Malnutrition Defined by the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) Criteria in Hospitalized Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Its Association with Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
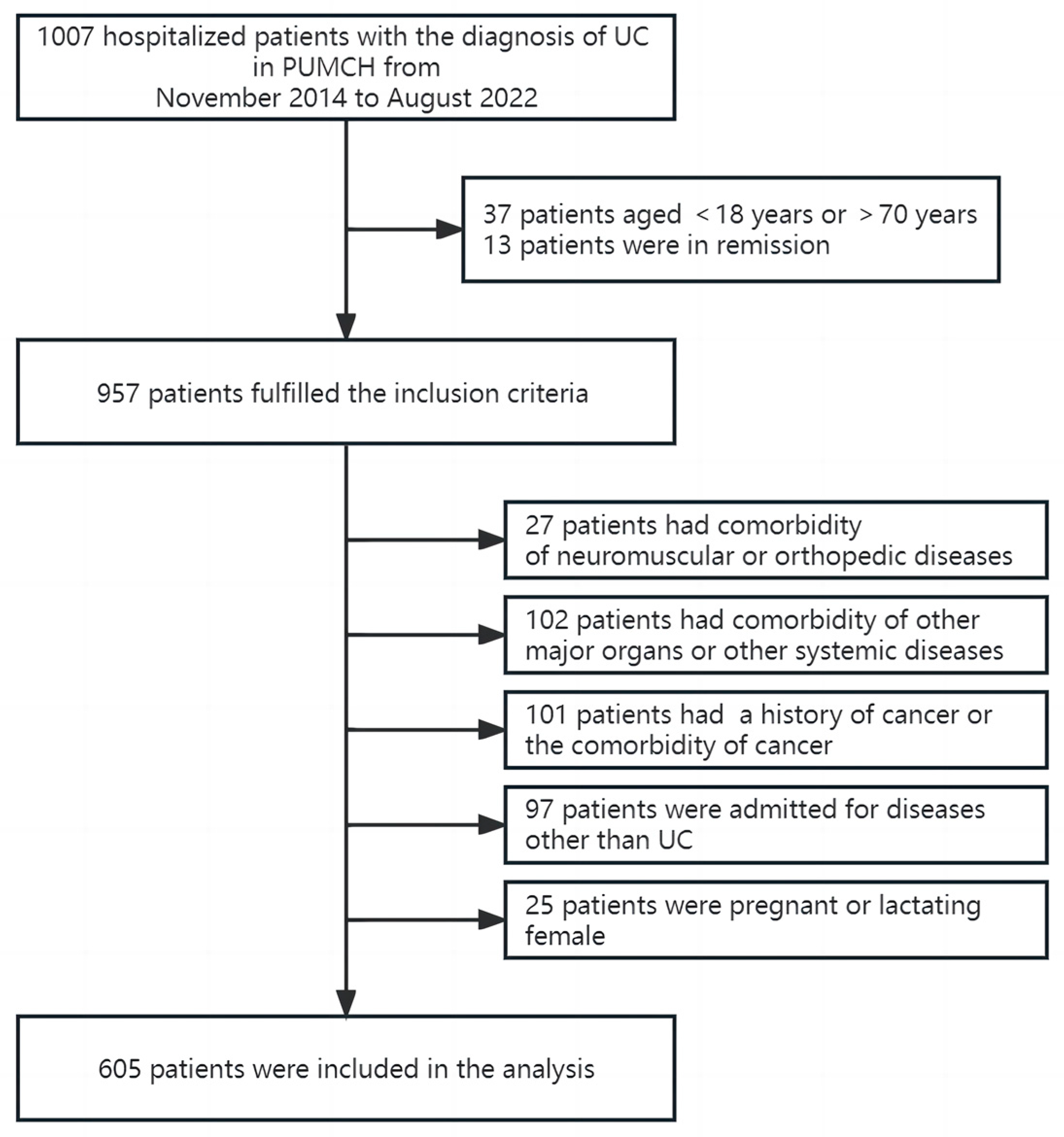
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Assessment of Nutritional Status
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of Malnutrition in UC Patients
3.3. Nutritional Support
3.4. Associations between Malnutrition and Prognosis in UC Patients
3.4.1. Extra-Intestinal Manifestations
3.4.2. Surgical Treatment
3.4.3. Opportunistic Infections
3.4.4. Length of Stay
3.4.5. Readmission
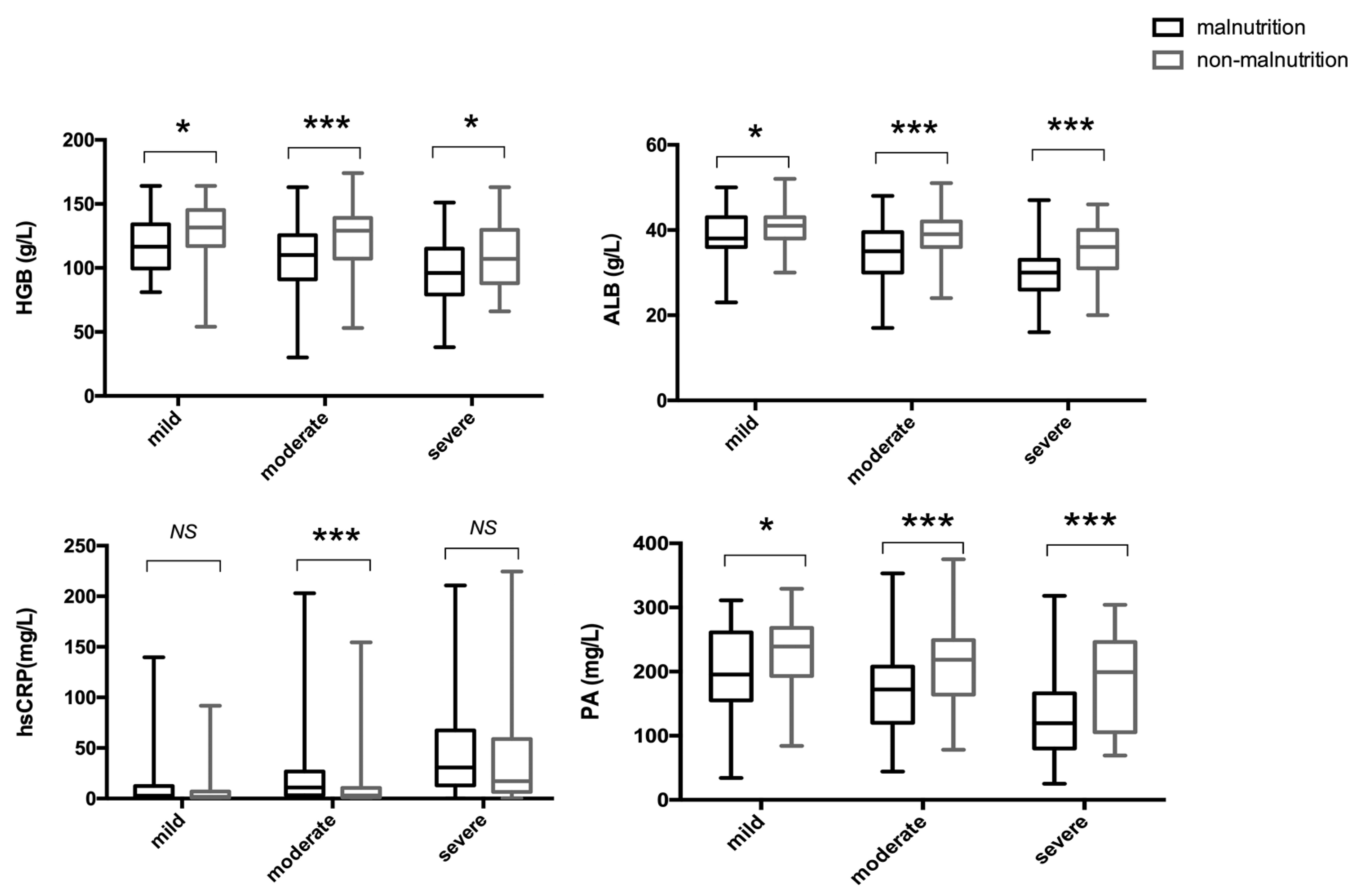
3.5. Associations between Malnutrition and Laboratory Indices in UC Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, T.; Wan, M.; Liu, G.; Zuo, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, X. Temporal Trends of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Burden in China from 1990 to 2030 with Comparisons to Japan, South Korea, the European Union, the United States of America, and the World. Clin. Epidemiol. 2023, 15, 583–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrieri, P.; Ribolsi, M.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Emerenziani, S.; Altomare, A.; Cicala, M. Nutritional Aspects in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ney, M.; Eslamparast, T.; Vandermeer, B.; Ismond, K.P.; Kroeker, K.; Halloran, B.; Raman, M.; Tandon, P. Systematic review of nutrition screening and assessment in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3823–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Escher, J.; Hebuterne, X.; Klek, S.; Krznaric, Z.; Schneider, S.; Shamir, R.; Stardelova, K.; Wierdsma, N.; Wiskin, A.E.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical Nutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 632–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Micic, D. Nutrition Considerations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021, 36, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, T.; Hanai, T.; Nishimura, K.; Unome, S.; Maeda, T.; Ogiso, Y.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, M. Usefulness of the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria to predict sarcopenia and mortality in patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2022, 52, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcı, C.; Tufan, G.; Özdemir, N.; Aksoy, S.; Öksüzoğlu, Ö.B.; Zengin, N.; Kars, A.; Halil, M. GLIM criteria as a valid tool for nutrition assessment and mortality prediction in treatment-naïve patients with cancer. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2023, 38, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.L.; Huang, D.D.; Pang, W.Y.; Zhou, C.J.; Wang, S.L.; Lou, N.; Ma, L.L.; Yu, Z.; Shen, X. Sarcopenia is an Independent Predictor of Severe Postoperative Complications and Long-Term Survival after Radical Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: Analysis from a Large-Scale Cohort. Medicine 2016, 95, e3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xi, B.; Yang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhao, M.; Bovet, P. Trends in the prevalence of overweight, obesity, and abdominal obesity among Chinese adults between 1993 and 2015. