Abstract
The relationship between vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol and various health outcomes is still debatable and uncertain. We conducted an umbrella review to identify the relationships between vitamin E intake or circulating tocopherol and health outcomes by merging and recalculating earlier meta-analyses. The connections that were found to be statistically significant were then classified into different evidence levels based on p values, between-study heterogeneity, prediction intervals, and small study effects. We finally included 32 eligible meta-analyses with four vitamin E sources and 64 unique health outcomes. Only the association between circulating α-tocopherol and wheeze or asthma in children was substantiated by consistent evidence. Suggestive evidence was suggested for seven results on endothelial function (supplemental vitamin E): serum C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations (supplemental vitamin E), cervical cancer (dietary vitamin E), esophageal cancer (dietary vitamin E), cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN, dietary vitamin E), pancreatic cancer (total vitamin E intake), and colorectal cancer (circulating α-tocopherol levels); all of these showed a protective effect consistent with the vitamin E source. In conclusion, our work has indicated that vitamin E is protective for several particular health outcomes. Further prospective studies are required when other factors that may contribute to bias are considered.
1. Introduction
Vitamin E, as one of the four fat-soluble vitamins, is an essential nutrient for the human body and is crucial to the health of the human body. As an antioxidant, it can protect polyunsaturated fatty acids in membranes from oxidation, regulate the production of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species, and modulate signal transduction [1].
It is used to describe eight kinds of plant sources of fat-soluble compounds (α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocopherols and α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocotrienols). However, only α-tocopherol meets the body’s requirement for vitamin E, based on the fact that it is the form preferentially retained by the body after vitamin E intake. α-tocopherol transfers a protein (α-TTP), expressed in the human liver, which is closely related to maintaining the circulating concentration of α-tocopherol; α-TTP protein is poor at recognizing the other seven forms of vitamin E [2]. Therefore, in the United States, the conclusion that only α-tocopherol meets the definition of vitamin E were supported by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which requires certain labeling of foods and supplements.
Vitamin E is widely found in foods and fruits in our daily lives, especially oils, nuts, and seeds [3]. Therefore, patients, healthcare providers, and people in general are concerned about the relationship between vitamin E and human health. There is a significant and quickly growing body of literature that examines the relationships between vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol levels and numerous disorders and illnesses. For example, according to some research, taking vitamin E supplements may help prevent cardiovascular disease (CVD) by acting as an antioxidant, preventing the oxidation of lipoproteins, and avoiding platelet aggregation [4]. However, some high-quality studies have not supported the prevention of CVD through vitamin E supplementation [5]. This discrepancy was also seen in research on the link between vitamin E and cancer [6]. In addition, epidemiological studies have indicated that vitamin E is also related to neurodegenerative diseases [7], age-related macular degeneration [8], non-alcoholic fatty liver, [9] and so on.
Therefore, we conducted this umbrella review in order to collect, summarize, and assess the quality and strength of the available evidence for meta-analysis, providing an overall picture of vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol with health outcomes and to establish high-quality evidence for therapeutic decisions.
2. Methods
Our protocol has been registered in PROSPERO (CRD42021292442).
2.1. Literature Search and Selection Criteria
We performed systematic searches in PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library of Systematic Reviews to identify systematic reviews and meta-analyses that investigated the relationships between vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol and various health outcomes up to November 2021. We used the following search strategy: (tocopherols OR terms related to vitamin E) AND (systematic review OR meta-analysis) using truncated terms for all fields (Table S1). Two authors conducted a literature search using the suggested search criteria for systematic reviews and meta-analyses in the SIGN guidance. Conflicts were settled through consensus. Additionally, we looked through the references of pertinent articles.
2.2. Selection of Meta-Analyses
Articles were eligible if they were meta-analyses and were conducted using a systematic approach. We included meta-analyses of observational (cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies) and randomized controlled trials (RCTs). We used the PRISMA flowchart to record the study selection process [10]. All eligible meta-analyses evaluated the relationship of vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol with any health outcomes. Studies on genetic variants for Vitamin E metabolism were the exception, as they did not examine any health outcomes for which vitamin E had been explored as the exposure of interest (for example, vitamin E receptor).
Studies conducted in laboratories and on animals were not included. We included each meta-analysis that was included in an article if it had one for each of the several health outcomes. To prevent the inclusion of duplicate studies, we only selected one meta-analysis for each health outcome when multiple meta-analyses addressed the same research issue. In that instance, we included the one with the most primary research or the one that has been updated most recently.
2.3. Data Extraction
The data was extracted by one author and was confirmed by another. We took note of the first author, publication year, vitamin E source, populations, number of studies, research design(s), funding details, and any conflicts of interest for each qualifying meta-analysis. We also extracted the risk ratio, odds ratio, mean differences, standardized mean differences, and weighted mean differences, as reported by the authors in the meta-analysis, and the corresponding 95% CI.
