitamin A intake and new-onset hypertension. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Etchegoyen, C.; Lombarte, M.; Matamoros, N.; Belizán, J.M.; Cormick, G. Mechanisms Involved in the Relationship between Low Calcium Intake and High Blood Pressure. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.J. Potential health concerns of dietary phosphorus: Cancer, obesity, and hypertension. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1301, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, M.C.; Ix, J.H. Dietary phosphorus, serum phosphorus, and cardiovascular disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1301, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepali, P.; Suresh, S.; Pikale, G.; Jhaveri, S.; Avanthika, C.; Bansal, M.; Islam, R.; Chanpura, A. Hypertension and the Role of Dietary Fiber. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Cui, L.; Qi, J.; Ojo, O.; Du, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. The effect of dietary fiber (oat bran) supplement on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2458–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, M.; Eini-Zinab, H.; Safaei, E.; Poursoleiman, F.; Amini, B.; Babashahi, M.; Barati, M.; Hekmatdoost, A. Determination of the level of evidence for the association between different food groups/items and dietary fiber intake and the risk of cardiovascular diseases and hypertension: An umbrella review. Nutr. Res. 2023, 111, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, A.L.; Liese, A.D.; Bell, R.A.; Dabelea, D.; Lawrence, J.M.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Standiford, D.A.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Association between the dietary approaches to hypertension diet and hypertension in youth with diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 2009, 53, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WS/T 586-2018; Screening for Overweight and Obesity among School-Age Children and Adolescents. National Health and Family Planning Commission of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Paruthi, S.; Brooks, L.J.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Hall, W.A.; Kotagal, S.; Lloyd, R.M.; Malow, B.A.; Maski, K.; Nichols, C.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Recommended Amount of Sleep for Pediatric Populations: A Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2016, 12, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Composing and Editorial Board of Physical Activity Guidelines for Chinese. Physical Activity Guidelines for Chinese (2021). Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2022, 56, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Feng, Y.; Qing, J.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, L.; Liang, X. The correlation between nuts and algae-less diet and children’s blood pressure: From a cross-sectional study in Chongqing. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2180024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.E.A.; Souza, M.R.; Gorgulho, B.M.; Pereira, R.A.; Cunha, D.B.; Souza, A.M.; Muraro, A.P.; Ferreira, M.G.; Rodrigues, P.R.M. Restricted dietary pattern may contribute to lowering blood pressure in adolescents with obesity: Study of Cardiovascular Risk in Adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2022, 40, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leermakers, E.T.M.; van den Hooven, E.H.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Moll, H.A.