Binge Eating (BE) and Obesity: Brain Activity and Psychological Measures before and after Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Research Procedures
2.3. fMRI Protocol
2.4. Assessments
2.5. Behavioral Data Analysis
2.6. fMRI Imaging Analysis
- (1)
- Food > Non-Food (NF)
- (2)
- High Energy Density Food (HEF) > Low Energy Density Food (LEF) at (a) baseline [Timepoint 1 (T1)], (b) 4 months post [Timepoint 2 (T2)], and (c) Timepoint 1 > Timepoint 2 (T1 > T2).
3. Results
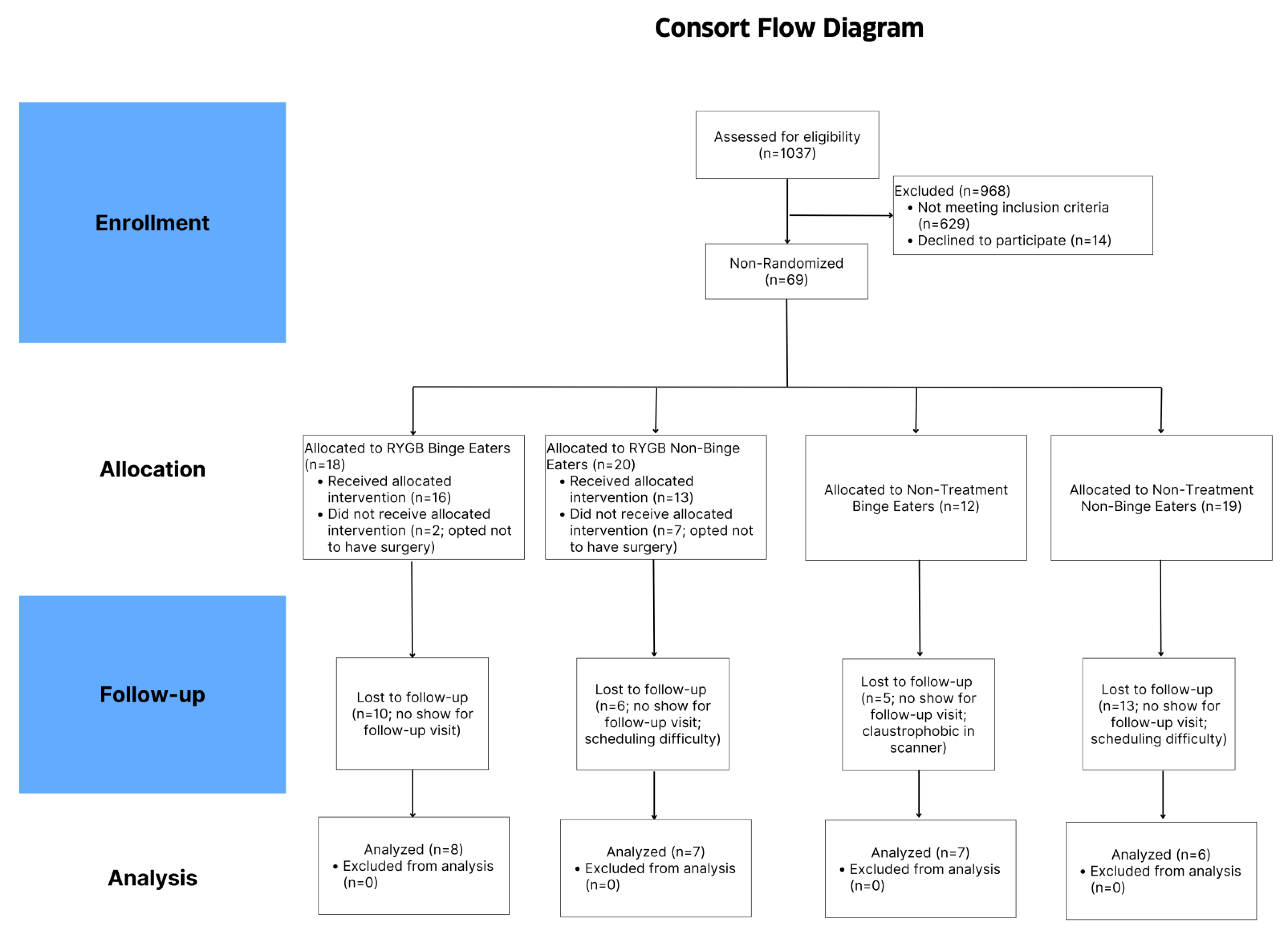
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. 4 Months Follow-Up (T2)
3.3. Baseline to 4 Months (T1 > T2)
3.4. fMRI Outcomes
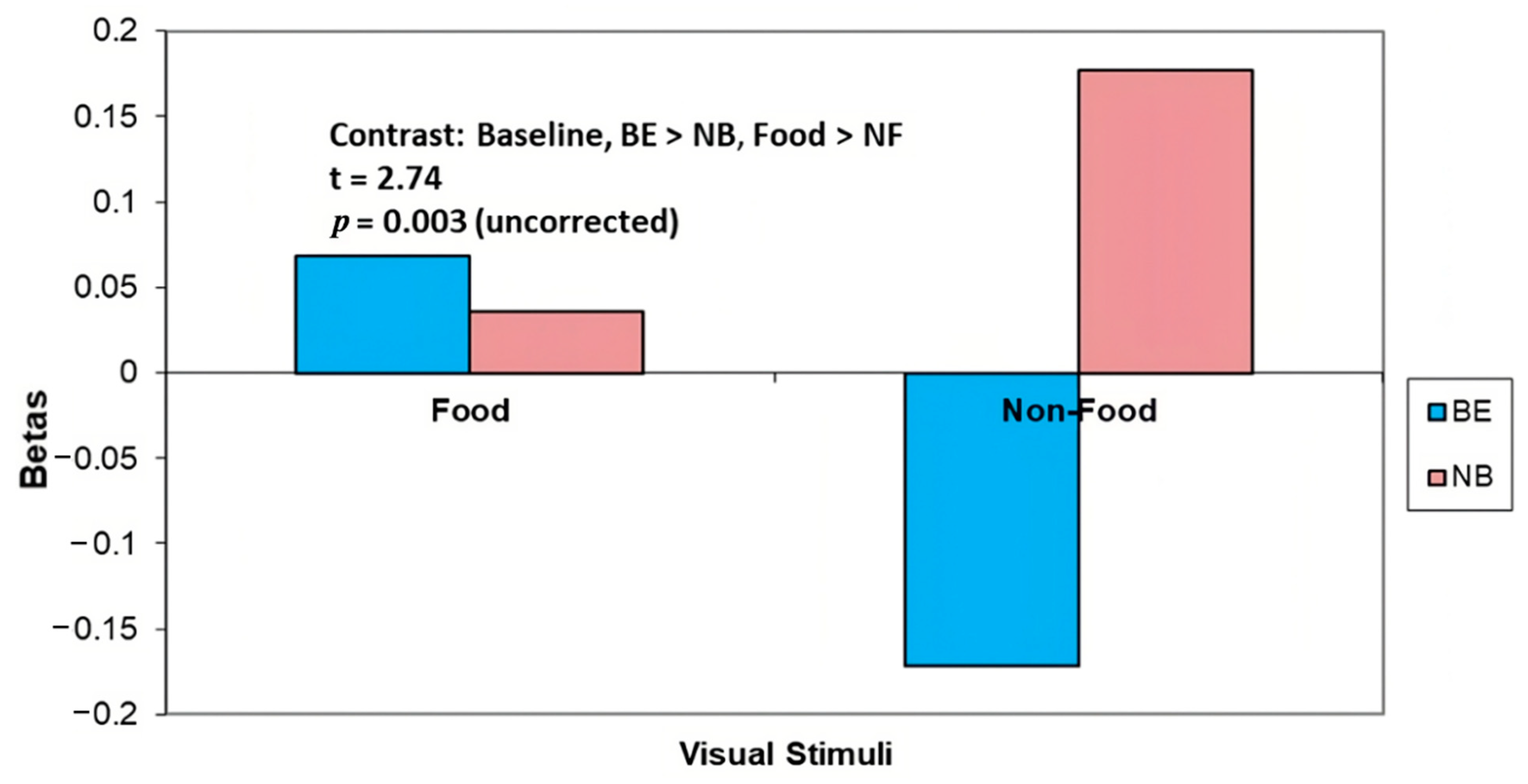
3.4.1. Baseline (T1)
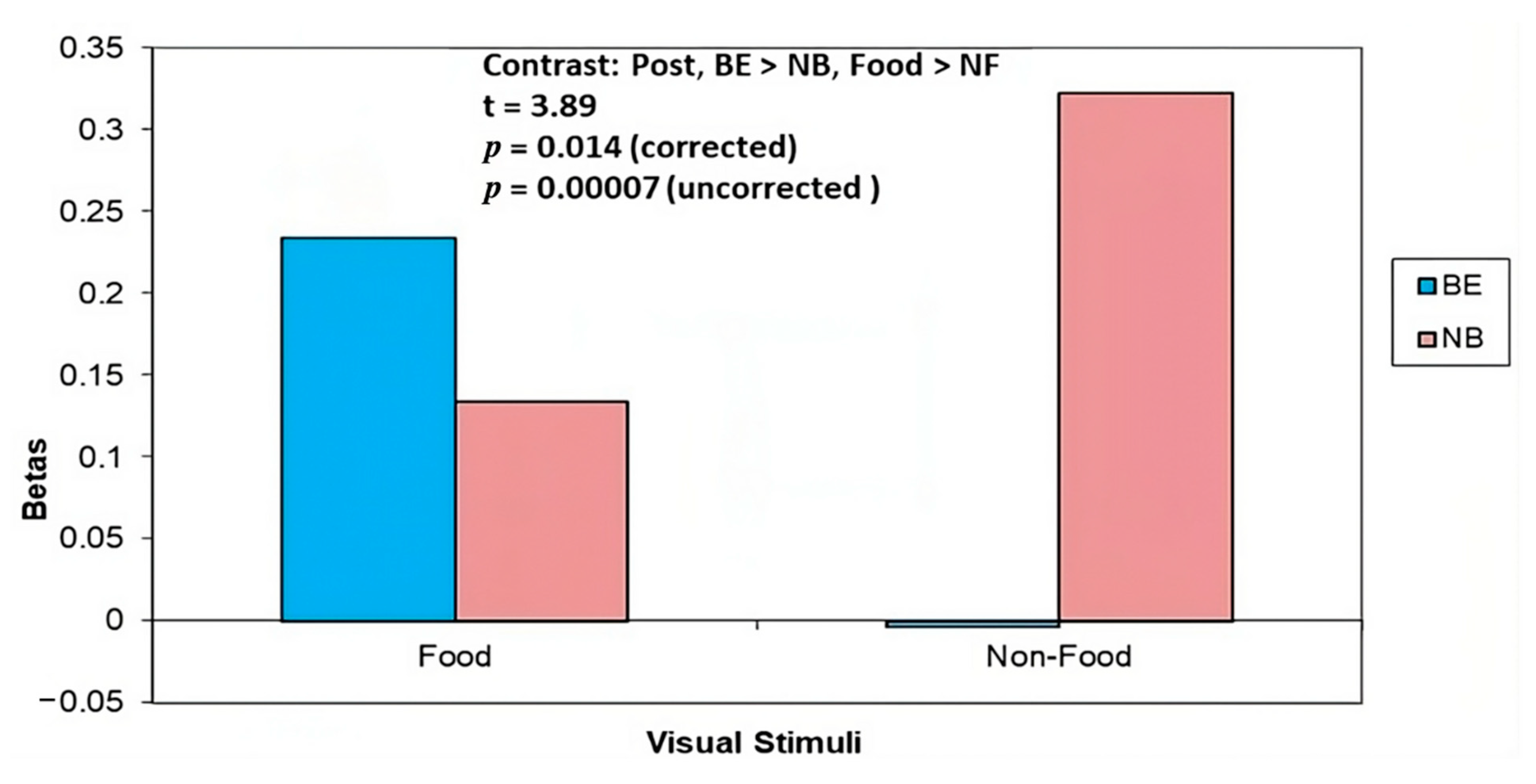
3.4.2. 4 Months Post (T2)
3.4.3. Change in Activation from Baseline to 4 Months Post (T1 > T2)
4. Discussion
4.1. Questionnaire Findings
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Albaugh, V.L.; He, Y.; Münzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D.; Yu, S.; Berthoud, H.-R. Regulation of Body Weight: Lessons Learned from Bariatric Surgery. Mol. Metab. 2023, 68, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estimate of Bariatric Surgery Numbers, 2011–2021. Available online: https://asmbs.org/resources/estimate-of-bariatric-surgery-numbers (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Baboumian, S.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Kothari, S.; McGinty, J.; Holst, J.; Geliebter, A. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (FMRI) of Neural Responses to Visual and Auditory Food Stimuli Pre and Post Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG). Neuroscience 2019, 409, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochner, C.N.; Kwok, Y.; Conceição, E.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Puma, L.M.; Carnell, S.; Teixeira, J.; Hirsch, J.; Geliebter, A. Selective Reduction in Neural Responses to High Calorie Foods Following Gastric Bypass Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochner, C.N.; Stice, E.; Hutchins, E.; Afifi, L.; Geliebter, A.; Hirsch, J.; Teixeira, J. Relation between Changes in Neural Responsivity and Reductions in Desire to Eat High-Calorie Foods Following Gastric Bypass Surgery. Neuroscience 2012, 209, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochner, C.N.; Laferrère, B.; Afifi, L.; Atalayer, D.; Geliebter, A.; Teixeira, J. Neural Responsivity to Food Cues in Fasted and Fed States Pre and Post Gastric Bypass Surgery. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 74, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, J.M.; Hancock, L.; Bruce, A.; Lepping, R.J.; Martin, L.; Lundgren, J.D.; Malley, S.; Holsen, L.M.; Savage, C.R. Changes in Brain Activation to Food Pictures after Adjustable Gastric Banding. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2012, 8, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulconbridge, L.F.; Ruparel, K.; Loughead, J.; Allison, K.C.; Hesson, L.A.; Fabricatore, A.N.; Rochette, A.; Ritter, S.; Hopson, R.D.; Sarwer, D.B.; et al. Changes in Neural Responsivity to Highly Palatable Foods Following Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass, Sleeve Gastrectomy, or Weight Stability: An FMRI Study. Obesity 2016, 24, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajnal, A.; Kovacs, P.; Ahmed, T.; Meirelles, K.; Lynch, C.J.; Cooney, R.N. Gastric Bypass Surgery Alters Behavioral and Neural Taste Functions for Sweet Taste in Obese Rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G967–G979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giel, K.E.; Bulik, C.M.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Hay, P.; Keski-Rahkonen, A.; Schag, K.; Schmidt, U.; Zipfel, S. Binge Eating Disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, L.; Konsor, M.; Cox, S. Binge Eating Before and After Bariatric Surgery. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbuti, M.; Brancati, G.E.; Calderone, A.; Fierabracci, P.; Salvetti, G.; Weiss, F.; Carignani, G.; Santini, F.; Perugi, G. Prevalence of Mood, Panic and Eating Disorders in Obese Patients Referred to Bariatric Surgery: Patterns of Comorbidity and Relationship with Body Mass Index. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zwaan, M.; Mitchell, J.E.; Raymond, N.C.; Spitzer, R.L. Binge Eating Disorder: Clinical Features and Treatment of a New Diagnosis. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 1994, 1, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Strien, T. Causes of Emotional Eating and Matched Treatment of Obesity. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnell, S.; Benson, L.