Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Adequacy of Nutrient Intake among Picky-Eating Children at Nutritional Risk in India: A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Ethics
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Growth in Children
3.2. Changes in Nutrient Intake of Children
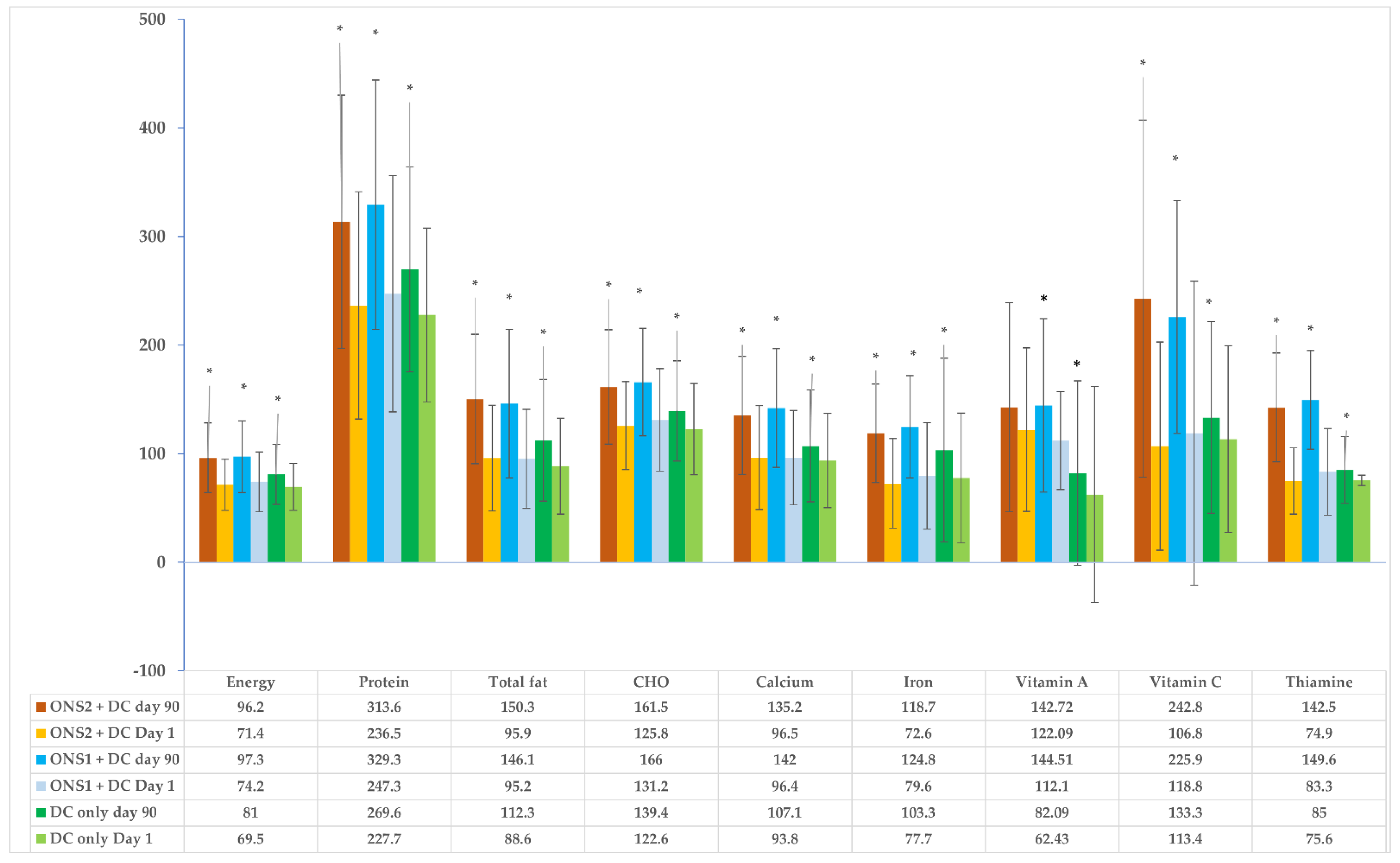
3.3. Changes in Nutrient Adequacy in Children
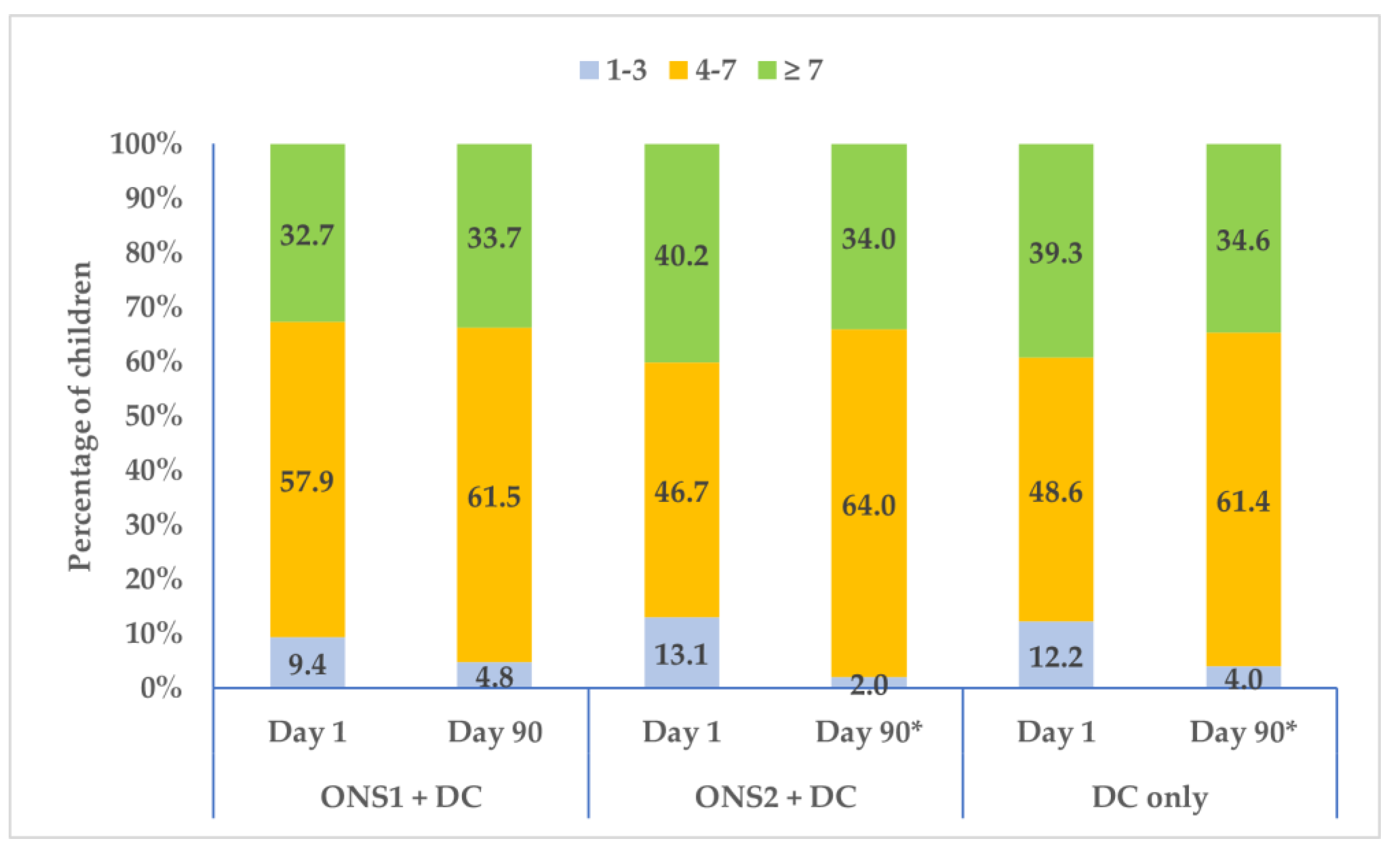
3.4. Changes in Food Consumption Pattern and Dietary Diversity over Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNICEF. Levels and Trends in Child Malnutrition: Key Findings of the 2020 Edition of the Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) and ICF. National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5), 2019–2021: India Fact Sheet; International Institute for Population Sciences: Mumbai, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) and ICF. National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4), 2016–2017: India Fact Sheet; Institute of Population Sciences: Mumbai, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, L.L.; Doub, A.E. Learning to eat: Birth to age 2 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 723s–728s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklaus, S.; Boggio, V.; Chabanet, C.; Issanchou, S. A prospective study of food variety seeking in childhood, adolescence and early adult life. Appetite 2005, 44, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, J.D.; Carruth, B.R.; Bounds, W.; Ziegler, P.; Reidy, K. Do food-related experiences in the first 2 years of life predict dietary variety in school-aged children? J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2002, 34, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.S.; Bhavani, K. Picky eating behaviour and its impact on growth among Pre-school children attending outpatient department of tertiary health care centre, Hyderabad: A Cross-Sectional study. Indian J. Prev. Amp. Soc. Med. 2022, 53, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.M.; Emmett, P.M. Picky eating in children: Causes and consequences. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona Cano, S.; Tiemeier, H.; Van Hoeken, D.; Tharner, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hofman, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; Hoek, H.W. Trajectories of picky eating during childhood: A general population study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascola, A.J.; Bryson, S.W.; Agras, W.S. Picky eating during childhood: A longitudinal study to age 11 years. Eat. Behav. 2010, 11, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, N.C.; An, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Donovan, S.M. Correlates of picky eating and food neophobia in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M.; Wernimont, S.M.; Northstone, K.; Emmett, P.M. Picky/fussy eating in children: Review of definitions, assessment, prevalence and dietary intakes. Appetite 2015, 95, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhao, A.; Cai, L.; Yang, B.; Szeto, I.M.Y.