Associations between High Protein Intake, Linear Growth, and Stunting in Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Outcome Assessment
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
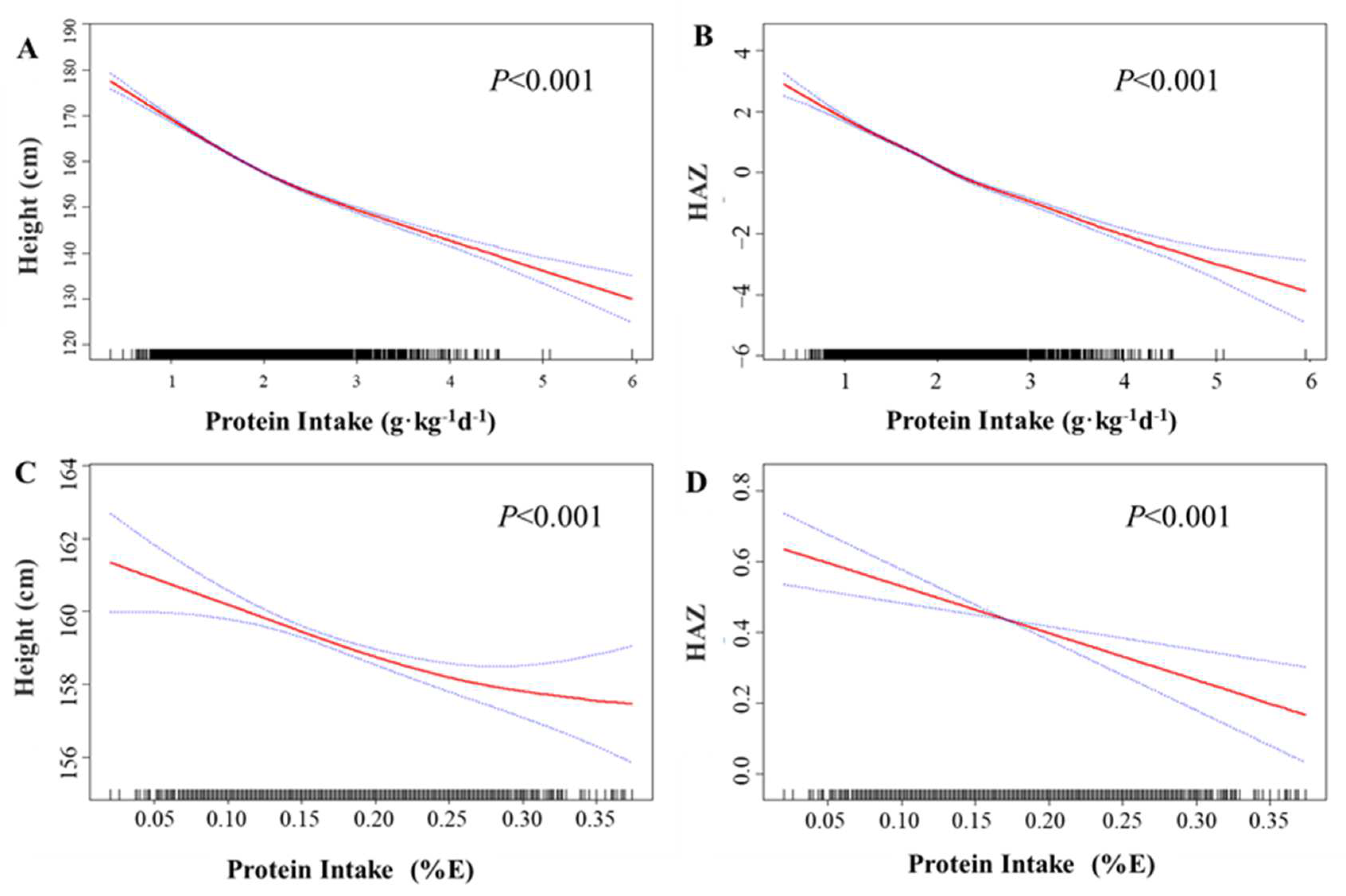
3.2. Association of Protein Intake with Linear Growth in Children and Adolescents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- De Onis, M.; WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Child Growth Standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr. 2006, 450, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Freer, J.; Orr, J.; Walton, R.; Storr, H.L.; Dunkel, L.; Prendergast, A.J. Does stunting still matter in high-income countries? Ann. Hum. Biol. 2023, 50, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaivada, T.; Akseer, N.; Akseer, S.; Somaskandan, A.; Stefopulos, M.; Bhutta, Z.A. Stunting in childhood: An overview of global burden, trends, determinants, and drivers of decline. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 777s–791s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Nutrition Targets 2025: Breastfeeding Policy Brief (WHO/NMH/NHD14. 7); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Inzaghi, E.; Pampanini, V.; Deodati, A.; Cianfarani, S. The Effects of Nutrition on Linear Growth. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, Z.A.; Millward, D.J.; Yayha, Z.A. Dietary protein and the regulation of long-bone and muscle growth in the rat. Clin. Sci. 1994, 87, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, A.; Schoenmakers, I.; Laskey, M.A.; de Bono, S.; Ginty, F.; Goldberg, G.R. Nutrition and bone growth and development. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2006, 65, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trumbo, P.; Schlicker, S.; Yates, A.A.; Poos, M. Dietary reference intakes for energy, carbohydrate, fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein and amino acids. (Commentary). J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2002, 102, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for protein. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Iborra, M.; Castanys-Munoz, E.; Oliveros, E.; Ramirez, M. Optimal Protein Intake in Healthy Children and Adolescents: Evaluating Current Evidence. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, W.; Yu, D.; Ju, L.; Guo, Q.; Fang, H.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Cai, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, L. Intakes of energy and macronutrients in 6-11 years old age group in 2016–2017 in China. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu J. Hyg. Res. 2021, 50, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Ju, H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, J.F.; Gong, D.P.; Guo, D.D.; Luo, S.Q.; Zhao, W.H. Food Frequency Questionnaire for Chinese Children Aged 12-17 Years: Validity and Reliability. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y. China Food Composition Table (Standard Edition); Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1220S–1228S, discussion 1229S–1231S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switkowski, K.M.; Jacques, P.F.; Must, A.; Kleinman, K.P.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Maternal protein intake during pregnancy and linear growth in the offspring. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Onis, M. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Li, X.; Gasevic, D.; Flores, A.B.; Yu, Z. BMI, waist circumference reference values for Chinese school-aged children and adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in pattern of pubertal changes in girls. Arch. Dis. Child. 1969, 44, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in the pattern of pubertal changes in boys. Arch. Dis. Child. 1970, 45, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.M.; Whitehouse, R.H. Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stages of puberty. Arch. Dis. Child. 1976, 51, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Melough, M.M.; Kim, D.; Sakaki, J.R.; Lee, J.; Choi, K.; Chun, O.K. Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality Are Associated with Standardized Height-for-Age among U.S. Children. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuiche, A.V.; Cureau, F.V.; Madalosso, M.M.; Telo, G.H.; Schaan, B.D. Association between socioeconomic and nutritional factors and height of Brazilian adolescents: Results from the Study of Cardiovascular Risk in Adolescents. Cad. Saude Publica 2022, 38, e00277321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkey, C.S.; Colditz, G.A.; Rockett, H.R.; Frazier, A.L.; Willett, W.C. Dairy consumption and female height growth: Prospective cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimujiang, A.; Colditz, G.A.; Gardner, J.D.; Park, Y.; Berkey, C.S.; Sutcliffe, S. Childhood diet and growth in boys in relation to timing of puberty and adult height: The Longitudinal Studies of Child Health and Development. Cancer Causes Control 2018, 29, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Remer, T. Adult Stature and Protein Intake During Childhood and Adolescence From 3 Years Onward. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e2833–e2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, K.V.; Erler, N.S.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Jaddoe, V.W.; van den Hooven, E.H.; Franco, O.H.; Voortman, T. Dietary Intake of Protein in Early Childhood Is Associated with Growth Trajectories between 1 and 9 Years of Age. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; He, J.; Fang, A.; Li, K. Effect of dietary protein intake on height and height growth of boys. Food Nutr. China 2016, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Xiao, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Jiang, C.; et al. Smad5 acts as an intracellular pH messenger and maintains bioenergetic homeostasis. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellur, G.; Sukhdeo, S.V.; Khan, M.T.; Sharan, K. Maternal high protein-diet programs impairment of offspring’s bone mass through miR-24-1-5p mediated targeting of SMAD5 in osteoblasts. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, C.M.; Bazer, F.W.; Johnson, G.A.; Wu, G. Impacts of maternal dietary protein intake on fetal survival, growth, and development. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | n | Protein Intake, g·kg−1·d−1 | Protein Intake, %E | Height (cm) | HAZ | Stunning | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | p | N (%) | p | ||
| Overall | 3299 | ||||||||||
| Basic characteristics | |||||||||||
| Gender | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.025 | ||||||
| Male | 1837 | 1.82 ± 0.66 | 15% ± 5% | 161.76 ± 13.63 | 0.55 ± 1.00 | 21 (1.14) | |||||
| Female | 1462 | 2.03 ± 0.60 | 19% ± 6% | 155.86 ± 9.65 | 0.31 ±0.92 | 31 (2.12) | |||||
| Age, years | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.052 | ||||||
| 9.0–12.0 | 1074 | 2.44 ± 0.67 | 18% ± 6% | 146.44 ± 8.48 | 0.74 ± 1.06 | 9 (0.84) | |||||
| 12.0–14.0 | 849 | 1.85 ± 0.48 | 17% ± 5% | 160.44 ± 7.85 | 0.61 ± 1.04 | 18 (2.12) | |||||
| >14.0 | 1376 | 1.54 ± 0.37 | 17% ± 5% | 168.16 ± 8.04 | 0.11 ± 0.87 | 25 (1.82) | |||||
| Ethnicity | 0.976 | 0.428 | 0.373 | 0.303 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Han Chinese | 3177 | 1.91 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 5% | 159.18 ± 12.41 | 0.44 ± 0.97 | 45 (1.42) | |||||
| Others | 122 | 1.91 ± 0.62 | 17% ± 6% | 158.16 ± 11.68 | 0.35 ± 1.07 | 7 (5.74) | |||||
| Premature | 0.279 | 0.558 | 0.115 | 0.996 | 0.543 | ||||||
| Yes | 3123 | 1.91 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 5% | 159.24 ± 12.41 | 0.44 ± 1.02 | 51 (1.63) | |||||
| No | 174 | 1.97 ± 0.62 | 17% ± 6% | 156.53 ± 11.58 | 0.44 ± 0.98 | 1 (0.57) | |||||
| Missing | 2 | 1.40 ± 0.30 | 14% ± 8% | 165.00 ± 2.69 | 0.50 ± 0.71 | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| Birth length, cm | <0.001 | 0.330 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.336 | ||||||
| Low | 651 | 2.02 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 5% | 156.78 ± 11.96 | 0.28 ± 1.01 | 13 (2.00) | |||||