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Voortman, T. A priori and a posteriori derived dietary patterns in infancy and cardiometabolic health in childhood: The role of body composition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, L.; Ciesielski, O.; Balcerczyk, A. Fat not so bad? The role of ketone bodies and ketogenic diet in the treatment of endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 206, 115346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Raimondo, D.; Buscemi, S.; Musiari, G.; Rizzo, G.; Pirera, E.; Corleo, D.; Pinto, A.; Tuttolomondo, A. Ketogenic Diet, Physical Activity, and Hypertension-A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, A.; Faghih, S.; Hojhabrimanesh, A.; Najafi, M.; Tangestani, H.; Atefi, M.; Teymouri, M.; Salehi, M.; Kamali, M.; Amanat, S.; et al. Greater adherence to the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) dietary pattern is associated with lower blood pressure in healthy Iranian primary school children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.L.; Singer, M.R.; Bradlee, M.L.; Djoussé, L.; Proctor, M.H.; Cupples, L.A.; Ellison, R.C. Intake of fruits, vegetables, and dairy products in early childhood and subsequent blood pressure change. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ma, J.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dong, B.; Zou, Z.; Prochaska, J.J. Secular Trends in Blood Pressure and Overweight and Obesity in Chinese Boys and Girls Aged 7 to 17 Years From 1995 to 2014. Hypertension 2018, 72, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, E.L.; Bell, C.S.; Samuel, J.P.; Poffenbarger, T.; Redwine, K.M.; Samuels, J.A. Race and Obesity in Adolescent Hypertension. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20161433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorof, J.M.; Lai, D.; Turner, J.; Poffenbarger, T.; Portman, R.J. Overweight, ethnicity, and the prevalence of hypertension in school-aged children. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wu, Y.; Wilson, R.F.; Segal, J.B.; Kim, M.T.; Wang, Y. Effect of childhood obesity prevention programs on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 2014, 129, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendia, J.R.; Bradlee, M.L.; Daniels, S.R.; Singer, M.R.; Moore, L.L. Longitudinal effects of dietary sodium and potassium on blood pressure in adolescent girls. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Fast food consumption and its associations with obesity and hypertension among children: Results from the baseline data of the Childhood Obesity Study in China Mega-cities. BMC Public. Health 2017, 17, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B. Dietary pattern analysis: A new direction in nutritional epidemiology. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2002, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikert, C.; Schulze, M.B. Evaluating dietary patterns: The role of reduced rank regression. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zha, M.; Zhu, Y.; Rahimi, K.; Rudan, I. Global Prevalence of Hypertension in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yi, Q.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, M.; Yang, Q.; Xia, W.; Ye, Z.; Song, P. Trends in Prevalence of Hypertension and Hypertension Phenotypes Among Chinese Children and Adolescents Over Two Decades (1991–2015). Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 627741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhanick, B.; Sosner, P.; Brochard, K.; Mounier-Véhier, C.; Plu-Bureau, G.; Hascoet, S.; Ranchin, B.; Pietrement, C.; Martinerie, L.; Boivin, J.M.; et al. Hypertension in Children and Adolescents: A Position Statement From a Panel of Multidisciplinary Experts Coordinated by the French Society of Hypertension. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 680803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