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Niu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Huang, A.; Wu, J. Characteristics of malnutrition according to Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria in non-surgical patients with irritable bowel disease. Nutrition 2021, 94, 111514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ge, X.; Ouyang, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J.; Zhu, W.; Cao, Q. Prevalence of Malnutrition, Its Risk Factors, and the Use of Nutrition Support in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, S59–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Dai, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Cao, Q.; Jing, X.; Jiang, H.; et al. Validation of the GLIM criteria for diagnosis of malnutrition and quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A multicenter, prospective, observational study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Midha, V.; Mahajan, R.; Verma, S.; Kakkar, C.; Grover, J.; Singh, D.; Kaur, R.; Masih, A.; Bansal, N.; et al. Evaluation of Nutritional Characteristics Reveals Similar Prevalence of Malnutrition in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.B.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Lim, W.K.; Maier, A.B. Prevalence of malnutrition comparing the GLIM criteria, ESPEN definition and MST malnutrition risk in geriatric rehabilitation patients: RESORT. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Krznaric, Z.; Pirlich, M. Diagnosis of malnutrition in patients with gastrointestinal diseases: Recent observations from a Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition perspective. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcil, V.; Levy, E.; Amre, D.; Bitton, A.; Sant’Anna, A.; Szilagy, A.; Sinnett, D.; Seidman, E.G. A Cross-Sectional Study on Malnutrition in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Is There a Difference Based on Pediatric or Adult Age Grouping? Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocirlan, M.; Ciocirlan, M.; Iacob, R.; Tantau, A.; Gheorghe, L.; Gheorghe, C.; Dobru, D.; Constantinescu, G.; Cijevschi, C.; Trifan, A.; et al. Malnutrition Prevalence in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Data from the National Romanian Database. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2019, 28, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Meyers, S.; O’Sullivan, P.; Barton, D.; Leleiko, N.; Janowitz, H.D. The metabolic impact of active ulcerative colitis. Energy expenditure and nitrogen balance. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1988, 10, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, Y.; Alexakis, C.; Mendall, M. Determinants of Weight Loss prior to Diagnosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Retrospective Observational Study. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 762191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, J.H.M.; Dijkhuizen, M.; Tap, P.; Witteman, B.J.M. Patient’s Dietary Beliefs and Behaviours in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. 2019, 37, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.J.; Chaparro, M.; Molina, B.; Merino, O.; Batanero, R.; Duenas-Sadornil, C.; Robledo, P.; Garcia-Albert, A.M.; Gomez-Sanchez, M.B.; Calvet, X.; et al. Prevalence of Malnutrition and Nutritional Characteristics of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.W.; Zisman, T.L. Interaction of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7868–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomer, M.C.E.; Cahill, O.; Baschali, A.; Partha Sarathy, P.; Sarantidou, M.; Mantzaris, G.J.; Gaya, D.R.; Katsanos, K.; Christodoulou, D.K.; Gerasimidis, K. A multicentre Study of Nutrition Risk Assessment in Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Attending Outpatient Clinics. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, E.; McNicholas, D.; Creavin, B.; Kelly, M.E.; Walsh, T.; Beddy, D. Sarcopenia and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.A.; Kennedy, N.A.; Raine, T.; Hendy, P.A.; Smith, P.J.; Limdi, J.K.; Hayee, B.; Lomer, M.C.E.; Parkes, G.C.; Selinger, C.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut 2019, 68, s1–s106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorindi, C.; Luceri, C.; Dragoni, G.; Piemonte, G.; Scaringi, S.; Staderini, F.; Nannoni, A.; Ficari, F.; Giudici, F. GLIM Criteria for Malnutrition in Surgical IBD Patients: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorindi, C.; Dragoni, G.; Scaringi, S.; Staderini, F.; Nannoni, A.; Ficari, F.; Giudici, F. Relationship between Nutritional Screening Tools and GLIM in Complicated IBD Requiring Surgery. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, M.A.; Hubner, M.; Demartines, N.; Larson, D.W.; Grass, F. Simple Clinical Screening Underestimates Malnutrition in Surgical Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease–An ACS NSQIP Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotto, D.; Atzeni, F.; Ardizzone, S.; Monteleone, G.; Giorgi, V.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Extra-intestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmiris, K.; Avgerinos, A.; Tavernaraki, A.; Zeglinas, C.; Karatzas, P.; Koukouratos, T.; Oikonomou, K.A.; Kostas, A.; Zampeli, E.; Papadopoulos, V.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Extra-intestinal Manifestations in a Large Cohort of Greek Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossum, A.M.; Palm, O.; Cvancarova, M.; Bernklev, T.; Jahnsen, J.; Moum, B.; Hoivik, M.L.; Group, I.S. The Impact of Spondyloarthritis and Joint Symptoms on Health-Related Quality of Life and Fatigue in IBD Patients. Results From a Population-Based Inception Cohort (20-Year Follow-up in the Ibsen Study). Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, R.B.; Taylor, K.M.; Morrissey, C.O.; Gardiner, B.J. Cytomegalovirus in inflammatory bowel disease: A clinical approach. Intern. Med. J. 2022, 52, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, R.S.; Allegretti, J.R. Diagnosis and management of Clostridioides difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 37, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, T.M.; Holubar, S.D.; Clancy, C.; Cheong, J.Y.; Jia, X.; Bhama, A.R.; Lightner, A.L.; Kessler, H.; Valente, M.; Liska, D. Outcomes of clostridioides difficile infection on inflammatory bowel disease patients undergoing colonic resection: A propensity score weighted NSQIP analysis. Am. J. Surg. 2023, 225, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sloot, K.W.J.; Voskuil, M.D.; Visschedijk, M.C.; Festen, E.A.M.; van Dullemen, H.M.; Weersma, R.K.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; van Leer-Buter, C.; Dijkstra, G. Latent cytomegalovirus infection does not influence long-term disease outcomes in inflammatory bowel disease, but is associated with later onset of disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannou, T.; Koeberle, S.; Manckoundia, P.; Aubry, R. Multifactorial immunodeficiency in frail elderly patients: Contributing factors and management. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. Lancet 2007, 369, 1641–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooren, C.; Wintjens, D.S.J.; de Jong, M.J.; van der Meulen-de Jong, A.E.; Romberg-Camps, M.J.; Becx, M.C.; Maljaars, J.P.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; Mahmmod, N.; Markus, T.; et al. Risk of impaired nutritional status and flare occurrence in IBD outpatients. Dig Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, B.R.; Kaysen, G. Serum albumin: Relationship to inflammation and nutrition. Semi. Dial. 2004, 17, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 605) | Malnutrition (n = 388) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 217) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female (%) | 263 (43.5%) | 176 (45.4%) | 87 (40.1%) | 0.210 |
| Age, years | 41.3 ± 12.8 | 40.7 ± 13.2 | 42.5 ± 12.2 | 0.107 |
| Age at diagnosis, years | 35.7 ± 12.5 | 35.9 ± 13.3 | 35.2 ± 11.1 | 0.466 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 20.8 ± 3.5 | 19.5 ± 3.0 | 23.2 ± 2.9 | <0.001 |
| Disease duration, months | 48 (12, 96) | 36 (12, 84) | 60 (24, 120) | <0.001 |
| Duration of follow-up, days | 459 (103, 1007) | 455 (110, 1043) | 486 (97, 970) | 0.763 |
| Length of stay, days | 15 (9, 22) | 18 (12, 26) | 9 (6, 15) | <0.001 |
| Disease Activity | <0.001 | |||
| Mild (%) | 114 (18.8%) | 39 (10.1%) | 75 (34.6%) | |
| Moderate (%) | 265 (43.8%) | 153 (39.4%) | 112 (51.6%) | |
| Severe (%) | 226 (37.4%) | 196 (50.5%) | 30 (13.8%) | |
| Disease extent | <0.001 | |||
| E1(%) | 25 (4.1%) | 6 (1.5%) | 19 (8.8%) | |