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Hirsch, J.; Geliebter, A. Amodal Brain Activation and Functional Connectivity in Response to High-Energy-Density Food Cues in Obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 2370–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.J.; Cedernaes, J.; Schiöth, H.B. Increased Prefrontal and Parahippocampal Activation with Reduced Dorsolateral Prefrontal and Insular Cortex Activation to Food Images in Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of FMRI Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donofry, S.D.; Stillman, C.M.; Erickson, K.I. A Review of the Relationship between Eating Behavior, Obesity and Functional Brain Network Organization. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 1157–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geliebter, A.; Ladell, T.; Logan, M.; Schweider, T.; Sharafi, M.; Hirsch, J. Responsivity to Food Stimuli in Obese and Lean Binge Eaters Using Functional MRI. Appetite 2006, 46, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.E.; Holsen, L.M.; Chambers, R.J.; Bruce, A.S.; Brooks, W.M.; Zarcone, J.R.; Butler, M.G.; Savage, C.R. Neural Mechanisms Associated with Food Motivation in Obese and Healthy Weight Adults. Obesity 2010, 18, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, I.; Berridge, K.C. ‘Liking’ and ‘Wanting’ in Eating and Food Reward: Brain Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 227, 113152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schienle, A.; Schäfer, A.; Hermann, A.; Vaitl, D. Binge-Eating Disorder: Reward Sensitivity and Brain Activation to Images of Food. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geliebter, A.; Benson, L.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Hirsch, J.; Carnell, S. Greater Anterior Cingulate Activation and Connectivity in Response to Visual and Auditory High-Calorie Food Cues in Binge Eating: Preliminary Findings. Appetite 2016, 96, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, R.G.; Potenza, M.N.; Grilo, C.M. The Neurobiology of Binge-Eating Disorder Compared with Obesity: Implications for Differential Therapeutics. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnell, S.; Gibson, C.; Benson, L.; Ochner, C.N.; Geliebter, A. Neuroimaging and Obesity: Current Knowledge and Future Directions: Neuroimaging and Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairburn, C.G.; Doll, H.A.; Welch, S.L.; Hay, P.J.; Davies, B.A.; O’Connor, M.E. Risk Factors for Binge Eating Disorder: A Community-Based, Case-Control Study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalarchian, M.A.; Wilson, G.T.; Brolin, R.E.; Bradley, L. Binge Eating in Bariatric Surgery Patients. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1998, 23, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.I.; Hiripi, E.; Pope Jr, H.G.; Kessler, R.C. The Prevalence and Correlates of Eating Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-J.; Geliebter, A.; Volkow, N.D.; Telang, F.W.; Logan, J.; Jayne, M.C.; Galanti, K.; Selig, P.A.; Han, H.; Zhu, W. Enhanced Striatal Dopamine Release during Food Stimulation in Binge Eating Disorder. Obesity 2011, 19, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, V.; Castellini, G.; Sauro, C.L.; Ravaldi, C.; Lapi, F.; Mannucci, E.; Rotella, C.M.; Faravelli, C. Correlations between Binge Eating and Emotional Eating in a Sample of Overweight Subjects. Appetite 2009, 53, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, H. Emotional Eating and Obesity in Adults: The Role of Depression, Sleep and Genes. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardi, V.; Leppanen, J.; Treasure, J. The Effects of Negative and Positive Mood Induction on Eating Behaviour: A Meta-Analysis of Laboratory Studies in the Healthy Population and Eating and Weight Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 57, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenberger, J.; Schnepper, R.; Arend, A.; Richard, A.; Voderholzer, U.; Naab, S.; Blechert, J. Emotional Eating across Different Eating Disorders and the Role of Body Mass, Restriction, and Binge Eating. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, M.S.; Allison, D.B.; Geliebter, A. Emotional Eating and Obesity: Theoretical Considerations and Practical Recommendations. In Overweight and Weight Management: The Health Professional’s Guide to Understanding and Practice; Aspen Publishers: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, S.; Brode, C. Predictors of Binge Eating among Bariatric Surgery Candidates: Disinhibition as a Mediator of the Relationship between Depressive Symptoms and Binge Eating. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofman, M.D.; Lent, M.R.; Swencionis, C. Maladaptive Eating Patterns, Quality of Life, and Weight Outcomes Following Gastric Bypass: Results of an Internet Survey. Obesity 2010, 18, 1938–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanos, P.K.; Michaelides, M.; Subrize, M.; Miller, M.L.; Bellezza, R.; Cooney, R.N.; Leggio, L.; Wang, G.-J.; Rogers, A.M.; Volkow, N.D.; et al. Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass Alters Brain Activity in Regions That Underlie Reward and Taste Perception. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount Sinai St. Luke’s Renamed Mount Sinai Morningside|Mount Sinai—New York. Available online: https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2020/mount-sinai-st-lukes-renamed-mount-sinai-morningside (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- MBSAQIP. Available online: https://asmbs.org/integrated-health/mbsaqip (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program. Available online: https://www.facs.org/quality-programs/accreditation-and-verification/metabolic-and-bariatric-surgery-accreditation-and-quality-improvement-program/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Surgical Outcomes and Quality Improvement Office Initiatives|Mount Sinai—New York. Available online: https://www.mountsinai.org/care/surgery/surgical-quality/quality-initiatives (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Ames, G.E.; Heckman, M.G.; Diehl, N.N.; Shepherd, D.M.; Holgerson, A.A.; Grothe, K.B.; Kellogg, T.A.; Bowers, S.P.; Clark, M.M. Guiding Patients Toward the Appropriate Surgical Treatment for Obesity: Should Presurgery Psychological Correlates Influence Choice Between Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass and Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy? Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geliebter, A.; Pantazatos, S.P.; McOuatt, H.; Puma, L.; Gibson, C.D.; Atalayer, D. Sex-Based FMRI Differences in Obese Humans in Response to High vs. Low Energy Food Cues. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 243, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thereaux, J.; Lesuffleur, T.; Païta, M.; Czernichow, S.; Basdevant, A.; Msika, S.; Millat, B.; Fagot-Campagna, A. Long-Term Follow-up after Bariatric Surgery in a National Cohort. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanita: Digital Scales for Body Fat & Weight, Bathroom, Kitchen & Food Scales for Precision Weight Measurement. Available online: https://www.tanita.com/en/ (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Conceição, E.; Machado, P.P. Obesity Disordered Eating Questionnaire-ODE: A Self-Report Measure for Dysfunctional Eating in Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade do Minho, Braga, Portugal, 2010; p. 65. [Google Scholar]
- Geliebter, A.; Aversa, A. Emotional Eating in Overweight, Normal Weight, and Underweight Individuals. Eat. Behav. 