A Diet Pattern Characterized by Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Is Associated with Lower Decision-Making Performance in the Iowa Gambling Task, Elevated Stress Exposure, and Altered Autonomic Nervous System Reactivity in Men and Women
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Iowa Gambling Task
2.2.2. Wheaton Chronic Stress Inventory
2.2.3. Habitual Diet
2.3. Autonomic Nervous System Activity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Diet Patterns on Iowa Gambling Task Performance
4.2. Influence of Diet Patterns on Chronic Stress Exposure
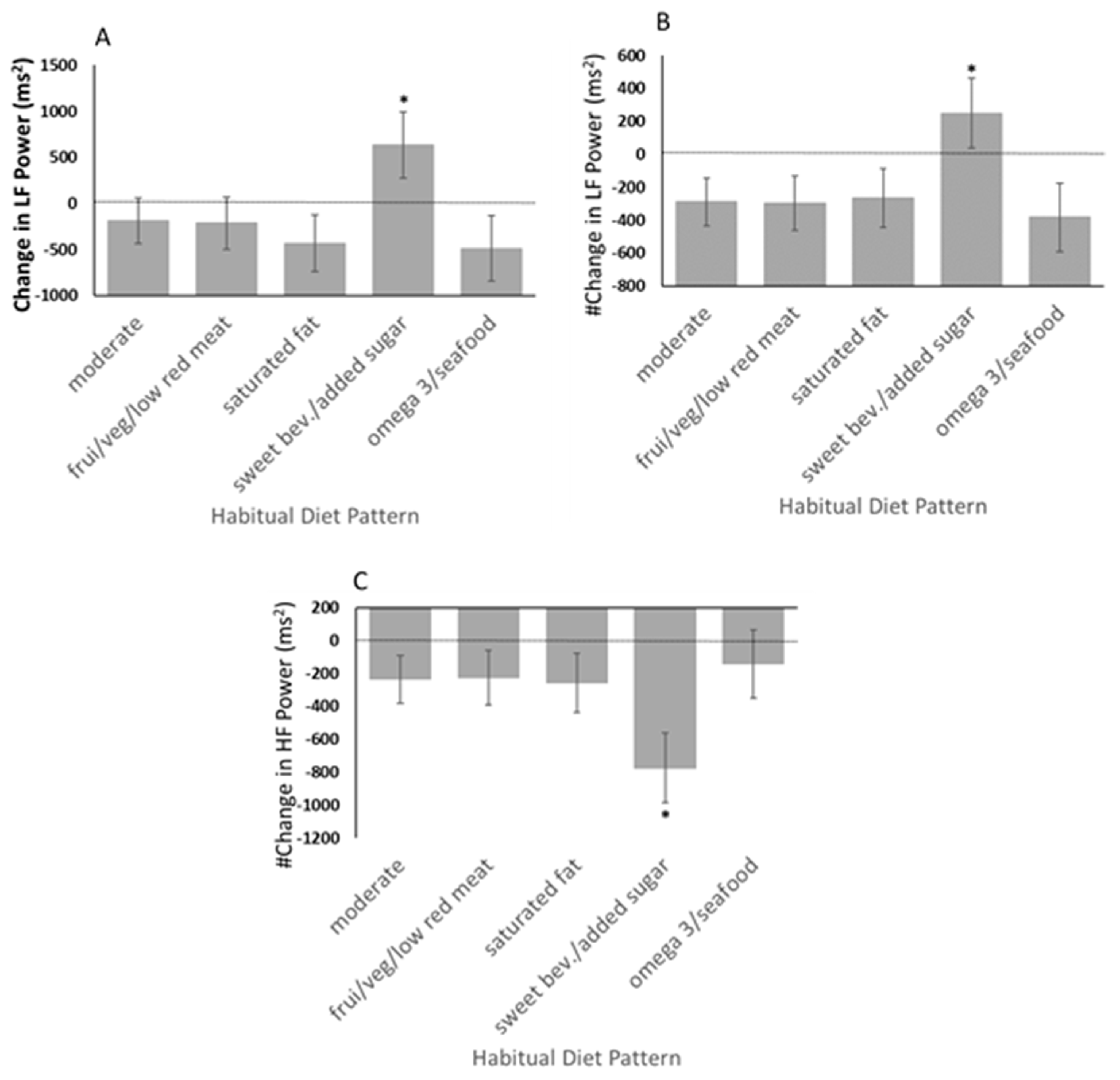
4.3. Influence of Diet Patterns on Autonomic Nervous System Activity
4.4. Overall Implications
4.5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dallman, M.F.; Pecoraro, N.; Akana, S.F.; La Fleur, S.E.; Gomez, F.; Houshyar, H.; Bell, M.E.; Bhatnagar, S.; Laugero, K.D.; Manalo, S. Chronic stress and obesity: A new view of “comfort food”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11696–11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, H.; Keim, N.L.; Laugero, K.D. Increasing Dietary Carbohydrate as Part of a Healthy Whole Food Diet Intervention Dampens Eight Week Changes in Salivary Cortisol and Cortisol Responsiveness. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, H.; Keim, N.; Laugero, K. Diet Quality for Sodium and Vegetables Mediate Effects of Whole Food Diets on 8-Week Changes in Stress Load. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witbracht, M.G.; Laugero, K.D.; Van Loan, M.D.; Adams, S.H.; Keim, N.L. Performance on the Iowa Gambling Task is related to magnitude of weight loss and salivary cortisol in a diet-induced weight loss intervention in overweight women. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.; Levitan, R.D.; Muglia, P.; Bewell, C.; Kennedy, J.L. Decision-making deficits and overeating: A risk model for obesity. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatti, R.; Bertella, L.; Albani, G.; Mauro, A.; Molinari, E.; Semenza, C. Decision-making in obesity: A study using the Gambling Task. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2006, 11, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo-Garcia, A.; Perez-Exposito, M.; Schmidt-Rio-Valle, J.; Fernandez-Serrano, M.J.; Cruz, F.; Perez-Garcia, M.; Lopez-Belmonte, G.; Martin-Matillas, M.; Martin-Lagos, J.A.; Marcos, A.; et al. Selective alterations within executive functions in adolescents with excess weight. Obesity 2010, 18, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, A.R.; Damasio, H.; Anderson, S.W. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition 1994, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, D.G.; Price, J.L. Amygdalo-cortical projections in the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 230, 465–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoesen, G.W. Neural systems of the non-human primate forebrain implicated in memory. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1985, 444, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Damasio, A.R.; Lee, G.P. Different contributions of the human amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex to decision-making. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5473–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeka, A.G.; Lokken, K.L. The Iowa gambling task as a measure of decision making in women with bulimia nervosa. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2006, 12, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, S.; Sang, C.N.T.; Jaussent, I.; Raingeard, I.; Bringer, J.; Jollant, F.; Courtet, P. Is decision making really impaired in eating disorders? Neuropsychology 2010, 24, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Adams, S.H.; Allen, L.H.; Laugero, K.D.; Newman, J.W.; Stephensen, C.B.; Burnett, D.J.; Witbracht, M.; Welch, L.C.; Que, E.S.; et al. A randomized controlled-feeding trial based on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans on cardiometabolic health indexes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldiviez, L.M.; Keim, N.L.; Laugero, K.D.; Hwang, D.H.; Huang, L.; Woodhouse, L.R.; Burnett, D.J.; Zerofsky, M.S.; Bonnel, E.L.; Allen, L.H.; et al. Design and implementation of a cross-sectional nutritional phenotyping study in healthy US adults. BMC Nutr. 2017, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitratos, S.M.; Hercules, M.; Stephensen, C.B.; Cervantes, E.; Laugero, K.D. Association between physiological stress load and diet quality patterns differs between male and female adults. