Relative Validity of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire for Disadvantaged Families in Hong Kong
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Dietary Assessments
2.3.1. Short Version FFQ
2.3.2. Three-Day Dietary Records
2.3.3. Dietary Data Analysis
2.3.4. Prevalence of Deficient or Excessive Dietary Intake
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of Excessive or Deficient Dietary Intake
3.3. Relative Validity of FFQ and Three-Day Dietary Records
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.3.2. Cross-Tabulation of Dietary Data Reported by FFQ and Dietary Records
3.3.3. One-Sample t-Test and Linear Regression for the FFQ and Dietary Records
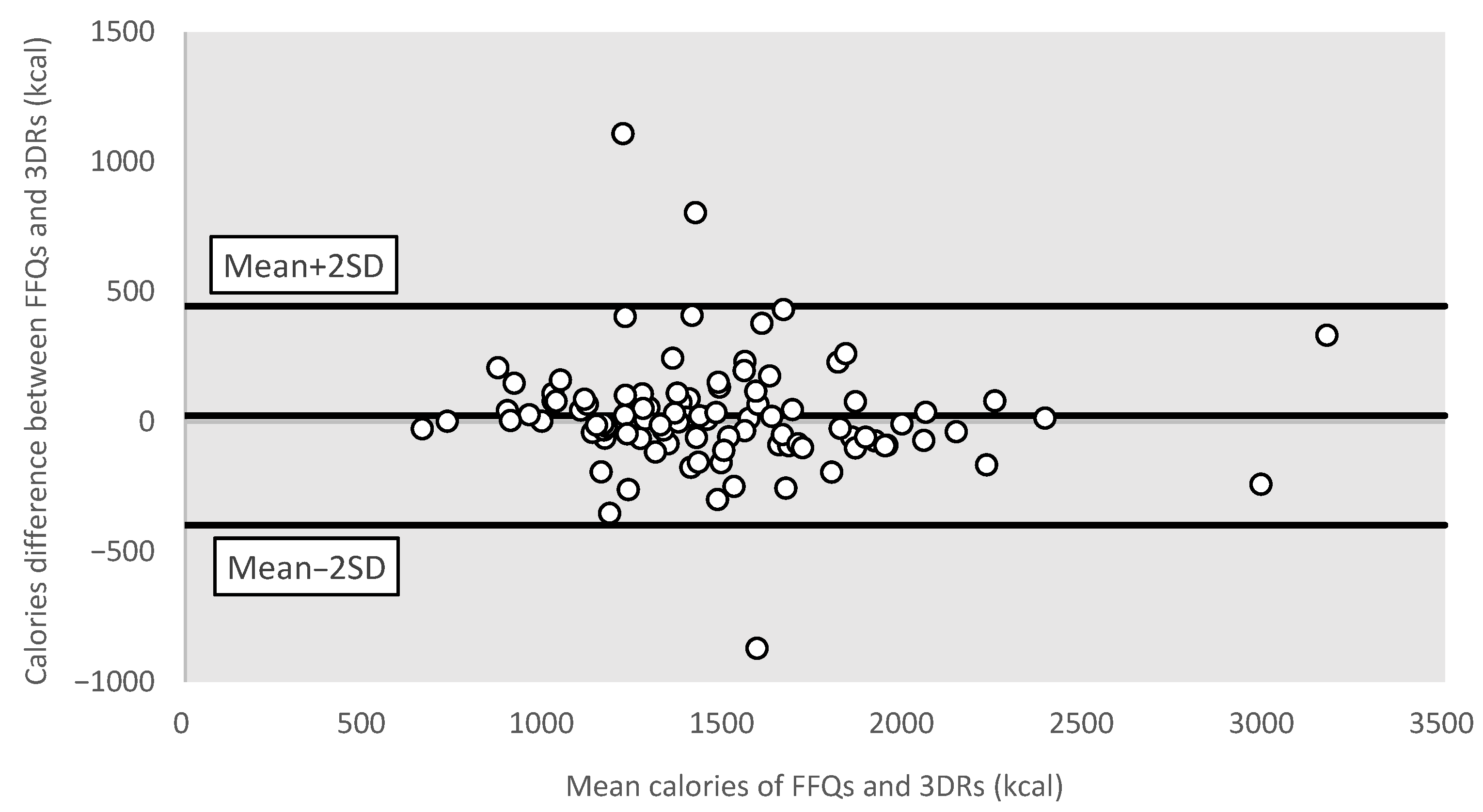
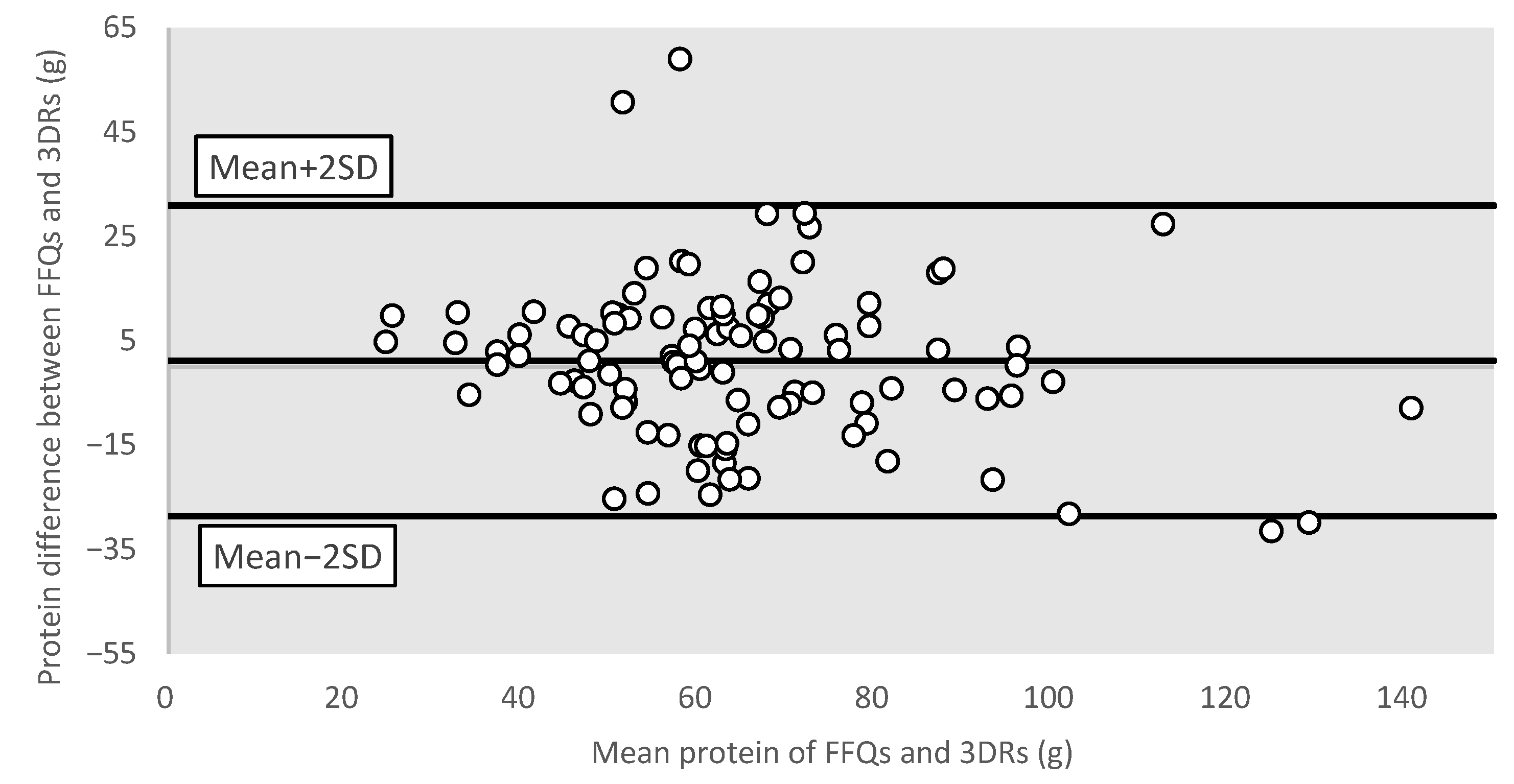
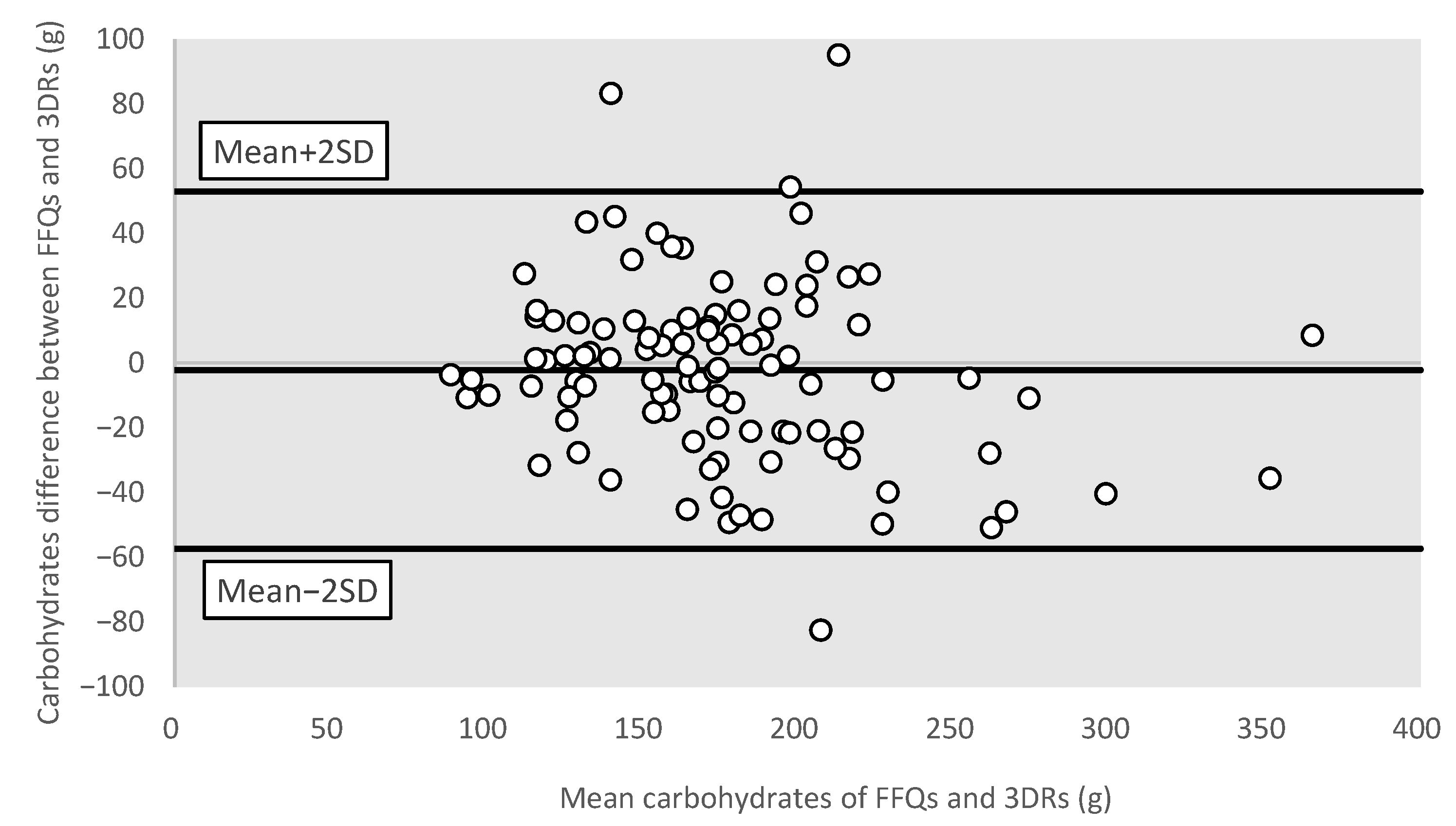
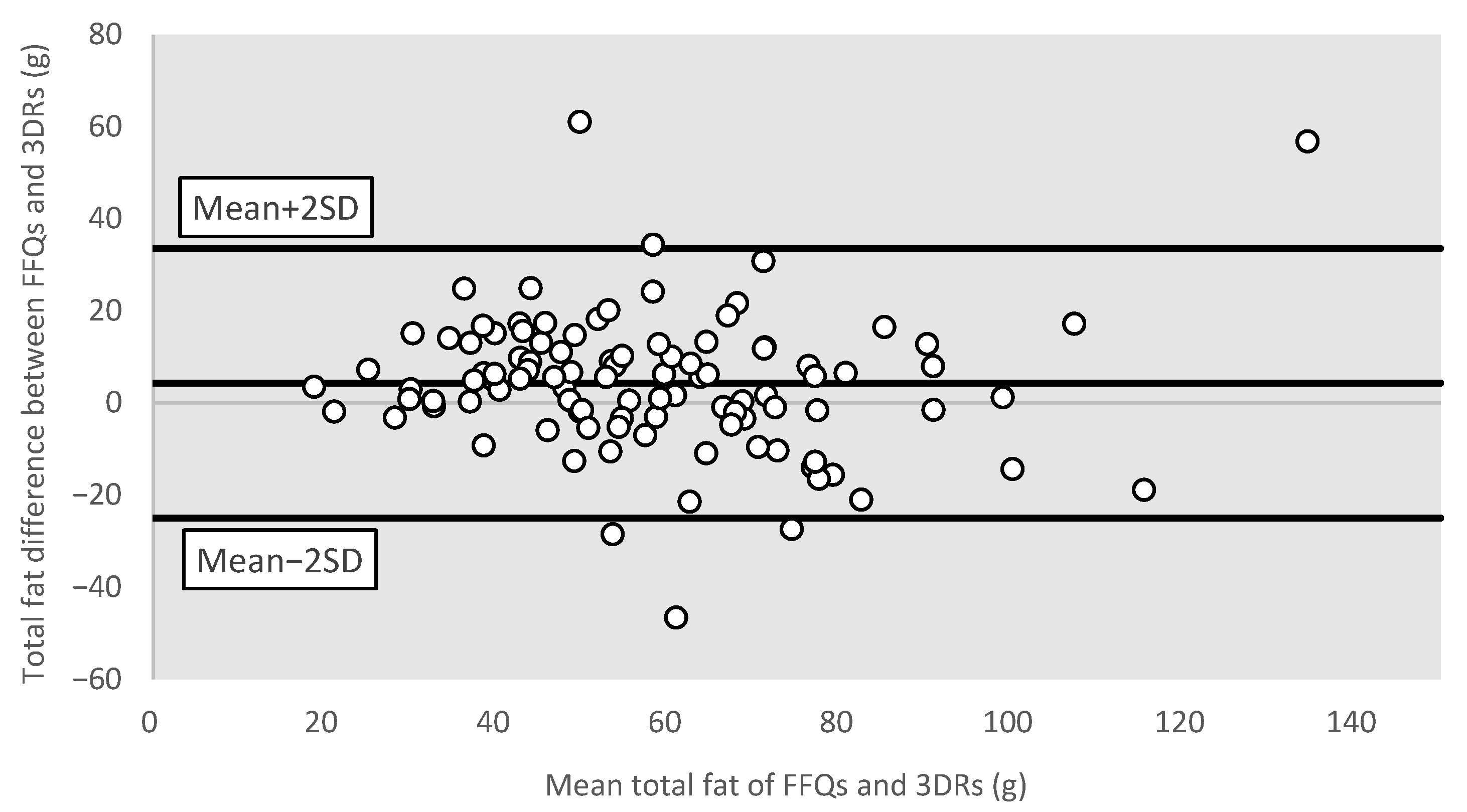
3.3.4. Bland–Altman Plots for Different Nutrients
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Main Findings
4.2. Prevalence of Deficient or Excessive Dietary Intakes
4.3. Relative Validity of Short Version FFQ
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Director-General’s Statement on IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-statement-on-ihr-emergency-committee-on-novel-coronavirus-(2019-nCov) (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Latest Situation of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Hong Kong. 2022. Available online: https://chp-dashboard.geodata.gov.hk/covid-19/en.html (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Wong, M.C.S.; Ng, R.W.Y.; Chong, K.C.; Lai, C.K.C.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Boon, S.S.; Chan, P.K.S. Stringent containment measures without complete city lockdown to achieve low incidence and mortality across two waves of COVID-19 in Hong Kong. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e003573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszynska, E.; Cofta, S.; Hernik, A.; Otulakowska-Skrzynska, J.; Springer, D.; Roszak, M.; Sidor, A.; Rzymski, P. Self-Reported Dietary Choices and Oral Health Care Needs during COVID-19 Quarantine: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yeoh, E.K.; Yung, T.K.C.; Wong, M.C.S.; Dong, D.; Chen, X.; Chan, M.K.Y.; Wong, E.L.Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Z.; et al. Change in eating habits and physical activities before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Hong Kong: A cross-sectional study via random telephone survey. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, T.K.C.; Tsang, S.Y.T.; Tam, D.D.S. Exacerbation of household food insecurity among low-income families in Hong Kong during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary, T.C.K.; Juliana, C.N.C.; Vincent, T.F.Y.; Chow, C.-C.; Lynn, W.W.T.; Cockram, C.S. A Low Socio-Economic Status Is an Additional Risk Factor for Glucose Intolerance in High Risk Hong Kong Chinese. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 17, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Meng, X.; Wild, S.H.; Gasevic, D.; Jackson, C.A. Socioeconomic status and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan: A systematic review. J. Glob. Health 2017, 7, 011103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Andrellucchi, A.; Doreste-Alonso, J.; Henríquez-Sánchez, P.; Cetin, I.; Serra-Majem, L. Dietary assessment methods for micronutrient intake in pregnant women: A systematic review. BJN 2009, 102, S64–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispim, S.P.; Ribeiro, R.C.L.; Silva, M.M.S.; Rosado, L.E.F.P.; Rosado, G.P. The influence of education in the validation process of a food frequency questionnaire for adults in Viçosa, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.; Li, S.; Leung, J.; Wh, T.; Chan, R. Reproducibility and Relative Validity of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire for Chinese Pregnant Women in Hong Kong. Austin J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 8, 1146. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.Y.; Hoi, B.P.; Wong, E.L. Lay health worker intervention in pre-diabetes management: Study protocol of a pragmatic randomized controlled trial for Chinese families living in inadequate houses. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 957754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werfalli, M.; Raubenheimer, P.J.; Engel, M.; Musekiwa, A.; Bobrow, K.; Peer, N.; Hoegfeldt, C.; Kalula, S.; Kengne, A.P.; Levitt, N.S. The effectiveness of peer and community health worker-led self-management support programs for improving diabetes health-related outcomes in adults in low- and-middle-income countries: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Leung, S.S.F.; Ho, S.C.; Lam, T.H.; Janus, E.D. A food frequency questionnaire for use in the Chinese population in Hong Kong: Description and examination of validity. Nutr. Res. 1997, 17, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese-Nutrition-Society. Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes, 2013rd ed.; Science Press Basic Theory: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Diet, Nutrition, and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases Report of a Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Willett, W. Nutritional Epidemiology, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Report of Population Health Survey 2014/2015; Surveillance and Epidemiology Branch, Centre for Health Protection, Department of Health, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government: Hong Kong, 2017.
- Drenjančević-Perić, I.; Jelaković, B.; Lombard, J.H.; Kunert, M.P.; Kibel, A.; Gros, M. High-salt diet and hypertension: Focus on the renin-angiotensin system. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2011, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietary Macro- and Micro-Nutrient Recommended Intake of Chinese People. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/yingyang/wsbz.shtml (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Dietary Fibre. Available online: https://www.chp.gov.hk/en/static/90018.html (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- The First Hong Kong Total Diet Study: Minerals. Available online: https://www.cfs.gov.hk/english/programme/programme_firm/files/Report_on_the_1st_HK_Total_Diet_Study_Minerals_e.