Lactational Changes of Phospholipids Content and Composition in Chinese Breast Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Human Milk Samples Collection
2.2. Quantification of PLs
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Anthropometric Characteristics
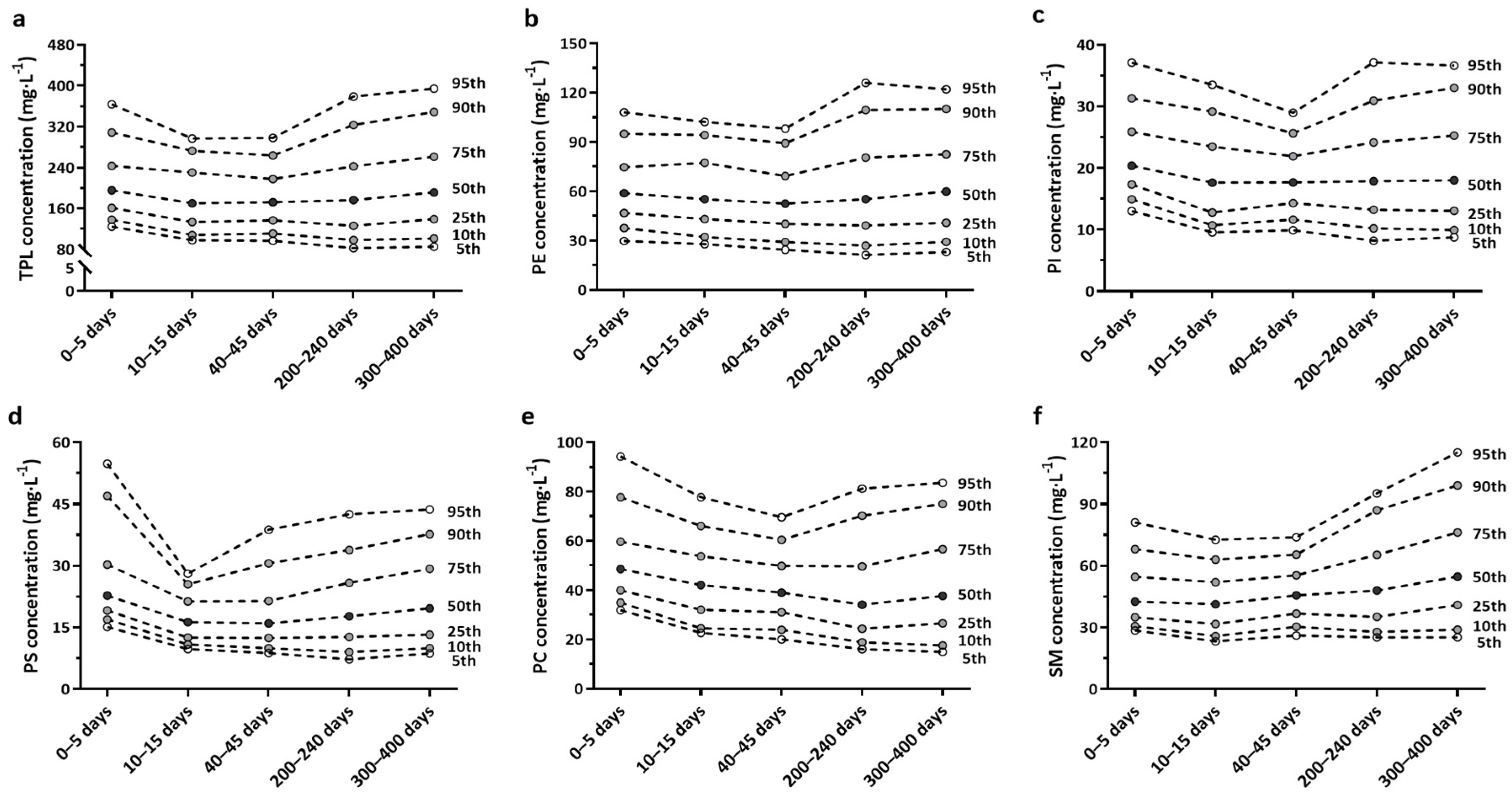
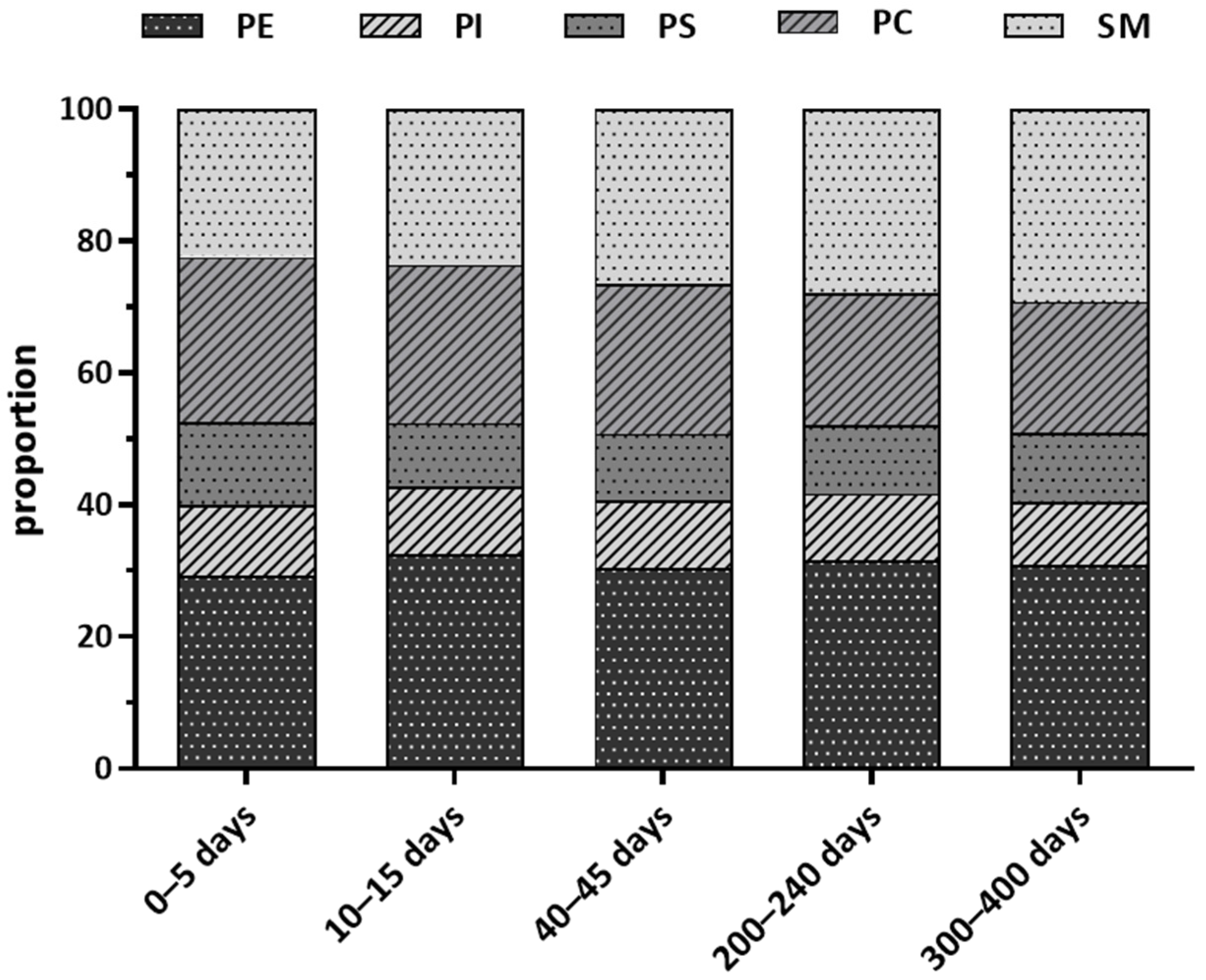
3.2. Total Phospholipid and Sub-Class Phospholipids in Human Milk
3.3. Differences in Total Phospholipid and Sub-Class Phospholipids Concentration over Lactation in Chinese Human Milk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- WHO. Guideline: Counselling of Women to Improve Breastfeeding Practices; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Kramer, M.S.; Kakuma, R. Optimal duration of exclusive breastfeeding. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD003517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.; Franca, G.V.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oddy, W.H. Breastfeeding, Childhood Asthma, and Allergic Disease. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70 (Suppl. 2), 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, L.; Akesson, B.; Holmberg, L. Vitamin E and fatty acid composition of human milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, R.G. Lipids in human milk. Lipids 1999, 34, 1243–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B. Lipids in human milk. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C. Milk fat globules enveloped by their biological membrane: Unique colloidal assemblies with a specific composition and structure. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, A.; Diego Quintaes, K.; Barbera, R.; Alegria, A. Phospholipids in Human Milk and Infant Formulas: Benefits and Needs for Correct Infant Nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shimizu, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Hanaka, S.; Abe, T.; Shimasaki, H.; Hisaki, H.; Nakajima, H. Comparison of the fatty acid composition of total lipids and phospholipids in breast milk from Japanese women. Pediatr. Int. 2000, 42, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Radlowski, E.C.; Conrad, M.S.; Li, Y.; Dilger, R.N.; Johnson, R.W. Early supplementation of phospholipids and gangliosides affects brain and cognitive development in neonatal piglets. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Kong, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Han, J. Milk phospholipids ameliorate mouse colitis associated with colonic goblet cell depletion via the Notch pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4608–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harzer, G.; Haug, M.; Bindels, J.G. Biochemistry of human milk in early lactation. Z. Ernahr. 