The Side-Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Increased BMI z-Score in Children with Overweight and Obesity in a Personalised Lifestyle Intervention One Year after the Start of the Pandemic in The Netherlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Lockdown Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Netherlands
2.4. Study Measurements
2.5. Lifestyle Intervention Determinants
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
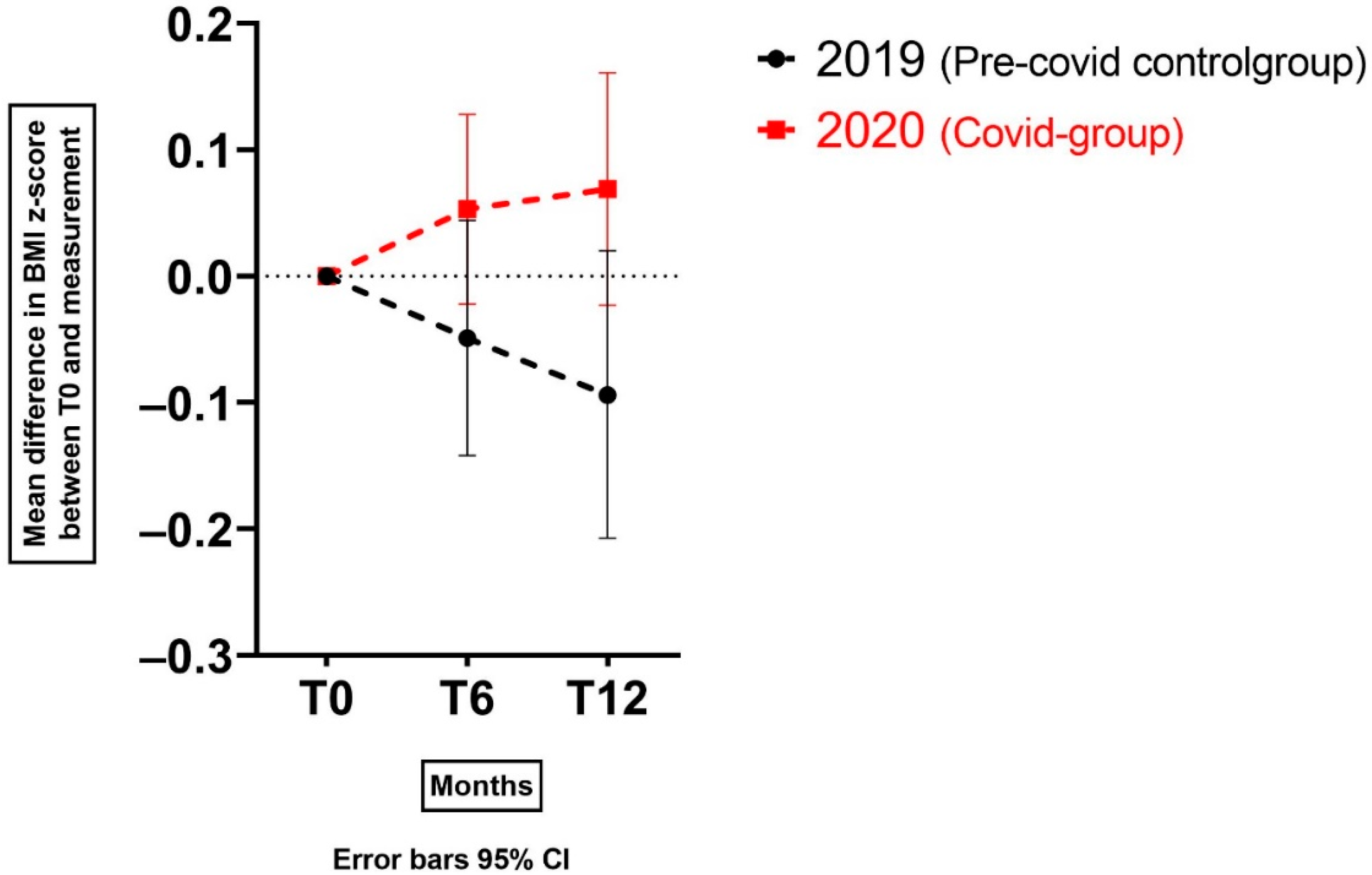
3.2. BMI z-Score Change for Children with Overweight and (Severe) Obesity on the Mid-Long Term after the Start of the COVID-19 Pandemic
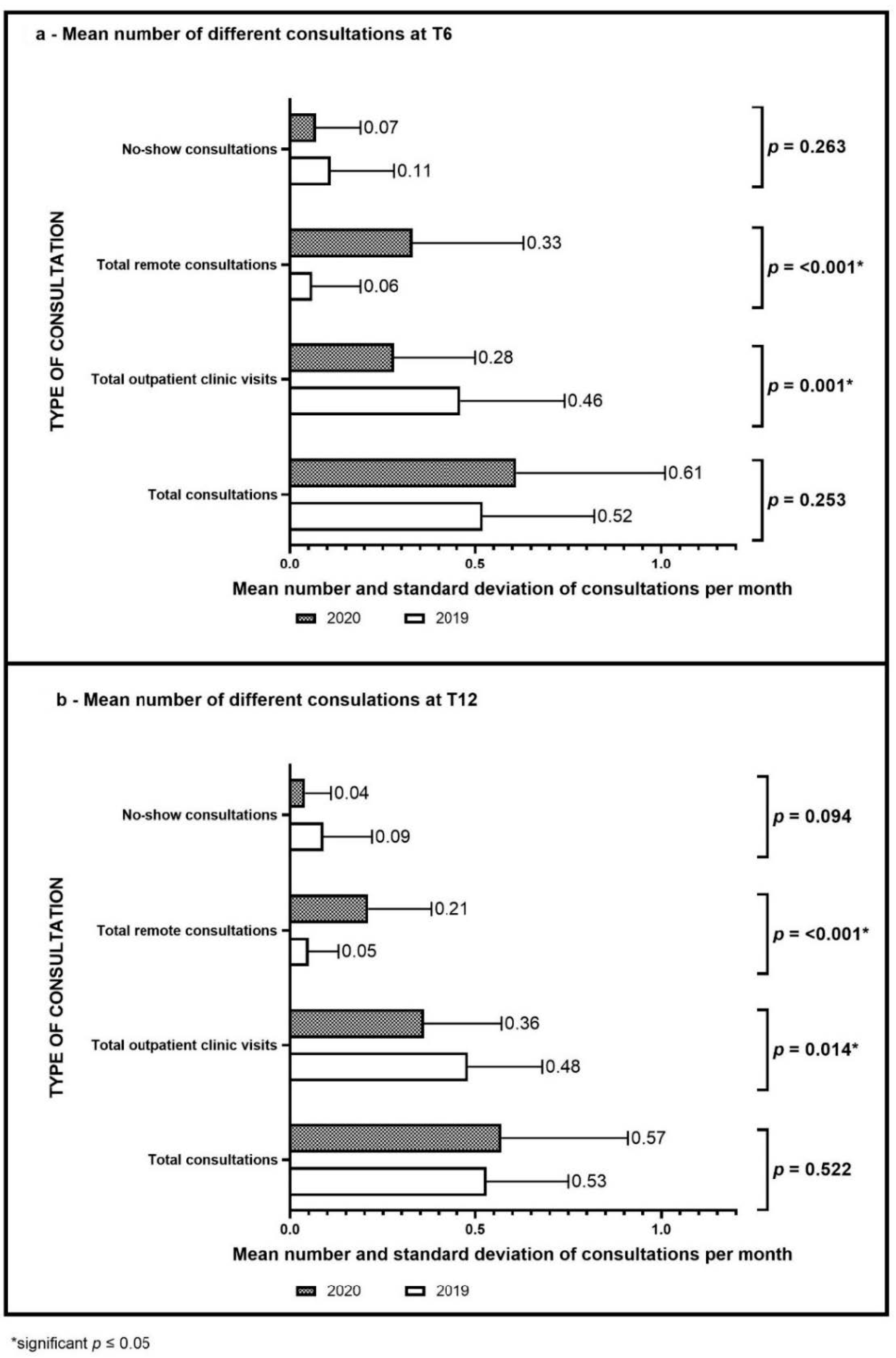
3.3. Lifestyle Intervention Changes during the COVID-19 Pandemic
3.4. Model 3: Creating a Model to Identify Family Characteristics Influencing BMI z-Score Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BMI z-score | Body mass index z-score |
| COACH | Centre for Overweight Adolescent and Children’s Healthcare |
References
- Coronavirus Measures in Brief. Coronavirus COVID-19. Government.nl Ministerie van Algemene Zaken. Published 20 July 2020. Available online: https://www.government.nl/topics/c/coronavirus-covid-19/tackling-new-coronavirus-in-the-netherlands/coronavirus-measures-in-brief (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Liguoro, I.; Pilotto, C.; Bonanni, M.; Ferrari, M.E.; Pusiol, A.; Nocerino, A.; Vidal, E.; Cogo, P. SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and newborns: A systematic review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Velde, G.; Lubrecht, J.; Arayess, L.; Van Loo, C.; Hesselink, M.; Reijnders, D.; Vreugdenhil, A. Physical activity behavior and screen time in Dutch children during the COVID-19 pandemic: Pre-, during- and post-school closures. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12779. [Google Scholar]
- di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: An Italian survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.L.; Caccavale, L.J.; Smith, D.; Bean, M.K. Food Insecurity, the Home Food Environment, and Parent Feeding Practices in the Era of COVID-19. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2020, 28, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysun, Ş.; Ş, M. Weight gain in children during the COVID-19 quarantine period. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 56, 1487–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayess, L.; Lubrecht, J.W.; Reijnders, R.; Hesselink, M.; Ten Velde, G.; Janse, A.; Von Rosenstiel, I.A.; van Mil, E.G.A.H.; Verweij, M.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E. Weight changes during the COVID-19 pandemic in children with and without overweight and obesity, and the effects of prior lifestyle intervention. Obes. Facts. (in press)..
