The Nephroprotective Effect of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) and Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) in Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity on Wistar Rats with Emphasis on the Evaluation of Novel Renal Biomarkers and the Antioxidant Capacity in Correlation with Nitro-Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Collection of Plant Components and Arrangement of Fruit Samples
2.3. Preparation of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Extracts
2.4. Experimental Rodents
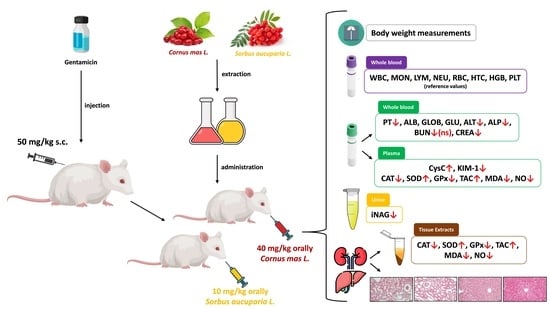
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Blood Analysis
2.6.1. Hematological Analysis
2.6.2. Biochemical Analysis
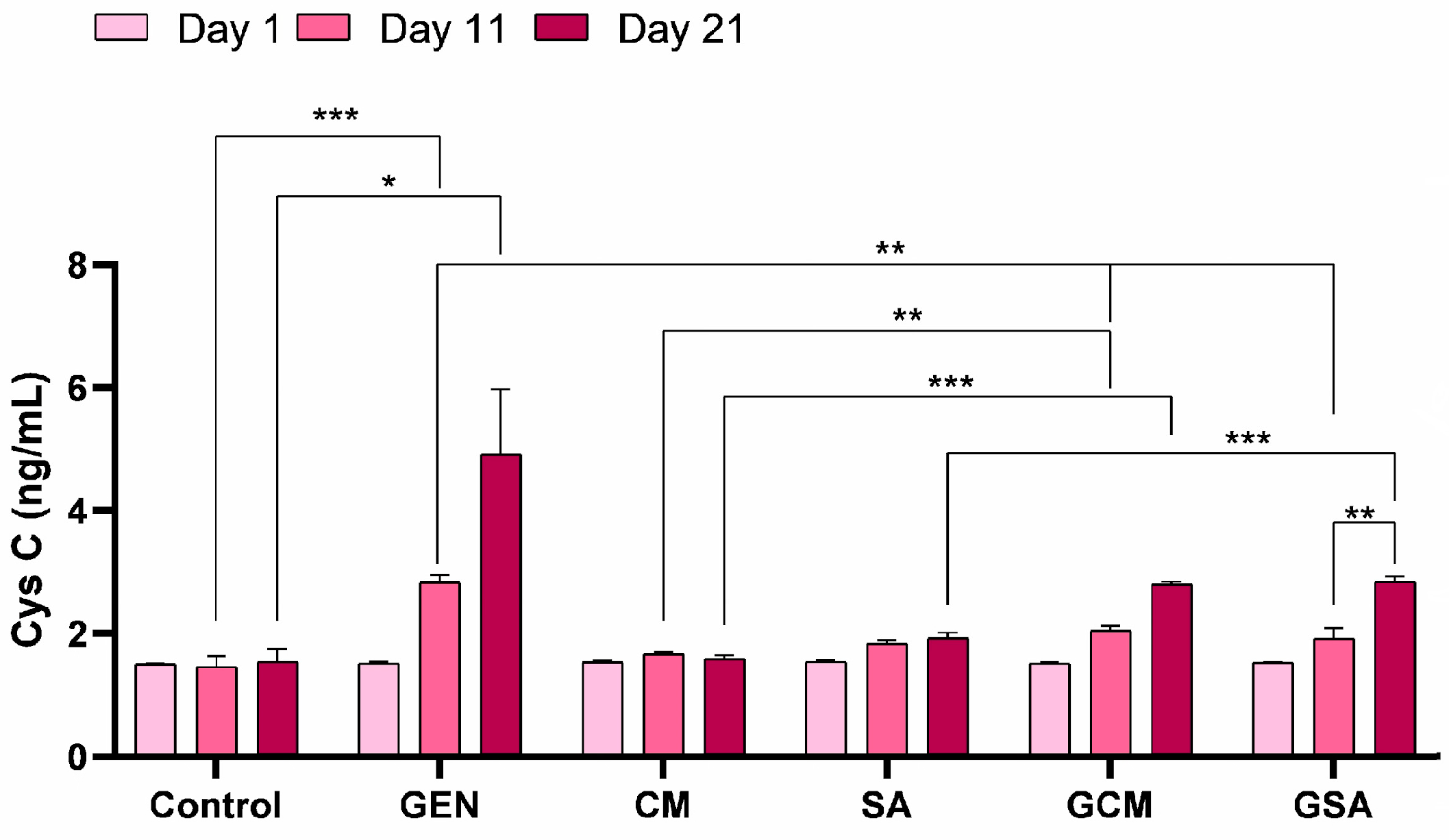
2.6.3. Rat Cystatin C (CysC) Activity Assay
2.6.4. Rat Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1) Activity Assay
2.6.5. Markers of Nitro-Oxidative Stress
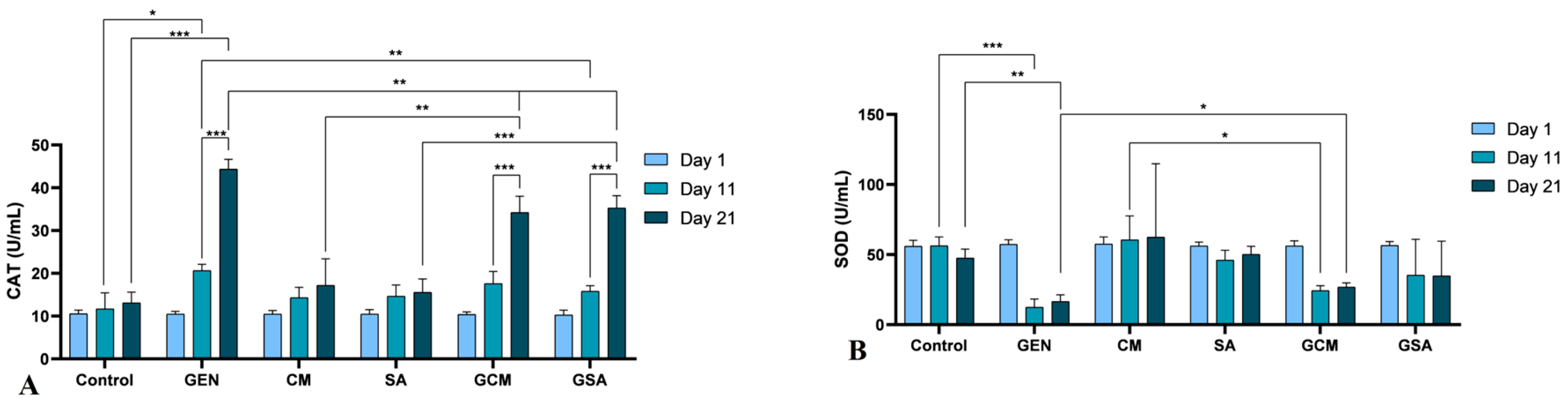
- Catalase (CAT) Activity Assay
- Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity Assay
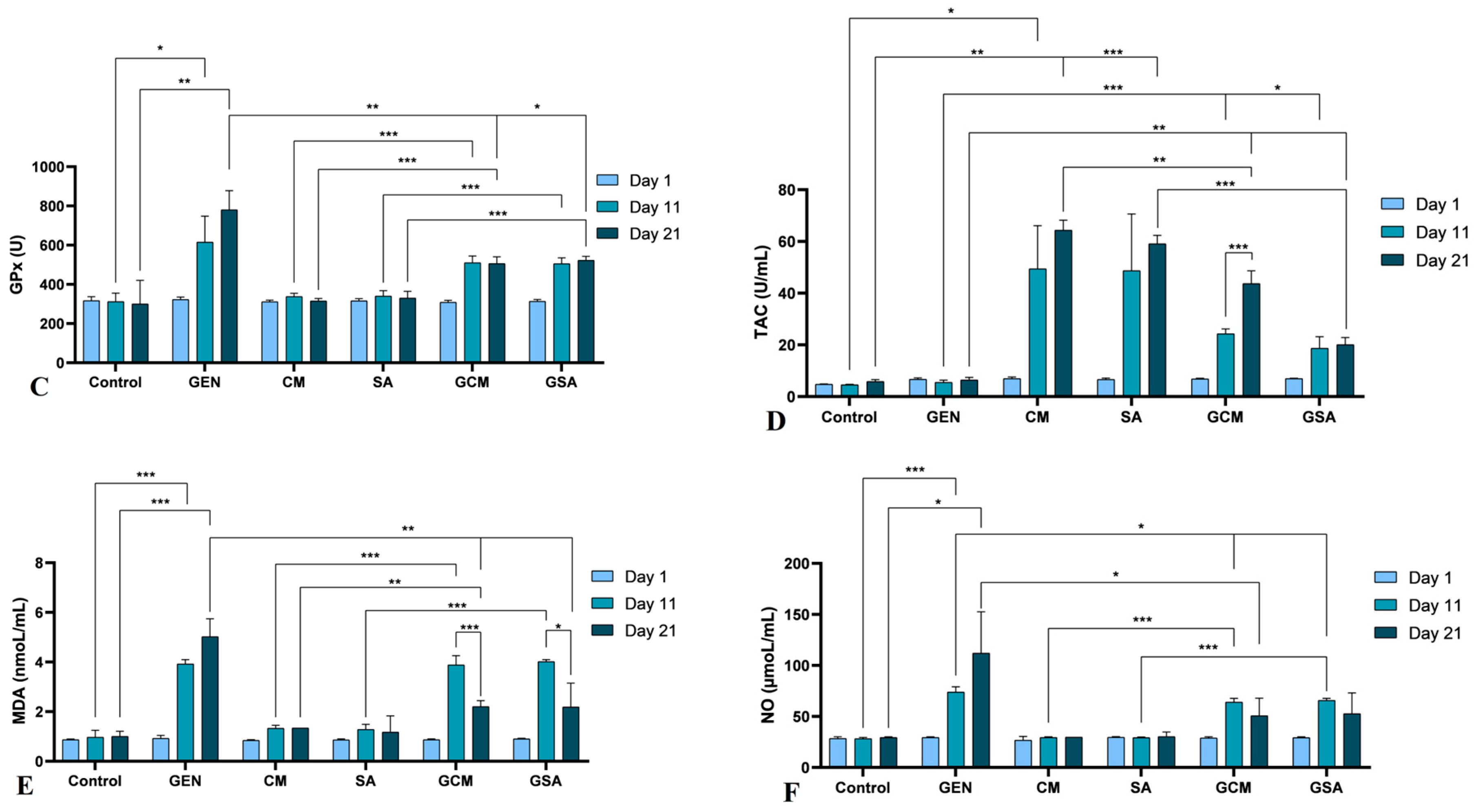
- Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) Activity Assay
- Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) Activity Assay
- Malondialdehyde (MDA) Activity Assay
- Nitric Oxide (NO) Activity Assay
2.7. Urine Analysis
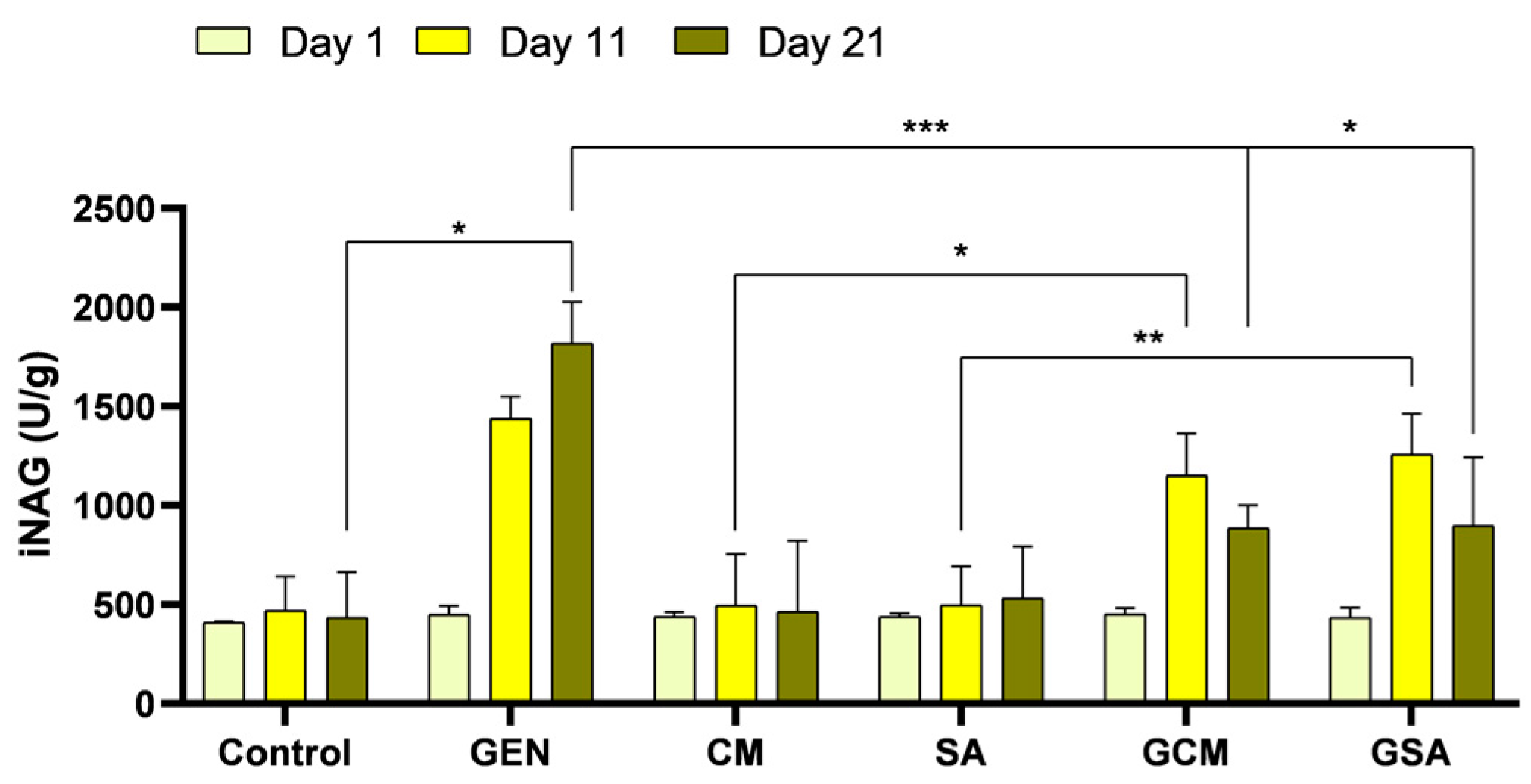
Urinary N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase Index (iNAG) Activity
2.8. Tissue Analysis
2.8.1. Preparation of Kidney and Liver Tissue Homogenates
2.8.2. Total Proteins
2.8.3. Markers of Nitro-Oxidative Stress
2.9. Histopathological Examination
- Renal tissue:
- Liver tissue:
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
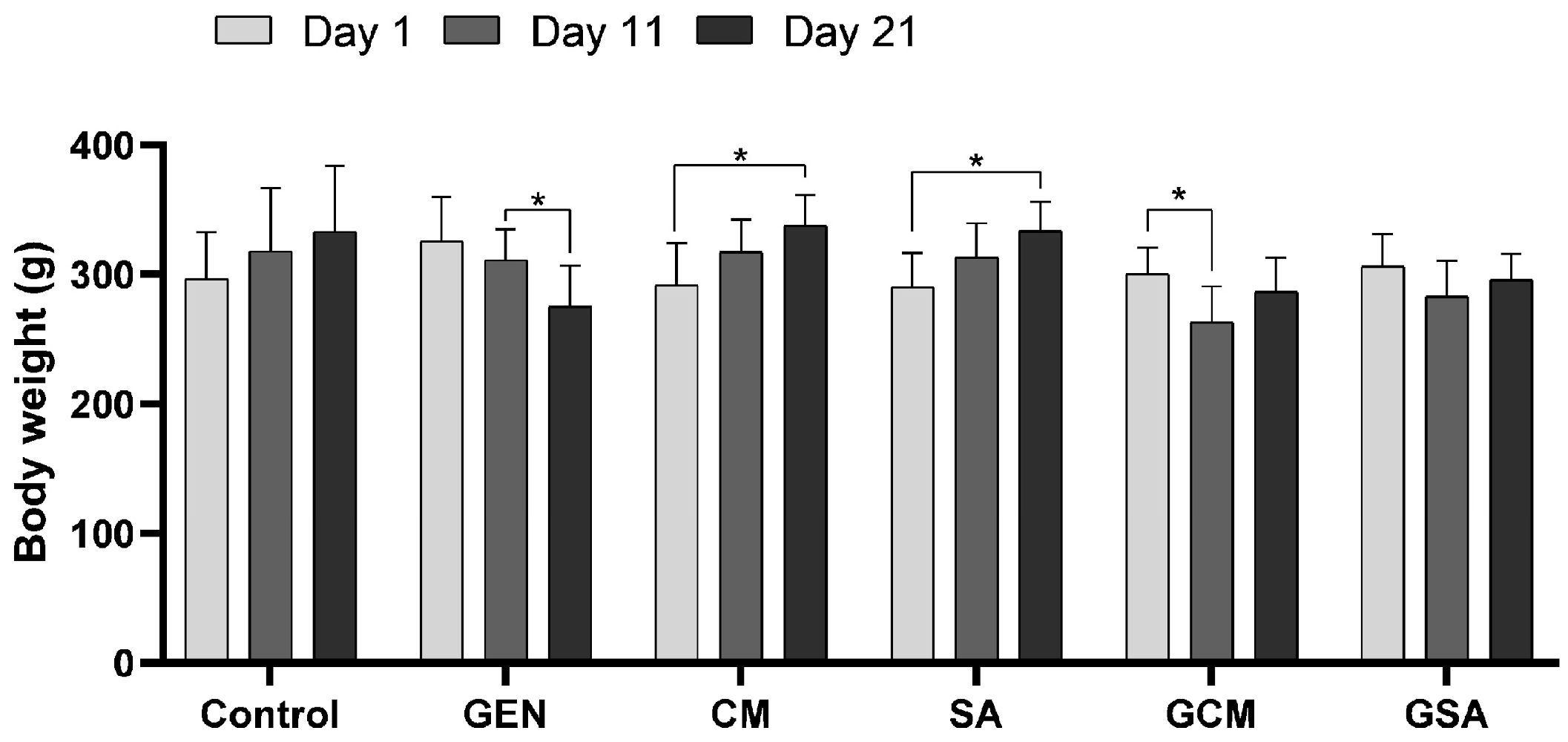
3.1. General Clinical Examination and Body Weight Monitoring
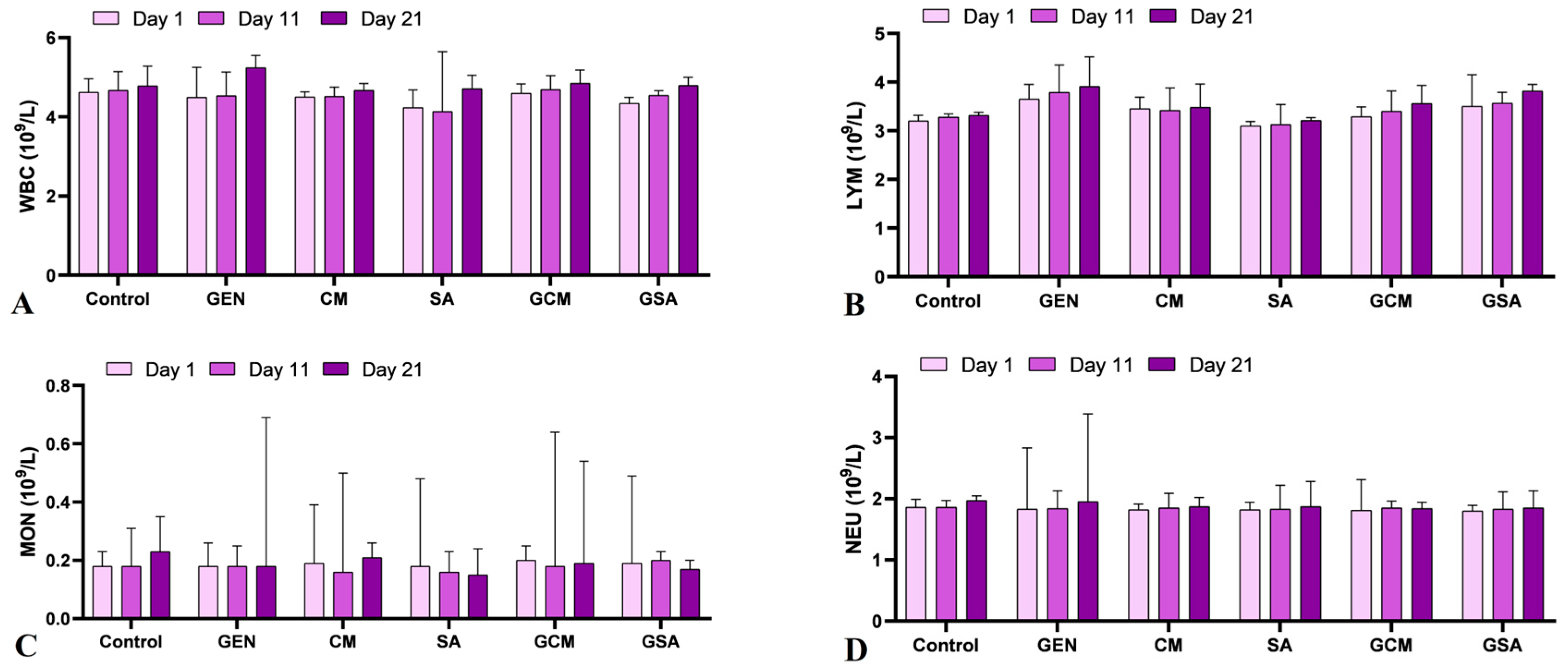
3.2. Hematological Profile
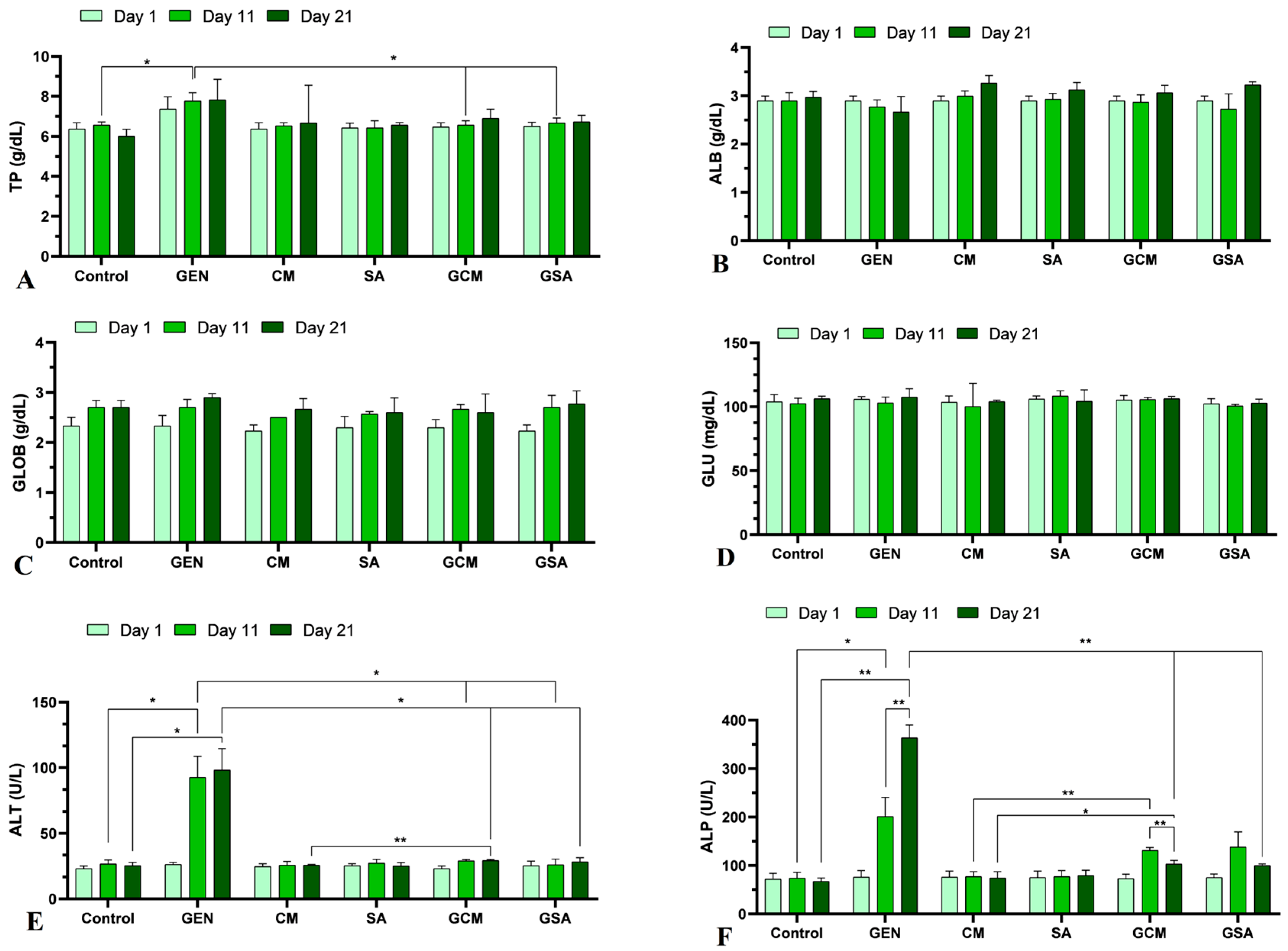
3.3. Biochemical Profile
3.4. Cystatin C (CysC) Activity Results
3.5. Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1) Activity Results
3.6. Urinary N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase Index (iNAG) Activity Results
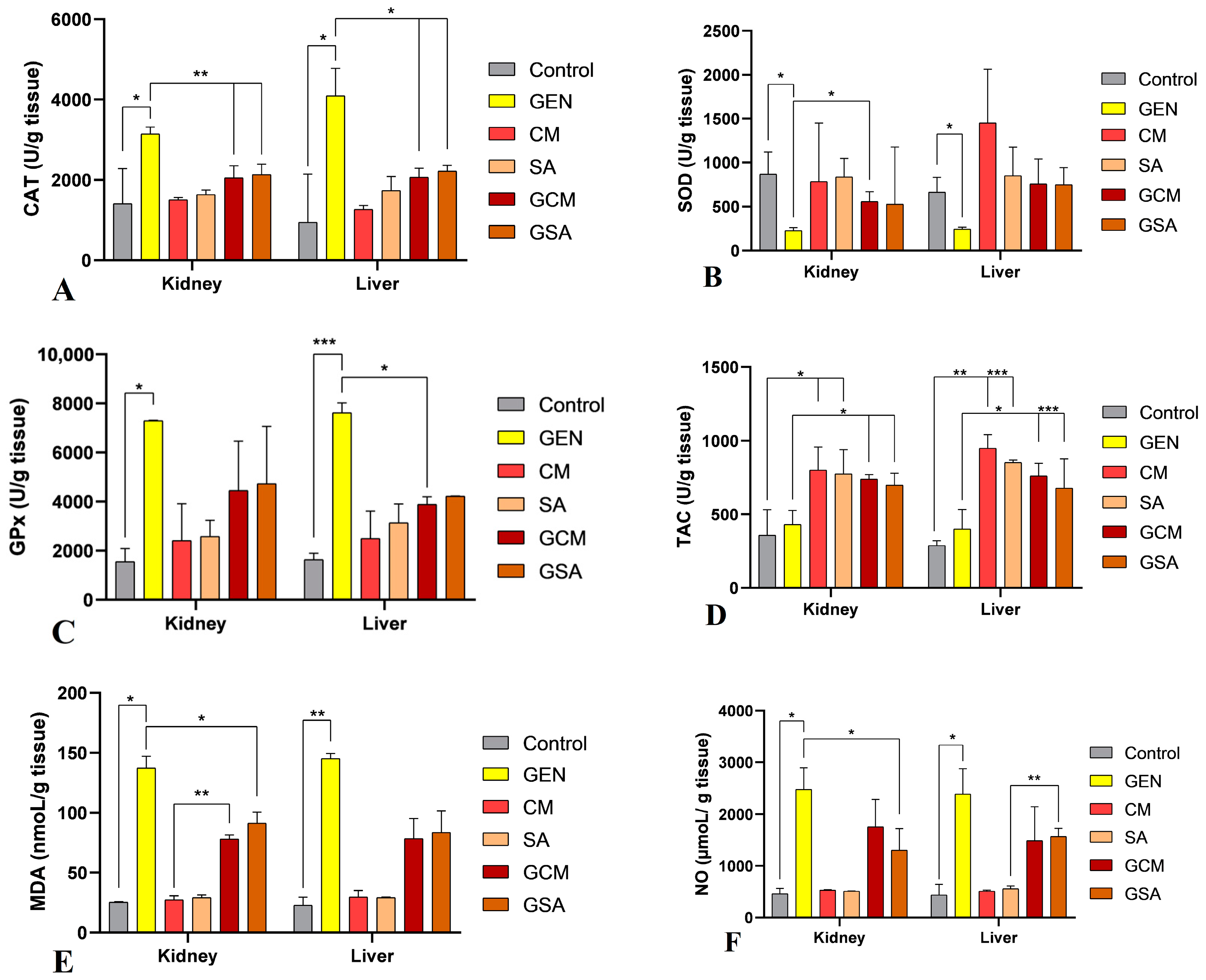
3.7. Nitro-Oxidative Stress Markers Activity Results
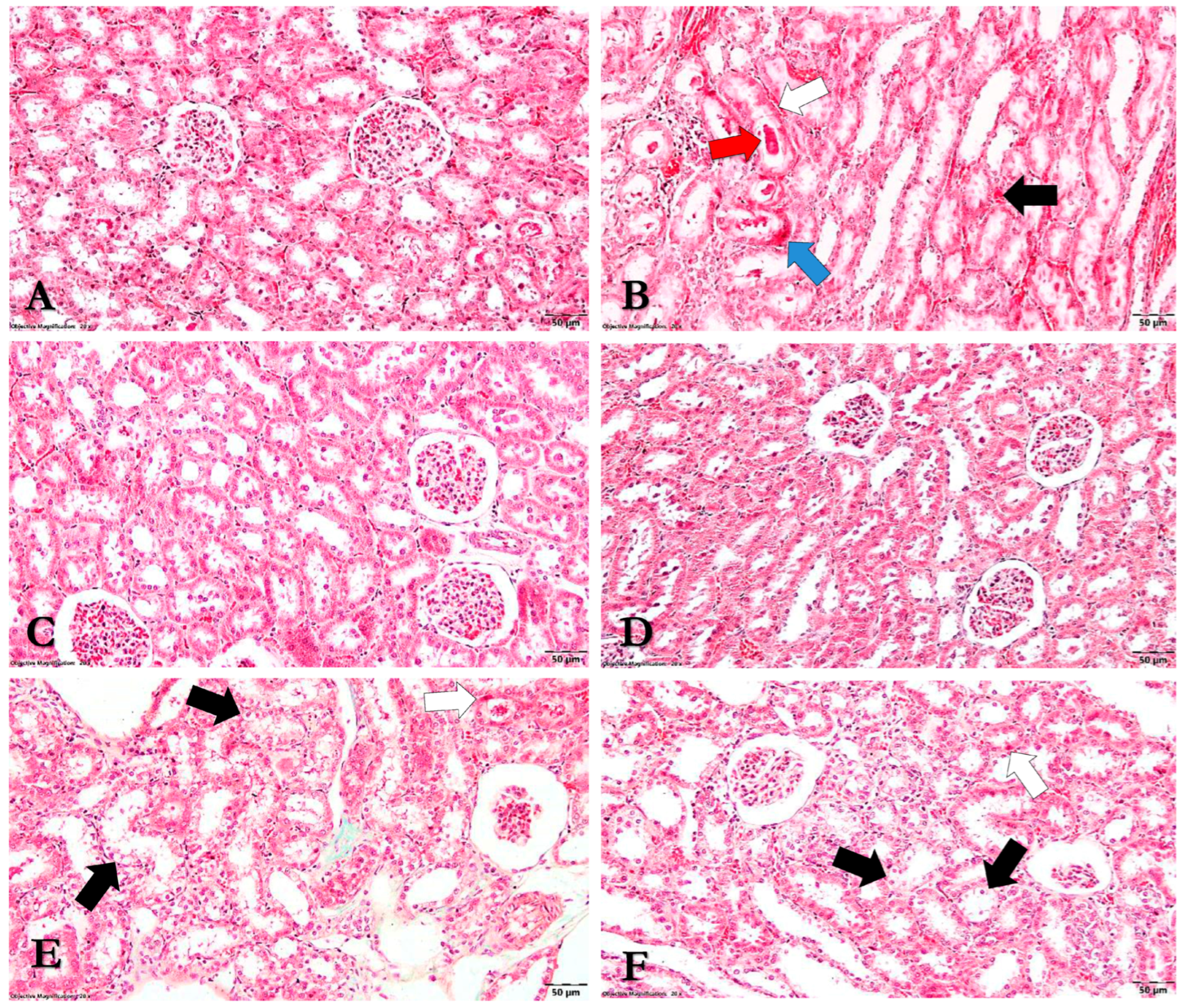
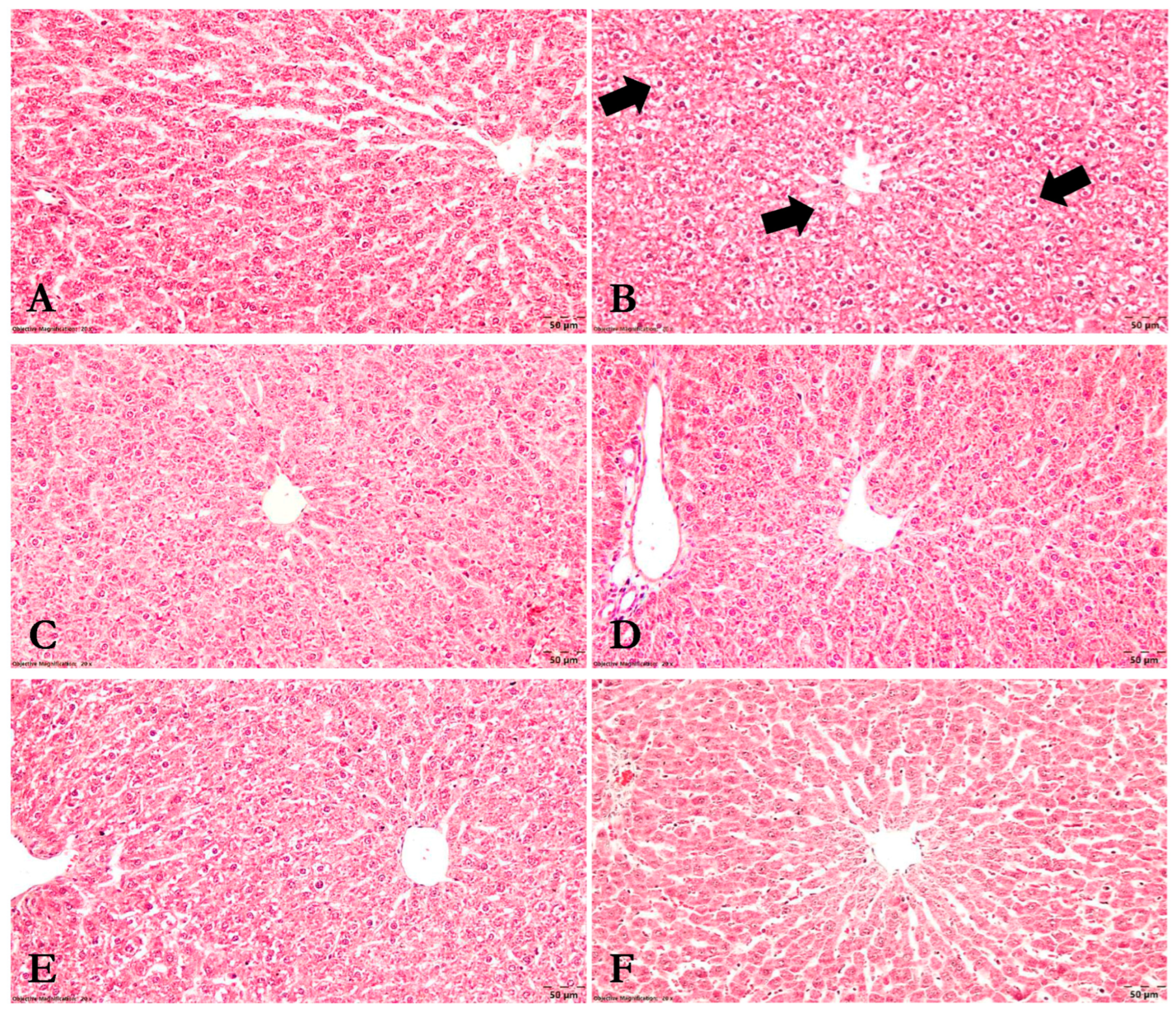
3.8. Histopathological Analysis
4. Discussions
4.1. The Effects of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts on Body Mass
4.2. The Effects of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts on Hematological Parameters
4.3. The Effects of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts on Total Proteins, Albumin, Globulins and Glucose
4.4. The Effects of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts on Liver Function
4.5. The Effects of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts on Renal Function
4.6. The Antioxidant Activity of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts
4.7. The Effects of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts on Nitro-Oxidative Markers
4.8. The Effects of Cornus mas L. and Sorbus aucuparia L. Extracts on Kidney and Liver Tissue
