Prospective Association between Total and Trimester-Specific Gestational Weight Gain Rate and Physical Growth Status in Children within 24 Months after Birth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
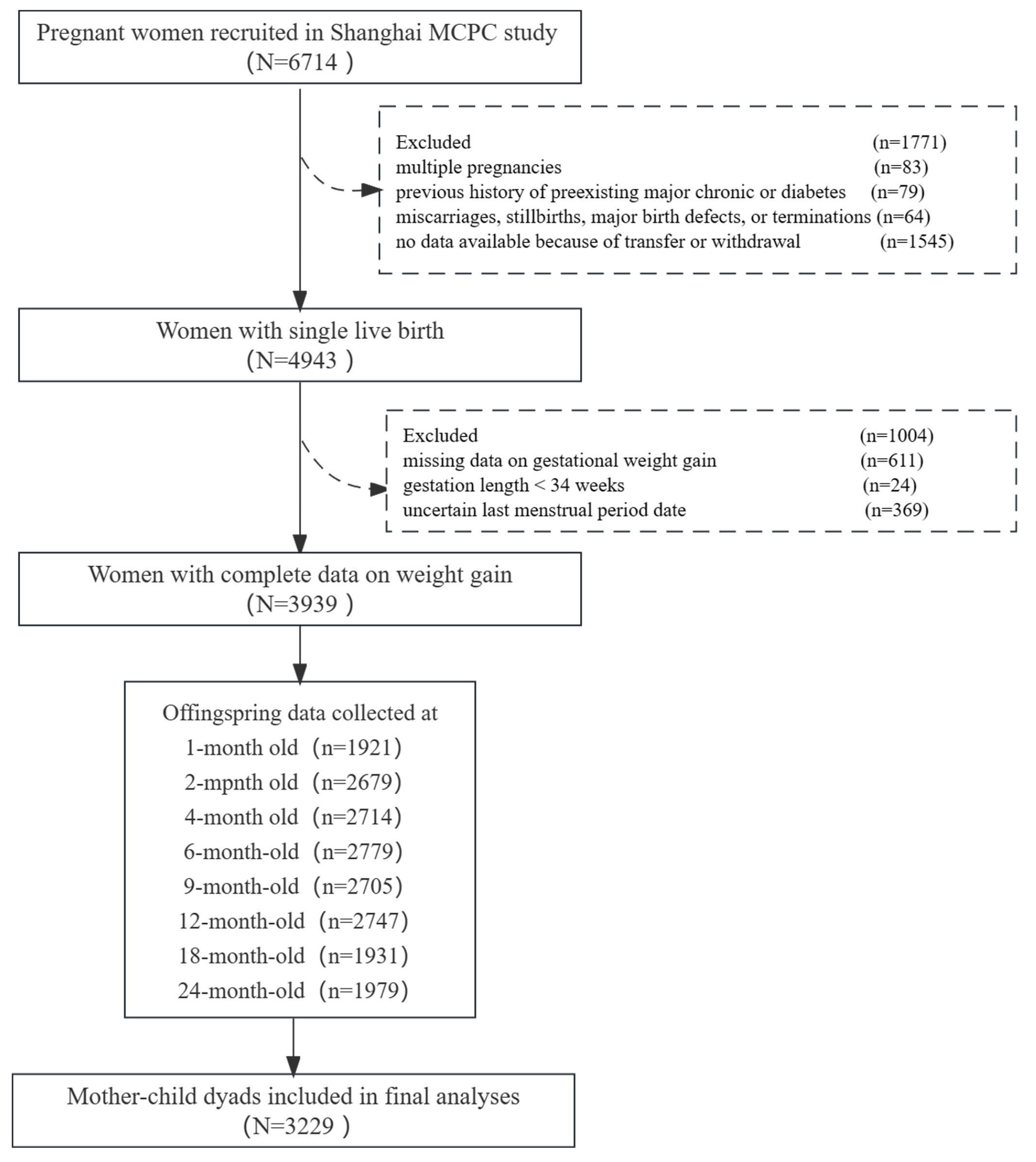
2.1. Study Samples
2.2. Total and Trimester-Specific Gestational Weight Gain Rate
2.3. Children’s Anthropometric Measures
2.4. Study Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
3.2. Effects of Total and Trimester-Specific GWGR on Children’s Physical Growth
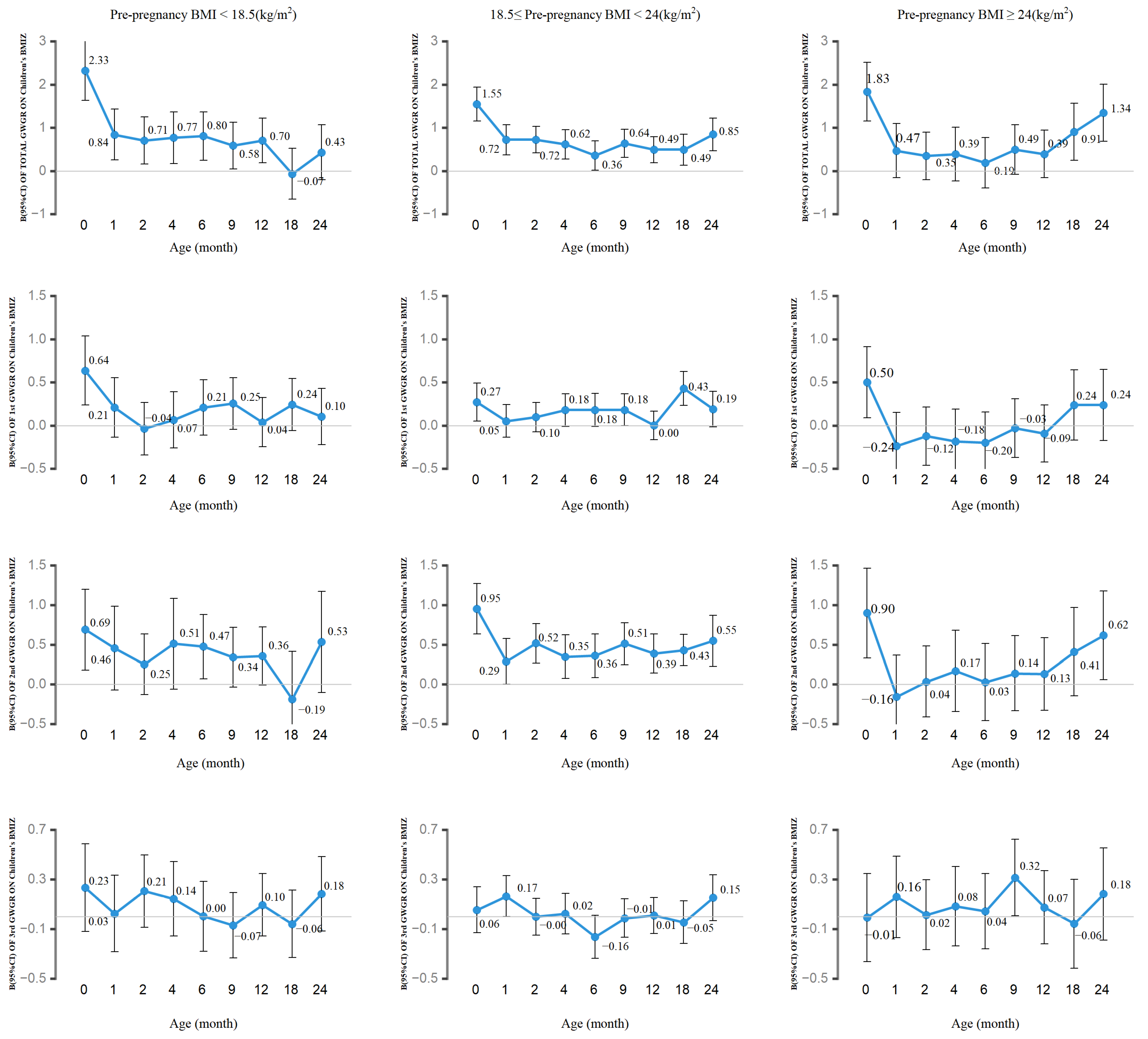
3.3. Association of Total and Trimester-Specific GWGR with Children’s BMIZ by Pre-Pregnancy BMI
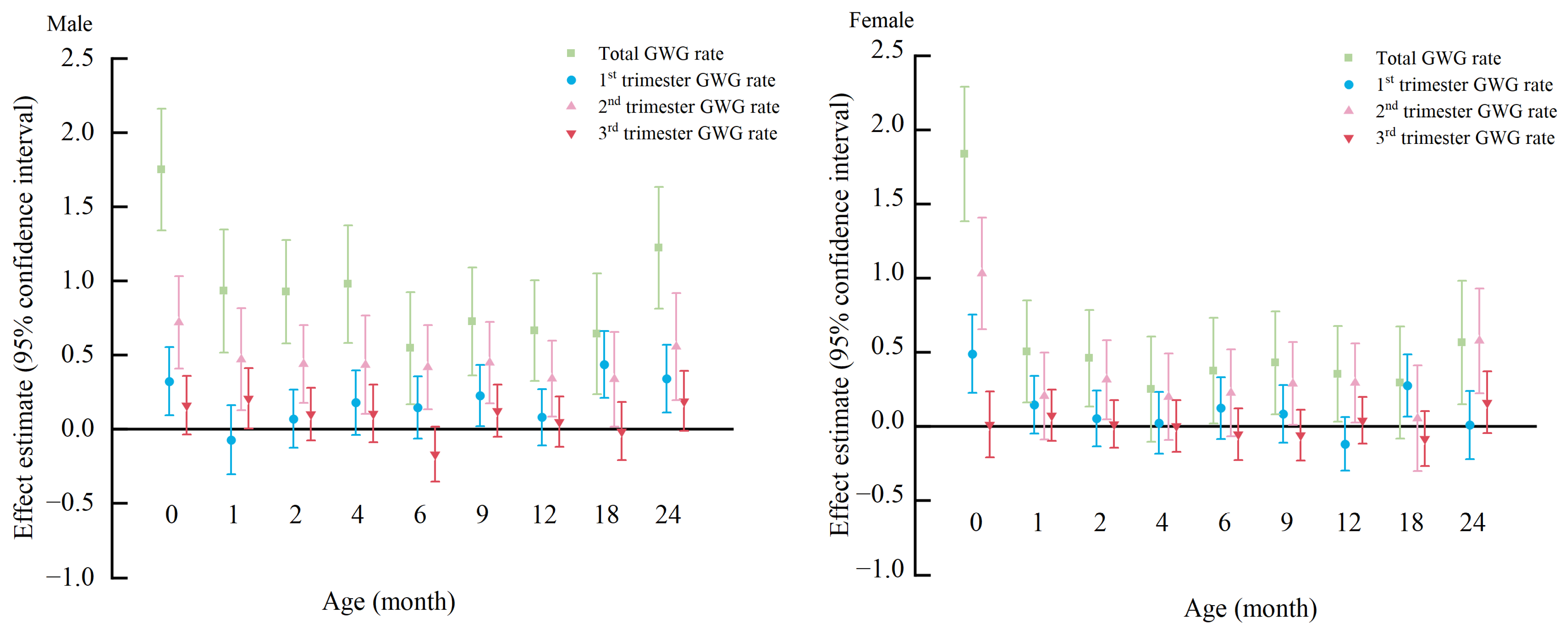
3.4. Association of Total and Trimester-Specific GWGR with Children’s BMIZ by Children’s Sex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogin, B.; Loucky, J. Plasticity. Political economy, and physical growth status of Guatemala Maya children living in the United States. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1997, 102, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudfeld, C.R.; McCoy, D.C.; Danaei, G.; Fink, G.; Ezzati, M.; Andrews, K.G.; Fawzi, W.W. Linear Growth and Child Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 135, E1266–E1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, H. Physical Growth Status and Feeding Methods of Chinese Infants with Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate Under 1 Year of Age. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemel, B.S.; Riley, E.M.; Stallings, V.A. Evaluation of methodology for nutritional assessment in children: Anthropometry, body composition, and energy expenditure. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Rising rural body-mass index is the main driver of the global obesity epidemic in adults. Nature 2019, 569, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobstein, T.; Jackson-Leach, R.; Moodie, M.L.; Hall, K.D.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Swinburn, B.A.; James, W.P.T.; Wang, Y.; McPherson, K. Child and adolescent obesity: Part of a bigger picture. Lancet 2015, 385, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.; Boyle, J.A.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; Rode, L.; et al. Association of Gestational Weight Gain with Maternal and Infant Outcomes A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2017, 317, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-N.; Chen, H.-S.; Hsu, H.-C. Maternal Prepregnancy Body Mass Index, Gestational Weight Gain, and Risk of Adverse Perinatal Outcomes in Taiwan: A Population-Based Birth Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effects of pre-pregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain on maternal and infant complications. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, P.M.; Mele, L.; Landon, M.B.; Ramin, S.M.; Reddy, U.M.; Casey, B.; Wapner, R.J.; Varner, M.W.; Rouse, D.J.; Thorp, J.M., Jr.; et al. Inadequate weight gain in overweight and obese pregnant women: What is the effect on fetal growth? Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 211, 137.e1–137.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro-Malysza, J.; Trojnar, M.; Skorzynska-Dziduszko, K.E.; Kimber-Trojnar, Z.; Darmochwal-Kolarz, D.; Czuba, M.; Leszczynska-Gorzelak, B. Leptin and Ghrelin in Excessive Gestational Weight Gain Association between Mothers and Offspring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehring, I.; Lehmann, S.; von Kries, R. Gestational weight gain in accordance to the IOM/NRC criteria and the risk for childhood overweight: A meta-analysis. Pediatr. Obes. 2013, 8, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badon, S.E.