Preparation of Red Ginseng Marc-Derived Gintonin and Its Application as a Skin Nutrient
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
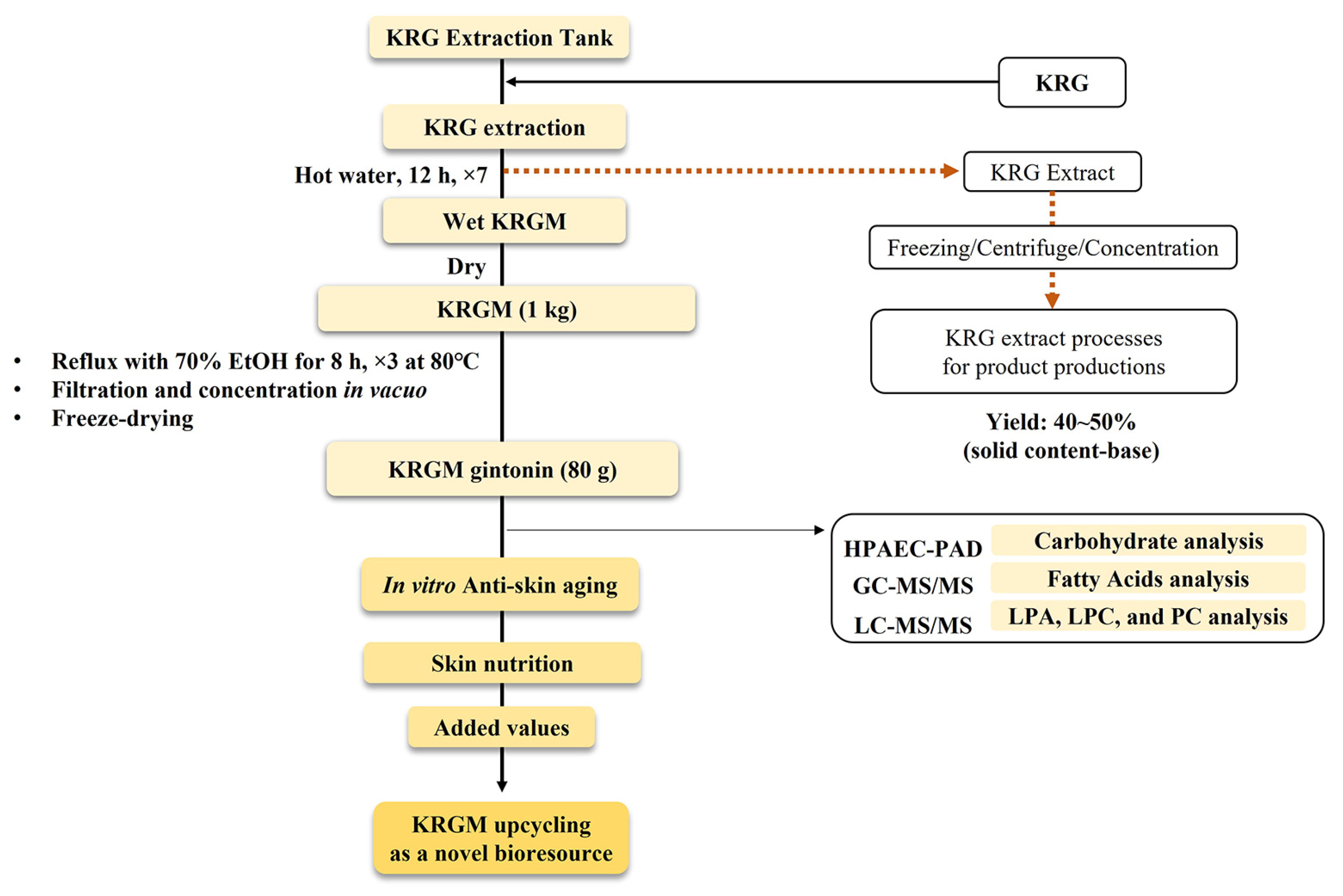
2.2. Preparation of KRGM Gintonin
2.3. Carbohydrate Analysis of KRGM Gintonin
2.4. Fatty Acids Analysis of KRGM Gintonin
2.5. LPA, LPC, and Phosphatidylcholine Analysis of KRGM Gintonin
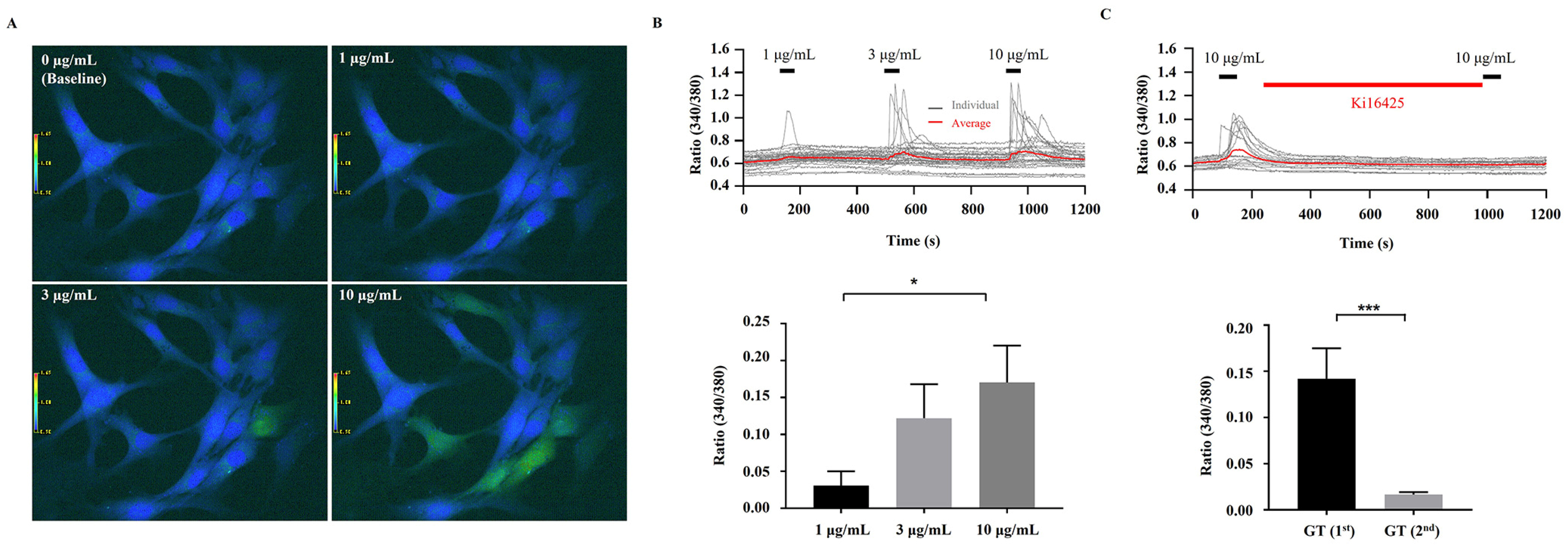
2.6. Intracellular Ca2+ Assay
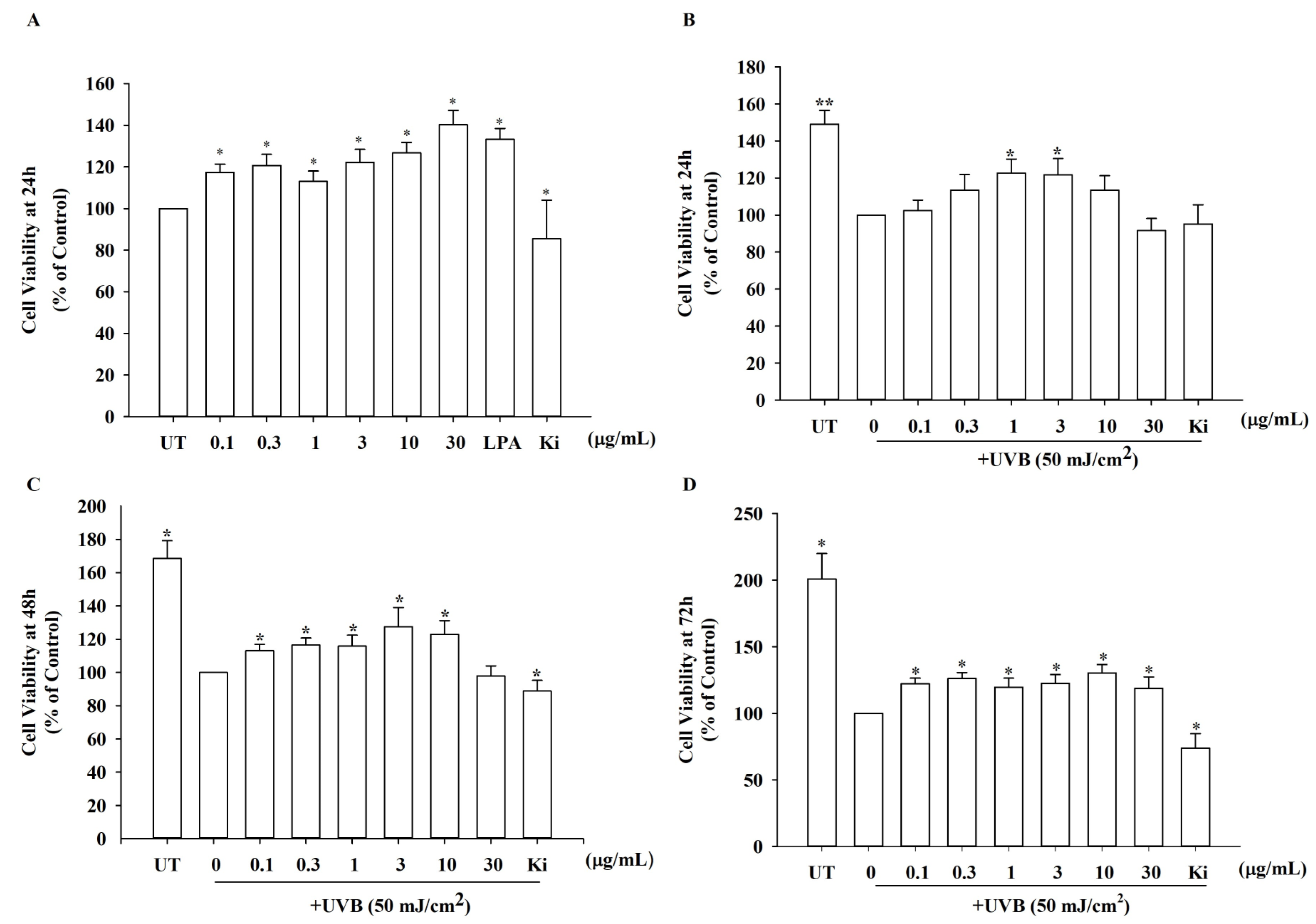
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
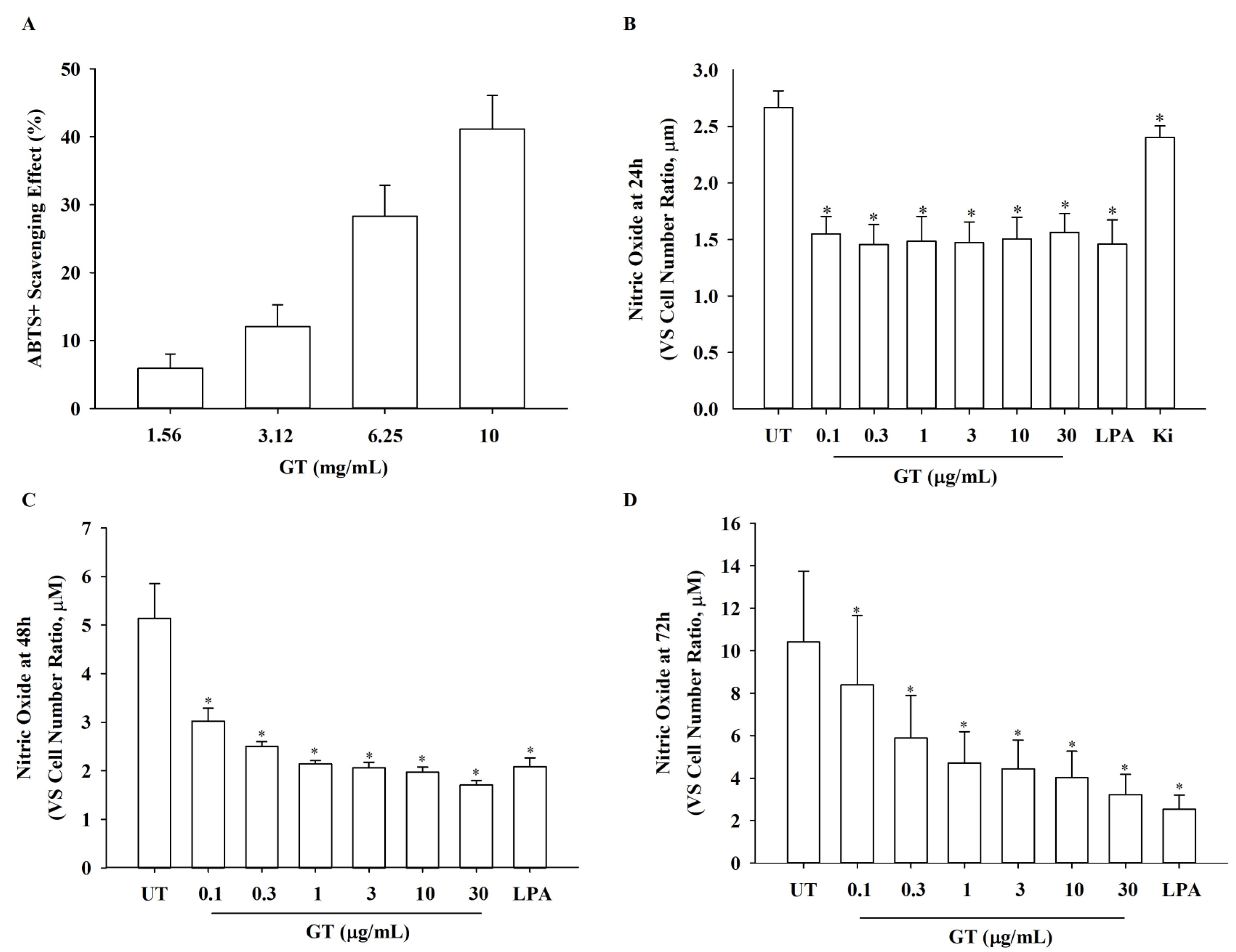
2.8. Analysis of ABTS+ Radical Scavenging Activity (H2O2-Specific Test)
2.9. Nitric Oxide Analysis
2.10. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Analysis
2.11. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Analysis
2.12. Scratch Wound Healing Assay
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of KRGM Gintonin from KRGM
3.2. Quantitation of LPA C18:2, LPC C18:2, and Phosphatidylcholine (PC C16:0–18:2 and C16:0–18:2) Free Fatty Acids in KRGM Gintonin
3.3. [Ca2+]i Transient Induction by KRGM Gintonin
3.4. Effects of KRGM Gintonin on the Viability of HDFs Exposed to UVB
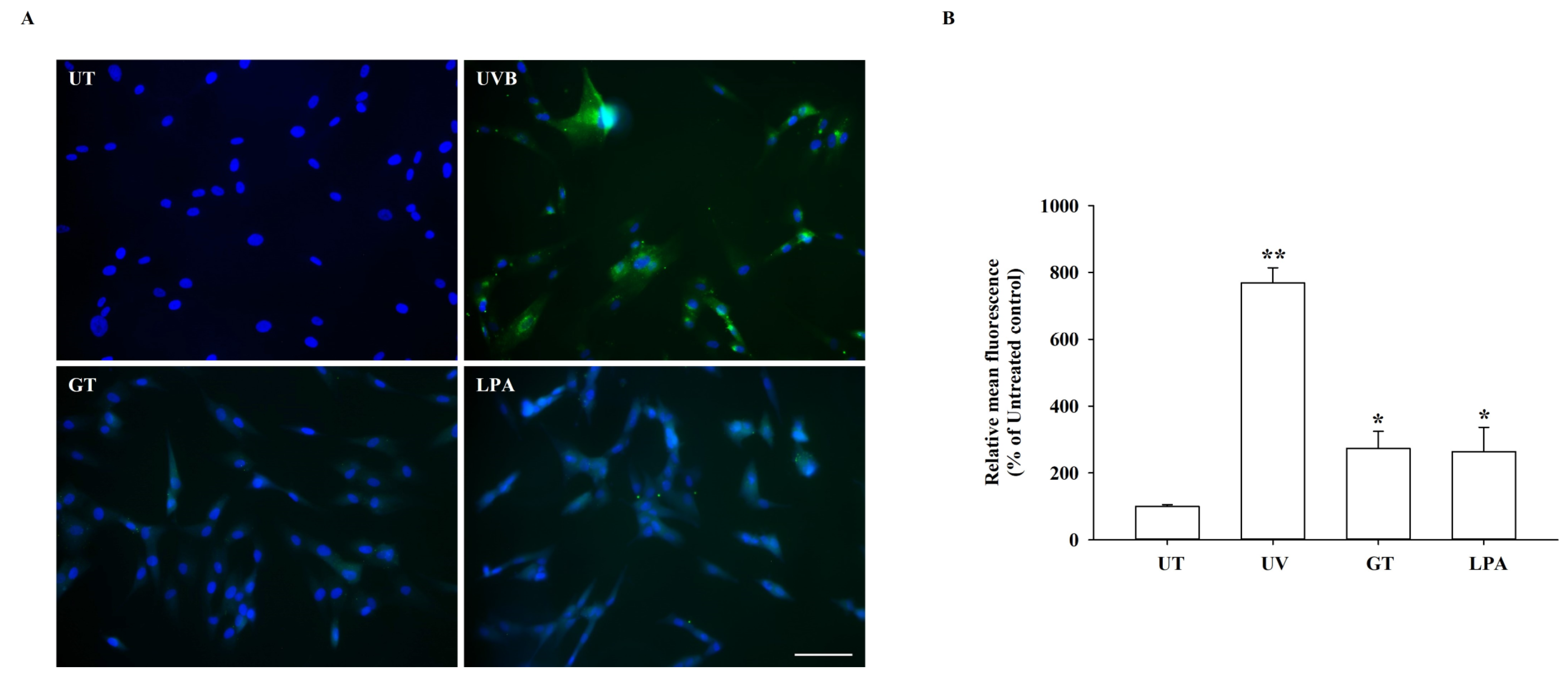
3.5. Effects of KRGM Gintonin on ABTS+ Radical, NO, and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production
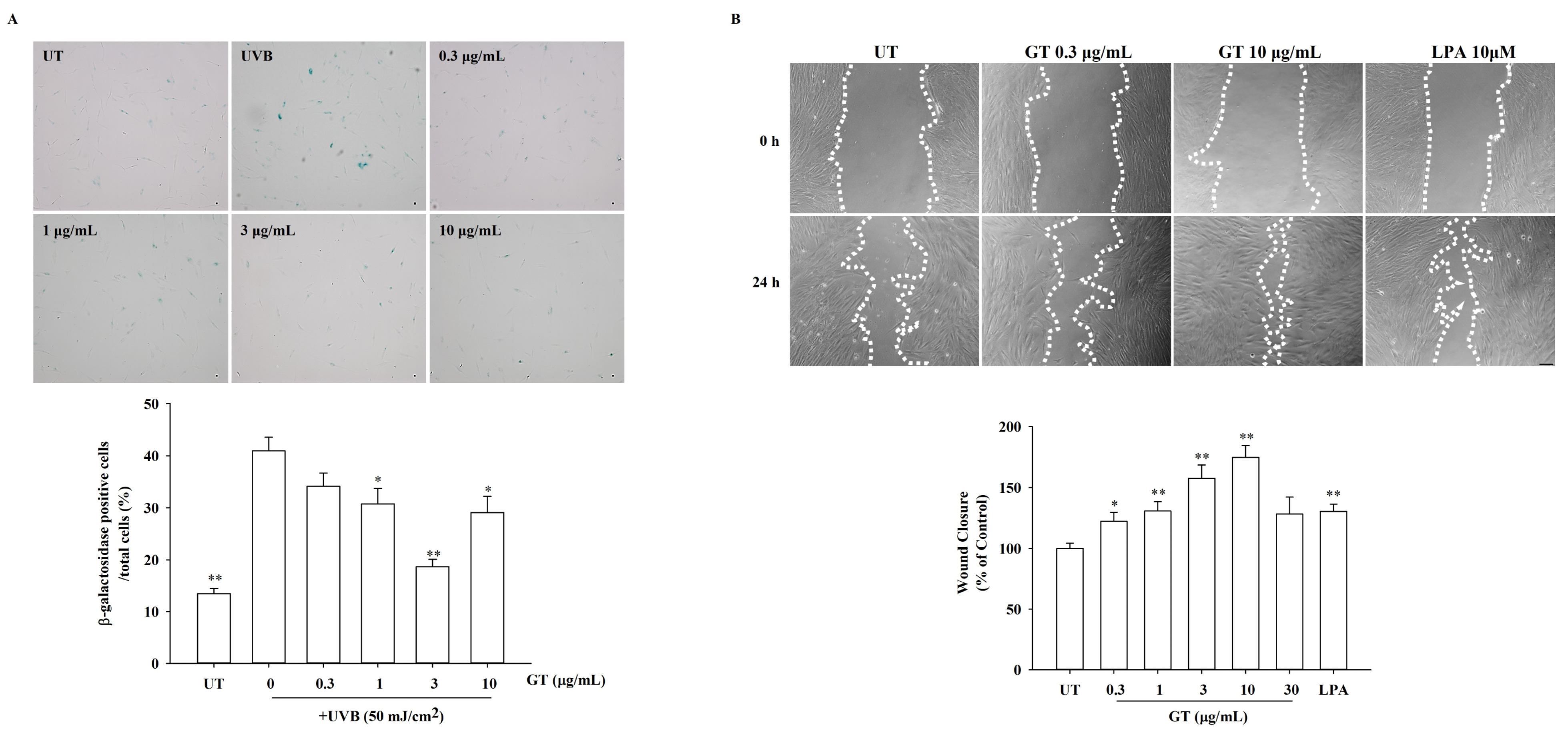
