Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via SIX1-Dependent TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
2.5. AO/EB Staining
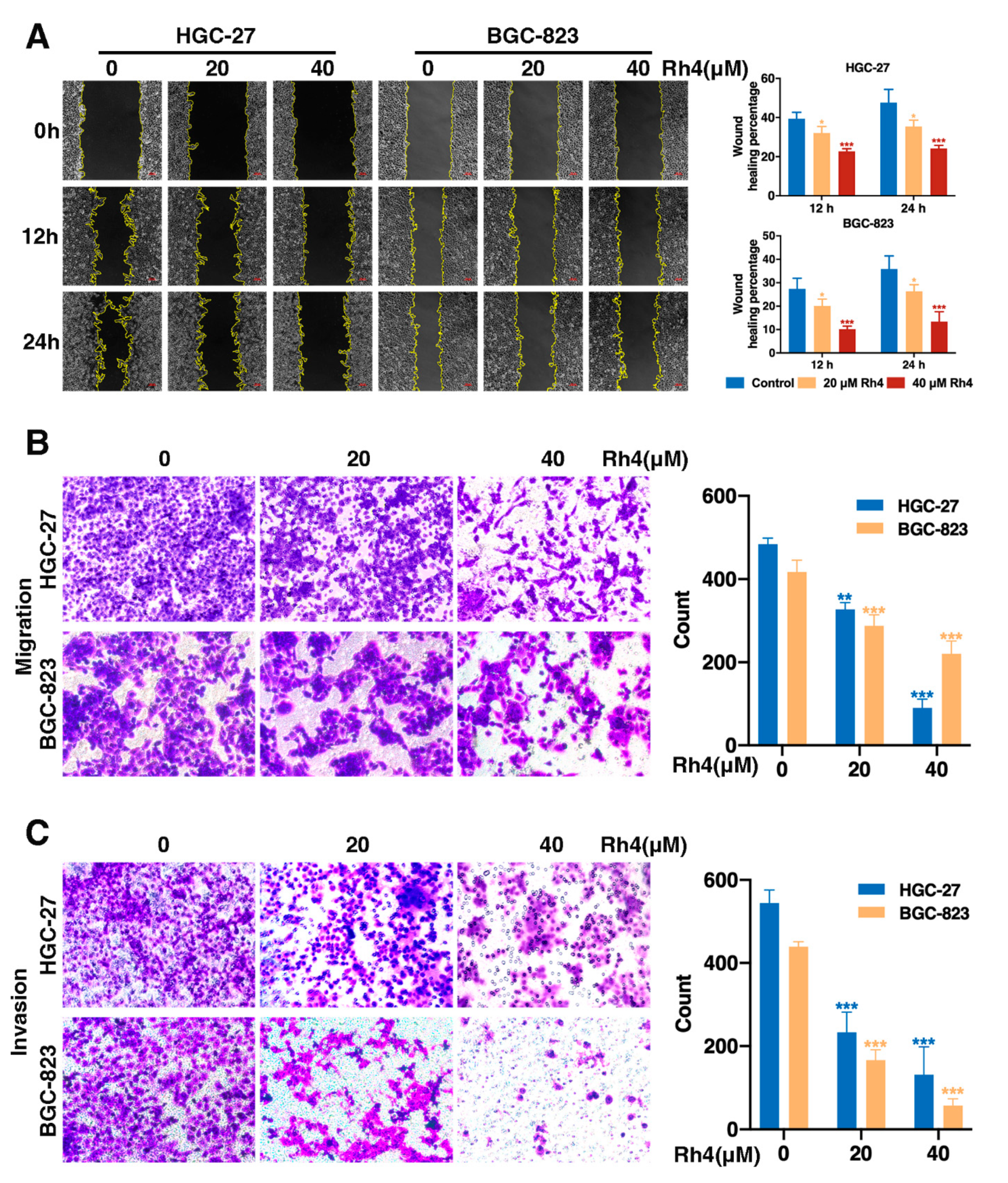
2.6. Wound Healing Assay
2.7. Transwell Assay
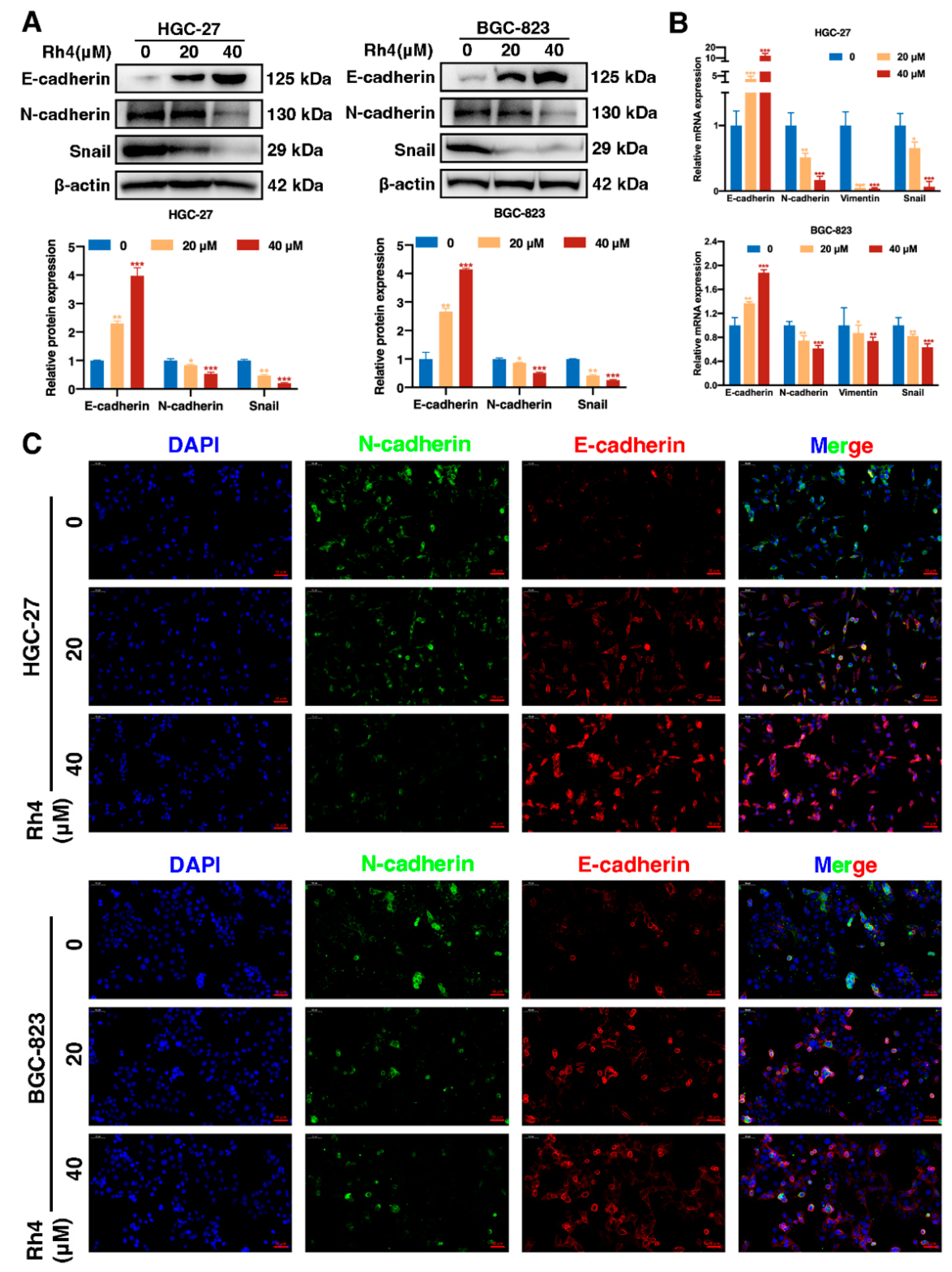
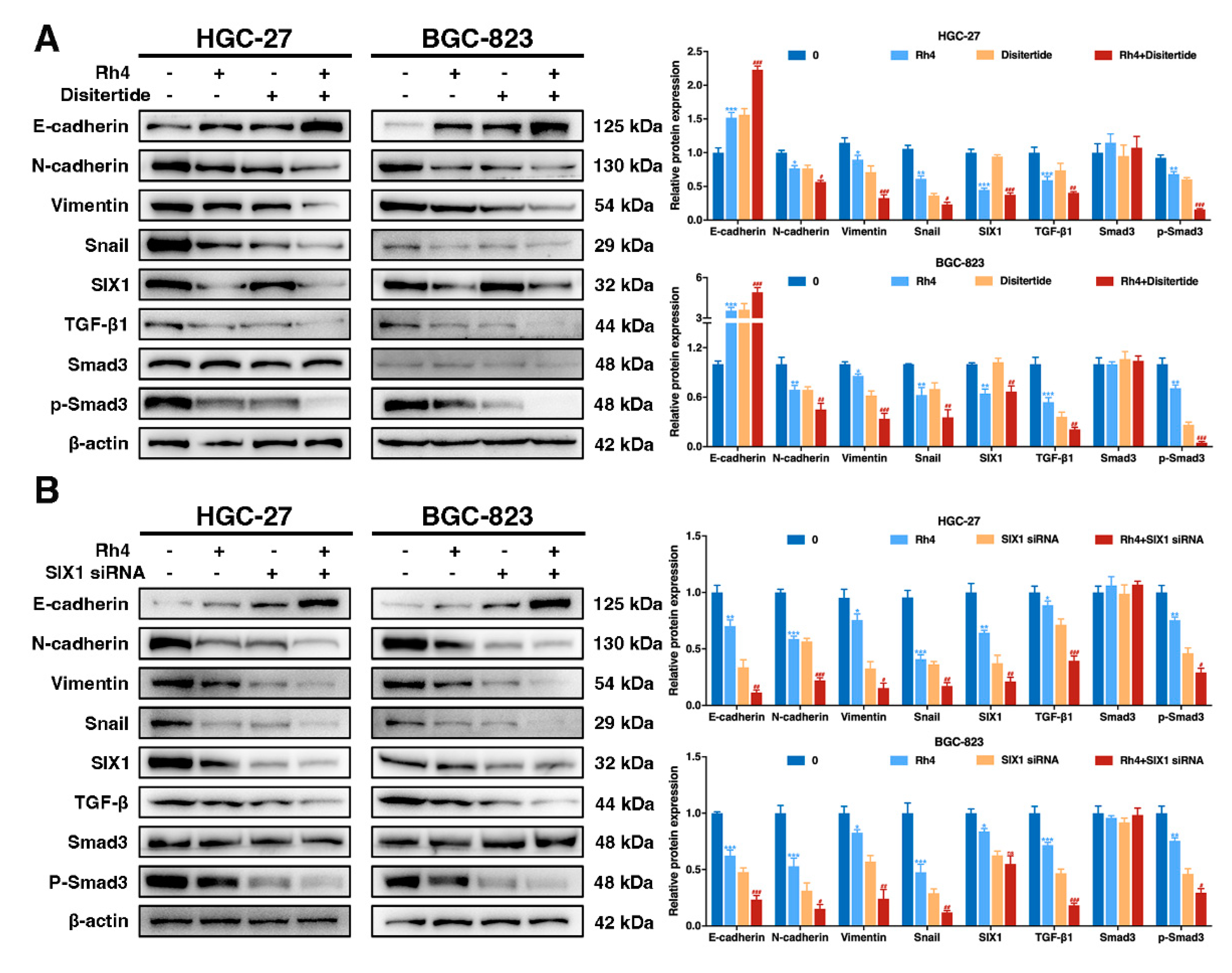
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.10. Proteomics Analysis
2.11. SiRNA Transfection
2.12. Tail Vein Injection Model
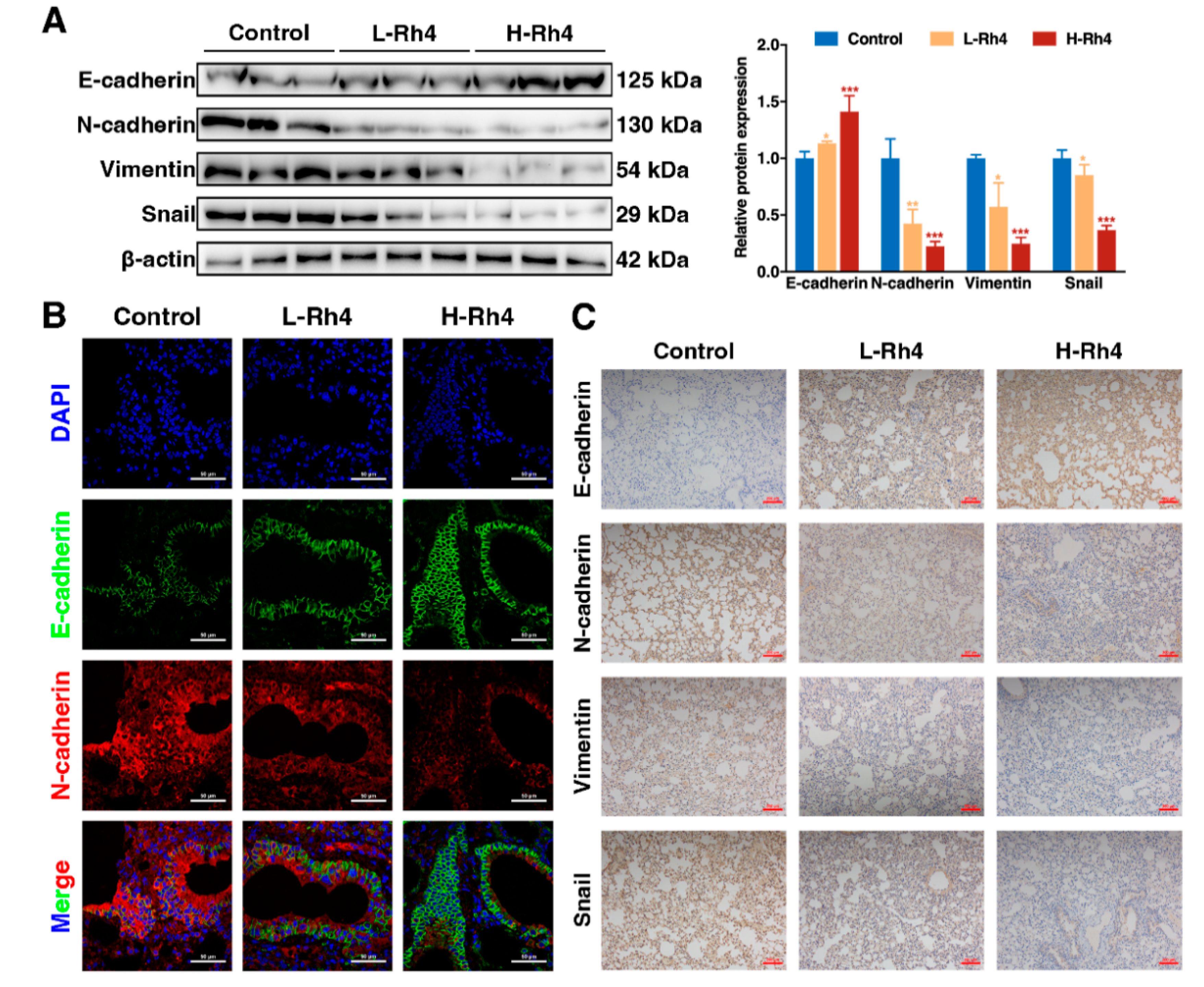
2.13. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry Assay (IHC)
2.14. Immunofluorescence Assay (IF)
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ginsenoside Rh4 Inhibited GC Cell Growth In Vitro
3.2. Ginsenoside Rh4 Restrains Migration and Invasion of GC Cells
3.3. Ginsenoside Rh4 Inhibited GC Metastasis In Vivo, and Causes Low Toxicity and Side-Effects
3.4. Ginsenoside Rh4 Reverses EMT In Vitro and In Vivo
3.5. SIX1 Is Involved in EMT Suppression by Rh4
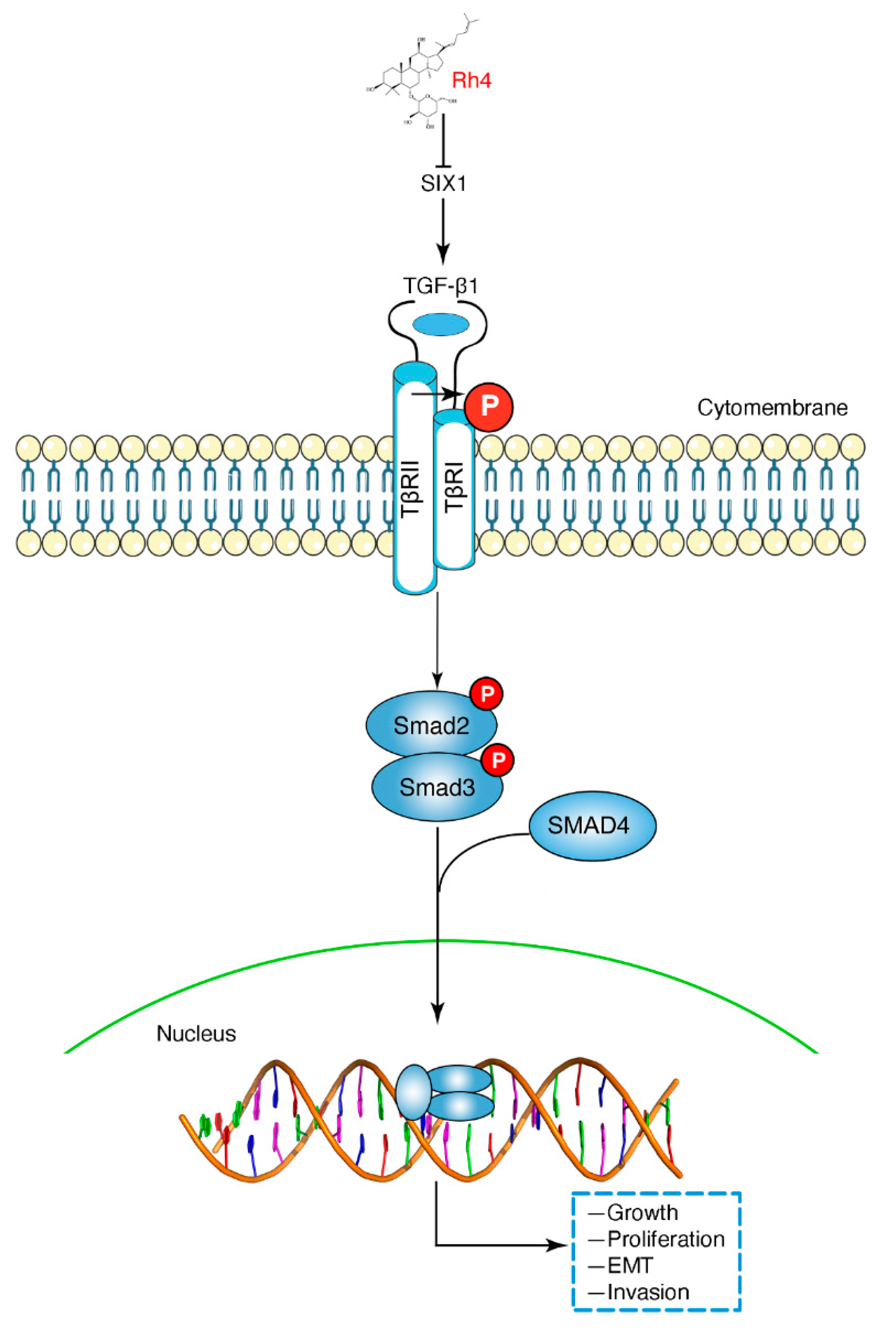
3.6. Ginsenoside Rh4 Reverses EMT through SIX1–TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Axis In Vitro and In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Lin, C.C.; Mariotto, A.B.; Kramer, J.L.; Rowland, J.H.; Stein, K.D.; Alteri, R.; Jemal, A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Christofori, G. EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.Y.; Lim, S.-C.; Lee, T.-B.; Han, S.I. Molecular Basis of Resveratrol-Induced Resensitization of Acquired Drug-Resistant Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, R.-L.; Xu, A.M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 2141–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, C.-X.; Fang, E.-H.; Wang, G.-B.; Tong, Q. Role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer initiation and progression. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5403–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y. CCR7 pathway induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition through up-regulation of Snail signaling in gastric cancer. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, L.A.; Gardner, A.; De Soyza, A.; Mann, D.A.; Fisher, A.J. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) driven epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is accentuated by tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) via crosstalk between the SMAD and NF-κB pathways. Cancer Microenviron. 2012, 5, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Tang, S.-J.; Sun, G.; Sun, K. CXCR7 mediates TGFβ1-promoted EMT and tumor-initiating features in lung cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petanidis, S.; Kioseoglou, E.; Domvri, K.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Carthy, J.M.; Anestakis, D.; Moustakas, A.; Salifoglou, A. In vitro and ex vivo vanadium antitumor activity in (TGF-β)-induced EMT. Synergistic activity with carboplatin and correlation with tumor metastasis in cancer patients. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 74, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Li, Q.; Wei, C.; Zou, H.; Li, S.; Cao, W.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ju, X.; Lan, J. TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: In vitro and clinical analyses of cell lines and nomadic Kazakh patients from northwest Xinjiang, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; So, Y.; Jeon, H.; Jeong, M.-H.; Choi, H.-K.; Ryu, S.-H.; Lee, S.-W.; Yoon, H.-G.; Choi, K.-C. TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and acetylation of Smad2 and Smad3 are negatively regulated by EGCG in human A549 lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolosova, I.; Nethery, D.; Kern, J.A. Role of Smad2/3 and p38 MAP kinase in TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition of pulmonary epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emadi-Baygi, M.; Nikpour, P.; Emadi-Andani, E. SIX1 overexpression in diffuse-type and grade III gastric tumors: Features that are associated with poor prognosis. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2015, 4, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nandi, S.; Martel, A.; Antoun, A.; Ioshikhes, I.; Blais, A. Discovery, optimization and validation of an optimal DNA-binding sequence for the Six1 homeodomain transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 8227–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, J.; Wei, M.; Shi, R.; Cai, C.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Ma, W. MiR-204-5p/Six1 feedback loop promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2729–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-X.; Wu, K.-J.; Tian, Y.-J.; Liu, Q.; Han, N.; He, X.-L.; Yuan, X.; Wu, G.S.; Wu, K.-M. Expression profile of SIX family members correlates with clinic-pathological features and prognosis of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Tamaoki, M.; Komatsuzaki, R.; Oue, N.; Taniguchi, H.; Komatsu, M.; Aoyagi, K.; Minashi, K.; Chiwaki, F.; Shinohara, H. SIX 1 maintains tumor basal cells via transforming growth factor-β pathway and associates with poor prognosis in esophageal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.L.; Iwanaga, R.; Drasin, D.J.; Micalizzi, D.S.; Vartuli, R.L.; Tan, A.-C.; Ford, H.L. The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-β signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 5162–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micalizzi, D.S.; Wang, C.-A.; Farabaugh, S.M.; Schiemann, W.P.; Ford, H.L. Homeoprotein Six1 increases TGF-β type I receptor and converts TGF-β signaling from suppressive to supportive for tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10371–10380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, R.; Wang, C.