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Xu, F.; Avalos, L.A.; Hedderson, M.M. Gestational weight gain, birthweight and early-childhood obesity: Between- and within-family comparisons. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bider-Canfield, Z.; Martinez, M.P.; Wang, X.; Yu, W.; Bautista, M.P.; Brookey, J.; Page, K.A.; Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H. Maternal obesity, gestational diabetes, breastfeeding and childhood overweight at age 2 years. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Boghossian, N.S.; Frongillo, E.A.; Cai, B.; Hazlett, L.J.; Liu, J. Associations of maternal gestational weight gain with the risk of offspring obesity and body mass index Z scores beyond the mean. Ann. Epidemiol. 2019, 32, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Field, A.E.; Frazier, A.L.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal Gestational Weight Gain and Offspring Weight in Adolescence. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 112, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N.; Cai, L.; Tan, W.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Associations of gestational weight gain with offspring thinness and obesity: By pre-pregnancy body mass index. Reprod. Health 2018, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, J.; Jaaskelainen, A.; Hartikainen, A.L.; Sovio, U.; Vaarasmaki, M.; Pouta, A.; Kaakinen, M.; Jarvelin, M.R. Maternal weight gain during the first half of pregnancy and offspring obesity at 16 years: A prospective cohort study. BJOG 2012, 119, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.A.; O’Callaghan, M.; Callaway, L.; Williams, G.; Najman, J.; Lawlor, D.A. Associations of Gestational Weight Gain with Offspring Body Mass Index and Blood Pressure at 21 Years of Age Evidence From a Birth Cohort Study. Circulation 2009, 119, 1720–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, L.C.; Ester, W.A.; Lumey, L.H.; Michels, K.B.; Wei, Y.; Cohn, B.A.; Susser, E.S.; Terry, M.B. Maternal weight gain in excess of pregnancy guidelines is related to daughters being overweight 40 years later. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 246.e1–246.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.A.; Mannan, M.; Doi, S.A.R. Gestational weight gain in relation to offspring obesity over the life course: A systematic review and bias- adjusted meta- analysis. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Taveras, E.M.; Kleinman, K.P.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Gillman, M.W. Gestational weight gain and child adiposity at age 3 years. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 196, 322.e1–322.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Aris, I.M.; Oken, E.; Ma, Y.; Ding, N.; Gao, M.; Wei, X.; Wen, D. Association of Total and Trimester-Specific Gestational Weight Gain Rate with Early Infancy Weight Status: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study in China. Nutrients 2019, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.M.; Stecher, L.; Brei, C.; Hauner, H. Mid-pregnancy weight gain is associated with offspring adiposity outcomes in early childhood. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.M.; Chesi, A.; Mentch, F.; Xiao, R.; Chiavacci, R.; Mitchell, J.A.; Kelly, A.; Hakonarson, H.; Grant, S.F.A.; Zemel, B.S.; et al. Body Mass Index (BMI) Trajectories in Infancy Differ by Population Ancestry and May Presage Disparities in Early Childhood Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smego, A.; Woo, J.G.; Klein, J.; Suh, C.; Bansal, D.; Bliss, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Bolling, C.; Crimmins, N.A. High Body Mass Index in Infancy May Predict Severe Obesity in Early Childhood. J. Pediatr. 2017, 183, 87–93.