Impact of Grape Seed Powder and Black Tea Brew on Lipid Digestion—An In Vitro Co-Digestion Study with Real Foods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Determination of Fat Content of Test Foods
2.4. In Vitro Digestion Simulation
2.5. Assessment of Fatty Acid Specific Lipolysis—Bioaccessible Fatty Acid Content
2.6. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
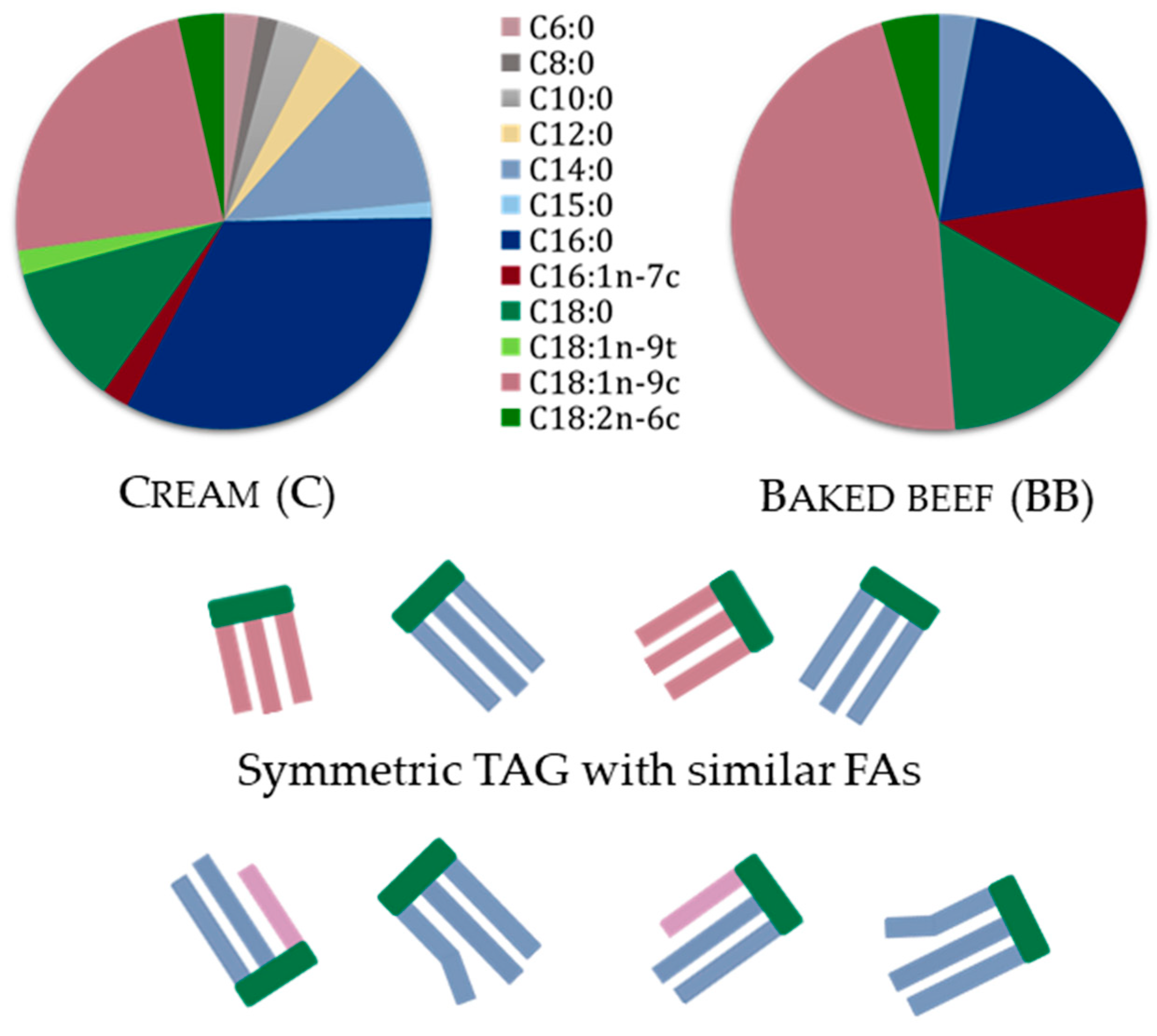
3.1. Substrate Test Foods with Different Fatty Acid and TAG Profile
3.2. Lipid Digestibility of Substrate Test Foods
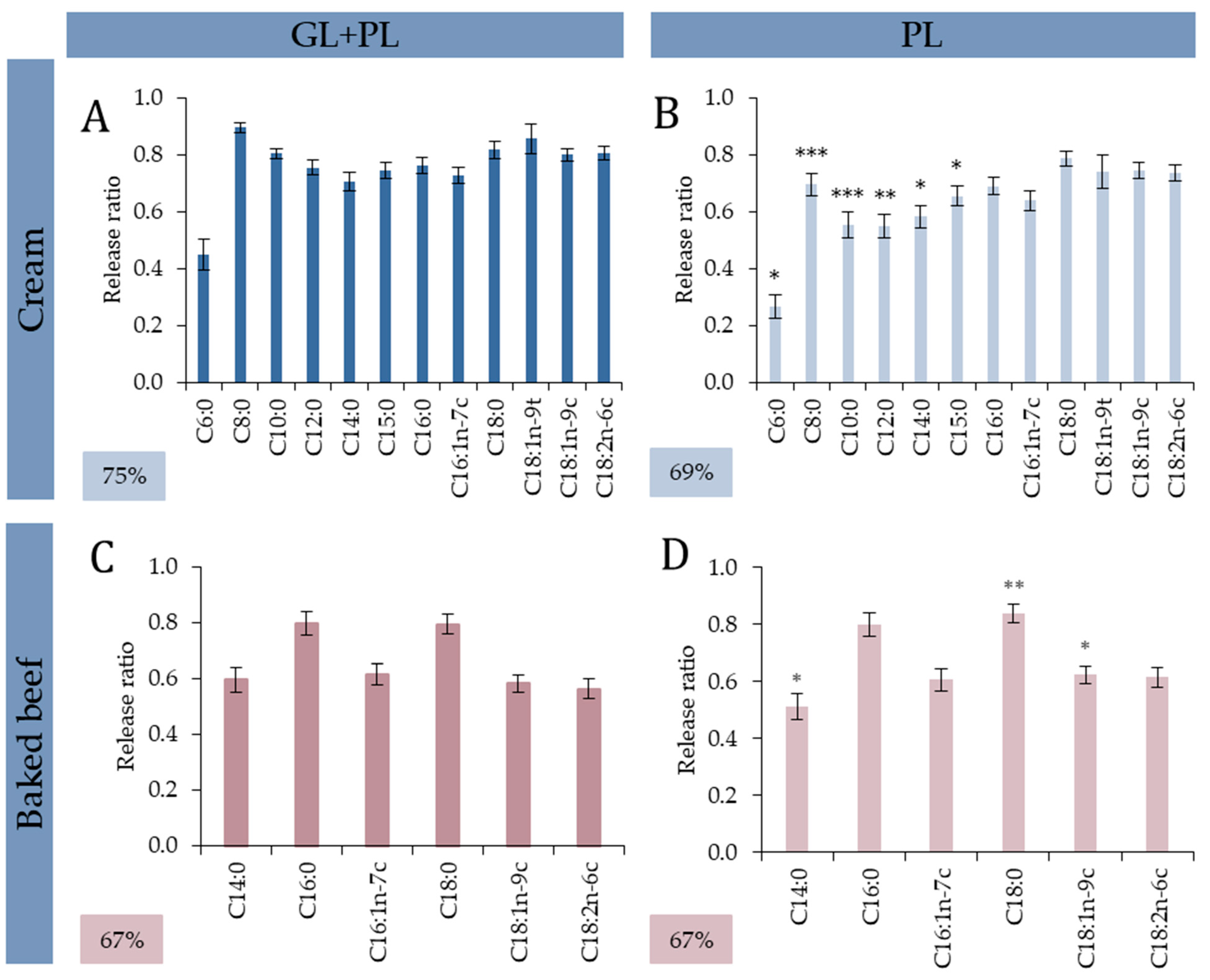
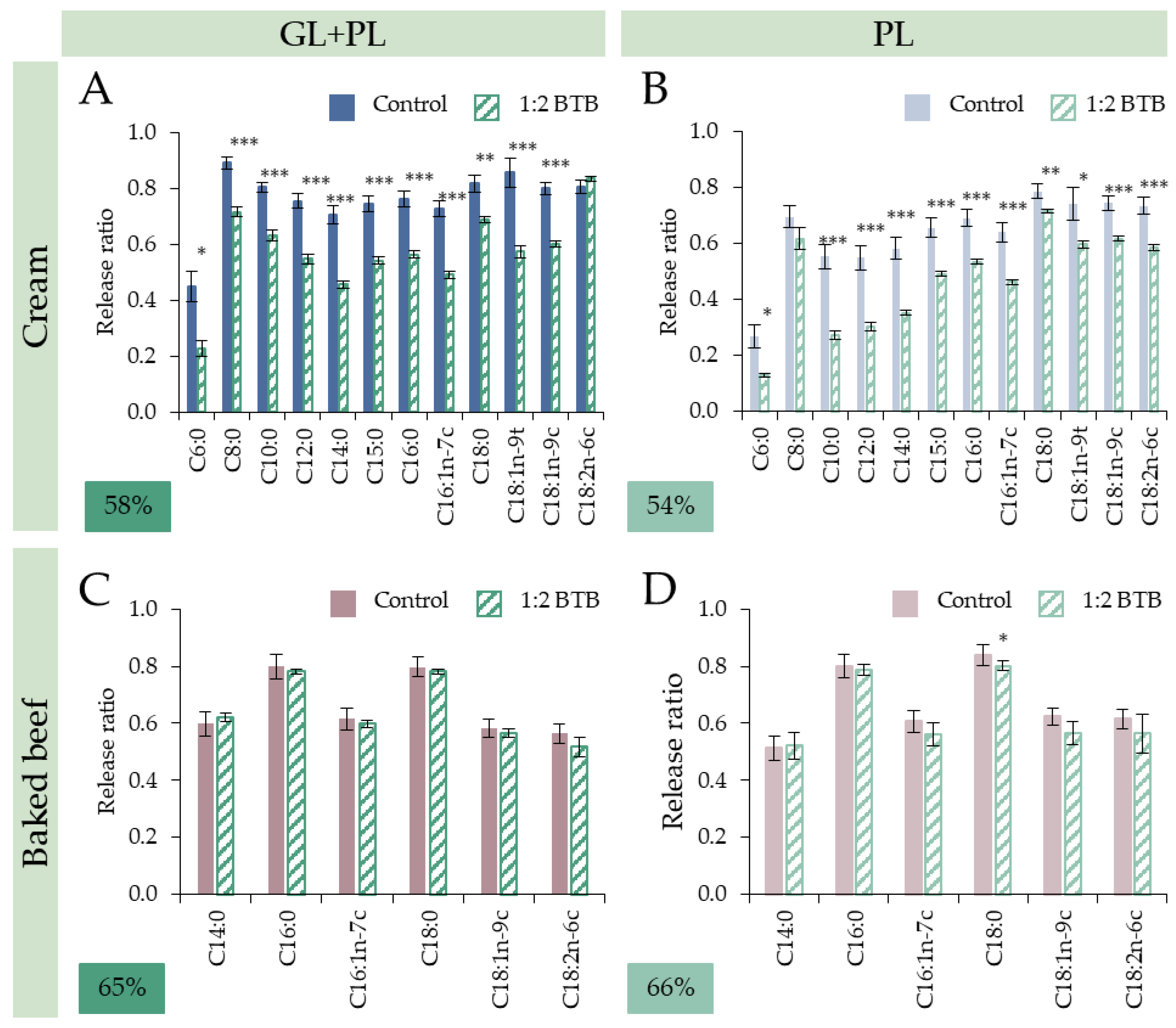
3.2.1. Cream: Addition of Gastric Lipase Specifically Ameliorated Release of SFCAs and MCFAs
3.2.2. Baked Beef: No Additional Effect of GL without Diversity of TAGs
3.3. Effect of GSP and BTB on Lipid Digestibility
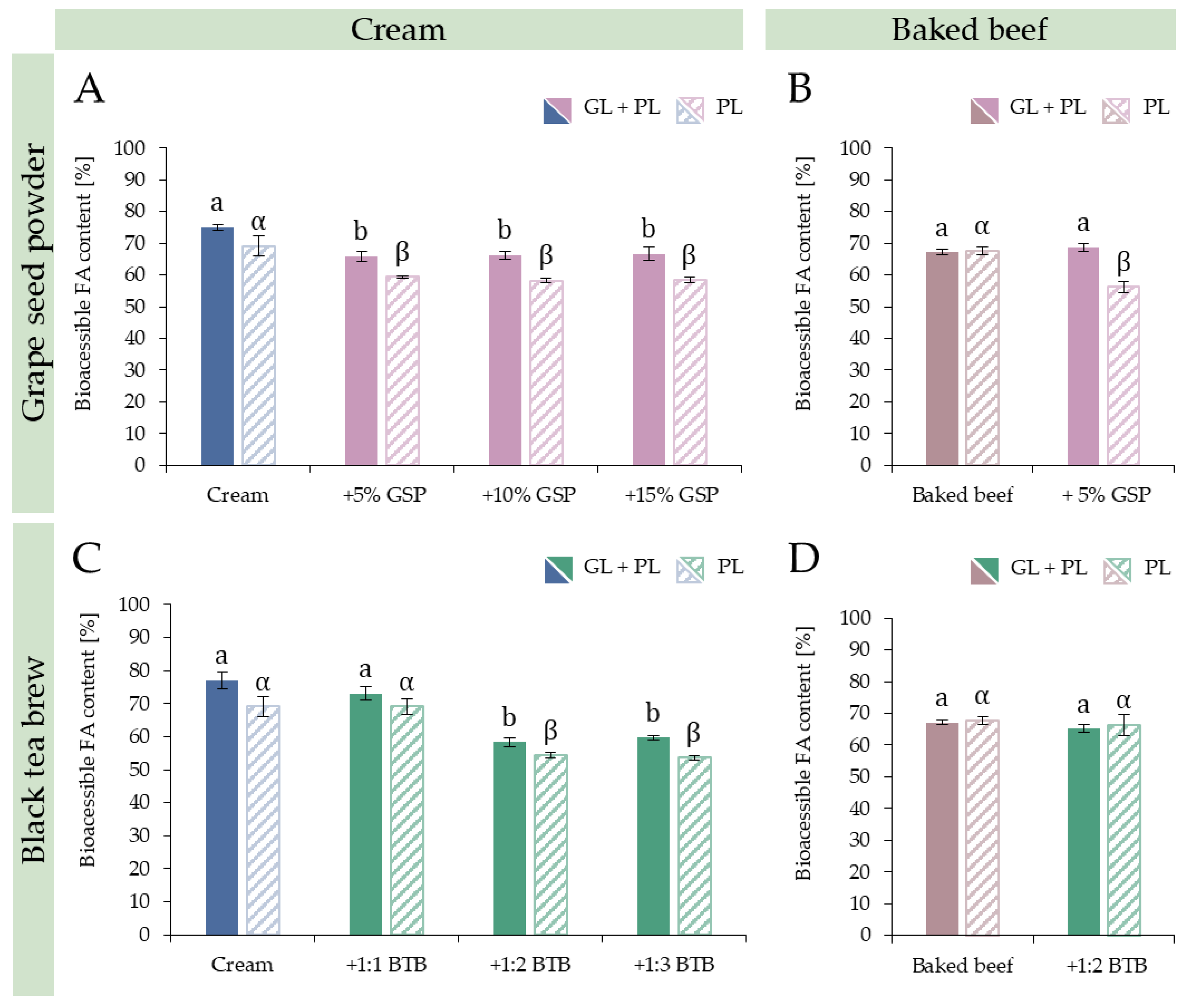
3.3.1. Dose and Substrate Dependency
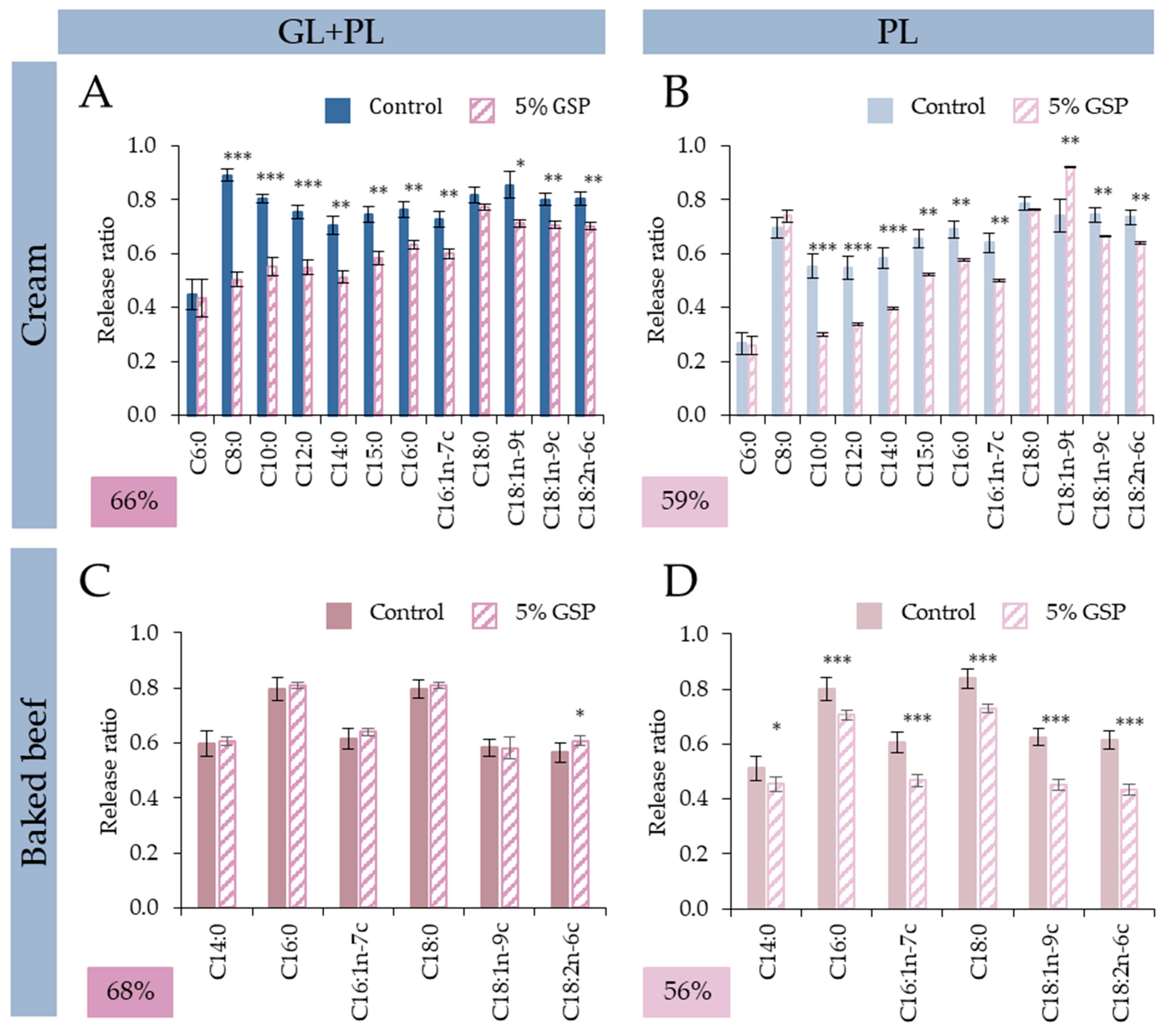
3.3.2. Fatty Acid Specific Effects: Reduced Digestibility of SCFAs and MCFAs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adults during 1980–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tune, J.D.; Goodwill, A.G.; Sassoon, D.J.; Mather, K.J. Cardiovascular Consequences of Metabolic Syndrome. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaki, C.; Liatis, S.; Kokkinos, A. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: Revisiting an Old Relationship. Metabolism 2019, 92, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; Regional Office for Europe. WHO European Regional Obesity Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022; ISBN 978-92-890-5773-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cercato, C.; Fonseca, F.A. Cardiovascular Risk and Obesity. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Popkin, B.M.; Du, S. Elevated Fat Intake Increases Body Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Adults: 1991–2015 Trends. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Mi, B.; Luo, W.; Chen, B.; Ma, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, B.; et al. Association between Long-Term Changes in Dietary Percentage of Energy from Fat and Obesity: Evidence from over 20 Years of Longitudinal Data. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Sharp, S.J.; Du, H.; van der A, D.L.; Halkjœr, J.; Schulze, M.B.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Jakobsen, M.U.; Boeing, H.; et al. Dietary Fat Intake and Subsequent Weight Change in Adults: Results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Cohorts. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raatz, S.; Conrad, Z.; Johnson, L.; Picklo, M.; Jahns, L. Relationship of the Reported Intakes of Fat and Fatty Acids to Body Weight in US Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suara, S.B.; Siassi, F.; Saaka, M.; Foroshani, A.R.; Asadi, S.; Sotoudeh, G. Dietary Fat Quantity and Quality in Relation to General and Abdominal Obesity in Women: A Cross-Sectional Study from Ghana. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beulen, Y.; Martínez-González, M.; van de Rest, O.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Sorlí, J.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Fiol, M.; Estruch, R.; Santos-Lozano, J.; Schröder, H.; et al. Quality of Dietary Fat Intake and Body Weight and Obesity in a Mediterranean Population: Secondary Analyses within the PREDIMED Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockner, R.K.; Manning, J.A. Fatty acid-binding protein in small intestine identification, isolation, and evidence for its role in cellular fatty acid transport. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 54, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansbach, C.M.; Gorelick, F. Development and Physiological Regulation of Intestinal Lipid Absorption. II. Dietary Lipid Absorption, Complex Lipid Synthesis, and the Intracellular Packaging and Secretion of Chylomicrons. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G645–G650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Hussain, M.M. Intestinal Lipid Absorption. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E1183–E1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, H. The Digestion of Dietary Triacylglycerols. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, A.H.; Jones, P.J.H. Lipids: Absorption and Transport. In Present Knowledge in Nutrition; Erdman, J.W., Macdonald, I.A., Zeisel, S.H., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 118–131. ISBN 978-0-470-95917-6. [Google Scholar]
- Armand, M. Lipases and Lipolysis in the Human Digestive Tract: Where Do We Stand? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-T.; Liu, X.-T.; Chen, Q.-X.; Shi, Y. Lipase Inhibitors for Obesity: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Garza, A.; Milagro, F.; Boque, N.; Campión, J.; Martínez, J. Natural Inhibitors of Pancreatic Lipase as New Players in Obesity Treatment. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chauhan, S. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors: The Road Voyaged and Successes. Life Sci. 2021, 271, 119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, L.; Palaniswamy, D.; Mohankumar, S.K. Targeting Obesity with Plant-Derived Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustanji, Y.; Issa, A.; Mohammad, M.; Hudaib, M.; Tawah, K.; Alkhatib, H.; Almasri, I.; Al-khalidi, B. Inhibition of Hormone Sensitive Lipase and Pancreatic Lipase by Rosmarinus Officinalis Extract and Selected Phenolic Constituents. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, K.; Matsuda, H.; Shimoda, H.; Nishida, N.; Kasajima, N.; Yoshino, T.; Morikawa, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Carnosic Acid, a New Class of Lipid Absorption Inhibitor from Sage. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, X.-P.; Lei, F.; Jiang, J.-F.; Li, J.; Xing, D.-M.; Du, L.-J. Pomegranate Leaf Attenuates Lipid Absorption in the Small Intestine in Hyperlipidemic Mice by Inhibiting Lipase Activity. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, D.A.; Ilic, N.; Poulev, A.; Brasaemle, D.L.; Fried, S.K.; Raskin, I. Inhibitory Effects of Grape Seed Extract on Lipases. Nutrition 2003, 19, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwibedi, V.; Jain, S.; Singhal, D.; Mittal, A.; Rath, S.K.; Saxena, S. Inhibitory Activities of Grape Bioactive Compounds against Enzymes Linked with Human Diseases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1399–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, M.; Fukui, Y.; Asami, S.; Toyoda-Ono, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Shibata, H.; Mitsunaga, T.; Hashimoto, F.; Kiso, Y. Inhibitory Effects of Oolong Tea Polyphenols on Pancreatic Lipase in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4593–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Wang, M.M.C.; Hsieh, S.-K.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Tzen, J.T.C. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition of Strictinin Isolated from Pu’er Tea (Cammelia Sinensis) and Its Anti-Obesity Effects in C57BL6 Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicas, S.; Mateo, J.J. Sustainability of Wine Production. Sustainability 2020, 12, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Gallego, R.; Silva, P. The Wine Industry By-Products: Applications for Food Industry and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaberi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Grapes (Vitis Vinifera) as a Potential Candidate for the Therapy of the Metabolic Syndrome. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serea, D.; Condurache, N.N.; Aprodu, I.; Constantin, O.E.; Bahrim, G.-E.; Stănciuc, N.; Stanciu, S.; Rapeanu, G. Thermal Stability and Inhibitory Action of Red Grape Skin Phytochemicals against Enzymes Associated with Metabolic Syndrome. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucier, C.; Mirabel, M.; Daviaud, F.; Longieras, A.; Glories, Y. Rapid Fractionation of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5732–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Islam, M.N.; Faruk, M.O.; Ashaduzzaman, M.; Dungani, R. Review on Tannins: Extraction Processes, Applications and Possibilities. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 135, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedea, V.S.; Echim, C.; Braicu, C.; Andjelkovic, M.; Verhe, R.; Socaciu, C. Composition in Polyphenols and Stability of the Aqueous Grape Seed Extract from the Romanian Variety “Merlot Recas”. J. Food Biochem. 2011, 35, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Pineda, A.M.; Carpenter, G.H.; García-Estévez, I.; Escribano-Bailón, M.T. Influence of Chemical Species on Polyphenol–Protein Interactions Related to Wine Astringency. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2948–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Kiefer, J.; Santini, A.; Lombardi-Boccia, G.; Souto, E.; Romani, A.; Lampe, A.; Ferrari Nicoli, S.; Gabrielli, P.; et al. Grape Seeds: Chromatographic Profile of Fatty Acids and Phenolic Compounds and Qualitative Analysis by FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy. Foods 2019, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantre, P.; Lairon, D. Recent Findings of Green Tea Extract AR25 (Exolise) and Its Activity for the Treatment of Obesity. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondoin, A.; Grussu, D.; Stewart, D.; McDougall, G.J. White and Green Tea Polyphenols Inhibit Pancreatic Lipase in Vitro. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glisan, S.L.; Grove, K.A.; Yennawar, N.H.; Lambert, J.D. Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase by Black Tea Theaflavins: Comparative Enzymology and In Silico Modeling Studies. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, M.; Louati, H.; Kamoun, J.; Kchaou, A.; Damak, M.; Gargouri, Y. Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase and Amylase by Extracts of Different Spices and Plants. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, R.; Mine, Y. The Impact of Oolong and Black Tea Polyphenols on Human Health. Food Biosci. 2019, 29, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xing, D.; Wang, C. Pancreatic Triglyceride Lipase Inhibitors Derived from Natural Products: How To Dig into the Truth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6097–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Factors Impacting Lipid Digestion and β-Carotene Bioaccessibility Assessed by Standardized Gastrointestinal Model (INFOGEST): Oil Droplet Concentration. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7126–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Factors Impacting Lipid Digestion and Nutraceutical Bioaccessibility Assessed by Standardized Gastrointestinal Model (INFOGEST): Oil. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9936–9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhou, H.; McClements, D.J. Application of Static in Vitro Digestion Models for Assessing the Bioaccessibility of Hydrophobic Bioactives: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 122, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkempinck, S.H.E.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Moens, L.G.; Carrillo, C.; Van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E.; Grauwet, T. Kinetic Approach to Study the Relation between in Vitro Lipid Digestion and Carotenoid Bioaccessibility in Emulsions with Different Oil Unsaturation Degree. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 41, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, H.; Antoniou, J.; Hategekimana, J.; Sharif, H.R.; Haider, J.; Liu, F.; Ali, B.; Rong, L.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Influence of Carrier Oil Type, Particle Size on in Vitro Lipid Digestion and Eugenol Release in Emulsion and Nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Lerma, J.; Asensio-Grau, A.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. Screening the Impact of Food Co-Digestion on Lipolysis under Sub-Optimal Intestinal Conditions. LWT 2020, 118, 108792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST Static In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSZ 20685:1980; Tea Fizikai És Kémiai Vizsgálata (Physico-Chemical Evaluation of Tea). Magyar Szabványügyi Hivatal: Budapest, Hungary, 1980.
