Caffeine Intake, Plasma Caffeine Level, and Kidney Function: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasma Caffeine Level Measurement and Data Sources
2.2. Definition of Caffeine Intake and Data Sources
2.3. Definition of the Outcomes and Data Sources
2.4. Statistical Analysis
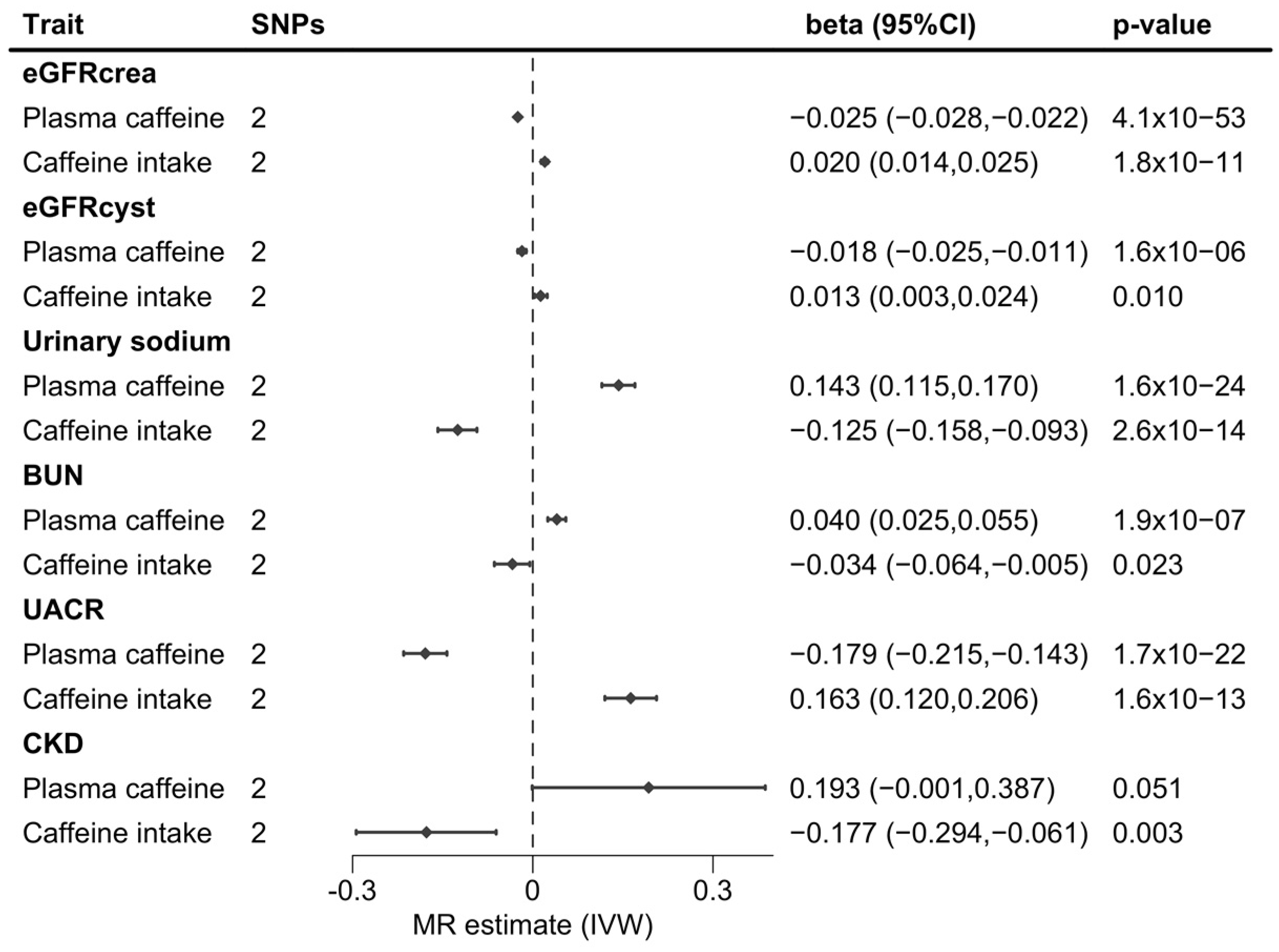
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Trait | Unit | Cohort(s) or Consortium | Simple Size or Cases/Sample Size | First Author, Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposures | PIVUS, SHIP-TREND, SKIPOGH, TwinGene, TwinsUK, ULSAM | |||
| Plasma caffeine level | SD | 9876 | Cornelis, 2016 [17] | |
| Caffeine intake | SD | ARIC, PLCO, NHS, HPFS, WGHS | 47,341 | Cornelis, 2011 [16] |
| Outcome | ||||
| eGFRcyst | log(mL/min/1.73 m2) | CKDGen + UK Biobank | 460,826 | Stanzick, 2021 [19] |
| eGFRcrea | log(mL/min/1.73 m2) | CKDGen + UK Biobank | 1,004,040 | Stanzick, 2021 [19] |
| Urinary sodium | SD | UK Biobank | 326,831 | Hemani, 2018 [23] |
| BUN | log/mg/dL) | CKDGen | 480,698 | Wuttke, 2019 [20] |
| UACR | log(mg/mmol) | CKDGen | 192,868 | Teumer, 2019 [21] |
| CKD | log(OR) | CKDGen | 41,395/439,303 | Wuttke, 2019 [20] |
References
- Reyes, C.M.; Cornelis, M.C. Caffeine in the Diet: Country-Level Consumption and Guidelines. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolignano, D.; Coppolino, G.; Barillà, A.; Campo, S.; Criseo, M.; Tripodo, D.; Buemi, M. Caffeine and the Kidney: What Evidence Right Now? J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.P.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. A Review on Renal Toxicity Profile of Common Abusive Drugs. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 17, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofovic, S.P.; Salah, E.M.; Jackson, E.K.; Melhem, M. Early renal injury induced by caffeine consumption in obese, diabetic ZSF1 rats. Ren. Fail. 2007, 29, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belibi, F.A.; Wallace, D.P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Christensen, M.; Reif, G.; Grantham, J.J. The effect of caffeine on renal epithelial cells from patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meca, R.; Balbo, B.E.; Ormanji, M.S.; Fonseca, J.M.; Iannuzzi, L.R.; Costa, E.S.; Onuchic, L.F.; Heilberg, I.P. Caffeine Accelerates Cystic Kidney Disease in a Pkd1-Deficient Mouse Model. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendramini, L.C.; Nishiura, J.L.; Baxmann, A.C.; Heilberg, I.P. Caffeine intake by patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardat-Rotar, L.; Puhan, M.A.; Braun, J.; Serra, A.L. Long-term effect of coffee consumption on autosomal dominant polycystic kidneys disease progression: Results from the Suisse ADPKD, a Prospective Longitudinal Cohort Study. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, E.A.; Selvin, E.; Grams, M.E.; Steffen, L.M.; Coresh, J.; Rebholz, C.M. Coffee Consumption and Incident Kidney Disease: Results From the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Thongprayoon, C.; Thamcharoen, N.; Panjawatanan, P.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Association of coffee consumption and chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2017, 71, e12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhee, J.H.; Nam, K.H.; An, S.Y.; Cha, M.U.; Lee, M.