Lactoferrin Alleviates Inflammation and Regulates Gut Microbiota Composition in H5N1-Infected Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses
2.2. Antimicrobial Peptide Diets
2.3. Animal Experiments
2.4. Histopathology
2.5. 16S rRNA Library Construction
2.6. Library Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
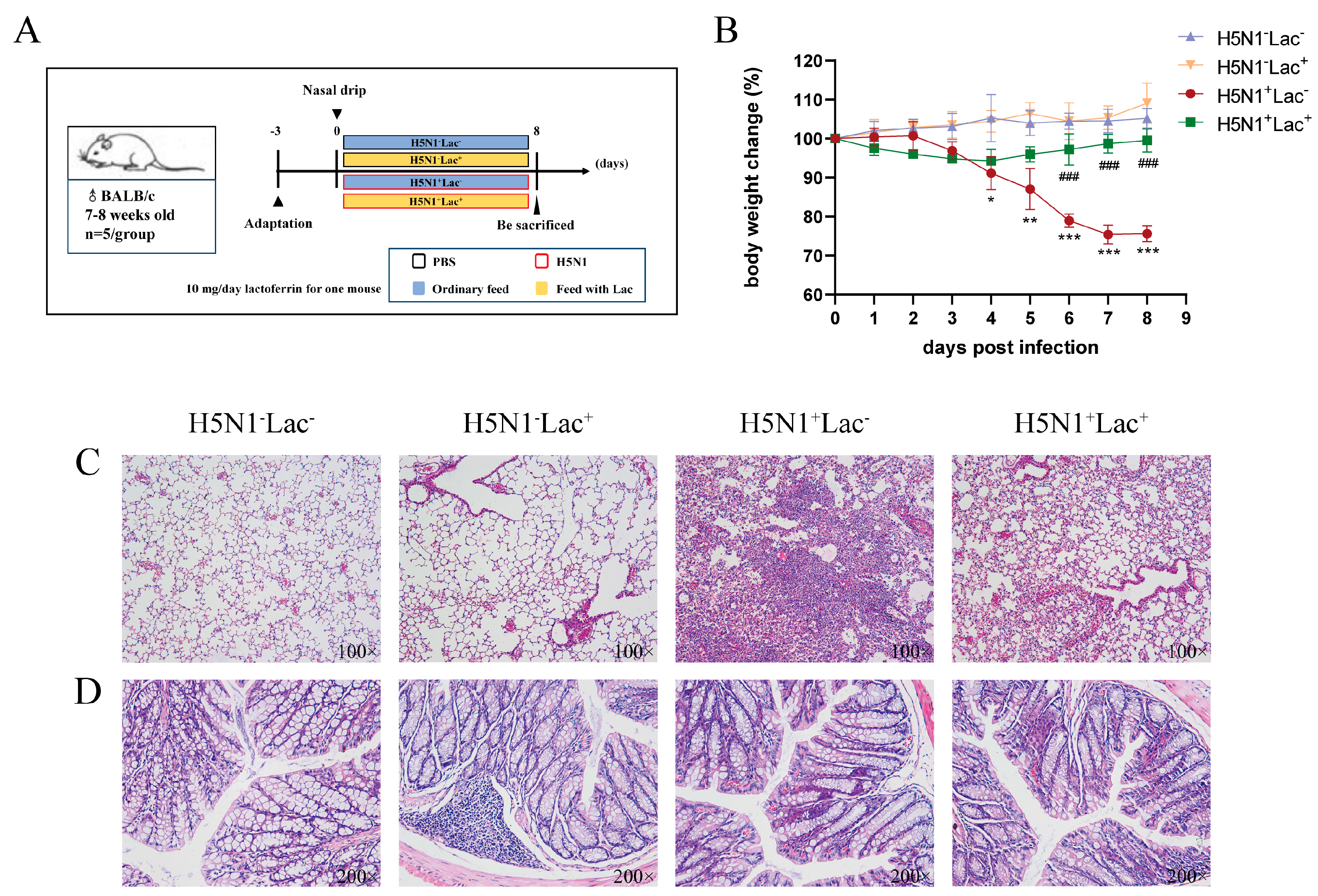
3.1. Effect of Lactoferrin on the Body Weight Change in Mice Infected with H5N1 Influenza Virus
3.2. Effect of Lactoferrin on the Histopathology of Mice Infected with the H5N1 Influenza Virus
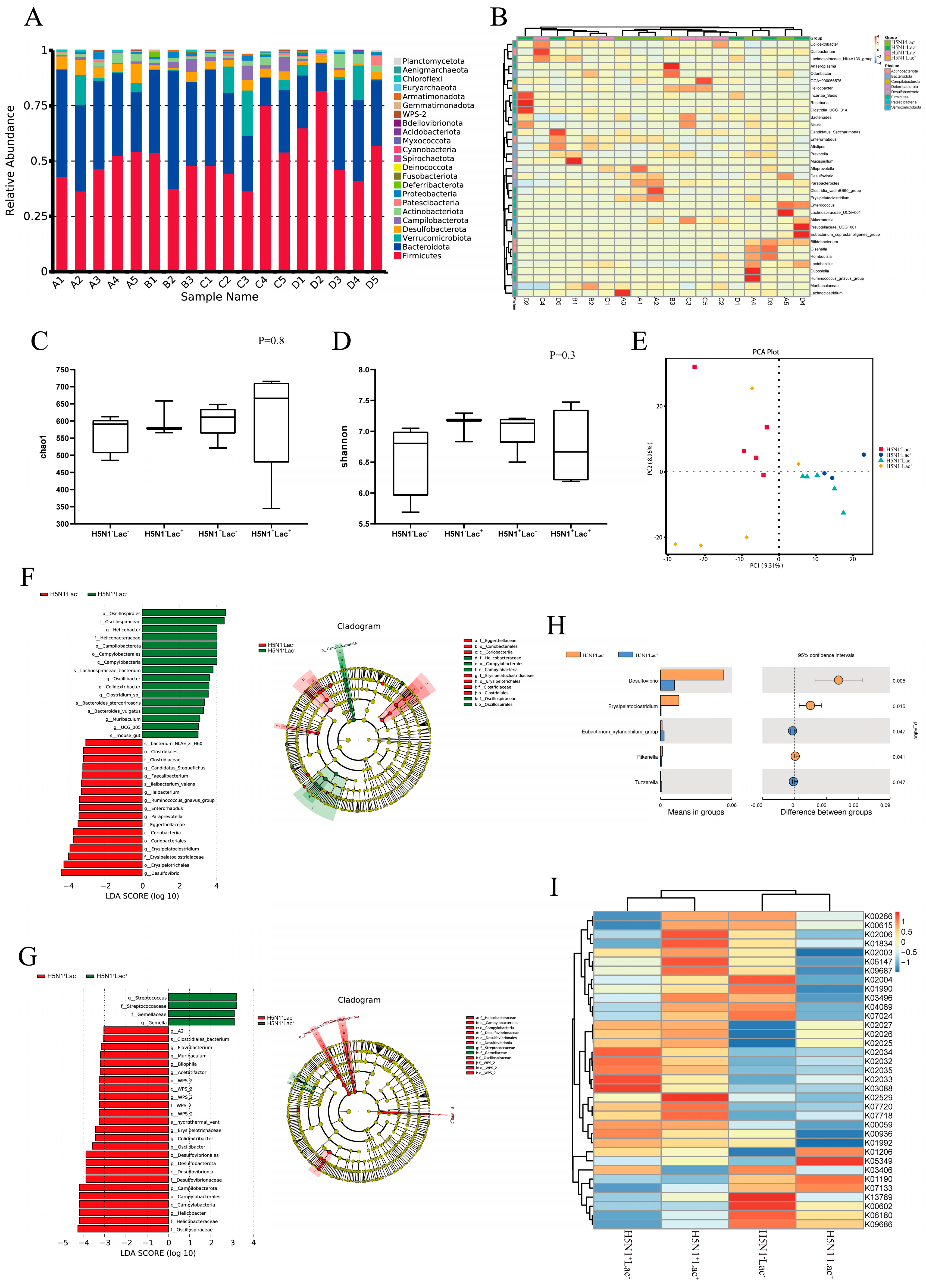
3.3. Lactoferrin Altered the Diversity and Composition of Colon Microbiota
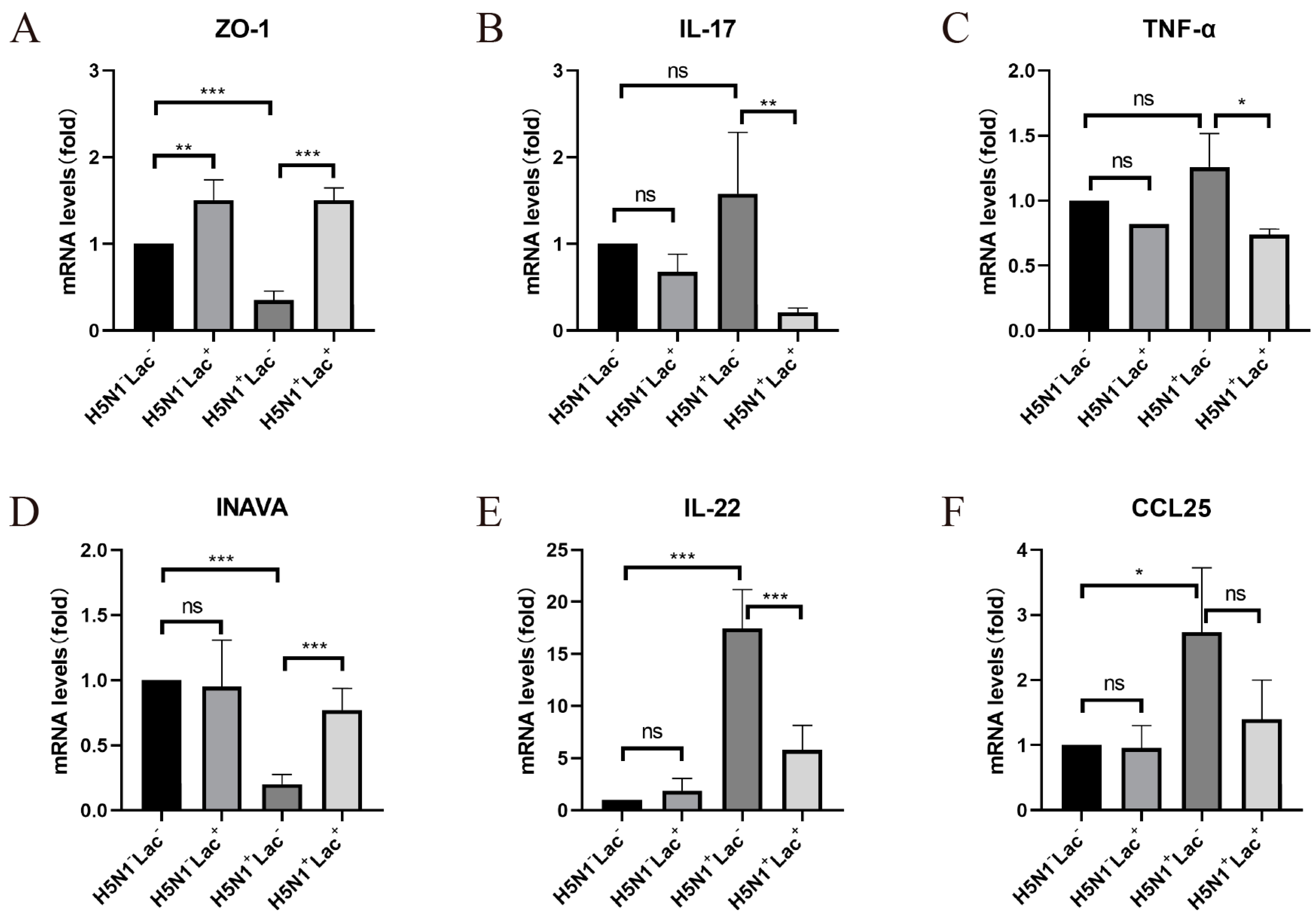
3.4. The Protective Effect of Lactoferrin on the Intestinal Barrier Structure
3.5. Effect of Lactoferrin on Inflammatory Cytokines
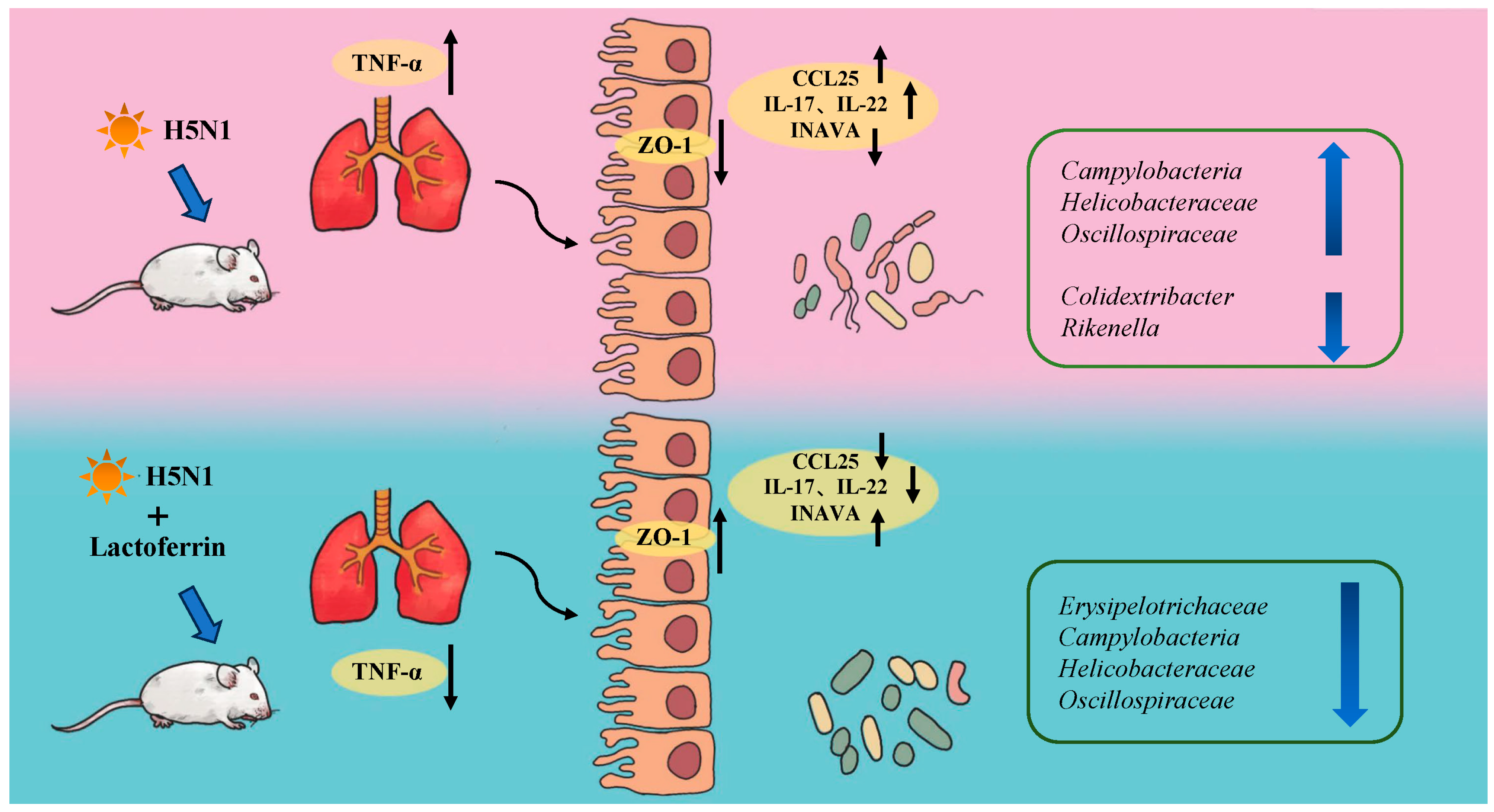
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magana, M.; Pushpanathan, M.; Santos, A.L.; Leanse, L.; Fernandez, M.; Ioannidis, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Apidianakis, Y.; Bradfute, S.; Ferguson, A.L.; et al. The value of antimicrobial peptides in the age of resistance. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e216–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazi, S.; Mohammadi, N.; Allahverdi, A.; Khalili, E.; Abdolmaleki, P. A review on antimicrobial peptides databases and the computational tools. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2022, 2022, baac011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, J.K.; Sharma, P.K. Mini Review on Antimicrobial Peptides, Sources, Mechanism and Recent Applications. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M. Antimicrobial Peptides: From Design to Clinical Application. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, B.; Lee, C.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, S.; Pierro, A. Protective effects of lactoferrin on injured intestinal epithelial cells. J Pediatr Surg 2019, 54, 2509–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baveye, S.; Elass, E.; Mazurier, J.; Spik, G.; Legrand, D. Lactoferrin: A multifunctional glycoprotein involved in the modulation of the inflammatory process. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1999, 37, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.C.; Shen, C.J.; Hsu, W.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Lin, H.T.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, C.M. Lactoferrin: An iron-binding antimicrobial protein against Escherichia coli infection. Biometals 2011, 24, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Tan, B.E.; Wu, M.M.; Yin, Y.L.; Li, T.J.; Yuan, D.X.; Li, L. Effects of composite antimicrobial peptides in weanling piglets challenged with deoxynivalenol: II. Intestinal morphology and function. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4750–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, H.; Shu, X.; Yin, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, J.; Chen, L.; Peng, K.; Xu, F.; Gu, W.; et al. Presence of Segmented Filamentous Bacteria in Human Children and Its Potential Role in the Modulation of Human Gut Immunity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroentero. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthold, R.V.; Fernandes, G.R.; Franco-de-Moraes, A.C.; Folchetti, L.G.D.; Ferreira, S.R.G. Gut microbiota interactions with the immunomodulatory role of vitamin D in normal individuals. Metabolism 2017, 69, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brestoff, J.R.; Artis, D. Commensal bacteria at the interface of host metabolism and the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 2006, 124, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Dittel, B.N. Interrelatedness between dysbiosis in the gut microbiota due to immunodeficiency and disease penetrance of colitis. Immunology 2015, 146, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salguero, M.V.; Al-Obaide, M.A.I.; Singh, R.; Siepmann, T.; Vasylyeva, T.L. Dysbiosis of Gram-negative gut microbiota and the associated serum lipopolysaccharide exacerbates inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 3461–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Roles of intestinal epithelial cells in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Maintenance of intestinal homeostasis by mucosal barriers. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.P.; Ding, S.J.; Yin, Y.L.