2003, 3, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, L.J.; Halperin, L.B.; Geliebter, A. Emotional Appetite Questionnaire. Construct Validity and Relationship with BMI. Appetite 2010, 54, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnhart, W.R.; Braden, A.L.; Price, E. Emotion Regulation Difficulties Interact with Negative, Not Positive, Emotional Eating to Strengthen Relationships with Disordered Eating: An Exploratory Study. Appetite 2021, 158, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdier, L.; Morvan, Y.; Kotbagi, G.; Kern, L.; Romo, L.; Berthoz, S. Examination of Emotion-Induced Changes in Eating: A Latent Profile Analysis of the Emotional Appetite Questionnaire. Appetite 2018, 123, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, M.R.; Butryn, M.L.; Didie, E.R.; Annunziato, R.A.; Thomas, J.G.; Crerand, C.E.; Ochner, C.N.; Coletta, M.C.; Bellace, D.; Wallaert, M. The Power of Food Scale. A New Measure of the Psychological Influence of the Food Environment. Appetite 2009, 53, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serier, K.N.; Belon, K.E.; Smith, J.M.; Smith, J.E. Psychometric Evaluation of the Power of Food Scale in a Diverse College Sample: Measurement Invariance across Gender, Ethnicity, and Weight Status. Eat. Behav. 2019, 35, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelleri, J.C.; Bushmakin, A.G.; Gerber, R.A.; Leidy, N.K.; Sexton, C.C.; Karlsson, J.; Lowe, M.R. Evaluating the Power of Food Scale in Obese Subjects and a General Sample of Individuals: Development and Measurement Properties. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4462-7458-3. [Google Scholar]
- Seed-Based d Mapping (Formerly Signed Differential Mapping)—FDR Online Calculator. Available online: https://www.sdmproject.com/utilities/?show=FDR (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Lynall, M.-E.; Bassett, D.S.; Kerwin, R.; McKenna, P.J.; Kitzbichler, M.; Muller, U.; Bullmore, E. Functional Connectivity and Brain Networks in Schizophrenia. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9477–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, M.; Aktar, R.; Raynel, S.; Hao, Z.; Mumphrey, M.B.; Berthoud, H.-R.; Blackshaw, L.A. Effects of Obesity and Gastric Bypass Surgery on Nutrient Sensors, Endocrine Cells, and Mucosal Innervation of the Mouse Colon. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalley, J.W.; Everitt, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. Impulsivity, Compulsivity, and Top-Down Cognitive Control. Neuron 2011, 69, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsegian, A.; See, R.E. Dysregulation of Dopamine and Glutamate Release in the Prefrontal Cortex and Nucleus Accumbens Following Methamphetamine Self-Administration and during Reinstatement in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauregui-Lobera, I.; Martinez-Quinones, J.V. Neuromodulation in Eating Disorders and Obesity: A Promising Way of Treatment? Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 2817–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, H.; Bhaumik, R.; Kinney, K.L.; Fitzgerald, J.M. Principal Component Analysis and Neural Predictors of Emotion Regulation. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 338, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, S.U.; Hare, T.A. BOLD Activity during Emotion Reappraisal Positively Correlates with Dietary Self-Control Success. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2023, 18, nsaa097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodside, D.B.; Colton, P.; Lam, E.; Dunlop, K.; Rzeszutek, J.; Downar, J. Dorsomedial Prefrontal Cortex Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Eating Disorders: An Open-Label Case Series. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyssen, A.; Meyer, A.H.; Messerli-Bürgy, N.; Forrer, F.; Vanhulst, P.; Lalanne, D.; Munsch, S. BED-Online: Acceptance and Efficacy of an Internet-Based Treatment for Binge-Eating Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial Including Waitlist Conditions. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2021, 29, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ethnic | RYGB a | NT |
|---|---|---|
| Hispanic or Latino | 60 (9) | 69.2 (9) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 40 (6) | 31.8 (4) |
| Racial | ||
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 0 | 0 |
| Asian | 0 | 0 |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 0 | 0 |
| Black or African American | 40 (6) | 61.5 (8) |
| White | 0 | 7.7 (1) |
| Other | 33.3 (5) | 15.4 (2) |
| Unknown | 26.7 (4) | 0 |
| More Than One | 0 | 15.4 (2) |
| BE | NB | RYGB | NT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 15 | 13 | 15 | 13 |
| Age (years) | 38.5 ± 12.5 | 32.3 ± 8.8 | 37.0 ± 10.4 | 33.9 ± 12.3 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 42.8 ± 4.0 | 43.3 ± 3.7 | 44.7 ± 3.9 | 41.1 ± 2.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 116.5 ± 15.3 | 115.7 ± 13.7 | 121.8 ± 13.4 | 109.5 ± 12.8 |
| Body fat (%) a | 50.3 ± 3.4 | 49.2 ± 3.8 | 50.9 ± 2.9 | 48.5 ± 3.9 |
| EMAQ Negative b | 5.7 ± 1.3 * | 4.0 ± 1.6 * | 4.9 ± 2.1 | 4.9 ± 0.8 |
| EMAQ Positive b | 4.6 ± 1.4 | 4.2 ± 1.5 | 3.9 ± 1.7 | 5.0 ± 0.7 |
| PFS Abstract b | 19.9 ± 8.3 * | 11.2 ± 3.6 * | 14.5 ± 7.5 | 17.5 ± 8.2 |
