Abstract
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) has a profound impact on cognitive and mental functioning, leading to lifelong impairment and significantly diminishing the quality of life for affected individuals. A healthy blood–brain barrier (BBB) plays a crucial role in guarding the brain against elevated levels of blood glutamate, making its permeability a vital aspect of glutamate regulation within the brain. Studies have shown the efficacy of reducing excess glutamate in the brain as a treatment for post-TBI depression, anxiety, and aggression. The purpose of this article is to evaluate the involvement of dietary glutamate in the development of depression after TBI. We performed a literature search to examine the effects of diets abundant in glutamate, which are common in Asian populations, when compared to diets low in glutamate, which are prevalent in Europe and America. We specifically explored these effects in the context of chronic BBB damage after TBI, which may initiate neurodegeneration and subsequently have an impact on depression through the mechanism of chronic glutamate neurotoxicity. A glutamate-rich diet leads to increased blood glutamate levels when contrasted with a glutamate-poor diet. Within the context of chronic BBB disruption, elevated blood glutamate levels translate to heightened brain glutamate concentrations, thereby intensifying neurodegeneration due to glutamate neurotoxicity.
1. Introduction
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) has long-term impacts on cognition and psychiatric conditions, including depression, anxiety, and aggression. Although there is a noted association between emotional effects and physical disability resulting from TBI, it has been shown that neuropsychiatric symptoms, including memory and cognitive impairment, anxiety, depression, social withdrawal, and aggression, can continue substantially after the initial brain injury, potentially persisting for decades [1]. These symptoms can hinder the rehabilitation process and resumption of employment and result in heavy reliance on the health care system [1]. These related psychiatric symptoms do not have a correlation with the severity of the initial injury or with pain [1].
It has been well demonstrated that TBI is associated with the development of a wide range of neuropsychiatric diseases [2,3]. A likely reason for the increased presence of neuropsychiatric diseases after TBI involves the general mechanisms governing these diseases and their relationship with chronic blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability and the effects of chronic glutamate neurotoxicity [3]. Depression is a common psychiatric condition in patients with TBI. A recently published, large meta-analysis, consisting of 82 studies in Europe, the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand with 392,834 patients, showed that the odds ratio for depression associated with mild TBI was 3.29 when compared to those without a history of mild TBI [4]. However, previous studies reported that depression after TBI occurred in 35% of cases, with a wide range from 10 to 77% [5,6,7]. This variability may be due to differences among the various populations included, the severity of TBI, the time since injury, and the diverse diagnostic tools utilized [8].
A relationship between depression and glutamate has been noted definitively for several decades [3]. Our previous work examined the impact of high blood glutamate levels on the development of post-traumatic depression, which was initiated by pathological increases in brain glutamate levels resulting from chronic BBB destruction (Figure 1). In this article, we aim to evaluate the involvement of dietary glutamate in the development of post-traumatic brain injury depression. We hypothesize that glutamate in diet can have an impact on blood glutamate levels and, therefore, depression following TBI. Furthermore, we examine the development of post-TBI depression in Asian countries that traditionally use a high-glutamate diet with the potential to increase blood glutamate levels, compared to countries that incorporate a diet without high glutamate levels, such as Europe, North America, Australia, and New Zealand.
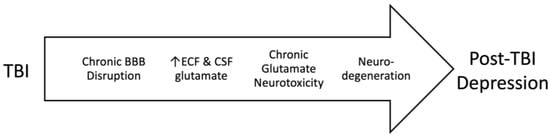
Figure 1.
The relationship between TBI, disruption in the blood–brain barrier, chronic glutamate neurotoxicity, and depression.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
We enacted a literature search to find studies that researched the effects of dietary glutamate in the context of chronic BBB destruction after TBI (Supplementary File S1). On 4 July 2023, we performed a wide search across many databases: MEDLINE (Ovid), Embase (Ovid), PsycINFO (Ovid), Web of Science Core Collection (Clarivate), Scopus (Elsevier), Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) (EBSCOhost), and the Cochrane Library (Wiley).
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
We included publications on the effects of a glutamate-rich diet, as traditional in Asian populations, compared with European and American diets poor in glutamate in the context of chronic BBB destruction after TBI. We used data from recent publications and meta-analyses to compare populations in Europe, the US, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand, with a total of 279,772 cases outside of Asia. The Asian sample included 2,285,938 cases from China, India, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Pakistan, and Taiwan (Supplementary Files S1 and S2).
3. Results
Our calculated odds ratio (OR) in the Asian group is 1.56 (95% CI 1.532–1.583; Z = 53.13; p < 0.001) compared to the European, American, Canadian, Australian, and New Zealand populations during the first year after TBI, which supports our assumption that the prevalence of depression after TBI is higher in Asian countries (see Supplementary Materials). As we noted above, there are significant differences in the assessment and diagnosis of depression in non-Asian countries compared to Asian countries, but we do not think they can fully explain the large differences in the prevalence of depression after TBI.
4. Discussion
4.1. Pathophysiology of Depression
Depression is one of the most widely observed neuropsychiatric consequences known to occur after TBI. A relationship between depression and glutamate has been confidently noted since the turn of the century [3]. A recent meta-analysis identified that increased blood glutamate levels are strongly correlated with the development of depression [9]. Glutamate is the most plentiful free amino acid in the brain, with concentrations in the plasma at 50–100 μM/L and in the whole brain at 150–300 μM/L. In the whole brain, the concentrations are 10,000–12,000 μM/kg, but only 1–10 μM/L in extracellular fluids. The facilitative and active transport mechanisms of the blood–brain barrier control the gradient between brain cells, blood, and extracellular fluids. A healthy BBB successfully impedes glutamate from traveling between the intraparenchymal and blood compartments. Several mechanisms evoke an increase in brain glutamate that is correlated with TBI (neuronal death, inflammation, impaired glutamatergic recycling and signaling, prolonged stress, astrocytic release of adenosine triphosphate, and other causes of elevated intraparenchymal glutamate), but we believe that the degree of the integrity of the BBB is the fundamental component that mediates the range of glutamate concentration in both healthy and damaged brains [3].
Many variables are implicated in the pathophysiology of depression following TBI, including neuroinflammation, neuroendocrine dysregulation, metabolic abnormalities, neurotransmitter and circuitry dysfunction, neurodegeneration, cell death, axonal injury, maladaptive neuroplasticity, glymphatic system disruption, and long-term disruption in the BBB. These mechanisms may integrate with each other and induce depression after TBI [10]. However, the foundational mechanisms and factors of post-TBI depression remain poorly understood and relatively understudied. Therefore, although there is a relatively high prevalence and severity of depression after TBI, existing treatment options are not completely reliable, as its neurobiological mechanisms are still somewhat unknown. More research studies and a better understanding of the mechanisms that govern post-TBI depression will be extremely beneficial to shape guidelines, protective strategies, and treatment modalities for this multi-faceted neuropsychiatric condition.
Theories about depression originate with several mechanisms, including dysregulation of serotonin and the involvement of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, as well as glutamate. Deregulation of the serotonin system is considered the main hypothesis for the development of depression. Pre-clinical and clinical studies have shown an association between major depressive disorder (MDD) and impaired serotonergic transmission as seen by decreases in serotonin neurons and their projections and increases in receptor autoinhibition [11,12]. Impaired responses to antidepressants have also been observed [11,12].
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are noted as the primary approach for depression according to clinical guidelines concerning TBI treatment. SSRIs raise the levels of serotonin attached to serotonergic postsynaptic receptors, which enables the mediation of several neuropsychiatric conditions including depression, obsessive compulsive disorder, and panic disorder. In the past few decades, some guidelines have suggested that SSRIs are an appropriate therapy for TBI-related depression. However, due to the paucity of robust studies and randomized clinical trials, guidelines for routine use could not be established. More recently, a number of studies have appeared that examined the efficacy of the SSRI sertraline for depression after TBI. These studies have shown that treatment with serotonin-based medications is not effective in restoring cognitive function after TBI, nor have any improvements been reported for post-traumatic stress disorder and post-traumatic anxiety. There remain differing opinions and no clear consensus on the effectiveness of SSRIs and other antidepressants in improving symptoms of post-traumatic depression [13,14,15]. Kreitzer et al. reviewed 1020 articles published prior to September 2017 and did not observe any benefit of antidepressant therapies compared to placebo in treating MDD after TBI [16].
