Abstract
Psoriasis, an autoimmune chronic inflammatory skin condition, has a high incidence in the general population, reaching 2–4%. Its pathogenesis involves an interplay of genetic factors, immune disturbances, and environmental factors. Within the environmental factors that aid the appearance of this autoimmune skin disease, the Western lifestyle and overall diet play important roles in the steady growth in psoriasis prevalence. Furthermore, psoriasis is associated with comorbidities such as psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and obesity. Accumulating evidence suggests that obesity is an important risk factor for psoriasis. Moreover, obesity aggravates established psoriasis, and a reduction in the body mass index can improve the clinical outcomes of psoriasis and increase the efficacy of standard psoriasis therapies. The possible connection between this autoimmune disease and obesity relies on the fact that white adipose tissue is an essential endocrine organ that secretes an array of immune mediators and inflammatory and metabolic factors with pro-inflammatory action. Thus, immune-mediated mechanisms in both psoriasis and obesity conditions are common factors. This paper describes the factors that link obesity with skin autoimmune disease and highlights the importance of the stimulatory or regulatory effects of nutrients and food in psoriasis and the possible improvement of psoriasis through nutritional strategies.
1. Introduction
Psoriasis (Ps) is a chronic, multi-etiological disease with a profound inflammatory pattern. It is experienced by around 3% of individuals worldwide, affecting mainly adults. Ps is associated with various comorbidities [1] and patients having an overall decreased quality of life [2]. Genetic factors combine with extrinsic factors to initiate psoriatic lesions. Among the extrinsic factors, trauma, infections, various medications, exposure to sunlight, stress, habitual factors (e.g., alcohol, smoking), obesity, and endocrine factors add to the panel of factors that induce and sustain Ps [3].
From a histological point of view, a psoriatic lesion is characterized by the hyper-proliferation of keratinocytes and increased infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and neutrophils). A dermatologist will evaluate the Ps lesion area and severity index (PASI), body surface area (BSA), and dermatology life quality index (DLQI) in order to classify the severity of the disease in a psoriatic patient [4]. According to the recent 2021 classification, Ps patients are classified as having mild, moderate, and severe forms based on the combined use of the PASI, BSA, and sPGA (static Physician Global Assessment). sPGA is performed by the dermatologist to assess erythema, induration, and scaling. A recently published algorithm can identify severe forms in patients that meet two out of three criteria (PASI ≥ 11 or BSA ≥ 10 or sPGA ≥ 3), mild forms in patients that meet two out of three criteria (PASI ≤ 3 or BSA ≤ 5 or sPGA ≤ 2) and have a DLQI of <5, and moderate forms of disease for patients that do not meet two out of three criteria (PASI ≥ 11 or BSA ≥ 10 or sPGA ≥ 3) but have a DLQI of ≥5. This recent classification relies on a ranking algorithm that can aid dermatologists in monitoring the disease’s clinical evolution and establishing a specific therapy for the patient [5].
Recently, obesity has been suggested to be one of the factors that clearly influence psoriatic events; the association showed that there is an increased prevalence of obesity in psoriasis patients, compared with the general population [6]. Fatty tissue is a reservoir of endocrine and pro-inflammatory factors that overwhelm the body’s homeostasis and further induce systemic deregulation in multiple organs. A general scheme depicting the factors that are present in obesity and Ps is presented in Figure 1.
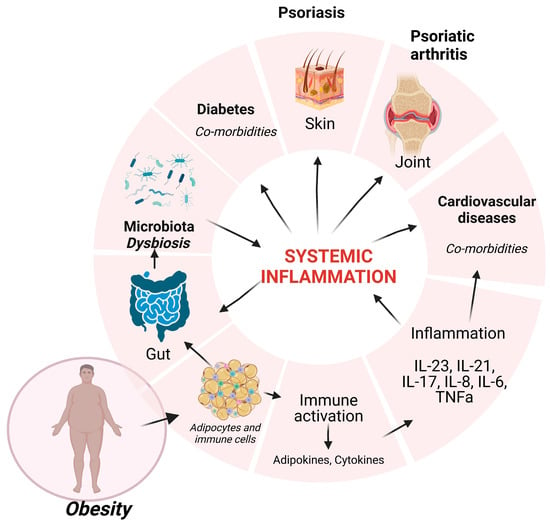
Figure 1.
Obesity influences the homeostasis of multiple systems. Adipocytes and immune cells resident in fat tissue induce pro-inflammatory factors that sustain chronic inflammation (IL-23, IL-21, IL-17, IL-8, IL-6, TNFα) that will generate systemic inflammation, inducing psoriatic events and comorbidities (diabetes, cardiovascular diseases). This systemic inflammation will deregulate the gut microbiota, and the induced dysbiosis will contribute to psoriasis. Created with BioRender.
Recent studies have evaluated nutritional regimens in psoriatic patients in order to improve the clinical outcomes of the disease. Clinical parameters associated with the metabolic profile and the inflammatory state of patients subjected to various diet regimens were evaluated. A low-calorie diet and a ketogenic diet, among others, improved all the tested parameters and clinically alleviated the psoriatic status of the patients [7,8].
Without being exhaustive, this review paper summarizes recent studies describing the link between Ps and obesity, the microbiota pattern inducing both obesity and autoimmune disease, a complex animal model of Ps and obesity that highlights new molecular mechanisms that govern these processes, and updated nutritional strategies that can contribute new adjuvant therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease.
2. Psoriatic Patients and Obesity
The multifactorial nature of Ps pathogenesis includes metabolic process disruption, among which obesity has been recognized as a novel risk factor with rising importance in Ps onset and severity. Both obesity and Ps are associated with a chronic pro-inflammatory status in which microbiome deregulation has been identified to play a leading role [9].
2.1. Obesity in Psoriasis Onset
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of ≥30 kg/m2, and this metabolic status poses both a significant global health concern and an economic burden [10]. In recent years, accumulating data has connected Ps incidence to excess body weight, as people suffering from Ps are usually overweight in comparison to the rest of the population. Interestingly, in May 2022, the WHO released a complex report that emphasized that obesity prevalence has almost tripled since 1975, and furthermore, over 60% of European citizens are overweight or even obese. The report highlights the cumulative inferences of the COVID-19 pandemic in respect of obesity, with all the repercussions that have resulted in terms of morbidity and mortality [11]. Obesity has thus acquired the roles of both a trigger and a contributor in the development of various diseases in which metabolic deregulation plays an important role, and Ps is one of these diseases. Moreover, a large meta-analysis of observational studies has suggested that obese people suffering from Ps have a higher risk of psoriatic arthritis, with a 6% surge in complications for every 1 kg/m2 increase in BMI [12].
Various studies have underlined novel insights regarding the severity of Ps lesions and the risk of obesity. Armstrong et al. explored the link between these two parameters in a meta-analysis that included over 2 million participants, of whom over 200,000 were patients with Ps. The authors showed that in Ps patients, the risk of obesity is over 50% compared to healthy subjects. Going further into the analysis, patients with more serious forms of Ps present a higher risk of obesity compared to patients diagnosed with the mild form. In addition, patients with Ps and normal body weight are prone to becoming obese in the future [13]. Along with more severe psoriatic lesions, psoriatic obese patients can also encounter several metabolic comorbidities (e.g., fatty liver, hyperlipidemia, etc.) that worsen their clinical disease profile. Additionally, an elevated BMI is a significant risk factor for many other disorders with a chronic autoimmune background, such as psoriatic arthritis (PsA) [10]. Moreover, patients with PsA experience serious metabolic- and inflammatory-driven comorbidities such as obesity, hypertension, or diabetes, as well as cardiovascular disease, in comparison with the general healthy population. The inflammatory milieu in PsA is attributed to adipose tissue, whose dysregulation maintains chronic low-grade systemic inflammation [14]. Therefore, in order to reduce the risk of developing metabolic complications, it is mandatory for Ps and PsA patients to control their BMI primarily through losing weight [15]. The most accessible strategy for lowering BMI and reducing adipose tissue in Ps patients is a low-calorie diet. Recently, diet as a potential therapeutic support method in Ps management has been exploited through the on-going Diet and Psoriasis Project, which aims to assess whether dietary factors are related to Ps severity (e.g., time-restricted eating vs. Mediterranean diet) [16].
According to various studies, body composition and body fat distribution are parameters that are more reliable than BMI, reflecting more accurately the patient’s nutritional status, and thus allowing observation of the in-depth correlation between weight and lesion severity, and monitoring the disease course. By using various refined methods that assess the nutritional status of psoriatic patients (e.g., bioimpedance analysis), the analysis of body composition has revealed that Ps is associated with elevated levels of body fat, visceral fat, and a diminished muscle mass [17], and thus bioimpedance analysis is endorsed as having a much better diagnostic power compared to BMI assessment alone [18].