1986, 25, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejrup, R.G.; Licht, T.R.; Hellgren, L.I. Fatty acid composition and phospholipid types used in infant formulas modifies the establishment of human gut bacteria in germ-free mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Council, C.S. Statistical and Monitoring Report of (National Program of Action for Child Development in China (2011–2020)) in 2018; China Information: Beijing, China, 2019; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Group, N.S. Timing of initiation, patterns of breastfeeding, and infant survival: Prospective analysis of pooled data from three randomised trials. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e266–e275. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, M.S.; Aboud, F.; Mironova, E.; Vanilovich, I.; Platt, R.W.; Matush, L.; Igumnov, S.; Fombonne, E.; Bogdanovich, N.; Ducruet, T.; et al. Breastfeeding and child cognitive development: New evidence from a large randomized trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Liu, J.; Hettinga, K.A.; Lai, J.; Zhou, P. Geography and ethnicity related variation in the Chinese human milk serum proteome. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7818–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Won, S.; Kim, Y.; Jung, J.A.; Li, D.; To, X.H.M.; Huynh, K.T.N.; Le, T.V.; et al. A Comparison of Vitamin and Lutein Concentrations in Breast Milk from Four Asian Countries. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Campos-Giménez, E.; Redeuil, K.; Lévèques, A.; Actis-Goretta, L.; Vinyes-Pares, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Thakkar, S. Concentrations of Carotenoids and Tocopherols in Breast Milk from Urban Chinese Mothers and Their Associations with Maternal Characteristics: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.; Deng, Z.; Liu, B.; Ye, W.; Fan, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, J. Investigation of amino acids and minerals in Chinese breast milk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3920–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Tian, F.; Cai, X.K.; Mao, Y.Y.; Cellar, N.A.; Zhao, Y.R.; Zhu, H.L. Determination of Five Phospholipids in Human Milk and Cow Milk by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-evaporative Light Scattering. China Dairy Ind. 2021, 49, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; MacGibbon, A.K.H.; Jan Mohamed, H.J.B.; Loy, S.; Rowan, A.; McJarrow, P.; Fong, B.Y. Determination of phospholipid concentrations in breast milk and serum using a high performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry–multiple reaction monitoring method. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 71, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Jin, Q.; Wang, M.; Lai, J.; Wang, X. Phospholipid Composition and Fat Globule Structure I: Comparison of Human Milk Fat from Different Gestational Ages, Lactation Stages, and Infant Formulas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13922–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrida, F.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Bertschy, E.; Fontannaz, P.; Masserey Elmelegy, I.; Tavazzi, I.; Marmet, C.; Sanchez-Bridge, B.; Thakkar, S.K.; De Castro, C.A.; et al. Temporal Changes of Human Breast Milk Lipids of Chinese Mothers. Nutrients 2016, 8, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Claumarchirant, L.; Cilla, A.; Matencio, E.; Sanchez-Siles, L.M.; Castro-Gomez, P.; Fontecha, J.; Alegría, A.; Lagarda, M.J. Addition of milk fat globule membrane as an ingredient of infant formulas for resembling the polar lipids of human milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.Q.; Guo, Z.; Huang, J.H.; Jin, Q.Z.; Cheong, L.Z.; Wang, X.G.; Xu, X.B. Human milk fat globules from different stages of lactation: A lipid composition analysis and microstructure characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7158–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Gallier, S. Nature’s complex emulsion: The fat globules of milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McJarrow, P.; Radwan, H.; Ma, L.; MacGibbon, A.K.H.; Hashim, M.; Hasan, H.; Obaid, R.S.; Naja, F.; Mohamed, H.J.J.; Al Ghazal, H.; et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharide, Phospholipid, and Ganglioside Concentrations in Breast Milk from United Arab Emirates Mothers: Results from the MISC Cohort. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, M.A.; Haymond, M.W. Regulation of lipid synthesis genes and milk fat production in human mammary epithelial cells during secretory activation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E700–E716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, B.; Hong, E.S.; Shin, J.A.; Qin, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, K.T. Correlations of Fat Content in Human Milk with Fat Droplet Size and Phospholipid Species. Molecules 2021, 26, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.K.; Giuffrida, F.; Cristina, C.H.; De Castro, C.A.; Mukherjee, R.; Tran, L.A.; Steenhout, P.; Lee, L.Y.; Destaillats, F. Dynamics of human milk nutrient composition of women from Singapore with a special focus on lipids. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2013, 25, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Liu, T.T.; Liang, X.