Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature in Obese Children and Adolescents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of Pediatric Obesity and Its Major Risk Factors
3. Main Complications Associated with Pediatric Obesity
4. Early Markers of Obesity-Related Complications
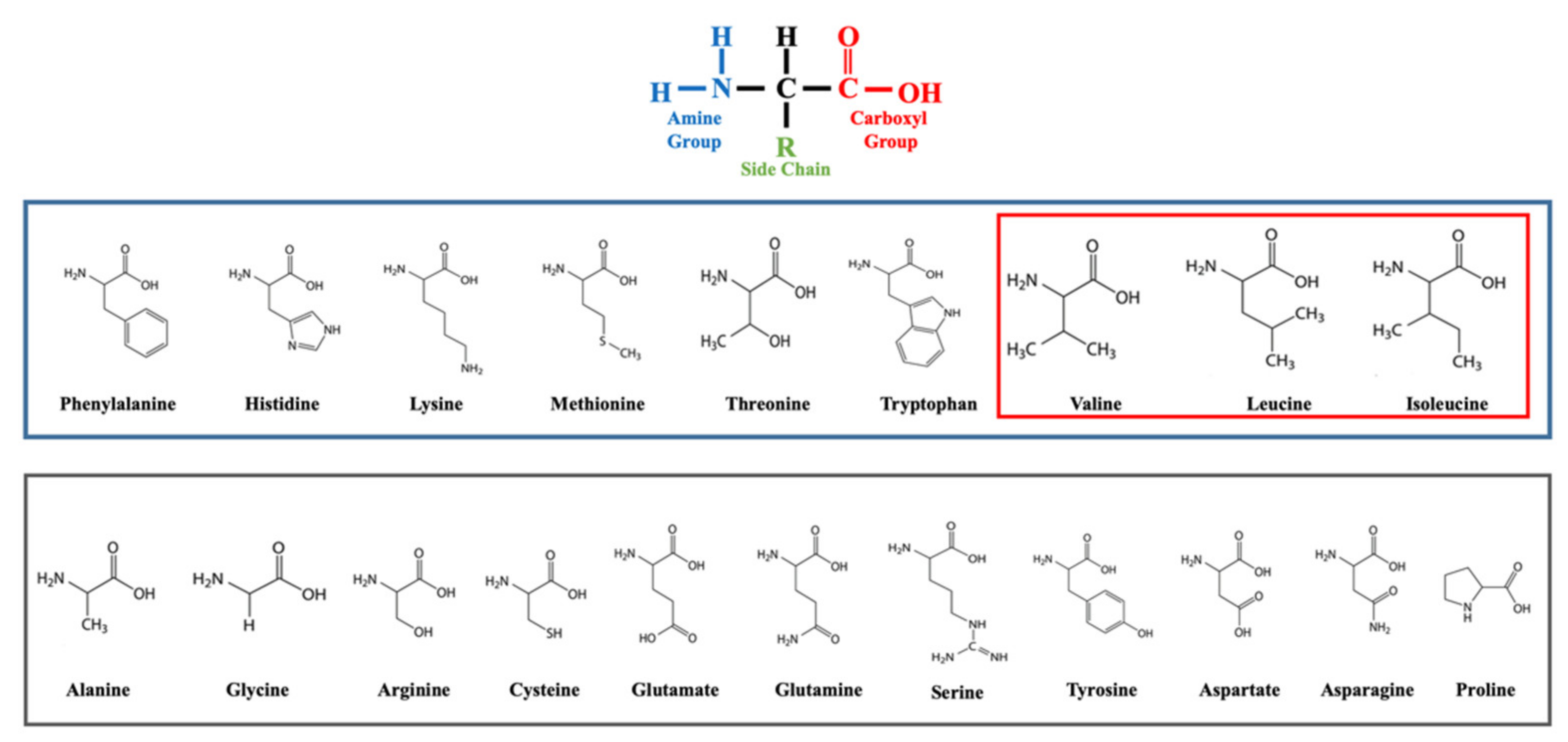
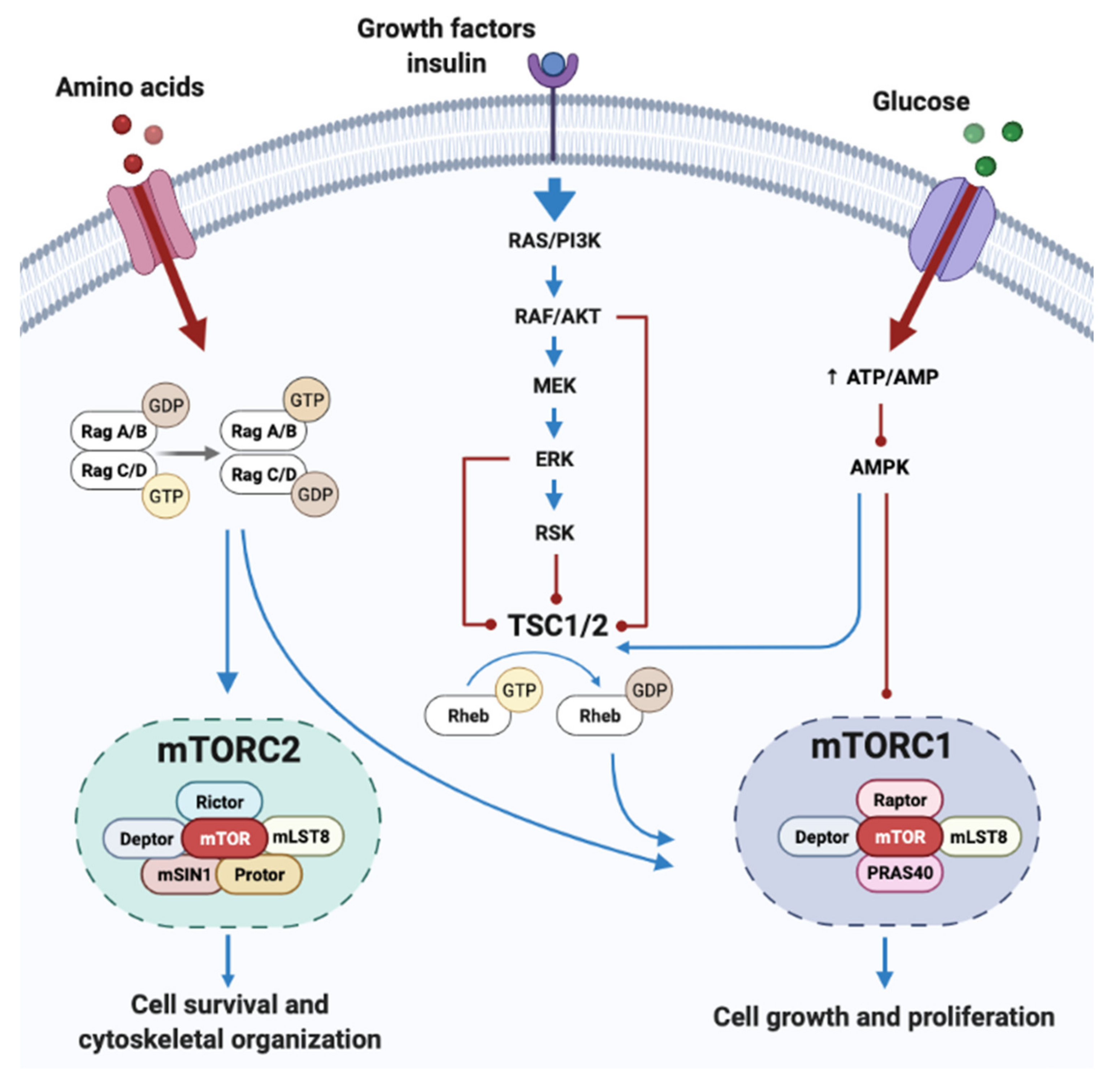
5. BCAAs: Function and Signaling
BCAA and mTORC Signaling Pathway
6. The Association of AAs in Obesity, IR and Metabolism in Youth
BCAAs as a Marker of Dietary Composition
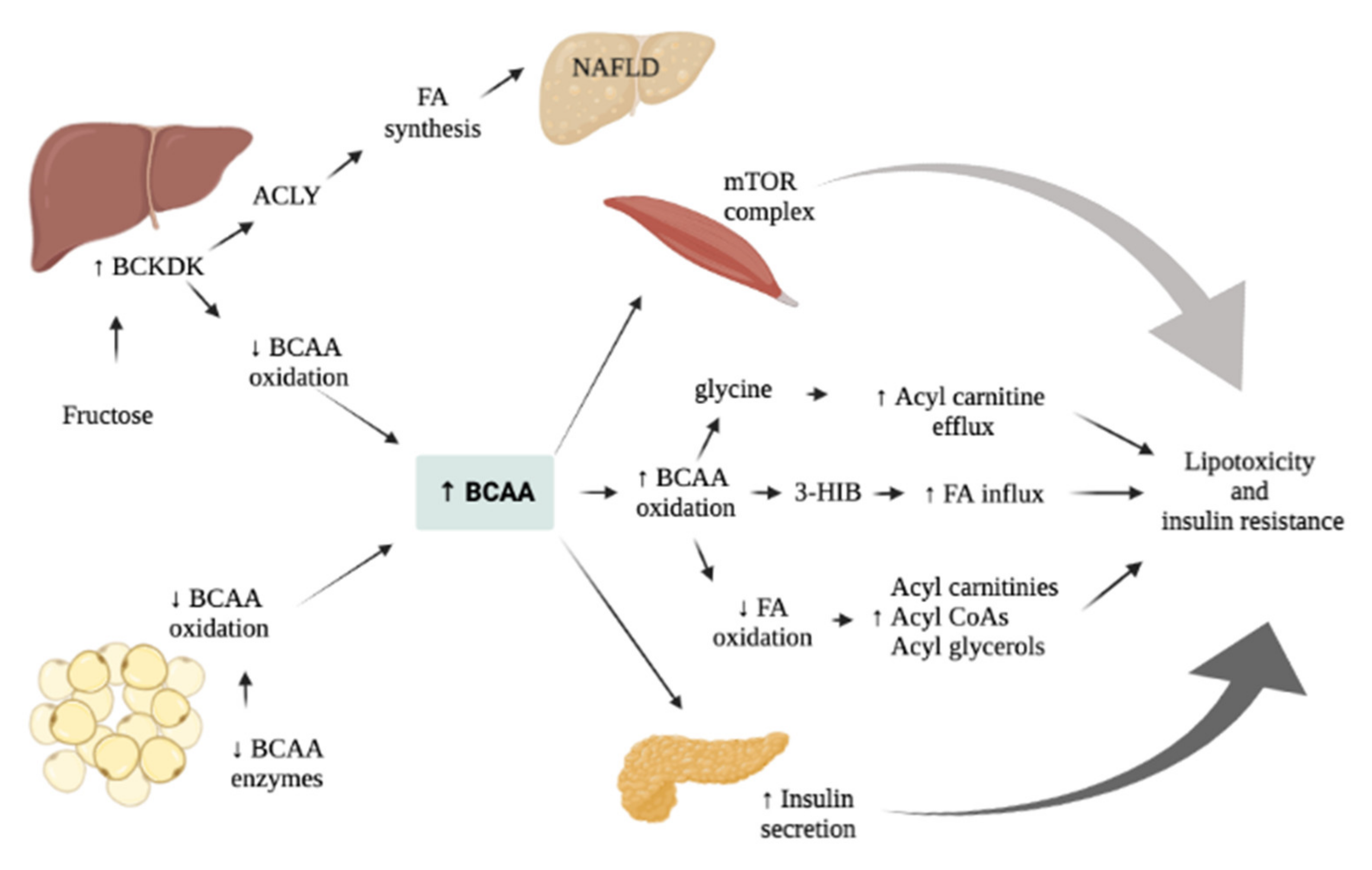
7. AAs Related Effect on Glucose and Liver Metabolism
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weihe, P.; Weihrauch-Blüher, S. Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: Diagnostic Criteria, Therapeutic Options and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, N.M.R.; Pelegrini, P.B.; Goersch, M.C. Nutrigenomics: Definitions and Advances of This New Science. J. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 2014, 202759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coughlin, S.S. Toward a Road Map for Global-Omics: A Primer on -Omic Technologies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and Metabolic Diseases: Where Do We Stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature That Differentiates Obese and Lean Humans and Contributes to Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohorko, N.; Petelin, A.; Jurdana, M.; Biolo, G.; Jenko-Pražnikar, Z. Elevated Serum Levels of Cysteine and Tyrosine: Early Biomarkers in Asymptomatic Adults at Increased Risk of Developing Metabolic Syndrome. Bio. Med. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 418681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tillin, T.; Hughes, A.D.; Wang, Q.; Würtz, P.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Sattar, N.; Forouhi, N.G.; Godsland, I.F.; Eastwood, S.V.; McKeigue, P.M.; et al. Diabetes Risk and Amino Acid Profiles: Cross-Sectional and Prospective Analyses of Ethnicity, Amino Acids and Diabetes in a South Asian and European Cohort from the SABRE (Southall And Brent REvisited) Study. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newbern, D.; Balikcioglu, P.G.; Balikcioglu, M.; Bain, J.; Muehlbauer, M.; Stevens, R.; Ilkayeva, O.; Dolinsky, D.; Armstrong, S.; Irizarry, K.; et al. Sex Differences in Biomarkers Associated With Insulin Resistance in Obese Adolescents: Metabolomic Profiling and Principal Components Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 4730–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felig, P.; Marliss, E.; Cahill, G.F. Plasma Amino Acid Levels and Insulin Secretion in Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 1969, 281, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, C.M.; Yu, B.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, P.; Tin, A.; Köttgen, A.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Selvin, E. Serum Metabolomic Profile of Incident Diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite Profiles and the Risk of Developing Diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Rosso, C.; Buzzigoli, E.; Marietti, M.; Latta, V.D.; Ciociaro, D.; Abate, M.L.