Post-Marketing Use of Teduglutide in a Large Cohort of Adults with Short Bowel Syndrome-Associated Chronic Intestinal Failure: Evolution and Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.1.1. Primary Outcome
2.1.2. Secondary Outcomes
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of SBS-CIF Patients
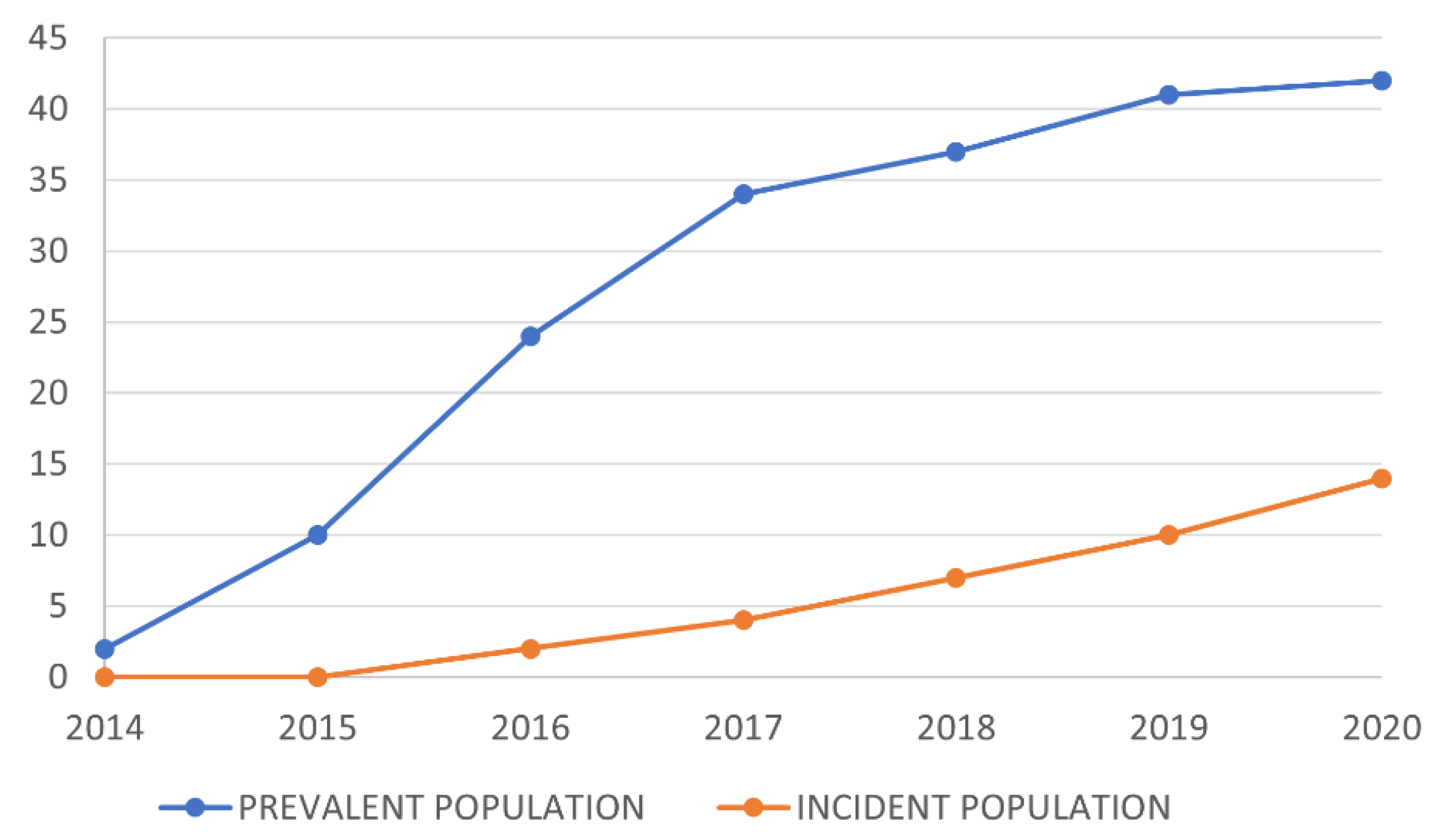
3.2. Evolution of Teduglutide-Treated Patients over Time
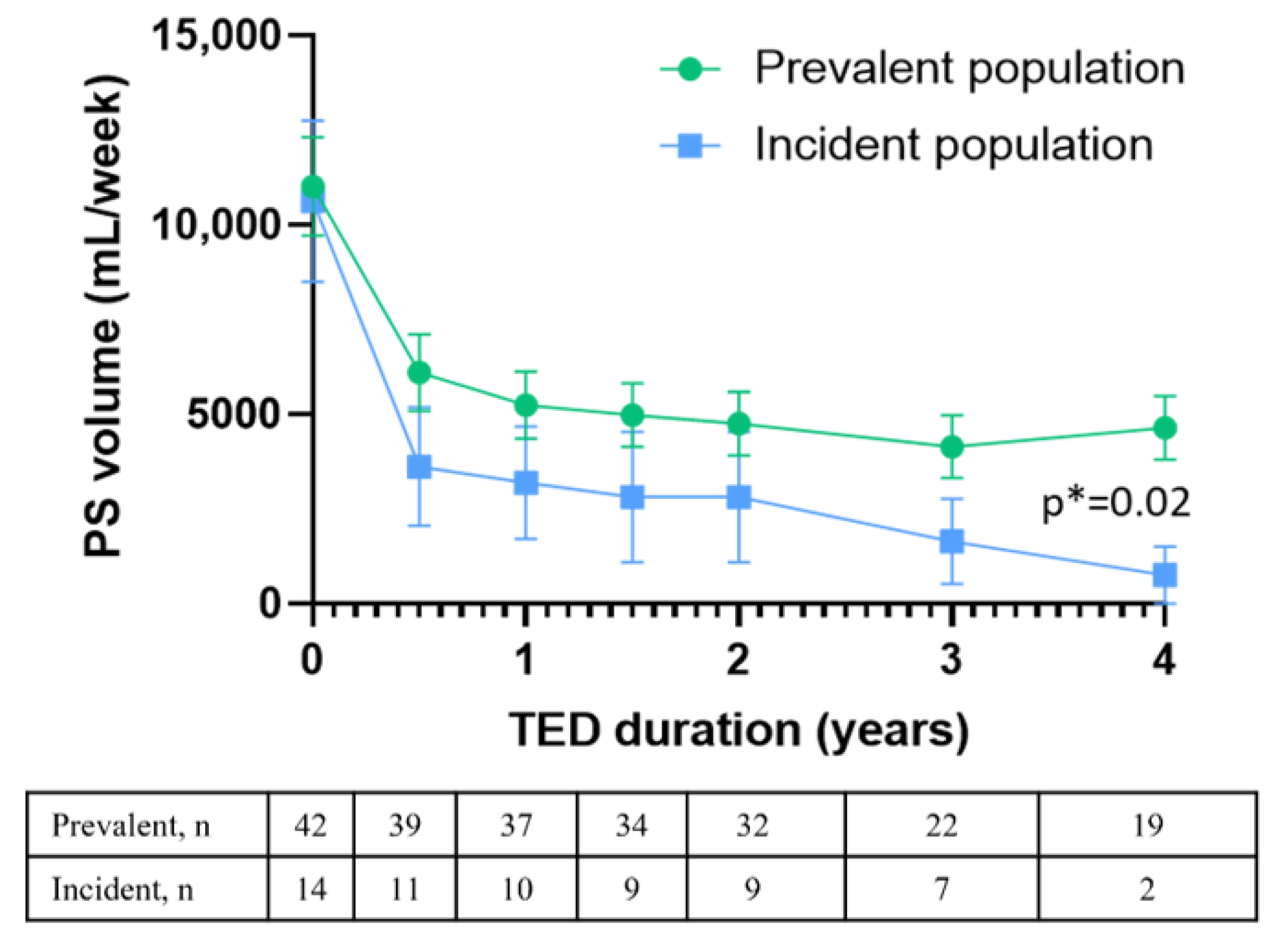
3.3. Long-Term Efficacy of Teduglutide
3.4. Teduglutide Retention and Discontinuation Rates
3.5. Assessment of Teduglutide Prescription Criteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pironi, L.; Corcos, O.; Forbes, A.; Holst, M.; Joly, F.; Jonkers, C.; Klek, S.; Lal, S.; Blaser, A.R.; Rollins, K.E.; et al. Intestinal failure in adults: Recommendations from the ESPEN expert groups. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billiauws, L.; Maggiori, L.; Joly, F.; Panis, Y. Medical and surgical management of short bowel syndrome. J. Visc. Surg. 2018, 155, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, E.; Bosaeus, I.; Nordgren, S. Quality of life and concerns in patients with short bowel syndrome. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L.; Arends, J.; Bozzetti, F.; Cuerda, C.; Gillanders, L.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Joly, F.; Kelly, D.; Lal, S.; Staun, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Chronic Intestinal Failure in Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 247–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brubaker, P.L. Glucagon-like Peptide-2 and the Regulation of Intestinal Growth and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1185–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Daoud, D.C.; Joly, F. The new place of enterohormones in intestinal failure. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, P.B.; Pertkiewicz, M.; Messing, B.; Iyer, K.; Seidner, D.L.; O’Keefe, S.J.; Forbes, A.; Heinze, H.; Joelsson, B. Teduglutide reduces need for parenteral support among patients with short bowel syndrome with intestinal failure. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1473–1481.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, F.; Seguy, D.; Nuzzo, A.; Chambrier, C.; Beau, P.; Poullenot, F.; Thibault, R.; Debeir, L.A.; Layec, S.; Boehm, V.; et al. Six-month outcomes of teduglutide treatment in adult patients with short bowel syndrome with chronic intestinal failure: A real-world French observational cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2856–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.; Schwartz, L.; Batisti, J.; Iyer, K.R. Single-center experience with the use of teduglutide in adult patients with short bowel syndrome. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevny, S.; Maasberg, S.; Rieger, A.; Karber, M.; Blüthner, E.; Knappe-Drzikova, B.; Thurmann, D.; Büttner, J.; Weylandt, K.-H.; Wiedenmann, B.; et al. Experience with teduglutide treatment for short bowel syndrome in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, S.; Maasberg, S.; Wehkamp, J.; Fusco, S.; Zopf, Y.; Herrmann, H.J.; Lamprecht, G.; Jacob, T.; Schiefke, I.; von Websky, M.W.; et al. Long-term results of teduglutide treatment for chronic intestinal failure–Insights from a national, multi-centric patient home-care service program. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 51, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.S.; Xie, J.; Tang, W.; Zhao, J.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Signorovitch, J.E. Identifying a subpopulation with higher likelihoods of early response to treatment in a heterogeneous rare disease: A post hoc study of response to teduglutide for short bowel syndrome. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puello, F.; Wall, E.; Herlitz, J.; Lozano, E.S.; Semrad, C.; Micic, D. Long-Term Outcomes with Teduglutide from a Single Center. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, P.B.; Gabe, S.M.; Seidner, D.L.; Lee, H.M.; Olivier, C. Factors Associated with Response to Teduglutide in Patients with Short-Bowel Syndrome and Intestinal Failure. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L.; Sasdelli, A.S.; Venerito, F.M.; Musio, A.; Pazzeschi, C.; Guidetti, M. Candidacy of adult patients with short bowel syndrome for treatment with glucagon-like peptide-2 analogues: A systematic analysis of a single centre cohort. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4065–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.; Taylor, M.; Abraham, A.; Teubner, A.; Soop, M.; Carlson, G.; Lal, S. Examining the pathophysiology of short bowel syndrome and glucagon-like peptide 2 analogue suitability in chronic intestinal failure: Experience from a national intestinal failure unit. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L.; Konrad, D.; Brandt, C.; Joly, F.; Wanten, G.; Agostini, F.; Chambrier, C.; Aimasso, U.; Zeraschi, S.; Kelly, D.; et al. Clinical classification of adult patients with chronic intestinal failure due to benign disease: An international multicenter cross-sectional survey. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Klag, T.; Wendler, J.; Bernhard, S.; Adolph, M.; Kirschniak, A.; Goetz, M.; Malek, N.; Wehkamp, J. GLP-2 analog teduglutide significantly reduces need for parenteral nutrition and stool frequency in a real-life setting. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756284818793343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbiest, A.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Joly, F.; Vanuytsel, T. The Role of a Colon-in-Continuity in Short Bowel Syndrome. Nutrients 2023, 15, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Dreuille, B.; Joly, F. Disease-modifying therapies in short bowel syndrome. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 65, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfy, A.; Kurin, M.; Shah, R.; Davitkov, P. Characterization of American teduglutide consumers from 2015 to 2020: A large database study. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norona, J.; Apostolova, P.; Schmidt, D.; Ihlemann, R.; Reischmann, N.; Taylor, G.; Köhler, N.; de Heer, J.; Heeg, S.; Andrieux, G.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 2 for intestinal stem cell and Paneth cell repair during graft-versus-host disease in mice and humans. Blood 2020, 136, 1442–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, C.; Booth, D.; Williamson, S.; Demchyshyn, L.L.; Potten, C.S. Teduglutide ([Gly2]GLP-2) protects small intestinal stem cells from radiation damage. Cell Prolif. 2004, 37, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Ge, H.; Pu, C.; Li, N. GLP2-GLP2R signal affects the viability and EGFR-TKIs sensitivity of PC9 and HCC827 cells. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvistendahl, M.K.; Naimi, R.M.; Enevoldsen, L.H.; Madsen, J.L.; Fuglsang, S.; Jeppesen, P.B. Effect of Glepaglutide, a Long-Acting Glucagon-Like Peptide-2 Analog, on Gastrointestinal Transit Time and Motility in Patients with Short Bowel Syndrome: Findings from a Randomized Trial. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, J.; Hvistendahl, M.K.; Freund, N.; Bolognani, F.; Meyer, C.; Jeppesen, P.B. Apraglutide, a novel glucagon-like peptide-2 analog, improves fluid absorption in patients with short bowel syndrome intestinal failure: Findings from a placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noelting, J.; Gramlich, L.; Whittaker, S.; Armstrong, D.; Marliss, E.; Jurewitsch, B.; Raman, M.; Duerksen, D.R.; Rn, D.S.; Lou, W.; et