Effect of Calcifediol on Physical Performance and Muscle Strength Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Registration Statement
2.2. Data Sources and Searches
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Quality Assessment
2.7. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
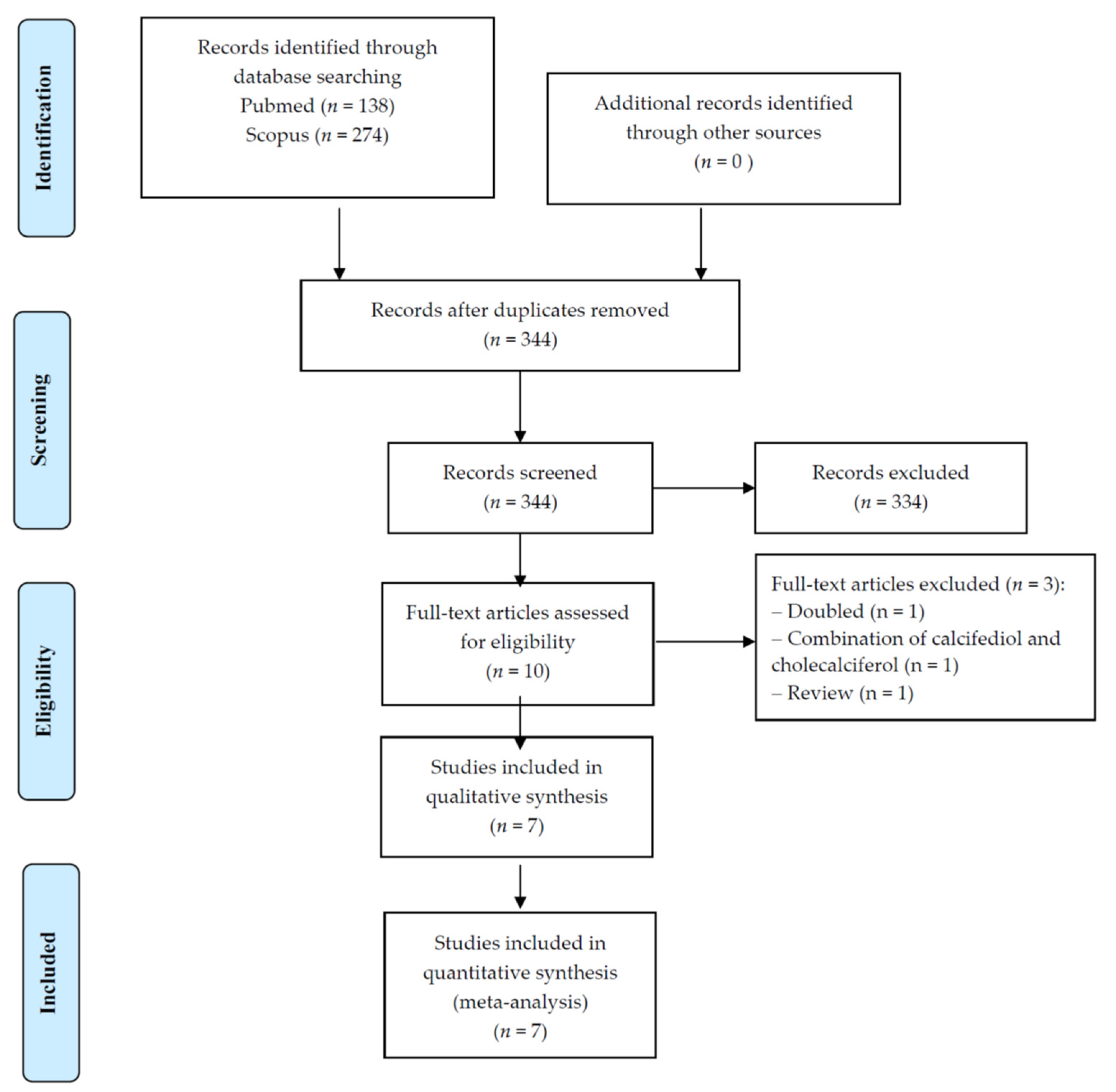
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study and Participants Characteristics
3.3. Meta-Analysis of Calcifediol on Physical Performance and Muscle Strength Parameters
3.4. Meta-Regression Analysis
3.5. Adverse Events
3.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charoenngam, N.; Holick, M.F. Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Farruggia, M.; Veronese, N.; Barbagallo, M. Vitamin D sources, metabolism, and deficiency: Available compounds and guidelines for its treatment. Metabolites 2021, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annweiler, C.; Schott, A.-M.; Berrut, G.; Fantino, B.; Beauchet, O. Vitamin D-related changes in physical performance: A systematic review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, M.; Deeg, D.J.; Lips, P. Low vitamin D and high parathyroid hormone levels as determinants of loss of muscle strength and muscle mass (sarcopenia): The Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5766–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remelli, F.; Vitali, A.; Zurlo, A.; Volpato, S. Vitamin D deficiency and sarcopenia in older persons. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bischoff, H.; Stähelin, H.; Tyndall, A.; Theiler, R. Relationship between muscle strength and vitamin D metabolites: Are there therapeutic possibilities in the elderly? Z. Für Rheumatol. 2000, 59, I39–I41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Gomez, J.; Bouillon, R. Is calcifediol better than cholecalciferol for vitamin D supplementation? Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecarnot, F.; Rogoli, D.; Maggi, S. Epidemiology of Sarcopenia. In Sarcopenia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Veronese, N.; Demurtas, J.; Soysal, P.; Smith, L.; Torbahn, G.; Schoene, D.; Schwingshackl, L.; Sieber, C.; Bauer, J.; Cesari, M. Sarcopenia and health-related outcomes: An umbrella review of observational studies. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 10, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Trevisan, C.; Bolzetta, F.; De Rui, M.; Solmi, M.; Sarton, L.; Musacchio, E.; Zambon, S.; Perissinotto, E.; et al. Poor Physical Performance Predicts Future Onset of Depression in Elderly People: Pro.V.A. Longitudinal Study. Phys. Ther. 2017, 97, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hangelbroek, R.W.; Vaes, A.M.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Verdijk, L.B.; Hooiveld, G.J.; van Loon, L.J.; De Groot, L.C.; Kersten, S. No effect of 25-hydroxyvitamin D supplementation on the skeletal muscle transcriptome in vitamin D deficient frail older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonnelli, S.; Tomai Pitinca, M.D.; Camarri, S.; Lucani, B.; Franci, B.; Nuti, R.; Caffarelli, C. Pharmacokinetic profile and effect on bone markers and muscle strength of two daily dosage regimens of calcifediol in osteopenic/osteoporotic postmenopausal women. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Stöcklin, E.; Sidelnikov, E.; Willett, W.C.; Edel, J.O.; Stähelin, H.B.; Wolfram, S.; Jetter, A.; Schwager, J. Oral supplementation with 25 (OH) D3 versus vitamin D3: Effects on 25 (OH) D levels, lower extremity function, blood pressure, and markers of innate immunity. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iolascon, G.; Moretti, A.; de Sire, A.; Calafiore, D.; Gimigliano, F. Effectiveness of calcifediol in improving muscle function in post-menopausal women: A prospective cohort study. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, C.; Baroni, M.; Bini, V.; Brozzetti, A.; Parretti, L.; Zengarini, E.; Lapenna, M.; Antinolfi, P.; Falorni, A.; Mecocci, P. Effects of weekly supplementation of cholecalciferol and calcifediol among the oldest-old people: Findings from a randomized pragmatic clinical trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrado, A.; Rotondo, C.; Cici, D.; Berardi, S.; Cantatore, F.P. Effects of Different Vitamin D Supplementation Schemes in Post-Menopausal Women: A Monocentric Open-Label Randomized Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaes, A.M.; Tieland, M.; Toussaint, N.; Nilwik, R.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.; de Groot, L.C. Cholecalciferol or 25-hydroxycholecalciferol supplementation does not affect muscle strength and physical performance in prefrail and frail older adults. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christakos, S.; Dhawan, P.; Verstuyf, A.; Verlinden, L.; Carmeliet, G. Vitamin D: Metabolism, molecular mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 365–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.A. Diagnosis and management of vitamin D dependent rickets. Front. Pediatrics 2020, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, J.; Naud, J.; Ouimet, D.; Demers, C.; Petit, J.-L.; Leblond, F.A.; Bonnardeaux, A.; Gascon-Barré, M.; Pichette, V. Reduced hepatic synthesis of calcidiol in uremia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeyama, K.I.; Kitanaka, S.; Sato, T.; Kobori, M.; Yanagisawa, J.; Kato, S. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1α-hydroxylase and vitamin D synthesis. Science 1997, 277, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.E.; Goodman, D.S. The turnover and transport of vitamin D and of a polar metabolite with the properties of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in human plasma. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.M.; Stuart, A.L.; Williamson, E.J.; Simpson, J.A.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Young, D.; Nicholson, G.C. Annual high-dose oral vitamin D and falls and fractures in older women: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 303, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burt, L.A.; Billington, E.O.; Rose, M.S.; Raymond, D.A.; Hanley, D.A.; Boyd, S.K. Effect of high-dose vitamin D supplementation on volumetric bone density and bone strength: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Gallagher, J.C.; Suiter, C. Medium doses of daily vitamin D decrease falls and higher doses of daily vitamin D3 increase falls: A randomized clinical trial. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 173, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, R.P.; Horst, R.L.; Cullen, D.M.; Armas, L.A. Vitamin D3 distribution and status in the body. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2009, 28, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minisola, S.; Cianferotti, L.; Biondi, P.; Cipriani, C.; Fossi, C.; Franceschelli, F.; Giusti, F.; Leoncini, G.; Pepe, J.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H. Correction of vitamin D status by calcidiol: Pharmacokinetic profile, safety, and biochemical effects on bone and mineral metabolism of daily and weekly dosage regimens. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 3239–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, B.W. Comparison of equilibrium and disequilibrium assay conditions for ergocalciferol, cholecalciferol and their major metabolites. J. Steroid Biochem. 1984, 21, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Castrillón, J.L.; Dueñas-Laita, A.; Brandi, M.L.; Jódar, E.; del Pino-Montes, J.; Quesada-Gómez, J.M.; Cereto Castro, F.; Gómez-Alonso, C.; Gallego Lopez, L.; Olmos Martinez, J.M. Calcifediol is superior to cholecalciferol in improving vitamin D status in postmenopausal women: A randomized trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 36, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetter, A.; Egli, A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Staehelin, H.B.; Stoecklin, E.; Goessl, R.; Henschkowski, J.