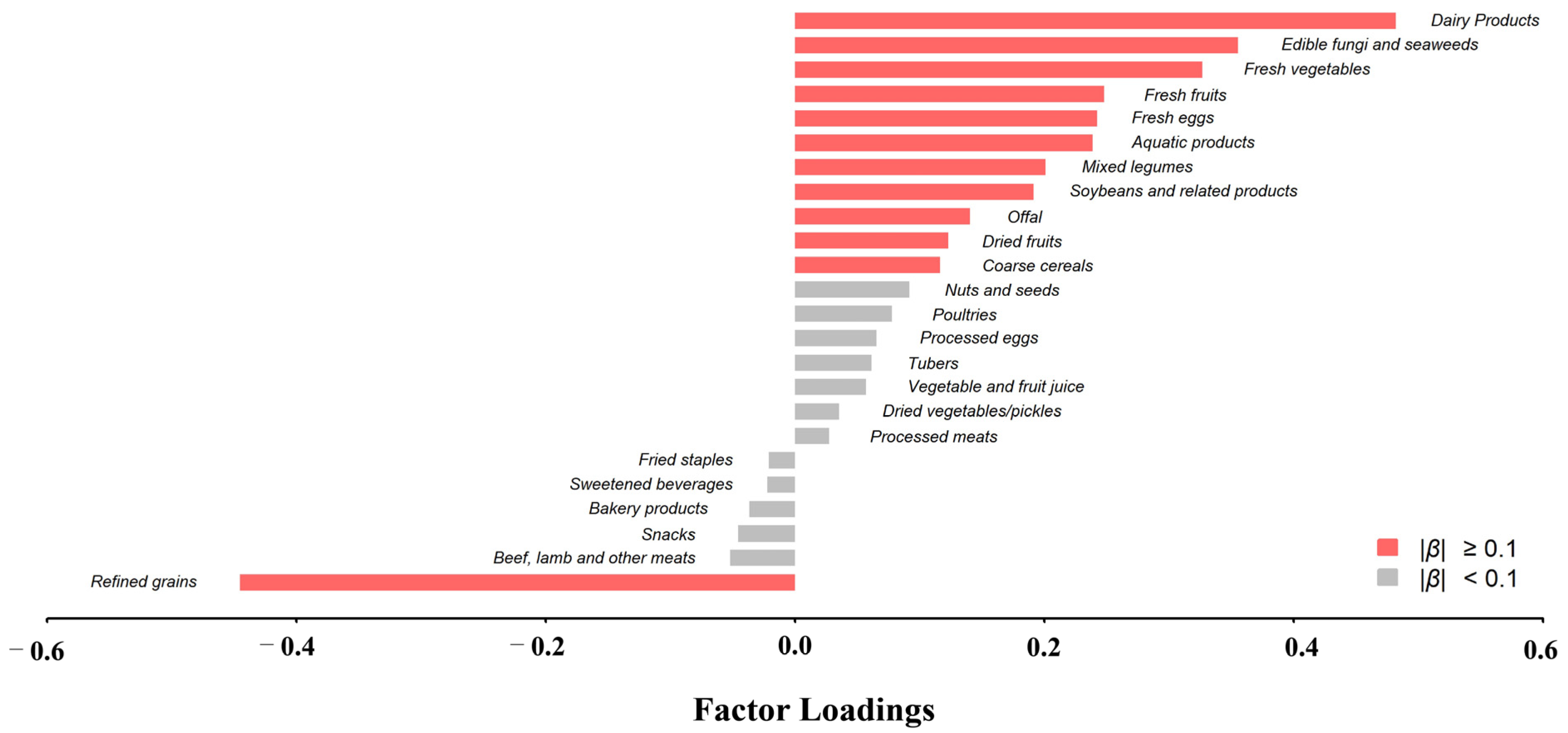
| Variables | Total (n, %) | Quintile | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | ||
| Gender * | ||||||
| Male | 26,100 (50.1) | 5622 (54.0) | 5234 (50.3) | 5092 (48.9) | 5156 (49.5) | 4996 (48.0) |
| Female | 25,980 (49.9) | 4794 (46.0) | 5182 (49.8) | 5324 (51.1) | 5260 (50.5) | 5420 (52.0) |
| Age (years) * | ||||||
| 6~11 | 27,567 (53.0) | 5156 (49.5) | 5787 (55.6) | 5767 (55.4) | 5667(54.4) | 5190 (49.8) |
| 12~17 | 24,513 (47.0) | 5260 (50.5) | 4629 (44.4) | 4649 (44.6) | 4749 (45.6) | 5226 (50.2) |
| BMI * | ||||||
| Normal | 41,352 (79.4) | 8738 (83.9) | 8493 (81.5) | 8326 (79.9) | 7950 (76.3) | 7845 (75.3) |
| Overweight | 5804 (11.1) | 984 (9.5) | 1039 (10.0) | 1091 (10.5) | 1293 (12.4) | 1397 (13.4) |
| Obese | 4924 (9.5) | 694 (6.7) | 884 (8.5) | 999 (9.6) | 1173 (11.3) | 1174 (11.3) |
| Living area * | ||||||
| Urban | 24,926 (47.9) | 2785 (26.7) | 3920 (37.6) | 4928 (47.3) | 6119 (58.8) | 7174 (68.9) |
| Rural | 27,154 (52.1) | 7631 (73.3) | 6496 (62.4) | 5488 (52.7) | 4297 (41.3) | 3242 (31.1) |
| Geographical region * | ||||||
| East | 18,909 (36.3) | 2034 (19.5) | 3052 (29.3) | 3814 (36.6) | 4599 (44.2) | 5410 (51.9) |
| Central | 16,553 (31.8) | 3728 (35.8) | 3514 (33.7) | 3352 (32.2) | 3051 (29.3) | 2908 (27.9) |
| West | 16,618 (31.9) | 4654 (44.7) | 3850 (37.0) | 3250 (31.2) | 2766 (26.6) | 2098 (20.1) |
| Maternal education * | ||||||
| Primary school or below | 13,690 (26.3) | 4149 (39.8) | 3254 (31.2) | 2558 (24.6) | 2046 (19.6) | 1683 (16.2) |
| Junior middle school | 31,821 (61.1) | 5799 (55.7) | 6344 (60.9) | 6589 (63.3) | 6599 (63.4) | 6490 (62.3) |
| High school or higher | 6569 (12.6) | 468 (4.5) | 818 (7.9) | 1269 (12.2) | 1771 (17.0) | 2243 (21.5) |
| Household income * | ||||||
| Not given | 32,691 (62.8) | 6674 (64.1) | 6416 (61.6) | 6443 (61.9) | 6485 (62.3) | 6673 (64.1) |
| Low | 7538 (14.5) | 1906 (18.3) | 1770 (17.0) | 1474 (14.2) | 1265 (12.1) | 1123 (10.8) |
| Medium | 8618 (16.6) | 1584 (15.2) | 1786 (17.2) | 1866 (17.9) | 1774 (17.0) | 1608 (15.4) |
| High | 323 (6.2) | 252 (2.4) | 444 (4.3) | 633 (6.1) | 892 (8.6) | 1012 (9.7) |
| Physical activity * | ||||||
| Adequate | 42,005 (80.7) | 1519 (14.6) | 1974 (19.0) | 2003 (19.2) | 2207 (21.2) | 2372 (22.8) |
| Inadequate | 10,075 (19.4) | 8897 (85.4) | 8442 (81.1) | 8413 (80.8) | 8209 (78.8) | 8044 (77.2) |
| Sedentary behavior (h) * | ||||||
| <2 | 7337 (14.1) | 1704 (16.4) | 1533 (14.7) | 1504 (14.4) | 1342 (12.9) | 1254 (12.0) |
| 2~3 | 13,242 (25.4) | 2684 (25.8) | 2667 (25.6) | 2716 (26.1) | 2659 (25.5) | 2516 (24.2) |
| ≥4 | 31,501 (60.5) | 6028 (57.9) | 6216 (59.7) | 6196 (59.5) | 6415 (61.6) | 6646 (63.8) |
| Sleep duration * | ||||||
| Adequate | 34,943 (67.1) | 3755 (36.1) | 3741 (35.9) | 3537 (34.0) | 3247 (31.2) | 2857 (27.4) |
| Inadequate | 17,137 (32.9) | 6661 (64.0) | 6675 (64.1) | 6879 (66.0) | 7169 (68.8) | 7559 (72.6) |
| Family history of HTN * | ||||||
| No | 34,566 (66.4) | 7612 (73.1) | 7278 (69.9) | 6835 (65.6) | 6486 (62.3) | 6355 (61.0) |