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M.; et al. Altered Amino Acid Concentrations in NAFLD: Impact of Obesity and Insulin Resistance: Gaggini et Al. Hepatology 2018, 67, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ottosson, F.; Brunkwall, L.; Ericson, U.; Nilsson, P.M.; Almgren, P.; Fernandez, C.; Melander, O.; Orho-Melander, M. Connection Between BMI-Related Plasma Metabolite Profile and Gut Microbiota. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butte, N.F.; Liu, Y.; Zakeri, I.F.; Mohney, R.P.; Mehta, N.; Voruganti, V.S.; Göring, H.; Cole, S.A.; Comuzzie, A.G. Global Metabolomic Profiling Targeting Childhood Obesity in the Hispanic Population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricò, D.; Prinsen, H.; Giannini, C.; Graaf, R.d.; Juchem, C.; Li, F.; Caprio, S.; Santoro, N.; Herzog, R.I. Elevated α-Hydroxybutyrate and Branched-Chain Amino Acid Levels Predict Deterioration of Glycemic Control in Adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perng, W.; Gillman, M.W.; Fleisch, A.F.; Michalek, R.D.; Watkins, S.M.; Isganaitis, E.; Patti, M.-E.; Oken, E. Metabolomic Profiles and Childhood Obesity: Metabolomic Profiles and Childhood Obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, S.E.; Shaham, O.; McCarthy, M.A.; Deik, A.A.; Wang, T.J.; Gerszten, R.E.; Clish, C.B.; Mootha, V.K.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Fleischman, A. Circulating Branched-Chain Amino Acid Concentrations Are Associated with Obesity and Future Insulin Resistance in Children and Adolescents: Branched-Chain Amino Acids and IR in Children. Pediatr. Obes. 2013, 8, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahl, S.; Yu, Z.; Kleber, M.; Singmann, P.; Holzapfel, C.; He, Y.; Mittelstrass, K.; Polonikov, A.; Prehn, C.; Römisch-Margl, W.; et al. Childhood Obesity Is Associated with Changes in the Serum Metabolite Profile. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalik, S.J.; Michaliszyn, S.F.; Heras, J.d.l.; Bacha, F.; Lee, S.; Chace, D.H.; DeJesus, V.R.; Vockley, J.; Arslanian, S.A. Metabolomic Profiling of Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Metabolism in Youth With Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goffredo, M.; Santoro, N.; Tricò, D.; Giannini, C.; D’Adamo, E.; Zhao, H.; Peng, G.; Yu, X.; Lam, T.; Pierpont, B.; et al. A Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature Characterizes Obese Adolescents with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Canela, M.; Toledo, E.; Clish, C.B.; Hruby, A.; Liang, L.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Razquin, C.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; et al. Plasma Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in the PREDIMED Trial. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, S.; Yan, W.; Xia, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C.; Peng, C.; Yan, F.; et al. Branched Chain Amino Acids Cause Liver Injury in Obese/Diabetic Mice by Promoting Adipocyte Lipolysis and Inhibiting Hepatic Autophagy. EBioMedicine 2016, 13, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mu, W.-C.; VanHoosier, E.; Elks, C.; Grant, R. Long-Term Effects of Dietary Protein and Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Metabolism and Inflammation in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lischka, J.; Schanzer, A.; Hojreh, A.; Ssalamah, A.B.; Item, C.B.; Gier, C.; Walleczek, N.; Metz, T.F.; Jakober, I.; Greber-Platzer, S.; et al. A Branched-chain Amino Acid-based Metabolic Score Can Predict Liver Fat in Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Afshin, A.; Alexander, L.T.; Anderson, H.R.