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Stern, P.H. Bone Regulators and Osteoporosis Therapy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, A.L.; Davies, P.S.W.; Hill, R.J.; Milne, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, R.X.; Heath, A.-L.M.; Grant, C.C.; Wall, C.R. Validation and calibration of the Eating Assessment in Toddlers FFQ (EAT FFQ) for children, used in the Growing Up Milk—Lite (GUMLi) randomised controlled trial. BJN 2021, 125, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mestral, C.; Mayén, A.-L.; Petrovic, D.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Bochud, M.; Stringhini, S. Socioeconomic Determinants of Sodium Intake in Adult Populations of High-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Public Health 2017, 107, e1–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Mean (±SD)/N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 42.1 (±8.0) |
| Sex (Female) | 99 (96.1) |
| BMI at enrolment (kg/m2) | 25.6 (±1.8) |
| Education | |
| Junior Secondary School or less | 63 (61.2) |
| Senior Secondary School | 30 (29.1) |
| Tertiary or above | 10 (9.7) |
| Working Status | |
| Working | 20 (19.4) |
| Non-working # | 83 (80.6) |
| Total Family Income (HKD) | |
| <10,000 | 43 (41.8) |
| 10,000–20,000 | 41 (39.8) |
| >20,000 | 19 (18.5) |
| Parameters | Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|
| Above DRIs | |
| Energy from Total Fat b | 68.9% |
| Energy from Saturated Fat b | 37.9% |
| Energy from Trans Fat d | 1.9% |
| Total Sugar b | 38.8% |
| Cholesterol d | 45.6% |
| Sodium d | 91.3% |
| Below DRIs | |
| Total Energy a | 82.5% |
| Protein e | 26.2% |
| Carbohydrates e | 13.6% |
| Total Dietary Fibre c | 97.1% |
| Water c | 77.7% |
| Vitamin C e | 62.1% |
| Calcium e | 92.2% |
| Copper e | 14.6% |
| Iron e | 92.2% |
| Magnesium e | 89.3% |
| Manganese c | 95.2% |
| Phosphorus e | 17.5% |
| Potassium c | 66.0% |
| Zinc e | 52.4% |
