Weight Loss and Sleep, Current Evidence in Animal Models and Humans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Obesity, Weight Loss and Sleep in Animal Models
2.1. Sleep Alterations in Obese and Diabetic Mouse Models
2.2. Caloric Restriction, Sleep Alterations and Body Weight in Animal Models
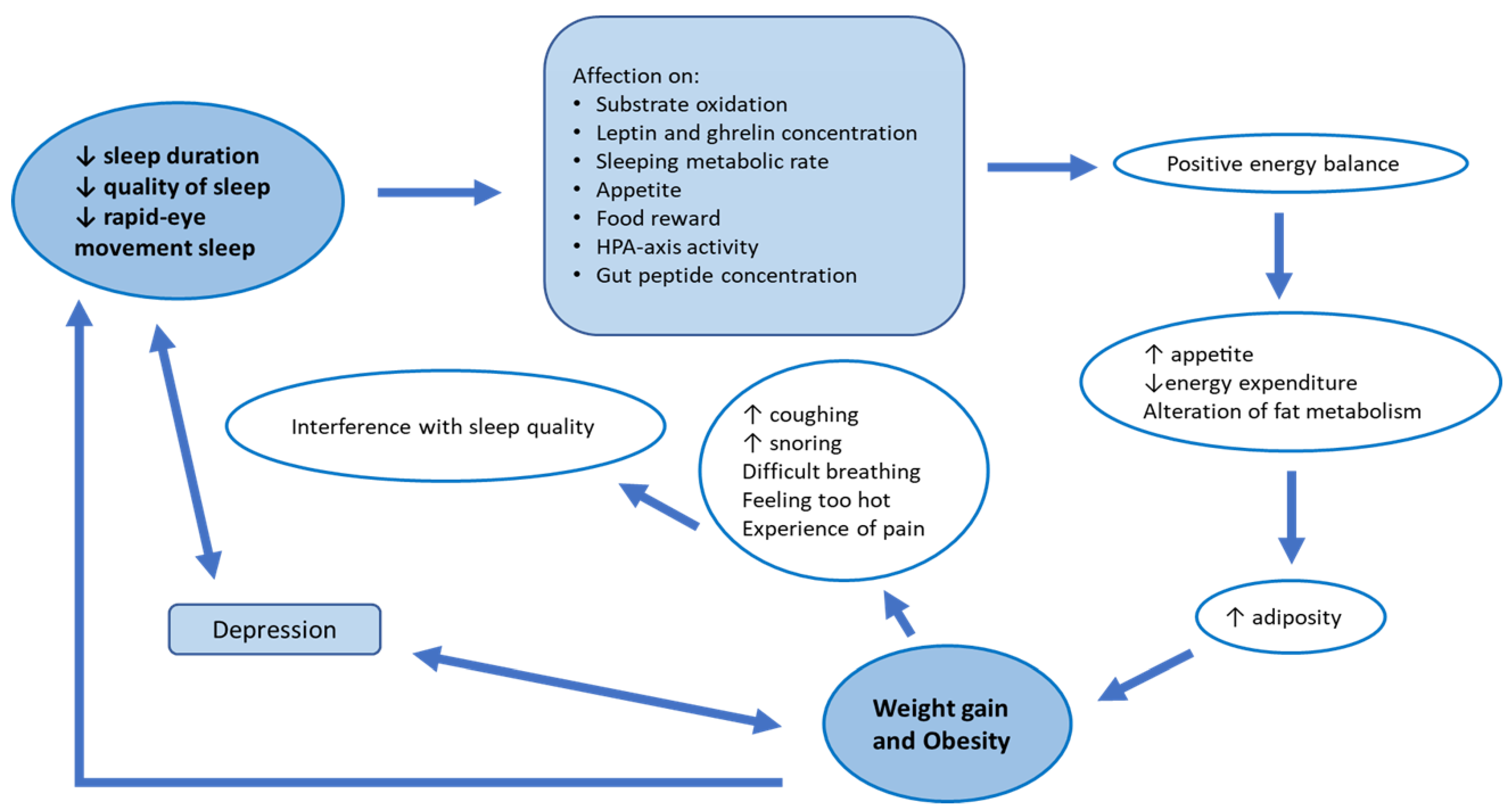
3. Obesity, Weight Loss and Sleep in Humans
3.1. Sleep Alterations in Obese and Diabetic Patients
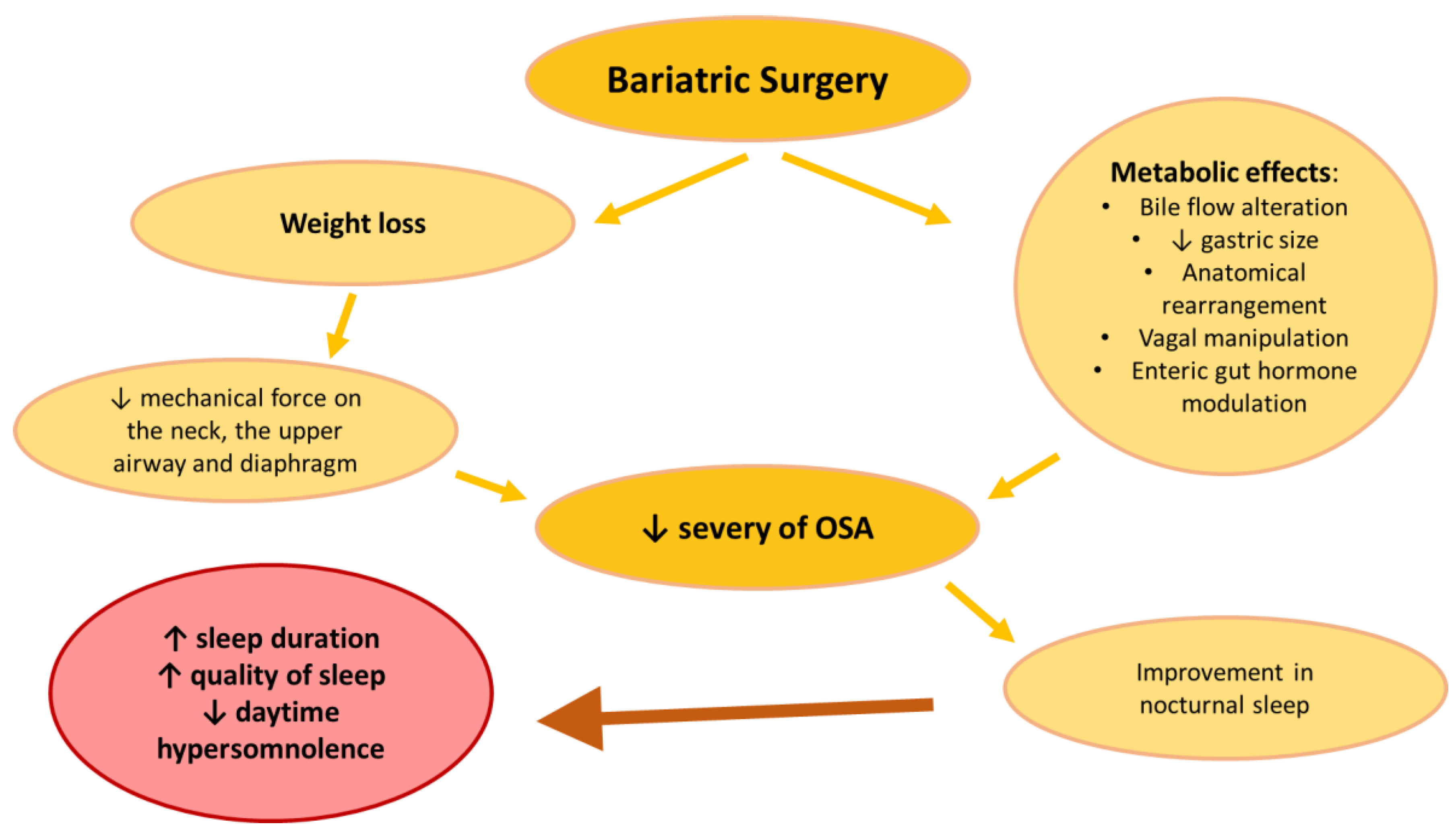
3.2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Weight Loss
3.3. Diet Interventions Aimed at Weight Loss and Sleep in Humans
3.4. Bariatric Surgery, Sleep and OSAS
4. Key Molecules Linking Metabolism and Sleep in Animals and Humans
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.C.; McPherson, K.; Marsh, T.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Brown, M. Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet 2011, 378, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, M.I.; Urciuoli, I.; Del Gaudio, G.; Polti, G.; Iannetti, G.; Gangitano, E.; Lori, E.; Lubrano, C.; Cantisani, V.; Sorrenti, S.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauderdale, D.S.; Knutson, K.L.; Rathouz, P.J.; Yan, L.L.; Hulley, S.B.; Liu, K. Cross-sectional and Longitudinal Associations Between Objectively Measured Sleep Duration and Body Mass Index: The CARDIA Sleep Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taheri, S. The link between short sleep duration and obesity: We should recommend more sleep to prevent obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krueger, P.M.; Friedman, E.M. Sleep duration in the United States: A cross-sectional population-based study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnissen, H.K.J.; Hulshof, T.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Chronobiology, endocrinology, and energy- and food-reward homeostasis. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Louis, G.; Williams, N.J.; Sarpong, D.; Pandey, A.; Youngstedt, S.; Zizi, F.; Ogedegbe, G. Associations between inadequate sleep and obesity in the US adult population: Analysis of the national health interview survey (1977–2009). BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, P.; Kim, K.; Buffington, C.K. Sleep Quality and Duration Before and After Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmer, R.; Legenbauer, T.; Müller, A.; de Zwaan, M.; Fischer, C.; Herpertz, S. Psychological outcome 4 years after restrictive bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, A.J.; Maggard-Gibbons, M.; Maher, A.R.; Booth, M.J.; Miake-Lye, I.; Beroes, J.M.; Shekelle, P.G. Mental Health Conditions Among Patients Seeking and Undergoing Bariatric Surgery: A Meta-analysis. JAMA 2016, 315, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.B.; Schachter, L.M.; O’brien, P.E.; Jones, K.; Grima, M.; Lambert, G.; Brown, W.; Bailey, M.; Naughton, M.T. Surgical vs conventional therapy for weight loss treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012, 308, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laposky, A.D.; Shelton, J.; Bass, J.; Dugovic, C.; Perrino, N.; Turek, F.W. Altered sleep regulation in leptin-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R894–R903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Bixler, E.O.; Fang, J. Sleep is increased by weight gain and decreased by weight loss in mice. Sleep 2008, 31, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, J.B.; Omori, T.; Guan, Z.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Bixler, E.O.; Fang, J. Sleep is increased in mice with obesity induced by high-fat food. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 87, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotou, M.; Meijer, J.H.; Deboer, T. Chronic high-caloric diet modifies sleep homeostasis in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laposky, A.D.; Bradley, M.A.; Williams, D.L.; Bass, J.; Turek, F.W. Sleep-wake regulation is altered in leptin-resistant (db/db) genetically obese and diabetic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R2059–R2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, T.; Wang, C.; Joshi, S.; O’Hara, B.F.; Gong, M.C.; Guo, Z. Active Time-Restricted Feeding Improved Sleep-Wake Cycle in db/db Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.; Le, H.D.; Melkani, G.C.; Panda, S. Time-restricted feeding attenuates age-related cardiac decline in Drosophila. Science 2015, 347, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; van Spyk, E.; Liu, Q.; Geyfman, M.; Salmans, M.L.; Kumar, V.; Ihler, A.; Li, N.; Takahashi, J.S.; Andersen, B. Time-Restricted Feeding Shifts the Skin Circadian Clock and Alters UVB-Induced DNA Damage. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honma, S. The mammalian circadian system: A hierarchical multi-oscillator structure for generating circadian rhythm. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijo-Ferreira, F.; Takahashi, J.S. Genomics of circadian rhythms in health and disease. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudic, R.D.; McNamara, P.; Curtis, A.-M.; Boston, R.C.; Panda, S.; HogenEsch, J.B.; Fitzgerald, G.A. BMAL1 and CLOCK, two essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in glucose homeostasis. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turek, F.W.; Joshu, C.; Kohsaka, A.; Lin, E.; Ivanova, G.; McDearmon, E.; Laposky, A.; Losee-Olson, S.; Easton, A.; Jensen, D.R.; et al. Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Circadian Clock Mutant Mice. Science 2005, 308, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, J.; Graff, C.; Dardente, H.; Pevet, P.; Challet, E. Feeding cues alter clock gene oscillations and photic responses in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of mice exposed to a light/dark cycle. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.A.; Velingkaar, N.; Makwana, K.; Chaudhari, A.; Kondratov, R. Calorie restriction regulates circadian clock gene expression through BMAL1 dependent and independent mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherji, A.; Kobiita, A.; Chambon, P. Shifting the feeding of mice to the rest phase creates metabolic alterations, which, on their own, shift the peripheral circadian clocks by 12 hours. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6683–E6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Rodríguez, V.A.; de Groot, M.H.M.; Rijo-Ferreira, F.; Green, C.B.; Takahashi, J.S. Mice under caloric restriction self-impose a temporal restriction of food intake as revealed by an automated feeder system. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 267–277.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaix, A.; Lin, T.; Le, H.D.; Chang, M.W.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Feeding Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice Lacking a Circadian Clock. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 303–319.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E.; Beyl, R.A.; Poggiogalle, E.; Hsia, D.S.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Reduces Appetite and Increases Fat Oxidation But Does Not Affect Energy Expenditure in Humans. Obesity 2019, 27, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukanovic, N.; la Spada, F.; Emmenegger, Y.; Niederhauser, G.; Preitner, F.; Franken, P. Depriving Mice of Sleep also Deprives of Food. Clocks Sleep. 2022, 4, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barf, R.P.; Meerlo, P.; Scheurink, A.J. Chronic sleep disturbance impairs glucose homeostasis in rats. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 2010, 819414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.M.; Melanson, E.L.; Frydendall, E.J.; Perreault, L.; Eckel, R.H.; Wright, K.P. Energy expenditure during sleep, sleep deprivation and sleep following sleep deprivation in adult humans. J. Physiol. 2011, 589 Pt 1, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangitano, E.; Gnessi, L.; Lenzi, A.; Ray, D. Chronobiology and Metabolism: Is Ketogenic Diet Able to Influence Circadian Rhythm? Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 756970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Chikahisa, S.; Shiuchi, T.; Shimizu, N.; Tanioka, D.; Uguisu, H.; Séi, H. Sleep profile during fasting in PPAR-alpha knockout mice. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 214, 112760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, A.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Wen, M. Ketogenic diet prevents chronic sleep deprivation-induced Alzheimer’s disease by inhibiting iron dyshomeostasis and promoting repair via Sirt1/Nrf2 pathway. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 998292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rique, G.L.N.; Rique, M.C.; de Souza Bonifácio, T.A.; Andrade, M.J.O.; Santos, N.A.D. Effects of vertical gastrectomy on sleep quality, eating behavior, and metabolic parameters in obese adults: A case study. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2022, 53, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.P.; Jessen, L.; Ryan, K.K.; Sisley, S.; Wilson–Pérez, H.E.; Stefater, M.A.; Gaitonde, S.G.; Sorrell, J.E.; Toure, M.; Berger, J.; et al. Weight-independent changes in blood glucose homeostasis after gastric bypass or vertical sleeve gastrectomy in rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, E.; Yang, Q.; Jin, L.; Sousa, K.M.; Dong, B.; Wang, Y.; Tu, J.; Ma, X.; Tian, J.; et al. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy confers metabolic improvements by reducing intestinal bile acids and lipid absorption in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019388118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibay, D.; Cummings, B.P. A Murine Model of Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 130, e56534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arble, D.M.; Sandoval, D.A.; Turek, F.W.; Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J. Metabolic effects of bariatric surgery in mouse models of circadian disruption. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenzano, A.; Tartaglia, N.; Ambrosi, A.; Tafuri, D.; Monda, M.; Messina, A.; Sessa, F.; Campanozzi, A.; Monda, V.; Cibelli, G.; et al. The Metabolic Rearrangements of Bariatric Surgery: Focus on Orexin-A and the Adiponectin System. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.A.; Subramaniam, R.; Brenner, T.; Tavakkoli, A.; Sheu, E.G. Weight and organ specific immune cell profiling of sleeve gastrectomy in mice. Metabolism 2021, 118, 154729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consensus Conference Panel; Watson, N.F.; Badr, M.S.; Belenky, G.; Bliwise, D.L.; Buxton, O.M.; Buysse, D.; Dinges, D.F.; Gangwisch, J.; Grandner, M.A.; et al. Recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult: A joint consensus statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.; Vecchierini, M.-F. Normative Sleep Data, Cognitive Function and Daily Living Activities in Older Adults in the Community. Sleep 2003, 28, 981–989. [Google Scholar]