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.M.; Spivack, J.G.; Faith, M.S.; Chesi, A.; Mitchell, J.A.; Kelly, A.; Grant, S.F.A.; McCormack, S.E.; Zemel, B.S. Infant BMI or Weight-for-Length and Obesity Risk in Early Childhood. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Weight Gain during Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hivert, M.-F.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Greater Early and Mid-Pregnancy Gestational Weight Gains are Associated with Excess Adiposity in Mid-Childhood. Obesity 2016, 24, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Wen, S.W.; Tan, H.; Zhou, S.; Ye, C.; Shen, M.; Smith, G.N.; Walker, M.C. Association of Timing of Weight Gain in Pregnancy with Infant Birth Weight. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kries, R.; Chmitorz, A.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Bayer, O.; Ensenauer, R. Late Pregnancy Reversal from Excessive Gestational Weight Gain Lowers Risk of Childhood Overweight—A Cohort Study. Obesity 2013, 21, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diesel, J.C.; Eckhardt, C.L.; Day, N.L.; Brooks, M.M.; Arslanian, S.A.; Bodnar, L.M. Is gestational weight gain associated with offspring obesity at 36 months? Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 10, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.L.; Boyle, J.A.; Harrison, C.L.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; et al. Gestational weight gain across continents and ethnicity: Systematic review and meta-analysis of maternal and infant outcomes in more than one million women. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgman, S.L.; Azad, M.B.; Persaud, R.R.; Chari, R.S.; Becker, A.B.; Sears, M.R.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Haqq, A.M.; et al. Impact of maternal pre-pregnancy overweight on infant overweight at 1year of age: Associations and sex-specific differences. Pediatr. Obes. 2018, 13, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-S.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Wei, C.; Shen, G.; Zhu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.-M.; Huang, T.; et al. Exclusive Breastfeeding Is Inversely Associated with Risk of Childhood Overweight in a Large Chinese Cohort. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Kit, B.K.; Flegal, K.M. Prevalence of Childhood and Adult Obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2014, 311, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyrskyj, A.L.; Kalu, R.; Koleva, P.T.; Bridgman, S.L. Fetal programming of overweight through the microbiome: Boys are disproportionately affected. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2016, 7, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Xia, B.; Ma, W.; Xiao, X.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y. Determination of antibiotic concentration in meconium and its association with fetal growth and development. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.R.; Perng, W.; Kleinman, K.P.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Oken, E. Associations of trimester-specific gestational weight gain with maternal adiposity and systolic blood pressure at 3 and 7 years postpartum. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 499.e1–499.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, L.; Tan, Y.; Sheng, F.; Song, Y.; Zhang, R.; Iuliano, A.D.; et al. Cohort profile: China respiratory illness surveillance among pregnant women (CRISP), 2015–2018. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, E.; Guo, J.; Pan, L.; Li, B.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, G. Maternal Pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index and Gestational Weight Gain on Offspring Overweight in Early Infancy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77809. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.S.; Olendzki, B.C.; Merriam, P.A.; Chiriboga, D.E.; Culver, A.L.; Li, W.J.; Hebert, J.R.; Ockene, I.S.; Griffith, J.A.; Pagoto, S.L. A randomized clinical trial comparing low-glycemic index versus ADA dietary education among individuals with type 2 diabetes. Nutrition 2008, 24, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.L.; Shi, W.J.; Yan, W.L.; Wang, X.L.; Luy, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Q. Chinese neonatal birth weight curve for different gestational age. Chin. J. Pediatr. 2015, 53, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Mao, Z.; Abdulai, T.; Liu, X.; Tu, R.; Wang, Y.; Qian, X.; Jiang, J.; et al. The association between PSQI score and hypertension in a Chinese rural population: The Henan rural cohort study. Sleep Med. 2019, 58, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, B.; Vistad, I.; Haakstad, L.A.H.; Berntsen, S.; Sagedal, L.R.; Lohne-Seiler, H.; Torstveit, M.K. Reliability and concurrent validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire short form among pregnant women. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ren, F.; Fun, B.; Wang, Z. Investigation of depressive symptoms in general population and application of CES-D. Chin. J. Neurol. 1987, 20, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Tang, L.; Guo, X. Prevalence of depression and the association between depressive symptoms and dietary behaviors among students in Beijing. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2022, 43, 715–717. [Google Scholar]
- Samakouri, M.; Bouhos, G.; Kadoglou, M.; Giantzelidou, A.; Tsolaki, K.; Livaditis, M. Standardization of the greek version of Zung’s self-rating anxiety scale (SAS). Psychiatriki 2012, 23, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Zou, J.; Ma, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H. Prospective associations between various prenatal exposures to maternal psychological stress and neurodevelopment in children within 24 months after birth. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 327, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisset, A.-S.; Tchernof, A.; Dube, M.-C.; Veillette, J.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Robitaille, J. Weight Gain Measures in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Womens Health 2011, 20, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Page, K.A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Risks and management during and after pregnancy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitanchez, D.; Ciangura, C.; Jacqueminet, S. How Can Maternal Lifestyle Interventions Modify the Effects of Gestational Diabetes in the Neonate and the Offspring? A Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses. Nutrients 2020, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavaroli, V.; Hopkins, S.A.; Biggs, J.B.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Seneviratne, S.N.; Baldi, J.C.; McCowan, L.M.E.; Cutfield, W.S.; Hofman, P.L.; Derraik, J.G.B. The associations between maternal BMI and gestational weight gain and health outcomes in offspring at age 1 and 7 years. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gillman, M.W. Developmental origins of health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1848–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, J.A.; Jones, P.G.; Peabody, J.L.; Knox, E.; Clark, R.H. Effect of antenatal and postnatal corticosteroid therapy on weight gain and head circumference growth in the nursery. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 99, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, J.A.; Jones, P.G.; Knox, E.; Clark, R.H. Does antenatal corticosteroid therapy affect birth weight and head circumference? Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 99, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Karachaliou, M.; Georgiou, V.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Chalkiadaki, G.; Daraki, V.; Koinaki, S.; Dermitzaki, E.; Sarri, K.; Vassilaki, M.; Kogevinas, M.; et al. Association of trimester-specific gestational weight gain with fetal growth, offspring obesity, and cardiometabolic traits in early childhood. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 502.e1–502.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrekera, B.; Colaizy, T.T.; Vasilakos, L.K.; Johnson, K.J.; Santillan, D.A.; Haskell, S.E.; Roghair, R.D. Origins of neonatal leptin deficiency in preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraegeloh-Mann, I. Imaging of early brain injury and cortical plasticity. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 190, S84–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.; Dehaene-Lambertz, G.; Kulikova, S.; Poupon, C.; Hueppi, P.S.; Hertz-Pannier, L. The Early Development of Brain White Matter: A Review of Imaging Studies in Fetuses, Newborns and Infants. Neuroscience 2014, 276, 48–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuebe, A.M.; Forman, M.R.; Michels, K.B. Maternal-recalled gestational weight gain, pre-pregnancy body mass index, and obesity in the daughter. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, J.; Yokota, I.; Iida, M.; Murakami, T.; Naito, E.; Ito, M.; Shima, K.; Kuroda, Y. Serum leptin concentration in cord blood: Relationship to birth weight and gender. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1642–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffeis, C.; Moghetti, P.; Vettor, R.; Lombardi, A.M.; Vecchini, S.; Tato, L. Leptin concentration in newborns’ cord blood: Relationship to gender and growth-regulating hormones. Int. J. Obes. 1999, 23, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Trevino-Garza, C.; Bosques-Padilla, F.J.; Estrada-Zuniga, C.M.; Mancillas-Adame, L.; Villarreal-Perez, J.Z.; Abrego-Moya, V.; Argente, J. Typical Leptin Fall Is Mitigated by Breastfeeding in Female Infants. Arch. Med. Res. 2010, 41, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helland, I.B.; Reseland, J.E.; Saugstad, O.D.; Drevon, C.A. Leptin levels in pregnant women and newborn infants: Gender differences and reduction during the neonatal period. Pediatrics 1998, 101, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Fleisch, A.; Hivert, M.-F.; Mantzoros, C.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. First and second trimester gestational weight gains are most strongly associated with cord blood levels of hormones at delivery important for glycemic control and somatic growth. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2017, 69, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, U.; Gressner, A.M. Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism: Review of pathobiochemical and clinical chemical aspects of leptin, ghrelin, adiponectin, and resistin. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1511–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, J. Energy balance in obesity. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Huxley, R.; Wu, Y.; Dibley, M.J. Temporal trends in overweight and obesity of children and adolescents from nine Provinces in China from 1991–2006. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2010, 5, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Subjects, Mean ± SD | Quartile of Total GWGR, Mean ± SD or n (%) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| or n (%) | Quartile 1 | Quartile 2 | Quartile 3 | Quartile 4 | ||
| n = 3229 | n = 807 | n = 806 | n = 809 | n = 807 | ||