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Cercy, K.; Charlson, F.J.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Comparative Risk Assessment of 79 Behavioural, Environmental and Occupational, and Metabolic Risks or Clusters of Risks, 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1659–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adults during 1980–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennerz, B.S.; Moss, A.; Schnurbein, J.v.; Bickenbach, A.; Bollow, E.; Brandt, S.; Luetke-Brintrup, D.; Mühlig, Y.; Neef, M.; Ose, C.; et al. Do Adolescents with Extreme Obesity Differ According to Previous Treatment Seeking Behavior? The Youth with Extreme Obesity Study (YES) Cohort. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiess, W.; Penke, M.; Sergeyev, E.; Neef, M.; Adler, M.; Gausche, R.; Körner, A. Childhood Obesity at the Crossroads. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 28, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kelly, A.S. Review of Childhood Obesity. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.C.; Lawlor, D.A.; Kimm, S.Y. Childhood Obesity. Lancet 2010, 375, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.S.; Barlow, S.E.; Quiros-Tejeira, R.E.; Scheimann, A.; Skelton, J.; Suskind, D.; Tsai, P.; Uko, V.; Warolin, J.P.; Xanthakos, S.A. Childhood Obesity for Pediatr. Gastroenterologists. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.Y.; Yoon, K.-H. Epidemic Obesity in Children and Adolescents: Risk Factors and Prevention. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speiser, P.W.; Rudolf, M.C.J.; Anhalt, H.; Camacho-Hubner, C.; Chiarelli, F.; Eliakim, A.; Freemark, M.; Gruters, A.; Hershkovitz, E.; Iughetti, L.; et al. Childhood Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1871–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzo, L.D.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating Habits and Lifestyle Changes during COVID-19 Lockdown: An Italian Survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, A.G.; Park, Y.; Herbstman, J.B.; Kinsey, E.W.; Wang, Y.C. COVID-19–Related School Closings and Risk of Weight Gain Among Children. Obesity 2020, 28, 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stockwell, S.; Trott, M.; Tully, M.; Shin, J.; Barnett, Y.; Butler, L.; McDermott, D.; Schuch, F.; Smith, L. Changes in Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviours from before to during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown: A Systematic Review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e000960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, D.A.; Duggal, P.; Cingolani, O. Obesity Could Shift Severe COVID-19 Disease to Younger Ages. Lancet 2020, 395, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; Geserick, M.; Gausche, R.; Beger, C.; Poulain, T.; Meigen, C.; Körner, A.; Keller, E.; Kiess, W.; Pfäffle, R. Age- and Weight Group-Specific Weight Gain Patterns in Children and Adolescents during the 15 Years before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, N.; Mainieri, F.; Chiarelli, F.; Mohn, A.; Giannini, C. Early Insulin-Resistance, T2D and Treatment Options in Childhood. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2021; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The Metabolic Syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, W.; Moreno, L.A.; Pigeot, I. Filling the Gap: International Reference Values for Health Care in Children. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, S2–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurnani, M.; Birken, C.; Hamilton, J. Childhood Obesity. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 62, 821–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagi, V.M.; Giannini, C.; Chiarelli, F. Insulin Resistance in Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohut, T.; Robbins, J.; Panganiban, J. Update on Childhood/Adolescent Obesity and Its Sequela. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighbariya, A.; Weiss, R. Insulin Resistance, Prediabetes, Metabolic Syndrome: What Should Every Pediatrician Know? J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, F.; Mohn, A. Early Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome in Children. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2017, 1, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wühl, E. Hypertension in Childhood Obesity. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giorgis, T.d.; Marcovecchio, M.L.; Giannini, C.; Chiavaroli, V.; Chiarelli, F.; Mohn, A. Blood Pressure from Childhood to Adolescence in Obese Youths in Relation to Insulin Resistance and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Giannini, C.; Pierpont, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Santoro, N.; Kursawe, R.; Shaw, M.; Duran, E.; Goldberg, R.; Dziura, J.; et al. Longitudinal Effects of MRI-Measured Hepatic Steatosis on Biomarkers of Glucose Homeostasis and Hepatic Apoptosis in Obese Youth. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchesini, G.; Brizi, M.; Bianchi, G.; Tomassetti, S.; Bugianesi, E.; Lenzi, M.; McCullough, A.J.; Natale, S.; Forlani, G.; Melchionda, N. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nobili, V.; Marcellini, M.; Devito, R.; Ciampalini, P.; Piemonte, F.; Comparcola, D.; Sartorelli, M.R.; Angulo, P. NAFLD in Children: A Prospective Clinical-Pathological Study and Effect of Lifestyle Advice. Hepatology 2006, 44, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgert, T.S.; Taksali, S.E.; Dziura, J.; Goodman, T.R.; Yeckel, C.W.; Papademetris, X.; Constable, R.T.; Weiss, R.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Savoye, M.; et al. Alanine Aminotransferase Levels and Fatty Liver in Childhood Obesity: Associations with Insulin Resistance, Adiponectin, and Visceral Fat. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4287–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, E.A. Steatohepatitis in Children. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2002, 16, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzaloni, G.; Grugni, G.; Minocci, A.; Moro, D.; Morabito, F. Liver Steatosis in Juvenile Obesity: Correlations with Lipid Profile, Hepatic Biochemical Parameters and Glycemic and Insulinemic Responses to an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Adamo, E.; Impicciatore, M.; Capanna, R.; Marcovecchio, M.L.; Masuccio, F.G.; Chiarelli, F.; Mohn, A.A. Liver Steatosis in Obese Prepubertal Children: A Possible Role of Insulin Resistance. Obesity 2008, 16, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Ballestri, S.; Fairweather, D.; Win, S.; Than, T.