Combined Newborn Screening Allows Comprehensive Identification also of Attenuated Phenotypes for Methylmalonic Acidurias and Homocystinuria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Newborn Screening
2.2. NGS2025 as Extension of the German National NBS Panel
2.3. Combined Multiple-Tier NBS Algorithm
2.4. Ethical Approval
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
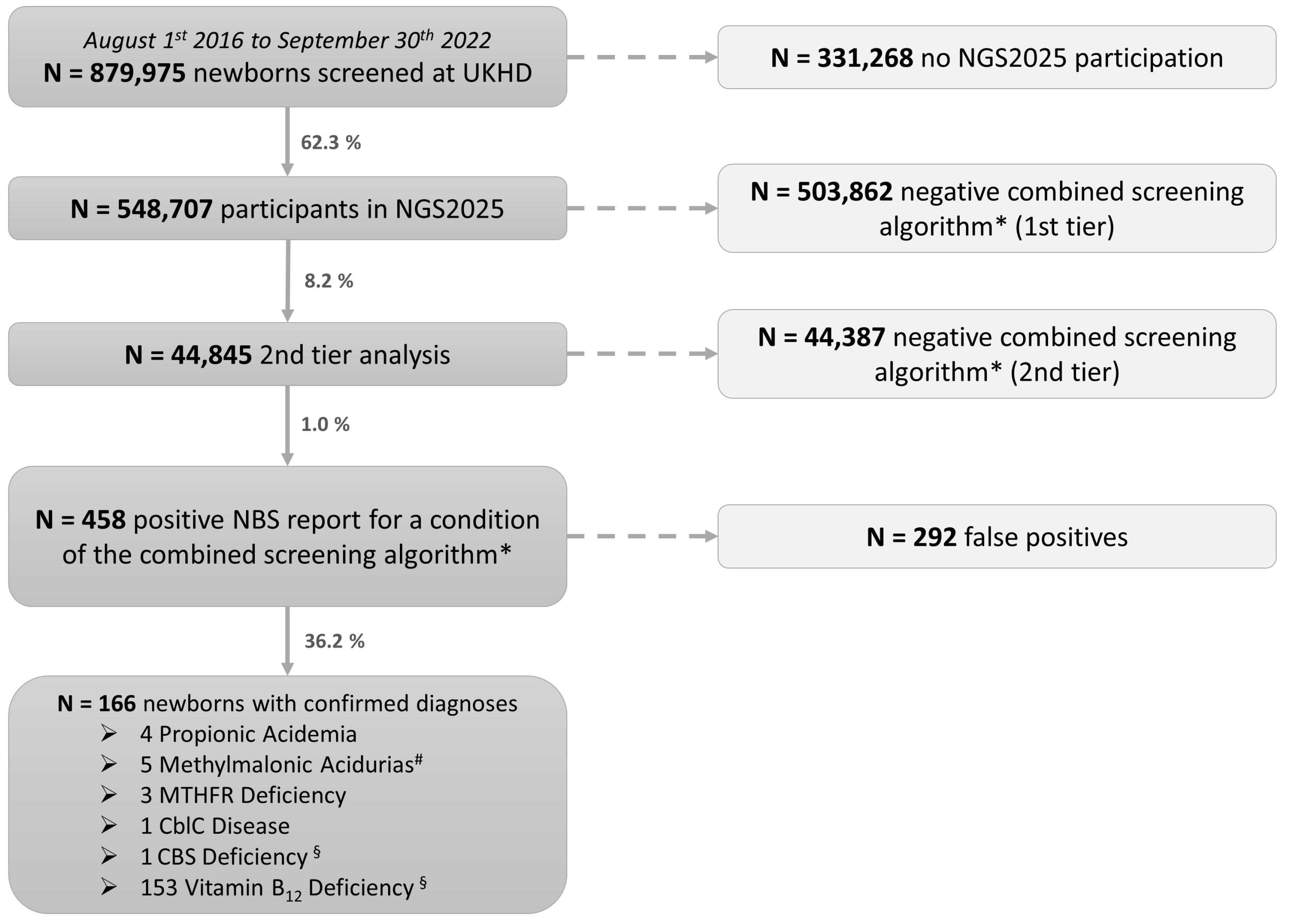
3.1. Study Population
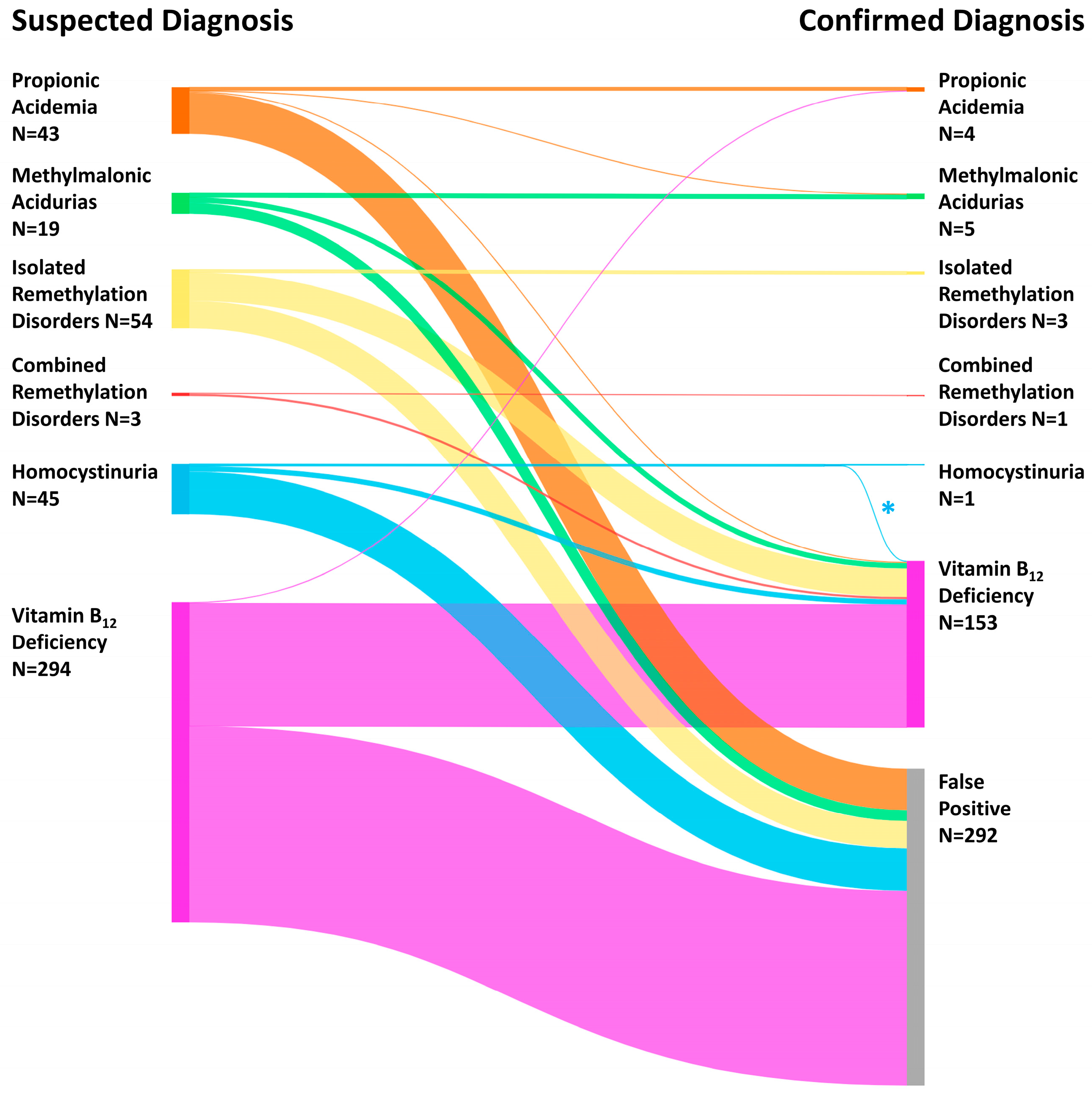
3.2. Suspected and Confirmed Diagnoses
3.3. Time to Treatment
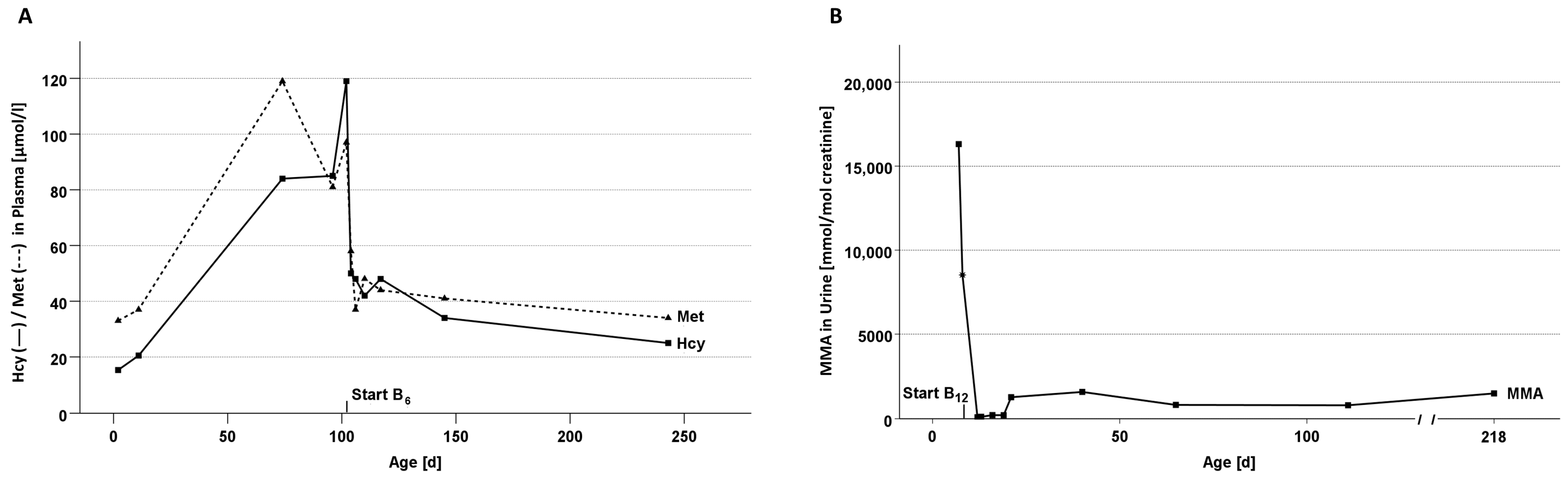
3.4. Case A: Vitamin B6-Responsive CBS Deficiency
3.5. Case B: Vitamin B12-Responsive Methylmalonic Aciduria, CblA-Type
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3-OH-PA | 3-Hydroxypropionic acid |
| C2 | Acetyl carnitine |
| C3 | Propionyl carnitine |
| C3/C2 | Propionyl carnitine-acetyl carnitine ratio |
| Cbl | Cobalamin |
| CBS | Cystathionine beta-synthase |
| DBS | Dried blood spot |
| Hcy | Total homocysteine |
| IMD | Inherited metabolic disease |
| MCA | Methylcitrate |
| Met | Methionine |
| Met/Phe | Methionine-phenylalanine ratio |
| MMA | Methylmalonic acid |
| MS/MS | Tandem mass spectrometry |
| MTHFR | Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase |
| MUT | Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase |
| NBS | Newborn screening |
| NGS2025 | Pilot panel “Newborn screening 2020/2025” |
| Phe | Phenylalanine |
| UKHD | Heidelberg University Hospital |
References
- Wilcken, B.; Wiley, V.; Hammond, J.; Carpenter, K. Screening newborns for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Lindner, M.; Kohlmüller, D.; Olgemöller, K.; Mayatepek, E.; Hoffmann, G.F. Expanded newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry: Results, outcome, and implications. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.M.; Jungner, Y.G. Principios y metodos del examen colectivo para identificar enfermedades. [Principles and practice of mass screening for disease]. Bol. Oficina Sanit. Panam. 1968, 65, 281–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- la Marca, G.; Malvagia, S.; Pasquini, E.; Innocenti, M.; Donati, M.A.; Zammarchi, E. Rapid 2nd-tier test for measurement of 3-oh-propionic and methylmalonic acids on dried blood spots: Reducing the false-positive rate for propionylcarnitine during expanded newborn screening by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Rivada, Á.; Conejero, A.C.; Martín-Hernández, E.; López, A.M.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Villarroya, E.C.; Quijada-Fraile, P.; Bellusci, M.; Calzada, S.C.; Martínez, A.B.; et al. Newborn screening for propionic, methylmalonic acidemia and vitamin b12 deficiency. Analysis of 588,793 newborns. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 35, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan-Schreier, H.; Kebbewar, M.