Roles of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
1.2. ω-3 PUFAs
2. Comorbid Cognitive Impairment in COPD Patients
2.1. Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease
2.2. Parkinson’s Disease
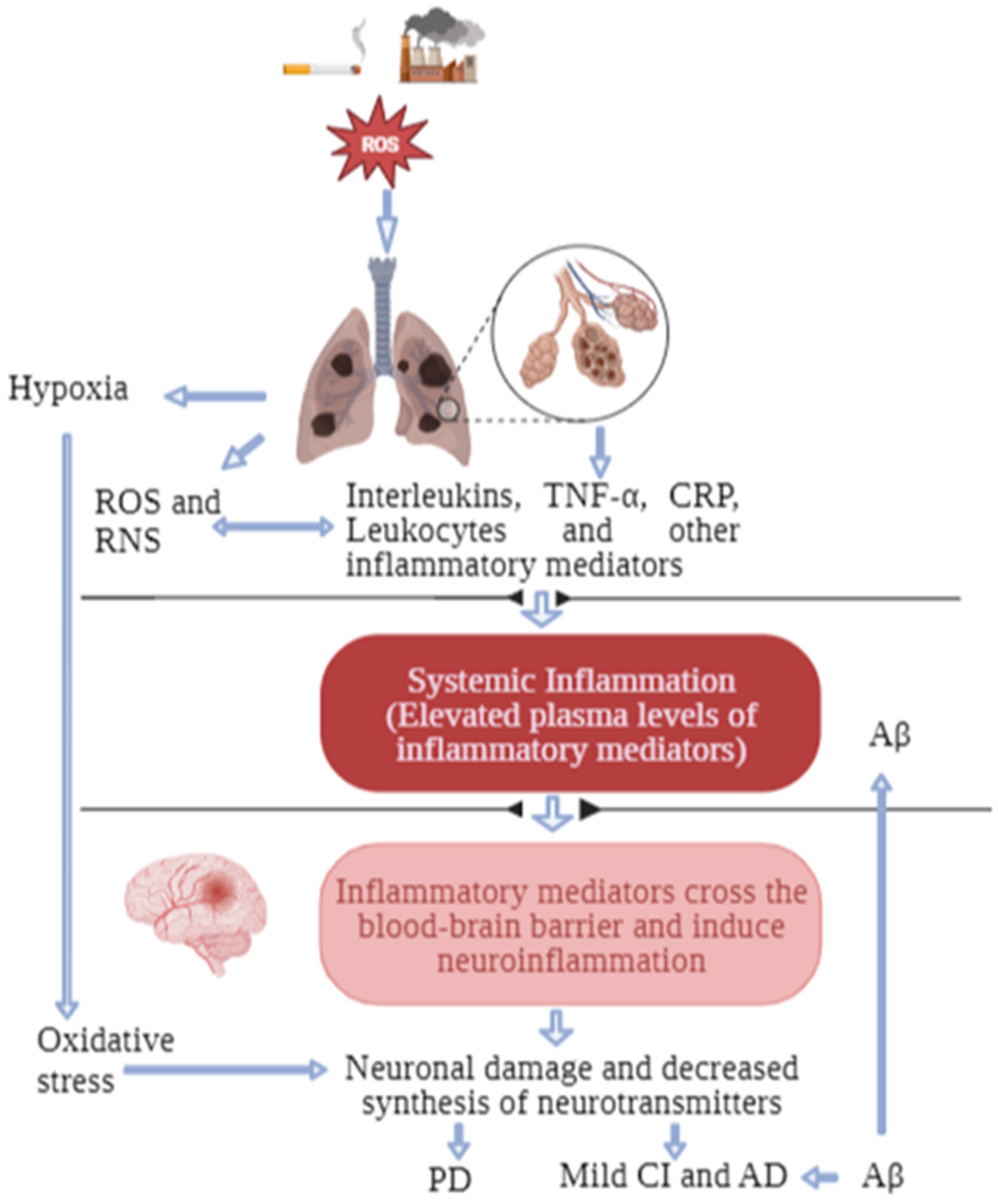
3. Possible Biological Links between COPD and Cognitive Impairment
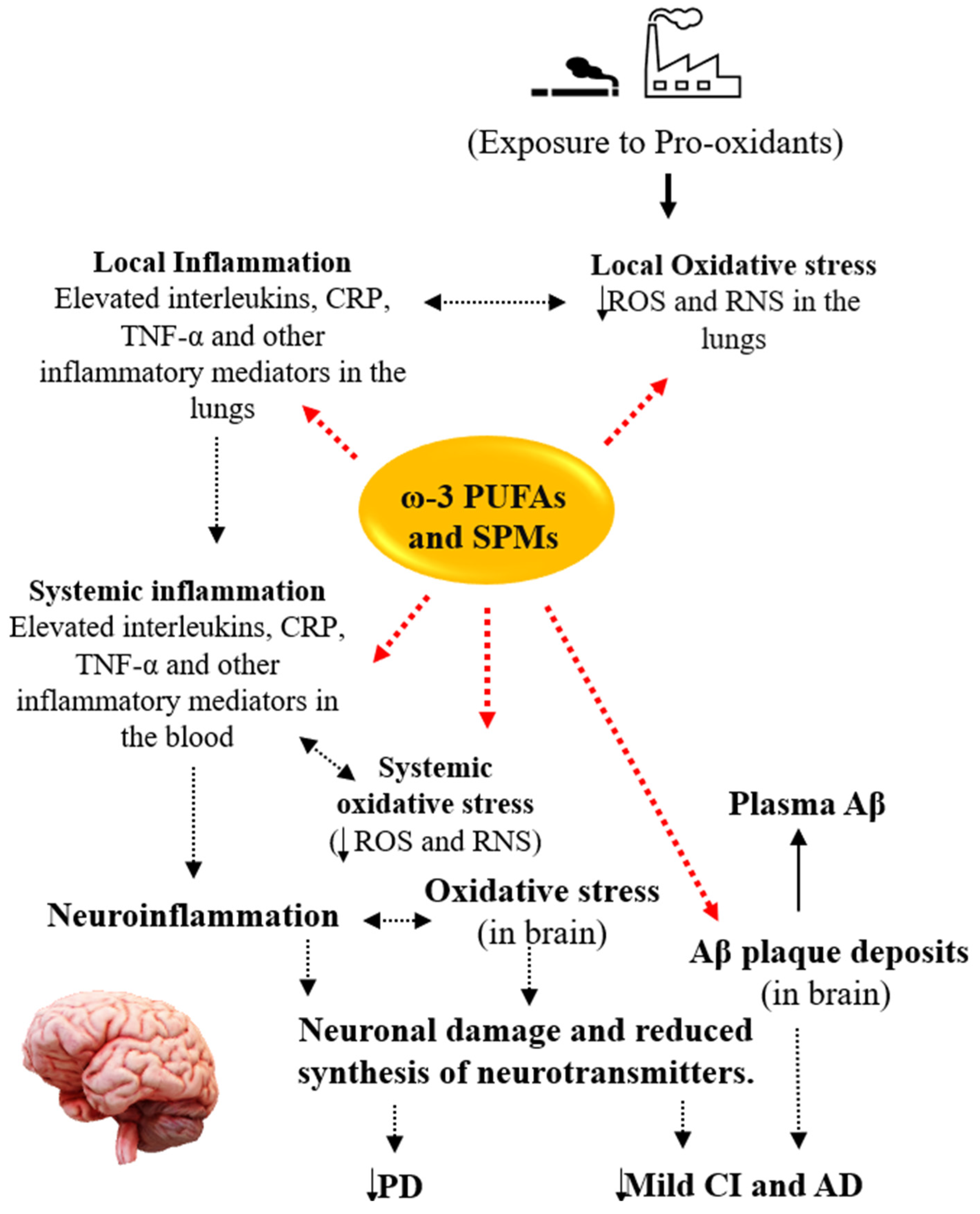
4. Potential Roles of ω-3 PUFAs in COPD and Comorbid Cognitive Impairment
4.1. Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease
4.2. Parkinson’s Disease
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid-beta |
| ALA | Alpha-linolenic acid |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CI | Cognitive impairment |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| HIF-1 | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 |
| HRQoL | Health-related quality of life |
| hs-CRP | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| L-DOPA | Levodopa |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MaR | Maresin |
| NF-kβ | Nuclear factor kappa-beta |
| Nrf-2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma |
| PR | Pulmonary rehabilitation |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RvD | Resolvin D |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| TSPO | Translocator protein |
| UPDRS | Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale |
| ω-3 PUFA | Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid |
References
- Christenson, S.A.; Smith, B.M.; Bafadhel, M.; Putcha, N. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2022, 399, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeloye, D.; Chua, S.; Lee, C.; Basquill, C.; Papana, A.; Theodoratou, E.; Nair, H.; Gasevic, D.; Sridhar, D.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global and regional estimates of COPD prevalence: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2015, 5, 020415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iheanacho, I.; Zhang, S.; King, D.; Rizzo, M.; Ismaila, A.S. Economic Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon Dis. 2020, 15, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeloye, D.; Song, P.; Zhu, Y.; Campbell, H.; Sheikh, A.; Rudan, I. Global, regional, and national prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2019: A systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattab, Y.; Alhassan, S.; Balaan, M.; Lega, M.; Singh, A.C. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2016, 39, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedzicha, J.A.; Seemungal, T.A. COPD exacerbations: Defining their cause and prevention. Lancet 2007, 370, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Liu, T.; Fan, H.; Chen, F.; Ding, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hou, S. Inflammatory Markers and the Risk of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.Q.; Man, S.F.; Senthilselvan, A.; Sin, D.D. Association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and systemic inflammation: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Thorax 2004, 59, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, H.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Liao, W.-C.; Liao, H.-F.; Huang, S.-Y.; Gałecki, P.; Su, K.-P.; Chang, J.P.-C. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Comorbid Mood Disorders in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2653. [Google Scholar]
- Pelgrim, C.E.; Peterson, J.D.; Gosker, H.R.; Schols, A.; van Helvoort, A.; Garssen, J.; Folkerts, G.; Kraneveld, A.D. Psychological co-morbidities in COPD: Targeting systemic inflammation, a benefit for both? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 842, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Koyama, Y.; Shimada, S. Inflammation From Peripheral Organs to the Brain: How Does Systemic Inflammation Cause Neuroinflammation? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 903455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.J.; Ditor, D.S. The common inflammatory etiology of depression and cognitive impairment: A therapeutic target. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.K. Hypoxia. 3. Hypoxia and neurotransmitter synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C743–C751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.; Nunes-Costa, D.; Cardoso, S.M.; Empadinhas, N.; Marugg, J.D. Enzyme Promiscuity in Serotonin Biosynthesis, From Bacteria to Plants and Humans. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 873555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Chen, S.; McAvay, G.J.; Tinetti, M.E. Effect of coexisting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cognitive impairment on health outcomes in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, C.; Lovell, J.; Johnson, M.; Shiell, K.; Ibrahim, J.E. The impact of cognitive impairment on self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review. Respir. Med. 2017, 129, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Lane, M.; Hockey, M.; Aslam, H.; Berk, M.; Walder, K.; Borsini, A.; Firth, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Berding, K.; et al. Diet and depression: Exploring the biological mechanisms of action. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.P.; Su, K.P. Nutrition and immunology in mental health: Precision medicine and integrative approaches to address unmet clinical needs in psychiatric treatments. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Chugh, V.; Gupta, A.K. Essential fatty acids as functional components of foods- a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2289–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Prasad, P.; Sreedhar, R.V.; Akhilender Naidu, K.; Shang, X.; Keum, Y.S. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs): Emerging Plant and Microbial Sources, Oxidative Stability, Bioavailability, and Health Benefits—A Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Wu, J.H. Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2047–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbeln, J.R. Fish consumption and major depression. Lancet 1998, 351, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.P.; Matsuoka, Y.; Pae, C.U. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Prevention of Mood and Anxiety Disorders. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2015, 13, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avallone, R.; Vitale, G.; Bertolotti, M. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Neurodegenerative Diseases: New Evidence in Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.Z.; Li, L.; Dong, C.W.; Tan, C.C.; Xu, W. The Relationship of Omega-3 Fatty Acids with Dementia and Cognitive Decline: Evidence from Prospective Cohort Studies of Supplementation, Dietary Intake, and Blood Markers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 1096–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.W.; Chung, A.W.; van den Broek, M.D.; Barrick, T.R.; Charlton, R.A.; Jones, P.W. Brain structure and function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A multimodal cranial magnetic resonance imaging study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Yohannes, A.M.; Chen, W.; Moga, A.M.; Leroi, I.; Connolly, M.J. Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Chronic Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Observational Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, e451.e1–e451.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Shi, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, A.; Guo, J.; Fang, Y. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Risk Factor for Cognitive Dysfunction: A Meta-Analysis of Current Studies. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 52, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siraj, R.A.; McKeever, T.M.; Gibson, J.E.; Gordon, A.L.; Bolton, C.E. Risk of incident dementia and cognitive impairment in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A large UK population-based study. Respir. Med. 2021, 177, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, S.; Pepin, V.; Rahayel, S.; Bertrand, J.A.; de Lorimier, M.; Rizk, A.; Desjardins, C.; Parenteau, S.; Beaucage, F.; Joncas, S.; et al. Mild cognitive impairment in moderate to severe COPD: A preliminary study. Chest 2012, 142, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carolis, A.; Giubilei, F.; Caselli, G.; Casolla, B.; Cavallari, M.; Vanacore, N.; Leonori, R.; Scrocchia, I.; Fersini, A.; Quercia, A.; et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is associated with altered neuropsychological performance in young adults. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2011, 1, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.M.; Ho, C.H.; Ko, S.C.; Li, C.Y. Increased Risk of Dementia in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Medicine 2015, 94, e930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.C.; Lin, C.L.; Chang, S.N.; Tu, C.Y.; Kao, C.H. The association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and dementia: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.J.; Wei, Y.F.; Lin, C.L.; Hsu, W.H. Effect of the asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease syndrome on the stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia: A national cohort study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12418–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanen, M.; Ngandu, T.; Laatikainen, T.; Tuomilehto, J.; Soininen, H.; Kivipelto, M. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma and the risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia: A population based CAIDE study. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2013, 10, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleutjens, F.; Spruit, M.A.; Ponds, R.; Vanfleteren, L.; Franssen, F.M.E.; Dijkstra, J.B.; Gijsen, C.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Janssen, D.J.A. The Impact of Cognitive Impairment on Efficacy of Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Patients With COPD. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindbergh, C.A.; Dishman, R.K.; Miller, L.S. Functional Disability in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2016, 26, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, O.; Turan, P.A.; Mirici, A. Parameters affecting inhalation therapy adherence in elderly patients with chronic obstructive lung disease and asthma. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.M.; Lin, T.C.; Li, C.Y.; Yang, Y.K. Dementia Increases Severe Sepsis and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Medicine 2015, 94, e967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-T.; Tsai, C.-L.; Lin, C.W.; Yeh, C.-B.; Wang, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-L. Association Between Antipsychotic Agents and Risk of Acute Respiratory Failure in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Chen, W.C.; Liao, W.C.; Tu, C.