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. Growth and Development in Chinese Pre-Schoolers with Picky Eating Behaviour: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Horst, K.; Deming, D.M.; Lesniauskas, R.; Carr, B.T.; Reidy, K.C. Picky eating: Associations with child eating characteristics and food intake. Appetite 2016, 103, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruth, B.R.; Ziegler, P.J.; Gordon, A.; Barr, S.I. Prevalence of picky eaters among infants and toddlers and their caregivers’ decisions about offering a new food. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, s57–s64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruth, B.R.; Skinner, J.; Houck, K.; Moran, J., 3rd; Coletta, F.; Ott, D. The phenomenon of picky eater: A behavioral marker in eating patterns of toddlers. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1998, 17, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Horst, K. Overcoming picky eating. Eating enjoyment as a central aspect of children’s eating behaviors. Appetite 2012, 58, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, T.M.; Musa-Veloso, K.; Ho, M.; Venditti, C.; Shahkhalili-Dulloo, Y. A Narrative Review of Childhood Picky Eating and Its Relationship to Food Intakes, Nutritional Status, and Growth. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M.; Northstone, K.; Wernimont, S.M.; Emmett, P.M. Macro- and micronutrient intakes in picky eaters: A cause for concern? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grulichova, M.; Kuruczova, D.; Svancara, J.; Pikhart, H.; Bienertova-Vasku, J. Association of Picky Eating with Weight and Height-The European Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood (ELSPAC-CZ). Nutrients 2022, 14, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Tolar-Peterson, T.; Reynolds, A.; Wall, C.; Reeder, N.; Rico Mendez, G. The Effects of Nutritional Interventions on the Cognitive Development of Preschool-Age Children: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-C. Association of Picky Eating with Growth, Nutritional Status, Development, Physical Activity, and Health in Preschool Children. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvik, P.; Ek, A.; Eli, K.; Somaraki, M.; Bottai, M.; Nowicka, P. Picky eating in an obesity intervention for preschool-aged children–what role does it play, and does the measurement instrument matter? Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Jones, L.; de Lauzon-Guillain, B.; Emmett, P.; Moreira, P.; Charles, M.A.; Lopes, C. Early problematic eating behaviours are associated with lower fruit and vegetable intake and less dietary variety at 4–5 years of age. A prospective analysis of three European birth cohorts. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharner, A.; Jansen, P.W.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Moll, H.A.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Tiemeier, H.; Franco, O.H. Bidirectional associations between fussy eating and functional constipation in preschool children. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, P.A.; Lin, L.H.; Noche, M., Jr.; Hernandez, V.C.; Cimafranca, L.; Lam, W.; Comer, G.M. Effect of oral supplementation on catch-up growth in picky eaters. Clin. Pediatr. 