| High | 2648 | 1.89 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 6% | 159.67 ± 12.41 | 0.48 ± 1.02 | 39 (1.47) | |||||
| Pubertal stage | 0.667 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.815 | |||||||
| Pre-puberty | 343 | 2.68 ± 0.71 | <0.001 | 17% ± 5% | 141.37 ± 6.61 | 0.42 ± 0.91 | 5 (1.46) | ||||
| Mid-puberty | 887 | 2.26 ± 0.65 | 17% ± 5% | 151.04 ± 9.72 | 0.64 ± 1.06 | 16 (1.80) | |||||
| Post-puberty | 2069 | 1.64 ± 0.41 | 17% ± 6% | 165.57 ± 8.66 | 0.36 ± 0.93 | 31 (1.50) | |||||
| Household income, CNY/years | 0.569 | 0.929 | 0.720 | <0.001 | 0.372 | ||||||
| <120,000 | 935 | 1.90 ± 0.62 | 17% ± 6% | 158.84 ± 11.95 | 0.30 ± 0.97 | 19 (2.03) | |||||
| 120,000–250,000 | 1126 | 1.90 ± 0.66 | 17% ± 6% | 159.38 ± 12.18 | 0.43 ± 0.98 | 19 (1.69) | |||||
| ≥250,000 | 1214 | 1.93 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 5% | 159.13 ± 12.87 | 0.56 ± 0.95 | 14 (1.15) | |||||
| Missing | 24 | 1.87 ± 0.77 | 17% ± 5% | 160.67 ± 13.78 | 0.18 ± 0.86 | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| Smoking status | 0.195 | 0.797 | <0.001 | 0.061 | 0.344 | ||||||
| no | 3244 | 1.91 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 6% | 158.99 ± 12.31 | 0.44 ± 1.02 | 52 (1.60) | |||||
| yes | 55 | 1.80 ± 0.75 | 17% ± 6% | 165.88 ± 14.14 | 0.22 ± 1.03 | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| Drinking status, standard drink/month | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.109 | 0.166 | ||||||
| Never | 2819 | 1.96 ± 0.65 | 17% ± 5% | 158.16 ± 12.35 | 0.46 ± 0.98 | 43 (1.53) | |||||
| <1 | 369 | 1.67 ± 0.53 | 16% ± 6% | 163.99 ± 11.11 | 0.34 ± 0.90 | 9 (2.44) | |||||
| ≥1 | 111 | 1.54 ± 0.39 | 16% ± 6% | 168.19 ± 9.67 | 0.33 ± 0.93 | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| MVPA, h/day | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.035 | ||||||
| <1.0 | 770 | 1.79 ± 0.56 | 18% ± 6% | 161.16 ± 11.00 | 0.21 ± 1.00 | 19 (2.47) | |||||
| 1–3 | 1505 | 1.88 ± 0.61 | 17% ± 5% | 159.91 ± 12.05 | 0.46 ± 1.01 | 21 (1.40) | |||||
| >3 | 1010 | 2.04 ± 0.72 | 16% ± 5% | 156.42 ± 13.29 | 0.60 ± 1.02 | 11 (1.09) | |||||
| Missing | 14 | 2.26 ± 0.96 | 18% ± 6% | 151.99 ± 16.03 | 0.07 ± 1.27 | 1 (7.14) | |||||
| Central obesity | <0.001 | 0.028 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.018 | ||||||
| No | 2784 | 2.01 ± 0.63 | 17% ± 5% | 158.47 ± 12.41 | 0.32 ± 0.96 | 50 (1.80) | |||||
| Yes | 515 | 1.40 ± 0.41 | 17% ± 6% | 162.50 ± 11.62 | 1.09 ± 1.09 | 2 (0.39) | |||||
| Length of nighttime sleep, h/day | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.824 | ||||||
| <8 | 635 | 1.52 ± 0.40 | 17% ± 6% | 167.93 ± 8.69 | 0.11 ± 0.88 | 11 (1.73) | |||||