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Liu, G. Macleaya cordata extract alleviated oxidative stress and altered innate immune response in mice challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, M.C.; Osborne, L.C.; Monticelli, L.A.; Doering, T.A.; Alenghat, T.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Paley, M.A.; Antenus, M.; Williams, K.L.; Erikson, J.; et al. Commensal bacteria calibrate the activation threshold of innate antiviral immunity. Immunity 2012, 37, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Czerkinsky, C. Mucosal immunity and vaccines. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, S45–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.C.; Zhu, H.Y.; Li, H.; Zeng, D.L.; Shi, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.; Ling, L.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, D.F. Regulating the balance of Th17/Treg cells in gut-lung axis contributed to the therapeutic effect of Houttuynia cordata polysaccharides on H1N1-induced acute lung injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; Wei, H.; Lian, Z.X.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Respiratory influenza virus infection induces intestinal immune injury via microbiota-mediated Th17 cell-dependent inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2397–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, N.; Wlodarska, M.; Finlay, B.B. The future of mucosal immunology: Studying an integrated system-wide organ. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, P.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zou, Z.; Yan, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; et al. IL-17 response mediates acute lung injury induced by the 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacManus, C.F.; Collins, C.B.; Nguyen, T.T.; Alfano, R.W.; Jedlicka, P.; de Zoeten, E.F. VEN-120, a Recombinant Human Lactoferrin, Promotes a Regulatory T Cell [Treg] Phenotype and Drives Resolution of Inflammation in Distinct Murine Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.F.; To, K.F.; Lam, W.W.; Ng, T.K.; Lee, K.C. The comparative pathology of severe acute respiratory syndrome and avian influenza A subtype H5N1—A review. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, C.; Wotring, J.W.; Zhang, C.J.; McCarty, S.M.; Fursmidt, R.; Pretto, C.D.