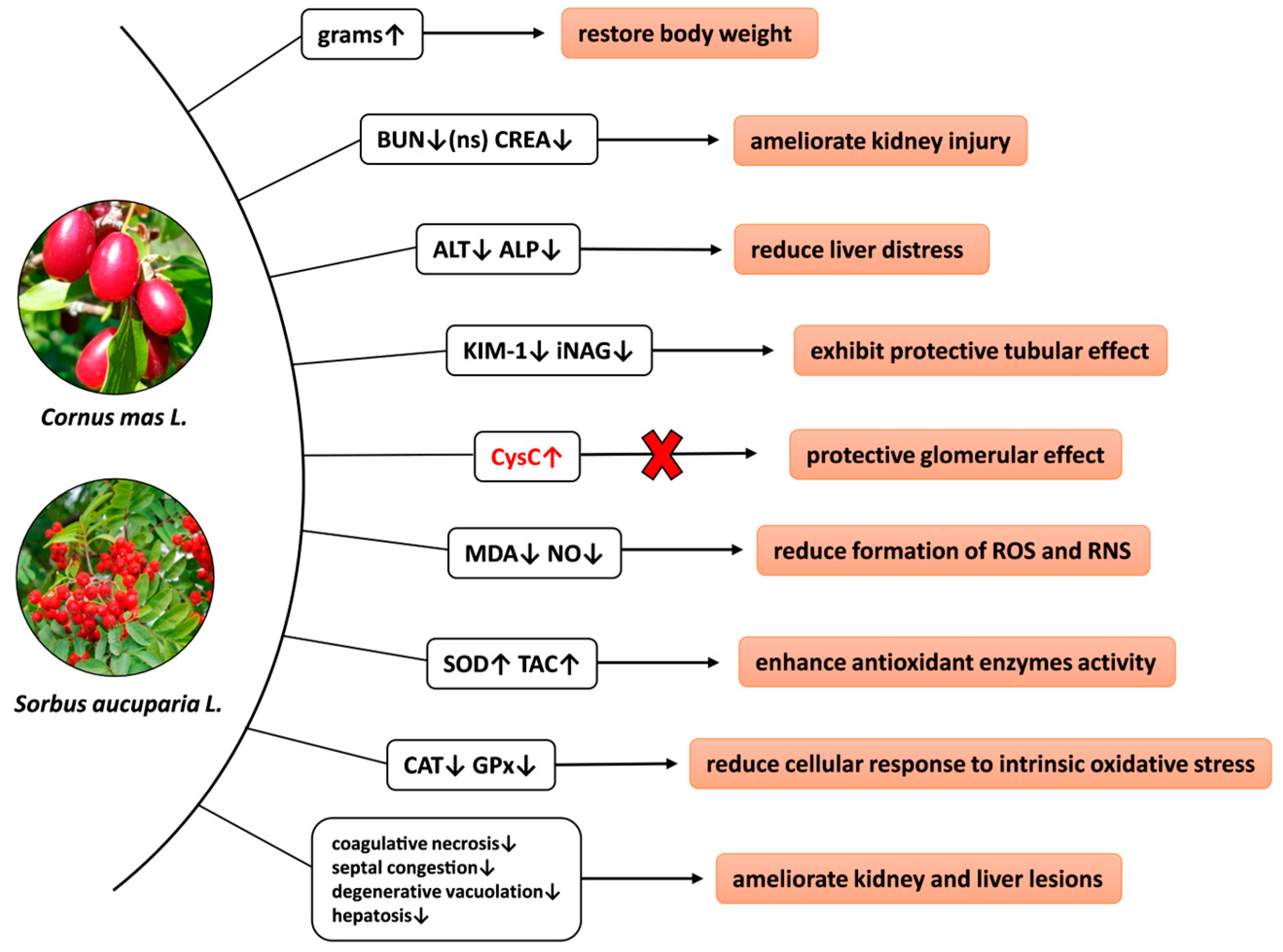
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwiatkowska, E.; Domański, L.; Dziedziejko, V.; Kajdy, A.; Stefańska, K.; Kwiatkowski, S. The Mechanism of Drug Nephrotoxicity and the Methods for Preventing Kidney Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gameiro, J.; Fonseca, J.A.; Outerelo, C.; Lopes, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury: From Diagnosis to Prevention and Treatment Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legatti, S.A.M.; El Dib, R.; Legatti, E.; Botan, A.G.; Camargo, S.E.A.; Agarwal, A.; Barretti, P.; Paes, A.C. Acute kidney injury in cats and dogs: A proportional meta-analysis of case series studies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.J.; Kellum, J.A.; Selby, N.M.; Zarbock, A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Goldstein, S.L.; Cerdá, J.; Chawla, L.S. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S.; Hossain, M.J.; Irfan, N.M.; Ahsan, T.; Arefin, M.S.; Rahman, A.; Alsubaie, A.; Alharthi, B.; Khandaker, M.U.; Bradley, D.A.; et al. Renoprotection of Selected Antioxidant-Rich Foods (Water Spinach and Red Grape) and Probiotics in Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Rats. Life 2022, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, H.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Chaar, M.; Lezeau, J.; Rump, A.; Taha, K.; Lesko, L.; Ait-Oudhia, S. A Review on Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity: Pathophysiological Mechanisms, Drug Classes, Clinical Management, and Recent Advances in Mathematical Modeling and Simulation Approaches. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, L.; Walker, D. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury. Companion Anim. 2015, 20, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petejova, N.; Martinek, A.; Zadrazil, J.; Kanova, M.; Klementa, V.; Sigutova, R.; Kacirova, I.; Hrabovsky, V.; Svagera, Z.; Stejskal, D. Acute Kidney Injury in Septic Patients Treated by Selected Nephrotoxic Antibiotic Agents—Pathophysiology and Biomarkers—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, P.; Rohilla, A.; Thangathirupathi, A. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: Do we have a promising therapeutic approach to blunt it? Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencheikh, N.; Bouhrim, M.; Kharchoufa, L.; Al Kamaly, O.M.; Mechchate, H.; Es-Safi, I.; Dahmani, A.; Ouahhoud, S.; El Assri, S.; Eto, B.; et al. The Nephroprotective Effect of Zizyphus lotus L. (Desf.) Fruits in a Gentamicin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model in Rats: A Biochemical and Histopathological Investigation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, Y.; Vicente-Vicente, L.; Morales, A.I.; López-Novoa, J.M.; López-Hernández, F.J. An Integrative Overview on the Mechanisms Underlying the Renal Tubular Cytotoxicity of Gentamicin. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 119, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randjelovic, P.; Veljkovic, S.; Stojiljkovic, N.; Sokolovic, D.; Ilic, I. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity in animals: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Excli J. 2017, 16, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, H.M.; Ozturkcan, S.A. Bioactive components and biological properties of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.): A comprehensive review. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiptiri-Kourpeti, A.; Fitsiou, E.; Spyridopoulou, K.; Vasileiadis, S.; Iliopoulos, C.; Galanis, A.; Vekiari, S.; Pappa, A.; Chlichlia, K. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Properties of Cornus mas L. Fruit Juice. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinda, B.; Kyriakopoulos, A.M.; Dinda, S.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Velegraki, A.; Markopoulos, C.; Dinda, M. Cornus mas L. (cornelian cherry), an important European and Asian traditional food and medicine: Ethnomedicine, phytochemistry and pharmacology for its commercial utilization in drug industry. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 670–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour-Jaghdani, F.; Shomali, T.; Gholipour-Shahraki, S.; Rahimi-Madiseh, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Cornus mas: A review on traditional uses and pharmacological properties. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, O.M.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Kusek, W.; Przeor, M. Functional properties of Cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.): A comprehensive review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2071–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenuta, M.C.; Deguin, B.; Loizzo, M.R.; Cuyamendous, C.; Bonesi, M.; Sicari, V.; Trabalzini, L.; Mitaine-Offer, A.-C.; Xiao, J.; Tundis, R. An Overview of Traditional Uses, Phytochemical Compositions and Biological Activities of Edible Fruits of European and Asian Cornus Species. Foods 2022, 11, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzydzan, O.; Brodyak, I.; Strugała-Danak, P.; Strach, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Gabrielska, J.; Sybirna, N. Biological Activity of Extracts of Red and Yellow Fruits of Cornus mas L.—An In Vitro Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity, Inhibitory Activity against α-Glucosidase, Acetylcholinesterase, and Binding Capacity to Human Serum Albumin. Molecules 2022, 27, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolak, H.; Czyzowska, A.; Sakač, M.; Mišan, A.; Đuragić, O.; Kregiel, D. Phenolic Compounds Contained in Little-known Wild Fruits as Antiadhesive Agents Against the Beverage-Spoiling Bacteria Asaia spp. Molecules 2017, 22, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmulescu, S.N.; Trandafir, I.; Cornescu, F. Antioxidant Capacity, Total Phenols, Total Flavonoids and Colour Component of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) Wild Genotypes. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2018, 47, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, S.; Göçmen, A.Y.; Karataş, E.; Tokpınar, A. Cornus mas L improves Antioxidant Status in the Liver, Lung, Kidney, Testis and Brain of Ehrlich Ascites Tumor Bearing Mice. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 2531–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.M.; Hassanalilou, T.; Khordadmehr, M.; Vardin, A.M.; Kohlan, A.B.; Khalili, L. Effects of Cornus mas Fruit Hydro-Methanolic Extract on Liver Antioxidants and Histopathologic Changes Induced by Cisplatin in Rats. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 35, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzydzan, O.; Bila, I.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Brodyak, I.; Sybirna, N. Antidiabetic effects of extracts of red and yellow fruits of cornelian cherries (Cornus mas L.) on rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6459–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobinaitė, R.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J.; Šarkinas, A.; Liaudanskas, M.; Žvikas, V.; Viškelis, P.; Venskutonis, P.R. Chemical composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities of the extracts isolated from the pomace of rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Olszewska, M.A. The Effects of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Extracts on Oxidative/Nitrative Modifications of Human Fibrinogen, Impact on Enzymatic Properties of Thrombin, and Hyaluronidase Activity In Vitro. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, E.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Patras, A.; Socaciu, C.; Pintea, A.; Tudor, C.; Sturza, R. The Influence of Temperature, Storage Conditions, pH, and Ionic Strength on the Antioxidant Activity and Color Parameters of Rowan Berry Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Owczarek, A.; Zakrzewska, A.; Magiera, A.; Olszewska, M.A. Novel insight into biological activity and phytochemical composition of Sorbus aucuparia L. fruits: Fractionated extracts as inhibitors of protein glycation and oxidative/nitrative damage of human plasma components. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarv, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Rätsep, R.; Aluvee, A.; Kazernavičiūtė, R.; Bhat, R. Antioxidants Characterization of the Fruit, Juice, and Pomace of Sweet Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Cultivated in Estonia. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurori, M.; Niculae, M.; Hanganu, D.; Pall, E.; Cenariu, M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Bunea, A.; Fiţ, N.; Andrei, S. Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytoprotective Effects of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) Fruit Extracts. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, L.H.; Cazarin, C.B.B.; Quatrin, A.; Minuzzi, N.M.; Nichelle, S.M.; Lamas, C.D.A.; Cagnon, V.H.A.; Morari, J.; Velloso, L.A.; Maróstica, M.R., Jr.; et al. Grape peel powder attenuates the inflammatory and oxidative response of experimental colitis in rats by modulating the NF-κB pathway and activity of antioxidant enzymes. Nutr. Res. 2020, 76, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laczkó-Zöld, E.; Szabó, D.; Fogarasi, E.; Tömösközi-Farkas, R.; Ştefănescu, R.; Varga, E.; Eşianu, S. Contribution to the Phytochemical Evaluation of Rowanberry Fruits (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Acta Medica Marisiensis 2018, 64, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitraş, D.