al. Survival of Patients with Short-Bowel Syndrome on Home Parenteral Nutrition: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Prevalent Population n = 156 | Incident Population n = 175 | p-Value (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female gender, n (%) | 85 (54) | 101 (58) | 0.6314 |
| Age at baseline (years), median (IQR) | 52.0 (36.0–65.3) | 61.0 (46–70) | <0.001 |
| Age at PS initiation (years), median (IQR) | 45.5 (26.0–57.5) | 60.0 (44.5–69.0) | <0.001 |
| Body weight at baseline, kg, median (IQR) | 59 (52–66) | 60 (50–69) | 0.7497 |
| BMI at baseline, kg/m2, median (IQR) | 21.4 (19.4–23.5) | 21.4 (18.6–24.3) | 0.82 |
| PS duration before baseline (months), median (IQR) | 75 (21–102) | 0 | <0.001 |
| SBS type, n (%) | |||
| Type 1a | 58 (37) | 52 (30) | 0.186 |
| Type 1b | 3 (2) | 31 (18) | <0.001 |
| Type 2 | 81 (52) | 68 (39) | 0.0229 |
| Type 3 | 14 (9) | 24 (14) | 0.2389 |
| Presence of ostomy | 66 (42) | 85 (49) | 0.2408 |
| Jejunostomy | 58 (37) | 74 (42) | 0.6039 |
| Colostomy | 8 (5) | 12 (7) | 1 |
| Remnant bowel length (cm), median (IQR) | 70 (30–100) | 105.4 (50–150) | <0.001 |
| Residual colon (%), median (IQR) | 50 (0–80) | 50.3 (0–90) | 0.1312 |
| SBS cause, n (%) | |||
| Mesenteric ischemia | 49 (31) | 56 (32) | 1 |
| Crohn’s disease | 21 (13) | 28 (16) | 0.6212 |
| CIPO | 20 (13) | 8 (5) | 0.0078 |
| Radiation enteritis | 13 (8) | 21 (12) | 0.3599 |
| Cancer | 4 (3) | 18 (10) | 0.0067 |
| Surgery complications | 10 (6) | 12 (7) | 1 |
| Other | 39 (25) | 32 (18) | 0.2229 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |||
| At least one comorbidity | 135 (87) | 163 (93) | 0.09571 |
| Chronic renal failure | 35 (22) | 24 (14) | 0.05414 |
| History of cancer | 35 (22) | 63 (36) | 0.0099 |
| Arterial hypertension | 35 (22) | 59 (34) | 0.0316 |
| History of obesity | 6 (4) | 15 (9) | 0.1249 |
| Heart disease | 0 (0) | 6 (3) | 0.0314 |
| Dyslipidemia | 11 (7) | 23 (13) | 0.1008 |
| Outcome, n (%) | |||
| Weaning from PS | 28 (18) | 38 (22) | 0.4727 |
| Death | 36 (23) | 20 (11) | 0.0075 |
| Parenteral nutrition at treatment initiation | |||
| PS volume (mL/week), median (IQR) | 9000 (6000–16,500) | 10,000 (5000–17,500) | 0.7151 |
| PS calories (kcal/week), median (IQR) | 6840 (4250–11,100) | 6840 (3200–10,050) | 0.2795 |
| Number of days of infusion/week, median (IQR) | 5 (4–7)) | 6 (4–7) | 0.1819 |
| Treatment with Teduglutide, n (%) | 42 (27) | 14 (8) | <0.001 |