- ISO 1444:2000; Meat and Meat Products. Determination of Free Fat Content. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- ISO 2450:2008; Cream—Determination of Fat Content—Gravimetric Method (Reference Method). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Tormási, J.; Abrankó, L. Assessment of Fatty Acid-Specific Lipolysis by In Vitro Digestion and GC-FID. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 12966-2:2017; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Gas Chromatography of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters—Part 2: Preparation of Methyl Esters of Fatty Acids. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Omar, K.A.; Gounga, M.E.; Liu, R.; Mwinyi, W.; Aboshora, W.; Ramadhan, A.H.; Sheha, K.A.; Wang, X. Triacylglycerol Composition, Melting and Crystallization Profiles of Lipase Catalysed Anhydrous Milk Fats Hydrolysed. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1230–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angers, P.; Tousignant, É.; Boudreau, A.; Arul, J. Regiospecific Analysis of Fractions of Bovine Milk Fat Triacylglycerols with the Same Partition Number. Lipids 1998, 33, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, W.W.; Clapperton, J.L. Structures of the Triglycerides of Cows’ Milk, Fortified Milks (Including. Infant Formulae), and Human Milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 1982, 35, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Yang, A.; Larsen, T.W.; Tume, R.K. Positional Analysis of Triacylglycerols from Bovine Adipose Tissue Lipids Varying in Degree of Unsaturation. Lipids 1998, 33, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantes-Garcia, M.R.; Verkempinck, S.H.E.; Guevara-Zambrano, J.M.; Andreoletti, C.; Hendrickx, M.E.; Grauwet, T. Enzymatic and Chemical Conversions Taking Place during in Vitro Gastric Lipid Digestion: The Effect of Emulsion Droplet Size Behavior. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrière, F.; Rogalska, E.; Cudrey, C.; Ferrato, F.; Laugier, R.; Verger, R. In Vivo and in Vitro Studies on the Stereoselective Hydrolysis of Tri- and Diglycerides by Gastric and Pancreatic Lipases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.; Rodriguez, J.; Carriere, F.; Krieger, N. Determination of the Quantitative Stereoselectivity Fingerprint of Lipases during Hydrolysis of a Prochiral Triacylglycerol. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 135, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Gallo, P.; Franceschetto, A.; Wong, J.C.M.; Marlow, M.; Zann, V.; Scholes, P.; Gershkovich, P. Chain Length Affects Pancreatic Lipase Activity and the Extent and PH–Time Profile of Triglyceride Lipolysis. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.J.; Lim, B.O.; Park, G.B.; Joo, S.T. Effects of Various Fiber Additions on Lipid Digestion during In Vitro Digestion of Beef Patties. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C653–C657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.; Holmberg, K.; Watzke, H.; Leser, M.E.; Miller, R. Lipases at Interfaces: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamothe, S.; Guérette, C.; Britten, M. Nutrient Release and Oxidative Stability during in Vitro Digestion of Linseed Oil Emulsions Produced from Cow Milk, Soy Drink, and Green Tea Extract. LWT 2020, 134, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tormási, J.; Abrankó, L. Impact of Grape Seed Powder and Black Tea Brew on Lipid Digestion—An In Vitro Co-Digestion Study with Real Foods. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102395
Tormási J, Abrankó L. Impact of Grape Seed Powder and Black Tea Brew on Lipid Digestion—An In Vitro Co-Digestion Study with Real Foods. Nutrients. 2023; 15(10):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102395
Chicago/Turabian StyleTormási, Judit, and László Abrankó. 2023. "Impact of Grape Seed Powder and Black Tea Brew on Lipid Digestion—An In Vitro Co-Digestion Study with Real Foods" Nutrients 15, no. 10: 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102395
APA StyleTormási, J., & Abrankó, L. (2023). Impact of Grape Seed Powder and Black Tea Brew on Lipid Digestion—An In Vitro Co-Digestion Study with Real Foods. Nutrients, 15(10), 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102395





