The Relationship between Self-Reported Sitting Time and Vitamin D Levels in Middle-Aged and Elderly Taiwanese Population: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Protocol and Search Question
2.2. Data Collection and Measurements
2.3. Assessment of Systemic Disease and Other Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, S.-M.; Shin, E.-A. Exploring Vitamin D Metabolism and Function in Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D: Production, Metabolism and Mechanisms of Action; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Holick, M.F. Resurrection of Vitamin D Deficiency and Rickets. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitamin D. Available online: https://ods-od-nih-gov.lib3.cgmh.org.tw:30443/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Rosen, C.J.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; Kovacs, C.S.; et al. IOM Committee Members Respond to Endocrine Society Vitamin D Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Endocrine Society Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C.; Manson, J.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; et al. The 2011 Report on Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What Clinicians Need to Know. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. High Prevalence of Vitamin D Inadequacy and Implications for Health. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, M.; Sahay, R. Rickets-Vitamin D Deficiency and Dependency. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, H.A.; Stähelin, H.B.; Dick, W.; Akos, R.; Knecht, M.; Salis, C.; Nebiker, M.; Theiler, R.; Pfeifer, M.; Begerow, B.; et al. Effects of Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation on Falls: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Staehelin, H.B.; Orav, J.E.; Stuck, A.E.; Theiler, R.; Wong, J.B.; Egli, A.; Kiel, D.P.; Henschkowski, J. Fall Prevention with Supplemental and Active Forms of Vitamin D: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ 2009, 339, b3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, P.; Fan, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Y. Global and Regional Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency in Population-Based Studies from 2000 to 2022: A Pooled Analysis of 7.9 Million Participants. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1070808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Healy, G.N.; Sugiyama, T.; Owen, N. “Too Much Sitting” and Metabolic Risk—Has Modern Technology Caught up with Us? Eur. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmot, E.G.; Edwardson, C.L.; Achana, F.A.; Davies, M.J.; Gorely, T.; Gray, L.J.; Khunti, K.; Yates, T.; Biddle, S.J.H. Sedentary Time in Adults and the Association with Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease and Death: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2895–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaards, C.M.; Hildebrandt, V.H.; Hendriksen, I.J.M. Correlates of Sedentary Time in Different Age Groups: Results from a Large Cross Sectional Dutch Survey. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, M.H.; Oh, Y.H. Sedentary Lifestyle: Overview of Updated Evidence of Potential Health Risks. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2020, 41, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.; McNamara, E.; Tainio, M.; de Sá, T.H.; Smith, A.D.; Sharp, S.J.; Edwards, P.; Woodcock, J.; Brage, S.; Wijndaele, K. Sedentary Behaviour and Risk of All-Cause, Cardiovascular and Cancer Mortality, and Incident Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Dose Response Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runacres, A.; Mackintosh, K.A.; Knight, R.L.; Sheeran, L.; Thatcher, R.; Shelley, J.; McNarry, M.A. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Sedentary Time and Behaviour in Children and Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibler, E.A.; Sardo Molmenti, C.L.; Dai, Q.; Kohler, L.N.; Warren Anderson, S.; Jurutka, P.W.; Jacobs, E.T. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Vitamin D Metabolites. Bone 2016, 83, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-Y.; Wang, H.-W.; Jiang, M.-Y. Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency and Associated Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in the United States. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1163737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rezende, L.F.M.; Rodrigues Lopes, M.; Rey-López, J.P.; Matsudo, V.K.R.; do Luiz, O.C. Sedentary Behavior and Health Outcomes: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.L.; Shih, C.C.; Chen, J.Y. Elevated homocysteine level as an indicator for chronic kidney disease in community-dwelling middle-aged and elderly populations in Taiwan: A community-based cross-sectional study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 964101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.L.; Shih, Y.H.; Huang, T.C.; Shih, C.C.; Chen, J.Y. Association between sedentary time and plasma leptin levels in middle-aged and older adult population in Taiwan: A community-based, cross-sectional study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1057497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.L.; Shih, C.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, J.Y. Elevated serum leptin levels are associated with lower renal function among middle-aged and elderly adults in Taiwan, a community-based, cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1047731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.L.; Huang, T.C.; Shih, C.C.; Chen, J.Y. Relationship between Leptin and Insulin Resistance among Community-Dwelling Middle-Aged and Elderly Populations in Taiwan. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.L.; Shih, C.C.; Huang, T.C.; Chen, J.Y. The Relationship between Elevated Homocysteine and Metabolic Syndrome in a Community-Dwelling Middle-Aged and Elderly Population in Taiwan. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.C.; Shih, Y.L.; Chen, J.Y. The association between homocysteine levels and cardiovascular disease risk among middle-aged and elderly adults in Taiwan. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; International Biometric Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, e1082–e1143. [Google Scholar]
- Inzucchi, S.; Bergenstal, R.; Fonseca, V.; Gregg, E.; Mayer-Davis, B.; Spollett, G.; Wender, R. American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. S1), S62–S69. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; De Zeeuw, D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and Classification of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Position Statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, W.J. Systemic Hypertension. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2007, 32, 201–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Hsu, H.-J.; Wu, I.-W.; Sun, C.-Y.; Ting, M.-K.; Lee, C.-C. Vitamin D Deficiency in Northern Taiwan: A Community-Based Cohort Study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, M.; Anderson, C.D. Influence of Age, Gender, Educational Level and Self-Estimation of Skin Type on Sun Exposure Habits and Readiness to Increase Sun Protection. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, J.C. Vitamin D and Aging. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 42, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-J.; Chang, H.-Y.; Pan, W.-H. Time Trend of Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome and Related Dietary Pattern in Taiwan: From NAHSIT 1993–1996 to NAHSIT 2005–2008. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 20, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Mathangasinghe, Y.; Jayawardena, R.; Hills, A.P.; Misra, A. Prevalence and Trends of Metabolic Syndrome among Adults in the Asia-Pacific Region: A Systematic Review. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, W.; Lun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Kanu, J.S.; Qiu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Mainland China: A Meta-Analysis of Published Studies. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makariou, S.E.; Challa, A.; Siomou, E.; Tellis, C.; Tselepis, A.; Elisaf, M.; Liberopoulos, E. Vitamin D Status and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Greek Adolescents with Obesity—The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation: A Pilot Study. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2020, 5, e64–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.; McAllister, R.; Morgan, A.; Rai, T.S.; McGilligan, V.; Ennis, M.; Page, C.; Kelly, C.; Peace, A.; Corfe, B.M.; et al. The Interdependency and Co-Regulation of the Vitamin D and Cholesterol Metabolism. Cells 2021, 10, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastorani, M.; Aghadavod, E.; Mirhosseini, N.; Foroozanfard, F.; Zadeh Modarres, S.; Amiri Siavashani, M.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Metabolic Profiles and Gene Expression of Insulin and Lipid Metabolism in Infertile Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Candidates for in Vitro Fertilization. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaaby, T.; Husemoen, L.L.N.; Pisinger, C.; Jørgensen, T.; Thuesen, B.H.; Fenger, M.; Linneberg, A. Vitamin D Status and Changes in Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Prospective Study of a General Population. Cardiology 2012, 123, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.C.M.; Cureau, F.V.; de Oliveira, C.L.; Giannini, D.T.; Bloch, K.V.; Kuschnir, M.C.C.; Dutra, E.S.; Schaan, B.D.; de Carvalho, K.M.B. Physical Activity but Not Sedentary Time Is Associated with Vitamin D Status in Adolescents: Study of Cardiovascular Risk in Adolescents (ERICA). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Urra, P.; Cristi-Montero, C.; Romero-Parra, J.; Zavala-Crichton, J.P.; Saez-Lara, M.J.; Plaza-Diaz, J. Passive Commuting and Higher Sedentary Time Is Associated with Vitamin D Deficiency in Adult and Older Women: Results from Chilean National Health Survey 2016–2017. Nutrients 2019, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortsman, J.; Matsuoka, L.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Lu, Z.; Holick, M.F. Decreased Bioavailability of Vitamin D in Obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedermaier, T.; Gredner, T.; Kuznia, S.; Schöttker, B.; Mons, U.; Brenner, H. Vitamin D Supplementation to the Older Adult Population in Germany Has the Cost-Saving Potential of Preventing Almost 30,000 Cancer Deaths per Year. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1986–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, T.-Y.; Lu, H.-T.; Kao, Y.-P.; Chien, S.-C.; Chen, H.-C.; Lin, L.-F. Understanding the Meaningful Places for Aging-in-Place: A Human-Centric Approach toward Inter-Domain Design Criteria Consideration in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Jing, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wan, Y. Recent Trends in Sedentary Time: A Systematic Literature Review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 25-Hydroxyvitamin D | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Deficiency (<20) | Insufficiency (20–30) | Sufficiency (>30) | ||
| Variable | n = 396 | n = 64 | n = 195 | n = 137 | p Value |
| Sitting time (hours/day) | 4.83 ± 2.66 | 6.34 ± 3.30 | 4.57 ± 2.40 | 4.51 ± 2.46 | <0.001 |
| 25 (OH) Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 28.32 ± 9.38 | 16.14 ± 2.57 | 25.15 ± 3.06 | 38.53 ± 7.09 | <0.001 |