| Maternal characteristics | ||||||
| Age at delivery (years) | 28.93 ± 4.09 | 28.54 ± 4.12 | 29.22 ± 4.11 | 28.69 ± 3.94 | 28.25 ± 4.07 | <0.001 |
| Education level | <0.001 | |||||
| Middle school and below | 285 (8.82) | 61 (7.56) | 57 (7.07) | 70 (8.65) | 97 (12.02) | |
| High school or same level | 410 (12.70) | 106 (13.14) | 91 (11.29) | 100 (12.367) | 113 (14.00) | |
| Junior college or same level | 1081 (33.48) | 251 (31.10) | 254 (31.51) | 281 (34.73) | 295 (36.56) | |
| College and above | 1453 (45.00) | 389 (48.20) | 404 (50.13) | 358 (44.25) | 302 (37.42) | |
| Annual family income | 0.392 | |||||
| <¥100,000 | 771 (23.88) | 183 (22.68) | 185 (22.95) | 199 (24.60) | 204 (25.28) | |
| ¥100,000–200,000 | 1551 (48.03) | 385 (47.71) | 388 (48.14) | 380 (46.97) | 398 (49.32) | |
| ¥200,000–300,000 | 600 (18.58) | 169 (20.94) | 155 (19.23) | 142 (17.55) | 134 (16.60) | |
| ≥¥300,000 | 307 (9.51) | 70 (8.67) | 78 (9.68) | 88 (10.88) | 71 (8.80) | |
| Second-hand smoking during pregnancy | 0.307 | |||||
| Yes | 781 (24.19) | 196 (24.29) | 180 (22.33) | 213 (26.33) | 192 (23.79) | |
| No | 2448 (75.81) | 611 (75.71) | 626 (77.67) | 596 (73.67) | 615 (76.21) | |
| Alcohol before pregnancy | 74 (2.29) | 13 (1.61) | 19 (2.36) | 19 (2.35) | 23 (2.85) | |
| Sleep quality during pregnancy | 0.334 | |||||
| Good | 1099 (34.04) | 279 (34.57) | 267 (33.13) | 264 (32.63) | 289 (35.81) | |
| Poor | 2130 (65.96) | 528 (65.43) | 539 (66.88) | 545 (67.37) | 518 (64.19) | |
| Physical activity intensity | 0.148 | |||||
| Low | 1327 (41.10) | 341 (42.26) | 328 (40.69) | 340 (42.03) | 318 (39.41) | |
| Medium | 1743 (53.98) | 422 (52.29) | 445 (55.21) | 439 (54.26) | 437 (54.15) | |
| High | 159 (4.92) | 44 (5.45) | 33 (4.09) | 30 (3.71) | 520 (6.44) | |
| Depression during pregnancy | 366 (11.33) | 88 (10.90) | 100 (12.41) | 92 (11.37) | 86 (10.66) | 0.696 |
| Anxiety during pregnancy | 401 (12.42) | 72 (8.92) | 106 (13.15) | 112 (13.84) | 111 (13.75) | 0.572 |
| Parity | <0.001 | |||||
| Primiparous | 1803 (55.84) | 405 (50.19) | 450 (55.83) | 454 (56.12) | 494 (61.21) | |
| Non-primiparous | 1426 (44.16) | 402 (49.81) | 356 (44.17) | 355 (43.88) | 313 (38.79) | |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | <0.001 | |||||
| <18.5 | 543 (16.82) | 105 (13.01) | 149 (18.49) | 142 (17.55) | 147 (18.22) | |
| 18.5–24 | 2170 (67.20) | 485 (60.10) | 550 (68.24) | 563 (69.59) | 572 (70.88) | |
| ≥24 | 516 (15.98) | 217 (26.89) | 107 (13.27) | 104 (12.86) | 88 (10.90) | |
| Gestational diabetes | 345 (10.68) | 158 (19.58) | 80 (9.93) | 55 (6.80) | 52 (6.44) | <0.001 |
| 1st trimester GWGR (kg/week) | 0.17 ± 0.24 | 0.10 ± 0.23 | 0.15 ± 0.20 | 0.18 ± 0.2015 | 0.27 ± 0.28 | <0.001 |
| 2nd trimester GWGR (kg/week) | 0.48 ± 0.18 | 0.36 ± 0.17 | 0.45 ± 0.14 | 0.51 ± 0.12 | 0.60 ± 0.19 | <0.001 |
| 3rd trimester GWGR (kg/week) | 0.57 ± 0.31 | 0.38 ± 0.33 | 0.54 ± 0.26 | 0.62 ± 0.24 | 0.75± 0.29 | <0.001 |
| Paternal characteristics | ||||||
| Age (years) | 29.97 ± 4.62 | 30.67 ± 4.52 | 30.19 ± 4.67 | 29.77 ± 4.46 | 29.24 ± 4.71 | <0.001 |
| FBMI category (kg/m2) | 0.486 | |||||
| <18.5 | 140 (4.34) | 32 (3.97) | 43 (5.33) | 31 (3.83) | 34 (4.21) | |
| 18.5–24 | 1615 (50.02) | 385 (47.71) | 402 (49.88) | 423 (52.29) | 405 (50.19) | |
| ≥24 | 1474 (45.64) | 390 (48.32) | 361 (44.79) | 331 (43.88) | 368 (45.60) | |
| Children’s characteristics | ||||||
| Sex | 0.391 | |||||
| Male | 1651 (51.13) | 400 (49.57) | 409 (50.74) | 409 (50.56) | 433 (53.66) | |
| Female | 1578 (48.87) | 407 (50.43) | 397 (49.26) | 400 (49.44) | 374 (46.34) | |
| Children Anthropometric Measures | Total GWGR c | 1st Trimester GWGR | 2nd Trimester GWGR a | 3rd Trimester GWGR bc | Pint d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kg/week) | (kg/week) | (kg/week) | (kg/week) | ||