Thus, the obesity–psoriasis–nutrition axis could be explored to decrease inflammation at the gut and skin levels. The result of such a strategy in terms of the disease course could be evaluated by measuring specific markers, such as decreases in C-reactive protein, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels; these parameters have been linked to a diet rich in soluble fibers [19].
2.2. Adipose Tissue Dysregulation in Psoriatic Patients
There are two forms of adipose tissue in humans: white tissue, which is the most abundant form and stores energy, and brown tissue, which is found especially in human newborns and plays an important role in regulating body temperature. Adipocytes are the most abundant cell type in white adipose tissue, along with pre-adipocytes (adipocytes that are unloaded yet contain lipids), endothelial cells, fibroblasts, leukocytes, and macrophages. Moreover, the number of macrophages in white adipose tissue has been found to be directly correlated with the degree of obesity [20].
Obesity can also be defined as an overbalance in the ratio between energy intake and energy consumption. As obesity evolves, body fat will excessively accumulate, giving rise to unhealthy white adipose tissue that becomes inflamed [21]. This adipose-related inflammation correlates further with chronic low-grade systemic inflammation. The specific low-inflammatory status is now a well-recognized mechanism for an increased risk of many serious pathologies (e.g., cardiovascular diseases), including those related to skin manifestation as Ps is [22,23].
In obesity, the alteration of adipogenesis is the leading step to the hypertrophy of adipocytes and further inflammation [24]. In this context, the modified adipose tissue will start to release a specific category of bioactive factor known as adipokines, whose types and levels depend on various factors such as the types of activated adipocytes (white or brown cells), number of cells, site, and interaction with other immune and non-immune cells. Moreover, in light of recent studies, adipose tissue should be considered not only a simple energy storage deposit but also a dynamic endocrine organ that actively intercedes in the regulation of inflammation, metabolism, and immunity, as well as in other physiological processes [25].
Studies in the last decade focusing on obesity onset have identified the entire flow of cellular processes involved in normal to hypertrophic adipose tissue transition, resulting in increased systemic inflammation and inhibition of adipogenesis. Excessive, unbalanced nutrition associated with other factors such as stress and/or a lack of physical exercise can lead to hypertrophy of adipocytes and eventually to obesity. Subsequently, mature adipocytes start to secrete free fatty acids and express an important array of pro-inflammatory adipokines (e.g., leptin, resistin, visfatin, chemerin, etc.) [26]. In addition, the expression of anti-inflammatory adiponectin is inhibited, which causes local inflammation and the recruitment of immune cells. There are increased numbers of locally infiltrating macrophages in obese adipose tissue, a process associated with fibrosis that also alters hormonal equilibrium [27]. Moreover, adipocytes and pre-adipocytes secrete a panel of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, including IL-6, CCL2, IL-1β, and TNF-α, which fuel low-grade systemic inflammation in obese individuals and induce metabolic syndrome [28].
In Ps patients with a severe course of the disease, increased blood levels of pro-inflammatory adipokines have been observed, and during lesion remission, these levels were found to be decreased. Additionally, serum levels of the anti-inflammatory adipokines omentin and adiponectin are significantly lower in patients with severe disease compared to patients with mild forms of Ps [28].
Considering the role of obesity in Ps development, some adipokines have been thoroughly studied in relation to the inflammatory milieu and severity of lesions. Studies from the last decade have claimed a role for adiponectin in the pathogenesis of Ps [29].
Adiponectin levels control a series of cytokines and the immune cellular balance of certain T lymphocyte subsets. Thus, in keratinocytes from Ps lesions, adiponectin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis and increases the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines [30,31]. At a cellular level, this would be translated as a restoration of the Th1-Th17/Th2 lymphocyte ratio, hindering IL-17A synthesis as a key part of adiponectin’s anti-inflammatory effects [32].
Adiponectin plasma levels correlate with a Ps patient’s weight and clinical outcomes. In the plasma of Ps patients, there are lower levels of adiponectin, resulting in an increased pro-inflammatory cytokine pattern and a decreased anti-inflammatory cytokine milieu [33], which may aggravate the severity of skin lesions [12]. Alternatively, with weight loss, the concentration of circulating adiponectin increases, concomitant with psoriatic lesion improvement [34].
Another adipokine, leptin, is involved in regulating the body’s energy balance and weight [35] by raising lipolysis and lowering hepatic lipogenesis [36]. In patients with obesity and psoriatic patients, leptin levels were found to be significantly increased, with a high level of leptin being directly correlated with BMI and with the PASI score [37]. Like adiponectin, leptin is responsible for increasing the pro-inflammatory cytokine pattern, which causes and favors keratinocyte proliferation. In addition, at the cellular level, leptin can impact T helper and dendritic cell functions, thus affecting the immunity processes in Ps [38].
Resistin is another adipokine currently regarded as a potential biomarker in Ps pathogenesis, as it induces a series of molecular and cellular events in psoriatic skin. Resistin is synthesized in adipose tissue mostly by macrophages and monocytes under pro-inflammatory conditions [39]. Further, resistin can induce keratinocyte proliferation via pro-inflammatory factors secreted by B lymphocytes [32]. Impacting the cellular immune network at the skin level, resistin plays an important role in Ps, as resistin can affect both the number and proliferation capacity of Foxp3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells. These deficiencies in Treg cell functionality reinforce the immune-related deregulation in Ps [40]. Prior studies have indicated a direct correlation between Ps severity and plasma resistin levels [41], while elevated plasma resistin levels in patients with Ps were strongly correlated with the DLQ index [32].
Chemerin is an adipokine produced mainly in white fat adipocytes, but is also produced by hepatocytes, and plays a role in the pathophysiology of Ps [42,43]. Although the precise function and mechanism of Ps pathogenesis are still in debate, positive correlations between systemic chemerin and obesity-related phenotypes (insulin resistance, BMI, serum triglycerides, etc.) have been registered, suggesting an important function of chemerin in metabolic diseases [44]. Another positive correlation between chemerin levels, inflammatory cytokines, and C-reactive protein was reported in Ps [45,46]. Chemerin acts as a chemotactic factor for human blood plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), promoting their migration and recruitment in psoriatic skin [47]. Skin exhibiting early and active lesions shows high expression of chemerin in the dermis, while skin exhibiting chronic lesions has low chemerin expression, associated with few pDCs in the dermis. Chemerin expression has been found to be upregulated mainly in fibroblasts linked with higher levels of chemerin mRNA than fibroblasts from healthy or unaffected psoriatic skin. Therefore, chemerin expression specifically labels the early phases of evolving skin psoriatic lesions [48]. The upregulation of chemerin in Ps was assessed in a recent study involving an imiquimod-induced mouse model of Ps. It was observed that intraperitoneal inoculation of an anti-chemerin antibody reduced epidermal proliferation and inflammation in the experimental mice, indicating that chemerin promotes keratinocyte proliferation and enhances the production of inflammatory cytokines, thereby aggravating the Ps. That study proposes chemerin as a forthcoming target for Ps treatment [49].
Other important adipokines, including retinol-binding protein-4, fetuin-A, and lipocalin-2, are being studied as potential mediators in obesity and Ps, although further studies are needed to support this hypothesis [34]. Nevertheless, apart from the cellular and molecular events that cause prolonged inflammation fueled by an array of pro-inflammatory markers, there is another component that impacts the behavior and lifestyle of obese psoriatic patients. Hence, the comorbidity picture of these individuals is completed by depression as a psychological stressor that contributes to the development of anxiety disorders [50,51]. Therefore, understanding the molecular mechanisms of the alterations suffered by adipose tissue in obesity is important because, through the metabolic and functional disorders suffered during the onset of obesity and through maintaining an inflammatory environment, adipose tissue could be analyzed as a potential multifaceted target in the management of obesity in Ps [27].
