Chlorophyll Inhibits the Digestion of Soybean Oil in Simulated Human Gastrointestinal System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Initial Lipid Digestion Emulsions
2.3. Model of Gastrointestinal Digestion In Vitro
2.4. Characterization of Particle Size and ζ-Potential
2.5. Observation of Microstructure
2.6. Analysis of Free Fatty Acid (FFA) Release and Hydrolysis Kinetics
2.7. Determination of Fatty Acid Composition
2.8. Determination of Pancreatic Lipase Activity
2.9. Molecular Docking
2.10. Fluorescence Titration
2.11. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectra
2.12. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Chlorophyll on Soybean Oil Digestion
3.1.1. Changes in FFA Release and Fatty Acids Composition
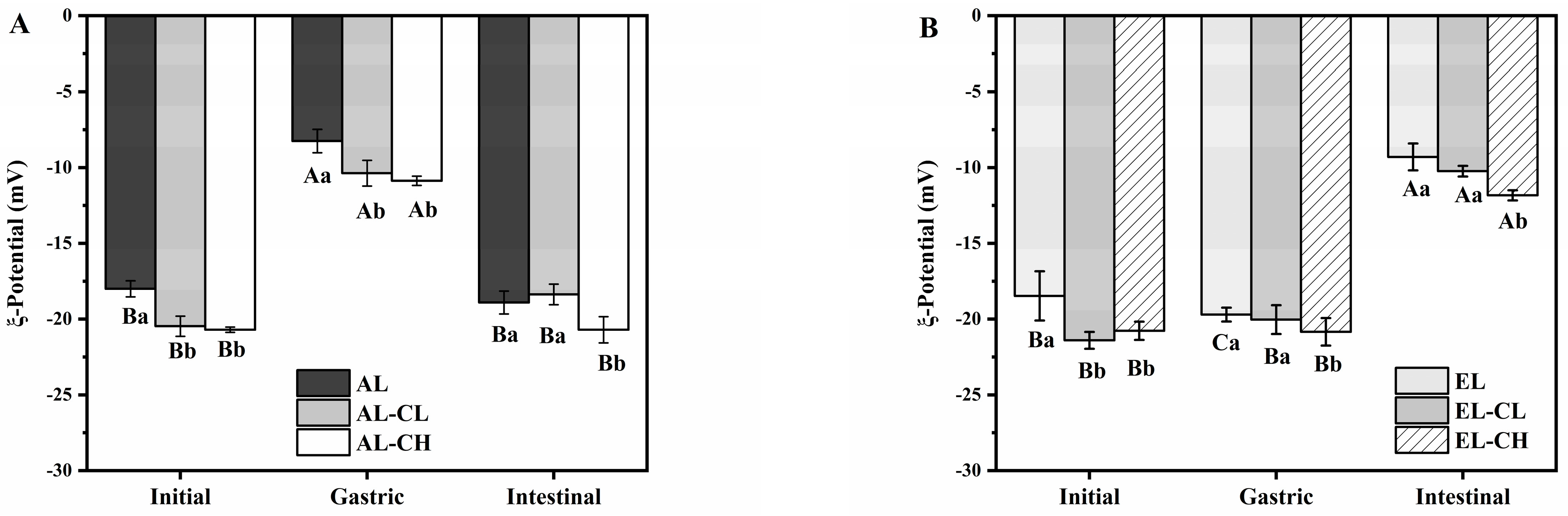
3.1.2. Evolutions of Oil Droplet Size and Surface Charge
3.2. Mechanism of Chlorophyll Inhibiting Lipid Digestion
3.2.1. Effect of Chlorophyll on the Activity of Pancreatic Lipase during Intestinal Digestion
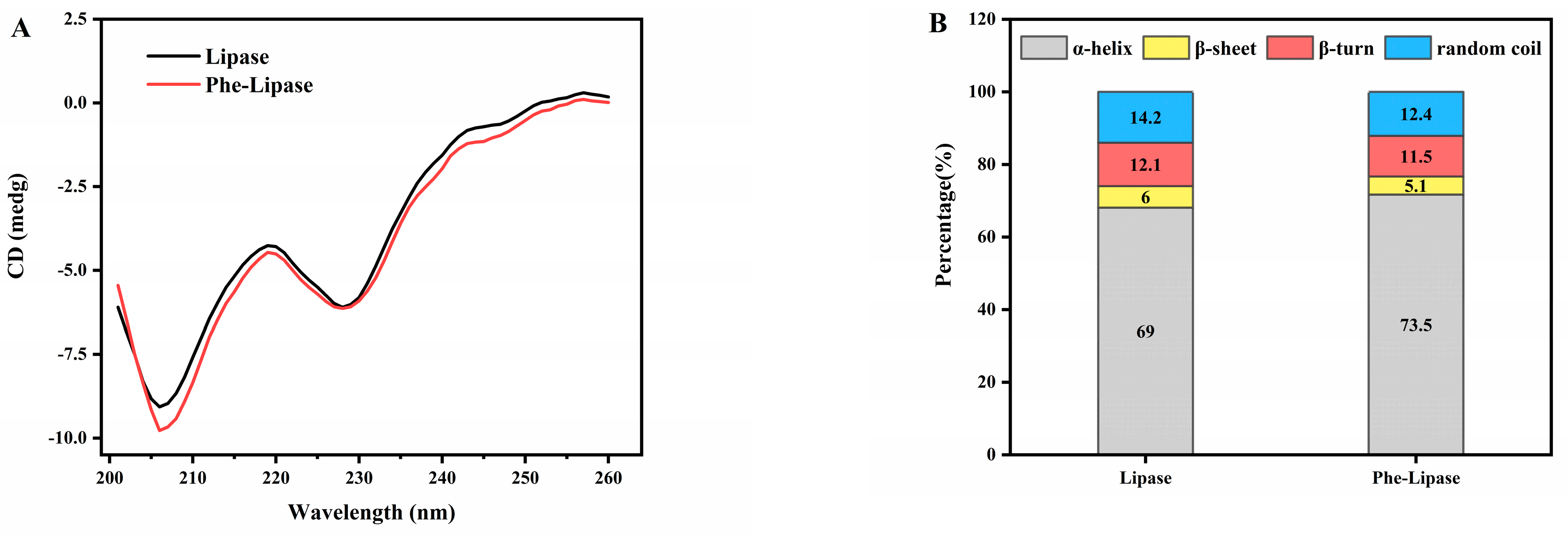
3.2.2. Effect of Pheophytin on Structure–Activity Relationships of Pancreatic Lipase
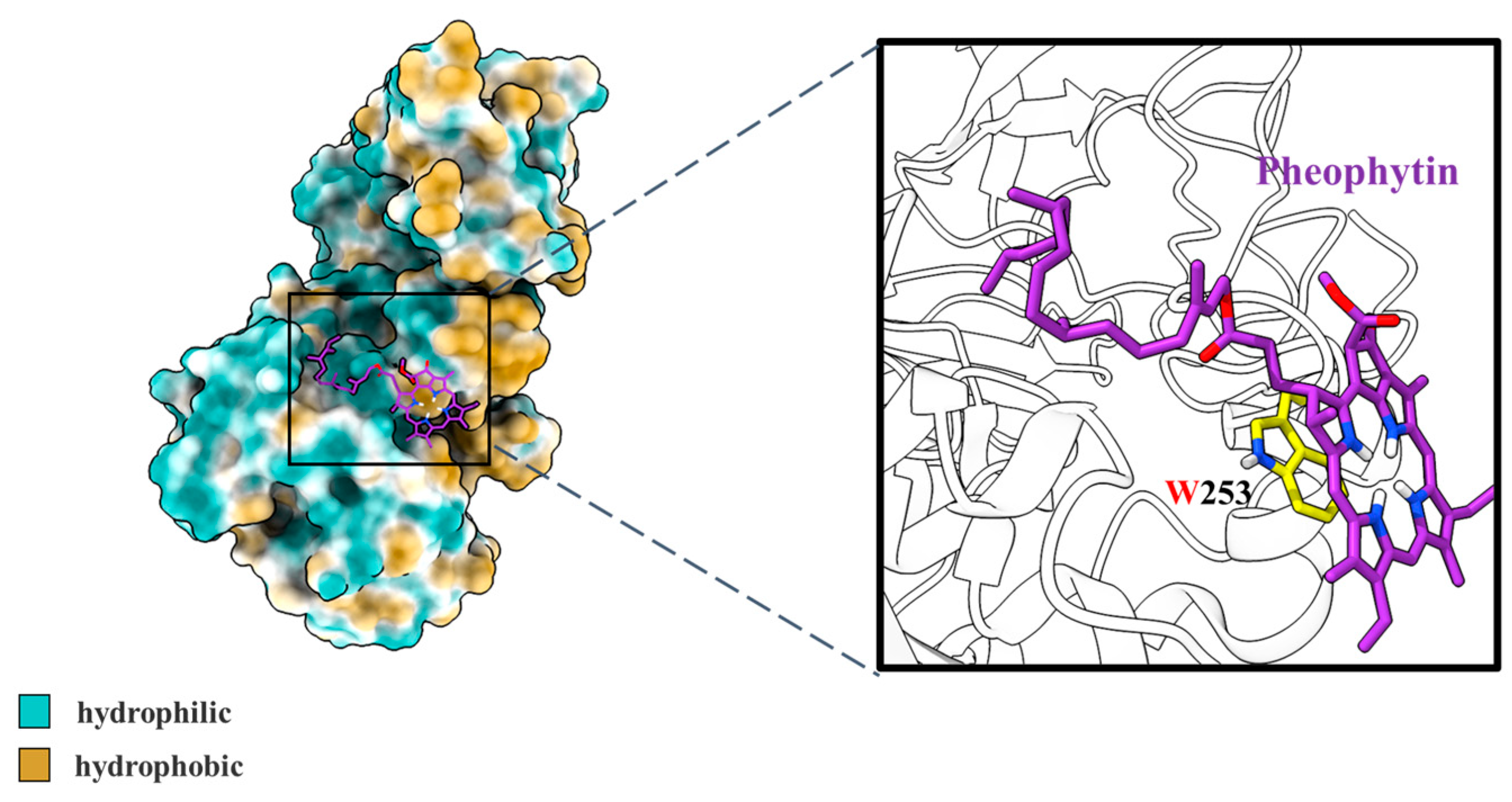
3.2.3. Molecular Docking Simulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holt, L.E. Dietary Fat—Its Role in Nutrition and Human Requirement. Jama-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1957, 164, 1890–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoh, C.C.; Min, D.B. Food Lipids: Chemistry, Nutrition, and Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, V.S.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Global obesity: Trends, risk factors and policy implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Cristobal, R.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Ordovas, J.M.; Martinez, J.A. Contribution of macronutrients to obesity: Implications for precision nutrition. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, A.M.; Jebb, S.A. Fast foods, energy density and obesity: A possible mechanistic link. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2003, 4, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Muniesa, P.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.-A.; Hu, F.B.; Despres, J.