-A.; Dreanca, A.I.; Pall, E.; Gal, A.F.; Rus, V.; Morohoschi, A.G.; Cotul, M.; Nan, M.I.; Andrei, S. Inhibition of Tumor Growth and Modulation of Antioxidant Activity of Rhodoxanthin Isolated from Taxus baccata Aril against B16F10 Murine Malignant Melanoma. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, F.; Li, C.; Pan, S. In vivo antioxidant activity of carotenoid powder from tomato byproduct and its use as a source of carotenoids for egg-laying hens. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.D.; Arunkumar, N.; Gokul, M. Potential Protective Role of Beta Carotene on Cadmium Induced Brain and Kidney Damage. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-6; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 2: Animal Welfare Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- AMVA Panel of Euthanasia. Amva Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Codea, A.R.; Mircean, M.; Sarpataki, O.; Sevastre, B.; Giurgiu, G.; Popovici, C.; Scurtu, I.; Neagu, D.; Oana, L. Urinary N-Acetyl-Beta-D-Glucosaminidase Index Activity Normal Values in Healthy Wistar Rats. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj-Napoca Vet. Med. 2018, 75, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelson, P.; Travacio, M.; Repetto, M.; Escobar, J.; Llesuy, S.; Lissi, E.A. Evaluation of Total Reactive Antioxidant Potential (TRAP) of Tissue Homogenates and Their Cytosols. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 388, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, C.T.E. An Accurate and Rapid Method for the Determination of Proteins in Small Amounts of Blood Serum and Plasma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1946, 16, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Delaney, C.A. Exotic Companion Medicine Handbook for Veterinarians; Wingers Publishing Incorporated: Lake Worth, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gumbar, S.; Bhardwaj, S.; Mehan, S.; Khan, Z.; Narula, A.S.; Kalfin, R.; Tabrez, S.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Wasi, S. Renal mitochondrial restoration by gymnemic acid in gentamicin-mediated experimental nephrotoxicity: Evidence from serum, kidney and histopathological alterations. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1218506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, F.; Yesmine, S.; Banu, S.G.; Chowdhury, I.A.; Hasan, R.; Chatterjee, T.K. Renoprotective effects of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni), amlodipine, valsartan, and losartan in gentamycin-induced nephrotoxicity in the rat model: Biochemical, hematological and histological approaches. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsamo, A.D.; Songmene, A.L.; Donfack, M.F.M.; Ngouateu, O.B.; Nguelefack, T.B.; Dimo, T. Aqueous Extract from Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Lauraceae) Stem Bark Ameliorates Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5543889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es Haghi, M.; Dehghan, G.; Banihabib, N.; Zare, S.; Mikaili, P.; Panahi, F. Protective effects of Cornus mas fruit extract on carbon tetrachloride induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Indian J. Nephrol. 