| Prevalent Population | Incident Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Percentage of the population initiating teduglutide (%) | ||
| 2015 | 5.13 | 0 |
| 2016 | 8.97 | 5.56 |
| 2017 | 6.41 | 2.44 |
| 2018 | 1.92 | 2.7 |
| 2019 | 2.56 | 2.04 |
| 2020 | 0.64 | 2.29 |
| Median duration of PS before teduglutide (months), median (IQR) | ||
| 2015 | 38.5 (21.3–124.8) | 0 |
| 2016 | 114.5 (45.8–169.3) | 11.0 (11.0–11.0) |
| 2017 | 55.5 (46.5–147.8) | 18.0 (15.0–21.0) |
| 2018 | 76.0 (70.0–140.0) | 16.5 (15.0–17.0) |
| 2019 | 138.0 (134.0–165.5) | 20.0 (20.0–24.5) |
| 2020 | 67.0 (67.0–67.0) | 11.0 (9.0–34.0) |
| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Contraindication | 6 | 31.6 |
| Acute pulmonary edema | 2 | 10.5 |
| Diagnosis of leukemia | 1 | 5.3 |
| Diagnosis of melanoma | 1 | 5.3 |
| Diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma | 1 | 5.3 |
| Severe septic shock caused by repeated bacterial translocations | 1 | 5.3 |
| Adverse events | 5 | 26.3 |
| Digestive symptoms | 4 | 21 |
| Injection site pain | 1 | 5.3 |
| No significant benefit | 4 | 21.1 |
| Desire of pregnancy | 2 | 10.5 |
| Patient’s decision | 1 | 5.3 |
| Poor compliance | 1 | 5.3 |
| Treated Patients n = 56 | Untreated Patients n = 275 | p-Value (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at follow-up initiation, years, median (IQR) | 49.5 (35.8–61.5) | 58.0 (43.5–70.0) | 0.0078 |
| Female gender, n (%) | 26 (46) | 160 (58) | 0.1421 |
| Body weight, kg, median (IQR) | 62.0 (55.3–68.8) | 59.0 (51.0–68.0) | 0.1312 |
| BMI, kg/m2, median (IQR) | 21.3 (19.2–23.0) | 21.4 (19.0–24.2) | 0.895 |
| PS duration before baseline (months), median (IQR) | 26.7 (1.3–111.8) | 0 (0–30.0) | <0.001 |
| Age at PS initiation, median (IQR) | 42 (25–55) | 55 (40–67) | <0.001 |
| Bowel anatomy features | |||
| Type 1a, n (%) | 17 (30) | 93 (34) | 0.7297 |
| Type 1b, n (%) | 3 (5) | 31 (11) | 0.232 |
| Type 2, n (%) | 28 (50) | 121 (44) | 0.4995 |
| Type 3, n (%) | 8 (14) | 30 (11) | 0.6223 |
| Colon in continuity, n (%) | 36 (64) | 151 (55) | 0.2534 |
| Presence of ostomy, n (%) | 24 (43) | 126 (46) | 0.6744 |
| Jejunostomy, n (%) | 20 (36) | 112 (41) | 0.6904 |
| Colostomy, n (%) | 4 (7) | 16 (6) | 0.5033 |
| Remnant bowel length (cm), median (IQR) | 68 (23–100) | 80 (45–150) | 0.0104 |
| Residual colon, n (%), median (IQR) | 60 (0–80) | 50 (0–90) | 0.637 |
| Reverse loop, n (%) | 4 (7) | 19 (7) | 1 |
| SBS cause | |||
| Mesenteric ischemia, n (%) | 19 (34) | 86 (31) | 0.8167 |
