The Acute Effect of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate on Hunger, the Plasma Concentration of Orexigenic Peptides and Hedonic Food Intake: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
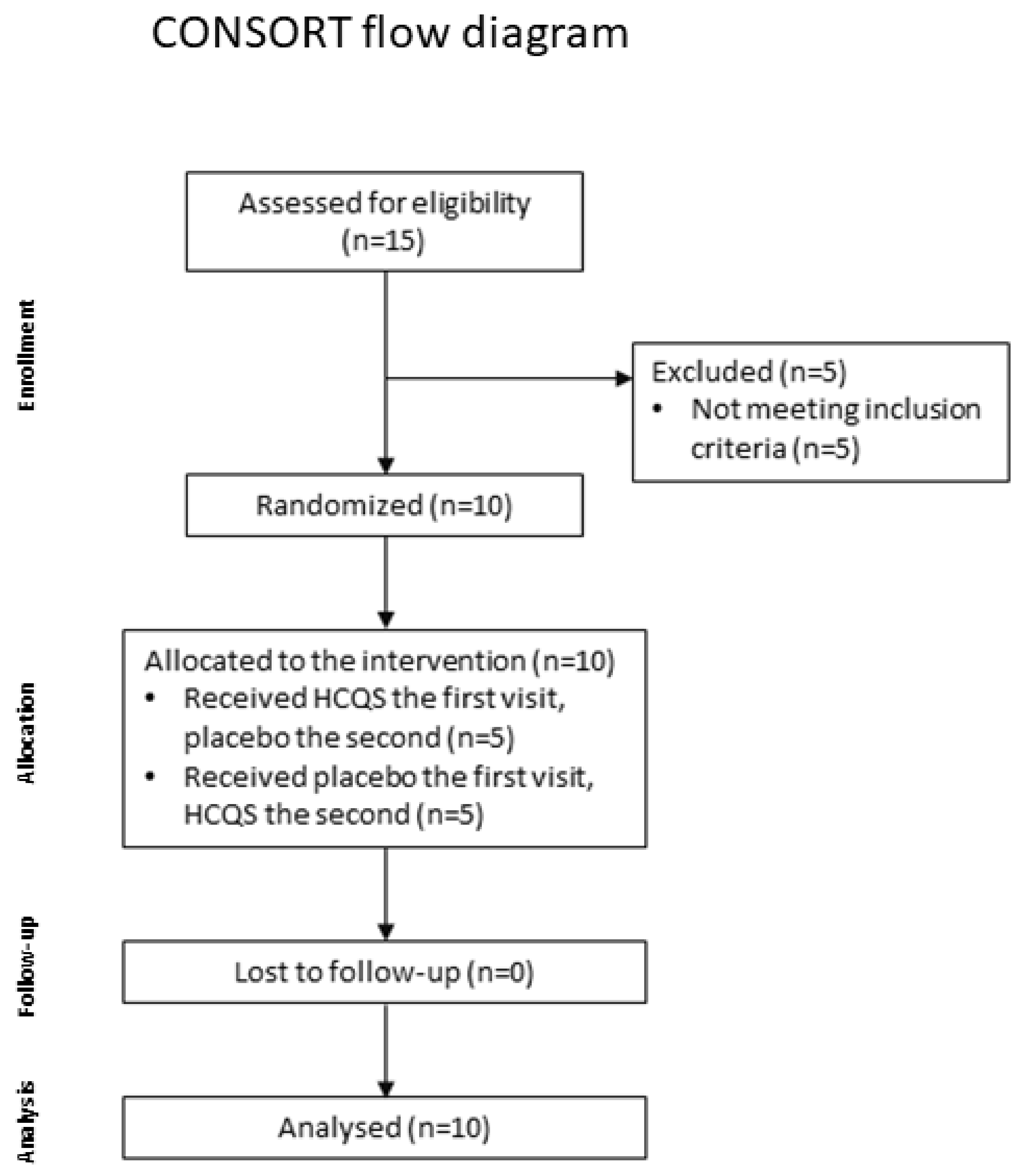
2.2. Study Population and Sample Size
2.3. Test Compounds
2.4. Study Design and Protocol
2.5. Hedonic Food Intake Measurement
2.6. Blood Collection
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Appetite-Related Sensations
3.3. Symptoms
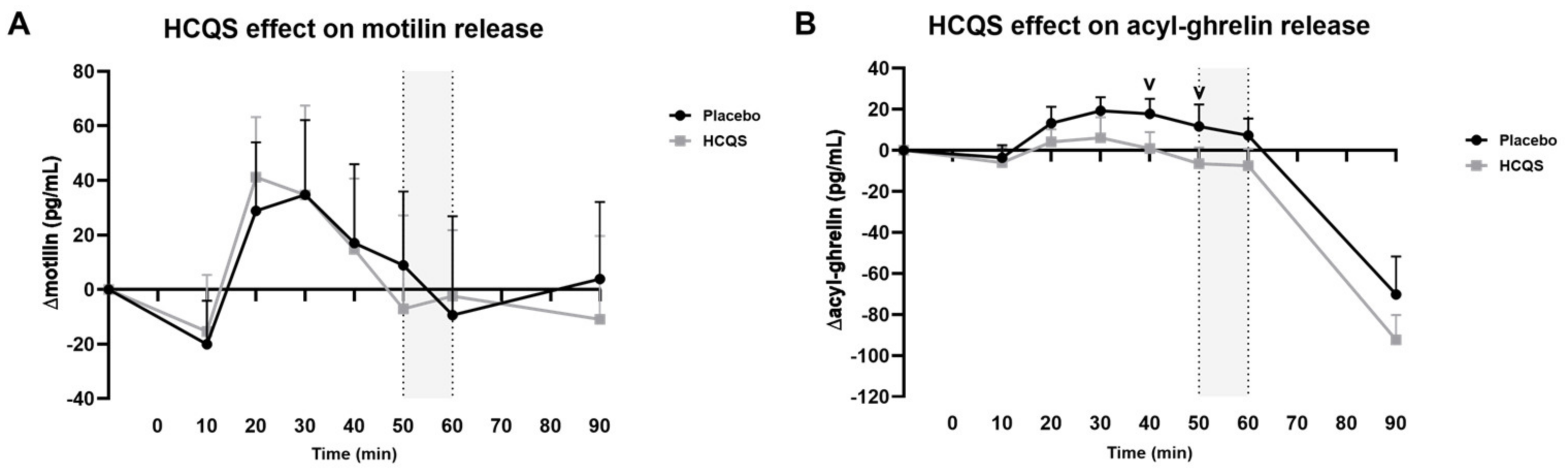
3.4. Orexigenic Gut Peptides
3.5. Effect on Insulin Release and Blood Glucose Levels
3.6. Chocolate Milkshake Intake
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glendinning, J.I. Is the bitter rejection response always adaptive? Physiol. Behav. 1994, 56, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, E.; Hoon, M.A.; Mueller, K.L.; Chandrashekar, J.; Ryba, N.J.P.; Zuker, C.S. A Novel Family of Mammalian Taste Receptors. Cell 2000, 100, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, J.; Mueller, K.L.; Hoon, M.A.; Adler, E.; Feng, L.; Guo, W.; Zuker, C.S.; Ryba, N.J.P. T2Rs Function as Bitter Taste Receptors. Cell 2000, 100, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höfer, D.; Püschel, B.; Drenckhahn, D. Taste receptor-like cells in the rat gut identified by expression of alpha-gustducin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6631–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandi, S.; Bromke, M.; Hübner, S.; Voigt, A.; Boehm, U.; Meyerhof, W.; Behrens, M. A Subset of Mouse Colonic Goblet Cells Expresses the Bitter Taste Receptor Tas2r131. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liszt, K.I.; Depoortere, I. Extra-oral bitter taste receptors: New targets against obesity? Peptides 2020, 127, 170284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszt, K.I.; Wang, Q.; Farhadipour, M.; Segers, A.; Thijs, T.; Nys, L.; Deleus, E.; Van Der Schueren, B.; Gerner, C.; Neuditschko, B.; et al. Human intestinal bitter taste receptors regulate innate immune responses and metabolic regulators in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e144828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, S.; Voigt, A.; Meyerhof, W.; Behrens, M. Expression profiling of Tas2r genes reveals a complex pattern along the mouse GI tract and the presence of Tas2r131 in a subset of intestinal Paneth cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avau, B.; Rotondo, A.; Thijs, T.; Andrews, C.N.; Janssen, P.; Tack, J.; Depoortere, I. Targeting extra-oral bitter taste receptors modulates gastrointestinal motility with effects on satiation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeure, W.; Deloose, E.; Tóth, J.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Oudenhove, L.V.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. The endocrine effects of bitter tastant administration in the gastrointestinal system: Intragastric versus intraduodenal administration. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 321, E1–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloose, E.; Janssen, P.; Corsetti, M.; Biesiekierski, J.; Masuy, I.; Rotondo, A.