Prolonged High-Fat Diet Consumption throughout Adulthood in Mice Induced Neurobehavioral Deterioration via Gut-Brain Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Behavioral Measurements
2.2.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.2.2. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) Test
2.2.3. Three-Chamber Social Test
2.2.4. Nesting Test and Marble Burying
2.2.5. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
2.2.6. Morris Water Maze (MWM)
2.3. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.4. ELISA Assay
2.5. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Alcian Blue (AB) Staining
2.6. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.7. 16SrRNA Sequencing Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
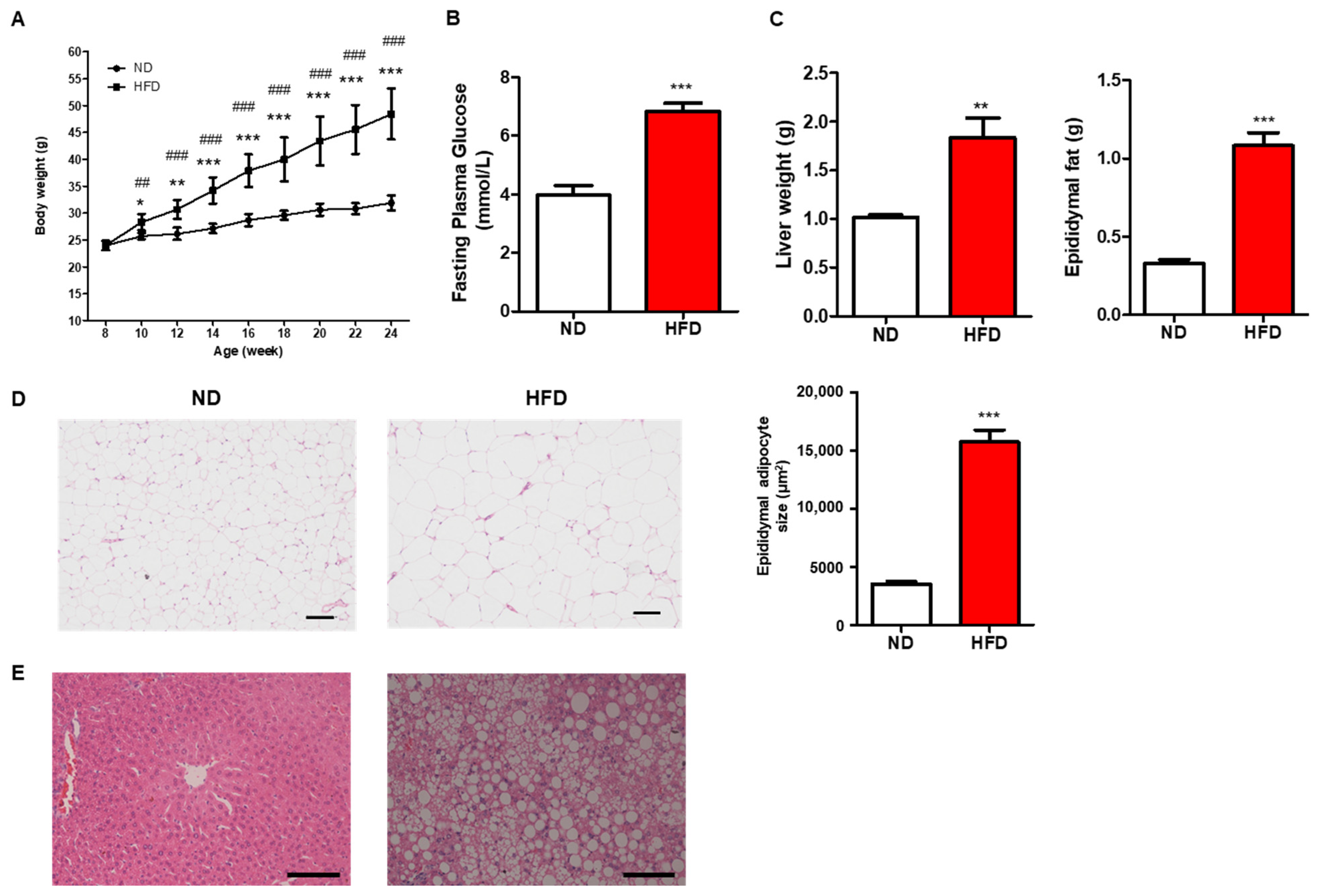
3.1. Prolonged HFD Intake Induces Metabolic Alterations
3.2. Prolonged HFD Intake Induces Neurobehavioral Disorders
3.2.1. Anxiety- and Depression-like Behavior
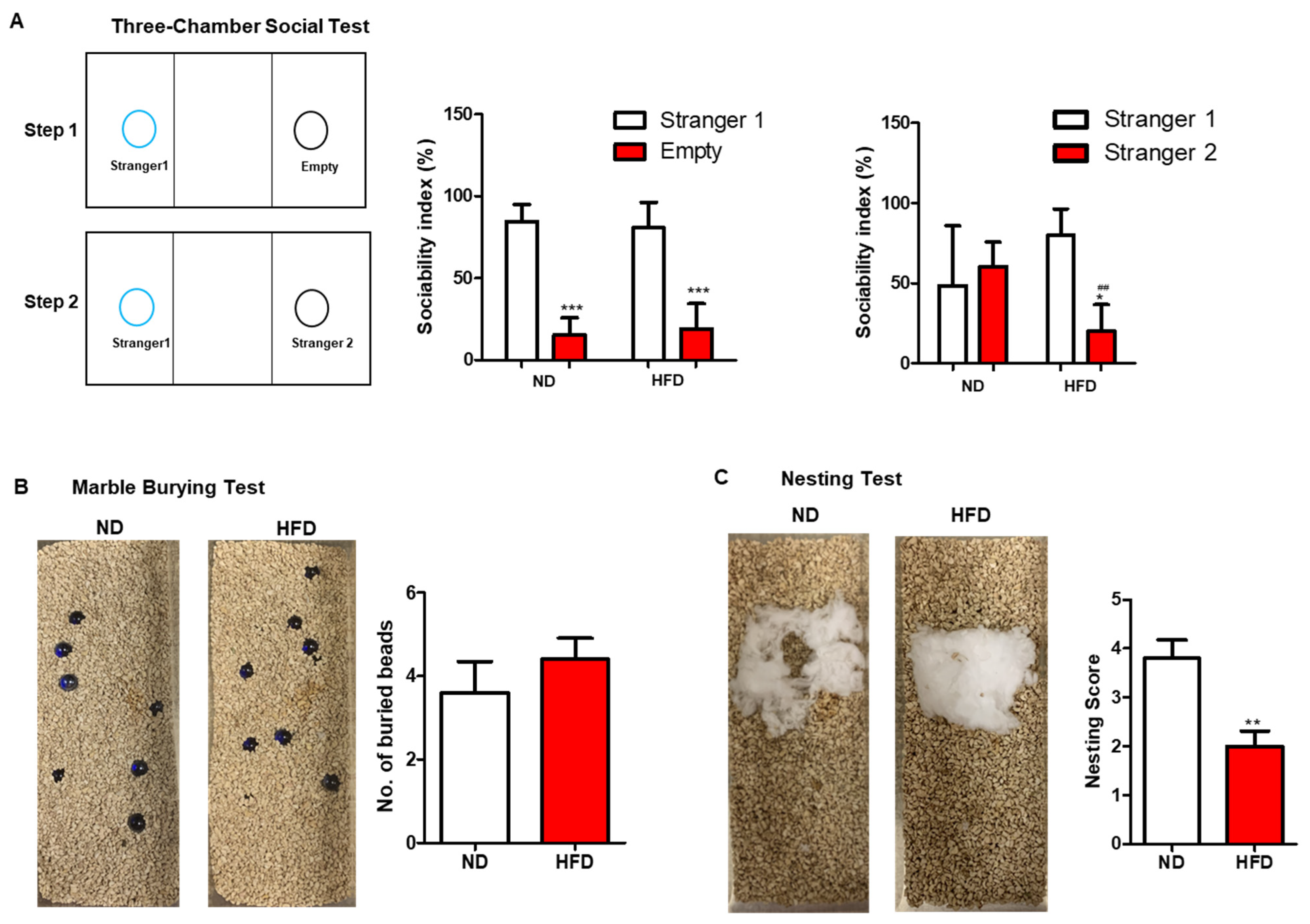
3.2.2. Autism-like or Social Behavior
3.2.3. Learning and Memory
3.3. Prolonged HFD Diet Induces Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis
3.4. Correlation Analysis between the Gut Microbiota Composition and Neurobehaviors
3.5. Prolonged HFD Intake Impairs Gut Barrier Integrity and Induces Inflammatory Responses in Mice
3.6. Prolonged HFD Intake Affects the Function of Neurons and the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins Involved in Blood-Brain-Barrier
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutheil, S.; Ota, K.T.; Wohleb, E.S.; Rasmussen, K.; Duman, R.S. High-Fat Diet Induced Anxiety and Anhedonia: Impact on Brain Homeostasis and Inflammation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1874–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilkha, N.; Kuperman, Y.; Kimchi, T. High-fat diet exacerbates cognitive rigidity and social deficiency in the BTBR mouse model of autism. Neuroscience 2017, 345, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordner, Z.A.; Tamashiro, K.L. Effects of high-fat diet exposure on learning & memory. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152 Pt B, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Kesby, J.; Kim, J.J.; Scadeng, M.; Woods, G.; Kado, D.M.; Olefsky, J.M.; Jeste, D.V.; Achim, C.L.; Semenova, S. Spatial Cognition in Adult and Aged Mice Exposed to High-Fat Diet. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Yao, X.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, D.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Long-term high-fat diet consumption by mice throughout adulthood induces neurobehavioral alterations and hippocampal neuronal remodeling accompanied by augmented microglial lipid accumulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 100, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Salbaum, J.M.; Luo, M.; Blanchard, E.; Taylor, C.M.; Welsh, D.A.; Berthoud, H.-R. Obese-type gut microbiota induce neurobehavioral changes in the absence of obesity. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, A.; García-Pardo, M.P.; López-Almela, I.; Campillo, I.; Maes, M.; Romani-Pérez, M.; Sanz, Y. Interplay Between the Gut-Brain Axis, Obesity and Cognitive Function. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L., IV; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuke, N.; Nagata, N.; Suganuma, H.; Ota, T. Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Endotoxemia with Dietary Factors. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarassishin, L.; Suh, H.S.; Lee, S.C. LPS and IL-1 differentially activate mouse and human astrocytes: Role of CD14. Glia 2014, 62, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Tucsek, Z.; Kiss, T.; Giles, C.B.; Tarantini, S.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Gautam, T.; Galvan, V.; Ballabh, P.; et al. Obesity in Aging Exacerbates Neuroinflammation, Dysregulating Synaptic Function-Related Genes and Altering Eicosanoid Synthesis in the Mouse Hippocampus: Potential Role in Impaired Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Decline. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeuter, A.K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Open Field Test for Measuring Locomotor Activity and Anxiety-Like Behavior. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kaidanovich-Beilin, O.; Lipina, T.; Vukobradovic, I.; Roder, J.; Woodgett, J.R. Assessment of social interaction behaviors. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 25, e2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M. Assessing nest building in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, P.V.; Sahu, R.; Mishra, D.K. Marble-burying behavior test as a murine model of compulsive-like behavior. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2020, 102, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueptow, L.M. Novel Object Recognition Test for the Investigation of Learning and Memory in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 2017, e55718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.Z.; Hassan, Z.; Che Has, A.T. Morris water maze: A versatile and pertinent tool for assessing spatial learning and memory. Exp. Anim. 2022, 71, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.R.; Tan, P.H.; Cheng, J.K.; Liu, Y.C.; Ji, R.R. Microglia: A promising target for treating neuropathic and postoperative pain, and morphine tolerance. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2011, 110, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paeratakul, S.; Ferdinand, D.P.; Champagne, C.M.; Ryan, D.H.; Bray, G.A. Fast-food consumption among US adults and children: Dietary and nutrient intake profile. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, W. How Western Diet and Lifestyle Drive the Pandemic of Obesity and Civilization Diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelinen, M.H.; Ngandu, T.; Helkala, E.; Tuomilehto, J.; Nissinen, A.; Soininen, H.; Kivipelto, M. Fat intake at midlife and cognitive impairment later in life: A population-based CAIDE study. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2008, 23, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasinetti, G.M.; Eberstein, J.A. Metabolic syndrome and the role of dietary lifestyles in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winocur, G.; Greenwood, C.E.; Piroli, G.G.; Grillo, C.A.; Reznikov, L.R.; Reagan, L.P.; McEwen, B.S. Memory impairment in obese Zucker rats: An investigation of cognitive function in an animal model of insulin resistance and obesity. Behav. Neurosci. 2005, 119, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehme, M.; van de Wouw, M.