- Ohayon, M.M.; Carskadon, M.A.; Guilleminault, C.; Vitiello, M.V. Meta-Analysis of Quantitative Sleep Parameters From Childhood to Old Age in Healthy Individuals Developing Normative Sleep Values Across the Human Lifespan. Sleep 2004, 27, 1255–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Cooper, D.; D’Elia, L.; Strazzullo, P.; Miller, M.A. Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knutson, K.L.; Van Cauter, E. Associations between sleep loss and increased risk of obesity and diabetes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1129, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaput, J.P.; Bouchard, C.; Tremblay, A. Change in sleep duration and visceral fat accumulation over 6 years in adults. Obesity 2014, 22, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Jung, J.Y.; Oh, C.M.; McIntyre, R.S.; Lee, J.H. Association between sleep duration, quality and body mass index in the Korean population. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, J.F.; Neven, A.K.; Tulen, J.H.M.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Miedema, H.M.E.; Tiemeier, H. Actigraphic sleep duration and fragmentation are related to obesity in the elderly: The Rotterdam Study. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; D’Elia, L.; Strazzullo, P.; Miller, M.A. Quantity and quality of sleep and incidence of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mezick, E.J.; Wing, R.R.; McCaffery, J.M. Associations of self-reported and actigraphy-assessed sleep characteristics with body mass index and waist circumference in adults: Moderation by gender. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engeda, J.; Mezuk, B.; Ratliff, S.; Ning, Y. Association between duration and quality of sleep and the risk of pre-diabetes: Evidence from NHANES. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Després, J.-P.; Bouchard, C.; Tremblay, A. Longer sleep duration associates with lower adiposity gain in adult short sleepers. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sparks, J.R.; Porter, R.R.; Youngstedt, S.D.; Bowyer, K.P.; Durstine, J.L.; Wang, X. Effects of moderate sleep restriction during 8-week calorie restriction on lipoprotein particles and glucose metabolism. Sleep Adv. 2020, 1, zpab001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.B.; Dixon, M.E.; Anderson, M.L.; Schachter, L.; O’Brien, P.E. Daytime sleepiness in the obese: Not as simple as obstructive sleep apnea. Obesity 2007, 15, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maugeri, A.; Medina-Inojosa, J.R.; Kunzova, S.; Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Sochor, O.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Geda, Y.E.; Vinciguerra, M. Sleep Duration and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness Are Associated with Obesity Independent of Diet and Physical Activity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhulst, S.L.; Franckx, H.; van Gaal, L.; de Backer, W.; Desager, K. The Effect of Weight Loss on Sleep-disordered Breathing in Obese Teenagers. Obesity 2009, 17, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuna, S.T.; Reboussin, D.M.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Millman, R.P.; Zammit, G.; Walkup, M.P.; Wadden, T.A.; Wing, R.R.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Spira, A.P.; et al. Effects of Weight Loss on Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity. Ten-Year Results of the Sleep AHEAD Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markofski, M.M.; Carrillo, A.E.; Timmerman, K.L.; Jennings, K.; Coen, P.M.; Pence, B.D.; Flynn, M.G. Exercise Training Modifies Ghrelin and Adiponectin Concentrations and Is Related to Inflammation in Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, T.L.; Ballard, R.D.; Weil, K.M.; Shepard, T.Y.; Scherzinger, A.L.; Stamm, E.R.; Sharp, T.A.; Eckel, R.H. Effects of Maintained Weight Loss on Sleep Dynamics and Neck Morphology in Severely Obese Adults. Obesity 2009, 17, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhoef, S.P.; Camps, S.G.; Gonnissen, H.K.; Westerterp, K.R.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Concomitant changes in sleep duration and body weight and body composition during weight loss and 3-mo weight maintenance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaput, J.P.; Drapeau, V.; Hetherington, M.; Lemieux, S.; Provencher, V.; Tremblay, A. Psychobiological impact of a progressive weight loss program in obese men. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 86, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaris, N.; Wadden, T.A.; Sarwer, D.B.; Diwald, L.; Volger, S.; Hong, P.; Baxely, A.; Minnick, A.M.; Vetter, M.L.; Berkowitz, R.I.; et al. Effects of a 2-year behavioral weight loss intervention on sleep and mood in obese individuals treated in primary care practice. Obesity 2015, 23, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, M.W.; Tan, A.; Schaffir, J.; Wegener, D.T. Sleep and weight loss in low-income overweight or obese postpartum women. BMC Obes. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elder, C.R.; Gullion, C.M.; Funk, K.L.; Debar, L.L.; Lindberg, N.M.; Stevens, V.J. Impact of sleep, screen time, depression and stress on weight change in the intensive weight loss phase of the LIFE study. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, M.E.; Starr, K.N.P.; Orenduff, M.; Mulder, H.S.; McDonald, S.R.; Spira, A.P.; Pieper, C.F.; Bales, C.W. Quality of life and mental health in older adults with obesity and frailty: Associations with a weight loss interventions. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasy, S.A.; Ostendorf, D.M.; Blankenship, J.M.; Grau, L.; Arbet, J.; Bessesen, D.H.; Melanson, E.L.; Catenacci, V.A. Effect of sleep on weight loss and adherence to diet and physical activity recommendations during an 18-month behavioral weight loss intervention. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.M.; Fava, J.; Subak, L.L.; Stone, K.; Hart, C.N.; Demos, K.; Wing, R. Sleep duration and weight loss among overweight/obese women enrolled in a behavioral weight loss program. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangitano, E.; Baxter, M.; Voronkov, M.; Lenzi, A.; Gnessi, L.; Ray, D. The interplay between macronutrients and sleep: Focus on circadian and homeostatic processes. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1166699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanini, M.Z.; Guallar-Castillón, P.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Lopez-Garcia, E. Mediterranean Diet and Changes in Sleep Duration and Indicators of Sleep quality in Older adults. Sleep 2017, 40, zsw083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Diehl, C.; Wood, A.C.; Redline, S.; Reid, M.; Johnson, D.A.; Maras, J.E.; Jacobs, D.R.; Shea, S.; Crawford, A.; St-Onge, M.-P. Mediterranean diet pattern and sleep duration and insomnia symptoms in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Sleep J. 2018, 41, zsy158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Aprano, S.; Framondi, L.; Di Matteo, R.; Laudisio, D.; Pugliese, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Sleep Quality in Obesity: Does Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Matter? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godos, J.; Ferri, R.; Caraci, F.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Castellano, S.; Galvano, F.; Grosso, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet is Associated with Better Sleep Quality in Italian Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Kim, J.E.; Armstrong, C.L.H.; Chen, N.; Campbell, W.W. Higher-protein diets improve indexes of sleep in energy-restricted overweight and obese adults: Results from 2 randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprio, M.; Moriconi, E.; Armani, A.; Fabbri, A.; Mantovani, G.; Mariani, S.; Lubrano, C.; Poggiogalle, E.; Migliaccio, S.; Donini, L.M.; et al. Very-low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in the management of metabolic diseases: Systematic review and consensus statement from the Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 1365–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.D.; Aminzadeh-gohari, S.; Tulipan, J.; Catalano, L.; Feichtinger, R.G. Ketogenic diet in the treatment of cancer—Where do we stand? Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Tozzi, R.; Gandini, O.; Watanabe, M.; Basciani, S.; Mariani, S.; Lenzi, A.; Gnessi, L.; Lubrano, C. Ketogenic diet as a preventive and supportive care for COVID-19 patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Tozzi, R.; Mariani, S.; Lenzi, A.; Gnessi, L.; Lubrano, C. Ketogenic Diet for Obese COVID-19 Patients: Is Respiratory Disease a Contraindication? A Narrative Review of the Literature on Ketogenic Diet and Respiratory Function. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 771047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willi, S.M.; Oexmann, M.J.; Wright, N.M.; Collop, N.A.; Key, L.L. The Effects of a High-protein, Low-fat, Ketogenic Diet on Adolescents With Morbid Obesity: Body Composition, Blood Chemistries, Sleep Abnormalities. Pediatrics 1998, 101, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.I.; Gomez-Arbelaez, D.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Granero, R.; Aguera, Z.; Jimenez-Murcia, S.; Sajoux, I.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Casanueva, F.F. Effect of a very low-calorie ketogenic diet on food and alcohol cravings, physical and sexual activity, sleep disturbances, and quality of life in obese patients. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalam, F.; Gabel, K.; Cienfuegos, S.; Ezpeleta, M.; Wiseman, E.; Varady, K.A. Alternate Day Fasting Combined with a Low Carbohydrate Diet: Effect on Sleep Quality, Duration, Insomnia Severity and Risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults with Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, M.I.; Paoletti, F.; Herbert, P.E. Obesity and bariatric intervention in patients with chronic renal disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 2326–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, M.I.; Deurloo, E.; Consorti, F.; Herbert, P.E. Body mass index affects kidney transplant outcomes: A cohort study over 5 years using a steroid sparing protocol. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1106087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzziferri, N.; Roshek, T.B.; Mayo, H.G.; Gallagher, R.; Belle, S.H.; Livingston, E.H. Long-term Follow-up After Bariatric Surgery. JAMA 2014, 312, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Tapia, I.E. Effects of obesity therapies on sleep disorders. Metabolism 2018, 84, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peromaa-Haavisto, P.; Tuomilehto, H.; Kössi, J.; Virtanen, J.; Luostarinen, M.