The HPA axis, because of its main contributions to the neuroendocrine system, also plays a critical role in the regulation of responses to stress [17]. The HPA axis mediates stimulations and feedback between the hypothalamus, pituitary, and adrenal glands, which assist in regulating glucocorticoid homeostasis [18]. After encountering a stress stimulus, the HPA axis is engaged through the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone and arginine vasopressin from the hypothalamus. The two hormones induce the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone into the bloodstream, which then causes cortisol production from the adrenal cortex [19]. At the same time, cortisol maintains its physiological function by providing negative feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary, leading to a reduction in the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone [20]. In depression, the functionality of this negative feedback loop is debilitated, causing hyperactivity of the HPA axis with higher cortisol levels. An increased level of basal cortisol has been observed to be predictive of depressive episodes [18,19,21,22].
4.2. Glutamatergic Hypothesis of Depression
Glutamate participates in most of the fast excitatory transmissions in the brain, and another amino acid neurotransmitter, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), impacts most inhibitory transmissions. Glutamate neurons and synapses comprise the largest neurotransmitter system in the brain, being second only to the GABAergic system [3]. Animal and human studies have demonstrated that the glutamate system is a contributing factor in the pathophysiology of depression [3]. Data have demonstrated increased glutamate levels in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and brains of patients with MDD, with evidence showing that antidepressants lower those levels [3]. Elevated glutamate levels have been noted in the frontal cortex as well based on postmortem samples of brain, CSF, and blood plasma of patients with MDD. Plasma glutamate levels, along with alanine and L-serine levels, indicate the disease’s severity [3]. The results of a meta-analysis of magnetic resonance spectroscopy additionally support the theory that glutamatergic neurotransmission plays a role in the pathophysiology of depression [23]. Studies have identified the relationship between dysregulated glutamate receptors and subtypes in postmortem brain samples of patients with MDD and depression [24]. Another meta-analysis by Luykx et al. [25] similarly observed region- and state-specific changes in depression related to concentrations of glutamate and glutamine, an essential amino acid that develops from glutamate conversion. Cumulatively, this evidence implies that disruptions to glutamate receptors and altered blood, plasma, and brain glutamate levels have an impact on the pathophysiology of depression. Research into depressive-like behavior in genetic models of impaired glutamate function and treatment of depression with glutamate-based antidepressants bolster this hypothesis [3].
Among the many factors that have an impact on the development of depression, heightened inflammatory activation of the immune system affects the periphery as well as the central nervous system (CNS) and, therefore, has a strong correlation with the condition. This is additionally evidenced by the strong correlated relationship between diseases with immune activation and symptoms of autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, and immune system activation during infections, like sepsis [26]. Similarly, inflammatory responses to TBI have been reviewed in depth [27]. Chronic/dysregulated inflammatory signaling is one proposed pathway leading to impairment and neural circuit dysregulation following TBI as well as mood and anxiety disorders [28]. Neuroinflammation caused by TBI may increase the likelihood of neuropsychiatric disorders directly through chronic inflammatory signaling following TBI or indirectly by inducing the neural immune system to overreact to homeostatic imbalance. However, anti-inflammatory treatments have shown limited efficacy in enhancing long-term TBI outcomes assessed based on mortality, cognitive function, and psychological symptoms [28]. There is much putative evidence that chronic inflammation after TBI increases the likelihood of mood and anxiety disorders, though it remains undetermined if inflammation is a primary factor or only a secondary indicator of the underlying pathology [28].
It has been acknowledged that TBI may have a correlation with related development of chronic neurodegenerative disorders, including mood illnesses [29,30]. A previous diagnosis of TBI has been indicated as a factor in the increased prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease and similar diseases, including early-onset dementias [31].
TBI has a complex pathobiological structure and, therefore, is a complicated neurological condition. The etiology of neurodegeneration has been firmly established as relating to β-amyloid, hyperphosphorylated tau deposition, and neurofibrillary tangles. Because TBI can induce a rapid elevation of these biomarkers, even at younger ages, it has led to a proposed pathobiological linkage between TBI and neurodegeneration [31]. Neuroimaging studies have identified atrophy of frontal and temporal connections in TBI patients that is separate from the acute phase of injury [30]. In the first through fourth years after injury, moderate-to-severe TBI patients have more diffuse white matter atrophy in comparison to control patients of the same age [32]. Animal studies have indicated that TBI can lead to continuing neurodegeneration in addition to associated cognitive or behavioral changes [31].
Until recently, it was unclear if the BBB was severely physically damaged after brain injury over the long term. Recent data using rodent models have shown that restoration of BBB integrity can occur only after 1–3 months or as long as 10 months after injury; restoration of BBB integrity in humans may take years [3]. The BBB is vitally important in preserving CNS homeostasis by limiting the movement of harmful substances from the circulating bloodstream into the brain parenchyma. BBB destruction can prompt and cause worsening of depression in several ways. Poor endothelial function and BBB breakdown cause cerebral perfusion impairments, thereby causing brain damage and compromised emotional and cognitive functions [18].
Other neurobiological factors, such as elevated levels of biomarkers after TBI associated with neurodegeneration, the flushing out of potentially toxic metabolites via the glymphatic system, neuroendocrine dysregulation, metabolic abnormalities, stress, and neurotransmitter and circuitry dysfunction [10,29,33], may also contribute to the development of post-TBI depression.
4.3. Glutamate Neurotoxicity
Glutamate neurotoxicity describes neurotoxicity resulting from excessive glutamate that causes neuronal degeneration and dysfunction [34,35,36,37]. Based on this relationship, recent studies on mood disorders have specifically addressed the glutamatergic system as a site for new therapeutic modalities for antidepressants and other methods [3,38,39]. A healthy BBB has been shown to effectively protect the brain from high glutamate levels in the blood. Also, the concentration of glutamate in the CSF is correlated with the concentration of glutamate in the blood after BBB disruption. Because CSF glutamate concentration is based on the level of BBB disruption, BBB permeability is an essential aspect in maintaining healthy levels of glutamate in the brain [40].
After acute brain injuries (including cerebral ischemia, hypoglycemia, ischemic strokes, and TBI), excitotoxicity may arise due to elevated extracellular glutamate levels, leading to the overactivation of ionotropic glutamate receptors [3,40].
It has also been proposed that chronic glutamate neurotoxicity occurs in some neurodegenerative diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease [3]. For these neurogenerative diseases, research suggests that chronic excitotoxicity takes place as a result of cellular death occurring over a longer period of time when neurons encounter increased glutamate, leading to a gradual progression toward cell death [3]. This understanding of the development of neurodegeneration due to glutamate neurotoxicity assists in providing new options for treating acute and chronic neurological conditions revolving around the glutamatergic system.
4.4. Diet as a Factor in Blood Glutamate Concentration
Blood glutamate concentrations are generally stable under physiological conditions, but a number of factors can influence the increase or decrease in its concentration. As suggested by the articles reviewed herein, dietary intake can have an impact on blood glutamate concentrations due to the presence of glutamate in many foods. Asian countries traditionally have a glutamate-rich diet and account for about 88% of global consumption of glutamate [41] and 94% of the world’s monosodium glutamate (MSG) production capacity [42]. MSG is a common flavor enhancer that is used in many cuisines around the world. It is particularly popular in East and Southeast Asian cooking, where it is often used in dishes such as soups, stir-fries, and marinades. Several pharmacokinetic studies have shed light on the dynamics of blood glutamate levels based on dietary intake. Rutten et al. administered oral glutamate doses of 30 mg per kilogram of body weight every 20 min for 220 min. They found that plasma glutamate levels peaked after 80 min at five times the basal value (601 ± 68 μmol/L). Further administration of the drug did not significantly increase glutamate levels, suggesting a saturable level of intestinal absorption and clearance [43].
MSG intake of 16.0 mg/kg of body weight is considered safe [42]. The average daily consumption of MSG is around 0.3–0.5 g/day in European countries and the United States [42] and 1.2–4 g/day in Asian countries [44]. However, its neurotoxicity in light of the chronic impairment associated with BBB permeability is of concern. Stegink et al. [45] conducted a study in which healthy subjects were given beef consommé containing 1 mg of glutamate per kilogram of body weight, alone or with supplemental MSG at doses of 25 or 50 mg/kg body weight. They observed a dose-dependent increase in plasma glutamate, which peaked at 30 min.