2014, 24, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeenezhad, E.; Nouryazdan, N.; Nasri, M.; Ahmadvand, H.; Sarabi, M.M. Cinnamic acid ameliorate gentamicin-induced liver dysfunctions and nephrotoxicity in rats through induction of antioxidant activities. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardin, A.M.; Khordadmehr, M.; Heidari, R.; Nouri, H.-O.-L.; Amirkhiz, M.B.; Abbasi, M.M. The Effects of Cornus mas Hydro-Methanolic Extract on Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 24, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeogu, C.O.; Kalu, M.E.; Famurewa, A.C.; Asogwa, N.T.; Onyeji, G.N.; Ikpemo, K.O. Nephroprotective Effect of Moringa Oleifera Seed Oil on Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats: Biochemical Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, and Antiapoptotic Pathways. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.C.; Potok, O.A.; Rifkin, D.; Estrella, M.M. Advantages, Limitations, and Clinical Considerations in Using Cystatin C to Estimate GFR. Kidney360 2022, 3, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmgren, L.; Öberg, C.; den Bakker, E.; Leion, F.; Siódmiak, J.; Åkesson, A.; Lindström, V.; Herou, E.; Dardashti, A.; Xhakollari, L.; et al. The complexity of kidney disease and diagnosing it—Cystatin C, selective glomerular hypofiltration syndromes and proteome regulation. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 293, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.L.I.I.; Al-Naimi, M.S.S. Pomegranate attenuates acute gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats: The potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Pomegranate 2019, 12, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, R.S.E.; El-Beih, N.M.; Zaahkouk, S.A.; El-Hussieny, E.A. Ameliorative Effect of Eruca sativa seeds and its rutin on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in male rats via targeting inflammatory status, oxidative stress and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1)/cystatin c expression. Indones. Biomed. J. 2022, 14, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Mitra, P.; Roy, S. Proficient Novel Biomarkers Guide Early Detection of Acute Kidney Injury: A Review. Diseases 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brilland, B.; Boud’hors, C.; Wacrenier, S.; Blanchard, S.; Cayon, J.; Blanchet, O.; Piccoli, G.B.; Henry, N.; Djema, A.; Coindre, J.-P.; et al. Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1): A potential biomarker of acute kidney injury and tubulointerstitial injury in patients with ANCA-glomerulonephritis. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galal, H.M.; Abd el-Rady, N.M. Aqueous garlic extract supresses experimental gentamicin induced renal pathophysiology mediated by oxidative stress, inflammation and Kim-1. Pathophysiology 2019, 26, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.N.; Jung, J.Y.; Hwang, S.; Park, J.W.; Kim, D.; Kwak, Y.H.