3.6. Effects of KRGM Gintonin on Cell Aging and In Vitro Wound Healing under UVB Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Ryu, J.H. Ginseng in traditional herbal prescriptions. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metwaly, A.M.; Lianlian, Z.; Luqi, H.; Deqiang, D. Black Ginseng and Its Saponins: Preparation, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Effects. Molecules 2019, 24, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.W.; Wills, R.B.H.; Stuart, D.L. Changes in neutral and malonyl ginsenosides in American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium) during drying, storage and ethanolic extraction. Food Chem. 2004, 86, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, J.N.; Wang, C.; Min, J.W.; Noh, H.Y.; Yang, D.C. Effect of white, red and black ginseng on physicochemical properties and ginsenosides. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.Y.; Moon, J.M.; Kim, B.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, G.S.; Yu, H.S.; Cho, S.I. Comparative study of Korean White Ginseng and Korean Red Ginseng on efficacies of OVA-induced asthma model in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeg, I.H.; So, S.H. The world ginseng market and the ginseng (Korea). J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Ryu, G.H. Effects of extrusion cooking on physicochemical properties of white and red ginseng (powder). J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Bae, B.S.; Park, H.W.; Ahn, N.G.; Cho, B.G.; Cho, Y.L.; Kwak, Y.S. Characterization of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.M.; Kim, Y.O.; Ali, M.; Kim, S.H.; Park, I.; Kim, E.