In studies involving the administration of 150 mg MSG/kg body weight as a bolus to healthy adults in the post-absorption state, plasma glutamate levels reached their peak after 45 min, exceeding the basal value by 19 times (594 ± 465 μmol/L), and returned to baseline at 180 min after administration [46]. Similar results were obtained by Fernstrom et al., who administered 160 mg MSG/kg body weight to healthy adults in the post-absorption state. They observed a peak in plasma glutamate levels (at 11 times the basal value [530 μmol/L]) after 60 min; by 180 min, the levels had returned to baseline [47]. Graham et al. conducted a study in which healthy young adults were orally administered 150 mg MSG/kg body weight, which resulted in peak plasma glutamate levels (8 times the basal value [437 μmol/L]) 30 or 45 min after administration. After 90 min, glutamate levels were no longer significantly elevated compared to baseline levels [48].
In addition, studies have noted the relevance of food intake on plasma glutamate levels. Tsai and Huang reported that after lunch and dinner, plasma glutamate levels increased 1.4-fold from baseline, with peak concentrations at about 60 min after a meal [49]. Stegink et al. [50] observed a similar magnitude of increase in plasma glutamate after healthy adults consumed a cooked liquid meal containing 55 mg of protein-bound glutamate per kilogram of body weight, reaching a 1.6-fold increase over baseline with a peak after 45 min. When the food contained 169 mg of protein-bound glutamate per kilogram of body weight, plasma glutamate concentrations increased 2.3-fold over baseline after 120–150 min.
Thus, we can conclude that the use of MSG results in a rapid increase in plasma glutamate levels, with a peak concentration of approximately 600–700 μmol/L at 30–60 min after ingestion, and the concentration then decreases to baseline within 90–180 min [51].
Although the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has deemed MSG safe for consumption, several animal studies have pointed to the potential negative effects associated with chronic MSG consumption. These adverse effects have been observed in different organs, such as the thymus, brain, pancreas, testis, liver, and kidney, and have been associated with several diseases, including obesity, hypertension, and headaches, as well as with asthma exacerbation and reproductive conditions [52].
Because glutamate plays an important role as an excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS, when it reaches excessive levels, the resultant excitotoxicity can lead to severe neuronal damage and cognitive and behavioral impairments. In one study on neonatal rats, overactivation of glutamate receptors was induced by MSG solution administration and resulted in irregularities in all amino acids, leading to behavioral changes such as screeching, tail stiffness, head nodding, and generalized convulsions or seizure-like conditions [53]. Another neonatal rat model showed excitotoxicity of glutamate, with cellular degeneration of 11.5% in the hippocampus of rats given MSG compared to rats in the control group [54]. Negative changes to dendritic arborization and dendritic spine density were also attributable to the cyto-excitotoxic effect of MSG, which leads to impairments in the hippocampus. In another study by Dief et al. [55], male Wistar rats that were administered MSG showed a reduction in cyclic-AMPK level in the hippocampus by 43% with oral MSG administration and by 31% with subcutaneous MSG administration compared to rats not given MSG. The MSG group also showed a two-fold increase in the Fas ligand, a substance involved in cell death [42]. One study placed MSG in drinking water that was available ad libitum to female rats in the last two weeks of pregnancy, and the rats born from the MSG group had reduced birth weight, increased weight at day 28 of life, decreased open-field activity and less lactation at day 35 of life, and made more maze errors at day 60 of life [56,57]. The neurotoxic effects of glutamate were also observed in another study in the cerebellar cortex of male albino rats receiving 3 g/kg/day [58].
Recent studies have revealed an intriguing interaction between the gut microbiota and the brain neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin, GABA, and glutamate [59]. These interactions provide new insights into the possible relationship between dietary factors, neurotransmitter functions, and psychiatric disorders such as depression. Some researchers have suggested that diets high in sodium glutamate may increase blood levels of glutamate and glutamic acid, leading to hyperglutamatergic neurotransmission. Hyperglutamatergic neurotransmission has been associated with several different psychiatric conditions, including depression [59]. Studies have shown that consuming a diet rich in sodium glutamate can lead to depressive behaviors in rodents, including decreased social interaction, anhedonia, and behavioral despair [59,60,61]. Preclinical studies have revealed a potential link between sodium glutamate intake and the development of anxious and depressive-like phenotypes [59]. Animal models receiving sodium glutamate showed increased anxiety and behavioral despair [62,63,64,65,66]. The behavior of rats suffering from post-traumatic depression and anxiety and receiving treatment aimed at reducing blood and CSF glutamate levels did not differ from that of naïve rats after the completion of treatment [67,68]. These data suggest that there is a very close relationship between dietary glutamate consumption and the development of depression.
4.5. Other Factors
In this review, we examined the effects of dietary glutamate in the context of BBB destruction following TBI as a trigger for the initiation of degenerative processes that can eventually lead to depression. However, there are many other factors besides glutamate that contribute to depression, including socioeconomic factors, gender, stress levels, chronic infections, and chronic illnesses. Also, in addition to dietary intake, other factors influence changes in blood glutamate levels, such as injury in the spinal cord and blood cell disruption [69,70]. In vitro studies have observed changes in the endothelial barrier due to exposure to soluble polymorphonuclear leukocyte-derived glutamate during inflammatory states [71]. Another possible pathway of glutamate is bone. In one study, osteoclasts were identified as secreting glutamate when stimulated with KCl or adenosine triphosphate [72]. The effects of stress [73], circadian rhythms [49], gender [74,75], age [76], and pain [77] on blood or plasma glutamate concentrations have also been documented.
4.6. Potential Treatment Strategies
Based on the theory of blood glutamate reduction for alleviating depression after TBI, we propose several potential treatment strategies (Figure 2).
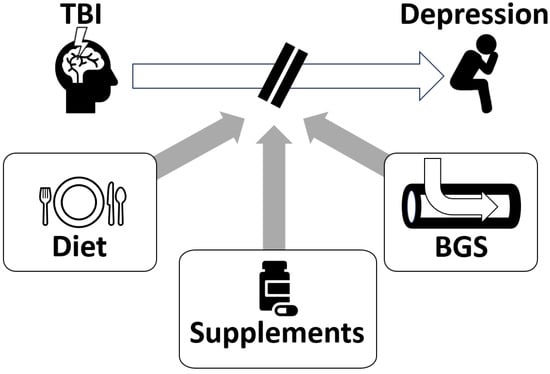
Figure 2.
Potential treatment strategies for post-TBI depression include dietary glutamate modulation, dietary supplements, and blood glutamate scavenging (BGS). Based on the role of glutamate in the pathophysiology of this condition, we hypothesize that these three approaches may be beneficial in alleviating depression after TBI.
4.6.1. Diet
In this review, we examined the role of a glutamate-rich diet in the development of depression. Although a glutamate-rich diet is not neurotoxic when the blood–brain barrier is healthy, there is strong evidence that when the barrier is compromised, chronic glutamate neurotoxicity can be a trigger for the development of neurodegeneration and subsequent depression. Based on this hypothesis, we can assume that a glutamate-poor diet can be considered as a potential method for the prevention of neurodegenerative processes and modulation of glutamate levels in patients’ diet can contribute to the treatment and prevention of depression.
4.6.2. Food Supplements
Dietary supplements have gained popularity in recent years as people look for effective yet simple and non-invasive strategies to improve health. Pyruvate serves as an important energy intermediate, as a critical component in the production of ATP, and as a basic energy currency of cells, and it has been approved as a dietary supplement. Oxaloacetate, an intermediate product of the citric acid cycle, is also a dietary supplement and has a significant impact on various metabolic pathways, including gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, amino acid synthesis, and fatty acid synthesis. Both of these substances can effectively reduce glutamate levels by breaking it down to alpha-ketoglutarate aspartate and alanine. Pyruvate and oxaloacetate are FDA-approved dietary supplements as over-the-counter drugs.
4.6.3. Blood Glutamate Scavenging
Excessively high levels of brain glutamate can also be mitigated by manipulating the brain–blood glutamate equilibrium and inducing excess glutamate from the brain’s interstitial fluid to flow into the body’s circulatory system [3]. Glutamate transporters on the endothelial cells of brain capillaries allow the extraction of glutamate from interstitial fluid [3]. This process of lowering the level of glutamate is known as blood glutamate scavenging. Blood glutamate scavenging is able to accomplish this without compromising mechanisms of learning since it does not involve the impediment or direct stimulation of synaptic glutamate receptors. Treatments that have been proven in a rat model to reduce the first neuroanatomical and neurological symptoms of TBI involves the administration of the enzymes glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase and serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase, and their co-substrates oxaloacetic acid and pyruvate [3].