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Frum, T.; Kadambi, N.S.; et al. Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105815118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Cheng, B.; Kalambhe, D.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, B.; et al. Lactoferrin-mediated macrophage targeting delivery and patchouli alcohol-based therapeutic strategy for inflammatory bowel diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1966–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.G.; Landreth, S.; Lu, Y.; Pandey, K.; Zhou, Y. A Replication-Defective Influenza Virus Harboring H5 and H7 Hemagglutinins Provides Protection against H5N1 and H7N9 Infection in Mice. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02154-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wan, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Leng, Y. Mesenchymal stem cells against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yu, M.; Sun, L.; Xiao, W.; Yang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Interferon-gamma-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha pathway. J. Interferon. Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.Y.; Li, H.; Lu, X.X.; Ling, L.J.; Weng, H.B.; Sun, W.; Chen, D.F.; Zhang, Y.Y. Houttuynia cordata polysaccharide alleviated intestinal injury and modulated intestinal microbiota in H1N1 virus infected. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Lei, Z.H.; Ping, J.H.; Su, J. Effect of rifaximin on gut-lung axis in mice infected with influenza A virus. Comp. Immunol. Microb. 2021, 75, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiwen, Z.; Rui, H.; Bingxi, Z.; Qingfeng, G.; Jifeng, Z.; Xuemei, W.; Beibei, W. Oral Administration of Bovine Lactoferrin-Derived Lactoferricin (Lfcin) B Could Attenuate Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Induced Intestinal Disease through Improving Intestinal Barrier Function and Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3932–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.N.; Li, S.L.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.Q.; Zheng, N. The Protective Effects of Lactoferrin on Aflatoxin M1-Induced Compromised Intestinal Integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Li, C.K.