We also retrieved the Egger’s p value to assess publication bias, estimates of the fraction of variance representing real variations in impact size (I2), and any estimate of variance between trials (τ2) [11]. Any ambiguity or differences were resolved through discussion.
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
Each meta-analysis was evaluated for methodological quality using Online AMSTAR 2, a metric for assessing systematic reviews; it is a 16-item checklist that makes up the AMSTAR 2 quality evaluation instrument [12]. The validity of a review and its results can be significantly affected by seven crucial criteria in AMSTAR 2. It should be noted that the selection of key items can be adjusted according to specific circumstances. Two researchers rated the methodological quality. Any differences were resolved by consensus.
Using the GRADE methodology, the strength of the evidence for each outcome covered by the umbrella review was assessed [13]. There are eight domains in it that have the potential to raise or decrease the confidence of the evidence. Evidence from eligible meta-analysis was ultimately assigned into four categories ranging from high quality to very low quality.
2.5. Data Analysis
We recalculated the selected meta-analysis for each health outcome using the precise relative risk estimates. We updated the summary effect size and associated 95% Cl using DerSimonian and Laird’s random-effects model, which takes into account heterogeneity both within and between trials. The between-study heterogeneity was recalculated using the Q test p value and I2 statistic. We also estimated the 95% prediction interval (PI) using recalculated data. The distribution of true effects, represented by the 95% PI, is where 95% of original research on the same issue will fall [14]. And correlations between vitamin E and the risk of health outcomes were divided into 4 categories (Table S2).
2.6. Patient Involvement
The questionnaires and health outcome measures for this study were not developed with input from any patients. No patients were consulted on the umbrella review’s research design or how to interpret the findings. We are planning to engage local policy maker to disseminate the research through social media and publish the summary of the findings at the website of the Cochrane China Center.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Meta-Analyses
We carefully reviewed 89 meta-analyses of 2288 articles retrieved from three databases, and we ultimately included 32 publications in our works, as seen in Figure 1. A total of 409 RCTs and 268 observational studies were all from the vitamin E supplementation group. 32 eligible meta-analyses provided 4 types of vitamin E sources and 64 unique health outcomes. Table 1 lists the general characteristics of all included studies. Table S3 provides a list of the 57 excluded articles. We reanalyzed the summary effects of all studies. Finally, detailed summary effects are presented in the form of dichotomous variables and continuous variables. One health outcome (1.6%) was supported by consistent evidence (Class I). 7 results (10.9%) were suggestive evidence (Class III), 23 results (35.9%) had suggestive evidence (Class IV) backing them up, and 33 results (51.6%) were nonsignificant (Class V).
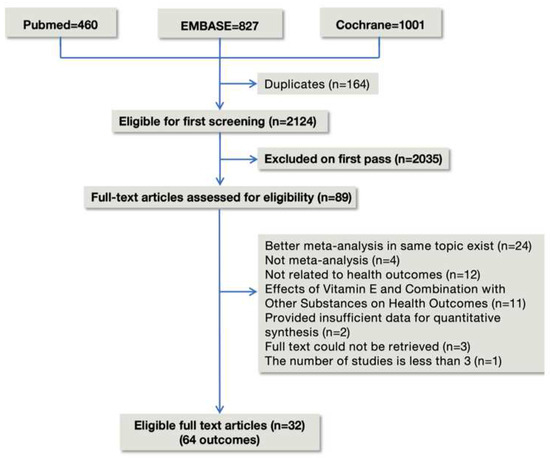
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the study selection for the umbrella review.

Table 1.
The results and the level of evidence of the effect of vitamin E and risk of health outcomes.
3.2. Supplemental Vitamin E Intake
Supplemental intake of vitamin E was the most extensively studied area, including 43 health outcomes. We divided these health outcomes into five categories, including cardiovascular system, special population (patients receiving hemodialysis, patients with renal impairment, patients with diabetes mellitus, children, and older adults), cancer, nerve system, and others. A total of 13 of the health outcomes used binary variable, with OR or RR as the effect metrics (Figure 2A). The remaining 30 health outcomes were selected as continuous variables, with mean difference (MD), standardized mean difference (SMD), or weighted mean difference (WMD) as effect metrics (Figure 2B). No studies were rated as consistent evidence (Class I).