5. Conclusions
High blood glutamate levels are strongly correlated with the development of post-traumatic brain injury depression. We theorize that BBB permeability is a determining component in the onset of neurodegeneration processes through glutamate neurotoxicity and the subsequent appearance of neuropsychiatric pathology. Therefore, methods of blood glutamate level reduction and restoration of BBB integrity may be effective tools for the treatment and prevention of post-TBI depression. Blood glutamate levels can be affected by a number of factors, both internal and external, that can cause significant increases, while a healthy BBB is able to successfully shield the brain from the neurotoxic effects of blood glutamate. Food intake of glutamate appears to be the most significant out of all the easily controllable factors that can increase blood glutamate levels. In chronic disorders involving BBB disruption following TBI, chronically high blood glutamate concentrations resulting from a glutamate-rich diet can be neurotoxic to the brain and initiate neurodegeneration processes that will eventually lead to depression. A low-glutamate diet, medications that target the glutamate system, and food supplements that reduce blood glutamate levels may be effective strategies for treating post-TBI depression.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu15214681/s1. File S1: Literature search results; File S2: Prevalence of post-TBI depression in Asian countries versus control group or indigenous population [78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171,172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185].
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the conceptualization, investigation, writing, and reviewing and editing of this manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Igor Merzlikin, Zavorotko Anastasia, and Frolov Oleksandr, MSc, from the Department of Biology and Methods of Teaching Biology, A. S. Makarenko Sumy State Pedagogical University, Sumy, Ukraine, for their contribution in data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Boyko, M.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Shelef, I.; Zvenigorodsky, V.; Severynovska, O.; Binyamin, Y.; Knyazer, B.; Frenkel, A.; Frank, D.; Zlotnik, A. Traumatic brain injury-induced submissive behavior in rats: Link to depression and anxiety. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenbaum, B.F.; Zlotnik, A.; Fleidervish, I.; Frenkel, A.; Boyko, M. Glutamate Neurotoxicity and Destruction of the Blood–Brain Barrier: Key Pathways for the Development of Neuropsychiatric Consequences of TBI and Their Potential Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruenbaum, B.F.; Zlotnik, A.; Frenkel, A.; Fleidervish, I.; Boyko, M. Glutamate Efflux across the Blood–Brain Barrier: New Perspectives on the Relationship between Depression and the Glutamatergic System. Metabolites 2022, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellewell, S.C.; Beaton, C.S.; Welton, T.; Grieve, S.M. Characterizing the risk of depression following mild traumatic brain injury: A meta-analysis of the literature comparing chronic mTBI to non-mTBI populations. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderfer, B.S.; Arciniegas, D.B.; Silver, J.M. Treatment of depression following traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2005, 20, 544–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.M.; Read, C.A. Psychiatric comorbidity following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2007, 21, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Reekum, R.; Cohen, T.; Wong, J. Can traumatic brain injury cause psychiatric disorders? J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, M.; Shakkour, Z.; Kobeissy, F.; Lawand, N. Depression following traumatic brain injury: A comprehensive overview. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoshita, M.; Umehara, H.; Watanabe, S.-Y.; Nakataki, M.; Kinoshita, M.; Tomioka, Y.; Tajima, A.; Numata, S.; Ohmori, T. Elevated peripheral blood glutamate levels in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, A.B.; Tanev, K. Neurobiological mechanisms of depression following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2023, 37, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Koga, N.; Hattori, K.; Matsuo, J.; Ota, M.; Hori, H.; Sasayama, D.; Teraishi, T.; Ishida, I.; Yoshida, F. Plasma amino acid profile in major depressive disorder: Analyses in two independent case-control sample sets. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 96, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahid-Ansari, F.; Albert, P.R. Rewiring of the serotonin system in major depression. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narapareddy, B.R.; Narapareddy, L.; Lin, A.; Wigh, S.; Nanavati, J.; Dougherty, J., III; Nowrangi, M.; Roy, D. Treatment of depression after traumatic brain injury: A systematic review focused on pharmacological and neuromodulatory interventions. Psychosomatics 2020, 61, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowinski, A.; Coetzer, R.; Byrne, C. Pharmacotherapy effectiveness in treating depression after traumatic brain injury: A meta-analysis. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.K.; Burke, J.F.; Upadhyayula, P.S.; Winkler, E.A.; Deng, H.; Robinson, C.K.; Pirracchio, R.; Suen, C.G.; Sharma, S.; Ferguson, A.R. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for treating neurocognitive and neuropsychiatric disorders following traumatic brain injury: An evaluation of current evidence. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, N.D.; Panenka, W.J. Antidepressants for depression after concussion and traumatic brain injury are still best practice. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightman, S.L.; Birnie, M.T.; Conway-Campbell, B.L. Dynamics of ACTH and cortisol secretion and implications for disease. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnaa002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yin, Y.; Du, L. Blood–brain barrier dysfunction in the pathogenesis of major depressive disorder. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 42, 2571–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bodegom, M.; Homberg, J.R.; Henckens, M.J.A.G. Modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by early life stress exposure. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherholz, M.L.; Schlesinger, N.; Androulakis, I.P. Chronopharmacology of glucocorticoids. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 151, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Cleare, A.J. Cortisol as a predictor of psychological therapy response in anxiety disorders—Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Anxiety Disord. 2017, 47, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochigaeva, K.; Druzhkova, T.; Yakovlev, A.; Onufriev, M.; Grishkina, M.; Chepelev, A.; Guekht, A.; Gulyaeva, N. Hair cortisol as a marker of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal Axis activity in female patients with major depressive disorder. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, S.; Takamiya, A.; Noda, Y.; Horita, N.; Wada, M.; Tsugawa, S.; Plitman, E.; Sano, Y.; Tarumi, R.; ElSalhy, M. Glutamatergic neurometabolite levels in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschwanden, A.; Karolewicz, B.; Feyissa, A.M.; Treyer, V.; Ametamey, S.M.; Johayem, A.; Burger, C.; Auberson, Y.P.; Sovago, J.; Stockmeier, C.A. Reduced metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 density in major depression determined by [11C] ABP688 PET and postmortem study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luykx, J.J.; Laban, K.G.; Van Den Heuvel, M.P.; Boks, M.P.M.; Mandl, R.C.W.; Kahn, R.S.; Bakker, S.C. Region and state specific glutamate downregulation in major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis of 1H-MRS findings. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Giuliani, F. The role of inflammation in depression and fatigue. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, C.N.; Morganti, J.M.; Bachstetter, A.D. Depression following a traumatic brain injury: Uncovering cytokine dysregulation as a pathogenic mechanism. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Risbrough, V.B.; Vaughn, M.N.; Friend, S.F. Role of inflammation in traumatic brain injury–associated risk for neuropsychiatric disorders: State of the evidence and where do we go from here. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottshall, J.L.; Agyemang, A.A.; O’Neil, M.; Wei, G.; Presson, A.; Hewins, B.; Fisher, D.; Mithani, S.; Shahim, P.; Pugh, M.J. Sleep quality: A common thread linking depression, post-traumatic stress, and post-concussive symptoms to biomarkers of neurodegeneration following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2022, 36, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoBue, C.; Cullum, C.M.; Didehbani, N.; Yeatman, K.; Jones, B.; Kraut, M.A.; Hart, J., Jr. Neurodegenerative dementias after traumatic brain injury. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faden, A.I.; Loane, D.J. Chronic neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury: Alzheimer disease, chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or persistent neuroinflammation? Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbota, K.D.M.; Sodhi, A.; Bendlin, B.B.; McLaren, D.G.; Xu, G.; Rowley, H.A.; Johnson, S.C. Longitudinal volumetric changes following traumatic brain injury: A tensor-based morphometry study. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2012, 18, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, J.L.; Ngwenya, L.B.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Neurotransmitter changes after traumatic brain injury: An update for new treatment strategies. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.-X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z.-H. Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezza, H.S.A.; Khadrawyb, Y.A. Glutamate excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2014, 8, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, A.; Tymianski, M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2010, 460, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, J.; Maher, P. Chronic glutamate toxicity in neurodegenerative diseases—What is the evidence? Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Zlotnik, A.; Semyonov, M.; Frenkel, A.; Boyko, M. Pathophysiology and Current Drug Treatments for Post-Stroke Depression: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoodoruth, M.A.S.; Estudillo-Guerra, M.A.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Nyundo, A.; Chapa-Koloffon, G.; Ouanes, S. Glutamatergic System in Depression and Its Role in Neuromodulatory Techniques Optimization. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 886918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, M.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Frank, D.; Natanel, D.; Negev, S.; Azab, A.N.; Barsky, G.; Knyazer, B.; Kofman, O.; Zlotnik, A. The Integrity of the Blood–Brain Barrier as a Critical Factor for Regulating Glutamate Levels in Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markits, I.H.S. Monosodium glutamate (MSG) chemical Economics Handbook. In Chemical Economics Handbook; S&P Global Commodity Insights: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–88. Available online: https://Ihsmarkit.Com/Products/Monosodium-Glutamate-Chemical-Economics-Handbook.html (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Kazmi, Z.; Fatima, I.; Perveen, S.; Malik, S.S. Monosodium glutamate: Review on clinical reports. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, E.P.A.; Engelen, M.P.K.J.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Deutz, N.E.P. Metabolic effects of glutamine and glutamate ingestion in healthy subjects and in persons with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Insawang, T.; Selmi, C.; Cha’on, U.; Pethlert, S.; Yongvanit, P.; Areejitranusorn, P.; Boonsiri, P.; Khampitak, T.; Tangrassameeprasert, R.; Pinitsoontorn, C. Monosodium glutamate (MSG) intake is associated with the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in a rural Thai population. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegink, L.D.; Filer, L.J., Jr.; Baker, G.L. Plasma glutamate concentrations in adult subjects ingesting monosodium L-glutamate in consomme. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 42, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegink, L.D.; Filer, L.J., Jr.; Baker, G.L. Effect of carbohydrate on plasma and erythrocyte glutamate levels in humans ingesting large doses of monosodium L-glutamate in water. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernstrom, J.D.; Cameron, J.L.; Fernstrom, M.H.; McConaha, C.; Weltzin, T.E.; Kaye, W.H. Short-term neuroendocrine effects of a large oral dose of monosodium glutamate in fasting male subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graham, T.E.; Sgro, V.; Friars, D.; Gibala, M.J. Glutamate ingestion: The plasma and muscle free amino acid pools of resting humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 278, E83–E89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.-J.; Huang, P.-C. Circadian variations in plasma and erythrocyte glutamate concentrations in adult men consuming a diet with and without added monosodium glutamate. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1002S–1004S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegink, L.D.; Filer, L.J., Jr.; Baker, G.L. Plasma and erythrocyte amino acid levels in normal adult subjects fed a high protein meal with and without added monosodium glutamate. J. Nutr. 1982, 112, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loï, C.; Cynober, L. Glutamate: A safe nutrient, not just a simple additive. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 78, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajihasani, M.M.; Soheili, V.; Zirak, M.R.; Sahebkar, A.; Shakeri, A. Natural products as safeguards against monosodium glutamateinduced toxicity. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 416–430. [Google Scholar]
- López-Pérez, S.J.; Ureña-Guerrero, M.E.; Morales-Villagrán, A. Monosodium glutamate neonatal treatment as a seizure and excitotoxic model. Brain Res. 2010, 1317, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beas-Zárate, C.; Pérez-Vega, M.a.I.; González-Burgos, I. Neonatal exposure to monosodium L-glutamate induces loss of neurons and cytoarchitectural alterations in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons of adult rats. Brain Res. 2002, 952, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dief, A.E.; Kamha, E.S.; Baraka, A.M.; Elshorbagy, A.K. Monosodium glutamate neurotoxicity increases beta amyloid in the rat hippocampus: A potential role for cyclic AMP protein kinase. Neurotoxicology 2014, 42, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieder, B.; Grimm, V.E. Prenatal monosodium glutamate (MSG) treatment given through the mother’s diet causes behavioral deficits in rat offspring. Int. J. Neurosci. 1984, 23, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieder, B.; Grimm, V.E. Prenatal Monosodium Glutamate Causes Long-Lasting Cholinergic and Adrenergic Changes in Various Brain Regions. J. Neurochem. 1987, 48, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, H.E.; El-Din Safwat, M.D.; Algaidi, S. The effect of monosodium glutamate on the cerebellar cortex of male albino rats and the protective role of vitamin C (histological and immunohistochemical study). J. Mol. Histol. 2012, 43, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J. Glutamate and depression: Reflecting a deepening knowledge of the gut and brain effects of a ubiquitous molecule. World J. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, T.S.S.; Asha, M.R.; Ramesh, B.N.; Rao, K.S.J. Understanding nutrition, depression and mental illnesses. Indian J. Psychiatry 2008, 50, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Fulton, S. Diet-induced obesity promotes depressive-like behaviour that is associated with neural adaptations in brain reward circuitry. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J. Dietary glutamate and the brain: In the footprints of a Jekyll and Hyde molecule. Neurotoxicology 2020, 80, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaolapo, O.J.; Onaolapo, A.Y.; Akanmu, M.A.; Olayiwola, G. Changes in spontaneous working-memory, memory-recall and approach-avoidance following “low dose” monosodium glutamate in mice. AIMS Neurosci. 2016, 3, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Vignesh, A.; Son, H.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, H.J. Glutamine supplementation ameliorates chronic stress-induced reductions in glutamate and glutamine transporters in the mouse prefrontal cortex. Exp. Neurobiol. 2019, 28, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraal, A.Z.; Arvanitis, N.R.; Jaeger, A.P.; Ellingrod, V.L. Could dietary glutamate play a role in psychiatric distress? Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quines, C.B.; Rosa, S.G.; Da Rocha, J.T.; Gai, B.M.; Bortolatto, C.F.; Duarte, M.M.M.F.; Nogueira, C.W. Monosodium glutamate, a food additive, induces depressive-like and anxiogenic-like behaviors in young rats. Life Sci. 2014, 107, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Shelef, I.; Zvenigorodsky, V.; Severynovska, O.; Fleidervish, I.; Knyazer, B.; Frenkel, A.; Zlotnik, A.; Kofman, O. Blood glutamate scavenging as a novel glutamate-based therapeutic approach for post-traumatic brain injury anxiety and social impairment. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Shelef, I.; Severynovska, O.; Gal, R.; Dubilet, M.; Zlotnik, A.; Kofman, O.; Boyko, M. Blood glutamate scavenging with pyruvate as a novel preventative and therapeutic approach for depressive-like behavior following traumatic brain injury in a rat model. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 832478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, H.; Kostovski, E.; Pirkmajer, S.; Song, M.; Lubarski, I.; Iversen, P.O.; Hjeltnes, N.; Widegren, U.; Chibalin, A.V. Influence of chronic and acute spinal cord injury on skeletal muscle Na+-K+-ATPase and phospholemman expression in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E864–E871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliprandi, A.; Longoni, M.; Stanzani, L.; Tremolizzo, L.; Vaccaro, M.; Begni, B.; Galimberti, G.; Garofolo, R.; Ferrarese, C. Increased plasma glutamate in stroke patients might be linked to altered platelet release and uptake. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, C.D.; Park, K.A.; Montalto, M.C.; Alapati, S.; Buras, J.A.; Stahl, G.L.; Colgan, S.P. Neutrophil-derived glutamate regulates vascular endothelial barrier function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14801–14811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, R.; Uehara, S.; Yatsushiro, S.; Juge, N.; Hua, Z.; Senoh, S.; Echigo, N.; Hayashi, M.; Mizoguchi, T.; Ninomiya, T. Secretion of L-glutamate from osteoclasts through transcytosis. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4175–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnik, A.; Klin, Y.; Kotz, R.; Dubilet, M.; Boyko, M.; Ohayon, S.; Shapira, Y.; Teichberg, V.I. Regulation of blood L-glutamate levels by stress as a possible brain defense mechanism. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 224, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacometti, L.L.; Barker, J.M. Sex differences in the glutamate system: Implications for addiction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 113, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, A.