| Age (year) | 64.91 ± 8.80 | 62.17 ± 8.58 | 65.55 ± 8.98 | 65.26 ± 8.47 | 0.020 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 0.87 ± 0.43 | 0.82 ± 0.31 | 0.84 ± 0.56 | 0.93 ± 0.22 | 0.102 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dl) | 141.07 ± 110.00 | 145.77 ± 119.08 | 146.69 ± 131.35 | 130.88 ± 61.71 | 0.372 |
| HDL-C (mg/dl) | 53.46 ± 14.48 | 53.98 ± 13.26 | 54.07 ± 14.39 | 52.35 ± 15.18 | 0.458 |
| LDL-C (mg/dl) | 109.69 ± 33.99 | 113.02 ± 37.08 | 109.66 ± 32.78 | 108.18 ± 34.34 | 0.348 |
| WC (cm) | 85.36 ± 10.83 | 84.55 ± 12.41 | 85.49 ± 11.01 | 85.54 ± 9.80 | 0.544 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 137.30 ± 17.49 | 137.39 ± 17.07 | 136.53 ± 17.15 | 138.36 ± 18.22 | 0.716 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 85.19 ± 10.98 | 85.94 ± 11.07 | 84.36 ± 10.81 | 86.01 ± 11.17 | 0.963 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.59 ± 3.84 | 25.87 ± 5.15 | 25.80 ± 3.66 | 25.18 ± 3.34 | 0.236 |
| Gender, male (%) | 164 (41.4%) | 14 (21.9%) | 70 (35.9%) | 80 (58.4%) | <0.001 |
| smoking (%) | 50 (12.6%) | 5 (7.8%) | 24 (12.3%) | 21 (15.3%) | 0.136 |
| drinking (%) | 28 (7.1%) | 3 (4.7%) | 10 (5.1%) | 15 (10.9%) | 0.052 |
| HTN (%) | 201 (50.9%) | 30 (46.9%) | 91 (46.7%) | 80 (58.4%) | 0.051 |
| DM (%) | 133 (33.6%) | 19 (29.7%) | 68 (34.9%) | 46 (33.6%) | 0.701 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 153 (38.6%) | 24 (37.5%) | 79 (40.5%) | 50 (36.5%) | 0.741 |
| CKD (%) | 100 (25.3%) | 16 (25.0%) | 41 (21.0%) | 43 (31.4%) | 0.150 |
| 25-Hydroxyvitamin D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted for Age | |||
| Variables | Correlation | p-Value | Correlation | p-Value |
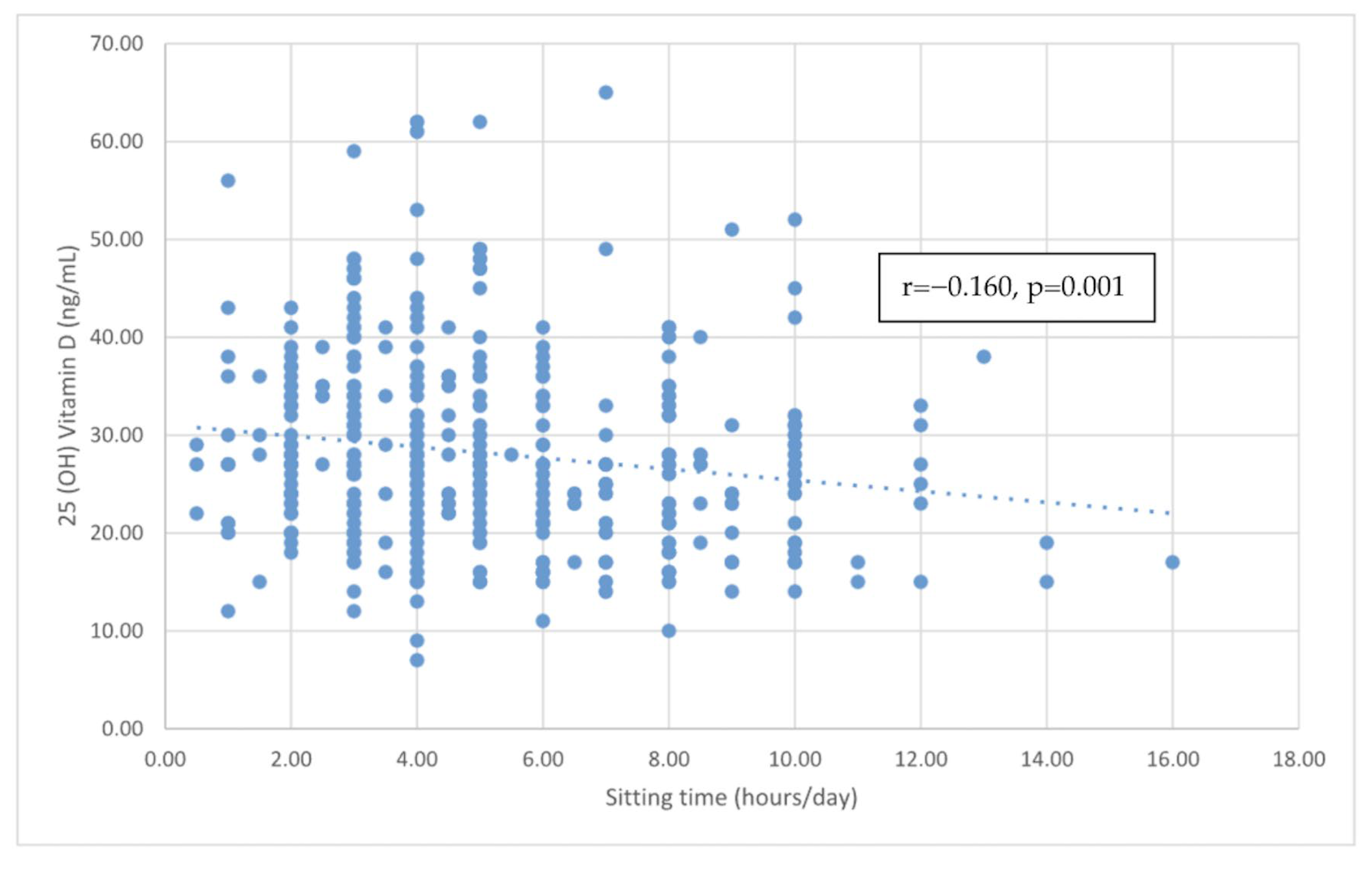
| Sitting time (hours/day) | −0.160 | <0.001 | −0.155 | 0.002 |
| Age (year) | 0.096 | 0.056 | NA | NA |
| Triglyceride (mg/dl) | −0.065 | 0.199 | −0.056 | 0.263 |
| HDL-C(mg/dl) | −0.026 | 0.610 | −0.029 | 0.564 |
| LDL-C (mg/dl) | −0.034 | 0.495 | −0.014 | 0.774 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | −0.084 | 0.097 | −0.078 | 0.120 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 0.015 | 0.770 | −0.006 | 0.901 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | β | p Value | B | SE | β | p Value | B | SE | β | p Value | |
| sitting time | −0.455 | 0.171 | −0.129 | 0.008 | −0.450 | 0.170 | −0.128 | 0.008 | −0.464 | 0.169 | −0.131 | 0.006 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Sitting time | 1.221 | 1.109 to 1.344 | <0.001 | 1.223 | 1.109 to 1.347 | <0.001 | 1.230 | 1.114 to 1.358 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-R.; Shih, Y.-L.; Shih, C.-C.; Chen, J.-Y. The Relationship between Self-Reported Sitting Time and Vitamin D Levels in Middle-Aged and Elderly Taiwanese Population: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224766
Chang Y-H, Lin C-R, Shih Y-L, Shih C-C, Chen J-Y. The Relationship between Self-Reported Sitting Time and Vitamin D Levels in Middle-Aged and Elderly Taiwanese Population: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(22):4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224766
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yu-Hsuan, Chun-Ru Lin, Yu-Lin Shih, Chin-Chuan Shih, and Jau-Yuan Chen. 2023. "The Relationship between Self-Reported Sitting Time and Vitamin D Levels in Middle-Aged and Elderly Taiwanese Population: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 15, no. 22: 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224766
APA StyleChang, Y.-H., Lin, C.-R., Shih, Y.-L., Shih, C.-C., & Chen, J.-Y. (2023). The Relationship between Self-Reported Sitting Time and Vitamin D Levels in Middle-Aged and Elderly Taiwanese Population: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 15(22), 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224766