| Parameters | FFQ | Three-Day DRs | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Median | 25th | 75th | Mean | SD | Median | 25th | 75th | |
| Energy (kcal) | 1486.2 | 410.2 | 1422.9 | 1205.3 | 1700.0 | 1462.1 | 427.8 | 1405.7 | 1204.2 | 1694.3 |
| Energy from Total Fat (kcal) | 539.1 | 189.7 | 517.5 | 424.9 | 636.8 | 500.9 | 197.1 | 496.5 | 347.6 | 629.9 |
| Energy from Saturated Fat (kcal) | 149.9 | 52.0 | 139.8 | 115.4 | 175.4 | 136.2 | 63.9 | 120.2 | 87.8 | 179.3 |
| Energy from Trans Fat (kcal) | 5.2 | 2.6 | 4.6 | 3.3 | 6.3 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| Protein (g) | 65.4 | 20.3 | 62.2 | 50.0 | 76.8 | 64.2 | 23.2 | 60.6 | 49.0 | 73.8 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 174.4 | 47.6 | 169.4 | 146.3 | 198.1 | 176.6 | 53.3 | 171.5 | 135.4 | 202.8 |
| Total Dietary Fibre (g) | 12.9 | 4.2 | 12.3 | 10.3 | 15.0 | 12.2 | 5.0 | 10.9 | 8.2 | 16.0 |
| Total sugar (g) | 46.1 | 19.9 | 44.1 | 30.8 | 59.8 | 35.8 | 19.0 | 33.8 | 21.4 | 44.8 |
| Total fat (g) | 60.1 | 21.1 | 57.9 | 47.3 | 70.8 | 55.8 | 21.9 | 55.2 | 38.7 | 70.6 |
| Saturated fat (g) | 16.7 | 5.8 | 15.5 | 12.8 | 19.5 | 15.1 | 7.1 | 13.4 | 9.8 | 19.9 |
| Trans fat (g) | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 316.6 | 134.0 | 289.7 | 218.6 | 380.2 | 307.0 | 143.9 | 282.9 | 205.6 | 406.0 |
| Water (g) | 2156.8 | 779.1 | 2070.6 | 1514.4 | 2705.9 | 2084.8 | 708.5 | 1989.1 | 1579.1 | 2668.6 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 96.5 | 41.7 | 86.8 | 66.3 | 128.3 | 77.1 | 46.5 | 71.6 | 42.2 | 101.8 |
| Calcium (mg) | 517.4 | 203.6 | 462.1 | 365.8 | 623.2 | 449.6 | 212.1 | 413.4 | 315.3 | 532.5 |
| Copper (mg) | 1.2 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| Iron (mg) | 9.8 | 3.1 | 9.5 | 7.5 | 11.5 | 8.2 | 3.5 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 9.9 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 227.0 | 68.3 | 217.7 | 183.5 | 257.6 | 200.3 | 70.8 | 193.6 | 153.7 | 227.3 |
| Manganese (mg) | 2.8 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 2.0 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 3.1 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 872.6 | 273.7 | 826.7 | 672.9 | 995.0 | 818.0 | 288.0 | 776.3 | 643.2 | 947.0 |