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, C.H.; Hsu, W.H. The association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. QJM Int. J. Med. 2015, 108, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.A.; Schrag, A. Psychosis, apathy, depression and anxiety in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihmer, Z.; Gonda, X.; Döme, P. Depression in Parkinson’s disease. Ideggyogy. Sz. 2014, 67, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yohannes, A.M.; Alexopoulos, G.S. Pharmacological treatment of depression in older patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Impact on the course of the disease and health outcomes. Drugs Aging 2014, 31, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coventry, P.A.; Gemmell, I.; Todd, C.J. Psychosocial risk factors for hospital readmission in COPD patients on early discharge services: A cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2011, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.P.; Niti, M.; Tan, W.C.; Cao, Z.; Ong, K.C.; Eng, P. Depressive symptoms and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Effect on mortality, hospital readmission, symptom burden, functional status, and quality of life. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio Iglesias, J.; Díez-Manglano, J.; López García, F.; Díaz Peromingo, J.A.; Almagro, P.; Varela Aguilar, J.M. Management of the COPD Patient with Comorbidities: An Experts Recommendation Document. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon Dis. 2020, 15, 1015–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, T.B.; Barker, R.A. Recent developments in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. F1000Res 2020, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.; Souza-Machado, A.; Valderramas, S.; Melo, A. The Effect of Levodopa on Pulmonary Function in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, P.W.; Kang, K.; Lee, H.W. Levodopa-induced respiratory dysfunction confirmed by levodopa challenge test: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Huang, C.; Lin, Y.; Dai, Q. Change of Serum Inflammatory Cytokines Levels in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Pneumonia and Lung Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820951807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNee, W. Systemic inflammatory biomarkers and co-morbidities of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Med. 2013, 45, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, S.; Ahmad, M.; Waseem, M.; Singh, S.; Nischal, A.; Dixit, R. Association between serum cytokine levels and severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Northern India. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2015, 18, 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, P.B. Role of inflammation in cognitive impairment: Results of observational epidemiological studies and clinical trials. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1207, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swardfager, W.; Lanctôt, K.; Rothenburg, L.; Wong, A.; Cappell, J.; Herrmann, N. A meta-analysis of cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Huang, X.; Li, F.; Ren, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M.; Wu, M. Association among plasma lactate, systemic inflammation, and mild cognitive impairment: A community-based study. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, M.T.; Euser, S.M.; De Craen, A.J.; Witteman, J.C.; Frölich, M.; Hofman, A.; Jolles, J.; Breteler, M.M.; Westendorp, R.G. Systemic markers of inflammation and cognitive decline in old age. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 708–716. [Google Scholar]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Natteru, P.A.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Saeed, D.; Zahoor, H.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.S.; Zaheer, A. Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Crişan, A.F.; Oancea, C.; Timar, B.; Fira-Mladinescu, O.; Crişan, A.; Tudorache, V. Cognitive impairment in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102468. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.L.; Liu, C.H.; Fu, A.S.; Wang, H.Y. Correlation study between the levels of serum MCP-1,SAA and cognitive function in patients with COPD-OSAHS. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 32, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.L.; Cao, G.Q.; Shen, L.L.; Xiang, Y.; Jiao, S.S.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, C.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Q.H.; Wang, Y.R.; et al. Serum Amyloid-Beta Levels are Increased in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Neurotox. Res. 2015, 28, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood–brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Haar, H.J.; Burgmans, S.; Jansen, J.F.; van Osch, M.J.; van Buchem, M.A.; Muller, M.; Hofman, P.A.; Verhey, F.R.; Backes, W.H. Blood-Brain Barrier Leakage in Patients with Early Alzheimer Disease. Radiology 2016, 281, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Sajja, R.K.; Park, J.H.; Naik, P.; Kaisar, M.A.; Cucullo, L. Impact of cigarette smoke extract and hyperglycemic conditions on blood–brain barrier endothelial cells. Fluids Barriers CNS 2015, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Sathe, T.; Fazio, V.; Mazzone, P.; Weksler, B.; Janigro, D.; Rapp, E.; Cucullo, L. Tobacco smoke: A critical etiological factor for vascular impairment at the blood–brain barrier. Brain Res. 2009, 1287, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelgrim, C.E.; Wang, L.; Peralta Marzal, L.N.; Korver, S.; van Ark, I.; Leusink-Muis, T.; Braber, S.; Folkerts, G.; Garssen, J.; van Helvoort, A.; et al. Increased exploration and hyperlocomotion in a cigarette smoke and LPS-induced murine model of COPD: Linking pulmonary and systemic inflammation with the brain. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2022, 323, L251–L265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobric, A.; De Luca, S.N.; Spencer, S.J.; Bozinovski, S.; Saling, M.M.; McDonald, C.F.; Vlahos, R. Novel pharmacological strategies to treat cognitive dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostwoud, L.; Gunasinghe, P.; Seow, H.J.; Ye, J.; Selemidis, S.; Bozinovski, S.; Vlahos, R. Apocynin and ebselen reduce influenza A virus-induced lung inflammation in cigarette smoke-exposed mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20983. [Google Scholar]
- Strzelak, A.; Ratajczak, A.; Adamiec, A.; Feleszko, W. Tobacco Smoke Induces and Alters Immune Responses in the Lung Triggering Inflammation, Allergy, Asthma and Other Lung Diseases: A Mechanistic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Qin, C.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Blood-brain barrier disruption induced cognitive impairment is associated with increase of inflammatory cytokine. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Hussain, B.; Chang, J. Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: Effects and mechanisms. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Sabermarouf, B.; Majdi, A.; Talebi, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Mahmoudi, J. Amyloid-beta: A crucial factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, Q.; Yang, X.; Kang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Li, G.; Li, C.; et al. Association of Cigarette Smoking With Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidation. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2018777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.S.A.; Oliver, P.L. ROS Generation in Microglia: Understanding Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 743. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, F.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J. Microglia and Neuroinflammation: Crucial Pathological Mechanisms in Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 825086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochocka, N.; Kaminska, B. Microglia Diversity in Healthy and Diseased Brain: Insights from Single-Cell Omics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, C.; Mecca, C.; Bianchi, R.; Giambanco, I.; Donato, R. The Pathophysiological Role of Microglia in Dynamic Surveillance, Phagocytosis and Structural Remodeling of the Developing CNS. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wang, Y.; Stetler, A.R.; Leak, R.K.; Hu, X.; Chen, J. Phagocytic microglia and macrophages in brain injury and repair. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, L.; Viotti, A.; Martino, G. Microglia in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration: From Understanding to Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 742065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Pan, R.; Shang, C.; Li, X.; Cheng, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. Translocator Protein 18 kDa (TSPO) Deficiency Inhibits Microglial Activation and Impairs Mitochondrial Function. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradburn, S.; Murgatroyd, C.; Ray, N. Neuroinflammation in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y. Cerebrospinal Fluid Inflammatory Cytokine Aberrations in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, H.M.; Hong, J.S. Parkinson’s disease and exposure to infectious agents and pesticides and the occurrence of brain injuries: Role of neuroinflammation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeer, P.L.; McGeer, E.G. Inflammation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2004, 10, S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Mishra, M.K.; Das, S.; Kaushik, D.K.; Basu, A. Tobacco carcinogen induces microglial activation and subsequent neuronal damage. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Prasedya, E.; Ambana, Y.; Martyasari, N.; Aprizal, Y.M.; Nurrijawati; Sunarpi. Short-term E-cigarette toxicity effects on brain cognitive memory functions and inflammatory responses in mice. Toxicol. Res. 2020, 36, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Sivandzade, F.; Alqahtani, F.; Sifat, A.; Cucullo, L. The cerebrovascular and neurological impact of chronic smoking on post-traumatic brain injury outcome and recovery: An in vivo study. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Adeluyi, A.; Guerin, L.; Fisher, M.L.; Galloway, A.; Cole, R.D.; Chan, S.S.; Wyatt, M.D.; Davis, S.W.; Freeman, L.R.; Ortinski, P.I. Microglia morphology and proinflammatory signaling in the nucleus accumbens during nicotine withdrawal. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax7031. [Google Scholar]
- McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingappan, K. NF-κB in Oxidative Stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Fan, M.; Wang, X. Hypoxia promotes dopaminergic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and shows benefits for transplantation in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Rajagopalan, S.; Siddiq, A.; Gwiazda, R.; Yang, L.; Beal, M.F.; Ratan, R.R.; Andersen, J.K. Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase protects against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity: Model for the potential involvement of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway in Parkinson disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29065–29076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shachar, D.; Eshel, G.; Finberg, J.P.; Youdim, M.B. The iron chelator desferrioxamine (Desferal) retards 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, M.; Yamamura, S.; Akashi, K.; Charron, C.E.; Haruki, K.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. Defect of adaptation to hypoxia in patients with COPD due to reduction of histone deacetylase 7. Chest 2012, 141, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Blanc, P.D.; Julian, L.J.; Yelin, E.H.; Katz, P.P.; Sidney, S.; Iribarren, C.; Eisner, M.D. COPD and cognitive impairment: The role of hypoxemia and oxygen therapy. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2010, 5, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Karamanli, H.; Ilik, F.; Kayhan, F.; Pazarli, A.C. Assessment of cognitive impairment in long-term oxygen therapy-dependent COPD patients. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 10, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.P.; Sood, S.; Atreja, A.; Agarwal, D. A comparison of cognitive functions in non-hypoxemic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients and age-matched healthy volunteers using mini-mental state examination questionnaire and event-related potential, P300 analysis. Lung India 2013, 30, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Negro, R.W.; Bonadiman, L.; Bricolo, F.P.; Tognella, S.; Turco, P. Cognitive dysfunction in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with or without Long-Term Oxygen Therapy (LTOT). Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2015, 10, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Fei, G.-H. The unique alterations of hippocampus and cognitive impairment in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, A.I.R.M.C. A Cognitive impairment in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease–a neuropsychological and spect study. J. Neurol. 2003, 2503, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ortapamuk, H.; Naldoken, S. Brain perfusion abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Comparison with cognitive impairment. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2006, 20, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Díaz, C.; García-Orozco, A.; Riera-Leal, A.; Padilla-Arellano, J.R.; Fafutis-Morris, M. Microbiota and Its Role on Viral Evasion: Is It With Us or Against Us? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Influence of Foods and Nutrition on the Gut Microbiome and Implications for Intestinal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9588. [Google Scholar]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Chidambaram, S.B.; Essa, M.M.; Rathipriya, A.G.; Bishir, M.; Ray, B.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Tousif, A.H.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Kashyap, R.S.; Friedland, R.P.; et al. Gut dysbiosis, defective autophagy and altered immune responses in neurodegenerative diseases: Tales of a vicious cycle. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 231, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 399–412. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.L. Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 5026–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Reynolds, R.; Tan, E.K.; Pettersson, S. The role of gut dysbiosis in Parkinson’s disease: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic options. Brain 2021, 144, 2571–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Liu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Teng, Z.; Li, S.; Yuan, H.; Huang, J.; Xiang, H.; Tang, H.; Wang, B.; et al. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis and Cognitive Impairment in Bipolar Disorder: Current Evidence. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 893567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Dong, K.; Chen, Q.; Lou, X.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; et al. Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiota and Kynurenine (Kyn) Pathway Activity as Potential Biomarkers in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, Z.; Kivity, S.; Yonath, H.; Yehuda, S. Smoking and the intestinal microbiome. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Pu, J.; Cao, W.; Pan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowerman, K.L.; Rehman, S.F.; Vaughan, A.; Lachner, N.; Budden, K.F.; Kim, R.Y.; Wood, D.L.A.; Gellatly, S.L.; Shukla, S.D.; Wood, L.G.; et al. Disease-associated gut microbiome and metabolome changes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.P. Mind-body interface: The role of n-3 fatty acids in psychoneuroimmunology, somatic presentation, and medical illness comorbidity of depression. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S1), 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Pei-Chen Chang, J. Personalised medicine in child and Adolescent Psychiatry: Focus on omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and ADHD. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 16, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Su, K.P.; Lu, M.L.; Huang, M.C.; Chen, C.C.; Shen, W.W. Polyunsaturated fatty acid deficit in patients with bipolar mania. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2003, 13, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conquer, J.A.; Tierney, M.C.; Zecevic, J.; Bettger, W.J.; Fisher, R.H. Fatty acid analysis of blood plasma of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, other types of dementia, and cognitive impairment. Lipids 2000, 35, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.Y.; Chiu, C.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Su, K.P. A meta-analytic review of polyunsaturated fatty acid compositions in dementia. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2012, 73, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.A.; Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C.; Rogers, P.J. Lower omega-3 fatty acid intake and status are associated with poorer cognitive function in older age: A comparison of individuals with and without cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo van Lent, D.; Egert, S.; Wolfsgruber, S.; Kleineidam, L.; Weinhold, L.; Wagner-Thelen, H.; Maier, W.; Jessen, F.; Ramirez, A.; Schmid, M.; et al. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Is Associated with Decreased Incidence of Alzheimer’s Dementia in the Oldest Old. Nutrients 2021, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.S.; Hung, C.F.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Chen, K.C.; Chen, N.C. Higher Serum DHA and Slower Cognitive Decline in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: Two-Year Follow-Up. Nutrients 2022, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, E.J.; Bongard, V.; Beiser, A.S.; Lamon-Fava, S.; Robins, S.J.; Au, R.; Tucker, K.L.; Kyle, D.J.; Wilson, P.W.; Wolf, P.A. Plasma phosphatidylcholine docosahexaenoic acid content and risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease: The Framingham Heart Study. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberger-Gateau, P.; Raffaitin, C.; Letenneur, L.; Berr, C.; Tzourio, C.; Dartigues, J.F.; Alpérovitch, A. Dietary patterns and risk of dementia: The Three-City cohort study. Neurology 2007, 69, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.O.; Cerhan, J.R.; Geda, Y.E.; Knopman, D.S.; Cha, R.H.; Christianson, T.J.; Pankratz, V.S.; Ivnik, R.J.; O’Connor, H.M.; Petersen, R.C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and reduced odds of MCI: The Mayo Clinic Study of Aging. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 21, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Evans, D.A.; Bienias, J.L.; Tangney, C.C.; Bennett, D.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Aggarwal, N.; Schneider, J. Consumption of fish and n-3 fatty acids and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Rest, O.; Wang, Y.; Barnes, L.L.; Tangney, C.; Bennett, D.A.; Morris, M.C. APOE ε4 and the associations of seafood and long-chain omega-3 fatty acids with cognitive decline. Neurology 2016, 86, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiao, J. Intakes of fish and polyunsaturated fatty acids and mild-to-severe cognitive impairment risks: A dose-response meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyarov, S.; Kotlyarova, A. Anti-Inflammatory Function of Fatty Acids and Involvement of Their Metabolites in the Resolution of Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund-Levi, Y.; Eriksdotter-Jönhagen, M.; Cederholm, T.; Basun, H.; Faxén-Irving, G.; Garlind, A.; Vedin, I.; Vessby, B.; Wahlund, L.O.; Palmblad, J. Omega-3 fatty acid treatment in 174 patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: OmegAD study: A randomized double-blind trial. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.K.; Shahar, S.; Chin, A.V.; Yusoff, N.A. Docosahexaenoic acid-concentrated fish oil supplementation in subjects with mild cognitive impairment (MCI): A 12-month randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology 2013, 225, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; You, J.; Cui, H.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, W.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, Q. The n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Supplementation Improved the Cognitive Function in the Chinese Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2017, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, R.K.; Kalt, W.; Shidler, M.D.; McDonald, J.; Summer, S.S.; Stein, A.L.; Stover, A.N.; Krikorian, R. Cognitive response to fish oil, blueberry, and combined supplementation in older adults with subjective cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 64, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, A.; Abbott, K.A.; McEvoy, M.; Schofield, P.W.; Garg, M.L. Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cognitive decline in non-demented adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, H.; Ge, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Yu, H. Effect of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids on mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurko-Mauro, K.; Alexander, D.D.; Van Elswyk, M.E. Docosahexaenoic acid and adult memory: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Luo, C.; Feng, Y.; Yao, X.; Shi, Z.; Liang, F.; Kang, J.X.; Wan, J.B.; Pei, Z.; Su, H. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote amyloid-β clearance from the brain through mediating the function of the glymphatic system. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xie, Y.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Q.; Huang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wan, J.B.; Yao, X.; Su, K.P.; et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote brain-to-blood clearance of β-Amyloid in a mouse model with Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez-Gutiérrez, L.; Fábrias, G.; Casas, J.; Wandosell, F. Diets with Higher ω-6/ω-3 Ratios Show Differences in Ceramides and Fatty Acid Levels Accompanied by Increased Amyloid-Beta in the Brains of Male APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.P.; Calon, F.; Morihara, T.; Yang, F.; Teter, B.; Ubeda, O.; Salem, N., Jr.; Frautschy, S.A.; Cole, G.M. A diet enriched with the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid reduces amyloid burden in an aged Alzheimer mouse model. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3032–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, E.; Zhu, M.; Toro, V.C.; Vedin, I.; Palmblad, J.; Cederholm, T.; Freund-Levi, Y.; Faxen-Irving, G.; Wahlund, L.O.; Basun, H.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acids enhance phagocytosis of Alzheimer’s disease-related amyloid-β42 by human microglia and decrease inflammatory markers. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 35, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Leppert, A.; Tan, S.; van der Gaag, B.; Li, N.; Schultzberg, M.; Hjorth, E. Maresin 1 attenuates pro-inflammatory activation induced by β-amyloid and stimulates its uptake. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, M.; Halder, R.C.; Sagong, B.; Ross, O.; Sayre, J.; Porter, V.; Bredesen, D.E. ω-3 Supplementation increases amyloid-β phagocytosis and resolvin D1 in patients with minor cognitive impairment. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera-Perez, H.M.; Lam, L.; Dang, J.; Jiang, W.; Rodriguez, F.; Rigali, E.; Weitzman, S.; Porter, V.; Rubbi, L.; Morselli, M.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acids increase the unfolded protein response and improve amyloid-β phagocytosis by macrophages of patients with mild cognitive impairment. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 4359–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Batlle, J.; Sauleda, J.; Balcells, E.; Gómez, F.P.; Méndez, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Barreiro, E.; Ferrer, J.J.; Romieu, I.; Gea, J.; et al. Association between Ω3 and Ω6 fatty acid intakes and serum inflammatory markers in COPD. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.J.; Baines, K.J.; Smart, J.M.; Gibson, P.G.; Wood, L.G. Rosuvastatin, lycopene and omega-3 fatty acids: A potential treatment for systemic inflammation in COPD; a pilot study. J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2016, 5, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Calder, P.C.; Laviano, A.; Lonnqvist, F.; Muscaritoli, M.; Öhlander, M.; Schols, A. Targeted medical nutrition for cachexia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, K.; Takahashi, H.; Kasai, C.; Kiyokawa, N.; Watanabe, T.; Fujii, S.; Kashiwagura, T.; Honma, M.; Satake, M.; Shioya, T. Effects of nutritional supplementation combined with low-intensity exercise in malnourished patients with COPD. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Su, X.; Lei, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2021, 16, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shaer, A.E.; Buddenbaum, N.; Shaikh, S.R. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, specialized pro-resolving mediators, and targeting inflammation resolution in the age of precision nutrition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Al-Qahtani, J.M.; El-Safty, S.A. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in large doses attenuate seizures, cognitive impairment, and hippocampal oxidative DNA damage in young kindled rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Jang, J.S.; Son, D.J.; Im, H.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.E.; Choi, W.R.; Han, S.B.; Hong, J.T. Antarctic Krill Oil Diet Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Impairment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgórzyńska, E.; Dziedzic, B.; Gorzkiewicz, A.; Stulczewski, D.; Bielawska, K.; Su, K.P.; Walczewska, A. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids improve the antioxidative defense in rat astrocytes via an Nrf2-dependent mechanism. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Jian, Z. Nrf2 Regulates Oxidative Stress and Its Role in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhen, J.; Dong, S.; Zhang, H.; Van Halm-Lutterodt, N.; Yuan, L. DHA and vitamin E antagonized the Aβ(25-35)-mediated neuron oxidative damage through activation of Nrf2 signaling pathways and regulation of CD36, SRB1 and FABP5 expression in PC12 cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, M.; Jonker, R.; Sulaiman, H.; Fisk, H.L.; Calder, P.C.; Deutz, N.E.P. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation improves postabsorptive and prandial protein metabolism in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.P.; Tseng, P.T.; Zeng, B.S.; Chang, C.H.; Su, H.; Chou, P.H.; Su, K.P. Safety of Supplementation of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Tseng, P.T.; Chen, N.Y.; Lin, P.C.; Lin, P.Y.; Chang, J.P.; Kuo, F.Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, M.C.; Su, K.P. Safety and tolerability of prescription omega-3 fatty acids: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 129, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, R.D.; Alvarez, M.T.; Wittnebel, L.D.; Sorenson, H.; Wettstein, R.; Vines, D.L.; Sikkema-Ortiz, J.; Gardner, D.D.; Wilkins, R.L. Medication adherence issues in patients treated for COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon Dis. 2008, 3, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, E.M.; van de Hei, S.J.; Dierick, B.J.H.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Kocks, J.W.H.; van Boven, J.F.M. Global burden of medication non-adherence in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma: A narrative review of the clinical and economic case for smart inhalers. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 3846–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, E.; Toniolo, S.; Pagnini, F.; Banfi, P. The Relationship Between Anxiety, Depression and Treatment Adherence in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon Dis. 2021, 16, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, F.; Goldman, S.M.; Umbach, D.M.; Chen, H.; Richardson, G.; Barber, M.R.; Meng, C.; Marras, C.; Korell, M.; Kasten, M.; et al. Dietary fat intake, pesticide use, and Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.D.; Ross, G.W.; White, L.R.; Sanderson, W.T.; Burchfiel, C.M.; Kashon, M.; Sharp, D.S.; Masaki, K.H.; Curb, J.D.; Petrovitch, H. Environmental, life-style, and physical precursors of clinical Parkinson’s disease: Recent findings from the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. J. Neurol. 2003, 250 (Suppl. S3), iii30–iii39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lau, L.M.; Bornebroek, M.; Witteman, J.C.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Breteler, M.M. Dietary fatty acids and the risk of Parkinson disease: The Rotterdam study. Neurology 2005, 64, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, H.; Fung, T.T.; Logroscino, G.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Hu, F.B.; Ascherio, A. Prospective study of dietary pattern and risk of Parkinson disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantzaris, M.; Loukaides, G.; Paraskevis, D.; Kostaki, E.G.; Patrikios, I. Neuroaspis PLP10™, a nutritional formula rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids with antioxidant vitamins including gamma-tocopherol in early Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 210, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Dadgostar, E.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Bahmani, F.; Abolhassani, J.; Aarabi, M.H.; Kouchaki, E.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z. The effects of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E co-supplementation on clinical and metabolic status in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 108, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Aghadavod, E.; Mafi, A.; Dadgostar, E.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Abolhassani, J.; Asemi, Z. The effects of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E co-supplementation on gene expression related to inflammation, insulin and lipid in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 176, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tan, L.; Wang, C.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, J. Polyunsaturated eicosapentaenoic acid changes lipid composition in lipid rafts. Eur. J. Nutr. 2006, 45, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterniti, I.; Impellizzeri, D.; Di Paola, R.; Esposito, E.; Gladman, S.; Yip, P.; Priestley, J.V.; Michael-Titus, A.T.; Cuzzocrea, S. Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates the early inflammatory response following spinal cord injury in mice: In-vivo and in-vitro studies. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, Z.; Toupchian, O.; Vatannejad, A.; Sotoudeh, G.; Teimouri, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Nasli-Esfahani, E.; Koohdani, F. Effects of DHA-enriched fish oil on gene expression levels of p53 and NF-κB and PPAR-γ activity in PBMCs of patients with T2DM: A randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim(s) responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zailani, H.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Liao, W.-C.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Huang, S.-Y.; Gałecki, P.; Su, K.-P.; Chang, J.P.-C. Roles of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204363
Zailani H, Satyanarayanan SK, Liao W-C, Hsu Y-T, Huang S-Y, Gałecki P, Su K-P, Chang JP-C. Roles of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204363
Chicago/Turabian StyleZailani, Halliru, Senthil Kumaran Satyanarayanan, Wei-Chih Liao, Yi-Ting Hsu, Shih-Yi Huang, Piotr Gałecki, Kuan-Pin Su, and Jane Pei-Chen Chang. 2023. "Roles of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204363
APA StyleZailani, H., Satyanarayanan, S. K., Liao, W.-C., Hsu, Y.-T., Huang, S.-Y., Gałecki, P., Su, K.-P., & Chang, J. P.-C. (2023). Roles of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review. Nutrients, 15(20), 4363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204363