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhou, J.; Dong, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Avian influenza A(H5N1) viruses can directly infect and replicate in human gut tissues. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Limaye, A.; Liu, J.-R.; Wu, T.-N. Potential probiotics for regulation of the gut-lung axis to prevent or alleviate influenza in vulnerable populations. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2023, 13, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinohe, T.; Pang, I.K.; Kumamoto, Y.; Peaper, D.R.; Ho, J.H.; Murray, T.S.; Iwasaki, A. Microbiota regulates immune defense against respiratory tract influenza A virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5354–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, V.; Nakata, T.; Desch, A.N.; Levesque, C.; Boroughs, A.; Guzman, G.; Cao, Z.; Creasey, E.; Yao, J.; Boucher, G.; et al. C1orf106 is a colitis risk gene that regulates stability of epithelial adherens junctions. Science 2018, 359, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, E.C.; Neumann, M.; Desai, M.S. Interactions of commensal and pathogenic microorganisms with the intestinal mucosal barrier. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, D.R.; Welsh, D.A.; Shellito, J.E. Regulation of lung immunity and host defense by the intestinal microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budden, K.F.; Gellatly, S.L.; Wood, D.L.; Cooper, M.A.; Morrison, M.; Hugenholtz, P.; Hansbro, P.M. Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis. Nat. Reviews. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, J.B.; Sorobetea, D.; Kiilerich, P.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Estelle, J.; Ma, T.; Madsen, L.; Kristiansen, K.; Svensson-Frej, M. Chronic Trichuris muris Infection Decreases Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiota and Concomitantly Increases the Abundance of Lactobacilli. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Song, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q. Ulva prolifera Polysaccharide-Manganese Alleviates Inflammation and Regulates Microbiota Composition in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 916552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, S.; Mazel-Sanchez, B.; Kandasamy, M.; Manicassamy, B.; Schmolke, M. Influenza A virus infection impacts systemic microbiota dynamics and causes quantitative enteric dysbiosis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Luu, L.D.W.; Lee, S.A.