| PFS Presence b | 22.3 ± 7.2 * | 14.5 ± 3.6 * | 16.9 ± 6.5 | 20.1 ± 7.1 |
| PFS Pleasure b | 22.5 ± 7.6 * | 14.3 ± 4.3 * | 16.8 ± 7.6 | 20.9 ± 6.9 |
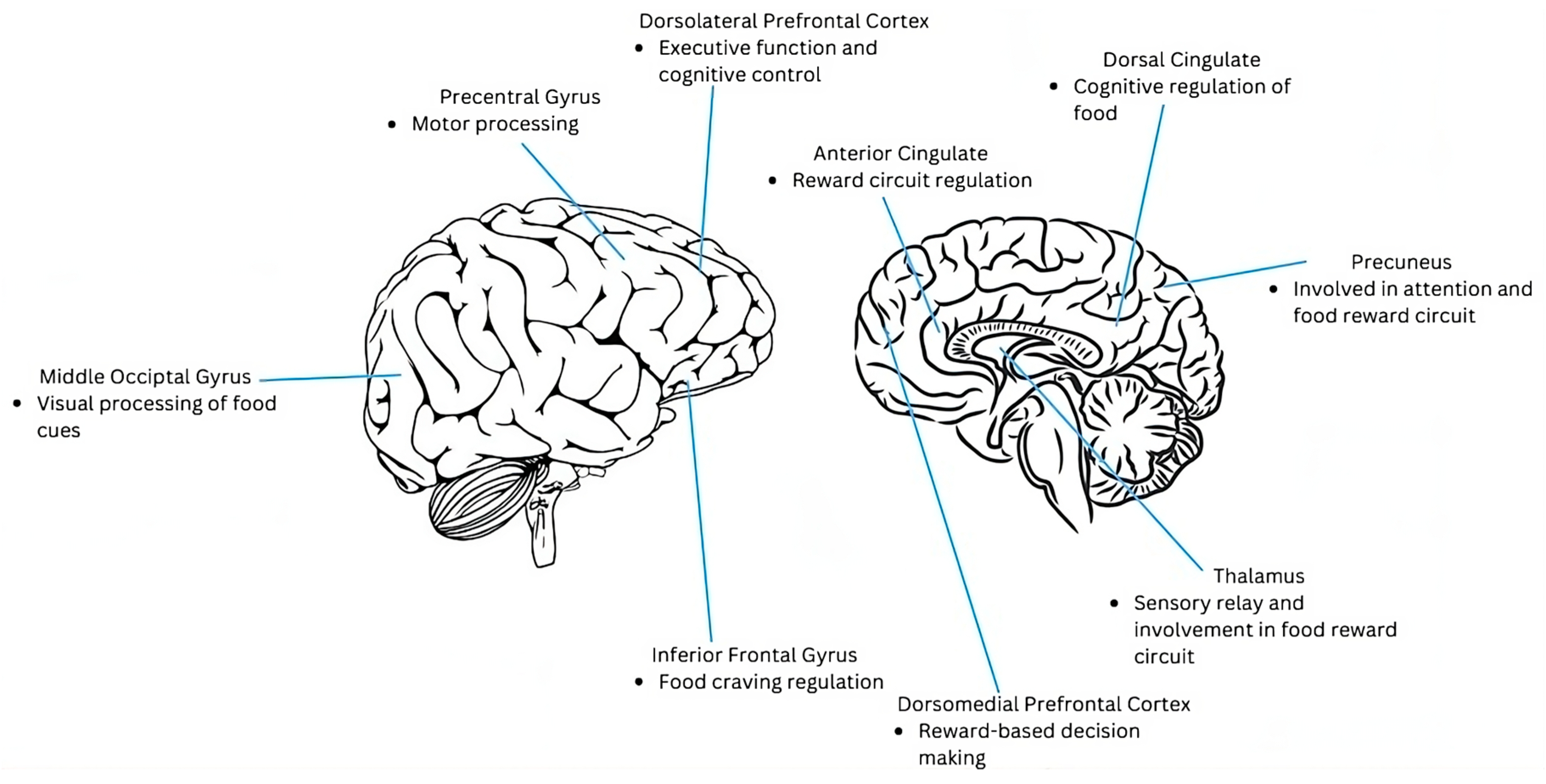
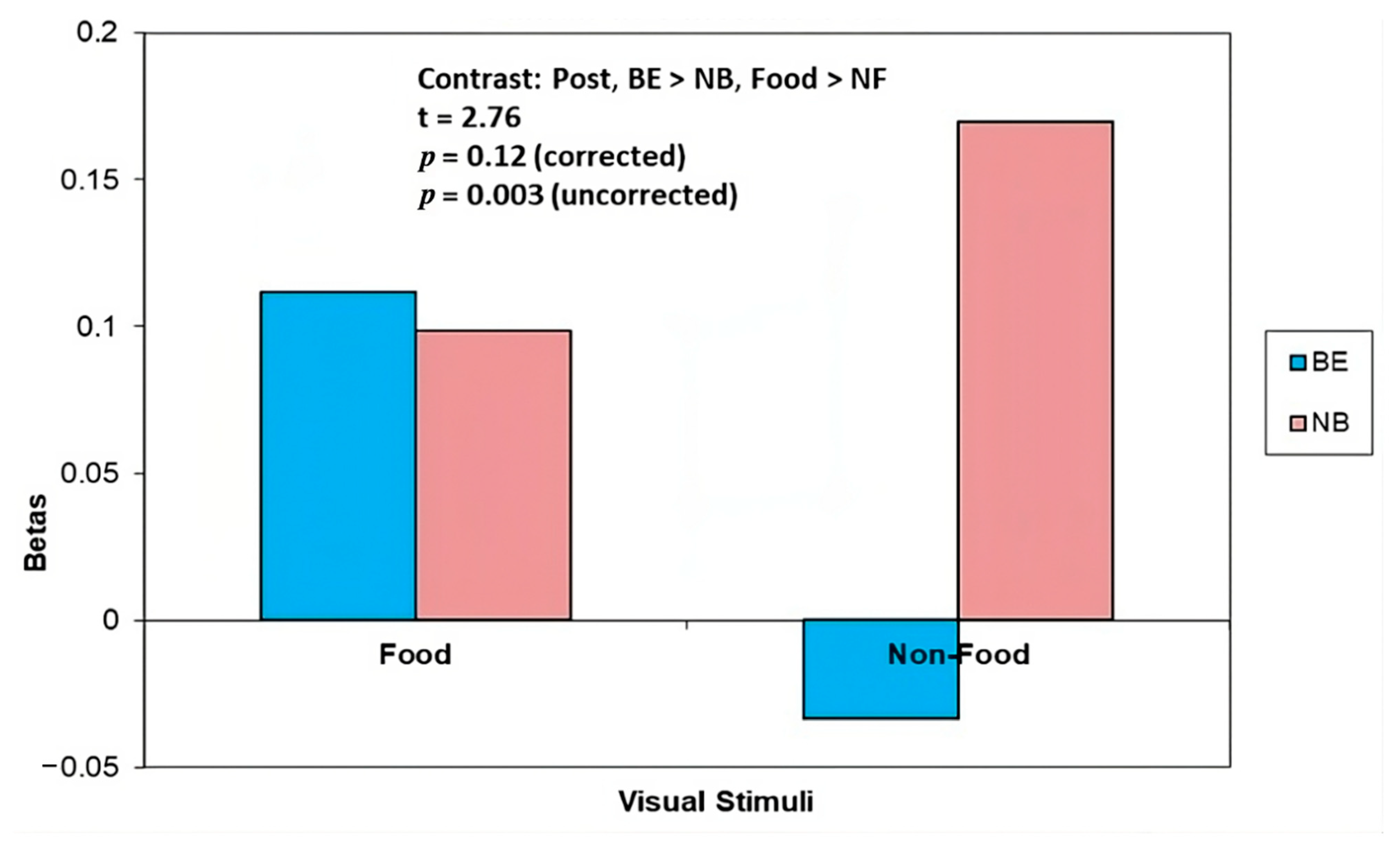
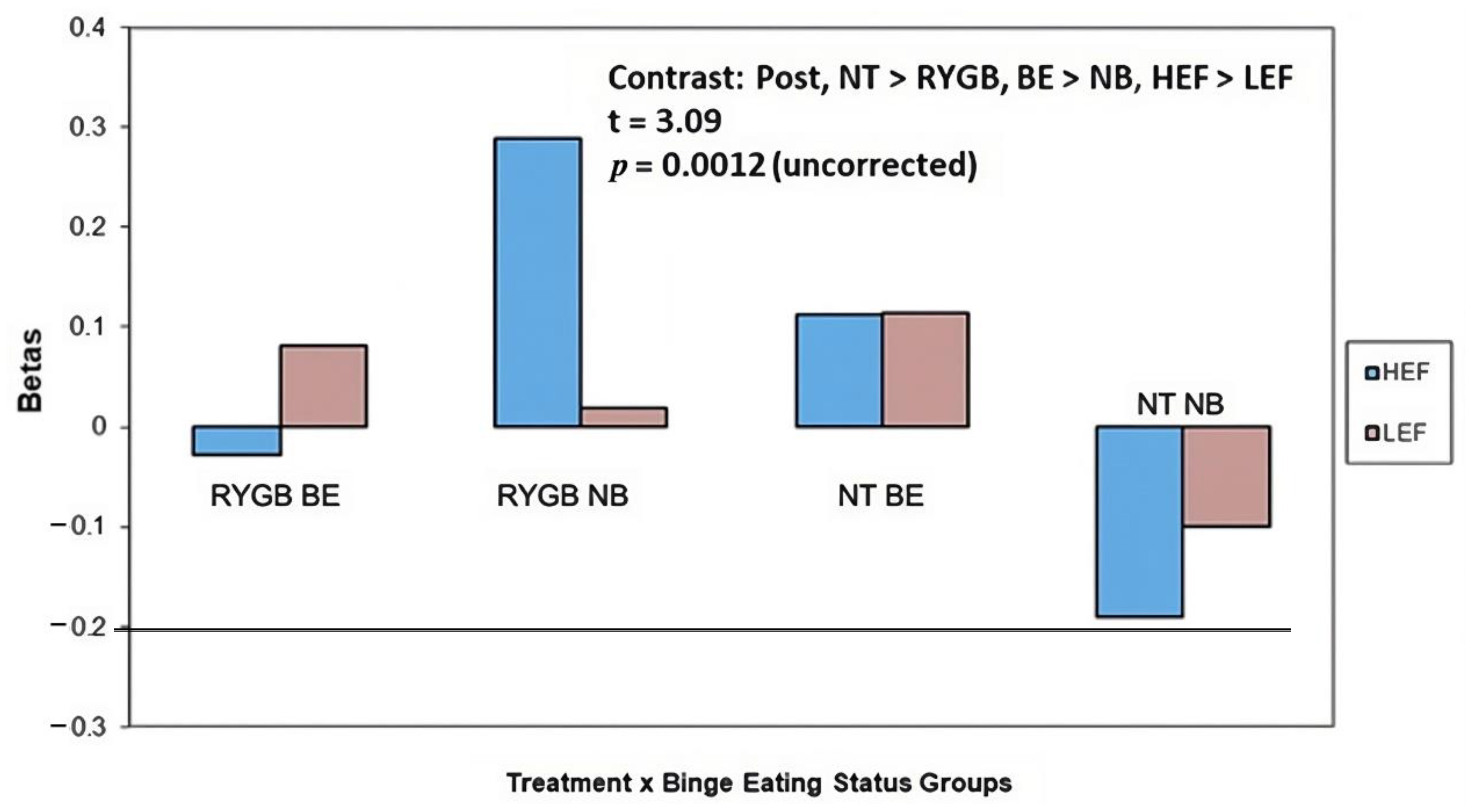
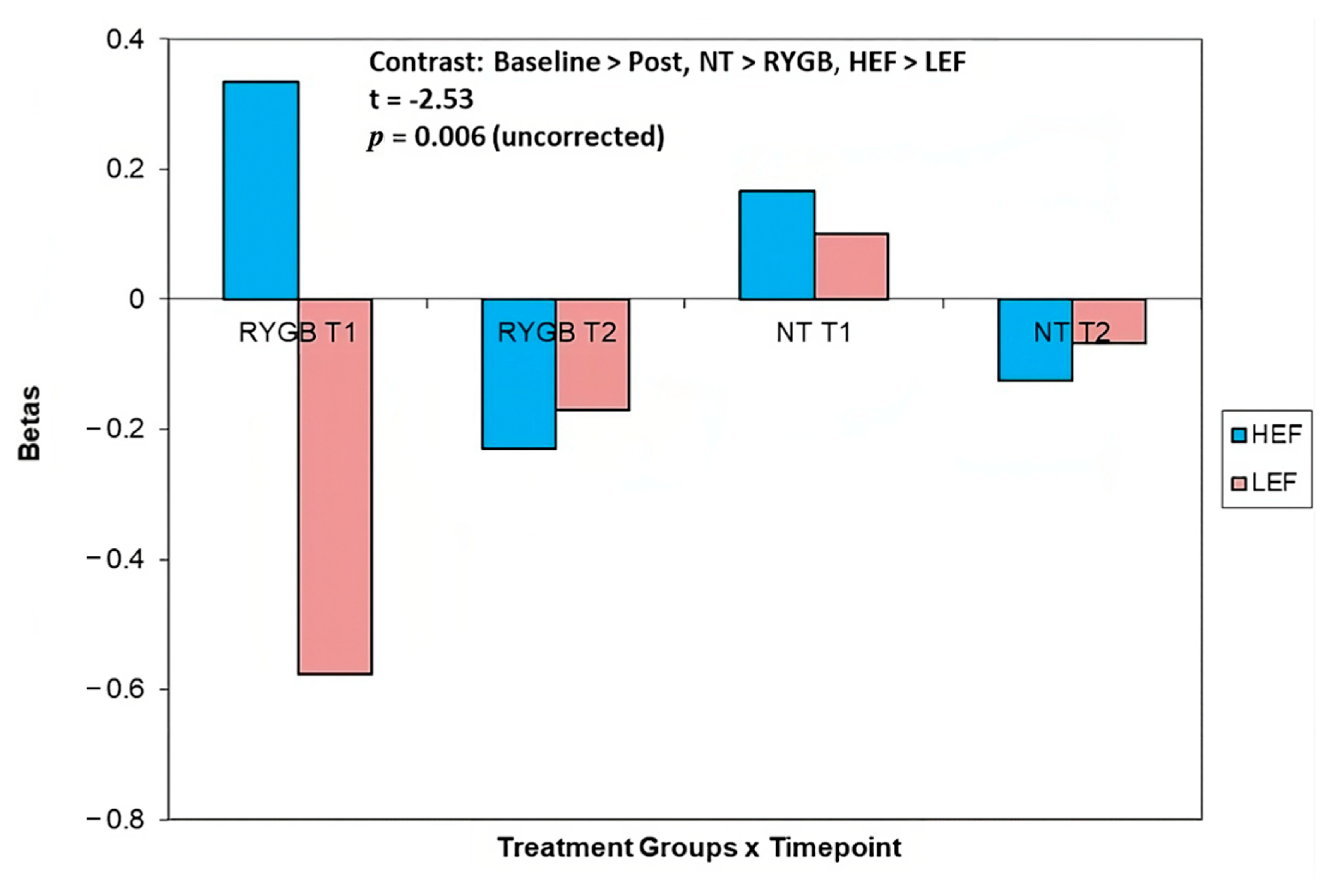
| ROI Coordinates (x, y, z) | ROI Label | Baseline BE > NB Food > NF | Post BE > NB Food > NF | Post NT > RYGB BE > NB HEF > LEF | Baseline > Post NT > RYGB HEF > LEF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −20, −64, 30 | Precuneus | 2.74 * | 2.76 * | 2.3 | −1.71 |
| 32, 36, 6 | Inferior Frontal Gyrus | 0.38 | 2.17 | 3.09 * | −1.14 |
| −6, 2, 36 | Dorsal Cingulate | 2.0 | 1.98 | 2.0 | −1.84 |
| 8, 58, 16 | Dorsomedial Prefrontal Cortex | 1.17 | −0.18 | 1.27 | −2.53 *a |
| 20, 38, 22 | Anterior Cingulate | 2.26 | 1.46 | 2.13 | −1.26 |
| −14, −22, 4 | Thalamus | 0.81 | 3.89 ** | 1.94 | −1.81 |
| 34, −70, 6 | Middle Occipital Gyrus | 1.16 | 0.41 | 3.06 * | −1.65 |
| 28, 22, 32 | Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex | 1.31 | 1.55 | 1.74 | −1.49 |
| −62, −12, 38 | Precentral Gyrus | 1.43 | 0.76 | 1.05 | −1.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baboumian, S.; Puma, L.; Swencionis, C.; Astbury, N.M.; Ho, J.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Geliebter, A. Binge Eating (BE) and Obesity: Brain Activity and Psychological Measures before and after Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB). Nutrients 2023, 15, 3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173808
Baboumian S, Puma L, Swencionis C, Astbury NM, Ho J, Pantazatos SP, Geliebter A. Binge Eating (BE) and Obesity: Brain Activity and Psychological Measures before and after Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB). Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173808
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaboumian, Shaunte, Lauren Puma, Charles Swencionis, Nerys M. Astbury, Jennifer Ho, Spiro P. Pantazatos, and Allan Geliebter. 2023. "Binge Eating (BE) and Obesity: Brain Activity and Psychological Measures before and after Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173808
APA StyleBaboumian, S., Puma, L., Swencionis, C., Astbury, N. M., Ho, J., Pantazatos, S. P., & Geliebter, A. (2023). Binge Eating (BE) and Obesity: Brain Activity and Psychological Measures before and after Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB). Nutrients, 15(17), 3808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173808