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Park, H.R.; Son, E.S.; Ahmad, A. Triterpene glycosides from red ginseng marc and their anti-inflammatory activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4203–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lim, T.; Kim, J.; Hwang, K.T. Physicochemical characteristics and sensory acceptability of crackers containing red ginseng marc. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, G.D.; Choi, I.H. Effects of dietary supplementation of red ginseng marc and alpha-tocopherol on the growth performance and meat quality of broiler chicken. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.K.; Park, S.B.; Kim, C.H. Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Red Ginseng By-product on Laying Performance, Blood Biochemistry, Serum Immunoglobulin and Microbial Population in Laying Hens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.Q.; Myint, A.A.; Kim, J. High-yield recovery of highly bioactive compounds from red ginseng marc using subcritical water extraction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 109, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Jang, S.G.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, E.Y.; Lee, K.W.; et al. Beneficial effects on skin health using polysaccharides from red ginseng by-product. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Pyo, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.W.; et al. Gintonin, Newly Identified Compounds from Ginseng, Is Novel Lysophosphatidic Acids-Protein Complexes and Activates G Protein-Coupled Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors with High Affinity. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, N.E.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, R.M.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.C.; Han, M.; Lee, E.H.; Park, J.; Nah, S.Y. Gintonin facilitates brain delivery of donepezil, a therapeutic drug for Alzheimer disease, through lysophosphatidic acid 1/3 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Lee, N.E.; Hwang, H.; Rhim, H.; Cho, I.H.; Nah, S.Y. Ginseng Gintonin Enhances Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen Release from Human Dermal Fibroblasts Through Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Interaction. Molecules 2019, 24, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Won, K.J.; Lee, R.; Cho, H.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Nah, S.Y. Wound Healing Effect of Gintonin Involves Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.C.; Hwang, S.H.; Nah, S.Y. Bioactive lipids in gintonin-enriched fraction from ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, H.C.; Park, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Lee, M.K.; et al. Gintonin, a novel ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, stimulates neurotransmitter release. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynkiewicz, G.; Poenie, M.; Tsien, R.Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Casas, J.L.; del Rio, J.A.; Acosta, M.; Garcia-Canovas, F. An enzymatic colorimetric method for measuring naringin using 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)(ABTS) in the presence of peroxidase. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 185, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Hoang, H.; Gu, L.; Wu, X.; Bacchiocca, M.; Howard, L.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Jacob, R. Assays for hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidant capacity (oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC(FL))) of plasma and other biological and food samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavinato, M.; Koziel, R.; Romani, N.; Weinmullner, R.; Jenewein, B.; Hermann, M.; Dubrac, S.; Ratzinger, G.; Grillari, J.; Schmuth, M.; et al. UVB-Induced Senescence of Human Dermal Fibroblasts Involves Impairment of Proteasome and Enhanced Autophagic Activity. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.J.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, R.M.; Cho, H.S.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.H.; Nah, S.Y. Protective Effects of Gintonin on Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced HT22 Cell Damages: Involvement of LPA1 Receptor-BDNF-AKT Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Ananthaswamy, H.N. Molecular mechanisms of photocarcinogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2002, 7, d765–d783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Hong, B.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Ding, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Dihydroquercetin composite nanofibrous membrane prevents UVA radiation-mediated inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress by modulating MAPKs/Nrf2 signaling in human epidermal keratinocytes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| LPA C18:2 (μg/mg) | LPC C18:2 (μg/mg) | PC C16:0–18:2 (μg/mg) | PC C18:2–18:2 (μg/mg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KRGM | 2.7 ± 0.41 | 9.87 ± 1.58 | 13.8 ± 2.52 | 14.8 ± 1.59 |
| Fatty Acids | Concentration (μg/mg) |
|---|---|
| Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) | 1.17 |
| Hexadecenoic acid (C16:1) | 3.16 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 77.28 |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) | 1.75 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2n6c) | 500.73 |
| Elaidic acid (C18:1n9t) | 11.62 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1n9c) | 16.15 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 2.85 |
| 11,14-Eicosadienoic acid (C20:2) | 1.88 |
| Arachidic acid (C20:4n6) | 0.45 |