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Mohar, B.; Kuts, R.; Gruenbaum, S.E.; Ohayon, S.; Boyko, M.; Klin, Y.; Sheiner, E.; Shaked, G. The effects of estrogen and progesterone on blood glutamate levels: Evidence from changes of blood glutamate levels during the menstrual cycle in women. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegink, L.D.; Filer, L.J.; Baker, G.L.; Bell, E.F. Plasma glutamate concentrations in 1-year-old infants and adults ingesting monosodium L-glutamate in consommé. Pediatr. Res. 1986, 20, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseldijk, F.; Fekkes, D.; Huygen, F.; Van De Heide-Mulder, M.; Zijlstra, F.J. Increased plasma glutamate, glycine, and arginine levels in complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.J.A.; Sterr, A. Long-term effects of mild traumatic brain injury on cognitive performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losoi, H.; Silverberg, N.D.; Wäljas, M.; Turunen, S.; Rosti-Otajärvi, E.; Helminen, M.; Luoto, T.M.; Julkunen, J.; Öhman, J.; Iverson, G.L. Recovery from mild traumatic brain injury in previously healthy adults. J. Neurotrauma 2016, 33, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amick, M.M.; Meterko, M.; Fortier, C.B.; Fonda, J.R.; Milberg, W.P.; McGlinchey, R.E. The deployment trauma phenotype and employment status in veterans of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2018, 33, E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.A.; O'Donnell, M.L.; Creamer, M.; McFarlane, A.C.; Clark, C.R.; Silove, D. The psychiatric sequelae of traumatic injury. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsford, J.L.; Nguyen, S.; Downing, M.; Bosch, M.; McKenzie, J.E.; Turner, S.; Chau, M.; Mortimer, D.; Gruen, R.L.; Knott, J. Factors associated with persistent post-concussion symptoms following mild traumatic brain injury in adults. J. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 51, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogoda, T.K.; Hendricks, A.M.; Iverson, K.M.; Stolzmann, K.L.; Krengel, M.H.; Baker, E.; Meterko, M.; Lew, H.L. Multisensory impairment reported by veterans with and without mild traumatic brain injury history. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2012, 49, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dretsch, M.N.; Silverberg, N.D.; Iverson, G.L. Multiple past concussions are associated with ongoing post-concussive symptoms but not cognitive impairment in active-duty army soldiers. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wäljas, M.; Iverson, G.L.; Lange, R.T.; Hakulinen, U.; Dastidar, P.; Huhtala, H.; Liimatainen, S.; Hartikainen, K.; Öhman, J. A prospective biopsychosocial study of the persistent post-concussion symptoms following mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léveillé, E.; Guay, S.; Blais, C.; Scherzer, P.; De Beaumont, L. Sex-related differences in emotion recognition in multi-concussed athletes. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2017, 23, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, S.; De Beaumont, L.; Henry, L.C.; Boulanger, Y.; Evans, A.C.; Bourgouin, P.; Poirier, J.; Théoret, H.; Lassonde, M. Sports concussions and aging: A neuroimaging investigation. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, W.C.; Franke, L.M.; Sima, A.P.; Cifu, D.X. Symptom trajectories after military blast exposure and the influence of mild traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2017, 32, E16–E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFrance Jr, W.C.; DeLuca, M.; Machan, J.T.; Fava, J.L. Traumatic brain injury and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures yield worse outcomes. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verfaellie, M.; Lafleche, G.; Spiro Iii, A.; Bousquet, K. Neuropsychological outcomes in OEF/OIF veterans with self-report of blast exposure: Associations with mental health, but not MTBI. Neuropsychology 2014, 28, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasterling, J.J.; Constans, J.I.; Hanna-Pladdy, B. Head injury as a predictor of psychological outcome in combat veterans. J. Trauma. Stress Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Trauma. Stress Stud. 2000, 13, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhaug, L.H.; Hagen, K.; Vik, A.; Stovner, L.J.; Follestad, T.; Pedersen, T.; Gravdahl, G.B.; Linde, M. Headache following head injury: A population-based longitudinal cohort study (HUNT). J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.M.; Walter, K.H.; Chard, K.M. Does a history of mild traumatic brain injury increase suicide risk in veterans with PTSD? Rehabil. Psychol. 2012, 57, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, D.J.; Kapson, H.S.; Lafleche, G.; Vasterling, J.J.; Marx, B.P.; Franz, M.; Verfaellie, M. Alterations in autobiographical memory for a blast event in Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom veterans with mild traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychology 2015, 29, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spira, J.L.; Lathan, C.E.; Bleiberg, J.; Tsao, J.W. The impact of multiple concussions on emotional distress, post-concussive symptoms, and neurocognitive functioning in active duty United States marines independent of combat exposure or emotional distress. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decq, P.; Gault, N.; Blandeau, M.; Kerdraon, T.; Berkal, M.; ElHelou, A.; Dusfour, B.; Peyrin, J.-C. Long-term consequences of recurrent sports concussion. Acta Neurochir. 2016, 158, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickevičiene, D.; Schrader, H.; Nestvold, K.; Surkiene, D.; Kunickas, R.; Stovner, L.J.; Sand, T. A controlled historical cohort study on the post-concussion syndrome. Eur. J. Neurol. 2002, 9, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurick, S.M.; Hoffman, S.N.; Sorg, S.; Keller, A.V.; Evangelista, N.D.; DeFord, N.E.; Sanderson-Cimino, M.; Bangen, K.J.; Delano-Wood, L.; Deoni, S. Pilot investigation of a novel white matter imaging technique in Veterans with and without history of mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, A.J.; Dougherty, A.L.; Tang, J.J.; Galarneau, M.R. Postconcussive symptom reporting among US combat veterans with mild traumatic brain injury from Operation Iraqi Freedom. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2013, 28, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polusny, M.A.; Kehle, S.M.; Nelson, N.W.; Erbes, C.R.; Arbisi, P.A.; Thuras, P. Longitudinal effects of mild traumatic brain injury and posttraumatic stress disorder comorbidity on postdeployment outcomes in national guard soldiers deployed to Iraq. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, L.J.; Fernandes, M.A. Effects of “diagnosis threat” on cognitive and affective functioning long after mild head injury. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2010, 17, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.; Smith, B.; Harp, J.; Herrold, A.; High Jr, W.M.; Babcock-Parziale, J.; Pape, T.L.-B. Exploring the relationship between mild traumatic brain injury exposure and the presence and severity of postconcussive symptoms among veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. PMR 2015, 7, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazi, A.; Tator, C.H.; Wennberg, R.; Ebraheem, A.; Green, R.E.A.; Collela, B.; Saverino, C.; Khodadadi, M.; Misquitta, K.; Tartaglia, M.C. Motor function in former professional football players with history of multiple concussions. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, M.L.; Binder, L.M.; O’Neil, M.E.; Zaccari, B.; Roost, M.S.; Golshan, S.; Huckans, M.; Fann, J.R.; Storzbach, D. Sensory sensitivity in operation enduring freedom/operation Iraqi freedom veterans with and without blast exposure and mild traumatic brain injury. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2018, 25, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.C.; Garber, B.; Zamorski, M.A. Prospective analysis of premilitary mental health, somatic symptoms, and postdeployment postconcussive symptoms. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dismuke-Greer, C.E.; Nolen, T.L.; Nowak, K.; Hirsch, S.; Pogoda, T.K.; Agyemang, A.A.; Carlson, K.F.; Belanger, H.G.; Kenney, K.; Troyanskaya, M. Understanding the impact of mild traumatic brain injury on veteran service-connected disability: Results from Chronic Effects of Neurotrauma Consortium. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker-Collo, S.; Theadom, A.; Jones, K.; Starkey, N.; Kahan, M.; Feigin, V. Depression and anxiety across the first 4 years after mild traumatic brain injury: Findings from a community-based study. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasterling, J.J.; Brailey, K.; Proctor, S.P.; Kane, R.; Heeren, T.; Franz, M. Neuropsychological outcomes of mild traumatic brain injury, post-traumatic stress disorder and depression in Iraq-deployed US Army soldiers. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 201, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A.J.; Iverson, G.L.; Wojtowicz, M.; Levi, C.R.; Kay-Lambkin, F.; Schofield, P.W.; Zafonte, R.; Shultz, S.R.; Lin, A.P.; Stanwell, P. MR spectroscopy findings in retired professional rugby league players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2017, 38, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoot, M.R.; Levin, H.S.; Smith, A.N.; Goldberg, G.; Wilde, E.A.; Walker, W.C.; Eapen, B.C.; Nolen, T.; Pugh, N.L. Pain and chronic mild traumatic brain injury in the US military population: A Chronic Effects of Neurotrauma Consortium study. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, J.; Mustapic, M.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Lange, R.; Gulyani, S.; Diehl, T.; Motamedi, V.; Osier, N.; Stern, R.A.; Kapogiannis, D. Higher exosomal tau, amyloid-beta 42 and IL-10 are associated with mild TBIs and chronic symptoms in military personnel. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.; Donnelly, J.P.; Warner, G.C.; Kittleson, C.J.; King, P.R. Longitudinal study of objective and subjective cognitive performance and psychological distress in OEF/OIF veterans with and without traumatic brain injury. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2018, 32, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippa, S.M.; Fonda, J.R.; Fortier, C.B.; Amick, M.A.; Kenna, A.; Milberg, W.P.; McGlinchey, R.E. Deployment-related psychiatric and behavioral conditions and their association with functional disability in OEF/OIF/OND veterans. J. Trauma. Stress 2015, 28, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.; Berglund, P.; Rönnbäck, L. Mental fatigue and impaired information processing after mild and moderate traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2009, 23, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.S.; Wickwire, E.M. Sleep disturbances among older adults following traumatic brain injury. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2020, 32, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderploeg, R.D.; Curtiss, G.; Luis, C.A.; Salazar, A.M. Long-term morbidities following self-reported mild traumatic brain injury. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2007, 29, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, A.; Lejbman, N.; Jeromin, A.; French, L.M.; Kim, H.-S.; Cashion, A.; Mysliwiec, V.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Gill, J. Peripheral total tau in military personnel who sustain traumatic brain injuries during deployment. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, S.B.; Woodward, M.; Kimbrel, N.A.; Meyer, E.C.; Kruse, M.I.; Dolan, S.; Gulliver, S.B. Deployment-related TBI, persistent postconcussive symptoms, PTSD, and depression in OEF/OIF veterans. Rehabil. Psychol. 2011, 56, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.D.; Primeau, M.; Sweet, J.J.; Lofland, K.R. Neuropsychological functioning in migraine headache, nonheadache chronic pain, and mild traumatic brain injury patients. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 1999, 14, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.M.; Fox, A.M.; Donnelly, J. Impaired practice effects following mild traumatic brain injury: An event-related potential investigation. Brain Inj. 2015, 29, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alway, Y.; McKay, A.; Ponsford, J.; Schönberger, M. Expressed emotion and its relationship to anxiety and depression after traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2012, 22, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theadom, A.; Parag, V.; Dowell, T.; McPherson, K.; Starkey, N.; Barker-Collo, S.; Jones, K.; Ameratunga, S.; Feigin, V.L.; Group, B.R. Persistent problems 1 year after mild traumatic brain injury: A longitudinal population study in New Zealand. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2016, 66, e16–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker-Collo, S.; Jones, A.; Jones, K.; Theadom, A.; Dowell, A.; Starkey, N.; Feigin, V.L. Prevalence, natural course and predictors of depression 1 year following traumatic brain injury from a population-based study in New Zealand. Brain Inj. 2015, 29, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenhuber, R.; Gentilini, M. Anxiety and depression after mild head injury: A case control study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, Z.Y.; Thomas, L.C.; Simon, J.E.; McCrea, M.; Guskiewicz, K.M. Association between history of multiple concussions and health outcomes among former college football players: 15-year follow-up from the NCAA concussion study (1999-2001). Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier-Toutant, F.; Guay, S.; Beaulieu, C.; Léveillé, É.; Turcotte-Giroux, A.; Papineau, S.D.; Brisson, B.; D’Hondt, F.; De Beaumont, L. Effects of repeated concussions and sex on early processing of emotional facial expressions as revealed by electrophysiology. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2018, 24, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Donald, C.L.; Barber, J.; Jordan, M.; Johnson, A.M.; Dikmen, S.; Fann, J.R.; Temkin, N. Early clinical predictors of 5-year outcome after concussive blast traumatic brain injury. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoge, C.W.; McGurk, D.; Thomas, J.L.; Cox, A.L.; Engel, C.C.; Castro, C.A. Mild traumatic brain injury in US soldiers returning from Iraq. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, K.D.; Soper, H.V.; Berenji, G.R. Executive functioning of combat mild traumatic brain injury. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2016, 23, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, A.J.; Mathias, J.L.; Fairweather-Schmidt, A.K.; Anstey, K.J. Anxiety and comorbid depression following traumatic brain injury in a community-based sample of young, middle-aged and older adults. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 213, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zeldovich, M.; Rauen, K.; Wu, Y.-J.; Covic, A.; Muller, I.; Haagsma, J.A.; Polinder, S.; Menon, D.; Asendorf, T. Longitudinal analyses of the reciprocity of depression and anxiety after traumatic brain injury and its clinical implications. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Donald, C.L.; Adam, O.R.; Johnson, A.M.; Nelson, E.C.; Werner, N.J.; Rivet, D.J.; Brody, D.L. Acute post-traumatic stress symptoms and age predict outcome in military blast concussion. Brain 2015, 138, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, K.M.; Pogoda, T.K. Traumatic brain injury among women veterans: An invisible wound of intimate partner violence. Med. Care 2015, 53, S112–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, Z.Y.; Marshall, S.W.; Harding Jr, H.P.; Guskiewicz, K.M. Nine-year risk of depression diagnosis increases with increasing self-reported concussions in retired professional football players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.P.; Helmer, D.A.; Harding, M.J.; Kosten, T.R.; Petersen, N.J.; Nielsen, D.A. Serotonin transporter genotype and mild traumatic brain injury independently influence resilience and perception of limitations in veterans. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, J.E.; Herrell, R.K.; Wynn, G.H.; Riviere, L.A.; Hoge, C.W. Mild traumatic brain injury (concussion), posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression in US soldiers involved in combat deployments: Association with postdeployment symptoms. Psychosom. Med. 2012, 74, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.B.; Jain, S.; Giacino, J.T.; Levin, H.; Dikmen, S.; Nelson, L.D.; Vassar, M.J.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Robertson, C.S. Risk of posttraumatic stress disorder and major depression in civilian patients after mild traumatic brain injury: A TRACK-TBI study. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didehbani, N.; Munro Cullum, C.; Mansinghani, S.; Conover, H.; Hart Jr, J. Depressive symptoms and concussions in aging retired NFL players. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2013, 28, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Battista, A.; Godfrey, C.; Soo, C.; Catroppa, C.; Anderson, V. Depression and health related quality of life in adolescent survivors of a traumatic brain injury: A pilot study. PloS One 2014, 9, e101842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strigo, I.A.; Spadoni, A.D.; Inslicht, S.S.; Simmons, A.N. Repeated exposure to experimental pain differentiates combat traumatic brain injury with and without post-traumatic stress disorder. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, E.C.; Cross, D.J.; Yarnykh, V.L.; Richards, T.; Martin, N.M.; Pagulayan, K.; Hoff, D.; Hart, K.; Mayer, C.; Tarabochia, M. Neuroimaging, behavioral, and psychological sequelae of repetitive combined blast/impact mild traumatic brain injury in Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomyea, J.; Lang, A.J.; Delano-Wood, L.; Jak, A.; Hanson, K.L.; Sorg, S.; Clark, A.L.; Schiehser, D.M. Neuropsychiatric predictors of Post-Injury headache after Mild-Moderate traumatic brain injury in veterans. Headache: J. Head Face Pain 2016, 56, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.G.; Leddy, J.J.; Hinds, A.L.; Shucard, J.; Sharma, T.; Hernandez, S.; Durinka, J.; Zivadinov, R.; Willer, B.S. An exploratory study of mild cognitive impairment of retired professional contact sport athletes. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2018, 33, E16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Minn, I.; Bienko, N.; Ambinder, E.B.; Xu, X.; Peters, M.E.; Dougherty, J.W.; Vranesic, M.; Koo, S.M. Imaging of glial cell activation and white matter integrity in brains of active and recently retired national football league players. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, D.J.; Legarreta, M.; Bueler, E.; King, J.; McGlade, E.; Yurgelun-Todd, D. Orbitofrontal cortical thinning and aggression in mild traumatic brain injury patients. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e00581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, C.; Geburek, A.J.; Rist, F.; Blumenroth, H.; Fischer, B.; Husstedt, I.; Arolt, V.; Schiffbauer, H.; Lohmann, H. Long-term cognitive and emotional consequences of mild traumatic brain injury. Psychol. Med. 2011, 41, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiehser, D.M.; Delano-Wood, L.; Jak, A.J.; Hanson, K.L.; Sorg, S.F.; Orff, H.; Clark, A.L. Predictors of cognitive and physical fatigue in post-acute mild–moderate traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2017, 27, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan-Goodinson, R.; Ponsford, J.; Schönberger, M. Validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale to assess depression and anxiety following traumatic brain injury as compared with the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 114, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskind, E.R.; Petrie, E.C.; Cross, D.J.; Pagulayan, K.; McCraw, K.; Hoff, D.; Hart, K.; Yu, C.