| Potassium (mg) | 1856.4 | 549.0 | 1763.8 | 1475.7 | 2175.3 | 1837.6 | 652.5 | 1735.6 | 1371.8 | 2146.9 |
| Sodium (mg) | 2989.2 | 711.3 | 2955.7 | 2610.0 | 3343.5 | 3334.8 | 1212.2 | 3121.6 | 2451.8 | 4147.2 |
| Zinc (mg) | 8.0 | 2.7 | 7.7 | 6.3 | 9.8 | 6.6 | 2.8 | 6.1 | 4.8 | 7.7 |
| Parameters | Pearson Correlation Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|
| Crude | Energy Adjusted | |
| Energy (kcal) | 0.87 ** | - |
| Energy from Total Fat (kcal) | 0.76 ** | - |
| Energy from Saturated Fat (kcal) | 0.68 ** | - |
| Energy from Trans Fat (kcal) | 0.61 ** | - |
| Protein (g) | 0.76 ** | 0.50 ** |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 0.85 ** | 0.68 ** |
| Total Dietary Fibre (g) | 0.78 ** | 0.69 ** |
| Total sugar (g) | 0.68 ** | 0.62 ** |
| Total fat (g) | 0.76 ** | 0.49 ** |
| Saturated fat (g) | 0.68 ** | 0.44 ** |
| Trans fat (g) | 0.61 ** | 0.49 ** |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 0.62 ** | 0.47 ** |
| Water (g) | 0.77 ** | 0.75 ** |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 0.60 ** | 0.55 ** |
| Calcium (mg) | 0.56 ** | 0.43 ** |
| Copper (mg) | 0.51 ** | 0.34 ** |
| Iron (mg) | 0.47 ** | 0.30 ** |
| Magnesium (mg) | 0.74 ** | 0.53 ** |
| Manganese (mg) | 0.49 ** | 0.27 ** |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 0.75 ** | 0.40 ** |
| Potassium (mg) | 0.75 ** | 0.61 ** |
| Sodium (mg) | 0.49 ** | 0.20 ** |
| Zinc (mg) | 0.56 ** | 0.21 ** |
| Parameters | Crude a | Adjusted for Energy a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Same Quartile | Adjacent Quartile b | Extreme Quartile c | Same Quartile | Adjacent Quartile b | Extreme Quartile c | |
| Energy (kcal) | 71.8 | 24.3 | 3.9 | - | - | - |
| Energy from Total Fat (kcal) | 60.2 | 35.0 | 4.9 | - | - | - |
| Energy from Saturated Fat (kcal) | 50.5 | 37.9 | 11.7 | - | - | - |
| Energy from Trans Fat (kcal) | 46.6 | 37.9 | 15.5 | - | - | - |
| Protein (g) | 49.5 | 35.9 | 14.6 | 41.7 | 40.8 | 17.5 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 61.2 | 30.1 | 8.7 | 61.2 | 30.1 | 8.7 |