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Wilrich, J.; Abdoh, G.; Ben-Omran, T.; Shahbek, N.; Bener, A.; Al Rifai, H.; Al Khal, A.L.; et al. Newborn population screening for classic homocystinuria by determination of total homocysteine from guthrie cards. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramer, G.; Abdoh, G.; Ben-Omran, T.; Shahbeck, N.; Ali, R.; Mahmoud, L.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Al Rifai, H.; Okun, J.G. Newborn screening for remethylation disorders and vitamin b(12) deficiency-evaluation of new strategies in cohorts from qatar and germany. World J. Pediatr. 2017, 13, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okun, J.G.; Gan-Schreier, H.; Ben-Omran, T.; Schmidt, K.V.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Gramer, G.; Abdoh, G.; Shahbeck, N.; Al Rifai, H.; Al Khal, A.L.; et al. Newborn screening for vitamin b(6) non-responsive classical homocystinuria: Systematical evaluation of a two-tier strategy. JIMD Rep. 2017, 32, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramer, G.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Feyh, P.; Klinke, G.; Monostori, P.; Mütze, U.; Posset, R.; Weiss, K.H.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Okun, J.G. Newborn screening for vitamin b(12) deficiency in germany-strategies, results, and public health implications. J. Pediatr. 2020, 216, 165–172.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.J.; Röschinger, W.; Blessing, H.; Lotz-Havla, A.S.; Schiergens, K.A.; Maier, E.M. Diagnostic challenges using a 2-tier strategy for methylmalonic acidurias: Data from 1.2 million dried blood spots. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 76, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, S.; Arranz, J.A.; Ormazabal, A.; Del Toro, M.; García-Cazorla, Á.; Navarro-Sastre, A.; López, R.M.; Meavilla, S.M.; de Los Santos, M.M.; García-Volpe, C.; et al. Implementation of second-tier tests in newborn screening for the detection of vitamin b(12) related acquired and genetic disorders: Results on 258,637 newborns. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matern, D.; Tortorelli, S.; Oglesbee, D.; Gavrilov, D.; Rinaldo, P. Reduction of the false-positive rate in newborn screening by implementation of ms/ms-based second-tier tests: The mayo clinic experience (2004–2007). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, D.K.; Piazza, A.L.; Pino, G.; Turgeon, C.; Matern, D.; Oglesbee, D.; Raymond, K.; Tortorelli, S.; Rinaldo, P. The combined impact of clir post-analytical tools and second tier testing on the performance of newborn screening for disorders of propionate, methionine, and cobalamin metabolism. Int. J. Neonatal. Screen 2020, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgeon, C.T.; Magera, M.J.; Cuthbert, C.D.; Loken, P.R.; Gavrilov, D.K.; Tortorelli, S.; Raymond, K.M.; Oglesbee, D.; Rinaldo, P.; Matern, D. Determination of total homocysteine, methylmalonic acid, and 2-methylcitric acid in dried blood spots by tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgore, M.B.; Platis, D.; Lim, T.; Isenberg, S.; Pickens, C.A.; Cuthbert, C.; Petritis, K. Development of a universal second-tier newborn screening lc-ms/ms method for amino acids, lysophosphatidylcholines, and organic acids. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 3187–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held, P.K.; Singh, E.; Schwoerer, J.S. Screening for methylmalonic and propionic acidemia: Clinical outcomes and follow-up recommendations. Int. J. Neonatal. Screen 2022, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mütze, U.; Walter, M.; Keller, M.; Gramer, G.; Garbade, S.F.; Gleich, F.; Haas, D.; Posset, R.; Grünert, S.C.; Hennermann, J.B.; et al. Health outcomes of infants with vitamin b(12) deficiency identified by newborn screening and early treated. J. Pediatr. 2021, 235, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R.; Chrastina, P.; Pavlíková, M.; Gouveia, S.; Ribes, A.; Kölker, S.; Blom, H.J.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Bártl, J.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; et al. Newborn screening for homocystinurias: Recent recommendations versus current practice. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kožich, V.; Sokolová, J.; Morris, A.A.M.; Pavlíková, M.; Gleich, F.; Kölker, S.; Krijt, J.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Blom, H.J.; et al. Cystathionine β-synthase deficiency in the e-hod registry-part i: Pyridoxine responsiveness as a determinant of biochemical and clinical phenotype at diagnosis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Kožich, V.; Rinaldo, P.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Merinero, B.; Pasquini, E.; Ribes, A.; Blom, H.J. Newborn screening for homocystinurias and methylation disorders: Systematic review and proposed guidelines. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörster, F.; Kölker, S.; Loeber, J.G.; Cornel, M.C.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Burgard, P. Newborn screening programmes in europe, arguments and efforts regarding harmonisation: Focus on organic acidurias. JIMD Rep. 2017, 32, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forny, P.; Hörster, F.; Ballhausen, D.; Chakrapani, A.; Chapman, K.A.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Dixon, M.; Grünert, S.C.; Grunewald, S.; Haliloglu, G.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of methylmalonic acidaemia and propionic acidaemia: First revision. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 566–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramer, G.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Feyh, P.; Klinke, G.; Monostori, P.; Okun, J.G.; Hoffmann, G.F. High incidence of maternal vitamin b(12) deficiency detected by newborn screening: First results from a study for the evaluation of 26 additional target disorders for the german newborn screening panel. World J. Pediatr. 