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Yun, H.R.; Kee, Y.K.; Park, J.T.; et al. Effects of Coffee Intake on Incident Chronic Kidney Disease: A Community-Based Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Med. 2018, 131, 1482–1490.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Siriopol, D.; Copur, S.; Tapoi, L.; Benchea, L.; Kuwabara, M.; Rossignol, P.; Ortiz, A.; Covic, A.; Afsar, B. Effect of Coffee Consumption on Renal Outcome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. J. Ren. Nutr. 2021, 31, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herber-Gast, G.C.M.; Essen, H.V.; Verschuren, W.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.; Spijkerman, A.M. Coffee and tea consumption in relation to estimated glomerular filtration rate: Results from the population-based longitudinal Doetinchem Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, N.; Shikata, K.; Makino, H.; Numata, T. Relationship between estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and metabolic syndrome in Japanese. Acta Med. Okayama 2010, 64, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi, S.; Palatini, P.; El-Sohemy, A. CYP1A2 Genetic Variation, Coffee Intake, and Kidney Dysfunction. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2247868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, M.C.; Monda, K.L.; Yu, K.; Paynter, N.; Azzato, E.M.; Bennett, S.N.; Berndt, S.I.; Boerwinkle, E.; Chanock, S.; Chatterjee, N.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies Regions on 7p21 (AHR) and 15q24 (CYP1A2) As Determinants of Habitual Caffeine Consumption. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, M.C.; Kacprowski, T.; Menni, C.; Gustafsson, S.; Pivin, E.; Adamski, J.; Artati, A.; Eap, C.B.; Ehret, G.; Friedrich, N.; et al. Genome-wide association study of caffeine metabolites provides new insights to caffeine metabolism and dietary caffeine-consumption behavior. Human. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 5472–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Palmer, A.A.; de Wit, H. Genetics of caffeine consumption and responses to caffeine. Psychopharmacology 2010, 211, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanzick, K.J.; Li, Y.; Schlosser, P.; Gorski, M.; Wuttke, M.; Thomas, L.F.; Rasheed, H.; Rowan, B.X.; Graham, S.E.; Vanderweff, B.R.; et al. Discovery and prioritization of variants and genes for kidney function in >1.2 million individuals. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuttke, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Sieber, K.B.; Feitosa, M.F.; Gorski, M.; Tin, A.; Wang, L.; Chu, A.Y.; Hoppmann, A.; et al. A catalog of genetic loci associated with kidney function from analyses of a million individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teumer, A.; Li, Y.; Ghasemi, S.; Prins, B.P.; Wuttke, M.; Hermle, T.; Giri, A.; Sieber, K.B.; Qiu, C.; Kirsten, H.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analyses and fine-mapping elucidate pathways influencing albuminuria. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Tighiouart, H.