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A. Sex Differences in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: State of the Art and Identification of Research Gaps. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azziz, R.; Carmina, E.; Chen, Z.; Dunaif, A.; Laven, J.S.E.; Legro, R.S.; Lizneva, D.; Natterson-Horowtiz, B.; Teede, H.J.; Yildiz, B.O. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulotta, G.; Iannella, G.; Vicini, C.; Polimeni, A.; Greco, A.; Vincentiis, M.d.; Visconti, I.C.; Meccariello, G.; Cammaroto, G.; Vito, A.D.; et al. Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Children: State of the Art. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitri, P. Fat and Bone in Children—Where Are We Now? Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 23, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmherzig, R.; Szperka, C.L. Pseudotumor Cerebri Syndrome in Children. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2019, 23, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, A.; Ghezzi, A.; Bar-Or, A.; Mikaeloff, Y.; Tardieu, M.; Banwell, B. Multiple Sclerosis in Children: An Update on Clinical Diagnosis, Therapeutic Strategies, and Research. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huppke, B.; Ellenberger, D.; Hummel, H.; Stark, W.; Röbl, M.; Gärtner, J.; Huppke, P. Association of Obesity With Multiple Sclerosis Risk and Response to First-Line Disease Modifying Drugs in Children. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, V.H. Obesity Facts and Their Influence on Renal Function Across the Life Span. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 704409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.-L.; Kazzi, N.G.; Lee, J.M. Cost-Effectiveness of Screening Strategies for Identifying Pediatric Diabetes Mellitus and Dysglycemia. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Styne, D.M.; Arslanian, S.A.; Connor, E.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Murad, M.H.; Silverstein, J.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Pediatric Obesity—Assessment, Treatment, and Prevention: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 709–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapiotis, S.; Holzer, G.; Schaller, G.; Haumer, M.; Widhalm, H.; Weghuber, D.; Jilma, B.; Röggla, G.; Wolzt, M.; Widhalm, K.; et al. A Proinflammatory State Is Detectable in Obese Children and Is Accompanied by Functional and Morphological Vascular Changes. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, M.V.; Estepa, R.M.; Camacho, R.M.; Estrada, R.C.; Luna, F.G.; Guitarte, F.B. Endothelial Dysfunction Is Related to Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarker Levels in Obese Prepubertal Children. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 156, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; Steffen, L.M.; Jacobs, D.R.; Steinberger, J.; Pankow, J.S.; Hong, C.-P.; Tracy, R.P.; Sinaiko, A.R. Relation of C-Reactive Protein to Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Youth. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saner, C.; Harcourt, B.E.; Pandey, A.; Ellul, S.; McCallum, Z.; Kao, K.-T.; Twindyakirana, C.; Pons, A.; Alexander, E.J.; Saffery, R.; et al. Sex and Puberty-Related Differences in Metabolomic Profiles Associated with Adiposity Measures in Youth with Obesity. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würtz, P.; Wang, Q.; Kangas, A.J.; Richmond, R.C.; Skarp, J.; Tiainen, M.; Tynkkynen, T.; Soininen, P.; Havulinna, A.S.; Kaakinen, M.