| BMIZ | |||||
| 0 month | 1.838 (1.543, 2.133) *** | 0.421 (0.253, 0.590) *** | 0.929 (0.695, 1.162) *** | 0.088 (−0.055, 0.231) | <0.001 |
| 1 month | 0.714 (0.451, 0.977) *** | 0.036 (−0.112, 0.184) | 0.272 (0.051, 0.492) * | 0.123 (−0.007, 0.254) | 0.364 |
| 2 month | 0.698 (0.459, 0.936) *** | 0.065 (−0.071, 0.201) | 0.374 (0.188, 0.560) *** | 0.050 (−0.069, 0.169) | 0.042 |
| 4 month | 0.613 (0.347, 0.879) *** | 0.105 (−0.046, 0.256) | 0.320 (0.099, 0.541) ** | 0.053 (−0.078, 0.185) | 0.297 |
| 6 month | 0.450 (0.190, 0.710) *** | 0.135 (−0.013, 0.284) | 0.323 (0.120, 0.527) ** | −0.114 (−0.242, 0.013) | 0.002 |
| 9 month | 0.602 (0.350, 0.854) *** | 0.165 (0.022, 0.308) * | 0.373 (0.178, 0.569) *** | 0.039 (−0.083, 0.162) | 0.069 |
| 12 month | 0.533 (0.298, 0.767) *** | −0.009 (−0.141, 0.123) | 0.310 (0.126, 0.495) ** | 0.050 (−0.066, 0.165) | 0.030 |
| 18 month | 0.486 (0.208, 0.764) *** | 0.177 (−0.064, 0.418) | 0.348 (0.193, 0.502) *** | −0.039 (−0.175, 0.096) | 0.003 |
| 24 month | 0.909 (0.617, 1.200) *** | 0.173 (0.011, 0.335) * | 0.542 (0.288, 0.795) *** | 0.181 (0.036, 0.326) * | 0.076 |
| HCZ | |||||
| 1 month | 0.675 (0.371, 0.980) *** | 0.182 (0.011, 0.353) * | 0.138 (−0.117, 0.393) | 0.016 (−0.135, 0.167) | 0.575 |
| 2 month | 0.480 (0.212, 0.748) *** | 0.143 (−0.009, 0.295) | −0.009 (−0.217, 0.199) | −0.010 (−0.144, 0.123) | 0.334 |
| 4 month | 0.365 (0.090, 0.639) ** | 0.190 (0.035, 0.346) * | −0.128 (−0.356, 0.101) | −0.049 (−0.184, 0.086) | 0.033 |
| 6 month | 0.469 (0.204, 0.734) ** | 0.243 (0.092, 0.394) ** | −0.096(−0.303, 0.112) | −0.024 (−0.154, 0.106) | 0.012 |
| 9 month | 0.335 (0.065, 0.606) * | 0.215 (0.062, 0.367) ** | −0.048 (−0.257, 0.162) | −0.039 (−0.171, 0.093) | 0.037 |
| 12 month | 0.428 (0.166, 0.690) ** | 0.239 (0.093, 0.386) ** | 0.084 (−0.121, 0.290) | −0.042 (−0.171, 0.087) | 0.041 |
| 18 month | 0.340 (0.035, 0.645) * | 0.145 (−0.024, 0.315) | −0.030 (−0.296, 0.235) | 0.027 (−0.122, 0.177) | 0.453 |
| 24 month | 0.439 (0.146, 0.733) ** | 0.248 (0.086, 0.411) ** | −0.037 (−0.292, 0.218) | −0.055 (−0.200, 0.091) | 0.025 |
| WAZ | |||||
| 0 month | 1.369 (1.156, 1.582) *** | 0.303 (0.181, 0.425) *** | 0.681 (0.512, 0.850) *** | 0.039 (−0.064, 0.143) | <0.001 |
| 1 month | 0.838 (0.584, 1.091) *** | 0.206 (0.064, 0.349) ** | 0.306 (0.093, 0.518) ** | −0.047 (−0.173, 0.079) | 0.070 |
| 2 month | 0.806 (0.585, 1.028) *** | 0.206 (0.079, 0.332) ** | 0.335 (0.162, 0.509) *** | −0.011 (−0.122, 0.100) | 0.027 |
| 4 month | 0.815 (0.565, 1.066) *** | 0.258 (0.116, 0.400) *** | 0.394 (0.186, 0.602) *** | −0.036 (−0.159, 0.088) | 0.005 |
| 6 month | 0.718 (0.472, 0.965) *** | 0.280 (0.140, 0.421) *** | 0.326 (0.133, 0.519) ** | −0.068 (−0.189, 0.053) | 0.001 |
| 9 month | 0.910 (0.667, 1.152) *** | 0.239 (0.101, 0.377) *** | 0.419 (0.230, 0.609) *** | 0.069 (−0.050, 0.187) | 0.057 |
| 12 month | 0.865 (0.638, 1.093) *** | 0.136 (0.007, 0.264) * | 0.402 (0.222, 0.581) *** | 0.138 (0.026, 0.251) * | 0.095 |
| 18 month | 0.817 (0.547, 1.087) *** | 0.383 (0.233, 0.534) *** | 0.276 (0.041, 0.512) * | 0.113 (−0.019, 0.245) | 0.135 |
| 24 month | 0.992 (0.722, 1.262) *** | 0.217 (0.066, 0.367) ** | 0.483 (0.248, 0.719) *** | 0.232 (0.098, 0.365) ** | 0.228 |
| LAZ | |||||
| 0 month | 0.313 (0.202, 0.424) *** | 0.140 (0.052, 0.227) ** | 0.057 (−0.006, 0.119) | −0.033 (−0.086, 0.021) | 0.034 |
| 1 month | 0.646 (0.343, 0.949) *** | 0.339 (0.170, 0.509) *** | 0.221 (−0.032, 0.473) | −0.245 (−0.394, −0.095) | <0.001 |
| 2 month | 0.565 (0.301, 0.830) *** | 0.293 (0.143, 0.443) *** | 0.132 (−0.074, 0.337) | −0.086 (−0.217, 0.046) | 0.006 |
| 4 month | 0.626 (0.364, 0.889) *** | 0.316 (0.168, 0.465) *** | 0.279 (0.062, 0.496) * | −0.135 (−0.272, 0.002) | <0.001 |