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Käkelä, P.; Victorzon, M. Obstructive sleep apnea: The effect of bariatric surgery after 12 months. A prospective multicenter trial. Sleep Med. 2017, 35, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, A.C.; Kaur, V.; Carey, I.; Al-Rubaye, H.; Mahawar, K.; Madhok, B.; Small, P.; McGlone, E.R.; Khan, O.A. Obstructive sleep apnea remission following bariatric surgery: A national registry cohort study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2021, 17, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Genio, G.; Limongelli, P.; del Genio, F.; Motta, G.; Docimo, L.; Testa, D. Sleeve gastrectomy improves obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS): 5 year longitudinal study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2016, 12, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhang, P.; Yu, H.; Di, J.; Han, X.; Yin, S.; Yi, H. Effect of Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery on Obstructive Sleep Apnea in a Chinese Population with Obesity and T2DM. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilektasli, E.; Dilektasli, A.G. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Improves Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Sleep Quality 6 Months Following Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holty, J.-E.C.; Parimi, N.; Ballesteros, M.; Blackwell, T.; Cirangle, P.T.; Jossart, G.H.; Kimbrough, N.D.; Rose, J.M.; Stone, K.L.; Bravata, D.M. Does Surgically Induced Weight Loss Improve Daytime Sleepiness? Obes. Surg. 2011, 21, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhosh, K.; Switzer, N.J.; El-Hadi, M.; Birch, D.W.; Shi, X.; Karmali, S. The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review. Obes. Surg. 2013, 23, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, H.; Avidor, Y.; Braunwald, E.; Jensen, M.D.; Pories, W.; Fahrbach, K.; Schoelles, K. Bariatric Surgery. JAMA 2004, 292, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Thumma, J.R.; Dimick, J.B. Reoperation and Medicare Expenditures After Laparoscopic Gastric Band Surgery. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashrafian, H.; le Roux, C.W.; Rowland, S.P.; Ali, M.; Cummin, A.R.; Darzi, A.; Athanasiou, T. Metabolic surgery and obstructive sleep apnoea: The protective effects of bariatric procedures. Thorax 2012, 67, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, T.F.; de Bruin, P.F.C.; de Bruin, V.M.S.; Lopes, P.M.; Lemos, F.N. Obesity, Hypersomnolence, and Quality of Sleep: The Impact of Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 1775–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, M.; Mamun, A.; Doi, S.; Clavarino, A. Is there a bi-directional relationship between depression and obesity among adult men and women? Systematic review and bias-adjusted meta analysis. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2016, 21, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stunkard, A.J.; Faith, M.S.; Allison, K.C. Depression and obesity. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Kritikou, I.; Calhoun, S.L.; Liao, D.; Bixler, E.O. Natural History of Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Role of Obesity, Weight Loss, Depression, and Sleep Propensity. Sleep 2015, 38, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; Punjabi, N.M. Diagnosis and Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. JAMA 2020, 323, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.-M.; Barnes, H.N.; Joosten, S.A.; Landry, S.A.; Dabscheck, E.; Mansfield, D.R.; Dharmage, S.C.; Senaratna, C.V.; Edwards, B.A.; Hamilton, G.S. The effect of surgical weight loss on obstructive sleep apnoea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 42, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenburg, D.L.; Lettieri, C.J.; Eliasson, A.H. Effects of Surgical Weight Loss on Measures of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busetto, L.; Enzi, G.; Inelmen, E.M.; Costa, G.; Negrin, V.; Sergi, G.; Vianello, A. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Morbid Obesity. Chest 2005, 128, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritscher, L.G.; Canani, S.; Mottin, C.C.; Fritscher, C.C.; Berleze, D.; Chapman, K.; Chatkin, J.M. Bariatric Surgery in the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Morbidly Obese Patients. Respiration 2007, 74, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Lin, L.; Austin, D.; Young, T.; Mignot, E. Short sleep duration is associated with reduced leptin, elevated ghrelin, and increased body mass index. PLoS Med. 2004, 1, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Gnessi, L.; Merli, M. Protein Catabolism and the Dysregulation of Energy Intake-Related Hormones May Play a Major Role in the Worsening of Malnutrition in Hospitalized Cirrhotic Patients. Livers 2022, 2, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poher, A.-L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Müller, T.D. Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism. Peptides 2018, 100, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, T.; Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Koizumi, M.; Damdindorj, B.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M. Ghrelin Regulates Insulin Release and Glycemia: Physiological Role and Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2008, 4, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yada, T.; Damdindorj, B.; Rita, R.S.; Kurashina, T.; Ando, A.; Taguchi, M.; Koizumi, M.; Sone, H.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; et al. Ghrelin signalling in β-cells regulates insulin secretion and blood glucose. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isgaard, J.; Granata, R. Ghrelin in cardiovascular disease and atherogenesis. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 340, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Yu, L. Potential role of ghrelin in the regulation of inflammation. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentirmai, E.; Kapás, L.; Krueger, J.M. Ghrelin microinjection into forebrain sites induces wakefulness and feeding in rats. Am. J. Physiol. -Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R575–R585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentirmai, E. Central but not systemic administration of ghrelin induces wakefulness in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannielli, P.C.; Molyneux, P.C.; Harrington, M.E.; Golombek, D.A. Ghrelin effects on the circadian system of mice. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2890–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szentirmai, E.; Kapas, L.; Sun, Y.; Smith, R.G.; Krueger, J.M. Spontaneous sleep and homeostatic sleep regulation in ghrelin knockout mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R510–R517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodosi, B.; Gardi, J.; Hajdu, I.; Szentirmai, E.; Obal, F., Jr.; Krueger, J.M. Rhythms of ghrelin, leptin, and sleep in rats: Effects of the normal diurnal cycle, restricted feeding, and sleep deprivation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, R1071–R1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nedeltcheva, A.V.; Kilkus, J.M.; Imperial, J.; Schoeller, D.A.; Penev, P.D. Insufficient Sleep Undermines Dietary Efforts to Reduce Adiposity. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Charlat, O.; Tartaglia, L.A.; Woolf, E.A.; Weng, X.; Ellis, S.J.; Lakey, N.D.; Culpepper, J.; More, K.J.; Breitbart, R.E.; et al. Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: Identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell 1996, 84, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G. Leptin Receptor Signaling and the Regulation of Mammalian Physiology. Recent. Prog. Horm. Res. 2004, 59, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, J.; Perrino, N.; Dugovic, C.; Bass, J.; Turek, F.W.; Laposky, A. Sleep alterations in ob/ob mice are reversed with chronic leptin repletion. In Sleep, Proceedings of the Conference 19th Annual Meeting of the Associated-Professional-Sleep-Societies, Denver, CO, USA, 18–23 June 2005; Amer Academy Sleep Medicine One Westbrook Corporate Center STE 920; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, IL, USA, 2005; p. A31. [Google Scholar]
- Oishi, K.; Ohyama, S.; Higo-Yamamoto, S. Chronic sleep disorder induced by psychophysiological stress induces glucose intolerance without adipose inflammation in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 2616–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, P.K.; Foppen, E.; Kalsbeek, A.; Challet, E. Sleep restriction acutely impairs glucose tolerance in rats. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, 12839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.M.; Barf, R.P.; Opp, M.R. Effects of sleep disruption and high fat intake on glucose metabolism in mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 68, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, A.; Bediako, I.A.; Paszkiewicz, R.L.; Kolka, C.M.; Bergman, R.N.; Broussard, J.L. Impact of sleep deprivation and high-fat feeding on insulin sensitivity and beta cell function in dogs. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J.; Byrne, M.M.; Plat, L.; Leproult, R.; van Cauter, E. Relationships between sleep quality and glucose regulation in normal humans. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 271, E261–E270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlund, I.M.; Carter, J.R. Sympathetic neural responses to sleep disorders and insufficiencies. Am. J. Physiol. -Heart Circ. Physiol. 2022, 322, H337–H349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.B.; Schoorlemmer, G.H.; Rocha, A.A.; Cravo, S.L. Increased sympathetic responses induced by chronic obstructive sleep apnea are caused by sleep fragmentation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupone, D.; Madden, C.J.; Cano, G.; Morrison, S.F. An orexinergic projection from perifornical hypothalamus to raphe pallidus increases rat brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 15944–15955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, L.; Seoane-Collazo, P.; Contreras, C.; González-García, I.; Martínez-Sánchez, N.; González, F.; Zalvide, J.; Gallego, R.; Diéguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; et al. A Functional Link between AMPK and Orexin Mediates the Effect of BMP8B on Energy Balance. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monda, M.; Viggiano, A.; Mondola, P.; de Luca, V. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis reduces hyperthermic reactions induced by hypocretin-1/orexin A. Brain Res. 2001, 909, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monda, M.; Viggiano, A.; Viggiano, A.; Fuccio, F.; de Luca, V. Injection of orexin A into the diagonal band of Broca induces sympathetic and hyperthermic reactions. Brain Res. 2004, 1018, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sunanaga, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Mori, T.; Sakurai, T.; Kanmura, Y.; Kuwaki, T. Orexin neurons are indispensable for stress-induced thermogenesis in mice. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 4117–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellayah, D.; Bharaj, P.; Sikder, D. Orexin is required for brown adipose tissue development, differentiation, and function. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villarroya, F.; Vidal-Puig, A. Beyond the sympathetic tone: The new brown fat activators. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hara, J.; Beuckmann, C.T.; Nambu, T.; Willie, J.T.; Chemelli, R.M.; Sinton, C.M.; Sugiyama, F.; Yagami, K.-I.; Goto, K.; Yanagisawa, M.; et al. Genetic ablation of orexin neurons in mice results in narcolepsy, hypophagia, and obesity. Neuron 2001, 30, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kok, S.W.; Overeem, S.; Visscher, T.L.; Lammers, G.J.; Seidell, J.C.; Pijl, H.; Meinders, A.E. Hypocretin deficiency in narcoleptic humans is associated with abdominal obesity. Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.A.; Menheere, P.P.; van Dielen, F.M.; Soeters, P.B.; Buurman, W.A.; Greve, J.W. Decreased plasma orexin-A levels in obese individuals. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espana, R.A.; Baldo, B.A.; Kelley, A.E.; Berridge, C.W. Wake-promoting and sleep-suppressing actions of hypocretin (orexin): Basal forebrain sites of action. Neuroscience 2001, 106, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methippara, M.M.; Alam, M.N.; Szymusiak, R.; McGinty, D. Effects of lateral preoptic area application of orexin-A on sleep-wakefulness. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 3423–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, D.C.; Upton, N.; Smith, M.I.; Hunter, A.J. The novel brain neuropeptide, orexin-A, modulates the sleep-wake cycle of rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, M.C.; Morales, F.R.; Chase, M.H. Effects on sleep and wakefulness of the injection of hypocretin-1 (orexin-A) into the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus of the cat. Brain Res. 2001, 901, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamantidis, A.R.; Zhang, F.; Aravanis, A.M.; Deisseroth, K.; de Lecea, L. Neural substrates of awakening probed with optogenetic control of hypocretin neurons. Nature 2007, 450, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.E.; Adamantidis, A.; Ohtsu, H.; Deisseroth, K.; de Lecea, L. Sleep homeostasis modulates hypocretin-mediated sleep-to-wake transitions. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10939–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zink, A.N.; Bunney, P.E.; Holm, A.A.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M. Neuromodulation of orexin neurons reduces diet-induced adiposity. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinhold, S.L.; Seeck-Hirschner, M.; Nowak, A.; Hallschmid, M.; Göder, R.; Baier, P.C. The effect of intranasal orexin-A (hypocretin-1) on sleep, wakefulness and attention in narcolepsy with cataplexy. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 262, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, A.C.; Chapman, H.; Taylor, C.; Moore, G.B.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Tadayyon, M.; Clapham, J.C.; Arch, J.R. Anorectic, thermogenic and anti-obesity activity of a selective orexin-1 receptor antagonist in ob/ob mice. Regul. Pept. 2002, 104, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verty, A.N.A.; Allen, A.M.; Oldfield, B.J. The endogenous actions of hypothalamic peptides on brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in the rat. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4236–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Bixler, E.O.; Papanicolaou, D.A.; Kales, A.; Stratakis, C.A.; Vela-Bueno, A.; Gold, P.W.; Chrousos, G.P. Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Correlates with the Overall Activities of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis and Sympathetic System in Healthy Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 3278–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follenius, M.; Brandenberger, G.; Simon, C.; Schlienger, L. Sleep REM Sleep in Humans Begins during Decreased Secretory Activity of the Anterior Pituitary. Sleep 1988, 11, 546–555. [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus, J.; Junghanns, K.; Hohagen, F. Sleep disturbances are correlated with decreased morning awakening salivary cortisol. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2004, 29, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, J.G.; Shipley, M.J.; Ferrie, J.E.; Kivimäki, M.; Kumari, M. Recurrent short sleep, chronic insomnia symptoms and salivary cortisol: A 10-year follow-up in the Whitehall II study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 68, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schorr, M.; Lawson, E.A.; Dichtel, L.E.; Klibanski, A.; Miller, K.K. Cortisol Measures Across the Weight Spectrum. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3313–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossum, E.F.C. Obesity and cortisol: New perspectives on an old theme. Obesity 2017, 25, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dalmazi, G.; Pagotto, U.; Pasquali, R.; Vicennati, V. Glucocorticoids and Type 2 Diabetes: From Physiology to Pathology. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 525093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Cauter, E.; Plat, L. Physiology of growth hormone secretion during sleep. J. Pediatr. 1996, 128, S32–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.H. Obesity, growth hormone and weight loss. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 316, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangitano, E.; Barbaro, G.; Susi, M.; Rossetti, R.; Spoltore, M.E.; Masi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Mariani, S.; Gnessi, L.; Lubrano, C. Growth Hormone Secretory Capacity Is Associated with Cardiac Morphology and Function in Overweight and Obese Patients: A Controlled, Cross-Sectional Study. Cells 2022, 11, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Corradini, S.G.; Lubrano, C.; Gnessi, L. La Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, una patologia epatica di interesse endocrinologico. L’endocrinologo 2021, 22, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Llorens, S.