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 240, 113538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.J.; Wheaton, B.; Lloyd, D.A. The Epidemiology of Social Stress. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1995, 60, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, G.; Woods, M.; Potosky, A.; Clifford, C. Validation of a self-administered diet history questionnaire using multiple diet records. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1990, 43, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, R.L.; Porges, S.; Thayer, J.; Ginsberg, J.P. Editorial: Heart Rate Variability, Health and Well-Being: A Systems Perspective. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, L.; Quintigliano, M.; Janiri, D.; De Martin, V.; Rogier, G.; Sani, G.; Janiri, L.; Velotti, P.; Gallese, V.; Speranza, A.M.; et al. Heart rate variability and interoceptive accuracy predict impaired decision-making in Gambling Disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 2021, 10, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucaroff, L.J.; Kievit, R.; Guinjoan, S.M.; Gerschcovich, E.R.; Cerquetti, D.; Leiguarda, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Vigo, D.E. Higher autonomic activation predicts better performance in iowa gambling task. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2011, 24, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alacreu-Crespo, A.; Costa, R.; Abad-Tortosa, D.; Salvador, A.; Serrano, M.A. Good decision-making is associated with an adaptive cardiovascular response to social competitive stress. Stress 2018, 21, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Tranel, D.; Damasio, A.R. The Iowa Gambling Task and the somatic marker hypothesis: Some questions and answers. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyckoff, E.P.; Evans, B.C.; Manasse, S.M.; Butryn, M.L.; Forman, E.M. Executive functioning and dietary intake: Neurocognitive correlates of fruit, vegetable, and saturated fat intake in adults with obesity. Appetite 2017, 111, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundborn, G.; Thornley, S.; Merriman, T.R.; Lang, B.; King, C.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Johnson, R.J. Are Liquid Sugars Different from Solid Sugar in Their Ability to Cause Metabolic Syndrome? Obesity 2019, 27, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Gao, X.; Scott, T.; Tucker, K.L. Habitual sugar intake and cognitive function among middle-aged and older Puerto Ricans without diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.P.; Shahar, S.; Haron, H.; Din, N.C. Habitual sugar intake and cognitive impairment among multi-ethnic Malaysian older adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, S.L.; Kisbu-Sakarya, Y.; Reynolds, K.D.; Boyle, S.; Cappelli, C.; Cox, M.G.; Dust, M.; Grenard, J.L.; Mackinnon, D.P.; Stacy, A.W. Inhibitory control effects in adolescent binge eating and consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and snacks. Appetite 2014, 81, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, D.; Petry, N.M. Predictors of decision-making on the Iowa Gambling Task: Independent effects of lifetime history of substance use disorders and performance on the Trail Making Test. Brain Cogn. 2008, 66, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xiao, L.; Xue, G.; Wong, S.; Ames, S.L.; Xie, B.; Bechara, A. Altered dynamics between neural systems sub-serving decisions for unhealthy food. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algren, M.H.; Ekholm, O.; Nielsen, L.; Ersboll, A.K.; Bak, C.K.; Andersen, P.T. Associations between perceived stress, socioeconomic status, and health-risk behaviour in deprived neighbourhoods in Denmark: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, W.E.; Ceballos, R.M.; Bishop, S.K.; McGregor, B.A.; Beresford, S.A. Perceived stress, behavior, and body mass index among adults participating in a worksite obesity prevention program, Seattle, 2005–2007. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2012, 9, E152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, A.; Almeida, O.P.; English, D.R.; Giles, G.G.; Flicker, L. Patterns of dietary intake and psychological distress in older Australians: Benefits not just from a Mediterranean diet. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2013, 25, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.; Ding, D.; Mihrshahi, S. Fruit and vegetable consumption and psychological distress: Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses based on a large Australian sample. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.; Rohrmann, S.; Vandeleur, C.L.; Mohler-Kuo, M.; Eichholzer, M. Associations between fruit and vegetable consumption and psychological distress: Results from a population-based study. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, A.A.; Belury, M.A.; Andridge, R.; Renna, M.E.; Rosie Shrout, M.; Malarkey, W.B.; Lin, J.; Epel, E.S.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Omega-3 supplementation and stress reactivity of cellular aging biomarkers: An ancillary substudy of a randomized, controlled trial in midlife adults. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbadoro, P.; Annino, I.; Ponzio, E.; Romanelli, R.M.; D’Errico, M.M.; Prospero, E.; Minelli, A. Fish oil supplementation reduces cortisol basal levels and perceived stress: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial in abstinent alcoholics. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasivam, T.; Moser, L.; Dempsey, G.; Colabelli, M.; Rosenberg, L.; Welch, M.; Begdache, L. The Association between High Intake of Omega-3 Fat Food, Perceived Stress and Mental Distress Levels. FASEB J. 2022, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, K.; Hipwell, A.E.; Bortner, J.; Hoffmann, A.; McAloon, R. Association between fatty acid supplementation and prenatal stress in African Americans: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 124, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelow, M.T.; Barnhart, W.R. The Influence of Math Anxiety, Math Performance, Worry, and Test Anxiety on the Iowa Gambling Task and Balloon Analogue Risk Task. Assessment 2017, 24, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laugero, K.D.; Keim, N.L. A Diet Pattern Characterized by Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Is Associated with Lower Decision-Making Performance in the Iowa Gambling Task, Elevated Stress Exposure, and Altered Autonomic Nervous System Reactivity in Men and Women. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183930
Laugero KD, Keim NL. A Diet Pattern Characterized by Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Is Associated with Lower Decision-Making Performance in the Iowa Gambling Task, Elevated Stress Exposure, and Altered Autonomic Nervous System Reactivity in Men and Women. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183930
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaugero, Kevin D., and Nancy L. Keim. 2023. "A Diet Pattern Characterized by Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Is Associated with Lower Decision-Making Performance in the Iowa Gambling Task, Elevated Stress Exposure, and Altered Autonomic Nervous System Reactivity in Men and Women" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183930
APA StyleLaugero, K. D., & Keim, N. L. (2023). A Diet Pattern Characterized by Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Is Associated with Lower Decision-Making Performance in the Iowa Gambling Task, Elevated Stress Exposure, and Altered Autonomic Nervous System Reactivity in Men and Women. Nutrients, 15(18), 3930. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183930