| 6 month | 0.670 (0.414, 0.926) *** | 0.318 (0.172, 0.464) *** | 0.146 (−0.054, 0.346) | 0.030 (−0.095, 0.156) | 0.040 |
| 9 month | 0.819 (0.555, 1.083) *** | 0.201 (0.051, 0.351) ** | 0.248 (0.043, 0.454) * | 0.068 (−0.061, 0.197) | 0.548 |
| 12 month | 0.844 (0.580, 1.108) *** | 0.244 (0.095, 0.392) ** | 0.316 (0.108, 0.524) ** | 0.186 (0.056, 0.316) ** | 0.930 |
| 18 month | 0.813 (0.493, 1.133) *** | 0.224 (0.045, 0.403) * | 0.256 (−0.023, 0.536) | 0.242 (0.086, 0.399) ** | 0.707 |
| 24 month | 0.594 (0.294, 0.895) *** | 0.138 (−0.028, 0.304) | 0.207 (−0.053, 0.468) | 0.174 (0.025, 0.323) * | 0.746 |
| WHZ | |||||
| 0 month | 1.756 (1.457, 2.054) *** | 0.415 (0.245, 0.585) *** | 0.892 (0.656, 1.128) *** | 0.097 (−0.048, 0.242) | <0.001 |
| 1 month | 0.428 (0.128, 0.727) ** | −0.134 (−0.302, 0.033) | 0.246 (0.098, 0.394) ** | 0.243 (0.096, 0.391) | 0.002 |
| 2 month | 0.536 (0.278, 0.794) *** | −0.031 (−0.177, 0.116) | 0.358 (0.157, 0.558) ** | 0.087 (−0.041, 0.216) | 0.017 |
| 4 month | 0.568 (0.303, 0.834) *** | 0.079 (−0.072, 0.230) | 0.310 (0.089, 0.531) ** | 0.065 (−0.066, 0.196) | 0.314 |
| 6 month | 0.458 (0.201, 0.716) *** | 0.141 (−0.006, 0.288) | 0.324 (0.123, 0.525) ** | −0.114 (−0.240, 0.012) | 0.001 |
| 9 month | 0.677 (0.428, 0.926) *** | 0.181 (0.039, 0.322) * | 0.391 (0.198, 0.584) *** | 0.046 (−0.075, 0.167) | 0.057 |
| 12 month | 0.663 (0.431, 0.894) *** | 0.035 (−0.095, 0.166) | 0.356 (0.173, 0.539) *** | 0.079 (−0.036, 0.193) | 0.029 |
| 18 month | 0.571 (0.299, 0.844) *** | 0.201 (−0.035, 0.437) | 0.373 (0.222, 0.524) *** | −0.006 (−0.139, 0.126) | 0.004 |
| 24 month | 0.945 (0.661, 1.229) *** | 0.187 (0.029, 0.345) * | 0.542 (0.295, 0.789) *** | 0.192 (0.050, 0.333) ** | 0.083 |
| Children Anthropometric Measures | Total GWGR c | 1st Trimester GWGR | 2nd Trimester GWGR a | 3rd Trimester GWGR bc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kg/week) | (kg/week) | (kg/week) | (kg/week) | |
| BMIZ | 0.659 (0.483, 0.835) *** | 0.133 (0.034, 0.233) ** | 0.312 (0.171, 0.452) *** | 0.057 (−0.029, 0.143) |
| HCZ | 0.422 (0.215, 0.629) *** | 0.206 (0.090, 0.322) ** | −0.017(−0.180−0.147) | −0.068 (−0.168, 0.033) |
| WAZ | 0.854 (0.674, 1.034) *** | 0.227 (0.125, 0.330) *** | 0.339 (0.196, 0.482) *** | 0.046 (−0.042, 0.134) |
| LAZ | 0.642 (0.434, 0.849) *** | 0.253 (0.136, 0.370) *** | 0.192 (0.028, 0.356) * | −0.037 (−0.138, 0.064) |
| WHZ | 0.626 (0.450, 0.802) *** | 0.111 (0.012, 0.211) * | 0.319 (0.178, 0.459) *** | 0.091 (0.005, 0.176) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Shang, B.; Ye, P.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H. Prospective Association between Total and Trimester-Specific Gestational Weight Gain Rate and Physical Growth Status in Children within 24 Months after Birth. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214523
Wang K, Shang B, Ye P, Wei Q, Zhang Y, Shi H. Prospective Association between Total and Trimester-Specific Gestational Weight Gain Rate and Physical Growth Status in Children within 24 Months after Birth. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214523
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ke, Bingzi Shang, Peiqi Ye, Qian Wei, Yunhui Zhang, and Huijing Shi. 2023. "Prospective Association between Total and Trimester-Specific Gestational Weight Gain Rate and Physical Growth Status in Children within 24 Months after Birth" Nutrients 15, no. 21: 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214523
APA StyleWang, K., Shang, B., Ye, P., Wei, Q., Zhang, Y., & Shi, H. (2023). Prospective Association between Total and Trimester-Specific Gestational Weight Gain Rate and Physical Growth Status in Children within 24 Months after Birth. Nutrients, 15(21), 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214523