| Total Dietary Fibre (g) | 52.4 | 39.8 | 7.8 | 46.6 | 42.7 | 10.7 |
| Total sugar (g) | 49.5 | 38.8 | 11.7 | 45.6 | 40.8 | 13.6 |
| Total fat (g) | 58.3 | 35.9 | 5.8 | 41.7 | 43.7 | 14.6 |
| Saturated fat (g) | 50.5 | 38.8 | 10.7 | 32.0 | 42.7 | 25.2 |
| Trans fat (g) | 43.7 | 41.7 | 14.6 | 31.1 | 37.9 | 31.1 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 48.5 | 37.9 | 13.6 | 43.7 | 34.0 | 22.3 |
| Water (g) | 58.3 | 33.0 | 8.7 | 61.2 | 31.1 | 7.8 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 49.5 | 39.8 | 10.7 | 45.6 | 37.9 | 16.5 |
| Calcium (mg) | 43.7 | 38.8 | 17.5 | 35.9 | 47.6 | 16.5 |
| Copper (mg) | 42.7 | 32.0 | 25.2 | 29.1 | 51.5 | 19.4 |
| Iron (mg) | 37.9 | 39.8 | 22.3 | 34.0 | 33.0 | 33.0 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 49.5 | 41.7 | 8.7 | 37.9 | 47.6 | 14.6 |
| Manganese (mg) | 43.7 | 39.8 | 16.5 | 38.8 | 39.8 | 21.4 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 53.4 | 31.1 | 15.5 | 38.8 | 40.8 | 20.4 |
| Potassium (mg) | 56.3 | 35.0 | 8.7 | 41.7 | 38.8 | 19.4 |
| Sodium (mg) | 41.7 | 37.9 | 20.4 | 33.0 | 42.7 | 24.3 |
| Zinc (mg) | 45.6 | 35.9 | 18.4 | 39.8 | 35.0 | 25.2 |
| Parameters | Mean Difference | p-Values | Beta-Coefficient | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) | 24.094 | 0.258 | −0.045 | 0.395 |
| Energy from Total Fat (kcal) | 38.171 | 0.005 * | −0.043 | 0.557 |
| Energy from Saturated Fat (kcal) | 13.684 | 0.005 * | −0.243 | 0.006 * |
| Energy from Trans Fat (kcal) | 3.387 | <0.001 * | 0.443 | <0.001 * |
| Protein (g) | 1.178 | 0.433 | −0.151 | 0.040 * |
| Carbohydrates (g) | −2.221 | 0.425 | −0.122 | 0.033 * |
| Total Dietary Fibre (g) | 0.714 | 0.024 * | −0.211 | 0.003 * |
| Total sugar (g) | 10.322 | <0.001 * | 0.051 | 0.561 |
| Total fat (g) | 4.298 | 0.004 * | −0.042 | 0.573 |
| Saturated fat (g) | 1.520 | 0.005 * | −0.243 | 0.006 * |
| Trans fat (g) | 0.376 | <0.001 * | 0.443 | <0.001 * |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 9.628 | 0.423 | −0.088 | 0.364 |