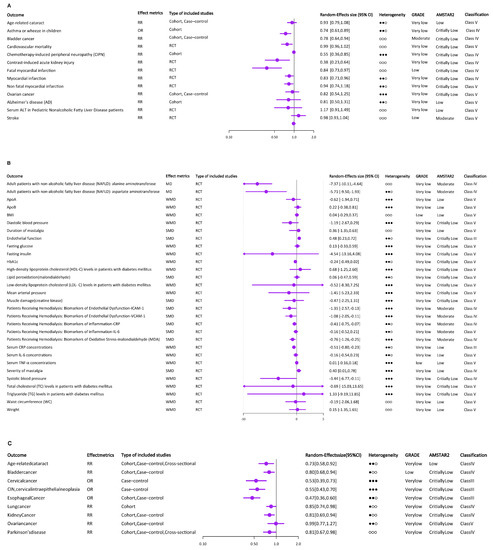
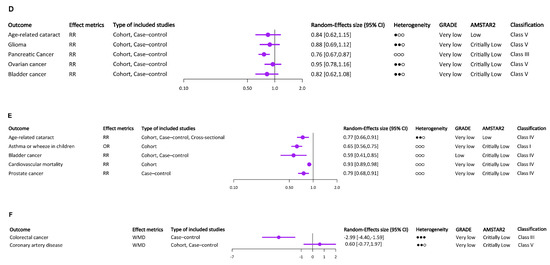
Figure 2.
The results and the level of evidence of the effect of vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol and risk of multiple health outcomes. (A) The results and the level of evidence of the effect of supplemental vitamin E and risk of health outcomes (binary variable). (B) The results and the level of evidence of the effect of supplemental vitamin E and risk of health outcomes (continuous variable). (C) The results and the level of evidence of the effect of dietary vitamin E and risk of health outcomes (binary variable). (D) The results and the level of evidence of the effect of total vitamin E and risk of health outcomes (binary variable). (E) The results and the level of evidence of the effect of circulating α-tocopherol levels and risk of health outcomes (binary variable). (F) The results and the level of evidence of the effect of circulating α-tocopherol levels and risk of health outcomes (continuous variable). ○○○ indicates I2 ≤ 25%, ●○○ indicates 25% < I2 ≤ 50%, ●●○ indicates 50% < I2 ≤ 75%, ●●● indicates I2 ≥ 75%.
3.2.1. Cardiovascular System
Supplemental vitamin E intake reduces mortality from CVD [15]. A meta-analysis of how adult vitamin E consumption affects inflammatory biomarkers provided more evidence for this conclusion. CRP testing is a highly effective cardiovascular mortality predictor. Based on an analysis of 26 RCTs in this meta-analysis, serum CRP concentrations were significantly lower after vitamin E supplementation. In contrast to serum CRP, the effect of vitamin E on IL-6 and TNF-α was not significant [16]. But interestingly, adult ApoA1 and ApoB levels, which are thought to be predictors of CVD, were not significantly affected by vitamin E supplementation [17]. Additionally, a single vitamin E supplement dramatically reduced myocardial infarction when compared to controls. And the decrease in deadly myocardial infarction was what caused this result [18]. Supplemental vitamin E has a protective effect on endothelial function [19]. Among the effects on blood pressure, vitamin E supplements only decreased systolic blood pressure (SBP) [20].
3.2.2. Cancer
Supplemental vitamin E was negatively related with the incidence of bladder cancer [21]. But there was no impact of vitamin E supplementation on the risk of ovarian cancer [22].
3.2.3. Special Population
In patients receiving hemodialysis, supplemental vitamin E may help alleviate oxidative stress and systemic inflammation [23]. Furthermore, vitamin E supplementation combined hydration significantly decreased the incidence of contrast-induced acute kidney damage (CIAKI) [24]. There was no clear relationship between vitamin E supplementation and HbA1c fasting glucose, insulin concentrations [25], and various blood lipid parameters [26] in diabetes mellitus patients. For children, lower probabilities of asthmatic disorders were related to maternal consumption of vitamin E [27]. Supplemental vitamin E, however, was not related to a lower level of blood ALT in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [28]. One meta-analysis’s results showed supplemental vitamin E consumption had a small effect on the likelihood of developing age-related cataracts (ARC) [29].
3.2.4. Nervous System
It was impossible to determine the precise link between supplementary vitamin E and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) due to follow-up issues with participants, missing data in the original included studies, and the high heterogeneity shown by the forest plots (I2 = 68%) [30]. Additionally, the effects of supplemental vitamin E on lowering stroke risk were still not supported by statistically meaningful data [31]. Interestingly, the incidence and signs of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) were improved by vitamin E supplementation [32].
3.2.5. Others
Adult patients with NAFLD who received additional vitamin E had lower liver enzyme levels than those of placebo patients [33]. Additionally, supplemental vitamin E intake can reduce mastalgia’s severity and duration. However, because of the studies’ high degrees of variability, the authors suggest more research utilizing common methodologies based on the CONSORT declaration [34]. Supplementation of vitamin E had no discernible impact on those common indicators of obesity [35].