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Intragastric infusion of denatonium benzoate attenuates interdigestive gastric motility and hunger scores in healthy female volunteers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liszt, K.I.; Deloose, E.; Canovai, E.; Thijs, T.; Farre, R.; Ceulemans, L.J.; Lannoo, M.; Tack, J.; Depoortere, I. Obesity alters adrenergic and chemosensory signaling pathways that regulate ghrelin secretion in the human gut. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4907–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaie, P.; Bitarafan, V.; Rose, B.D.; Lange, K.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Horowitz, M.; Feinle-Bisset, C. Quinine Effects on Gut and Pancreatic Hormones and Antropyloroduodenal Pressures in Humans–Role of Delivery Site and Sex. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e2870–e2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Wu, S.V.; Reeve, J.R., Jr.; Rozengurt, E. Bitter stimuli induce Ca2+ signaling and CCK release in enteroendocrine STC-1 cells: Role of L-type voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C726–C739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Egan, J.M.; Jang, H.J. Denatonium induces secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 through activation of bitter taste receptor pathways. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iven, J.; Biesiekierski, J.R.; Zhao, D.; Deloose, E.; O’Daly, O.G.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J.; Van Oudenhove, L. Intragastric quinine administration decreases hedonic eating in healthy women through peptide-mediated gut-brain signaling mechanisms. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschöp, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: Structure and function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Iwanaga, T.; Fujita, T.; Yanaihara, N. Do enterochromaffin (EC) cells contain motilin? Arch. Histol. Jpn. 1980, 43, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Cook, M.A.; Dryburgh, J.R. Motilin, a Gastric Motor Activity-Stimulating Polypeptide: Final Purification, Amino Acid Composition, and C-Terminal Residues. Gastroenterology 1972, 62, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, J.; Deloose, E.; Ang, D.; Scarpellini, E.; Vanuytsel, T.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Depoortere, I. Motilin-induced gastric contractions signal hunger in man. Gut 2016, 65, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, B.D.; Bitarafan, V.; Rezaie, P.; Fitzgerald, P.C.E.; Horowitz, M.; Feinle-Bisset, C. Comparative Effects of Intragastric and Intraduodenal Administration of Quinine on the Plasma Glucose Response to a Mixed-Nutrient Drink in Healthy Men: Relations with Glucoregulatory Hormones and Gastric Emptying. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Zvi, I.; Kivity, S.; Langevitz, P.; Shoenfeld, Y. Hydroxychloroquine: From malaria to autoimmunity. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 42, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, D.J. Pharmacology of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine. In Hydroxychloroquine Chloroquine Retinopathy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, A.; Shudler, M.; Levit, A.; Niv, M.Y. BitterDB: A database of bitter compounds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D413–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deloose, E.; Corsetti, M.