2.3. Microbiota in Obese Psoriatic Patients
Contributing to the multifactorial etiology of Ps, an altered microbiota can be an important trigger in obesity development, as a strong relationship has been documented between the microorganisms that inhabit internal and external body surfaces and are present in autoimmune diseases [52]. Firmicutes, Bacteroides, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria represent >98% of the gut microbiota. In respect of Ps, several studies have demonstrated that the relative abundances of Proteobacteria and Bacteroides decrease while the relative abundances of Actinobacteria and Firmicutes increase [53,54]. Like in Ps, in obese subjects, changes in the gut microbiota composition have been registered and significant alterations have been observed in the Firmicutes and Bacteroidota (F/R) ratio compared to normal-weight subjects. The F/B ratio is now broadly recognized as a critical marker in controlling normal gut homeostasis and is an important indicator of the gut microbiota’s status [53]. Variations in F/B lead to dysbiosis, and this ratio was found to be increased in obesity and decreased in some inflammatory conditions, such as Ps [55] and inflammatory bowel disease [56,57]. Some microbiota disturbances at the level of Clostridium innocuum, Eubacterium dolichum, Catenibacterium mitsuokai, Lactobacillus reuteri, Lactobacillus sakei, and Actinobacteria have also been described in obesity, reinforcing gut microbiota dysbiosis as one of the crucial characteristics of this condition [58]. Moreover, in obese psoriatic patients, a state of chronic inflammation is fueled by pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipokines generated by white fat adipocytes and characterized by high levels of IL-17, IL-23, TNFα, and IFNγ, supporting the relation between the microbiome and obesity in psoriatic individuals [59,60,61]. The volume of research in the field that is focused on the comorbidities of Ps is increasing, and recent studies have proved that the intestinal microbiota in patients with obesity suffering from Ps undergoes changes in terms of composition and abundance [62].
3. Animal Experimental Models—Direct Proof of the Link between Psoriasis and a High-Fat Diet
Gut and Skin Microbiome in Animal Models of Psoriasis
Animal models are important tools by which to study skin autoimmune diseases and the mechanisms that underlie their generation [63]. Within the animal models used in this area, imiquimod (IMQ)-induced Ps mice were historically used in the first established model and, hence, are the most commonly used subjects. IMQ is basically a toll-like receptor 7 (TLR-7) agonist that induces skin inflammation in mice, the inflicted skin condition having Ps characteristics [64]. In this type of model, several important clues have been found regarding the skin–gut axis. It was reported several years ago that depletion of the microbiota using antibiotics ameliorated Ps skin inflammation [65], as the microbiota was disturbed by Ps induction [66]. Lactobacillus predominates in the gut microbiota of Ps mice treated with antibiotics [67]. The skin neuroendocrine system has specific activities [68] and regulates several important pathways, such as the inflammatory status and microbiome elements. Skin neuroendocrine system deregulation can cause known inflammatory-mediated pathologies such as Ps, allergies, or atopic dermatitis [69].
Contradictory results have been published regarding the skin microbiota in the Ps-model context, but a recent study has shown that in this model, significant deregulations can be found in the alpha- and beta-types of bacteria comprising the skin’s microbiota. In the gut microbiota, the species Lactobacillus intestinalis, Lactobacillus reuteri, and Bacteroides uniformis were identified in IMQ mice. Additionally, in the skin microbiota, the species Staphylococcus lentus was identified in IMQ mice. Moreover, correlations between some microbes residing in the intestine and the skin were observed, sustaining the skin–gut–microbiota link in Ps animal models [70]. Lactobacillus intestinalis, Lactobacillus reuteri, and Lactobacillus taiwanensis were found to be significantly higher in the guts of Ps mice [70], and, interestingly, knowing the beneficial actions of Lactobacillus reuteri on the host immune system [71], it seems that in this mouse model, a compensatory immune response was obtained.
In another recent study using a gnotobiotic mouse model of Ps, several new additional clues were identified regarding the skin–gut microbiota in the context of experimental Ps [67]. Previously, it was shown that the presence of intestinal microbiota promotes IMQ-induced skin inflammation and augments the Th17 response [72]. During IMQ-induced skin inflammation, it was shown that there was a decrease in skin microbial diversity. This process was also shown in patients with Ps [73]. Milder skin inflammation in mice is associated with an abundance of Proteobacteria and low abundances of Staphylococci and Streptococci [73].
In another animal model of IMQ-induced Ps, stool samples from healthy donors and Ps patients were used to populate mice’s gut flora. The evolution of Ps in the IMQ-induced mice was aggravated when Ps patient stool was used in comparison to the healthy donor stool. Actually, healthy fecal microbiota protected against the Treg/Th17 imbalance. Sequencing of 16S rRNA showed that Lactobacillus reuteri is enriched in the fecal and cutaneous microbiomes of healthy mice compared to Ps mice. Adding Lactobacillus reuteri induced the expression of the anti-inflammatory gene IL-10, reducing the Th17 cell populations and inflammation in Ps mice with gut microbiota dysbiosis [74].
With the advent of genetic engineering technologies, several Ps-mouse models have been designed to overexpress or eliminate gene(s) of interest [75]. There are known to be a few global gene knock-in or knockout mouse models developing a Ps-like phenotype (Supplementary Material Table S1) or other genetic designs that modulate mutant alleles [76,77]. Supplementary Material Table S1 presents the main engineered mouse models of Ps [78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85].
Other new animal models involve cell-specific overexpression. The cloning methodology has offered researchers models using KC-specific promoters (keratin [K] 5, K10, K6, K14, involucrin, and loricrin) that overexpress an array of cytokines, adhesion molecules, growth factors, and hormone levels [86,87,88,89,90], leading to inflammation (Supplementary Material Table S2). Moreover, in a K14eIL17Aind/þ mouse model, an increase in circulating IL-17A promotes vascular inflammation, arthritis, and ocular inflammation [89,90].
Other models with mutations in the CARD14 gene have caused Ps and matched the finding that in Ps patients, CARD14 mutations were detected [91]. The Card14E138A/þ (gain-of-function) and Card14DQ136/þ mutations induced in mice spontaneous Ps-like skin inflammation with increases in IL-23/IL-17A cytokine production [88,92]. Moreover, genetically engineered models have been challenged with various pro-inflammatory cytokines to augment skin inflammation. These acute IL-23-induced animal models [93] and Rag2e/e mutated mice [94] provided information regarding various cellular and molecular events within Ps development.
IMQ-induction in, e.g., IL17ra mouse models, has shown the contributions of cell type and gene expression in Ps development [95]. In very new Ps animal models, it was demonstrated that the topical application of small interfering RNA (siRNA) can target genes of interest. The models are evolving, although some cost limitations will hinder their large-scale utilization. Although costly, this approach is more efficient in terms of time–cost parameters compared to the new lines of engineered mouse models [96,97,98].
Animal models have shown that deregulations of the microbiome induced by the Western diet can elicit inflammation and impact the severity of the Ps phenotype [99].
Results obtained from the aforementioned animal models of Ps have shown that gut microbiota dysbiosis influences the development of Ps and therefore it could be a potential therapy target in Ps patients.
4. Nutritional Therapeutical Strategies in Psoriasis
4.1. Skin–Gut Link—Inflammation Is the Trigger of Deregulation
The notion of an axis that links the gut and the skin, influenced by the microbiome, has gained increased importance in the last few years. The inflammation that resides in the largest human organ, the skin, can induce malfunction of the intestinal barrier and, hence, gut microbiome deregulation and sustained inflammatory mediators/metabolites that contribute to systemic inflammation [53,100,101]. There is cross-talk between the gut microbiota and elements of the immune system, in which the gut microbiome has an important role in the development and regulation of the immune system’s innate and adaptive components [102]. Any disorder of the gut microbiome can trigger an immune response [103]. Inflammation that is both localized and systemic can be induced by microbiota alterations residing on the epithelial surface. In inflammatory bowel disease patients, bacteria deregulation that induces local inflammation leads to mucosal damage and increased permeability of the gut mucosa [104]. This damage increases the pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-12, IFN-γ) that will leak into the systemic circulation, spreading the inflammation [104]. While Ps is a skin disorder, it has a clear systemic inflammatory pattern [105] because it induces inflammation in other organs and systems. Moreover, as already stated, Ps is associated with metabolic disorders [106]; hence, Ps patients can have increased BMI, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes, coronary artery disease, and so on [107], all of which describe the main Ps comorbidities [28].
In the last few years, abundant studies have researched the link between skin physiological integrity and gastrointestinal health, showing strong cross-talk between the skin and the gut [108,109]. Ramírez-Boscá et al. showed several years ago that bacterial DNA that appends to the gut microbiome can be identified in the peripheral blood of Ps patients [110]. Recent technologies (e.g., next-generation sequencing protocols) have been thoroughly used to investigate the complex intestinal microbiota composition [111].
The notion of a gut–skin axis relies on two equally important players: the microbiome and skin autoimmunity. Ps is aided by the deregulation of the intestinal barrier, an increase in inflammatory mediators, and the systemic effect of bacterial metabolites [53].