| cis 13,16-Docosedienoic acid (C22:2) | 0.51 |
| Docosanoic acid (C22:0) | 0.88 |
| Name | Amount (mg/mg) |
|---|---|
| Fucose | 0.012 |
| Rhamnose | 0.008 |
| Arabinose | 0.058 |
| Galactose | 0.016 |
| Glucose | 0.335 |
| Xylose | 0.009 |
| Fructose | 0.008 |
| Total | 0.446 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, R.; Kim, J.-H.; Hwang, H.; Rhim, H.; Hwang, S.-H.; Cho, I.-H.; Kim, D.-G.; Kim, H.-C.; Nah, S.-Y. Preparation of Red Ginseng Marc-Derived Gintonin and Its Application as a Skin Nutrient. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112574
Lee R, Kim J-H, Hwang H, Rhim H, Hwang S-H, Cho I-H, Kim D-G, Kim H-C, Nah S-Y. Preparation of Red Ginseng Marc-Derived Gintonin and Its Application as a Skin Nutrient. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112574
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Rami, Ji-Hun Kim, Hongik Hwang, Hyewhon Rhim, Sung-Hee Hwang, Ik-Hyun Cho, Do-Geun Kim, Hyoung-Chun Kim, and Seung-Yeol Nah. 2023. "Preparation of Red Ginseng Marc-Derived Gintonin and Its Application as a Skin Nutrient" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112574
APA StyleLee, R., Kim, J.-H., Hwang, H., Rhim, H., Hwang, S.-H., Cho, I.-H., Kim, D.-G., Kim, H.-C., & Nah, S.-Y. (2023). Preparation of Red Ginseng Marc-Derived Gintonin and Its Application as a Skin Nutrient. Nutrients, 15(11), 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112574