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yishake, D.; Lu, X.T.; Yang, M.T.; Man, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.L. Profiling of phospholipid molecular species in human breast milk of Chinese mothers and comprehensive analysis of phospholipidomic characteristics at different lactation stages. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, M.T.; Pawlak, R.; Dean, L.L.; Christis, A.; Friend, L. A cross-sectional study of fatty acids and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in human milk from lactating women following vegan, vegetarian, and omnivore diets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miliku, K.; Duan, Q.L.; Moraes, T.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Lefebvre, D.L.; Sears, M.R.; Subbarao, P.; Field, C.J.; et al. Human milk fatty acid composition is associated with dietary, genetic, sociodemographic, and environmental factors in the CHILD Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhuo, C.F.; Liu, B.; Ye, W.H.; Tao, L.; Zheng, L.F.; Chen, L.; Deng, Z.Y.; Li, G.Y.; Gong, Z.Q.; et al. Temporal Changes of Phospholipids Fatty Acids and Cholesterol in Breast Milk and Relationship with Diet. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, W.; Yang, K.; Jiang, T.; Hou, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, T.; et al. Quantitative profiling of glycerides, glycerophosphatides and sphingolipids in Chinese human milk with ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, L.; Brambilla, P.; Mazzocchi, A.; Harslof, L.B.; Ciappolino, V.; Agostoni, C. DHA Effects in Brain Development and Function. Nutrients 2016, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Ma, D.; Shui, G.; Wong, P.; Cazenave-Gassiot, A.; Zhang, X.; Wenk, M.R.; Goh, E.L.; Silver, D.L. Mfsd2a is a transporter for the essential omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid. Nature 2014, 509, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, K.C.W.; Goss, V.M.; Townsend, J.P.; Koster, G.; Clark, H.W.; Postle, A.D. Postnatal adaptations of phosphatidylcholine metabolism in extremely preterm infants: Implications for choline and PUFA metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E. Phospholipid synthesis and transport in mammalian cells. Traffic 2015, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Briard-Bion, V.; Ménard, O.; Beaucher, E.; Rousseau, F.; Fauquant, J.; Leconte, N.; Robert, B. Fat globules selected from whole milk according to their size: Different compositions and structure of the biomembrane, revealing sphingomyelin-rich domains. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H. The fetal origins of memory: The role of dietary choline in optimal brain development. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, S131–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozarda Ilcol, Y.; Uncu, G.; Ulus, I.H. Free and phospholipid-bound choline concentrations in serum during pregnancy, after delivery and in newborns. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 110, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moukarzel, S.; Wiedeman, A.M.; Soberanes, L.S.; Dyer, R.A.; Innis, S.M.; Lamers, Y. Variability of Water-Soluble Forms of Choline Concentrations in Human Milk during Storage, after Pasteurization, and among Women. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caudill, M.A. Pre- and postnatal health: Evidence of increased choline needs. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, B.; Gibb, R. Brain plasticity and behaviour in the developing brain. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2011, 20, 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, P.J. A lipid matrix model of membrane raft structure. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L. Distribution and fatty acid composition of phosphoglycerides in normal human brain. J. Lipid Res. 1968, 9, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Akbar, M.; Kim, Y.S. Phosphatidylserine-dependent neuroprotective signaling promoted by docosahexaenoic acid. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2010, 82, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takasuga, S.; Sasaki, T. Phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate: Metabolism and physiological functions. J. Biochem. 2013, 154, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Restuccia, D.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Puoci, F.; Cirillo, G.; Vinci, G.; Picci, N. Determination of Phospholipids in Food Samples. Food Rev. Int. 2012, 28, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | 0–5 Days (n = 259) | 10–15 Days (n = 254) | 40–45 Days (n = 630) | 200–240 Days (n = 576) | 300–400 Days (n = 551) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mothers | |||||
| Age (years) | 29.18 ± 3.47 | 29.06 ± 3.27 | 29.60 ± 3.29 | 29.96 ± 3.43 | 30.26 ± 3.43 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 21.66 ± 3.13 | 21.50 ± 2.99 | 21.42 ± 2.97 | 20.80 ± 2.56 | 21.01 ± 2.77 |
| Gestationalweight gain (kg) | 14.60 ± 4.58 | 14.85 ± 4.68 | 14.72 ± 4.92 | 14.52 ± 5.41 | 14.21 ± 5.35 |
| Delivery mode | |||||
| Vaginaldelivery | 155 (61.5%) | 151 (60.6%) | 352 (56.3%) | 361 (63.1%) | 332 (60.8%) |
| Caesarean | 97 (38.5%) | 98 (39.4%) | 273 (43.7%) | 211 (36.9%) | 214 (39.2%) |
| Infants | |||||
| Birth weight (kg) | 3.38 ± 0.41 | 3.39 ± 0.41 | 3.35 ± 0.40 | 3.52 ± 0.67 | 3.65 ± 0.82 |
| Birth length (cm) | 49.84 ± 1.49 | 49.97 ± 1.36 | 49.84 ± 1.49 | 53.41 ± 7.76 | 54.42 ± 9.59 |
| Infant gender | |||||