2018, 14, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monostori, P.; Klinke, G.; Richter, S.; Baráth, Á.; Fingerhut, R.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Kölker, S.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Gramer, G.; Okun, J.G. Simultaneous determination of 3-hydroxypropionic acid, methylmalonic acid and methylcitric acid in dried blood spots: Second-tier lc-ms/ms assay for newborn screening of propionic acidemia, methylmalonic acidemias and combined remethylation disorders. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reischl-Hajiabadi, A.T.; Garbade, S.F.; Feyh, P.; Weiss, K.H.; Mütze, U.; Kölker, S.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Gramer, G. Maternal vitamin b(12) deficiency detected by newborn screening-evaluation of causes and characteristics. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemeinsamer Bundesausschuss. Richtlinie des Gemeinsamen Bundesausschusses über die Früherkennung von Krankheiten bei Kindern (Kinder-Richtlinie). 2022. Available online: https://www.g-ba.de/downloads/62-492-3038/Kinder-RL_2022-12-15_iK-2022-12-15.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg. Pilotprojekt zur Erweiterung des Neugeborenenscreenings um 28 Zusätzliche Zielkrankheiten. 2023. Available online: https://www.klinikum.uni-heidelberg.de/fachliche-zentren/dietmar-hopp-stoffwechselzentrum/neugeborenenscreening/pilotprojekt-ngs-2020 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Mütze, U.; Garbade, S.F.; Gramer, G.; Lindner, M.; Freisinger, P.; Grünert, S.C.; Hennermann, J.; Ensenauer, R.; Thimm, E.; Zirnbauer, J.; et al. Long-term outcomes of individuals with metabolic diseases identified through newborn screening. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20200444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Diodato, D.; Schwahn, B.; Schiff, M.; Bandeira, A.; Benoist, J.F.; Burlina, A.; Cerone, R.; Couce, M.L.; Garcia-Cazorla, A.; et al. Guidelines for diagnosis and management of the cobalamin-related remethylation disorders cblc, cbld, cble, cblf, cblg, cblj and mthfr deficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.A.; Kožich, V.; Santra, S.; Andria, G.; Ben-Omran, T.I.; Chakrapani, A.B.; Crushell, E.; Henderson, M.J.; Hochuli, M.; Huemer, M.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, L.; Lysne, V.; Bjørke-Monsen, A.L.; Behringer, S.; Grünert, S.C.; Spiekerkoetter, U.; Jacobsen, D.W.; Blom, H.J. Biomarkers and algorithms for the diagnosis of vitamin b12 deficiency. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Statistik der Geburten: Lebendgeborene in Deutschland. 