| 8–9 | 1205 | 1.72 ± 0.49 | 17% ± 5% | 163.91 ± 9.67 | 0.39 ± 1.00 | 21 (1.74) | |||||
| ≥9 | 1442 | 2.25 ± 0.68 | 18% ± 6% | 151.19 ± 10.97 | 0.64 ± 1.05 | 20 (1.39) | |||||
| Missing | 16 | 1.88 ± 0.72 | 16% ± 4% | 159.47 ± 15.31 | 0.00 ± 0.89 | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| Protein intake, g·kg−1·d−1 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Q1 | 825 | 1.22 ± 0.19 | 14% ± 5% | 170.23 ± 8.24 | 0.66 ± 1.00 | 3 (0.36) | |||||
| Q2 | 824 | 1.64 ± 0.09 | 17% ± 5% | 163.60 ± 8.18 | 0.50 ± 0.94 | 5 (0.61) | |||||
| Q3 | 825 | 2.00 ± 0.12 | 18% ± 6% | 157.09 ± 8.44 | 0.43 ± 0.99 | 18 (2.18) | |||||
| Q4 | 825 | 2.80 ± 0.49 | 18% ± 5% | 145.66 ± 8.86 | 0.17 ± 0.88 | 26 (3.15) | |||||
| Biochemical indexes | |||||||||||
| Serum vitamin D3, ng/mL | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.383 | ||||||
| T1 | 1093 | 1.76 ± 0.54 | 18% ± 6% | 162.38 ± 10.49 | 0.29 ± 0.95 | 15 (1.37) | |||||
| T2 | 1093 | 1.89 ± 0.61 | 17% ± 6% | 159.54 ± 11.94 | 0.50 ± 1.04 | 22 (2.01) | |||||
| T3 | 1094 | 2.08 ± 0.72 | 17% ± 5% | 155.54 ± 13.49 | 0.53 ± 1.05 | 15 (1.37) | |||||
| Serum Ca, mmol/L | <0.001 | 0.594 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.745 | ||||||
| Low | 697 | 1.79 ± 0.55 | 17% ± 5% | 162.11 ± 10.99 | 0.33 ± 0.92 | 12 (1.72) | |||||
| High | 2584 | 1.94 ± 0.66 | 17% ± 6% | 158.40 ± 12.60 | 0.47 ± 0.98 | 40 (1.55) | |||||
| Serum Zn, mg/L | 0.048 | 0.015 | 0.003 | 0.919 | 0.582 | ||||||
| T1 | 1092 | 1.95 ± 0.65 | 17% ± 6% | 158.21 ± 12.25 | 0.45 ± 0.97 | 14 (1.28) | |||||
| T2 | 1094 | 1.89 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 5% | 159.41 ± 12.37 | 0.43 ± 0.98 | 20 (1.83) | |||||
| T3 | 1093 | 1.89 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 5% | 159.97 ± 12.42 | 0.44 ± 0.97 | 18 (1.65) | |||||
| Serum vitamin A, μg/mL | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.181 | 0.666 | ||||||
| T1 | 1087 | 2.10 ± 0.68 | 18% ± 6% | 155.48 ± 12.27 | 0.40 ± 0.93 | 20 (1.84) | |||||
| T2 | 1091 | 1.95 ± 0.61 | 17% ± 6% | 158.45 ± 11.76 | 0.44 ± 0.99 | 17 (1.56) | |||||
| T3 | 1102 | 1.69 ± 0.56 | 16% ± 5% | 163.59 ± 11.68 | 0.48 ± 0.99 | 15 (1.36) | |||||
| Dietary fat intake (g/d) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.137 | 0.241 | ||||||
| T1 | 1100 | 1.69 ± 0.56 | 15% ± 5% | 160.16 ± 13.03 | 0.48 ± 0.98 | 14 (1.27) | |||||
| T2 | 1099 | 1.97 ± 0.61 | 19% ± 5% | 157.88 ± 12.02 | 0.40 ± 0.97 | 15 (1.36) | |||||
| T3 | 1100 | 2.08 ± 0.69 | 18% ± 5% | 159.40 ± 11.97 | 0.44 ± 0.97 | 23 (2.09) | |||||
| Dietary carbohydrate intake (g/d) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.040 | 0.431 | ||||||
| T1 | 1100 | 2.11 ± 0.69 | 18% ± 5% | 159.36 ± 12.07 | 0.46 ± 0.98 | 19 (1.73) | |||||