| Female | 125 (49.6%) | 125 (50.2%) | 312 (49.9%) | 282 (49.3%) | 264 (49.4%) |
| Male | 127 (50.4%) | 124 (49.8%) | 313 (50.1%) | 290 (50.7%) | 282 (50.6%) |
| PLs | 0–5 Days (n = 259) | 10–15 Days (n = 254) | 40–45 Days (n = 630) | 200–240 Days (n = 576) | 300–400 Days (n = 551) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | |||||
| PE | 61.85 ± 1.78 ab | 61.46 ± 1.79 ab | 56.26 ± 1.13 b | 62.67 ± 1.18 a | 65.25 ± 1.22 a |
| PI | 21.91 ± 0.49 a | 19.12 ± 0.49 b | 18.48 ± 0.31 b | 19.34 ± 0.32 b | 19.75 ± 0.33 b |
| PS | 26.61 ± 0.67 a | 17.49 ± 0.67 d | 18.88 ± 0.42 cd | 20.28 ± 0.44 c | 22.09 ± 0.45 b |
| PC | 52.28 ± 1.20 a | 44.82 ± 1.21 b | 41.45 ± 0.76 bc | 39.40 ± 0.80 c | 42.83 ± 0.82 b |
| SM | 46.30 ± 1.33 c | 43.26 ± 1.33 c | 47.41 ± 0.84 c | 53.33 ± 0.88 b | 60.58 ± 0.90 a |
| TPL | 208.95 ± 5.03 ab | 186.15 ± 5.06 bc | 182.47 ± 3.19 c | 195.02 ± 3.34 b | 210.50 ± 3.43 a |
| Model 2 | |||||
| PE | 61.23 ± 1.77 ab | 60.85 ± 1.78 ab | 56.39 ± 1.12 b | 62.78 ± 1.17 a | 65.53 ± 1.20 a |
| PI | 21.74 ± 0.48 a | 18.95 ± 0.48 bc | 18.52 ± 0.31 c | 19.37 ± 0.32 bc | 19.83 ± 0.33 b |
| PS | 26.55 ± 0.67 a | 17.44 ± 0.67 d | 18.89 ± 0.42 cd | 20.86 ± 0.44 c | 22.12 ± 0.45 b |
| PC | 52.14 ± 1.20 a | 44.68 ± 1.21 b | 41.48 ± 0.76 bc | 39.43 ± 0.80 c | 42.90 ± 0.82 b |
| SM | 46.54 ± 1.32 c | 43.49 ± 1.33 c | 47.36 ± 0.84 c | 53.28 ± 0.88 b | 60.47 ± 0.90 a |
| TPL | 208.20 ± 5.03 ab | 185.41 ± 5.05 c | 182.64 ± 3.19 c | 195.15 ± 3.33 bc | 210.85 ± 3.42 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.-T.; Lan, Q.-Y.; Liang, X.; Mao, Y.-Y.; Cai, X.-K.; Tian, F.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.-R.; Zhu, H.-L. Lactational Changes of Phospholipids Content and Composition in Chinese Breast Milk. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081539
Yang M-T, Lan Q-Y, Liang X, Mao Y-Y, Cai X-K, Tian F, Liu Z-Y, Li X, Zhao Y-R, Zhu H-L. Lactational Changes of Phospholipids Content and Composition in Chinese Breast Milk. Nutrients. 2022; 14(8):1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081539
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Meng-Tao, Qiu-Ye Lan, Xue Liang, Ying-Yi Mao, Xiao-Kun Cai, Fang Tian, Zhao-Yan Liu, Xiang Li, Yan-Rong Zhao, and Hui-Lian Zhu. 2022. "Lactational Changes of Phospholipids Content and Composition in Chinese Breast Milk" Nutrients 14, no. 8: 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081539
APA StyleYang, M.-T., Lan, Q.-Y., Liang, X., Mao, Y.-Y., Cai, X.-K., Tian, F., Liu, Z.-Y., Li, X., Zhao, Y.-R., & Zhu, H.-L. (2022). Lactational Changes of Phospholipids Content and Composition in Chinese Breast Milk. Nutrients, 14(8), 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081539