| Water (g) | 71.966 | 0.153 | 0.107 | 0.136 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 19.358 | <0.001 * | −0.136 | 0.178 |
| Calcium (mg) | 67.761 | <0.001 * | −0.053 | 0.620 |
| Copper (mg) | 0.239 | <0.001 * | −0.004 | 0.971 |
| Iron (mg) | 1.671 | <0.001 * | −0.183 | 0.126 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 26.718 | <0.001 * | −0.041 | 0.595 |
| Manganese (mg) | 0.335 | 0.003 * | 0.100 | 0.389 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 54.544 | 0.007 * | −0.058 | 0.444 |
| Potassium (mg) | 18.774 | 0.665 | −0.197 | 0.010 * |
| Sodium (mg) | −345.572 | 0.001 * | −0.684 | <0.001 * |
| Zinc (mg) | 1.366 | <0.001 * | −0.077 | 0.466 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, V.W.-K.; Chan, C.Y.; Hoi, B.P.-K.; Chan, J.H.-Y.; Li, L.; Li, M.Y.-Y.; Chung, E.S.-K.; Sin, H.H.-F.; Wong, E.L.-Y.; Lo, K.K.-H. Relative Validity of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire for Disadvantaged Families in Hong Kong. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122668
Chan VW-K, Chan CY, Hoi BP-K, Chan JH-Y, Li L, Li MY-Y, Chung ES-K, Sin HH-F, Wong EL-Y, Lo KK-H. Relative Validity of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire for Disadvantaged Families in Hong Kong. Nutrients. 2023; 15(12):2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122668
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Vicky Wai-Ki, Crystal Ying Chan, Becky Pek-Kei Hoi, Joyce Ho-Yi Chan, Liz Li, Maggie Ying-Yee Li, Edwin Shun-Kit Chung, Henry Ho-Fai Sin, Eliza Lai-Yi Wong, and Kenneth Ka-Hei Lo. 2023. "Relative Validity of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire for Disadvantaged Families in Hong Kong" Nutrients 15, no. 12: 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122668
APA StyleChan, V. W.-K., Chan, C. Y., Hoi, B. P.-K., Chan, J. H.-Y., Li, L., Li, M. Y.-Y., Chung, E. S.-K., Sin, H. H.-F., Wong, E. L.-Y., & Lo, K. K.-H. (2023). Relative Validity of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire for Disadvantaged Families in Hong Kong. Nutrients, 15(12), 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122668