| E2(%) | 99 (16.4%) | 50 (12.9%) | 49 (22.6%) | |
| E3(%) | 481 (79.5%) | 332 (85.6%) | 149 (68.7%) | |
| Patients accompanied by opportunistic infection (%) | 153 (25.3%) | 126 (32.5%) | 27 (12.4%) | <0.001 |
| Patients with extra-intestinal manifestations (%) | 101 (16.7%) | 68 (17.5%) | 33 (15.2%) | 0.463 |
| Patients treated with surgery (%) | 79 (13.1%) | 65(16.8%) | 14 (6.5%) | <0.001 |
| Total (n = 516) | Patients with Readmission (n = 205) | Patients without Readmission (n = 311) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease duration, months | 48 (12, 96) | 36 (12, 84) | 48 (24, 120) | 0.001 |
| Disease Activity | <0.001 | |||
| Mild (%) | 93 (18.0%) | 24 (11.7%) | 69 (22.2%) | |
| Moderate (%) | 229 (44.4%) | 83 (40.5%) | 146 (46.9%) | |
| Severe (%) | 194 (37.6%) | 98 (47.8%) | 96 (30.9%) | |
| Disease extent | 0.142 | |||
| E1 (%) | 18 (3.5%) | 6 (2.9%) | 12 (3.9%) | |
| E2 (%) | 90 (17.4%) | 28 (13.7%) | 62 (19.9%) | |
| E3 (%) | 408 (79.1%) | 171 (83.4%) | 237 (76.2%) | |
| Patients accompanied by opportunistic infection (%) | 135 (26.2%) | 61 (29.8%) | 74 (23.8%) | 0.132 |
| Patients with extra-intestinal manifestations (%) | 75 (14.5%) | 37 (18.0%) | 38 (12.2%) | 0.066 |
| Prevalence of malnutrition (%) | 332 (64.3%) | 156 (76.1%) | 176 (56.6%) | <0.001 |
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malnutrition | 1.738 | 1.128–2.677 | 0.012 |
| Disease activity | 1.457 | 1.102–1.927 | 0.008 |
| Disease duration | 0.996 | 0.993–0.999 | 0.011 |
| Extra-intestinal manifestations | 1.505 | 0.898–2.525 | 0.121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, W.; Yan, P.; Wang, F.; Bai, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yu, K. Malnutrition Defined by the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) Criteria in Hospitalized Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Its Association with Clinical Outcomes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163572
Wei W, Yan P, Wang F, Bai X, Wang J, Li J, Yu K. Malnutrition Defined by the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) Criteria in Hospitalized Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Its Association with Clinical Outcomes. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163572
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Wei, Pengguang Yan, Fang Wang, Xiaoyin Bai, Jing Wang, Jingnan Li, and Kang Yu. 2023. "Malnutrition Defined by the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) Criteria in Hospitalized Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Its Association with Clinical Outcomes" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163572
APA StyleWei, W., Yan, P., Wang, F., Bai, X., Wang, J., Li, J., & Yu, K. (2023). Malnutrition Defined by the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) Criteria in Hospitalized Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Its Association with Clinical Outcomes. Nutrients, 15(16), 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163572