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Wu, R.; Riordan, S.M.; Lan, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. Analysis of complete Campylobacter concisus genomes identifies genomospecies features, secretion systems and novel plasmids and their association with severe ulcerative colitis. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Role of emerging Campylobacter species in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, J.; Chen, N.; Amenta, P.S.; Fukui, H.; Oshima, T.; Tomita, T.; Miwa, H.; Lim, K.J.; Das, K.M. Helicobacter pylori associated chronic gastritis, clinical syndromes, precancerous lesions, and pathogenesis of gastric cancer development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5461–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Zeglinas, C.; Artemaki, F.; Doulberis, M.; Kazakos, E.; Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J. Helicobacter pylori infection and esophageal adenocarcinoma: A review and a personal view. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, Z.; Yang, P.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Zha, L.; Zhang, C. Absorption of Codonopsis pilosula Saponins by Coexisting Polysaccharides Alleviates Gut Microbial Dysbiosis with Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Model Mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1781036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Mao, G.; Yan, L.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Tian, D.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chen, S. Effect of the sulfation pattern of sea cucumber-derived fucoidan oligosaccharides on modulating metabolic syndromes and gut microbiota dysbiosis caused by HFD in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.W.; Li, K.Y.; Lee, Y.; Chen, M.J. Preventive Effects of Lactobacillus Mixture against Chronic Kidney Disease Progression through Enhancement of Beneficial Bacteria and Downregulation of Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7353–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Wu, M.M.; Tan, B.E.; Yin, Y.L.; Li, T.J.; Xiao, D.F.; Li, L. Effects of composite antimicrobial peptides in weanling piglets challenged with deoxynivalenol: I. Growth performance, immune function, and antioxidation capacity. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4772–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wu, M.M.; Shao, F.Y.; Tan, B.E.; Li, T.J.; Ren, W.K.; Yin, J.; Wang, J.; He, Q.H.; Yin, Y.L.; et al. Metabolic profiles in the response to supplementation with composite antimicrobial peptides in piglets challenged with deoxynivalenol. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Designated Oligo Nucleotides (5′→3′) | GenBank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH-F | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG | NM_001289726.2 |
| GAPDH-R | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG | |
| INAVA-F | TGCCGAAGTTAAATGAAATACC | NM_001405152.1 |
| INAVA-R | CATGATGAGTTTCTGGGAAGAG | |
| IL-17-F | CAGACTACCTCAACCGTTCCAC | NM_010552.3 |
| IL-17-R | TCCAGCTTTCCCTCCGCATTGA | |
| TNF-α-F | GGTGCCTATGTCTCAGCCTCTT | NM_001278601.1 |
| TNF-α-R | GCCATAGAACTGATGAGAGGGAG | |
| CCL25-F | CCGGCATGCTAGGAATTATCA | NM_009138.3 |
| CCL25-R | GGCACTCCTCACGCTTGTACT | |
| IL-22-F | GCTTGAGGTGTCCAACTTCCAG | NM_016971.2 |
| IL-22-R | ACTCCTCGGAACAGTTTCTCCC | |
| ZO-1-F | ACTCCCACTTCCCCAAAAAC | NM_001163574.2 |
| ZO-1-R | CCACAGCTGAAGGACTCACA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Han, S.; He, H. Lactoferrin Alleviates Inflammation and Regulates Gut Microbiota Composition in H5N1-Infected Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153362
Huang Y, Zhang P, Han S, He H. Lactoferrin Alleviates Inflammation and Regulates Gut Microbiota Composition in H5N1-Infected Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153362
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yanyi, Peiyang Zhang, Shuyi Han, and Hongxuan He. 2023. "Lactoferrin Alleviates Inflammation and Regulates Gut Microbiota Composition in H5N1-Infected Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153362
APA StyleHuang, Y., Zhang, P., Han, S., & He, H. (2023). Lactoferrin Alleviates Inflammation and Regulates Gut Microbiota Composition in H5N1-Infected Mice. Nutrients, 15(15), 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153362