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, E.J. Role of the urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase/creatinine (NAG/Cr) ratio in discriminating between true and false pyuria in sterile urine bag specimens. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2021, 17, 442.e441–442.e447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.I.; Fujioka, Y.; Tsujino, T.; Ishida, T.; Hirata, K.I. Association between urinary N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase activity–urinary creatinine concentration ratio and risk of disability and all-cause mortality. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codea, A.R.; Mircean, M.; Nagy, A.; Sarpataky, O.; Sevastre, B.; Stan, R.L.; Hangan, A.C.; Popovici, C.; Neagu, D.; Purdoiu, R.; et al. Melatonine and Erythropoietin Prevents Gentamicin Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Farmacia 2019, 67, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, R.; Zaharie, S.I.; Diaconu, M.; Damian, A.; Varut, M.C.; Aurori, M.; Tabaran, A.F.; Constantinescu, E.; Codea, A.R.; Caragea, D.C. Ginkgo biloba nephroprotective effects in animal models with vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity. Rev. Romana Med. Vet. 2021, 31, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, R.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, F. Protective effect of Cistanche deserticola on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard, D.F.; Ballo, M.; Soudre, A.; Tindano, B.; Bah, S.; Bayala, B. Effects of fruits of aqueous extract of Sarcocephalus latifolius b. on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 7, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomşa, A.M.; Răchişan, A.L.; Pandrea, S.L.; Benea, A.; Uifălean, A.; Toma, C.; Popa, R.; Pârvu, A.E.; Junie, L.M. Curcumin and Vitamin C Attenuate Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Modulating Distinctive Reactive Species. Metabolites 2023, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavec, T.; Nemec-Svete, A.; Butinar, J.; Tozon, N.; Prezelj, M.; Kandel, B.; Kessler, M. Antioxidant status in canine cancer patients. Acta Vet. 2008, 58, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Christo, J.S.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Mouro, M.G.; Cenedeze, M.A.; de Jesus Simões, M.; Schor, N.; Higa, E.M.S. Nitric oxide (NO) is associated with gentamicin (GENTA) nephrotoxicity and the renal function recovery after suspension of GENTA treatment in rats. Nitric Oxide 2011, 24, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; Manzano-Pech, L.; Rubio-Ruíz, M.E.; Soto, M.E.; Guarner-Lans, V. Nitrosative Stress and Its Association with Cardiometabolic Disorders. Molecules 2020, 25, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, C.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite: Biochemistry, pathophysiology and development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metin, T.O. Hepatoprotective effect of pycnogenol in gentamicin-induced liver injury in rats. Ann. Med. Res. 2023, 30, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Groups | Total Proteins (mg/g Tissue) | |