2022. Available online: https://www-genesis.destatis.de/genesis/online?operation=abruftabelleBearbeiten&levelindex=1&levelid=1679393907457&auswahloperation=abruftabelleAuspraegungAuswaehlen&auswahlverzeichnis=ordnungsstruktur&auswahlziel=werteabruf&code=12612-0001&auswahltext=&werteabruf=Werteabruf#abreadcrumb (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Zayed, H. Propionic acidemia in the arab world. Gene 2015, 564, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, M.R.; Hörster, F.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Haliloglu, G.; Karall, D.; Chapman, K.A.; Huemer, M.; Hochuli, M.; Assoun, M.; Ballhausen, D.; et al. Proposed guidelines for the diagnosis and management of methylmalonic and propionic acidemia. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Rivada, Á.; Pérez, L.P.; Ruiz-Sala, P.; Navarrete, R.; Conejero, A.C.; Fraile, P.Q.; López, A.M.; Belanger-Quintana, A.; Martín-Hernández, E.; Bellusci, M.; et al. Diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism within the expanded newborn screening in the madrid region. JIMD Rep. 2022, 63, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschocke, J.; Kebbewar, M.; Gan-Schreier, H.; Fischer, C.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Wilrich, J.; Abdoh, G.; Ben-Omran, T.; Shahbek, N.; Lindner, M.; et al. Molecular neonatal screening for homocystinuria in the qatari population. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 1021–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterschmitt, M.J.; Simmons, J.R.; Levy, H.L. Reduction of false negative results in screening of newborns for homocystinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röschinger, W.S.S.; Schuhmann, E.; Nennstiel-Ratzel, U.; Roscher, A.A.; Olgemöller, B. Neue zielerkrankungen im neugeborenenscreening. Monatsschrift Kinderheilkd. 2015, 2015, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mütze, U.; Henze, L.; Gleich, F.; Lindner, M.; Grünert, S.C.; Spiekerkoetter, U.; Santer, R.; Blessing, H.; Thimm, E.; Ensenauer, R.; et al. Newborn screening and disease variants predict neurological outcome in isovaleric aciduria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, E.M.; Liebl, B.; Röschinger, W.; Nennstiel-Ratzel, U.; Fingerhut, R.; Olgemöller, B.; Busch, U.; Krone, N.; Kries, R.V.; Roscher, A.A. Population spectrum of acadm genotypes correlated to biochemical phenotypes in newborn screening for medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 25, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posset, R.; Kölker, S.; Gleich, F.; Okun, J.G.; Gropman, A.L.; Nagamani, S.C.S.; Scharre, S.; Probst, J.; Walter, M.E.; Hoffmann, G.F.; et al. Severity-adjusted evaluation of newborn screening on the metabolic disease course in individuals with cytosolic urea cycle disorders. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 131, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Baumgartner, M.R. The clinical presentation of cobalamin-related disorders: From acquired deficiencies to inborn errors of absorption and intracellular pathways. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 686–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörster, F.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Viardot, C.; Suormala, T.; Burgard, P.; Fowler, B.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Garbade, S.F.; Kölker, S.; Baumgartner, E.R. Long-term outcome in methylmalonic acidurias is influenced by the underlying defect (mut0, mut-, cbla, cblb). Pediatr. Res. 2007, 62, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörster, F.; Garbade, S.F.; Zwickler, T.; Aydin, H.I.; Bodamer, O.A.; Burlina, A.B.; Das, A.M.; De Klerk, J.B.C.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Geb, S.; et al. Prediction of outcome in isolated methylmalonic acidurias: Combined use of clinical and biochemical parameters. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2009, 32, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörster, F.; Tuncel, A.T.; Gleich, F.; Plessl, T.; Froese, S.D.; Garbade, S.F.; Kölker, S.; Baumgartner, M.R. Delineating the clinical spectrum of isolated methylmalonic acidurias: Cbla and mut. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heringer, J.; Valayannopoulos, V.; Lund, A.M.; Wijburg, F.A.; Freisinger, P.; Barić, I.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Burgard, P.; Burlina, A.B.; Chapman, K.A.; et al. Impact of age at onset and newborn screening on outcome in organic acidurias. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haijes, H.A.; Molema, F.; Langeveld, M.; Janssen, M.C.; Bosch, A.M.; van Spronsen, F.; Mulder, M.F.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Jans, J.J.M.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; et al. Retrospective evaluation of the dutch pre-newborn screening cohort for propionic acidemia and isolated methylmalonic acidemia: What to aim, expect, and evaluate from newborn screening? J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Suspected Diagnosis (N) | Results of Confirmatory Tests | Confirmed Diagnosis (N) | Positive Predictive Value (PPV) | Estimated Birth Prevalences [1:X] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmation of the Initially Suspected Diagnosis | Confirmation of Another Diagnosis of the Algorithm | False Positives | For the Initially Suspected Diagnosis | For Any Diagnosis of the Algorithm | Study Cohort [95% CI] | Reports from Literature | |||
| Propionic Acidemia (PA) | 43 | 3 | 2 (1× B12D, 1× MMA) | 38 | 4 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 137,177 [136,814–137,540] | 5000 (Saudi Arabia) [33]–150,000 [34,35] |
| Methylmalonic Acidurias (MMA) | 19 | 4 | 5 (B12D) | 10 | 5 | 0.21 | 0.47 | 109,741 [109,451–110,032] | 50,000–200,000 [10,34,35] |
| Isolated Remethylation Disorders | 54 | 3 | 26 (B12D) | 25 | 3 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 182,902 [182,419–183,387] | No valid data [20] |