3.3. Dietary Vitamin E Intake
Most of the meta-analyses on the relationship between vitamin E and cancer focused on this section, which contained nice health outcomes, seven of which were cancer related. Interestingly, with the exception of ovarian cancer, which did not have any association with dietary vitamin E, the other included cancers were inversely associated with dietary vitamin E intake [22], including lung cancer [36], kidney cancer [37], cervical cancer, CIN [38], esophageal cancer [39], and bladder cancer [21]. According to dose–response analyses, lung cancer risk decreased by 5% with each 2 mg/d increase in dietary vitamin E consumption. Dietary vitamin E intake was related to ARC and PD in addition to health outcomes related to cancer. It had a strong correlation with a lower incidence of ARC [29]. Etminan et al. discovered that vitamin E consumption in the diet protects against PD [40]. All of the health outcomes used a binary variable, with OR or RR as the effect metrics (Figure 2C). And no studies were rated as consistent evidence (Class I).
3.4. Total Vitamin E Intake
Similarly, except for ovarian cancer, all other cancers included were inversely associated with total vitamin E intake, including glioma [41], pancreatic cancer [42], and bladder cancer [21]. A lower incidence of both cancer and ARC was strongly associated with total vitamin E consumption [29]. All of the health outcomes used a binary variable, with RR as the effect metrics (Figure 2D). And only studies on the link between pancreatic cancer and total vitamin E intake were rated as suggestive evidence (Class III).
3.5. Circulating α-Tocopherol Levels
Circulating α-tocopherol’s results are shown in Figure 2E,F. Seven meta-analyses examined the association between circulating α-tocopherol levels and health outcomes, including ARC [29], asthma or wheeze in children [27], bladder cancer [21], cardiovascular mortality [15], colorectal cancer [43], CVD [44], and prostate cancer [45]. Except that circulating α-tocopherol levels did not significantly reduce the risk of CVD, there was a protective association between circulating α-tocopherol levels and the remaining six health outcomes. The association between circulating α-tocopherol levels and asthma or wheeze in children was rated as consistent evidence (Class I).
3.6. Heterogeneity between Primary Studies
We reanalyzed I2 values, which were used to assess study heterogeneity, for the included meta-analyses by random effects model (Table 1). We reanalyzed 22 health outcomes from the included meta-analyses and found significant heterogeneity (I2 > 75%); furthermore, 21 health outcomes from included meta-analyses detected moderate heterogeneity (I2 > 50%). A low level of heterogeneity (I2 > 25%) was observed in four health outcomes from included meta-analyses. The remaining 17 health outcomes from included meta-analyses showed no heterogeneity (I2 > 0%).
3.7. Publication Bias of Included Studies
By using Egger’s test, we identified publication bias in 32 health outcomes. There was statistical evidence of publication bias for four health outcomes (Table 1). This included bladder cancer (dietary vitamin E), esophageal cancer (dietary vitamin E), pancreatic cancer (total vitamin E intake), and asthma or wheeze in children (circulating α-tocopherol levels).
3.8. AMSTAR and GRADE Classification of Included Studies
Using online AMSTAR 2, we evaluated the methodological quality. In Table S4, for each of the included meta-analyses, unique AMSTAR data were shown. And they were rated as having high, moderate, poor, and critically low quality. With regard to quality of evidence, a total of three meta-analyses (9.4%) were classified as moderate. Seven meta-analyses (21.9%) were graded as low quality. The remaining 22 meta-analyses (68.8%) were classified as critically low. Due to the small sample size, bias risk, inconsistent results, and imprecision, none of them were given a high ranking. Detailed GRADE scores for every health outcome were summarized in Table S5.
4. Discussion
This detailed comprehensive review included 32 publications including 4 types of vitamin E source and 64 unique health outcomes from 409 RCTs and 268 observational studies. The role of vitamin E has been studied in a wide range of health outcomes, including cancers, CVD, autoimmune diseases, renal diseases, metabolic diseases, respiratory diseases, and aging diseases. Among them, the most studied diseases are still focused on cancers and CVD. For the meta-analysis of RCTs, outcomes were only limited to supplemental vitamin E. Only six meta-analyses of health outcomes in supplemental vitamin E group came from observational studies, including ARC, AD, cardiovascular mortality, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, and childhood asthmatic diseases; among them, the association between the first four health outcomes and supplemental vitamin E was not significant, and the last two health outcomes had beneficial associations with supplemental vitamin E. The remaining three meta-analyses of vitamin E sources and related health outcomes were based on original studies from observational studies.