| Yes | 17,514 (33.6) | 2804 (26.9) | 3138 (30.1) | 3581 (34.4) | 3930 (37.7) | 4061 (39.0) |
| Second-hand smoking exposure | ||||||
| No | 29,817 (57.3) | 6077 (58.3) | 5979 (57.4) | 5973 (57.3) | 5833 (56.0) | 5955 (57.2) |
| Yes | 22,263 (42.8) | 4339 (41.7) | 4437 (42.6) | 4443 (42.7) | 4583 (44.0) | 4461 (42.8) |
| Dietary Pattern | Blood Pressure Outcomes | Quintile | N | No. of Cases | OR (95%CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude Model | Model I | Model II | |||||
| PDP | Elevated BP | Q1 | 10,416 | 1380 | † | Reference | Reference |
| Q2 | 10,416 | 1323 | 0.903 (0.832, 0.98) | 0.894 (0.822, 0.972) | |||
| Q3 | 10,416 | 1341 | 0.883 (0.813, 0.958) | 0.878 (0.806, 0.957) | |||
| Q4 | 10,416 | 1295 | 0.881 (0.812, 0.956) | 0.885 (0.810, 0.966) | |||
| Q5 | 10,416 | 1274 | 0.838 (0.772, 0.91) | 0.849 (0.755, 0.931) | |||
| P-trend | <0.0001 | 0.0114 | |||||
| HTN | Q1 | 10,416 | 666 | † | Reference | Reference | |
| Q2 | 10,416 | 648 | 0.939 (0.84, 1.051) | 0.909 (0.81, 1.02) | |||
| Q3 | 10,416 | 638 | 0.904 (0.808, 1.012) | 0.876 (0.779, 0.986) | |||
| Q4 | 10,416 | 649 | 0.888 (0.793, 0.994) | 0.882 (0.781, 0.996) | |||
| Q5 | 10,416 | 585 | 0.79 (0.703, 0.887) | 0.795 (0.694, 0.911) | |||
| P-trend | <0.0001 | 0.0018 | |||||
| DASH | Elevated BP | Q1 | 10,128 | 1295 | † | Reference | Reference |
| Q2 | 13,079 | 1690 | 0.979 (0.906, 1.059) | 0.991 (0.915, 1.073) | |||
| Q3 | 9660 | 1184 | 0.912 (0.838, 0.993) | 0.94 (0.861, 1.025) | |||
| Q4 | 8059 | 1036 | 0.943 (0.863, 1.03) | 0.983 (0.897, 1.078) | |||
| Q5 | 11,154 | 1408 | 0.899 (0.828, 0.975) | 0.958 (0.876, 1.048) | |||
| P-trend | 0.0055 | 0.3389 | |||||
| HTN | Q1 | 10,128 | 639 | † | Reference | Reference | |
| Q2 | 13,079 | 802 | 0.933 (0.838, 1.039) | 0.944 (0.846, 1.053) | |||
| Q3 | 9660 | 561 | 0.871 (0.775, 0.980) | 0.902 (0.799, 1.018) | |||
| Q4 | 8059 | 508 | 0.927 (0.821, 1.046) | 0.973 (0.858, 1.104) | |||
| Q5 | 11,154 | 676 | 0.861 (0.769, 0.964) | 0.928 (0.820, 1.050) | |||
| P-trend | 0.0135 | 0.3623 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ju, L.; Piao, W.; Wei, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, D. Association of the Protective Dietary Pattern for Blood Pressure with Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 6–17 Years Old: Data from China Nutrition and Health Surveillance (2015–2017). Nutrients 2023, 15, 4927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234927
Li Y, Yang Y, Ju L, Piao W, Wei X, Zhao L, Yu D. Association of the Protective Dietary Pattern for Blood Pressure with Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 6–17 Years Old: Data from China Nutrition and Health Surveillance (2015–2017). Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234927
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuge, Yuxiang Yang, Lahong Ju, Wei Piao, Xiaoqi Wei, Liyun Zhao, and Dongmei Yu. 2023. "Association of the Protective Dietary Pattern for Blood Pressure with Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 6–17 Years Old: Data from China Nutrition and Health Surveillance (2015–2017)" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234927
APA StyleLi, Y., Yang, Y., Ju, L., Piao, W., Wei, X., Zhao, L., & Yu, D. (2023). Association of the Protective Dietary Pattern for Blood Pressure with Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 6–17 Years Old: Data from China Nutrition and Health Surveillance (2015–2017). Nutrients, 15(23), 4927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234927