The gut microbiome comprises diverse bacterial species, protozoa, viruses, and fungi. These populations are found mainly in the lower gut and are in a symbiotic relationship with the human host [112]. Aerobic species are specific to the small intestine, while anaerobic species are found in the colon [113]. The main bacterial phyla within the gastrointestinal tract are Firmicutes (Bacillota), Bacteroidota, Actinobacteria, and Proteobacteria. The actual composition depends on the host’s diet, age, and environmental conditions [114]. In addition to diet and lifestyle, genetic predisposition defines gut microbiome individuality [115].
The symbiotic gut microbiome is crucial to intestinal permeability regulation, metabolism, and the functioning of the immune system [116]. It is known that the gut microbiome triggers immuno-protective responses against potential pathogens, having an indirect effect on the immune system. Concomitantly, the gut microbiota can have a direct effect by binding competitively to epithelial cells, inducing immune tolerance to environmental and dietary antigens [117].
The notion of “gut dysbiosis”, representing a composition and biodiversity imbalance, was found to be associated with Ps and its comorbidities, e.g., inflammatory arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, depression, and obesity [118,119]. As the gut microbiome deregulates skin homeostasis [120], the assertion was also proven to be correct in the opposite case, as many gastrointestinal diseases have skin manifestations [121]. Gut dysbiosis causes negative impacts on skin integrity and function [122,123]. At the molecular level, microbes disrupting the intestinal barrier and skin homeostasis interfere with mucosal immunity components and signaling pathways that regulate epidermal differentiation [124]. As previously mentioned, the metabolites of gut microbes can inflict cutaneous pathology and hinder the immune response [125]. Bacterial metabolites such as p-cresol and phenol synthesized by Clostridioides difficile have been proven to be gut dysbiosis biomarkers. These metabolites can enter the blood circulation and accumulate on the skin, causing skin dryness, disrupting the skin’s function as a physical barrier, hindering epidermal differentiation, and affecting keratinization [126]. Innate and adaptive immune arms are also affected by dysbiosis in Ps [127,128,129]. The main immune cell found to be deregulated in Ps is the T cell, where its function and differentiation are altered; these processes have a clear imbalance in Treg and Th17 [67,130].
The molecular link between the microbiome and the immune system is established through the coupling of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and their receptor pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). In this family of receptors, toll-like receptors (TLRs) and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing proteins (NODs) are the receptors expressed by a variety of the host’s immune cells. The gut microbiome is the main source of peptide-glycans, molecules that prime innate immune cells via two PRRs (e.g., NOD1, NOD2) expressed by an array of cells, from intestinal epithelial cells such as Paneth cells to immune cells such as macrophages and DCs [131]. Paneth cells, residing at the base of the small intestinal mucosa crypts, have an important role because they secrete key mediators of host–microbe interactions, balancing the colonizing microbiota and the immune protection against enteric pathogens [132]. NODs are also very important, as demonstrated in Nod1- and Nod2-deficient mice, which exhibit a weakened intestinal barrier to microbes and decreased production of antimicrobial peptides, a- and b-defensins, and RegIII-gamma [131]. In humans, individuals that bear mutations in NOD2 have a high susceptibility to Crohn’s disease development [133,134].
Thus, the host’s PRRs interaction with bacterial antigens induces immune system priming by commensal bacteria [128]. In addition to innate immunity, the adaptive arm is influenced by commensal bacteria. Therefore, this interaction balances the effector T cell population and Treg cells. Moreover, B cell activation leads to specific immunoglobulin A production [135]. In a recent animal model of induced Ps, it was demonstrated that gut dysbiosis enhances Th17-induced skin inflammation [67]. Furthermore, the action of Th-17 affects metabolite production and immune cell activation through the IL-23/IL-17 axis signaling pathway, with these processes inducing keratinocyte hyperproliferation [115]. In animal models, it was shown that the gut microbiome and gut dysbiosis induce chronic systemic inflammation due to pro-inflammatory cytokines unbalancing activated effector T cells and increasing epithelial permeability [101,128]. Gut dysfunction and inflammation were observed in Ps patients [53,136] because the specific alterations in the metabolic gut environment were based on the activation of specific PRPs expressed on the gut epithelial cells. Gut permeability increases as inflammatory cytokines like TNF modify the integrity of epithelial cell junctions. This phenomenon activates effector T cells and unbalances Treg cells, and, hence, autoimmune reactions develop. Chronic systemic inflammation is installed, and metabolites, toxins, and bacteria will enter the systemic circulation as the intestinal barrier is hindered [137]. In the circulation, lipoteichoic acid and lipopolysaccharides are shed from the circulating microorganisms, further promoting the pro-inflammatory status [138]. Endotoxin-peptidoglycan superantigens are related to the autoimmune status of Ps. It was shown that Ps patients test positive for toxins from gut bacteria antigens in skin tests. Hence, biomarkers indicating intestinal permeability (e.g., claudin 3 and fatty acid binding protein) can be found to be elevated in Ps patients [138]. If these alterations in the intestinal microbiota are already a certainty in Ps and obesity, the need to assess these changes has accelerated research towards the discovery of biomarkers to evaluate the affected intestinal barrier. Thus, in a recent study highlighting the gut microbiome’s impact on skin health, high levels of claudin-3 and intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as biomarkers of an injured intestinal barrier have been detected in Ps patients [57,139].
4.2. Nutritional Strategies—Reducing Obesity and Inflammatory Status Is the Main Target
4.2.1. Low-Calorie Diet
A recent meta-analysis of the studies that link diet to Ps [140,141] has shown that a low-calorie diet is the most important type of diet that induces clear clinical benefits in Ps. Earlier studies have shown that a caloric restriction of 500 kcal below the calculated dietary requirement and comprising 60% carbohydrate, 25% fat, 15% protein, and an exercise level of 40 min at least 4 times per week improves Ps clinical symptoms considerably. After 24 weeks of this regimen, in the diet group, PASI scores of 75 and 50 were achieved by a significant number of patients [142]. New data that evaluated caloric restriction in Ps patients have shown a regression in the lesions after 4 weeks of dieting. Moreover, a significant reduction in the standard parameters was recorded (DLQI, VAS pain, and VAS pruritus), while PASI scores showed a significant 50% reduction [7]. Ps is known to lead to deregulated biochemical parameters in terms of folic acid, vitamin B12, calcium, bilirubin, cortisol, LDL, and total cholesterol [143]. After the diet, all these parameters significantly improved. As high levels of folic acid and vitamin B12 improve the clinical condition in Ps [143], patients subjected to caloric restriction showed increases in these parameters, and their clinical outcomes improved. Hypocalcemia is another risk factor in Ps. The low-calorie diet [7] indicated an increase in calcium. An antioxidant metabolite, bilirubin, is registered in low concentrations in Ps patients [144], and after dieting, its concentration increases. Low cortisol levels are associated with the psoriatic condition, probably related to the stress that is experienced by these patients [145], and after dieting, the cortisol levels increased [144].
As there are several co-morbidities associated with the Ps condition, the alleviation of these comorbidities has also been studied in the low-calorie regimen. Hence, Ps is associated with cardiovascular diseases. Peripheral arterial tonometry, plasma markers of endothelial function, and standard cardiovascular parameters were evaluated in Ps patients. A low-calorie diet (e.g., 800–1000 kcal/day for 8 weeks) continued for 8 weeks at 1200 kcal/day in Ps patients induced significant reductions in blood pressure and resting heart rate, along with the normalization of several other biochemical parameters (total cholesterol, very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor) [146].
The Mediterranean diet, as opposed to the Western diet, was also studied in the Greek population and linked to Ps. A study published in 2019 showed a decrease in PASI scores when patients had a diet rich in vegetables, fish, and extra virgin olive oil, whereas there was an increase in the PASI when the diet was rich in dairy products [147].
4.2.2. Gluten-Free Diet
A gluten-free diet represents avoidance of this protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, with a benefit for Ps patients [148]. Interestingly, gluten intake increased the risk of Ps in patients already diagnosed with celiac disease [149]. Moreover, IgA antigliadin (AGA), which is an antibody common for celiac disease, was also found to be increased in Ps patients [150].
Over 20 years ago, positive results were published in Ps patients consuming a gluten-free diet for 3 months, significantly improving their PASI score [151]. The same group has shown that AGA-positive patients subjected to a gluten-free diet had a reduction in Ki67-positive cells in their psoriatic lesions [152,153], meaning a less proliferative status of the lesions. Other groups confirmed that one year of a gluten-free diet improved the PASI score in groups that had high levels of IgA against gliadin peptides [154].