-E.; Raskind, M.A.; Cook, D.G. Cerebrocerebellar hypometabolism associated with repetitive blast exposure mild traumatic brain injury in 12 Iraq war Veterans with persistent post-concussive symptoms. NeuroImage 2011, 54, S76–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapeau, J.; Gosselin, N.; Peretz, I.; McKerral, M. Emotional recognition from dynamic facial, vocal and musical expressions following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2017, 31, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.P.; Downing, M.G.; Ponsford, J.L. Key Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) items associated with DSM-IV depressive and anxiety disorder 12-months post traumatic brain injury. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 236, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahm, J.; Wong, D.; Ponsford, J. Validity of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales in assessing depression and anxiety following traumatic brain injury. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 151, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, N.S.; Smith, R.; Vanuk, J.R.; Raikes, A.C.; Killgore, W.D.S. Resting-state functional connectivity as a biomarker of aggression in mild traumatic brain injury. Neuroreport 2018, 29, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guskiewicz, K.M.; Marshall, S.W.; Bailes, J.; McCrea, M.; Harding, H.P.; Matthews, A.; Mihalik, J.R.; Cantu, R.C. Recurrent concussion and risk of depression in retired professional football players. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astafiev, S.V.; Zinn, K.L.; Shulman, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Exploring the physiological correlates of chronic mild traumatic brain injury symptoms. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 11, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.D.; Berisha, V.; Chiang, C.C.; Ross, K.; Schwedt, T.J. Less cortical thickness in patients with persistent post-traumatic headache compared with healthy controls: An MRI study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2018, 58, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikes, A.C.; Bajaj, S.; Dailey, N.S.; Smith, R.S.; Alkozei, A.; Satterfield, B.C.; Killgore, W.D.S. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) correlates of self-reported sleep quality and depression following mild traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, H.; Marchand, A.; Guay, S. Specificity of cognitive and behavioral complaints in post-traumatic stress disorder and mild traumatic brain injury. Behav. Sci. 2015, 5, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberg, A.B.; Serruya, M.; Gepty, A.; Intenzo, C.; Lewis, T.; Amen, D.; Russell, D.S.; Wintering, N. Clinical comparison of 99mTc exametazime and 123I Ioflupane SPECT in patients with chronic mild traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 2014, 9, e87009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnell, A.J.; Kim, M.S.; Silva, M.A.; Vanderploeg, R.D. Incidence of postconcussion symptoms in psychiatric diagnostic groups, mild traumatic brain injury, and comorbid conditions. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2012, 26, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponheim, S.R.; McGuire, K.A.; Kang, S.S.; Davenport, N.D.; Aviyente, S.; Bernat, E.M.; Lim, K.O. Evidence of disrupted functional connectivity in the brain after combat-related blast injury. NeuroImage 2011, 54, S21–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, J.; Spielman, L.A.; Yarusi, B.B.; Wang, Y.; Silver, J.M.; Ghajar, J. Chronic post-concussion neurocognitive deficits. II. Relationship with persistent symptoms. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, R.A.; Haswell, C.C.; Selgrade, E.S.; Massoglia, D.; Liu, C.; Weiner, J.; Marx, C.E.; Group, M.W.; Cernak, I.; McCarthy, G. Effects of chronic mild traumatic brain injury on white matter integrity in Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 2986–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himanen, L.; Portin, R.; Tenovuo, O.; Taiminen, T.; Koponen, S.; Hiekkanen, H.; Helenius, H. Attention and depressive symptoms in chronic phase after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2009, 23, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, J.A.; Gunstad, J. Postconcussive symptom report: The relative influence of head injury and depression. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2002, 24, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, W.C.; McDonald, S.D.; Ketchum, J.M.; Nichols, M.; Cifu, D.X. Identification of transient altered consciousness induced by military-related blast exposure and its relation to postconcussion symptoms. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2013, 28, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, G.W.; Kepe, V.; Siddarth, P.; Ercoli, L.M.; Merrill, D.A.; Donoghue, N.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Martinez, J.; Omalu, B.; Bailes, J. PET scanning of brain tau in retired national football league players: Preliminary findings. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 21, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskin, S.A. The relationship between sexual abuse and mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 1997, 11, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Sun, J.; Kim, H.-K.; Lee, Y.S.; Oh, B.-M.; Park, H.Y.; Leigh, J.-H. Incidence of depression after traumatic brain injury: A nationwide longitudinal study of 2.2 million adults. J. Neurotrauma 2022, 39, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolze, T.; Franke, S.; Haybaeck, J.; Moehler, M.; Grimminger, P.P.; Lang, H.; Roth, W.; Gockel, I.; Kreuser, N.; Bläker, H. Mismatch repair deficiency, chemotherapy and survival for resectable gastric cancer: An observational study from the German staR cohort and a meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petousis, S.; Christidis, P.; Margioula-Siarkou, C.; Liberis, A.; Vavoulidis, E.; Margioula-Siarkou, G.; Vatopoulou, A.; Papanikolaou, A.; Mavromatidis, G.; Dinas, K. Axillary lymph node dissection vs. sentinel node biopsy for early-stage clinically node-negative breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 306, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, M.S.; Shechter, O.; Gallo, E.S.; Martin, S.D.; Jones, E.; Doncel, G.F.; Borenstein, R. Ginkgolic acid inhibits herpes simplex virus type 1 skin infection and prevents zosteriform spread in mice. Viruses 2021, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, J.; Valdés Hernández, M.d.C. Impact of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure on cognitive function and neurodegeneration in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2023, 13, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liu, H.; He, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Hu, J. Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and Their Associations with Inflammatory Biomarkers in the Chronic Phase Following Traumatic Brain Injuries. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 1304. [Google Scholar]
- Tomar, S.; Sharma, A.; Jain, A.; Sinha, V.; Gupta, I. Study of fatigue and associated factors in traumatic brain injury and its correlation with insomnia and depression. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.; Jain, A.; Sharma, A.; Mittal, R.; Gupta, I. Role of sertraline in posttraumatic brain injury depression and quality-of-life in TBI. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2014, 9, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Mittal, R.S.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, I.D. Study of insomnia and associated factors in traumatic brain injury. Asian J. Psychiatry 2014, 8, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, Y.; Khan, S.; Rana, P.; Dhandapani, M.; Ghai, S.; Gopichandran, L.; Dhandapani, S. Cognitive, behavioral, and functional impairments among traumatic brain injury survivors: Impact on caregiver burden. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2020, 11, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, A.; Ranjan, J.K.; Pandey, N.; Asthana, H.S. Clinical and affective correlates of cognitive functioning in complicated mild and moderate traumatic brain injury patients belonging to rural areas. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2021, 12, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasiya, A.; Pandey, N.; Ranjan, J.K.; Asthana, H.S. Neurocognitive and Affective Sequelae Following Complicated Mild and Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury: A Case Series. Neurol. India 2021, 69, 56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ubukata, S.; Ueda, K.; Fujimoto, G.; Ueno, S.; Murai, T.; Oishi, N. Extracting apathy from depression syndrome in traumatic brain injury by using a clustering method. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 34, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Kwon, H.G. Relationship between depression and dorsolateral prefronto-thalamic tract injury in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looi, M.C.; Idris, Z.; Kumaran, T.; Thyagarajan, D.; Abdullah, J.M.; Ghani, A.R.I.; Ismail, M.I. A Study of 309 Patients and at One Year Follow-Up for Depression after Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2023, 40, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kader, D.A.; Onyechi, C.I.; Ikedum, I.V.; Fattah, A.; Zafar, S.; Bhat, S.; Malik, M.A.; Bheesham, N.; Qadar, L.T.; Cheema, M.S. Depression and anxiety in patients with a history of traumatic brain injury: A case-control study. Cureus 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-R.; Chiu, W.-T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Yu, W.-Y.; Huang, S.-J.; Tsai, M.-D. Longitudinal changes in the health-related quality of life during the first year after traumatic brain injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).