- Pietrobelli, A.; Pecoraro, L.; Ferruzzi, A.; Heo, M.; Faith, M.; Zoller, T.; Antoniazzi, F.; Piacentini, G.; Fearnbach, S.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Lifestyle Behaviors in Children with Obesity Living in Verona, Italy: A Longitudinal Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2020, 28, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, A.G.; Park, Y.; Herbstman, J.B.; Kinsey, E.W.; Wang, Y.C. COVID-19-Related School Closings and Risk of Weight Gain Among Children. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2020, 28, 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franckle, R.; Adler, R.; Davison, K. Accelerated Weight Gain among Children during Summer Versus School Year and Related Racial/Ethnic Disparities: A Systematic Review. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2014, 11, E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, N.T.; Snethen, J.A.; Greenberg, C.S.; Frenn, M.; Kilanowski, J.F.; Gance-Cleveland, B.; Burke, P.J.; Lewandowski, L. When Pandemics Collide: The Impact of COVID-19 on Childhood Obesity. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2020, 56, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, A.; Kelley, G.A.; Cottrell, L.E.; Giacobbi, P., Jr.; Innes, K.E.; Lilly, C.L. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk factors: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styne, D.M.; Arslanian, S.A.; Connor, E.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Murad, M.H.; Silverstein, J.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Pediatric Obesity-Assessment, Treatment, and Prevention: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 709–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijks, J.M.; Plat, J.; Dorenbos, E.; Penders, B.; Gerver, W.-J.M.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.; Gerver, W. Association of TSH With Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Overweight and Obese Children During Lifestyle Intervention. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rijks, J.; Karnebeek, K.; Van Dijk, J.-W.; Dorenbos, E.; Gerver, W.-J.; Stouthart, P.; Plat, J.; Vreugdenhil, A. Glycaemic Profiles of Children With Overweight and Obesity in Free-living Conditions in Association With Cardiometabolic Risk. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnebeek, K.; Thapar, S.; Willeboordse, M.; Van Schayck, O.C.P.; E Vreugdenhil, A.C. Comorbidities in Primary vs Secondary School Children With Obesity and Responsiveness to Lifestyle Intervention. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3803–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortmaker, S.L.; Must, A.; Perrin, J.M.; Sobol, A.M.; Dietz, W.H. Social and Economic Consequences of Overweight in Adolescence and Young Adulthood. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelone, F.; Specchia, M.L.; Veneziano, M.A.; Capizzi, S.; Bucci, S.; Mancuso, A.; Ricciardi, W.; De Belvis, A.G. Economic impact of childhood obesity on health systems: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2011, 13, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidell, J.C.; Halberstadt, J. The Global Burden of Obesity and the Challenges of Prevention. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. 2), 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijks, J.; Plat, J.; Mensink, R.; Dorenbos, E.; Buurman, W.; Vreugdenhil, A. Children with morbid obesity benefit equally as children with overweight and obesity from an on-going care program. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3572–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerie van Algemene Zaken, COVID-19: Additional Measures in Schools, the Hospitality Sector and Sport, News Item | Government.nl. 2020. Available online: https://www.government.nl/latest/news/2020/03/15/additional-measures-in-schools-the-hospitality-sector-and-sport (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Ministerie van Onderwijs, Cultuur en Wetenschap, Alle Scholen Weer Open, Nieuwsbericht | Rijksoverheid.nl. 2020. Available online: https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/actueel/nieuws/2020/08/31/alle-scholen-weer-open (accessed on 20 December 2021). (In Dutch).
- Government.nl. Lockdown in Order to Minimise Contact between People. 2021. Available online: https://www.government.nl/latest/news/2020/12/14/lockdown-in-order-to-minimise-contact-between-people (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Talma, H.; Schonbeck, Y.; Bakker, B.; Hirasing, R.A.; van Buuren, S. Groeidiagrammen 2010. Handleiding bij het Meten en Wegen van Kinderen en het Invullen van Groeidiagrammen. TNO: Leiden, the Netherlands, 2011. Available online: https://repository.tno.nl/islandora/object/uuid%3A5460503b-1519-4db0-8309-d8a63ecca01e (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- TNO. Growth Calculator for Youth Healthcare in the Netherlands 2020. Available online: https://tnochildhealthstatistics.shinyapps.io/JGZRichtlijnLengtegroei (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Cole, T.J.; Roede, M.J. Centiles of body mass index for Dutch children aged 0-20 years in 1980 - a baseline to assess recent trends inobesity. Ann. Hum. Biol. 1999, 26, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnebeek, K.; Rijks, J.M.; Dorenbos, E.; Gerver, W.-J.M.; Plat, J.