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.; Olavarría-Ramírez, L.; Lyons, K.; Fouhy, F.; Golubeva, A.V.; Moloney, G.M.; Minuto, C.; Sandhu, K.V.; et al. Mid-life microbiota crises: Middle age is associated with pervasive neuroimmune alterations that are reversed by targeting the gut microbiome. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2567–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, C.R.; Fischer, M.E.; Pinto, A.A.; Chen, Y.; Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; Tsai, M.Y.; Tweed, T.S.; Cruickshanks, K.J. Brain Aging in Midlife: The Beaver Dam Offspring Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carola, V.; D’Olimpio, F.; Brunamonti, E.; Mangia, F.; Renzi, P. Evaluation of the elevated plus-maze and open-field tests for the assessment of anxiety-related behaviour in inbred mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 134, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, S.; Morris, T. Physical activity and obesity research in the Asia-Pacific: A review. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2012, 24, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, H.M.; Christiansen, K.J.; Sullivan, E.L. The role of maternal obesity in the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Ke, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Lv, P.; Li, F.; Chen, Y. Metformin Alleviates Autistic-Like Behaviors Elicited by High-Fat Diet Consumption and Modulates the Crosstalk Between Serotonin and Gut Microbiota in Mice. Behav. Neurol. 2022, 2022, 6711160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian Furlan, F.; Marriott, A.; Gill, D.; Kaleko, M. Maternal treatment with oral intestinal alkaline phosphatase mitigates high fat diet-induced cognitive disorders in offspring mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 392, 112701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley-Brits, K.; Deng, Y.; Song, W. Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 53, e2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ge, T.; Leng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Fan, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, R. The Role of Neural Plasticity in Depression: From Hippocampus to Prefrontal Cortex. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 6871089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, G.; Frodl, T. The hippocampus in major depression: Evidence for the convergence of the bench and bedside in psychiatric research? Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, M.; Fusco, S.; Mainardi, M.; Scala, F.; Natale, F.; Lapenta, R.; Mattera, A.; Rinaudo, M.; Puma, D.D.L.; Ripoli, C.; et al. Brain insulin resistance impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory by increasing GluA1 palmitoylation through FoxO3a. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichelt, A.C.; Lemieux, C.A.; Princz-Lebel, O.; Singh, A.; Bussey, T.J.; Saksida, L.M. Age-dependent and region-specific alteration of parvalbumin neurons, perineuronal nets and microglia in the mouse prefrontal cortex and hippocampus following obesogenic diet consumption. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.J.; Basri, B.; Sominsky, L.; Soch, A.; Ayala, M.T.; Reineck, P.; Gibson, B.C.; Barrientos, R.M. High-fat diet worsens the impact of aging on microglial function and morphology in a region-specific manner. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 74, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, E.; Corrada, M.M.; Kahle-Wrobleski, K.; Kim, R.C.; Sarsoza, F.; Goodus, M.; Kawas, C.H. Synaptic proteins, neuropathology and cognitive status in the oldest-old. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, D.R.; Vallortigara, J.; Alghamdi, A.; Howlett, D.; Hortobágyi, T.; Johnson, M.; Attems, J.; Newhouse, S.; Ballard, C.; Thomas, A.J.; et al. Assessment of ZnT3 and PSD95 protein levels in Lewy body dementias and Alzheimer’s disease: Association with cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibbò, S.; Ianiro, G.; Giorgio, V.; Scaldaferri, F.; Masucci, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G. The role of diet on gut microbiota composition. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4742–4749. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Gao, J.; Ke, W.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, R.; Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, F.; et al. Resveratrol reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice via modulating the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynönen, U.; Rasinkangas, P.; Satokari, R.; Paulin, L.; de Vos, W.M.; Pietilä, T.E.; Kant, R.; Palva, A. Isolation and whole genome sequencing of a Ruminococcus-like bacterium, associated with irritable bowel syndrome. Anaerobe 2016, 39, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudani, S.; Torrisi, S.A.; Alboni, S.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.; Benatti, C.; Rivi, V.; Moloney, R.D.; Fuochi, V.; Furneri, P.M.; Drago, F.; et al. Gut microbiota alterations promote traumatic stress susceptibility associated with p-cresol-induced dopaminergic dysfunctions. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 107, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.K.; Park, H.T.; Ghim, J.; Kwon, Y.; Jeon, J.; Kim, M.-S.; Jee, Y.-K.; Gho, Y.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podbielska, M.; Das, A.; Smith, A.W.; Chauhan, A.; Ray, S.K.; Inoue, J.; Azuma, M.; Nozaki, K.; Hogan, E.L.; Banik, N.L. Neuron-microglia interaction induced bi-directional cytotoxicity associated with calpain activation. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; Lin, X.; Chiou, J. Prolonged High-Fat Diet Consumption throughout Adulthood in Mice Induced Neurobehavioral Deterioration via Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020392
Wu H, Zhang W, Huang M, Lin X, Chiou J. Prolonged High-Fat Diet Consumption throughout Adulthood in Mice Induced Neurobehavioral Deterioration via Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020392
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Haicui, Wenxiu Zhang, Mingyue Huang, Xueying Lin, and Jiachi Chiou. 2023. "Prolonged High-Fat Diet Consumption throughout Adulthood in Mice Induced Neurobehavioral Deterioration via Gut-Brain Axis" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020392
APA StyleWu, H., Zhang, W., Huang, M., Lin, X., & Chiou, J. (2023). Prolonged High-Fat Diet Consumption throughout Adulthood in Mice Induced Neurobehavioral Deterioration via Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients, 15(2), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020392