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Intragastric infusion of the bitter tastant quinine suppresses hormone release and antral motility during the fasting state in healthy female volunteers. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, M.P.; Al-Badri, M.R.; Azar, S.T. A favorable effect of hydroxychloroquine on glucose and lipid metabolism beyond its anti-inflammatory role. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 5, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhbahaie, F.; Amini, M.; Gharipour, M.; Aminoroaya, A.; Taheri, N. The effect of hydroxychloroquine on glucose control and insulin resistance in the prediabetes condition. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2016, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoshuk, L.M.; Duffy, V.B.; Miller, I.J. PTC/PROP tasting: Anatomy, psychophysics, and sex effects. Physiol. Behav. 1994, 56, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stice, E.; Spoor, S.; Bohon, C.; Veldhuizen, M.G.; Small, D.M. Relation of reward from food intake and anticipated food intake to obesity: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2008, 117, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloose, E.; Vos, R.; Corsetti, M.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Endogenous motilin, but not ghrelin plasma levels fluctuate in accordance with gastric phase III activity of the migrating motor complex in man. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, S.; Laermans, J.; Verhulst, P.-J.; Thijs, T.; Tack, J.; Depoortere, I. Bitter taste receptors and α-gustducin regulate the secretion of ghrelin with functional effects on food intake and gastric emptying. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitarafan, V.; Fitzgerald, P.C.E.; Little, T.J.; Meyerhof, W.; Wu, T.; Horowitz, M.; Feinle-Bisset, C. Effects of Intraduodenal Infusion of the Bitter Tastant, Quinine, on Antropyloroduodenal Motility, Plasma Cholecystokinin, and Energy Intake in Healthy Men. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, G.J. Why is motilin active in some studies with mice, rats, and guinea pigs, but not in others? Implications for functional variability among rodents. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2022, 10, e00900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloose, E.; Vos, R.; Janssen, P.; Van den Bergh, O.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. The motilin receptor agonist erythromycin stimulates hunger and food intake through a cholinergic pathway1. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloose, E.; Janssen, P.; Lannoo, M.; Van der Schueren, B.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Higher plasma motilin levels in obese patients decrease after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery and regulate hunger. Gut 2016, 65, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Deloose, E.; Iven, J.; Weltens, N.; Depoortere, I.; O’Daly, O.; Tack, J.; Van Oudenhove, L. The motilin agonist erythromycin increases hunger by modulating homeostatic and hedonic brain circuits in healthy women: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.; Lo, K.; Tham, S.; Pahl, M.; Lomiwes, D.; Cooney, J.; Wohlers, M.; Gopal, P. New Zealand Bitter Hops Extract Reduces Hunger during a 24 h Water Only Fast. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitznegg, P.; Bloom, S.R.; Christofides, N.; Besterman, H.; Domschke, W.; Domschke, S.; Wünsch, E.; Demling, L. Release of motilin in man. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1976, 39, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Christofides, N.D.; Bloom, S.R.; Besterman, H.S.; Adrian, T.E.; Ghatei, M.A. Release of motilin by oral and intravenous nutrients in man. Gut 1979, 20, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhof, W.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Brockhoff, A.; Chudoba, E.; Bufe, B.; Appendino, G.; Behrens, M. The molecular receptive ranges of human TAS2R bitter taste receptors. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McChesney, E.W. Animal toxicity and pharmacokinetics of hydroxychloroquine sulfate. Am. J. Med. 1983, 75, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilbronn, L.K.; Smith, S.R.; Martin, C.K.; Anton, S.D.; Ravussin, E. Alternate-day fasting in nonobese subjects: Effects on body weight, body composition, and energy metabolism1,2. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cienfuegos, S.; Gabel, K.; Kalam, F.; Ezpeleta, M.; Wiseman, E.; Pavlou, V.; Lin, S.; Oliveira, M.L.; Varady, K.A. Effects of 4- and 6-h Time-Restricted Feeding on Weight and Cardiometabolic Health: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Adults with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 366–378.e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Fasted Period | Fed Period | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQR (mm) | IQR (mm) | |||
| Placebo | HCQS | Placebo | HCQS | |
| Belching | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Nausea | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Fullness | 45 (0–441) | 0 (0–86) | 1175 (169–1481) | 1490 (851–1666) |
| Cramps | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| Pain | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruilova Sosoranga, E.; Verbeure, W.; Geysen, H.; Thijs, T.; Matthys, C.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. The Acute Effect of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate on Hunger, the Plasma Concentration of Orexigenic Peptides and Hedonic Food Intake: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194264
Ruilova Sosoranga E, Verbeure W, Geysen H, Thijs T, Matthys C, Depoortere I, Tack J. The Acute Effect of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate on Hunger, the Plasma Concentration of Orexigenic Peptides and Hedonic Food Intake: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194264
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuilova Sosoranga, Emily, Wout Verbeure, Hannelore Geysen, Theo Thijs, Christophe Matthys, Inge Depoortere, and Jan Tack. 2023. "The Acute Effect of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate on Hunger, the Plasma Concentration of Orexigenic Peptides and Hedonic Food Intake: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 15, no. 19: 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194264
APA StyleRuilova Sosoranga, E., Verbeure, W., Geysen, H., Thijs, T., Matthys, C., Depoortere, I., & Tack, J. (2023). The Acute Effect of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate on Hunger, the Plasma Concentration of Orexigenic Peptides and Hedonic Food Intake: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 15(19), 4264. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194264