2003, 42, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarudin, M.S.; Shahril, M.R.; Haron, H.; Kadar, M.; Safii, N.S.; Hamzaid, N.H. Interventions for Picky Eaters among Typically Developed Children-A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J. Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.G.; Christian, P.; Vidaletti, L.P.; Gatica-Domínguez, G.; Menon, P.; Black, R.E. Revisiting maternal and child undernutrition in low-income and middle-income countries: Variable progress towards an unfinished agenda. Lancet 2021, 397, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Yalawar, M.; Saibaba, P.V.; Bhatnagar, S.; Ghosh, A.; Jog, P.; Khadilkar, A.V.; Kishore, B.; Paruchuri, A.K.; Pote, P.D.; et al. Oral Nutritional Supplementation Improves Growth in Children at Malnutrition Risk and with Picky Eating Behaviors. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.K.; Hurley, K.M.; Shamim, A.A.; Shaikh, S.; Chowdhury, Z.T.; Mehra, S.; Wu, L.; Christian, P. Complementary Food Supplements Increase Dietary Nutrient Adequacy and Do Not Replace Home Food Consumption in Children 6–18 Months Old in a Randomized Controlled Trial in Rural Bangladesh. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Kishore, B.; Shaikh, I.; Satyavrat, V.; Kumar, A.; Shah, T.; Pote, P.; Shinde, S.; Berde, Y.; Low, Y.L.; et al. Effect of oral nutritional supplementation on growth and recurrent upper respiratory tract infections in picky eating children at nutritional risk: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2186–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Tong, M.; Zhao, D.; Leung, T.F.; Zhang, F.; Hays, N.P.; Ge, J.; Ho, W.M.; Northington, R.; Terry, D.L.; et al. Randomized controlled trial to compare growth parameters and nutrient adequacy in children with picky eating behaviors who received nutritional counseling with or without an oral nutritional supplement. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2014, 7, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.T.; Estorninos, E.; Capeding, M.R.; Oliver, J.S.; Low, Y.L.; Rosales, F.J. Impact of long-term use of oral nutritional supplement on nutritional adequacy, dietary diversity, food intake and growth of Filipino preschool children. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Paik, H.Y.; Yoon, J.; Ryu, B.; Shim, J.E. Effects of multiple herb formula SEC-22 supplementation on dietary intake, picky eating behaviors, and growth indices in thin preschool children. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2015, 9, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flax, V.L.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Reinhart, G.A.; Bentley, M.E. Provision of lipid-based nutrient supplements to Honduran children increases their dietary macro- and micronutrient intake without displacing other foods. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2015, 11 (Suppl. 4), 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flax, V.L.; Ashorn, U.; Phuka, J.; Maleta, K.; Manary, M.J.; Ashorn, P. Feeding patterns of underweight children in rural Malawi given supplementary fortified spread at home. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2008, 4, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ickes, S.B.; Adair, L.S.; Brahe, C.A.; Thirumurthy, H.; Charles, B.; Myhre, J.A.; Bentley, M.E.; Ammerman, A.S. Impact of lipid-based nutrient supplementation (LNS) on children’s diet adequacy in Western Uganda. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2015, 11 (Suppl. 4), 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. The WHO Child Growth Standards. Available online: https://www.who.int/childgrowth/standards/en/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- ICMR (Indian Council of Medical Research). Recommended Dietary Allowances and Estimated Average Requirements. A Report of the Expert Group of the Indian Council of Medical Research; National Institute of Nutrition: Hyderabad, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ICMR (Indian Council of Medical Research). National Institute of Nutrition/Indian Council of Medical Research. Dietary Guidelines for Indians; National Institute of Nutrition: Hyderabad, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, G.; Ballard, T.; Dop, M.C. Guidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary Diversity; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott Nutrition. Oral Nutritional Supplementation in Picky Eating Children: NCT02523027 14 August 2015. 2015. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02523027?term=oral+nutritional+supplementation&cntry=IN&draw=2&rank=2 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Abbott Nutrition International India. A Study of an Oral Nutritional Supplementation in Picky Eating Children: CTRI/2015/10/006330, 29 October 2015. 2015. Available online: https://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pdf_generate.php?trialid=12708&EncHid=&modid=&compid=%27,%2712708det%27 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Vijayananthan, A.; Nawawi, O. The importance of Good Clinical Practice guidelines and its role in clinical trials. Biomed Imaging Interv. J. 2008, 4, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, D. Medical Statistics from Scratch, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Walson, J.L.; Berkley, J.A. The impact of malnutrition on childhood infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretchmer, N.; Beard, J.L.; Carlson, S. The role of nutrition in the development of normal cognition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 997s–1001s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachs, T.D. Relation of mild-to-moderate malnutrition to human development: Correlational studies. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 2245s–2254s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Farmer, A.P.; Girard, M.; Peterson, K. Preschool children’s eating behaviours are related to dietary adequacy and body weight. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, C.; Schmitz, G.; Agras, W.S. Is picky eating an eating disorder? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2008, 41, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstein, S.; Laniado, D.; Glick, B. Does picky eating affect weight-for-length measurements in young children? Clin. Pediatr. 