| Crohn’s disease, n (%) | 12 (21) | 37 (13) | 0.1851 |
| CIPO, n (%) | 5 (9) | 23 (8) | 1 |
| Radiation enteritis, n (%) | 3 (5) | 31 (11) | 0.232 |
| Cancer, n (%) | 0 | 22 (8) | 0.0335 |
| Surgery complications, n (%) | 3 (5) | 19 (7) | 1 |
| Other, n (%) | 14 (25) | 57 (21) | 0.6393 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| At least one comorbidity, n (%) | 47 (84) | 251 (91) | 0.1282 |
| Chronic renal failure, n (%) | 15 (27) | 44 (16) | 0.0835 |
| History of cancer, n (%) | 4 (7) | 94 (34) | <0.001 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 14 (25) | 80 (29) | 0.6482 |
| History of obesity, n (%) | 3 (5) | 18 (7) | 1 |
| Heart disease, n (%) | 1 (2) | 5 (2) | 1 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 3 (5) | 31 (11) | 0.232 |
| Parenteral nutrition features | |||
| PS volume (mL/week), median (IQR) | 8800 (5000–12,500) | 9885 (5909–17,500) | 0.4231 |
| PS calories (kcal/week), median (IQR) | 6000 (2390–9375) | 6840 (3420–10,550) | 0.3666 |
| Number of days of infusion/week, median (IQR) | 5 (4–6) | 6 (4–7) | 0.0417 |
| Population | |||
| Prevalent, n (%) | 42 (75) | 114 (42) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Dreuille, B.; Nuzzo, A.; Bataille, J.; Mailhat, C.; Billiauws, L.; Le Gall, M.; Joly, F. Post-Marketing Use of Teduglutide in a Large Cohort of Adults with Short Bowel Syndrome-Associated Chronic Intestinal Failure: Evolution and Outcomes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112448
de Dreuille B, Nuzzo A, Bataille J, Mailhat C, Billiauws L, Le Gall M, Joly F. Post-Marketing Use of Teduglutide in a Large Cohort of Adults with Short Bowel Syndrome-Associated Chronic Intestinal Failure: Evolution and Outcomes. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112448
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Dreuille, Brune, Alexandre Nuzzo, Julie Bataille, Charlotte Mailhat, Lore Billiauws, Maude Le Gall, and Francisca Joly. 2023. "Post-Marketing Use of Teduglutide in a Large Cohort of Adults with Short Bowel Syndrome-Associated Chronic Intestinal Failure: Evolution and Outcomes" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112448
APA Stylede Dreuille, B., Nuzzo, A., Bataille, J., Mailhat, C., Billiauws, L., Le Gall, M., & Joly, F. (2023). Post-Marketing Use of Teduglutide in a Large Cohort of Adults with Short Bowel Syndrome-Associated Chronic Intestinal Failure: Evolution and Outcomes. Nutrients, 15(11), 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112448