-A.; Micalizzi, D.S.; Harrell, J.C.; Jedlicka, P.; Sartorius, C.A.; Kabos, P.; Farabaugh, S.M.; Bradford, A.P.; Ford, H.L. Expression of Six1 in luminal breast cancers predicts poor prognosis and promotes increases in tumor initiating cells by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, W.-P.; Wei, X.-F. Silencing SIX1 inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition through regulating TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ompson Coon, J.; Ernst, E. Panax ginseng: A systematic review of adverse effects and drug interactions. Focus Altern. Complement. Erapies 2002, 7, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.-Z.; Searle, J.; He, T.-C.; Yuan, C.-S.; Du, W. Ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis and paraptosis-like cell death in colorectal cancer cells through activation of p53. Cancer Lett. 2011, 301, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, D. The Preparation of Ginsenoside Rg5, Its Antitumor Activity against Breast Cancer Cells and Its Targeting of PI3K. Nutrients 2020, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.S.; Ham, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, J.H.; Cho, E.-J.; Yamabe, N. Heat-processed Panax ginseng and diabetic renal damage: Active components and action mechanism. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayeh, T.; Jung, K.-H.; Jeong, H.Y.; Park, J.-H.; Song, Y.-B.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Kang, H.-S.; Cho, J.Y.; Oh, J.-W.; Kim, S.-K. Korean red ginseng saponin fraction downregulates proinflammatory mediators in LPS stimulated RAW264. 7 cells and protects mice against endotoxic shock. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.