4.2.3. Supplements
Fish oil has been involved in many supplements that Ps patients use in order to alleviate their symptoms. In 2014, a meta-analysis of several studies regarding fish oil supplementation in Ps observed that while some studies have shown moderate results, others have not found any relevance [155]. Recently, in a large cohort of individuals (over 25,000 enrolled subjects of both sexes), vitamin D (2000 IU/day) and/or omega-3 fatty acids (1000 mg/day) were supplemented in their diet, and the group was followed up for 5 years, registering Ps incidence among other autoimmune diseases. The results of the study show that in the supplemented group, the incidence of autoimmune diseases, including Ps, was reduced by over 22% [156].
Herbal products were also found to be useful in Chinese Ps patients, with improvements in their clinical parameters [157]. The obtained results are difficult to interpret in order to draw a conclusion, as there were various plants and preparations. Out of all of them, it seems that a herbal supplement from Tripterygium wilfordii was effective as an addition to conventional therapy (cyclosporine and acitretin), leading to an increased percentage of patients achieving PASI-60 [158].
5. Discussion
Ps is a worldwide health issue impacting the quality of life of over 60% of diagnosed patients, which mainly includes those with moderate to severe forms of Ps [159,160]. Ps patients experience higher rates of comorbidities, with metabolic syndrome included [161]. In general, Ps has two age peaks of onset: One between 20 and 30 years of age and the second between 50 and 60 years [162]. In Western countries, both age groups are stricken by metabolic deregulation, including obesity. Ps has many triggers, and it is still unclear whether obesity triggers Ps or vice versa. There are arguments for both cases. Thus, the incidence of Ps in obese individuals is high, and Ps patients can gain weight. However, normalizing Ps patient weight will have a major positive impact on the disease. Moreover, weight loss can have a positive impact on classical Ps medications, improving their efficacy. The common denominator of Ps and obesity is the inflammatory process; therefore, all means that reduce the chronic inflammatory status will improve Ps outcomes. Within the reduction of inflammation in Ps patients, regulating gut dysbiosis through diet and nutrients remains an important tool. Several types of diets and supplements have been evaluated in relation to obesity and Ps. Out of all of the tested regimens, a low-calorie diet is the most important type of diet that induces clear clinical benefits in Ps. As Ps is known to be an autoimmune inflammatory disease, the key phrase used in the dieting and/or diet supplementation of patients is “reduction of systemic inflammation”. The reduction in systemic inflammation, obesity reduction, and dysbiosis regulation will reflect directly on disease severity.
6. Conclusions
In recent years, we have witnessed an increasing array of studies actively investigating the relationship between obesity, the gut microbiome, and Ps. As gut microbes may influence the pathogenesis of Ps, the microbiome composition, diversity, and relative abundance in Ps individuals strengthen the gut–skin axis. Gut dysbiosis deregulates the epithelial barrier; therefore, microbial metabolites that circulate outside the gut epithelial barrier can cause systemic inflammation. Gut–skin axis functionality can induce an inflammatory effect due to a gut microbiome imbalance [57]. Modulating the gut microbiome and systemic chronic inflammation can improve the symptoms of Ps. Of the methods that can normalize the systemic inflammation recognized in Ps, diet and supplements can actively improve Ps symptomatology and, hence, the patients’ quality of life.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu15163528/s1, Table S1: Recent genetically engineered mouse models of Ps; Table S2: Ps animal model that over-expresses keratinocyte-cell-specific promoters.
Author Contributions
C.C. literature search, data collection, original draft preparation; M.S., A.M. and M.N. writing—review and editing; M.N. and C.C. conceptualization, methodology, supervision, project administration, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Core Program and implemented with the support of NASR, project PN 23.16.01.03/2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Considering that only previously published papers were used for the systematic review, there are no ethical concerns with this study. The institutional review board confirmed that no ethical approval was needed.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rachakonda, T.D.; Schupp, C.W.; Armstrong, A.W. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Arruda, L.; de Moraes, A. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 144, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadler, E.D.; Ortel, B.; Mehlis, S.L. Biologics for the primary care physician: Review and treatment of psoriasis. Dis. Mon. 2018, 65, 51–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, A.; Mufti, A.; Sibbald, R.G. Diagnosis and Management of Cutaneous Psoriasis: A Review. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2019, 32, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Boquete, L.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Llamas-Velasco, M.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; de la Cueva, P.; Belinchón, I. A New Classification of the Severity of Psoriasis: What’s Moderate Psoriasis? Life 2021, 11, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budu-Aggrey, A.; Brumpton, B.; Tyrrell, J.; Watkins, S.; Modalsli, E.H.; Celis-Morales, C.; Ferguson, L.D.; Vie, G.Å.; Palmer, T.; Fritsche, L.G.; et al. Evidence of a causal relationship between body mass index and psoriasis: A mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, G.; Pagano, I.; Grimaldi, M.; Marino, C.; Molettieri, P.; Santoro, A.; Stillitano, I.; Romano, R.; Montoro, P.; D’ursi, A.M.; et al. Effect of Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Psoriasis Patients: A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Based Metabolomic Study. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Megna, M.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Frias-Toral, E.; Fabbrocini, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in patients with psoriasis and obesity: An update for dermatologists and nutritionists. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.; Simon, J.C.; Saalbach, A. Psoriasis: Obesity and Fatty Acids. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Ogdie, A.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Helliwell, P.S.; Germino, R.; Stockert, L.; Young, P.; Joseph, W.; Mundayat, R.; Graham, D.; et al. Impact of baseline body mass index on the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, G.; Duran, P.; Vera, I.; Bermúdez, V. Exploring the Links between Obesity and Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. The association between psoriasis and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumthekar, A.; Ogdie, A. Obesity and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Narrative Review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, K.; Duan, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F. A Comparison of Clinical Characteristics in Overweight/Obese and Normal Weight Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris: A Bicentric Retrospective Observational Study. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanesco, S.; Hall, W.; Gibson, R.; Griffiths, C.; Maruthappu, T. Approaches to nutrition intervention in plaque psoriasis, a multi-system inflammatory disease-The Diet and Psoriasis Project (DIEPP). Nutr. Bull. 2022, 47, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, T.; Gullick, N.J.; Hutchinson, C.E.; Barber, T.M. Psoriatic disease and body composition: A systematic review and narrative synthesis. PLoS ONE. 2020, 15, e0237598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, M.; Talamonti, M.; Perino, F.; Servoli, S.; Giordano, D.; Chimenti, S.; De Simone, C.; Peris, K. Bioelectrical impedance analysis to define an excess of body fat: Evaluation in patients with psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2017, 28, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, N.; Hoashi, T.; Saeki, H. Nutrition and Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haczeyni, F.; Bell-Anderson, K.S.; Farrell, G.C. Causes and mechanisms of adipocyte enlargement and adipose expansion. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.-J. Emerging Roles of Adipose Tissue in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis in Obesity. JID Innov. 2021, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, G.; Fabbrocini, G.; Di Caprio, R.; Raimondo, A.; Scala, E.; Balato, N.; Balato, A. Psoriasis, Cardiovascular Events, and Biologics: Lights and Shadows. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyl-Surdacka, K.M.; Gerkowicz, A.; Bartosińska, J.; Kowal, M.; Przepiórka-Kosińska, J.; Surdacki, G.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G. Analysis of serum chemerin concentrations in psoriatic patients in relation to metabolic abnormalities. Postepy. Dermatol. Alergol. 2019, 36, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, J.; Miškić, B.; Mikšić, Š.; Juranić, B.; Ćosić, V.; Schwarz, D.; Včev, A. Adipogenesis as a Potential Anti-Obesity Target: A Review of Pharmacological Treatment and Natural Products. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisondi, P.; Fostini, A.C.; Fossà, I.; Girolomoni, G.; Targher, G. Psoriasis and the metabolic syndrome. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.J.; Shi, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.Y.; Fan, Y.M. Adiponectin levels in patients with psoriasis: A meta-analysis. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raucci, R.; Rusolo, F.; Sharma, A.; Colonna, G.; Castello, G.; Costantini, S. Functional and structural features of adipokine family. Cytokine 2013, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słuczanowska-Głabowska, S.; Staniszewska, M.; Marchlewicz, M.; Duchnik, E.; Łuczkowska, K.; Safranow, K.; Machaliński, B.; Pawlik, A. Adiponectin, Leptin and Resistin in Patients with Psoriasis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavoso, N.C.; Pinto, J.M.; Soares, M.M.S.; Diniz, M.D.S.; Júnior, A.L.T. Psoriasis in obesity: Comparison of serum levels of leptin and adiponectin in obese subjects—Cases and controls. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2019, 94, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Su, X.; Peng, D.; Zhao, M.; Su, Y. New insights into different adipokines in linking the pathophysiology of obesity and psoriasis. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, M.; Surcel, M.; Constantin, C. Systemic Circulating Leptin—Aiding New Dimension of Immune-Related Skin Carcinogenesis and Lipid Metabolism. SEE J. Immunol. 2023, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopytalska, K.; Baranowska-Bik, A.; Roszkiewicz, M.; Bik, W.; Walecka, I. The role of leptin in selected skin diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakou, A.; Patsatsi, A.; Sotiriadis, D.; Goulis, D.G. Serum Leptin, Resistin, and Adiponectin Concentrations in Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Dermatology 2017, 233, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Yoo, J.A.; Yoon, H.; Han, T.; Yoon, J.; An, S.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, J. The Role of Leptin in the Association between Obesity and Psoriasis. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.; Kant, S.; Pandey, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Resistin in metabolism, inflammation, and disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockenhuber, K.; Hegazy, A.N.; West, N.; Ilott, N.E.; Stockenhuber, A.; Bullers, S.J.; Thornton, E.E.; Arnold, I.C.; Tucci, A.; Waldmann, H.; et al. Foxp3+ T reg cells control psoriasiform inflammation by restraining an IFN-I–driven CD8+ T cell response. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroutoglou, K.; Papadavid, E.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Dalamaga, M. Deciphering the Association between Psoriasis and Obesity: Current Evidence and Treatment Considerations. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautbauer, S.; Wanninger, J.; Eisinger, K.; Hader, Y.; Beck, M.; Kopp, A.; Schmid, A.; Weiss, T.S.; Dorn, C.; Buechler, C. Chemerin is highly expressed in hepatocytes and is induced in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis liver. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 95, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Raimondo, A.; Lembo, S.; Fausti, F.; Dini, V.; Costanzo, A.; Monfrecola, G.; Balato, N.; Ayala, F.; Romanelli, M.; et al. Crosstalk between skin inflammation and adipose tissue-derived products: Pathogenic evidence linking psoriasis to increased adiposity. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.C.; Sinal, C.J. Chemerin: At the crossroads of inflammation and obesity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechler, C.; Feder, S.; Haberl, E.M.; Aslanidis, C. Chemerin Isoforms and Activity in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, G.; Wu, Q.-F. Chemerin: A multifaceted adipokine involved in metabolic disorders. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 238, R79–R94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, D.; Alimohammadi, S.; Bai, P.; Szöllősi, A.G.; Szántó, M. Antigen-Presenting Cells in Psoriasis. Life 2022, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C.; Scarponi, C.; Pallotta, S.; Daniele, R.; Bosisio, D.; Madonna, S.; Fortugno, P.; Gonzalvo-Feo, S.; Franssen, J.-D.; Parmentier, M.; et al. Chemerin expression marks early psoriatic skin lesions and correlates with plasmacytoid dendritic cell recruitment. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.-M.; Sun, X.-Y.; Cui, W.-Y.; Cao, Y.-C. Chemerin Exacerbates Psoriasis by Stimulating Keratinocyte Proliferation and Cytokine Production. Curr. Med. Sci. 2023, 43, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.D.; Moazzami, K.; Wittbrodt, M.T.; Nye, J.A.; Lima, B.B.; Gillespie, C.F.; Rapaport, M.H.; Pearce, B.D.; Shah, A.J.; Vaccarino, V. Diet, Stress and Mental Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölsken, S.; Krefting, F.; Schedlowski, M.; Sondermann, W. Common Fundamentals of Psoriasis and Depression. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2021, 101, adv00609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. Skin and Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis: Gaining Insight into the Pathophysiology of It and Finding Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Stec, A.; Chrabaszcz, M.; Knot, A.; Waskiel-Burnat, A.; Rakowska, A.; Olszewska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis: An Updated Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrani, C.; Di Nisio, A.; Paschou, S.A.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Graziadio, C.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. On Behalf of the Obesity Programs of Nutrition Education Research and Assessment Opera Group. From Gut Microbiota through Low-Grade Inflammation to Obesity: Key Players and Potential Targets. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovesy, L.; Masterson, D.; Rosado, E.L. Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thye, A.Y.-K.; Bah, Y.-R.; Law, J.W.-F.; Tan, L.T.-H.; He, Y.-W.; Wong, S.-H.; Thurairajasingam, S.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H.; Letchumanan, V. Gut–Skin Axis: Unravelling the Connection between the Gut Microbiome and Psoriasis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, T. The interplay between oral microbiota, gut microbiota and systematic diseases. J. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2213112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bander, Z.; Nitert, M.D.; Mousa, A.; Naderpoor, N. The Gut Microbiota and Inflammation: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, L.; Al-Jaber, H.; Prince, M.S.; Elrayess, M.A. Role of Inflammatory Cytokines, Growth Factors and Adipokines in Adipogenesis and Insulin Resistance. Inflammation 2022, 45, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilchowski, S.M. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis: From Pathogens to Pathology. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2022, 15, S25–S28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.-M.; Fan, X.-Y.; Jin, Y.-L.; Li, X.; Wu, S.-R.; Ge, W.-W.; Lv, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-K.; Chen, J.-G. Gut–Brain–Skin Axis in Psoriasis: A Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 11, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surcel, M.; Huică, R.-I.; Munteanu, A.N.; Isvoranu, G.; Ciotaru, D.; Constantin, C.; Bratu, O.; Căruntu, C.; Neagu, M.; Ursaciuc, C. Phenotypic changes of lymphocyte populations in psoriasiform dermatitis animal model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 17, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flutter, B.; Nestle, F.O. TLRs to cytokines: Mechanistic insights from the imiquimod mouse model of psoriasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 3138–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanvit, P.; Konkel, J.E.; Jiao, X.; Kasagi, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, R.; Chia, C.; Ajami, N.J.; Smith, D.P.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Antibiotics in neonatal life increase murine susceptibility to experimental psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyohara, H.; Sujino, T.; Teratani, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Arai, M.M.; Nomura, E.; Harada, Y.; Aoki, R.; Koda, Y.; Mikami, Y.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist–Induced Dermatitis Causes Severe Dextran Sulfate Sodium Colitis by Altering the Gut Microbiome and Immune Cells. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 7, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlikova, Z.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kverka, M.; Rossmann, P.; Dvorak, J.; Novosadova, I.; Kostovcik, M.; Coufal, S.; Srutkova, D.; Prochazkova, P.; et al. Crucial Role of Microbiota in Experimental Psoriasis Revealed by a Gnotobiotic Mouse Model. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Manna, P.R.; Tuckey, R.C. On the role of skin in the regulation of local and systemic steroidogenic activities. Steroids 2015, 103, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Slominski, R.M.; Raman, C.; Chen, J.Y.; Athar, M.; Elmets, C. Neuroendocrine signaling in the skin with a special focus on the epidermal neuropeptides. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C1757–C1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinno-Hashimoto, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chang, L.; Fujita, Y.; Ishima, T.; Matsue, H.; Hashimoto, K. Abnormal composition of microbiota in the gut and skin of imiquimod-treated mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, R.L.; Mubiru, D.L.; Kriegel, M.A. Friend or foe? Lactobacillus in the context of autoimmune disease. Adv. Immunol. 2020, 146, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zákostelská, Z.; Málková, J.; Klimešová, K.; Rossmann, P.; Hornová, M.; Novosádová, I.; Stehlíková, Z.; Kostovčík, M.; Hudcovic, T.; Štepánková, R.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Promotes Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation by Enhancing Th17 Response. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseyenko, A.V.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; De Souza, A.; Strober, B.; Gao, Z.; Bihan, M.; Li, K.; Methé, B.A.; Blaser, M.J. Community differentiation of the cutaneous microbiota in psoriasis. Microbiome 2013, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Zeng, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Kong, C.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, Z.M.; Huang, J.T.; Xu, Y.Y.; Mao, Y.Q.; Cai, P.R.; et al. Gut and Cutaneous Microbiome Featuring Abundance of Lactobacillus reuteri Protected Against Psoriasis-Like Inflammation in Mice. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6175–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Ward, N.L. Mouse Models of Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, M.P.; Manzke, V.; Erpenbeck, L. Animal models of psoriasis—Highlights and drawbacks. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parab, S.; Doshi, G. The Experimental Animal Models in Psoriasis Research: A Comprehensive Review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 109897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.; Diener, N.; Zahner, S.P.; Tripp, C.; Backer, R.A.; Karram, K.; Jiang, A.; Mellman, I.; Stoitzner, P.; Clausen, B.E. E-Cadherin is Dispensable to Maintain Langerhans Cells in the Epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibrian, D.; Castillo-González, R.; Fernández-Gallego, N.; de la Fuente, H.; Jorge, I.; Saiz, M.L.; Punzón, C.; Ramírez-Huesca, M.; Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Fresno, M.; et al. Targeting L-type amino acid transporter 1 in innate and adaptive T cells efficiently controls skin inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 199–214.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, B.; Szántó, M.; Hegedűs, C.; Antal, D.; Szödényi, A.; Márton, J.; Méhes, G.; Virág, L.; Szegedi, A.; Bai, P. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 depletion enhances the severity of inflammation in an imiquimod-induced model of psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, C.; Huard, A.; Sirait-Fischer, E.; Dillmann, C.; Brüne, B.; Weigert, A. S1PR4-dependent CCL2 production promotes macrophage recruitment in a murine psoriasis model. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soley, B.d.S.; Silva, L.M.; Mendes, D.A.G.B.; Báfica, A.; Pesquero, J.B.; Bader, M.; Witherden, D.A.; Havran, W.L.; Calixto, J.B.; Otuki, M.F.; et al. B1 and B2 kinin receptor blockade improves psoriasis-like disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3535–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovhannisyan, Z.; Liu, N.; Khalil-Aguero, S.; Panea, C.; VanValkenburgh, J.; Zhang, R.; Lim, W.K.; Bai, Y.; Fury, W.; Huang, T.; et al. Enhanced IL-36R signaling promotes barrier impairment and inflammation in skin and intestine. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaax1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamani, C.; Antoniadou, I.T.; Dimou, A.; Andreou, E.; Kostakis, G.; Sideri, A.; Vitsos, A.; Gkavanozi, A.; Sfiniadakis, I.; Skaltsa, H.; et al. Optimization of psoriasis mouse models. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2021, 108, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Sosa, T.; Sánchez, M.B.; Pietrobon, E.O.; Fernandez-Muñoz, J.M.; Zoppino, F.C.M.; Neira, F.J.; Germanó, M.J.; Cargnelutti, D.E.; Innocenti, A.C.; Jahn, G.A.; et al. Desmoglein-4 Deficiency Exacerbates Psoriasiform Dermatitis in Rats While Psoriasis Patients Displayed a Decreased Gene Expression of DSG4. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 625617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, A.C.; Ludwig, J.E.; Fritz, Y.; Rozic, R.; Swindell, W.R.; Tsoi, L.C.; Gruzska, D.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Xing, X.; Diaconu, D.; et al. KLK6 expression in skin induces PAR1-mediated psoriasiform dermatitis and inflammatory joint disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3151–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.R.; Blumenschein, W.; Murphy, E.; Diveu, C.; Wiekowski, M.; Abbondanzo, S.; Lucian, L.; Geissler, R.; Brodie, S.; Kimball, A.B.; et al. IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2–dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, G.; Huang, J.; Songyang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Lin, X. Gain-of-Function Mutation of Card14 Leads to Spontaneous Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation through Enhanced Keratinocyte Response to IL-17A. Immunity 2018, 49, 66–79.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxford, A.L.; Karbach, S.; Kurschus, F.C.; Wörtge, S.; Nikolaev, A.; Yogev, N.; Klebow, S.; Schüler, R.; Reissig, S.; Piotrowski, C.; et al. IL-6 Regulates Neutrophil Microabscess Formation in IL-17A-Driven Psoriasiform Lesions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbach, S.; Croxford, A.L.; Oelze, M.; Schüler, R.; Minwegen, D.; Wegner, J.; Koukes, L.; Yogev, N.; Nikolaev, A.; Reißig, S.; et al. Interleukin 17 Drives Vascular Inflammation, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Arterial Hypertension in Psoriasis-Like Skin Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2658–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.T.; Cao, L.; Roberson, E.D.; Duan, S.; Helms, C.A.; Nair, R.P.; Duffin, K.C.; Stuart, P.E.; Goldgar, D.; Hayashi, G.; et al. Rare and Common Variants in CARD14, Encoding an Epidermal Regulator of NF-kappaB, in Psoriasis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellett, M.; Meier-Schiesser, B.; Mohanan, D.; Schairer, R.; Cheng, P.; Satoh, T.; Kiefer, B.; Ospelt, C.; Nobbe, S.; Thome, M.; et al. CARD14 Gain-of-Function Mutation Alone Is Sufficient to Drive IL-23/IL-17–Mediated Psoriasiform Skin Inflammation In Vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2010–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Lou, F.; Yin, Q.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Bai, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cai, W.; Ke, F.; et al. RIG-I antiviral signaling drives interleukin-23 production and psoriasis-like skin disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, B.; Haase, I.; Eckelt, B.; Paxian, S.; Flaig, M.J.; Ghoreschi, K.; Nedospasov, S.A.; Mailhammer, R.; Debey-Pascher, S.; Schultze, J.L.; et al. Crosstalk between Keratinocytes and Adaptive Immune Cells in an IκBα Protein-Mediated Inflammatory Disease of the Skin. Immunity 2007, 27, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, S.; Mohebiany, A.N.; Waisman, A.; Kurschus, F.C. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis in Mice Depends on the IL-17 Signaling of Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, J.; Bao, X.; Yi, X.; Peng, C.; Chen, W.; Zhen, T.; Shi, Y.; Xing, K.; Zhu, S.; et al. Inhibition of phospholipases suppresses progression of psoriasis through modulation of inflammation. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, C.; Bai, X.; Wang, G. Upregulated E3 ligase tripartite motif-containing protein 21 in psoriatic epidermis ubiquitylates nuclear factor-κB p65 subunit and promotes inflammation in keratinocytes. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 184, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B. EZH2 is involved in psoriasis progression by impairing miR-125a-5p inhibition of SFMBT1 and leading to inhibition of the TGFβ/SMAD pathway. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 2040622320987348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wu, X.; Yu, S.; Huynh, M.; Jena, P.K.; Nguyen, M.; Wan, Y.-J.Y.; Hwang, S.T. Short-Term Exposure to a Western Diet Induces Psoriasiform Dermatitis by Promoting Accumulation of IL-17A–Producing γδ T Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.T.; Toussi, A.; Maverakis, N.; Marusina, A.I.; Barton, V.R.; Merleev, A.A.; Luxardi, G.; Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Maverakis, E. The cutaneous and intestinal microbiome in psoriatic disease. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 218, 108537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szántó, M.; Dózsa, A.; Antal, D.; Szabó, K.; Kemény, L.; Bai, P. Targeting the gut-skin axis—Probiotics as new tools for skin disorder management? Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, D.; Wsson, M.K.; Kumar, P.; Karthikeyan, G.; Kaushik, N.K.; Goel, C.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, H. Dysbiosis disrupts gut immune homeostasis and promotes gastric diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Inoue, R.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Naito, Y.; Andoh, A. Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, N.J. Management of psoriasis as a systemic disease: What is the evidence? Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surcel, M.; Munteanu, A.; Isvoranu, G.; Ibram, A.; Caruntu, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Unconventional Therapy with IgY in a Psoriatic Mouse Model Targeting Gut Microbiome. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-N.; Han, K.; Park, Y.-G.; Lee, J.H. Metabolic syndrome is associated with an increased risk of psoriasis: A nationwide population-based study. Metabolism 2019, 99, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinaghi, F.; Tekin, H.G.; Burisch, J.; Wu, J.J.; Thyssen, J.P.; Egeberg, A. Global prevalence and bidirectional association between psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.A.; Monteleone, G.; McLaughlin, J.T.; Paus, R. The gut-skin axis in health and disease: A paradigm with therapeutic implications. Bioessays 2016, 38, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Boscá, A.; Navarro-López, V.; Martínez-Andrés, A.; Such, J.; Francés, R.; de la Parte, J.H.; Asín-Llorca, M. Identification of bacterial DNA in the peripheral blood of patients with active psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 670–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchetti, L.; Nardelli, C. Gut microbiome investigation in celiac disease: From methods to its pathogenetic role. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.R.; Nguyen, M.; Vaughn, A.R.; Notay, M.; Burney, W.A.; Sandhu, S.; Sivamani, R.K. The skin and gut microbiome and its role in common dermatologic conditions. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, A.M.; Agace, W.W. Regional specialization within the intestinal immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, C.; Tan, J.; Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R. The nutrition-gut microbiome-physiology axis and allergic diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.-F.; Hern Tan, L.T.; Ramadas, A.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Lee, L.-H. Exploring the Role of Gut Bacteria in Health and Disease in Preterm Neonates. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.W.Y.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Wong, S.H.; Letchumanan, V.; Lee, L.-H. The chemistry of gut microbiome in health and diseases. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.R.; Roesch, L.; Thiago, P.; Russell, J.T.; Pepine, C.J.; Holbert, R.C.; Raizada, M.K.; Triplett, E.W. Depression phenotype identified by using single nucleotide exact amplicon sequence variants of the human gut microbiome. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4277–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Stratigou, T.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Dalamaga, M. Understanding the role of the gut microbiome and microbial metabolites in obesity and obesity-associated metabolic disorders: Current evidence and perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, A.M.; Gallo, R.L. Host-microbiome interactions and recent progress into understanding the biology of acne vulgaris. Microbiome 2018, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloster, H.; Gebauer, L.; Mistur, R. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease. In Absolute Dermatology Review; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Hong, S.-J. Antibiotics-Induced Dysbiosis of Intestinal Microbiota Aggravates Atopic Dermatitis in Mice by Altered Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkowska-Pruszyńska, B.; Gerkowicz, A.; Krasowska, D. The gut microbiome alterations in allergic and inflammatory skin diseases—An update. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisinha, S. The potential impact of gut microbiota on your health:Current status and future challenges. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 34, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelson, D.R.; Welsh, D.A.; Shellito, J.E. Regulation of lung immunity and host defense by the intestinal microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Masuoka, N.; Kano, M.; Iizuka, R. Bifidobacterium fermented milk and galacto-oligosaccharides lead to improved skin health by decreasing phenols production by gut microbiota. Benef. Microbes 2014, 5, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.P.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Sonnenburg, J.L. Pursuing Human-Relevant Gut Microbiota-Immune Interactions. Immunity 2019, 51, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiewicz, M.M.; Dryden, G.W.; Chhabra, A.; Alard, P. Relationship between gut microbiota and development of T cell associated disease. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4195–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Littman, D.R.; Abramson, S.B. Microbiome in Inflammatory Arthritis and Human Rheumatic Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, S.-R.; Tampa, M.; Caruntu, C.; Sarbu, M.-I.; Mitran, C.-I.; Mitran, M.-I.; Matei, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Advances in Understanding the Immunological Pathways in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.J.; Zhou, J.Y.; Geddes, K.; Rubino, S.J.; Cho, J.H.; Girardin, S.E.; Philpott, D.J. Nod1 and Nod2 signaling does not alter the composition of intestinal bacterial communities at homeostasis. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.C.; Bevins, C.L. Paneth Cells: Maestros of the Small Intestinal Crypts. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugot, J.-P.; Chamaillard, M.; Zouali, H.; Lesage, S.; Cézard, J.-P.; Belaiche, J.; Almer, S.; Tysk, C.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gassull, M.; et al. Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 2001, 411, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Bonen, D.K.; Inohara, N.; Nicolae, D.L.; Chen, F.F.; Ramos, R.; Britton, H.; Moran, T.; Karaliuskas, R.; Duerr, R.H.; et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 2001, 411, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kawamoto, S.; Maruya, M.; Fagarasan, S. GALT: Organization and dynamics leading to IgA synthesis. Adv. Immunol. 2010, 107, 153–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, M.B.; Dogra, S.; Vaiphei, K.; Vaishnavi, C.; Sinha, S.; Sharma, A. Evaluation of subclinical gut inflammation using faecal calprotectin levels and colonic mucosal biopsy in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassukas, I.D.; Gaitanis, G.; Katsanos, K.H.; Christodoulou, D.K.; Tsianos, E.; Vlachos, C. Psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease: Links and risks. Psoriasis: Targets Ther. 2016, 6, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.J.E.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Bacterial Dysbiosis and Translocation in Psoriasis Vulgaris. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, R.; Akter, S.; Tamanna, S.K.; Mazumder, L.; Esti, I.Z.; Banerjee, S.; Akter, S.; Hasan, R.; Acharjee, M.; Hossain, S.; et al. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: Gut-Skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2096995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Bartholomew, E.; Yeroushalmi, S.; Hakimi, M.; Bhutani, T.; Liao, W. Dietary Intervention and Supplements in the Management of Psoriasis: Current Perspectives. Psoriasis 2022, 12, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pona, A.; Haidari, W.; Kolli, S.S.; Feldman, S.R. Diet and psoriasis. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Abuabara, K. Diet and Weight Loss as a Treatment for Psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. 2010, 146, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aronson, P.J. Cases of psoriasis improved by lowering homocysteine using 4-7 mg folic acid, vitamins B6 and B12 previously worsened using 1-2 mg daily folic acid, B6 and B12 folic acid. J. Transl. Sci. 2017, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Balta, I.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Ozturk, C.; Demirkol, S.; Celik, T.; Kilic, S.; Demir, M.; Iyisoy, A. Bilirubin levels and their association with carotid intima media thickness and high-sensitivity Creactive protein in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 15, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, A.; Verhoeven, E.; Kraaimaat, F.; De Jong, E.; De Brouwer, S.; Schalkwijk, J.; Sweep, F.; Van De Kerkhof, P. How stress gets under the skin: Cortisol and stress reactivity in psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.; Zachariae, C.; Christensen, R.; Geiker, N.R.; Schaadt, B.K.; Stender, S.; Astrup, A.; Hansen, P.R.; Skov, L. Effect of weight loss on the cardiovascular risk profile of obese patients with psoriasis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014, 94, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korovesi, A.; Dalamaga, M.; Kotopouli, M.; Papadavid, E. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is independently associated with psoriasis risk, severity, and quality of life: A cross-sectional observational study. Int J Dermatol. 2019, 58, e164–e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passali, M.; Josefsen, K.; Frederiksen, J.L.; Antvorskov, J.C. Current evidence on the efficacy of gluten-free diets in multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, type 1 diabetes and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, A.M.; Qureshi, A.A.; Thompson, J.M.; Li, T.; Cho, E. Gluten intake and risk of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and atopic dermatitis among United States women. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, B.K.; Millsop, J.W.; Debbaneh, M.; Koo, J.; Linos, E.; Liao, W. Diet and psoriasis, part II: Celiac disease and role of a gluten-free diet. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaëlsson, G.; Gerdén, B.; Hagforsen, E.; Nilsson, B.; Pihl-Lundin, I.; Kraaz, W.; Hjelmquist, G.; Lööf, L. Psoriasis patients with antibodies to gliadin can be improved by a gluten-free diet. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaëlsson, G.; Ahs, S.; Hammarström, I.; Lundin, I.P.; Hagforsen, E. Gluten-free diet in psoriasis patients with antibodies to gliadin results in decreased expression of tissue transglutaminase and fewer Ki67 + cells in the dermis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2003, 83, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaëlsson, G.; Kristjánsson, G.; Lundin, I.P.; Hagforsen, E. Palmoplantar pustulosis and gluten sensitivity: A study of serum antibodies against gliadin and tissue transglutaminase, the duodenal mucosa and effects of gluten-free diet. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolchak, N.A.; Tetarnikova, M.K.; Theodoropoulou, M.S.; Michalopoulou, A.P.; Theodoropoulos, D.S. Prevalence of antigliadin IgA antibodies in psoriasis vulgaris and response of seropositive patients to a gluten-free diet. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2018, 11, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millsop, J.W.; Bhatia, B.K.; Debbaneh, M.; Koo, J.; Liao, W. Diet and psoriasis, part III: Role of nutritional supplements. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.; Cook, N.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Friedman, S.; Walter, J.; Bubes, V.; Kotler, G.; Lee, I.M.; Manson, J.E.; Costenbader, K.H. Vitamin D and marine omega 3 fatty acid supplementation and incident autoimmune disease: VITAL randomized controlled trial. BMJ 2022, 376, e066452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Kuai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Luo, Y.; Ru, Y.; Xing, M.; Li, H.; Sun, X.; et al. Chinese Herbal Medicine for Psoriasis: Evidence From 11 High-Quality Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 599433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Deng, J.; Tang, N.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, C. Efficacy and safety of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on psoriasis vulgaris: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 2623085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.S.; Nijsten, T.; Feldman, S.R.; Margolis, D.J.; Rolstad, T. Psoriasis Is Common, Carries a Substantial Burden Even When Not Extensive, and Is Associated with Widespread Treatment Dissatisfaction. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2004, 9, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Feldman, S.R.; Stern, R.S.; Thomas, J.; Rolstad, T.; Margolis, D.J. Determinants of quality of life in patients with psoriasis: A study from the US population. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. Psoriasis and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W. Psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).