2010, 49, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volger, S.; Sheng, X.; Tong, L.M.; Zhao, D.; Fan, T.; Zhang, F.; Ge, J.; Ho, W.M.; Hays, N.P.; Yao, M. Nutrient intake and dietary patterns in children 2.5–5 years of age with picky eating behaviours and low weight-for-height. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 26, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohde, J.F.; Händel, M.N.; Stougaard, M.; Olsen, N.J.; Trærup, M.; Mortensen, E.L.; Heitmann, B.L. Relationship between pickiness and subsequent development in body mass index and diet intake in obesity prone normal weight preschool children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, D.Y.T.; Jacob, A. Perception of picky eating among children in Singapore and its impact on caregivers: A questionnaire survey. Asia Pac. Fam. Med. 2012, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, A.T.; Fiorito, L.; Lee, Y.; Birch, L.L. Parental pressure, dietary patterns, and weight status among girls who are “picky eaters”. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.L.; Perrin, E.M.; Peterson, K.E.; Brophy Herb, H.E.; Horodynski, M.A.; Contreras, D.; Miller, A.L.; Appugliese, D.P.; Ball, S.C.; Lumeng, J.C. Association of Picky Eating with Weight Status and Dietary Quality Among Low-Income Preschoolers. Acad. Pediatr. 2018, 18, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannotti, L.L.; Dulience, S.J.; Green, J.; Joseph, S.; François, J.; Anténor, M.L.; Lesorogol, C.; Mounce, J.; Nickerson, N.M. Linear growth increased in young children in an urban slum of Haiti: A randomized controlled trial of a lipid-based nutrient supplement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, G.P.; Fry, C.; Sorensen, K.; Casewell, C.; Collins, L.; Cunjamalay, A.; Simpson, M.; Wall, A.; Van Wyk, E.; Ward, M. Energy-dense, low-volume paediatric oral nutritional supplements improve total nutrient intake and increase growth in paediatric patients requiring nutritional support: Results of a randomised controlled pilot trial. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, P.; Katona-Apte, J. The interaction between nutrition and infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nutrients | ONS1 | ONS2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per 100 g | Per Serving (45.5 g) | Per 100 g | Per Serving (45.5 g) | |
| Energy (Kcal) | 462 | 210.21 | 468 | 212.94 |
| Protein (g) | 14.1 | 6.42 | 14.1 | 6.42 |
| Total Fat (g) | 17.0 | 7.74 | 23.4 | 10.65 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 62.74 | 28.54 | 50.21 | 22.85 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 44 | 20.02 | 44 | 20.02 |
| Vitamin A (mcg) | 305 | 138.78 | 305 | 138.78 |
| Thiamin (mg) | 0.9 | 0.41 | 0.9 | 0.41 |
| Iron (mg) | 5.5 | 2.50 | 5.5 | 2.50 |
| Calcium (mg) | 386 | 175.63 | 386 | 175.63 |
| ONS1 + DC (n = 107) | ONS2 + DC (n = 107) | DC-Only (n = 107) | Total (n = 321) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONS1 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS2 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS1 + DC vs. ONS2 + DC-Only | |||||
| Age in years a Median (Q1, Q3) | |||||||