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Feldman, H.I.; Greene, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Manzi, J.; Van Lente, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Estimating glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine and cystatin C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Woolf, B.; Gill, D. Appraisal of the causal effect of plasma caffeine on adiposity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease: Two sample mendelian randomisation study. BMJ Med. 2023, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, O.J.; Pirastu, N.; Poole, R.; Fallowfield, J.A.; Hayes, P.C.; Grzeszkowiak, E.J.; Taal, M.W.; Wilson, J.F.; Parkes, J.; Roderick, P.J. Coffee Consumption and Kidney Function: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.; Hwang, S.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, S.W.; Oh, K.H.; Ahn, C.; Kim, Y.H. The ratio of urinary sodium and potassium and chronic kidney disease progression. Medicine 2018, 97, e12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuarrie, E.P.; Traynor, J.P.; Taylor, A.H.; Freel, E.M.; Fox, J.G.; Jardine, A.G.; Mark, P.B. Association between urinary sodium, creatinine, albumin, and long-term survival in chronic kidney disease. Hypertension 2014, 64, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, M.; Nakayama, M.; Sakoh, T.; Yoshitomi, R.; Fukui, A.; Katafuchi, E.; Tsuda, S.; Nakano, T.; Tsuruya, K.; Kitazono, T. Blood urea nitrogen is independently associated with renal outcomes in Japanese patients with stage 3–5 chronic kidney disease: A prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, B.; Scuvée, É.; Scuvée-Moreau, J.; Seutin, V.; Jouret, F. Mechanisms of caffeine-induced diuresis. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Josse, A.R.; Da Costa, L.A.; Campos, H.; El-Sohemy, A. Associations between polymorphisms in the AHR and CYP1A1-CYP1A2 gene regions and habitual caffeine consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Exposure | Effect Allele | Other Allele | Beta | SE | p-Value | Gene | EAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma caffeine | |||||||
| rs4410790 | T | C | 0.109 | 0.015 | 1.80 × 10−10 | AHR | 0.36 |
| rs2472297 | C | T | 0.150 | 0.016 | 1.00 × 10−17 | CYP1A2 | 0.73 |
| Caffeine intake | |||||||
| rs4410790 | C | T | 0.150 | 0.017 | 2.36 × 10−19 | AHR | 0.38 |
| rs2470893 | T | C | 0.120 | 0.016 | 5.15 × 10−14 | CYP1A2 | 0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giontella, A.; de La Harpe, R.; Cronje, H.T.; Zagkos, L.; Woolf, B.; Larsson, S.C.; Gill, D. Caffeine Intake, Plasma Caffeine Level, and Kidney Function: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204422
Giontella A, de La Harpe R, Cronje HT, Zagkos L, Woolf B, Larsson SC, Gill D. Caffeine Intake, Plasma Caffeine Level, and Kidney Function: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204422
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiontella, Alice, Roxane de La Harpe, Héléne T. Cronje, Loukas Zagkos, Benjamin Woolf, Susanna C. Larsson, and Dipender Gill. 2023. "Caffeine Intake, Plasma Caffeine Level, and Kidney Function: A Mendelian Randomization Study" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204422
APA StyleGiontella, A., de La Harpe, R., Cronje, H. T., Zagkos, L., Woolf, B., Larsson, S. C., & Gill, D. (2023). Caffeine Intake, Plasma Caffeine Level, and Kidney Function: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients, 15(20), 4422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204422