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A. Pharmacokinetics of oral vitamin D3 and calcifediol. Bone 2014, 59, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, C.; Romagnoli, E.; Pepe, J.; Russo, S.; Carlucci, L.; Piemonte, S.; Nieddu, L.; McMahon, D.J.; Singh, R.; Minisola, S. Long-term bioavailability after a single oral or intramuscular administration of 600,000 IU of ergocalciferol or cholecalciferol: Implications for treatment and prophylaxis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Shao, A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Hathcock, J.; Giovannucci, E.; Willett, W.C. Benefit–risk assessment of vitamin D supplementation. Osteoporos. Int. 2010, 21, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossini, M.; Adami, S.; Viapiana, O.; Fracassi, E.; Idolazzi, L.; Povino, M.R.; Gatti, D. Dose-dependent short-term effects of single high doses of oral vitamin D3 on bone turnover markers. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2012, 91, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, M.; Gatti, D.; Viapiana, O.; Fracassi, E.; Idolazzi, L.; Zanoni, S.; Adami, S. Short-term effects on bone turnover markers of a single high dose of oral vitamin D3. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E622–E626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, M.; Seelaender, M.; Sotiropoulos, A.; Coletti, D.; Lancha Jr, A.H. Vitamin D, muscle recovery, sarcopenia, cachexia, and muscle atrophy. Nutrition 2019, 60, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Borchers, M.; Gudat, F.; Dürmüller, U.; Stähelin, H.; Dick, W. Vitamin D receptor expression in human muscle tissue decreases with age. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, C.M.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Hamrick, M.W.; Holick, M.F.; Gunton, J.E. The roles of vitamin D in skeletal muscle: Form, function, and metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 33–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzik, K.P.; Kaczor, J.J. Mechanisms of vitamin D on skeletal muscle function: Oxidative stress, energy metabolism and anabolic state. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bang, W.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, K.-T.; Cho, D.-C.; Sung, J.-K.; Han, I.-B.; Kim, D.-H.; Kwon, B.K.; Kim, C.H.; Park, K.-S. Relationships between vitamin D and paraspinal muscle: Human data and experimental rat model analysis. Spine J. 2018, 18, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, Z.C.; Craig, T.A.; Folmes, C.D.; Wang, X.; Lanza, I.R.; Schaible, N.S.; Salisbury, J.L.; Nair, K.S.; Terzic, A.; Sieck, G.C. 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulates mitochondrial oxygen consumption and dynamics in human skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1514–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Priemel, M.; von Domarus, C.; Klatte, T.O.; Kessler, S.; Schlie, J.; Meier, S.; Proksch, N.; Pastor, F.; Netter, C.; Streichert, T. Bone mineralization defects and vitamin D deficiency: Histomorphometric analysis of iliac crest bone biopsies and circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D in 675 patients. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopidis, K.; Giannos, P.; Katsikas Triantafyllidis, K.; Kechagias, K.S.; Mesinovic, J.; Witard, O.C.; Scott, D. Effect of vitamin D monotherapy on indices of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockton, K.A.; Mengersen, K.; Paratz, J.D.; Kandiah, D.; Bennell, K.L. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on muscle strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Loenneke, J.P.; Jo, E.; Wilson, G.J.; Zourdos, M.C.; Kim, J.-S. The effects of endurance, strength, and power training on muscle fiber type shifting. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglia, L.; Niramitmahapanya, S.; da Silva Morais, M.; Rivas, D.A.; Harris, S.S.