Most meta-analyses that have included only observational studies have shown associations that are limited by the false positive caveats that accompany the evidence from observational studies, and very few, if any, may translate to effective interventions when tested in RCTs. In addition, not all meta-analyses of included RCTs can yield accurate associations, especially when the sample size of the RCTs is limited and the level of statistical significance is weak. For example, although the umbrella review suggests that supplemental vitamin E may benefit indicators of oxidative stress and inflammation in hemodialysis patients, given the limited quality of the included RCTs and the heterogeneity of the results reported in the available trials, we still favor following the new guidelines for nutrition in CKD [46], which support that there is insufficient proof to advise them to take vitamin E supplements. According to the results of this umbrella review, there was only consistent evidence of a beneficial association between circulating α-tocopherol levels and asthma or wheeze in children in both randomized and observational evidence. However, given that this meta-analysis included observational studies, both the Grade and AMSTAR2 grades were very low.
Among all the health outcomes associated with vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol, this umbrella review demonstrated that vitamin E demonstrated a protective effect in 31 health outcomes, including 16 related to supplemental vitamin E (including alanine aminotransferase and spartate aminotransferase indicators in adult patients with NAFLD, oxidative stress and inflammation indicators in hemodialysis patients, childhood asthma, bladder cancer, CIPN, contrast-induced acute kidney injury, endothelial function, systolic blood pressure, myocardial infarction and fatal myocardial infarction, and severity of mastalgia), 8 related to dietary vitamin E (including ARC, Parkinson’s disease, and various cancers: bladder cancer, cervical cancer, CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, and kidney cancer), 1 related to total vitamin E (pancreatic cancer), and 6 related to circulating α-tocopherol levels (including ARC, asthma or wheeze in children, cardiovascular mortality, and 3 types of cancers: bladder cancer, colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer). Vitamin E did not show a significant effect on the remaining 33 health outcomes. There were 27, 1, 4, and 1 health outcomes associated with supplemental vitamin E, dietary vitamin E, total vitamin E, and circulating α-tocopherol levels, respectively. No negative associations were found between vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol and health outcomes in this umbrella review. This result also broadens the use of vitamin E for some specific health outcomes. For example, this umbrella review suggested that supplemental vitamin E was not related with reduced level of serum ALT in pediatric NAFLD patients. However, the 2018 guidelines suggested appropriate doses of vitamin E for children with biopsied NAFLD, although further study is needed before vitamin E can be widely recommended in clinical practice [47]. This also indicates that the use of appropriate doses of vitamin E in pediatric NAFLD patients is acceptable until more robust research evidence is available.
Additionally, more than half of the meta-analyses of observational studies (17/27) reported nominally statistically significant protective associations. However, meta-analyses of RCTs reported nominally statistically significant pooled results for only 15 of 37 healthy outcomes (including alanine aminotransferase and spartate aminotransferase indicators in adult patients with NAFLD, oxidative stress and inflammation indicators in hemodialysis patients, serum CRP concentrations, CIPN, contrast-induced acute kidney injury, endothelial function, systolic blood pressure, myocardial infarction and fatal myocardial infarction, and severity of mastalgia). This result may be due to the lower statistical power of the meta-analysis of included RCTs and the fact that the results of RCTs are more conservative than those of observational studies. In the results of this umbrella review, none of the very promising results found in meta-analyses of observational studies have been tested in meta-analyses of RCTs.
Cancer and CVD are the two most studied diseases in this umbrella review, and the underlying mechanism of vitamin E’s role in these two diseases may be closely related to its powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant abilities [48]. According to the 2014 USPSTF, it is insufficient to support the claim that supplementing with vitamin E does not lower the development either of cardiovascular disease or cancer in healthy populations without known nutritional deficiencies. Adequate evidence shows that vitamin E supplementation has either little or no substantial harm. Therefore, the USPSTF draws the conclusion that supplementing with vitamin E has no discernible advantage in terms of preventing cancer or cardiovascular disease [49]. The revised USPSTF recommendation statement from 2022 reiterates the main finding of the statement from 2014, but it further urges intake of foods high in antioxidant vitamins and other nutrients for general health and wellness as well as for particular preventative purposes [50]. In this umbrella review, although no studies were classified as consistent or highly suggestive evidence, dietary vitamin E showed positive protective effects on most cancer types (except for ovarian cancer). Therefore, the conclusions of this umbrella review are also consistent with USPSTF recommendations. With the deepening of related research, a growing body of preclinical research shows that the structure of vitamin E is a crucial element in the prevention of cancer caused by vitamin E. Mechanistic studies, in particular, have demonstrated that γ, δ, γ, and δ-tocotrienols are significantly more potent than α-tocopherol in blocking many cancer-prevention pathways [51]. In contrast to α-tocopherol, which is largely unmetabolized, γ-tocopherol, δ-tocopherol, γ-tocotrienol, and δ-tocotrienol are easily metabolized, and their long-chain metabolites 13′-COOHs are special dual inhibitors of COXs and 5-LOX and have stronger anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects than some vitamers that are not metabolized [52,53]. Most dietary vitamin E or vitamin E supplements exert their effects in the human body in the form of α-tocopherol [54]. Therefore, this may partially explain why the risk of ovarian cancer was not associated with supplemental or dietary vitamin E in this umbrella review. This also suggests that future RCTs should focus more on the effect of intake of one specific vitamin E isoforms on cancer.