| Combined Remethylation Disorders | 3 | 1 | 2 (B12D) | 0 | 1 | 0.33 | 1 | 548,707 [547,256–550,161] | No valid data [20] |
| Homocystinuria | 45 | 1 * | 6 * (B12D) | 39 | 1 * | 0.02 | 0.13 | 548,707 [547,256–550,161] | 1800 (Qatar) [36]–200,000 [37]–900,000 [30] |
| Neonatal Vitamin B12 Deficiency (B12D) | 294 | 113 | 1 (PA) | 180 # | 153 * | 0.38 | 0.39 | 3586 § [3577–3596] | 2000 [11]–3600 [9,17,23]–30,000 [38] |
| TOTAL | 458 | 125 * | 42 * | 292 | 166 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 3305 [3297–3314] | |
| Disease Name, Number (N) of Patients | Age at First NBS Report [days] | Age at Start of Therapy [days] | Age at Disease Confirmation [days] | Symptomatic at First NBS Report | Additional Information | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propionic Acidemia | |||||||
| N = 4 | PA-1 | 7 | 8 | 8 | No | Suspected diagnosis: Vitamin B12 deficiency | |
| PA-2 | 6 | 6 | 7 | Yes | Mild hyperammonemia, metabolic acidosis | ||
| PA-3 | 0 | at birth # | 0 | No | High-risk screening (sibling of PA-2) | ||
| PA-4 | 3 | at birth # | 3 | No | High-risk screening, pre-natal diagnosis | ||
| Methylmalonic Acidurias | |||||||
| N = 5 | MMA-1 | 15 | 15 | 16 | No | Partial vitamin B12-responsiveness, MUT-type | |
| MMA-2 | 8 | 2 | 3 | Yes | Mild hyperammonemia | MUT-type | |
| MMA-3 | 8 | 8 | 9 | Yes | Mild hyperammonemia, metabolic acidosis | MUT-type | |
| MMA-4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | No | MUT-type | ||
| MMA-5 * | 6 | 7 | 7 | No | Full vitamin B12-responsiveness, CblA-type | ||
| Isolated Remethylation Disorders | |||||||
| N = 3 | MTHFR-1 | 8 | 8 | 9 | No | High-risk screening | |
| MTHFR-2 | 6 | 6 | 12 | No | |||
| MTHFR-3 | 52 | 59 | 59 | Yes | Muscular hypotonia | Recall delayed due to IT-technical complications | |
| Combined Remethylation Disorders | |||||||
| N = 1 | CblC | 8 | 8 | 8 | Yes | Feeding difficulties, hypothermia | |
| Homocystinuria | |||||||
| N = 1 | CBS * | 9 | 30 | 30 (B12D)/ 102 (CBS) | No | Full vitamin B6-responsiveness, additional vitamin B12 deficiency | |
| Neonatal Vitamin B12 Deficiency | |||||||
| N = 153 | Median (range) | No | One patient was symptomatic (mild muscular hypotonia) at start of therapy (116 days) due to delayed confirmatory diagnostics despite tracking by NBS laboratory [17] | ||||
| 8.5 (5–52) | 31 (6–157) | 30 (6–145) | |||||
| TOTAL | |||||||
| N = 166 | Median (range) | N = 161 no N = 5 yes | |||||
| 8 (0–52) | 30 (0–157) | 29 (0–145) | |||||
| Age at Sampling: | 41 h | 12 d | 27 d | 74 d | 96 d | 102 d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Values UKHD | ||||||||
| DBS (NBS): | ||||||||
| 1st tier: | Met/Phe | 0.26–0.56 | 0.57 | 0.94 | ||||
| Met [µmol/l] | 11–35 11–40 (ext #) | 33 | 37 | |||||
| 2nd tier: | Hcy [µmol/l] | 0.1–12 0–15 (ext #) | 15.3 | 20.5 | ||||
| Confirmatory diagnostics: | ||||||||
| Plasma: | ||||||||
| Hcy [µmol/l] | 2–14 | 34 | 84 | 85 | 119 | |||