| T2 | 1099 | 1.95 ± 0.60 | 19% ± 5% | 158.05 ± 11.95 | 0.38 ± 0.97 | 20 (1.82) | |||||
| T3 | 1100 | 1.67 ± 0.55 | 14% ± 5% | 160.02 ± 13.03 | 0.48 ± 0.96 | 13 (1.18) | |||||
| Parental characteristics | |||||||||||
| Fathers’ height, cm | 0.047 | 0.283 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Q1 | 680 | 1.96 ± 0.67 | 17% ± 6% | 157.01 ± 12.48 | −0.00 ± 0.92 | 31 (4.56) | |||||
| Q2 | 1031 | 1.93 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 6% | 158.44 ± 12.01 | 0.27 ± 0.90 | 14 (1.36) | |||||
| Q3 | 721 | 1.89 ± 0.60 | 17% ± 5% | 159.79 ± 11.73 | 0.61 ± 0.90 | 2 (0.28) | |||||
| Q4 | 824 | 1.88 ± 0.65 | 17% ± 5% | 161.14 ± 13.00 | 0.87 ± 0.94 | 4 (0.49) | |||||
| Missing | 43 | 1.78 ± 0.68 | 17% ± 6% | 160.93 ± 11.78 | 0.47 ± 0.90 | 1 (2.33) | |||||
| Mothers’ height, cm | <0.001 | 0.158 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Q1 | 834 | 1.99 ± 0.66 | 17% ± 6% | 156.44 ± 11.97 | 0.05 ± 0.92 | 29 (3.48) | |||||
| Q2 | 674 | 1.95 ± 0.63 | 17% ± 5% | 157.51 ± 12.09 | 0.29 ± 0.91 | 12 (1.78) | |||||
| Q3 | 939 | 1.87 ± 0.63 | 17% ± 6% | 160.56 ± 12.03 | 0.54 ± 0.93 | 8 (0.85) | |||||
| Q4 | 827 | 1.85 ± 0.63 | 17% ± 5% | 161.57 ± 12.71 | 0.85 ± 0.94 | 3 (0.36) | |||||
| Missing | 25 | 2.12 ± 0.84 | 18% ± 6% | 160.28 ± 13.37 | 0.28 ± 0.86 | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| Fathers’ education, years | <0.001 | 0.557 | 0.021 | <0.001 | 0.006 | ||||||
| ≤9 years | 605 | 1.84 ± 0.57 | 17% ± 5% | 160.19 ± 11.10 | 0.18 ± 0.97 | 17 (2.81) | |||||
| 10~12 years | 764 | 1.88 ± 0.64 | 17% ± 6% | 159.61 ± 12.48 | 0.32 ± 0.97 | 16 (2.09) | |||||
| 13~15 years | 941 | 1.91 ± 0.62 | 17% ± 6% | 158.82 ± 12.25 | 0.49 ± 0.97 | 13 (1.38) | |||||
| ≥16 years | 948 | 2.00 ± 0.70 | 17% ± 5% | 158.33 ± 13.16 | 0.66 ± 0.93 | 5 (0.53) | |||||
| Missing | 41 | 1.75 ± 0.67 | 17% ± 6% | 161.44 ± 11.77 | 0.45 ± 0.89 | 1 (2.44) | |||||
| Mothers’ education, years | <0.001 | 0.182 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤9 years | 721 | 1.81 ± 0.56 | 17% ± 6% | 160.19 ± 11.40 | 0.17 ± 0.98 | 23 (3.19) | |||||
| 10~12 years | 921 | 1.87 ± 0.62 | 17% ± 6% | 159.88 ± 12.36 | 0.40 ± 0.97 | 16 (1.74) | |||||
| 13~15 years | 923 | 1.96 ± 0.66 | 17% ± 5% | 158.81 ± 12.60 | 0.52 ± 0.97 | 12 (1.30) | |||||
| ≥16 years | 714 | 2.01 ± 0.70 | 17% ± 5% | 157.44 ± 12.89 | 0.67 ± 0.90 | 1 (0.14) | |||||
| Missing | 20 | 1.95 ± 0.78 | 18% ± 7% | 163.55 ± 12.36 | 0.26 ± 0.80 | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| Mothers’ age, years | <0.001 | 0.818 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.350 | ||||||
| T1 | 1044 | 2.12 ± 0.70 | 17% ± 5% | 153.67 ± 12.05 | 0.55 ± 1.05 | 15 (1.44) | |||||
| T2 | 950 | 1.92 ± 0.60 | 17% ± 6% | 159.64 ± 11.69 | 0.44 ± 1.01 | 12 (1.26) | |||||