This umbrella review suggests that supplemental vitamin E intake improves endothelial function, reduces myocardial infarction, and reduces mortality from CVD. In terms of cardiovascular mortality, the circulating α-tocopherol levels suggest the same conclusion. However, circulating α-tocopherol levels did not appear to be related to the risk of CVD. This paradoxical and interesting phenomenon caught our attention. According to the existing epidemiological studies, increasing vitamin E intake can reduce the risk of CVD. However, this effect was only shown in people who used high-dose vitamin E supplements daily for more than 2 years [55]. It could be concluded that the dose of vitamin E intake was crucial in the process of its effect. This might be related to the levels of circulating α-tocopherol in food or supplements, which were eventually mainly utilized by the human body to exert their effects. It might also be that high doses of vitamin E intake ensure the enrichment of other isoforms of tocopherols or tocotrienols in human circulation to exert a protective effect against CVD. For example, some studies confirmed an inverse association between γ-tocopherol supplementation alone and the risk of coronary heart disease [56]. Therefore, future studies should fully consider the possible effect of vitamin E supplementation dose and effective tocopherols or tocotrienols circulating concentrations on outcomes when developing individualized medication strategies for CVD patients.
This umbrella review has systematically integrated the current evidence about the associations between vitamin E intakes or circulating α-tocopherol and multiple health outcomes for the first time. Generally, effect metrics with 95% CI are used to determine the link between exposure and outcomes, but if studies demonstrate significant heterogeneity or publication bias, this connection has to be questioned [57]. We were the first to evaluate the quality and strength of the evidence from all included meta-analyses using the AMSTAR2 and GRADE classification methods. Nevertheless, some possible limitations should be noted. Firstly, a relatively large number of the meta-analyses were “Critically Low” in the AMSTAR2 classification as well as “Very low” in GRADE categorizations. This phenomenon was largely caused by many studies not assessing the potential impact of risk of bias in individual studies on meta-analysis results and did not consider the risk of bias in individual studies when discussing review results. For GARDE categorization, serious imprecision derived from limited studies numbers and population numbers as well as considerate confidence intervals for the estimates of effect sizes. Undetected publication bias is due to the fact that most of the original studies did not report funnel plots or Egger p values. Furthermore, few studies met the upgrading items, including a relatively large magnitude of effect and beneficial plausible confounding factors. There is no statistical association between AMSTAR2 and GRADE, since the rating domains differ. Secondly, small populations and studies were included in some of the eligible meta-analyses, which likely contributed to publication bias. Another limitation of our study is that we were not able to accurately assess vitamin E intake from different sources across the studies because we were not able to extract data on vitamin E intake. In addition, the intake of the sources of vitamin E intake varied among the various original studies included in the meta-analysis. For example, the umbrella review showed that adding extra vitamin E to the diet of adults with NAFLD reduced their liver enzyme levels. Given the current lack of approved drugs to treat NAFLD, the mainstay of patient care for NAFLD remains tailoring diet and other lifestyle changes to the needs of each individual patient. Vitamin E is often considered as the first line of defense against NAFLD when dietary and other lifestyle changes are not enough [58]. However, with the deepening of research, some studies support that the long-term use of vitamin E in NAFLD patients may affect the mortality of patients [59]. It can be concluded that the choice of safe therapeutic dose of vitamin E still needs to be further explored. The specific dose of vitamin E supplementation should also be considered in the design of future studies. In this umbrella review, most meta-analyses produced pooled effects of the original studies, which measured vitamin E exposure by whether vitamin E was consumed or not. This may also partly explain the source of heterogeneity in the meta-analysis. Nevertheless, this umbrella review provides a bird’s eye view of the available evidence examining the association between vitamin E intakes or circulating α-tocopherol and multiple health outcomes and a comprehensive assessment of the strength of the available evidence and can indicate potential priorities for future research. In the future, there is still a need for clinicians and trialists to conduct RCTs to fill the current gap of high-quality evidence between vitamin E and most health outcomes.