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Samarghandian, S. An Overview of the Role of Adipokines in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.B. The complex role of adipokines in obesity, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 731–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opp, M.R. Cytokines and sleep. Sleep Med. Rev. 2005, 9, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, J.M. The Role of Cytokines in Sleep Regulation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3408–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapsimalis, F.; Richardson, G.; Opp, M.R.; Kryger, M. Cytokines and normal sleep. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2005, 11, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, S.; Lanteri, P.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Magnavita, N.; Scoditti, E. Role of sleep deprivation in immune-related disease risk and outcomes. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R.; Carroll, J.E. Sleep disturbance, sleep duration, and inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies and experimental sleep deprivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irwin, M.R.; Opp, M.R. Sleep Health: Reciprocal Regulation of Sleep and Innate Immunity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- TAISHI, P.; Chen, Z.; Obál, F., Jr.; Hansen, M.K.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J.; Krueger, J.M. Sleep-Associated Changes in Interleukin-1β mRNA in the Brain. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998, 18, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Papanicolaou, D.A.; Bixler, E.O.; Kales, A.; Tyson, K.; Chrousos, G.P. Elevation of plasma cytokines in disorders of excessive daytime sleepiness: Role of sleep disturbance and obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.-L.; Tang, Y.-Z.; Ni, C.-L.; Yang, M.; Song, H.-N.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.-Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.-Q. Impact of inflammatory markers on the relationship between sleep quality and incident cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, M.J.; Volek, J.S. Weight loss leads to reductions in inflammatory biomarkers after a very-low-carbohydrate diet and a low-fat diet in overweight men. Clin. Sci. 2004, 107, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forsythe, L.K.; Wallace, J.M.W.; Livingstone, M.B.E. Obesity and inflammation: The effects of weight loss. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2008, 21, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslick, S.; Williams, E.J.; Berthon, B.S.; Wright, T.; Karihaloo, C.; Gately, M.; Wood, L.G. Weight Loss and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Reduce Systemic Inflammation in Monocytes and Adipose Tissue Macrophages from Obese Subjects. Nutrients 2022, 14, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.C.F.; Braga, V.d.A.; Silva, M.D.S.d.F.; Cruz, J.d.C.; Santos, S.H.S.; Monteiro, M.M.d.O.; Balarini, C.d.M. Adipokines, diabetes and atherosclerosis: An inflammatory association. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, A.; Mohammadi, I.; Sadeghi, M.; Brühl, A.B.; Sadeghi-Bahmani, D.; Brand, S. Evaluation of Plasma/Serum Adiponectin (An Anti-Inflammatory Factor) Levels in Adult Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2022, 12, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlman, J.; Seppä, J.; Herder, C.; Peltonen, M.; Peuhkurinen, K.; Gylling, H.; Vanninen, E.; Tukiainen, H.; Punnonen, K.; Partinen, M.; et al. Effect of weight loss on inflammation in patients with mild obstructive sleep apnea. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Frias, C.; Figueroa-Vega, N.; Malacara, J.M. Sleep Extension Increases the Effect of Caloric Restriction Over Body Weight and Improves the Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation in Adolescents With Obesity. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 66, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gangitano, E.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Bellini, M.I.; Urciuoli, I.; Monterisi, S.; Mariani, S.; Ray, D.; Gnessi, L. Weight Loss and Sleep, Current Evidence in Animal Models and Humans. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3431. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153431
Gangitano E, Martinez-Sanchez N, Bellini MI, Urciuoli I, Monterisi S, Mariani S, Ray D, Gnessi L. Weight Loss and Sleep, Current Evidence in Animal Models and Humans. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3431. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153431
Chicago/Turabian StyleGangitano, Elena, Noelia Martinez-Sanchez, Maria Irene Bellini, Irene Urciuoli, Stefania Monterisi, Stefania Mariani, David Ray, and Lucio Gnessi. 2023. "Weight Loss and Sleep, Current Evidence in Animal Models and Humans" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3431. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153431
APA StyleGangitano, E., Martinez-Sanchez, N., Bellini, M. I., Urciuoli, I., Monterisi, S., Mariani, S., Ray, D., & Gnessi, L. (2023). Weight Loss and Sleep, Current Evidence in Animal Models and Humans. Nutrients, 15(15), 3431. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153431