| 1–3 years (n = 170) | 2.53 (2.29, 2.74) | 2.47 (2.18, 2.79) | 2.51 (2.27, 2.72) | 2.49 (2.20, 2.74) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 4–6 years (n = 151) | 3.41 (3.19, 3.67) | 3.34 (3.17, 3.66) | 3.40 (3.20, 3.74) | 3.38 (3.18, 3.71) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Total (n = 321) | 2.94 (2.46, 3.38) | 3.01 (2.47, 3.35) | 2.92 (2.47, 3.37) | 2.93 (2.47, 3.35) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Gender b, n (%) (n = 321) | 0.485 | 0.678 | 0.648 | ||||
| Male (n = 193) | 70 (65.4) | 63 (58.9) | 60 (56.1) | 193 (60.1) | |||
| Female (n = 128) | 37 (34.6) | 44 (41.1) | 47 (43.9) | 128 (39.9) | |||
| Family type b, n (%) (n = 321) | 0.769 | 0.519 | 0.569 | ||||
| Nuclear (n = 227) | 74 (69.2) | 81 (75.7) | 72 (67.3) | 227 (70.7) | |||
| Joint (n = 94) | 33 (30.8) | 26 (24.3) | 35 (32.7) | 94 (29.3) | |||
| Maternal age (years) c Mean (SD), (n = 321) | 27.85 (4.04) | 28.30 (3.42) | 27.78 (3.60) | 27.98 (3.69) | 0.880 | 0.878 | 0.878 |
| Maternal employment b, n (%) (n = 321) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||||
| Employed Full time | 16 (15.0) | 19 (17.8) | 14 (13.1) | 49 (15.3) | |||
| Employed Part time | 2 (1.9) | 2 (1.9) | 2 (1.9) | 6 (1.9) | |||
| Unemployed | 20 (18.7) | 20 (18.7) | 21 (19.6) | 61 (19.0) | |||
| Voluntary not working | 69 (64.5) | 66 (61.7) | 70 (65.4) | 205 (63.9) | |||
| Paternal age (years) c Mean (SD), (n = 320) | 32.57 (4.23) | 33.13 (4.56) | 32.32 (3.74) | 32.67 (4.19) | 0.645 | 0.414 | 0.610 |
| Paternal employment b, n (%) (n = 321) | 0.669 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||||
| Employed Full time | 106 (99.1) | 103 (96.3) | 105 (98.1) | 314 (97.8) | |||
| Employed Part time | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (1.9) | 3 (0.9) | |||
| Unemployed | 1 (0.9) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 2(0.6) | |||
| Anthropometry d Mean (SD) | |||||||
| Weight (kg) (n = 321) | 11.18 (1.51) | 11.12 (1.58) | 11.04 (1.57) | 11.11 (1.55) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Height (cm) (n = 321) | 88.89 (6.97) | 89.08 (7.19) | 88.38 (7.15) | 88.78 (7.09) | 1.000 | 0.935 | 1.000 |
| BMI (kg/m2) (n = 321) | 14.11 (0.48) | 13.98 (0.57) | 14.10 (0.67) | 14.06 (0.58) | 0.986 | 0.055 | 0.090 |
| MUAC (cm) (n = 321) | 14.11 (1.47) | 14.00 (1.39) | 14.11 (1.37) | 14.08 (1.41) | 0.847 | 0.787 | 0.847 |
| ONS1 + DC | ONS2 + DC | DC-Only | p-Value for Day 1 * | p-Value for Day 90 * | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient | Day 1 (n = 107) | Day 90 (n = 104) | Mean/Median Difference | p-Value | Day 1 (n = 107) | Day 90 (n = 100) | Mean/Median Difference | p-Value | Day 1 (n = 107) | Day 90 (n = 101) | Mean/Median Difference | p-Value | ONS1 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS2 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS1 + DC vs. ONS2 + DC-Only | ONS1 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS2 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS1 + DC vs. ONS2 + DC-Only |
| Energy (Kcal) | 880.87 (299.89) | 1163.02 (366.33) | 281.9 (422.2) | <0.001 | 853.12 (249.70) | 1149.36 (357.09) | 277.59 (70.64, 469.34) | <0.001 | 825.46 (259.45) | 960.39 (309.30) | 130.6 (336.7) | <0.001 | 0.475 | 0.895 | 0.895 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.916 |