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Fielding, R.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B. A randomized study on the effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on skeletal muscle morphology and vitamin D receptor concentration in older women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1927–E1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouillon, R.; Manousaki, D.; Rosen, C.; Trajanoska, K.; Rivadeneira, F.; Richards, J.B. The health effects of vitamin D supplementation: Evidence from human studies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 18, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Country | Sample Size | Condition | Daily Calcifediol Supplementation | Mean Age (SD) | Females (%) | Mean Serum 25(OH)D Levels (SD) nmol/L (Baseline vs. Follow-Up) | Follow-Up (Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bischoff-Ferrari, 2012 [17] | USA | 10 | Healthy | 20 µg | 59.5 (6.3) | 100 | 34.1 (9.1) 173.68 (11.9) | 16 |
| Corrado, 2021 [20] | Italy | 26 | Post-menopausal | 20 µg | 60.9 (8.1) | 100 | 37.93 (11.8) 167 (108.0) | 24 |
| Gonnelli, 2021 (20 µg/day) [16] | Italy | 25 | Osteopenia/ osteoporosis | 20 µg | 62.4 (7.4) | 100 | 40.5 (12.8) 148.3 (12.5) | 24 |
| Gonnelli, 2021 (30 µg/day) [16] | Italy | 25 | Osteopenia/ osteoporosis | 30 µg | 61.5 (8.3) | 100 | 30.7 (10.2) 180.8 (12.5) | 24 |
| Hangelbroek, 2019 [15] | The Netherlands | 10 | Frailty | 10 µg | 71.8 (5.7) | 40 | 69.9 (18.3) 87.3 (20.6) | 24 |
| Iolascon, 2017 (longitudinal) [18] | Italy | 113 | Osteoporosis | 20 µg | 68.0 (9.1) | 100 | 27.1 (18.3) 105.5 (27.6) | 24 |
| Ruggiero, 2019 [19] | Italy | 34 | Hospitalized for any cause | 20 µg | 82.1 (5.7) | 22 | 33.3 (1.3) 91.3 (42.3) | 32 |
| Vaes, 2018 [21] | The Netherlands | 26 | Frailty/ pre-frailty | 10 µg | 73.1 (6.0) | 46 | 38.1 (2.9) 100 (5) | 24 |
| Total | 269 | Osteopenia/osteoporosis, n = 3; frailty/pre-frailty, n = 2; hospital, n = 1; post-menopausal, n = 1; healthy, n = 1 | 30 µg, n = 1; 20 µg, n = 5; 10 µg, n = 2 | 67.4 (7.1) | Only females. n = 5; mixed, n = 3 | 39 (11.4) 132 (30) | Median = 24 |
| Parameter | Number of Comparisons | Number of Participants | SMD | 95% CI | p Value | I2 | Egger’s Test (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chair rise time | 2 | 72 | 0.759 | −0.980 | 2.499 | 0.39 | 90.4 | Not possible |
| Gait speed | 1 | 52 | 2.500 | 1.768 | 3.232 | <0.0001 | − | Not possible |
| SPPB | 2 | 278 | −0.012 | −1.237 | 1.213 | 0.99 | 93.6 | Not possible |
| Timed up and go | 3 | 124 | −0.264 | −3.412 | 2.883 | 0.87 | 97.9 | −35.8 (p = 0.63) |
| Handgrip strength | 5 | 446 | 0.532 | 0.305 | 0.758 | <0.0001 | 20.2 | 0.75 (p = 0.63) |
| Leg extension | 4 | 318 | 0.641 | 0.346 | 0.935 | <0.0001 | 18.8 | 0.75 (p = 0.69) |
| Leg flexion | 3 | 92 | 0.304 | −0.791 | 1.399 | 0.59 | 82.9 | 4.02 (p = 0.20) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbagallo, M.; Veronese, N.; Di Prazza, A.; Pollicino, F.; Carruba, L.; La Carrubba, A.; Dominguez, L.J. Effect of Calcifediol on Physical Performance and Muscle Strength Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091860
Barbagallo M, Veronese N, Di Prazza A, Pollicino F, Carruba L, La Carrubba A, Dominguez LJ. Effect of Calcifediol on Physical Performance and Muscle Strength Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091860
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbagallo, Mario, Nicola Veronese, Agnese Di Prazza, Francesco Pollicino, Luca Carruba, Anna La Carrubba, and Ligia J. Dominguez. 2022. "Effect of Calcifediol on Physical Performance and Muscle Strength Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091860
APA StyleBarbagallo, M., Veronese, N., Di Prazza, A., Pollicino, F., Carruba, L., La Carrubba, A., & Dominguez, L. J. (2022). Effect of Calcifediol on Physical Performance and Muscle Strength Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 14(9), 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091860