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Adiposity in Young Adults: Mendelian Randomization Analysis and Effects of Weight Change. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaikkonen, J.E.; Würtz, P.; Suomela, E.; Lehtovirta, M.; Kangas, A.J.; Jula, A.; Mikkilä, V.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Juonala, M.; Rönnemaa, T.; et al. Metabolic Profiling of Fatty Liver in Young and Middle-aged Adults: Cross-sectional and Prospective Analyses of the Young Finns Study. Hepatology 2017, 65, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijada, Z.; Paoli, M.; Zerpa, Y.; Camacho, N.; Cichetti, R.; Villarroel, V.; Arata-Bellabarba, G.; Lanes, R. The Triglyceride/HDL-Cholesterol Ratio as a Marker of Cardiovascular Risk in Obese Children; Association with Traditional and Emergent Risk Factors. Pediatr. Diabetes 2008, 9, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Dunn, W.; Norman, G.J.; Pardee, P.E.; Middleton, M.S.; Kerkar, N.; Sirlin, C.B. SAFETY Study: Alanine Aminotransferase Cutoff Values Are Set Too High for Reliable Detection of Pediatric Chronic Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molleston, J.P.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Yates, K.P.; Murray, K.F.; Cummings, O.W.; Lavine, J.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Scheimann, A.O.; Unalp-Arida, A. Histological Abnormalities in Children with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Normal or Mildly Elevated Alanine Aminotransferase Levels. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattick, J.S.A.; Kamisoglu, K.; Ierapetritou, M.G.; Androulakis, I.P.; Berthiaume, F. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation: Impact on Signaling and Relevance to Critical Illness: Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2013, 5, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Short, K.R.; Chadwick, J.Q.; Teague, A.M.; Tullier, M.A.; Wolbert, L.; Coleman, C.; Copeland, K.C. Effect of Obesity and Exercise Training on Plasma Amino Acids and Amino Metabolites in American Indian Adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3249–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.J.; Adams, S.H. Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Metabolic Signalling and Insulin Resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, K.S.; Short, K.R. Hormonal and Signaling Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1547S–1552S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, S.H.; D’Alessio, D.; Thomas, G. Nutrient Overload, Insulin Resistance, and Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1, S6K1. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. Signaling Pathways and Molecular Mechanisms through Which Branched-Chain Amino Acids Mediate Translational Control of Protein Synthesis. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 227S–231S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jhanwar-Uniyal, M.; Wainwright, J.V.; Mohan, A.L.; Tobias, M.E.; Murali, R.; Gandhi, C.D.; Schmidt, M.H. Diverse Signaling Mechanisms of MTOR Complexes: MTORC1 and MTORC2 in Forming a Formidable Relationship. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2019, 72, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabanal-Ruiz, Y.; Otten, E.G.; Korolchuk, V.I. MTORC1 as the Main Gateway to Autophagy. Essays Biochem. 