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E. Changes in Free-Living Glycemic Profiles after 12 Months of Lifestyle Intervention in Children with Overweight and with Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, S.; Zeller, M.; Claytor, R.; Santangelo, M.; Khoury, P.R.; Daniels, S.R. The Relationship of Health Outcomes to Improvement in BMI in Children and Adolescents. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.M.; Byrne, S.; Thompson, A.; Ratnam, N.; Blair, E.; Bulsara, M.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A. Increasing Body Mass Index z-Score Is Continuously Associated with Complications of Overweight in Children, Even in the Healthy Weight Range. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 92, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfley, D.E.; Tibbs, T.L.; Van Buren, D.; Reach, K.P.; Walker, M.S.; Epstein, L.H. Lifestyle interventions in the treatment of childhood overweight: A meta-analytic review of randomized controlled trials. Health Psychol. 2007, 26, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuemmeler, B.F.; Lovelady, C.A.; Zucker, N.L.; Østbye, T. Parental obesity moderates the relationship between childhood appetitive traits and weight. Obesity 2012, 21, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.A.; Alava, M.H.; Kelly, M.P.; Campbell, M.J. Family lifestyle dynamics and childhood obesity: Evidence from the millennium cohort study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, M.; Nasiri, A. Concerns of parents about children's overweight and obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2021, 63, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegert, J.M.; Vitiello, B.; Plener, P.L.; Clemens, V. Challenges and burden of the Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic for child and adolescent mental health: A narrative review to highlight clinical and research needs in the acute phase and the long return to normality. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2020, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootens-Wiegers, P.; van den Eynde, E.; Halberstadt, J.; Seidell, J.C.; Dedding, C. The “Stages towards Completion Model”: What helps and hinders children with overweight or obesity and their parents to be guided towards, adhere to and complete a group lifestyle intervention. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-Being 2020, 15, 1735093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.M.; Yunker, A.G.; DeFendis, A.; Xiang, A.H.; Page, K.A. BMI status and associations between affect, physical activity and anxiety among U.S. children during COVID-19. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotarjova, J.; Ten Velde, G.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E. Effects of multidisciplinary interventions on weight loss and health outcomes in children and adolescents with morbid obesity. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.S.A.; Karim, Q.A. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant: A new chapter in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerie van Algemene Zaken. (14 December 2021); Evening Closures Prolonged, Primary Schools to Shut a Week Early before Christmas. News Item | Government.nl. Available online: https://www.government.nl/latest/news/2021/12/14/evening-closures-prolonged-primary-schools-to-shut-a-week-early-before-christmas (accessed on 16 December 2021).

| 2020 (COVID-19 Group) | 2019 (Control Group) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 71 | N = 48 | ||
| Age, mean (SD); years | 12.6 (3.1) | 11.7 (2.5) | 0.094 |
| Gender, % female (N) | 49.3 (N = 35) | 52.1 (N = 25) | 0.765 |
| BMI score (SD); kg/mg | 28.59 (5.95) | 27.56 (3.46) | 0.237 |
| BMI z-score (SD) | 3.09 (0.70) | 3.11 (0.60) | 0.888 |
| IOTF at T0 | 0.744 | ||
| Overweight, % (N) | 33.8 (N = 24) | 29.2 (N = 14) | |
| Obesity, % (N) | 40.8 (N = 29) | 47.9 (N = 23) | |
| Severe obesity, % (N) | 25.4 (N = 18) | 22.9 (N = 11) | |
| Months in intervention at T0 (SD) mean | 13.1 (18.3) | 15.0 (18.7) | 0.578 |
| <1 year since start intervention at T0, % (N) | 59.2 (N = 42) | 64.6 (N = 31) | |
| >1 year since start intervention at T0, % (N) | 40.8 (N = 29) | 35.4 (N = 17) | 0.551 |
| Ethnicity | 0.856 | ||
| Dutch, % (N) | 62.9 (N = 39) # | 64.6 (N = 31) | |
| Migration background, % (N) | 37.1 (N = 23) # | 35.4 (N = 17) | |
| Parental factors | |||
| BMI mother, mean (SD); kg/mg | 28.41 (4.99) ^ | 30.31 (6.08)^ | 0.068 |
| BMI father, mean (SD); kg/mg | 29.67 (4.91) ^^ | 29.48 (4.82) ^^ | 0.845 |
| Having a mother with obesity, % (N) | 40.6 (N = 28) ^ | 46.8 (N = 22) ^ | 0.506 |
| Having a father with obesity, % (N) | 36.7 (N = 22) ^^ | 42.5% (N = 17) ^^ | 0.558 |
| Having≥1 parent with obesity, % (N) | 63.5 (N = 40) ^^^ | 65.1 (N = 28) ^^^ | 0.864 |
| Educational level mother | |||
| Low, % (N) | 38.9 (N = 21) ◊ | 34.9 (N = 15) ◊ | 0.16 |
| Medium, % (N) | 40.7 (N = 22) ◊ | 27.9 (N = 12) ◊ | |
| High, % (N) | 20.4 (N = 11) ◊ | 37.2 (N = 16) ◊ | |
| Educational level father | |||
| Low, % (N) | 32.0 (N = 16) ◊◊ | 34.1 (N = 14) ◊◊ | 0.89 |
| Medium, % (N) | 34.0 (N = 17) ◊◊ | 36.6 (N = 15) ◊◊ | |
| High, % (N) | 34.0 (N = 17) ◊◊ | 29.3 (N = 12) ◊◊ |
| T6 | p-Value ^ | T12 | p-Value ^ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||
| BMI z-score increase, mean (SD) change for subgroup | 0.24 (0.03) N = 30 | 0.14 (0.04) N = 19 | 0.047 * | 0.32 (0.04) N = 29 | 0.10 (0.05) N = 18 | <0.001 * |
| BMI z-score decrease or stabilisation, mean (SD) change for subgroup | −0.16 (0.03) N = 28 | −0.27 (0.04) N = 20 | 0.010 * | −0.23 (0.05) N = 19 | −0.34 (0.06) N = 13 | 0.178 |
| Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value | Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| Year [2020 versus 2019] at T6 | +0.14 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.033 * | +0.15 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.024 * |
| Year [2020 versus 2019] at T12 | +0.18 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.014 * | +0.18 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.016 * |
| Centre [Maastricht] | +0.04 | −0.10 | 0.18 | 0.602 | +0.05 | −0.09 | 0.19 | 0.472 |
| Contact moments outpatient clinic/month | +0.05 | −0.15 | 0.25 | 0.635 | +0.05 | −0.15 | 0.25 | 0.609 |
| Remote contact moments/month | −0.03 | −0.24 | 0.17 | 0.752 | −0.00 | −0.21 | 0.20 | 0.993 |
| No-show appointments per month | +0.43 | 0.07 | 0.80 | 0.021 * | +0.41 | 0.05 | 0.77 | 0.025 * |
| >=1 Year in intervention at baseline | −0.02 | −0.14 | 0.09 | 0.680 | −0.02 | −0.13 | 0.10 | 0.772 |
| Having a mother with obesity | +0.13 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.019 * | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arayess, L.; Knockaert, N.; Winkens, B.; Lubrecht, J.W.; Verweij, M.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E. The Side-Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Increased BMI z-Score in Children with Overweight and Obesity in a Personalised Lifestyle Intervention One Year after the Start of the Pandemic in The Netherlands. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091942
Arayess L, Knockaert N, Winkens B, Lubrecht JW, Verweij M, Vreugdenhil ACE. The Side-Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Increased BMI z-Score in Children with Overweight and Obesity in a Personalised Lifestyle Intervention One Year after the Start of the Pandemic in The Netherlands. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091942
Chicago/Turabian StyleArayess, Lisanne, Nienke Knockaert, Bjorn Winkens, Judith W. Lubrecht, Marjoke Verweij, and Anita C. E. Vreugdenhil. 2022. "The Side-Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Increased BMI z-Score in Children with Overweight and Obesity in a Personalised Lifestyle Intervention One Year after the Start of the Pandemic in The Netherlands" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091942
APA StyleArayess, L., Knockaert, N., Winkens, B., Lubrecht, J. W., Verweij, M., & Vreugdenhil, A. C. E. (2022). The Side-Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Increased BMI z-Score in Children with Overweight and Obesity in a Personalised Lifestyle Intervention One Year after the Start of the Pandemic in The Netherlands. Nutrients, 14(9), 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091942