|---|---|---|
| Kidney | Liver | |
| Control | 27.15 ± 4.13 | 25.18 ± 3.63 |
| Gentamicin | 42.87 ± 23.19 | 78.84 ± 21.95 |
| Cornus mas L. | 22.57 ± 4.18 | 40.50 ± 20.67 |
| Sorbus aucuparia L. | 28.82 ± 4.29 | 38.66 ± 4.75 |
| Gentamicin + Cornus mas L. | 40.87 ± 17.03 | 59.53 ± 15.28 |
| Gentamicin + Sorbus aucuparia L. | 31.93 ± 8.58 | 44.22 ± 7.59 |
| Experimental Groups | Histopathological Score (HS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney | Liver | |||
| Mean ± S.D | Range | Mean ± S.D | Range | |
| Control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gentamicin | 3.5 ± 0.57 a | 3–4 | 3 e | 3 |
| Cornus mas L. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sorbus aucuparia L. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gentamicin + Cornus mas L. | 1.0 ± 1.0 b,c | 0–2 | 0 f | 0 |
| Gentamicin + Sorbus aucuparia L. | 0.66 ± 1.15 b,d | 0–2 | 0 f | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aurori, M.; Andrei, S.; Dreanca, A.I.; Morohoschi, A.G.; Cotul, M.; Niculae, M.; Nan, M.I.; Codea, A.R.; Gal, A.F. The Nephroprotective Effect of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) and Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) in Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity on Wistar Rats with Emphasis on the Evaluation of Novel Renal Biomarkers and the Antioxidant Capacity in Correlation with Nitro-Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204392
Aurori M, Andrei S, Dreanca AI, Morohoschi AG, Cotul M, Niculae M, Nan MI, Codea AR, Gal AF. The Nephroprotective Effect of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) and Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) in Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity on Wistar Rats with Emphasis on the Evaluation of Novel Renal Biomarkers and the Antioxidant Capacity in Correlation with Nitro-Oxidative Stress. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204392
Chicago/Turabian StyleAurori, Mara, Sanda Andrei, Alexandra Iulia Dreanca, Andreea Georgiana Morohoschi, Mihaela Cotul, Mihaela Niculae, Monica Irina Nan, Andrei Răzvan Codea, and Adrian Florin Gal. 2023. "The Nephroprotective Effect of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) and Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) in Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity on Wistar Rats with Emphasis on the Evaluation of Novel Renal Biomarkers and the Antioxidant Capacity in Correlation with Nitro-Oxidative Stress" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204392
APA StyleAurori, M., Andrei, S., Dreanca, A. I., Morohoschi, A. G., Cotul, M., Niculae, M., Nan, M. I., Codea, A. R., & Gal, A. F. (2023). The Nephroprotective Effect of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) and Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) in Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity on Wistar Rats with Emphasis on the Evaluation of Novel Renal Biomarkers and the Antioxidant Capacity in Correlation with Nitro-Oxidative Stress. Nutrients, 15(20), 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204392