| Met [µmol/l] | 15–35 | - * | 119 | 81 | 97 | |||
| MMA [µmol/l] | 0–0.26 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.22 | n/a | |||
| Vitamin B12 [pmol/l] | 160–670 | 136 | 959 | 497 | 576 | |||
| Folic acid [nmol/l] | 4.5–21 | >45 | 36 | >45 | >45 | |||
| Holo-Transcobalamin [µmol/l] | >60 | 47 | >150 | n/a | n/a | |||
| Urine: | ||||||||
| MMA [mmol/molCrea] | 0–10 | 6.7 | 2.5 | n/a | 6.1 | |||
| Treatment (all oral): | ||||||||
| Vitamin B12: |  | |||||||
| Folic acid: |  § § | |||||||
| Vitamin B6: |  | |||||||
| Age at Sampling: | 40 h | 6 d | 8 d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Values UKHD | |||||
| DBS (NBS): | |||||
| 1st tier: | C3 [µmol/l] | 0−5.5 | 16.3 | 9.1 | 53.8 |
| C3/2 | 0−0.22 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 1.4 | |
| 2nd tier: | MMA [µmol/l] | 0−2.35 | 466.3 | ||
| 3-OH-PA [µmol/l] | 0−77.5 | 109.5 | |||
| MCA [µmol/l] | 0−0.34 | 7.8 | |||
| Hcy [µmol/l] | 0.1−12 | 9.4 | |||
| Confirmatory diagnostics: | |||||
| Plasma: | |||||
| Ammonium [µmol/l] | 12−53 | 27 | |||
| Urine: | |||||
| MMA [mmol/mol creatinine] | 0−18 | 5767 | |||
| MCA [mmol/mol creatinine] | 0−9 | 68 | |||
| MMA-stable isotope quantification [mmol/mol creatinine] | 0−10 | 8363 | |||
| Treatment: | |||||
| Carnitine: |  | ||||
| Vitamin B12: |  | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schnabel, E.; Kölker, S.; Gleich, F.; Feyh, P.; Hörster, F.; Haas, D.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Morath, M.; Gramer, G.; Röschinger, W.; et al. Combined Newborn Screening Allows Comprehensive Identification also of Attenuated Phenotypes for Methylmalonic Acidurias and Homocystinuria. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153355
Schnabel E, Kölker S, Gleich F, Feyh P, Hörster F, Haas D, Fang-Hoffmann J, Morath M, Gramer G, Röschinger W, et al. Combined Newborn Screening Allows Comprehensive Identification also of Attenuated Phenotypes for Methylmalonic Acidurias and Homocystinuria. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153355
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchnabel, Elena, Stefan Kölker, Florian Gleich, Patrik Feyh, Friederike Hörster, Dorothea Haas, Junmin Fang-Hoffmann, Marina Morath, Gwendolyn Gramer, Wulf Röschinger, and et al. 2023. "Combined Newborn Screening Allows Comprehensive Identification also of Attenuated Phenotypes for Methylmalonic Acidurias and Homocystinuria" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153355
APA StyleSchnabel, E., Kölker, S., Gleich, F., Feyh, P., Hörster, F., Haas, D., Fang-Hoffmann, J., Morath, M., Gramer, G., Röschinger, W., Garbade, S. F., Hoffmann, G. F., Okun, J. G., & Mütze, U. (2023). Combined Newborn Screening Allows Comprehensive Identification also of Attenuated Phenotypes for Methylmalonic Acidurias and Homocystinuria. Nutrients, 15(15), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153355