-P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.; Alfredo Martinez, J. Obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finucane, M.M.; Stevens, G.A.; Cowan, M.J.; Danaei, G.; Lin, J.K.; Paciorek, C.J.; Singh, G.M.; Gutierrez, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Bahalim, A.N.; et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: Systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet 2011, 377, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand, S.S.; Hawkes, C.; de Souza, R.J.; Mente, A.; Dehghan, M.; Nugent, R.; Zulyniak, M.A.; Weis, T.; Bernstein, A.M.; Krauss, R.M.; et al. Food Consumption and its Impact on Cardiovascular Disease: Importance of Solutions Focused on the Globalized Food System A Report From the Workshop Convened by the World Heart Federation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1590–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abete, I.; Astrup, A.; Alfredo Martinez, J.; Thorsdottir, I.; Zulet, M.A. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome: Role of different dietary macronutrient distribution patterns and specific nutritional components on weight loss and maintenance. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowska, D.; Podsedek, A.; Redzynia, M.; Zyzelewicz, D. Effects of Fruit Extracts on Pancreatic Lipase Activity in Lipid Emulsions. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.M.; Kravchuk, O.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S. Effect of different hydrocolloids on texture, rheology, tribology and sensory perception of texture and mouthfeel of low-fat pot-set yoghurt. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klaochanpong, N.; Puncha-arnon, S.; Uttapap, D.; Puttanlek, C.; Rungsardthong, V. Octenyl succinylation of granular and debranched waxy starches and their application in low-fat salad dressing. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Guo, J.; Courville, A.B.; Boring, J.; Brychta, R.; Chen, K.Y.; Darcey, V.; Forde, C.G.; Gharib, A.M.; Gallagher, I.; et al. Effect of a plant-based, low-fat diet versus an animal-based, ketogenic diet on ad libitum energy intake. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoumaki, M.V.; Moschakis, T.; Scholten, E.; Biliaderis, C.G. In vitro lipid digestion of chitin nanocrystal stabilized o/w emulsions. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Dai, T.; Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Bai, L.; Rojas, O.J.; McClements, D.J. Chitin nanocrystals reduce lipid digestion and β-carotene bioaccessibility: An in-vitro INFOGEST gastrointestinal study. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Su, H.; Sun, C.; Zheng, X.; Chen, W. Recent advances in understanding the anti-obesity activity of anthocyanins and their biosynthesis in microorganisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Milajerdi, A.; Varkaneh, H.K.; Gorjipour, M.M.; Esmaillzadeh, A. The effects of curcumin supplementation on body weight, body mass index and waist circumference: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Duan, R.; Tang, L.; Hu, X.; Geng, F.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Binding mechanism and functional evaluation of quercetin 3-rhamnoside on lipase. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lee, J.; Hernandez, M.A.S.; Mazitschek, R.; Ozcan, U. Treatment of Obesity with Celastrol. Cell 2015, 161, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anhe, F.F.; Nachbar, R.T.; Varin, T.V.; Trottier, J.; Dudonne, S.; Le Barz, M.; Feutry, P.; Pilon, G.; Barbier, O.; Desjardins, Y.; et al. Treatment with camu camu (Myrciaria dubia) prevents obesity by altering the gut microbiota and increasing energy expenditure in diet-induced obese mice. Gut 2019, 68, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Wit, N.J.W.; Afman, L.A.; Mensink, M.; Muller, M. Phenotyping the effect of diet on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, A.S.; Meikle, P.J.; Carey, A.L.; Kingwell, B.A. Brown adipose tissue and lipid metabolism: New strategies for identification of activators and biomarkers with clinical potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 192, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girousse, A.; Langin, D. Adipocyte lipases and lipid droplet-associated proteins: Insight from transgenic mouse models. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.Z.; Yan, L.; Yin, S.W.; Tang, C.H.; Yang, X.Q. Development of Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Gliadin/Proanthocyanidins Hybrid Particles (GPHPs) and the Fate of Lipid Oxidation and Digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Ma, M.; Zhao, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; He, X.; Xue, C.; Tang, Q. Drug-guided screening for pancreatic lipase inhibitors in functional foods. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4644–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Hirazawa, C.; Ohya, T.; Yoshikawa, R.; Mizutani, T.; Ma, N.; Moriyama, M.; Ito, T.; Matsuzaki, C. The Edible Brown Seaweed Sargassum horneri (Turner) C. Agardh Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity, Diabetes, and Hepatic Steatosis in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.L.; Ye, A.Q.; Liu, C.M.; Liu, W.; Singh, H. Structure and integrity of liposomes prepared from milk- or soybean-derived phospholipids during in vitro digestion. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Mondal, S.; Seo, H.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Marine natural pigments as potential sources for therapeutic applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Blakeslee, J. Digestion, absorption, and cancer preventative activity of dietary chlorophyll derivatives. Nutr. Res. 2007, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Hu, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Chlorophyll Supplementation in Early Life Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity and Modulates Gut Microbiota in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1801219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Liao, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Beneficial effects of a chlorophyll-rich spinach extract supplementation on prevention of obesity and modulation of gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Biological transformation of chlorophyll-rich spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) extracts under in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carriere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menard, O.; Bourlieu, C.; De Oliveira, S.C.; Dellarosa, N.; Laghi, L.; Carriere, F.; Capozzi, F.; Dupont, D.; Deglaire, A. A first step towards a consensus static in vitro model for simulating full-term infant digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; McClements, D.J. New Mathematical Model for Interpreting pH-Stat Digestion Profiles: Impact of Lipid Droplet Characteristics on in Vitro Digestibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8085–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. On the role of bile salts in the digestion of emulsified lipids. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Zhou, L.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Aggregation induced by the synergy of sodium chloride and high-pressure improves chlorophyll stability. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlen, M.H. The centenary of the Stern-Volmer equation of fluorescence quenching: From the single line plot to the SV quenching map. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C-Photochem. Rev. 2020, 42, 100338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLoid, G.M.; Sohal, I.S.; Lorente, L.R.; Molina, R.M.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Stevanovic, A.; Zhang, R.; McClements, D.J.; Geitner, N.K.; Bousfield, D.W.; et al. Reducing Intestinal Digestion and Absorption of Fat Using a Nature-Derived Biopolymer: Interference of Triglyceride Hydrolysis by Nanocellulose. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 6469–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Gu, Q.; Li, J.; Fan, L. Modulating in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of nanocellulose-stabilized pickering emulsions by altering cellulose lengths. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Qiu, B.; Jia, M.; Liu, W.; Guo, X.-F.; Li, N.; Xu, Z.-X.; Du, F.-L.; Xu, T.; Li, D. Effects of alpha-linolenic acid intake on blood lipid profiles:a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2894–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.W.; Qu, J.; Black, D.D.; Tso, P. Regulation of intestinal lipid metabolism: Current concepts and relevance to disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellesi, F.A.; Martinez, M.J.; Pizones Ruiz-Henestrosa, V.M.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Comparative behavior of protein or polysaccharide stabilized emulsion under in vitro gastrointestinal conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Zhi, Z.; Cheng, H.; Chen, S.; Ye, X. Antioxidant and pancreatic lipase inhibitory effects of flavonoids from different citrus peel extracts: An in vitro study. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, H.I.; Lee, K.W.; Kang, T.H. Anti-Obesity Effect of DKB-117 through the Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase and alpha-Amylase Activity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, E.A.; Vedenkina, N.S.; Ivkova, M.N. Fluorescence and Location of Tryptophan Residues in Protein Molecules. Photochem. Photobiol. 1973, 18, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, I.J.; Davidov-Pardo, G.; Ludescher, R.D.; McClements, D.J. Fluorescence quenching study of resveratrol binding to zein and gliadin: Towards a more rational approach to resveratrol encapsulation using water-insoluble proteins. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinatti, C.; Mello, L.B.; Loh, W. Thermodynamic Study of the Micellization of Zwitterionic Surfactants and Their Interaction with Polymers in Water by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6002–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.P.; Sanguansri, L.; Augustin, M.A. Binding of resveratrol with sodium caseinate in aqueous solutions. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayour, N.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Eskandari, M.H.; Esteghlal, S.; Nekoei, A.-R.; Gahruie, H.H.; Tatar, M.; Naghibalhossaini, F. Nanoencapsulation of quercetin and curcumin in casein-based delivery systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housaindokht, M.R.; Zaeri, Z.R.; Bahrololoom, M.; Chamani, J.; Bozorgmehr, M.R. Investigation of the behavior of HSA upon binding to amlodipine and propranolol: Spectroscopic and molecular modeling approaches. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 85, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Xie, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W. Discovery of anthocyanins from cranberry extract as pancreatic lipase inhibitors using a combined approach of ultrafiltration, molecular simulation and spectroscopy. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8527–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, Z. Acteoside: A lipase inhibitor from the Chinese tea Ligustrum purpurascens kudingcha. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
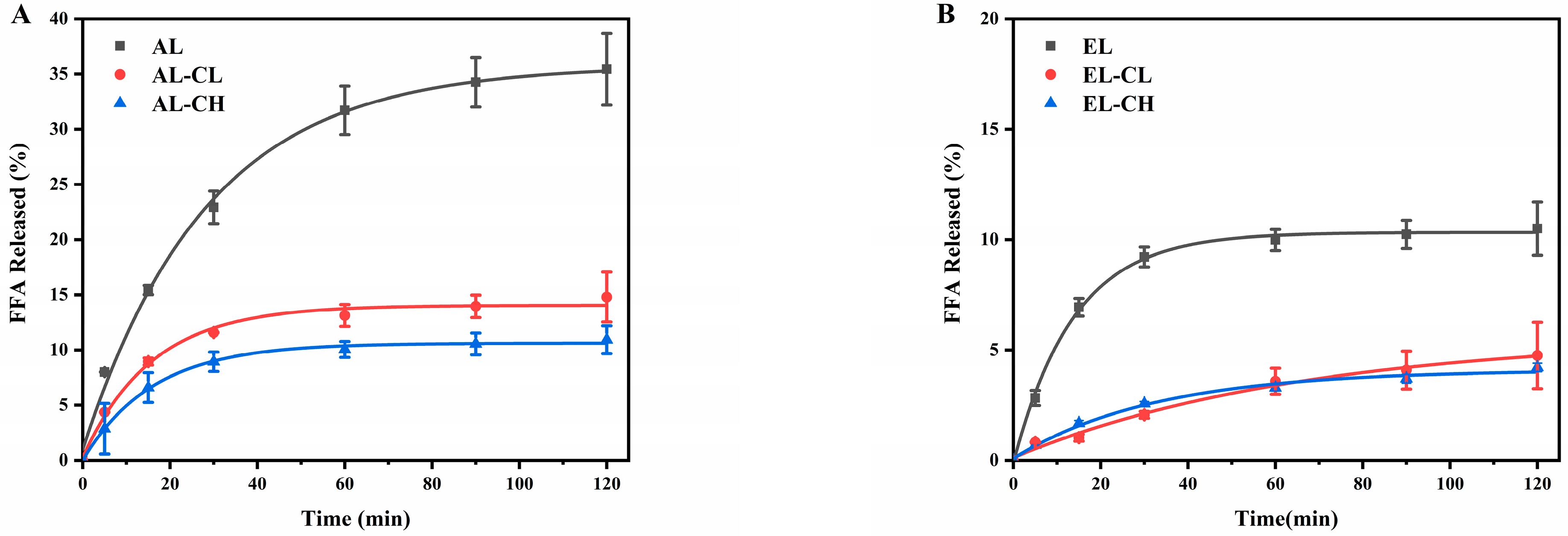



| Group | Apparent Rate Constant k (×10−2 s−1) | Regression Coefficient (R2) |
|---|---|---|
| AL | 3.76 | 0.9985 |
| AL-CL | 3.06 | 0.9569 |
| AL-CH | 3.67 | 0.9699 |
| EL | 4.11 | 0.9436 |
| EL-CL | 2.22 | 0.9905 |
| EL-CH | 3.76 | 0.9985 |
| Fatty Acids | AL | AL-CL | AL-CH | EL | EL-CL | EL-CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12:0 | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a |
| C14:0 | 0.14 ± 0.00 b | 0.14 ± 0.00 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.00 c | 0.11 ± 0.00 c | 0.11 ± 0.00 c |
| C15:0 | 0.05 ± 0.00 c | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 e | 0.03 ± 0.00 d | 0.04 ± 0.00 c |
| C16:0 | 15.01 ± 0.53 b | 15.85 ± 0.18 ab | 16.4 ± 0.77 a | 12.31 ± 0.05 c | 12.44 ± 0.11 c | 12.39 ± 0.03 c |
| C16:1 | 0.17 ± 0.00 b | 0.17 ± 0.00 ab | 0.18 ± 0.00 a | 0.12 ± 0.00 d | 0.13 ± 0.00 c | 0.12 ± 0.00 cd |
| C17:0 | 0.23 ± 0.01 b | 0.24 ± 0.00 ab | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 c | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | 0.16 ± 0.00 c |
| C18:0 | 8.12 ± 0.31 b | 8.50 ± 0.13 ab | 8.88 ± 0.48 a | 5.71 ± 0.04 c | 5.67 ± 0.08 c | 5.71 ± 0.02 c |