In conclusion, this umbrella review extensively studied a wide range of relationships between vitamin E intake or circulating α-tocopherol and various health outcomes. There are some indications that vitamin E may be associated with several health outcomes. However, no firm general conclusion can be drawn about benefits. Associations between dietary vitamin E, total vitamin E and circulating α-tocopherol levels, and relevant health outcomes have only been validated in observational studies, but these associations were either not statistically significant or not verified in meta-analyses that included RCTs. RCTs for cancer-related outcomes are clearly lacking. Additionally, evidence from the meta-analysis of RCTs suggested that supplemental vitamin E was associated with 15 health outcomes. These health outcomes may not need to be extensively investigated in future studies. However, for health outcomes with low quality of evidence, the association with vitamin E still needs further research and better designed trials to draw firm conclusions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu15153301/s1, Table S1. Search strategy; Table S2. Summary of evidence classification for meta-analyses; Table S3. The list of excluded meta-analyses by full text screening with exclusion reason; Table S4. Assessments of AMSTAR scores; Table S5. GRADE classification of quality of evidence of all included meta-analyses.
Author Contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows—Z.X. and L.L. designed and conducted research and wrote the paper; Z.J. and Y.M. analyzed data; and H.L., X.J., B.L. and K.W. had primary responsibility for final content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by 1.3.5 project for disciplines of excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (ZYGD18011) and The National Natural Science Fund of China: The Role and Mechanism of Autophagy Mediated by β Adrenergic Receptor in Mechanical Stimulation Induced Biological and Functional Changes in Bladder Cell (81873601).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, G.Y.; Han, S.N. The Role of Vitamin E in Immunity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, M.G.; Head, B. Vitamin E: How much is enough, too much and why! Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 177, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. FoodData Centralexternal Link Disclaimer; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Rychter, A.M.; Hryhorowicz, S.; Słomski, R.; Dobrowolska, A.; Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. Antioxidant effects of vitamin E and risk of cardiovascular disease in women with obesity—A narrative review. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.M.; Cook, N.R.; Gaziano, J.M.; Gordon, D.; Ridker, P.M.; Manson, J.E.; Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E. Vitamin E in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer: The Women’s Health Study: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2005, 294, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, H.Y.; Tan, W.D.; Liao, W.; Wong, W.F. Vitamin E therapy beyond cancer: Tocopherol versus tocotrienol. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icer, M.A.; Arslan, N.; Gezmen-Karadag, M. Effects of vitamin E on neurodegenerative diseases: An update. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2021, 81, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, W.G.; Glynn, R.J.; Chew, E.Y.; Buring, J.E. Vitamin E and age-related macular degeneration in a randomized trial of women. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podszun, M.C.; Frank, J. Impact of vitamin E on redox biomarkers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Gavaghan, D.; Egger, M. Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: Power of statistical tests and prevalence in the literature. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2000, 53, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, F.; Guyatt, G.; Zuk, V.; Vandvik, P.O.; Alba, A.C.; Mustafa, R.; Vernooij, R.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Munn, Z.; Roshanov, P.; et al. GRADE Guidelines 28: Use of GRADE for the assessment of evidence about prognostic factors: Rating certainty in identification of groups of patients with different absolute risks. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 121, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Deeks, J.J. Interpretation of random effects meta-analyses. BMJ 2011, 342, d549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Parohan, M.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary and circulating vitamin C, vitamin E, β-carotene and risk of total cardi-ovascular mortality: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 1872–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbaghi, O.; Sadeghian, M.; Nazarian, B.; Sarreshtedari, M.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Maleki, V.; Alizadeh, M.; Shokri, A.; Sadeghi, O. The effect of vitamin E supplementation on selected inflammatory biomarkers in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedi-Kalajahi, F.; Zarezadeh, M.; Dehghani, A.; Musazadeh, V.; Kolahi, A.; Shabbidar, S.; Djafarian, K. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the impact of oral vitamin E supplementation on apolipoproteins A1 and B100. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, L.; Perri, L.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Iacoviello, L.; De Gaetano, G.; Violi, F. Supplementation with vitamin E alone is associated with reduced myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashor, A.W.; Siervo, M.; Lara, J.; Oggioni, C.; Afshar, S.; Mathers, J.C. Effect of vitamin C and vitamin E supplementation on endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, M.R.; Safabakhsh, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Asbaghi, O.; Khosroshahi, M.Z. Effect of vitamin E supplementation on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Shi, F.; Qu, Y. Association of vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E and risk of bladder cancer: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Meng, F.; Tian, T.; Xu, J.; Yan, F. Association of vitamin E on the risk of ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20193311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.U.; Yeom, J.; Kim, W. Beneficial Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation on Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.H.; Kim, S.N.; Park, H.W.; Chung, S.; Kim, K.S. Could vitamin E prevent contrast-induced acute kidney injury? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, S.; Tao, A.; Chen, G.; Zhang, M. Influence of vitamin E supplementation on glycaemic control: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.; Falahi, E.; Barakatun-Nisak, M.Y.; Hanipah, Z.N.; Redzwan, S.M.; Yusof, L.M.; Gheitasvand, M.; Rezaie, F. Systematic review and meta-analyses of vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) supplementation and blood lipid parameters in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Does vitamin E prevent asthma or wheeze in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhy, A.A.; Al-Hussaini, A.A.; Nobili, V. Does vitamin E improve the outcomes of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Saudi Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2014, 20, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Xie, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhang, D. Vitamin E and risk of age-related cataract: A meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of vitamin E supplementation on the risk and progression of AD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.C.; Lim, R.; Lee, K.W.; Ooi, C.Y.; Chuan, D.R.; Looi, I.; Hay, Y.K.; Khan, N.A.K. Effects of vitamin E on stroke: A systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2021, 6, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shan, H.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Dai, H.; Ye, Z. Vitamin E for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 684550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadarlis, A.; Antza, C.; Bakaloudi, D.R.; Doundoulakis, I.; Kalopitas, G.; Samara, M.; Dardavessis, T.; Maris, T.; Chourdakis, M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The effect of vitamin E supplementation in adult patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, K.; Charandabi, S.M.A.; Hasanzade, R.; Mirghafourvand, M. Effect of vitamin E on severity and duration of cyclic mastalgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, M.R.; Jamshidi, S.; Zarezadeh, M.; Khorshidi, M.; Olang, B.; Hezaveh, Z.S.; Sohouli, M.; Aryaeian, N. Can vitamin E supplementation affect obesity indices? A systematic review and meta-analysis of twenty-four randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Bo, Y.C.; Liu, X.X.; Qiu, C.G. Association of dietary vitamin E intake with risk of lung cancer: A dose-response meta-analysis. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 26, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Huang, Y.; Yi, S.; Fang, Z.; Li, L. Association of vitamin E intake with reduced risk of kidney cancer: A meta-analysis of obser-vational studies. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2015, 21, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, X. Effect of vitamin E supplementation on uterine cervical neoplasm: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Xu, F.; Qiao, T. Association between dietary vitamin E intake and esophageal cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etminan, M.; Gill, S.S.; Samii, A. Intake of vitamin E, vitamin C, and carotenoids and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S. Vitamin E intake is not associated with glioma risk: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 43, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, Q.; Tang, T.; Yang, Z. Vitamin E intake and pancreatic cancer risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shu, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Zheng, R.; Ma, D.; Yang, C.; Guan, X. Link between risk of colorectal cancer and serum vitamin E levels: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. Medicine 2017, 96, e7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Hou, X.; Shi, J. Circulating tocopherols and risk of coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xu, Q. Blood α-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol levels and risk of prostate cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for nutrition in CKD: 2020 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 64, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Natural forms of vitamin E as effective agents for cancer prevention and therapy. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, V.A.; US Preventive Services Task Force. Vitamin, mineral, and multivitamin supplements for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, M. USPSTF recommends against beta carotene or vitamin E supplements for preventing CVD or cancer in adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, Jc110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Natural forms of vitamin E: Metabolism, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities and their role in disease pre-vention and therapy. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yin, X.; Lill, M.A.; Danielson, M.L.; Freiser, H.; Huang, J. Long-chain carboxychromanols, metabolites of vitamin E, are potent inhibitors of cyclooxy-genases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20464–20469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Park, N.Y.; Rostgaard-Hansen, A.L.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Q. Vitamin E metabolite 13′-carboxychromanols inhibit pro-inflammatory enzymes, induce apoptosis and autophagy in human cancer cells by modulating sphingolipids and suppress colon tumor development in mice. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayden, H.J.; Traber, M.G. Absorption, lipoprotein transport, and regulation of plasma concentrations of vitamin E in humans. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stonehouse, W.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Thompson, C.H.; Abeywardena, M.Y. Short term effects of palm-tocotrienol and palm-carotenes on vascular function and cardiovascular disease risk: A randomised controlled trial. Atherosclerosis 2016, 254, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozen, E.; Demirel, T.; Ozer, N.K. Vitamin E: Regulatory role in the cardiovascular system. Iubmb Life 2019, 71, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.L.; Jeong, G.H.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kronbichler, A.; Van Der Vliet, H.J.; Grosso, G.; Galvano, F.; Aune, D.; Kim, J.Y.; et al. Tea consumption and risk of cancer: An umbrella review and meta-analysis of observa-tional studies. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1437–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumpail, B.J.; Li, A.A.; John, N.; Sallam, S.; Shah, N.D.; Kwong, W.; Cholankeril, G.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. The Role of Vitamin E in the Treatment of NAFLD. Diseases 2018, 6, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Gluud, L.L.; Simonetti, R.G.; Gluud, C. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2007, 297, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).