| Protein (g) | 26.14 (10.08) | 35.34 (11.50) | 7.89 (−0.16, 15.61) | <0.001 | 25.02 (9.00) | 33.36 (10.72) | 8.81 (10.84) | <0.001 | 24.12 (8.16) | 28.59 (9.81) | 4.39 (9.60) | <0.001 | 0.524 | 0.866 | 0.866 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.199 |
| CHO (g) | 131.15 (47.08) | 166.0 (49.57) | 34.3 (61.19) | <0.001 | 125.79 (40.48) | 161.51 (52.59) | 32.87 (−1.34, 61.00) | <0.001 | 122.61 (42.02) | 139.35 (46.19) | 16.32 (51.19) | 0.002 | 0.601 | 0.769 | 0.769 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.419 |
| Total Fat (g) | 23.79 (11.37) | 36.52 (17.09) | 12.63 (16.59) | <0.001 | 23.96 (12.21) | 37.57 (14.88) | 13.51 (15.91) | <0.001 | 22.16 (11.05) | 28.07 (14.02) | 5.68 (14.32) | <0.001 | 0.772 | 0.772 | 0.872 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.281 |
| Iron (mg) | 5.39 (3.14) | 8.56 (3.05) | 3.18 (3.76) | <0.001 | 5.01 (2.91) | 8.16 (3.01) | 2.91 (1.01, 5.44) | <0.001 | 5.42 (4.70) | 6.99 (5.31) | 0.65 (−0.39, 2.60) | <0.001 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.237 |
| Calcium (mg) | 407.51 (185.31) | 603.08 (236.86) | 195.3 (247.8) | <0.001 | 406.47 (193.89) | 571.10 (223.17) | 168.6 (232.0) | <0.001 | 395.74 (184.98) | 452.72 (219.93) | 52.31 (237.8) | 0.029 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.419 |
| Vitamin A (mcg) | 229.14 (93.47) | 295.59 (155.96) | 24.11 (−8.10, 125.47) | <0.001 | 249.2 (135.19) | 297.17 (217.57) | 7.66 (−26.47, 87.26) | 0.067 | 128.84 (215.09) | 168.71 (177.16) | 20.25 (−10.28, 88.97) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.377 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.233 |
| Thiamin (mg) | 0.57 (0.25) | 1.03 (0.29) | 0.46 (0.34) | <0.001 | 0.51 (0.19) | 0.97 (0.30) | 0.46 (0.34) | <0.001 | 0.52 (0.21) | 0.58 (0.20) | 0.06 (0.24) | 0.016 | 0.489 | 0.942 | 0.489 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.058 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 28.29 (31.76) | 54.40 (24.58) | 27.09 (16.19, 45.00) | <0.001 | 25.65 (21.54) | 58.98 (39.83) | 23.64 (12.09, 44.09) | <0.001 | 27.68 (22.14) | 32.25 (21.07) | 3.66 (−6.41, 17.89) | 0.013 | 0.643 | 0.773 | 0.643 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.839 |
| ONS1 + DC | ONS2 + DC | DC-Only | p-Value for Day 1 * | p-Value for Day 90 * | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Groups | Day 1 (n = 107) | Day 90 (n = 104) | Mean/Median Difference | p-Value | Day 1 (n = 107) | Day 90 (n = 100) | Mean/Median Difference | p-Value | Day 1 (n = 107) | Day 90 (n = 101) | Mean/Median Difference | p-Value | ONS1 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS2 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS1 + DC vs. ONS2 + DC-Only | ONS1 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS2 + DC vs. DC-Only | ONS1 + DC vs. ONS2 + DC-Only |
| Milk and its products | 225.57 (112.26) | 193.90 (128.97) | −32.08 (140.1) | 0.021 | 220.27 (128.19) | 193.69 (127.13) | −26.94 (132.1) | 0.044 | 215.64 (135.73) | 211.19 (103.98) | −6.69 (118.9) | 0.573 | 0.899 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.502 | 0.502 | 0.962 |