| C18:1n9c | 21.85 ± 0.16 a | 21.47 ± 0.06 ab | 21.24 ± 0.29 b | 21.49 ± 0.38 ab | 21.67 ± 0.08 ab | 21.46 ± 0.01 ab |
| C18:2n6c | 46.51 ± 0.57 c | 45.01 ± 0.31 d | 43.37 ± 0.95 e | 51.66 ± 0.30 a | 51.03 ± 0.17 ab | 49.99 ± 0.04 b |
| C18:3n3 | 6.08 ± 0.23 d | 6.56 ± 0.03 c | 7.52 ± 0.18 b | 6.85 ± 0.07 c | 7.61 ± 0.03 b | 8.83 ± 0.04 a |
| C20:0 | 0.47 ± 0.04 ab | 0.50 ± 0.03 a | 0.48 ± 0.04 ab | 0.41 ± 0.03 c | 0.42 ± 0.02 bc | 0.42 ± 0.03 bc |
| C20:1 | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.19 ± 0.01 b | 0.24 ± 0.00 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.23 ± 0.00 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 a |
| C21:0 | 0.11 ± 0.01 ab | 0.13 ± 0.02 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 bc | 0.09 ± 0.01 bc | 0.09 ± 0.00 bc | 0.08 ± 0.01 c |
| C20:4n6 | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | 0.11 ± 0 a | 0.12 ± 0.02 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 b |
| C22:0 | 0.59 ± 0.02 a | 0.61 ± 0.05 a | 0.61 ± 0.07 a | 0.45 ± 0.02 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 c | 0.06 ± 0.01 c |
| C22:1n9 | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.23 ± 0.02 a | 0.13 ± 0.02 b | 0.15 ± 0.06 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 b |
| C24:0 | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 0.22 ± 0.00 ab | 0.20 ± 0.00 b | 0.21 ± 0.03 ab | 0.19 ± 0.02 b | 0.18 ± 0.03 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Chlorophyll Inhibits the Digestion of Soybean Oil in Simulated Human Gastrointestinal System. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091749
Wang X, Li Y, Shen S, Yang Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y. Chlorophyll Inhibits the Digestion of Soybean Oil in Simulated Human Gastrointestinal System. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091749
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao, Yuanyuan Li, Suxia Shen, Zhaotian Yang, Haifeng Zhang, and Yan Zhang. 2022. "Chlorophyll Inhibits the Digestion of Soybean Oil in Simulated Human Gastrointestinal System" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091749
APA StyleWang, X., Li, Y., Shen, S., Yang, Z., Zhang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Chlorophyll Inhibits the Digestion of Soybean Oil in Simulated Human Gastrointestinal System. Nutrients, 14(9), 1749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091749