-S. Roles of ginsenosides in inflammasome activation. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Park, J.-S.; Ma, Y.; Ma, H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, G.-R.; Yoo, H.-S.; Hong, J.-T.; Roh, Y.-S. Ginseng Saponin Enriched in Rh1 and Rg2 Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Inhibiting Inflammasome Activation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, C.; Niu, S.; Fan, B.; Gu, D.; Jiang, K.; Li, R.; Li, S. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates hepatic insulin resistance induced by high-fat and high-sugar by inhibiting inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 854, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Nam, K.H.; Yi, S.A.; Park, J.W.; Han, J.-W.; Lee, J. Ginsenoside Rg3 Induces Browning of 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by Activating AMPK Signaling. Nutrients 2020, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.; Zhang, Y.-l.; Ma, C.-j.; Li, M.-q.; Tang, C.-y.; Yang, Y.-f.; Zeng, J.-h.; Huang, X.-y.; Yi, J.; Wang, X.-m. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 against hyperphosphorylated tau-induced diabetic retinal neurodegeneration via activation of IRS-1/Akt/GSK3β signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8348–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. 20S-dihydroprotopanaxadiol, a ginsenoside derivative, boosts innate immune responses of monocytes and macrophages. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, N.-I.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, J.D.; Lee, C.B.; Kim, S.I. Ginsenoside Rh4, a genuine dammarane glycoside from Korean red ginseng. Planta Medica 1996, 62, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Du, X.; Xiong, M.; Cui, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T. Ginsenoside Rd attenuates breast cancer metastasis implicating derepressing microRNA-18a-regulated Smad2 expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y. Effects of ginsenoside compound K combined with cisplatin on the proliferation, apoptosis and epithelial mesenchymal transition in MCF-7 cells of human breast cancer. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Qi, B.; Yuan, D.; Dong, S.; Guo, D.; Zhang, C.; Yu, M. Suppression of PMA-induced tumor cell invasion and migration by ginsenoside Rg1 via the inhibition of NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Li, L.; Guo, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, S.; Lei, L.; Xu, L. RNF8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Ju, P.; Liu, R.; Yeo, S.P.; Xia, Y.; Owlanj, H.; Feng, Z. Silencing of diphthamide synthesis 3 (Dph3) reduces metastasis of murine melanoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gu, C.; Zhong, D.; Shi, L.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, S. Induction of autophagy counteracts the anticancer effect of cisplatin in human esophageal cancer cells with acquired drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 2014, 355, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qiu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. AP-2β inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis through Slug and Snail to suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.-H.; Shin, B.-k.; Kim, N.J.; Chang, S.-Y.; Park, J.H. Protective effect of ginsenosides Rk3 and Rh4 on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in vitro and in vivo. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.A.; Kim, E.H.; Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. KG-135 Inhibits COX-2 Expression by Blocking the Activation of JNK and AP-1 in Phorbol Ester–Stimulated Human Breast Epithelial Cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1095, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Hui, J.; Mi, Y.; Ma, P.; Ma, X.; Fan, D.; Yang, H. Protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol-type saponins ameliorate glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus in high-fat diet/streptozocin-induced mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majc, B.; Sever, T.; Zarić, M.; Breznik, B.; Turk, B.; Lah, T.T. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition as the driver of changing carcinoma and glioblastoma microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Mani, S.A.; Donaher, J.L.; Ramaswamy, S.; Itzykson, R.A.; Come, C.; Savagner, P.; Gitelman, I.; Richardson, A.; Weinberg, R.A. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 2004, 117, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kong, J.; Chang, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, A. EGF induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through phospho-Smad2/3-Snail signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, G.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y. The high expression of long non-coding RNA PANDAR indicates a poor prognosis for colorectal cancer and promotes metastasis by EMT pathway. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, K.; Miao, C.; Xu, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Su, S.; Wang, Z. Silencing Trim59 inhibits invasion/migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway in bladder cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, R. Nobiletin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by antagonizing the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2767–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ren, Z.; Li, P.; Yu, D.; Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Liu, H. Six1: A critical transcription factor in tumorigenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Organ index | Control | Normal | Normal + H-Rh4 (100 mg/kg) | L-Rh4 (50 mg/kg) | H-Rh4 (100 mg/kg) | Oxaliplatin (10 mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | 0.52 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 0.50 ± 0.04 | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.54 ± 0.03 | 0.53 ± 0.05 |
| Liver | 5.46 ± 0.25 | 5.43 ± 0.46 | 5.39 ± 0.16 | 5.88 ± 0.62 | 5.22 ± 0.18 | 4.79 ± 0.32 |
| Spleen | 1.45 ± 0.23 | 1.44 ± 0.18 | 1.47 ± 0.15 | 1.50 ± 0.19 ## | 1.41 ± 0.28 ## | 0.39 ± 0.12 ** |
| Lung | 0.78 ± 0.16 | 0.72 ± 0.09 | 0.73 ± 0.15 | 0.71 ± 0.07 | 0.72 ± 0.13 | 0.71 ± 0.15 |
| Kidney | 1.44 ± 0.16 | 1.47 + 0.11 | 1.46 ± 0.09 | 1.49 ± 0.20 | 1.45 ± 0.16 | 1.47 ± 0.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Ma, P.; Duan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, S.; Mi, Y.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via SIX1-Dependent TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081564
Jiang H, Ma P, Duan Z, Liu Y, Shen S, Mi Y, Fan D. Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via SIX1-Dependent TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Pathway. Nutrients. 2022; 14(8):1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081564
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Hongbo, Pei Ma, Zhiguang Duan, Yannan Liu, Shihong Shen, Yu Mi, and Daidi Fan. 2022. "Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via SIX1-Dependent TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Pathway" Nutrients 14, no. 8: 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081564
APA StyleJiang, H., Ma, P., Duan, Z., Liu, Y., Shen, S., Mi, Y., & Fan, D. (2022). Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via SIX1-Dependent TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Pathway. Nutrients, 14(8), 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081564