| T3 | 1267 | 1.74 ± 0.56 | 17% ± 6% | 163.11 ± 11.49 | 0.37 ± 0.99 | 25 (1.97) | |||||
| Models | Protein Intake, g·kg−1·d−1 | Protein Intake, %E | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Height | HAZ | Body Height | HAZ | |||||
| β (95%CI) | p | β (95%CI) | p | β (95%CI) | p | β (95%CI) | p | |
| Crude model | −9.45 (−9.72, −9.18) | <0.001 | −0.21 (−0.25, −0.18) | <0.001 | −2.20 (−2.61, −1.78) | <0.001 | −0.09 (−0.12, −0.05) | <0.001 |
| Model I | −5.79 (−6.12, −5.45) | <0.001 | −0.78 (−0.83, −0.73) | <0.001 | −0.50 (−0.72, −0.28) | <0.001 | −0.04 (−0.07, −0.01) | 0.018 |
| Model II | −5.78 (−6.12, −5.45) | <0.001 | −0.79 (−0.84, −0.74) | <0.001 | −0.48 (−0.70, −0.26) | <0.001 | −0.04 (−0.07, −0.01) | 0.014 |
| Pubertal Stage | Boys | Girls | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Body Height | HAZ | n | Body Height | HAZ | |||||
| β (95%CI) | p | β (95%CI) | p | β (95%CI) | p | β (95%CI) | p | |||
| Pre-puberty | 266 | −3.92 (−4.52, −3.32) | <0.001 | −0.61 (−0.71, −0.50) | <0.001 | 77 | −3.97 (−5.54, −2.40) | <0.001 | −0.60 (−0.88, −0.31) | <0.001 |
| Mid-puberty | 580 | −6.53 (−7.15, −5.91) | <0.001 | −0.94 (−1.03, −0.84) | <0.001 | 307 | −4.69 (−5.45, −3.93) | <0.001 | −0.77 (−0.90, −0.64) | <0.001 |
| Post-puberty | 991 | −5.82 (−6.55, −5.08) | <0.001 | −0.73 (−0.83, −0.62) | <0.001 | 1078 | −4.79 (−5.38, −4.20) | <0.001 | −0.69 (−0.79, −0.60) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, T.; Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Kong, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Yao, P.; et al. Associations between High Protein Intake, Linear Growth, and Stunting in Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224821
Xiong T, Wu Y, Hu J, Xu S, Li Y, Kong B, Zhang Z, Chen L, Tang Y, Yao P, et al. Associations between High Protein Intake, Linear Growth, and Stunting in Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(22):4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224821
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Ting, Yuanjue Wu, Jiazhen Hu, Shiqi Xu, Yan Li, Binxuan Kong, Zhuangyu Zhang, Liangkai Chen, Yuhan Tang, Ping Yao, and et al. 2023. "Associations between High Protein Intake, Linear Growth, and Stunting in Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 15, no. 22: 4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224821
APA StyleXiong, T., Wu, Y., Hu, J., Xu, S., Li, Y., Kong, B., Zhang, Z., Chen, L., Tang, Y., Yao, P., Xiong, J., & Li, Y. (2023). Associations between High Protein Intake, Linear Growth, and Stunting in Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 15(22), 4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224821