| Pulses | 24.58 (27.70) | 20.37 (18.00) | −0.06 (−16.31, 10.76) | 0.528 | 16.63 (13.23) | 18.38 (15.71) | 2.60 (19.24) | 0.179 | 16.00 (14.83) | 24.44 (35.79) | 4.92 (−7.02, 15.70) | 0.013 | 0.088 | 0.442 | 0.348 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Meat, fish, poultry | 9.95 (20.44) | 25.49 (37.68) | 0.00 (0.00, 30.89) | <0.001 | 17.40 (33.79) | 20.29 (29.99) | 0.00 (0.00, 16.72) | 0.088 | 12.70 (22.54) | 19.59 (31.66) | 0.00 (0.00, 16.67) | 0.017 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.860 | 0.969 | 0.969 |
| Fruits and Vegetables | 88.86 (80.06) | 111.5 (77.21) | 21.32 (94.67) | 0.024 | 86.78 (66.64) | 110.23 (83.36) | 22.44 (95.32) | 0.021 | 84.16 (74.99) | 110.83 (77.67) | 27.70 (−20.52, 69.55) | 0.001 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Tubers | 15.68 (31.85) | 18.03 (37.42) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.61) | 0.819 | 13.84 (26.75) | 19.03 (32.61) | 0.00 (0.00, 14.11) | 0.169 | 18.98 (35.37) | 17.51 (34.51) | 0.00 (0.00, 11.35) | 0.734 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.917 |
| Cereals | 90.11 (46.28) | 100.82 (42.90) | 10.42 (56.99) | 0.065 | 84.25 (38.00) | 96.30 (47.81) | 7.17 (−21.33, 39.83) | 0.053 | 82.23 (39.25) | 95.30 (46.25) | 13.15 (49.48) | 0.009 | 0.750 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.667 | 0.905 | 0.667 |
| Fats | 13.60 (10.93) | 17.68 (14.64) | 4.00 (14.84) | 0.007 | 11.89 (11.20) | 16.9 (13.60) | 3.43 (−2.56, 11.67) | <0.001 | 11.59 (10.39) | 18.76 (13.68) | 6.81 (14.61) | <0.001 | 0.208 | 0.923 | 0.208 | 0.787 | 0.741 | 0.787 |
| Sugars | 10.62 (10.73) | 11.06 (15.98) | −1.58 (−5.33, 3.53) | 0.247 | 10.79 (13.92) | 12.55 (21.58) | 0.00 (−5.05, 3.72) | 0.602 | 10.83 (12.10) | 14.50 (18.76) | 0.00 (−3.66, 7.32) | 0.231 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.215 | 0.292 | 0.850 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, F.; Yalawar, M.; Suryawanshi, P.; Ghosh, A.; Jog, P.; Khadilkar, A.V.; Kishore, B.; Paruchuri, A.K.; Pote, P.D.; Mandyam, R.D.; et al. Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Adequacy of Nutrient Intake among Picky-Eating Children at Nutritional Risk in India: A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112528
Anwar F, Yalawar M, Suryawanshi P, Ghosh A, Jog P, Khadilkar AV, Kishore B, Paruchuri AK, Pote PD, Mandyam RD, et al. Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Adequacy of Nutrient Intake among Picky-Eating Children at Nutritional Risk in India: A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112528
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Fahmina, Menaka Yalawar, Pranali Suryawanshi, Apurba Ghosh, Pramod Jog, Anuradha Vaman Khadilkar, Bala Kishore, Anil Kumar Paruchuri, Prahalad D. Pote, Ravi D. Mandyam, and et al. 2023. "Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Adequacy of Nutrient Intake among Picky-Eating Children at Nutritional Risk in India: A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112528
APA StyleAnwar, F., Yalawar, M., Suryawanshi, P., Ghosh, A., Jog, P., Khadilkar, A. V., Kishore, B., Paruchuri, A. K., Pote, P. D., Mandyam, R. D., Shinde, S., & Shah, A. (2023). Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Adequacy of Nutrient Intake among Picky-Eating Children at Nutritional Risk in India: A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 15(11), 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112528