2017, 61, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis, M.D.; Baum, J.I.; Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. Mechanisms Involved in the Coordinate Regulation of MTORC1 by Insulin and Amino Acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8287–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neishabouri, S.H.; Hutson, S.M.; Davoodi, J. Chronic Activation of MTOR Complex 1 by Branched Chain Amino Acids and Organ Hypertrophy. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1167–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.C.; Yoshizawa, F.; Anthony, T.G.; Vary, T.C.; Jefferson, L.S.; Kimball, S.R. Leucine Stimulates Translation Initiation in Skeletal Muscle of Postabsorptive Rats via a Rapamycin-Sensitive Pathway. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, A.K.; Anthony, T.G.; Anthony, J.C.; Jefferson, L.S.; Kimball, S.R. The MTOR Signaling Pathway Mediates Control of Ribosomal Protein MRNA Translation in Rat Liver. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamzina, L.; Veilleux, A.; Bergeron, S.; Marette, A. Increased Activation of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathway in Liver and Skeletal Muscle of Obese Rats: Possible Involvement in Obesity-Linked Insulin Resistance. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, G.; Marzocchi, R.; Agostini, F.; Marchesini, G. Update on Nutritional Supplementation with Branched-Chain Amino Acids. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2005, 8, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, Y.; Murakami, T.; Nakai, N.; Nagasaki, M.; Harris, R.A. Exercise Promotes BCAA Catabolism: Effects of BCAA Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle during Exercise. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1583S–1587S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blommaart, E.F.C.; Luiken, J.J.F.P.; Blommaart, P.J.E.; Woerkom, G.M.v.; Meijer, A.J. Phosphorylation of Ribosomal Protein S6 Is Inhibitory for Autophagy in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagata, C.; Nakamura, K.; Wada, K.; Tsuji, M.; Tamai, Y.; Kawachi, T. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Intake and the Risk of Diabetes in a Japanese Community: The Takayama Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segovia-Siapco, G.; Khayef, G.; Pribis, P.; Oda, K.; Haddad, E.; Sabaté, J. Animal Protein Intake Is Associated with General Adiposity in Adolescents: The Teen Food and Development Study. Nutrients 2019, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hermanussen, M. Nutritional Protein Intake Is Associated with Body Mass Index in Young Adolescents. Georgian Med. News 2008, 156, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau, M.; Guénard, F.; Garneau, V.; Allam-Ndoul, B.; Lemieux, S.; Pérusse, L.; Vohl, M.-C. Associations Between Dietary Protein Sources, Plasma BCAA and Short-Chain Acylcarnitine Levels in Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isanejad, M.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Thomson, C.A.; Tinker, L.; Larson, J.C.; Qi, Q.; Qi, L.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.M.; Phillips, L.S.; Prentice, R.L.; et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acid, Meat Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the Women’s Health Initiative. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, V.S.; Li, Y.; Tobias, D.K.; Pan, A.; Hu, F.B. Dietary Protein Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in US Men and Women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Duffley, L.; Pulinilkunnil, T. Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Catabolizing Enzymes in Intertissue Signaling, Metabolic Remodeling, and Energy Homeostasis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8711–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Natali, A.; Camastra, S.; Nannipieri, M.; Mari, A.; Adam, K.-P.; Milburn, M.V.; Kastenmüller, G.; Adamski, J.; Tuomi, T.; et al. Early Metabolic Markers of the Development of Dysglycemia and Type 2 Diabetes and Their Physiological Significance. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suhre, K.; Meisinger, C.; Döring, A.; Altmaier, E.; Belcredi, P.; Gieger, C.; Chang, D.; Milburn, M.V.; Gall, W.E.; Weinberger, K.M.; et al. Metabolic Footprint of Diabetes: A Multiplatform Metabolomics Study in an Epidemiological Setting. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, C.; Oh, S.F.; Wada, S.; Rowe, G.C.; Liu, L.; Chan, M.C.; Rhee, J.; Hoshino, A.; Kim, B.; Ibrahim, A.; et al. A Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolite Drives Vascular Fatty Acid Transport and Causes Insulin Resistance. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.C.; Watkins, S.M.; Lorenzo, C.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Il’yasova, D.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Haffner, S.M.; Hanley, A.J. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Insulin Metabolism: The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, M.-S. The Emerging Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Insulin Resistance and Metabolism. Nutrients 2016, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lackey, D.E.; Lynch, C.J.; Olson, K.C.; Mostaedi, R.; Ali, M.; Smith, W.H.; Karpe, F.; Humphreys, S.; Bedinger, D.H.; Dunn, T.N.; et al. Regulation of Adipose Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism Enzyme Expression and Cross-Adipose Amino Acid Flux in Human Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E1175–E1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- She, P.; Horn, C.V.; Reid, T.; Hutson, S.M.; Cooney, R.N.; Lynch, C.J. Obesity-Related Elevations in Plasma Leucine Are Associated with Alterations in Enzymes Involved in Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1552–E1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herman, M.A.; She, P.; Peroni, O.D.; Lynch, C.J.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose Tissue Branched Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Metabolism Modulates Circulating BCAA Levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 11348–11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batch, B.C.; Shah, S.H.; Newgard, C.B.; Turer, C.B.; Haynes, C.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.; Patel, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Appel, L.J.; et al. Branched Chain Amino Acids Are Novel Biomarkers for Discrimination of Metabolic Wellness. Metabolism 2013, 62, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perng, W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Sordillo, J.; Hivert, M.; Oken, E. Metabolomic Profiles of Overweight/Obesity Phenotypes During Adolescence: A Cross-Sectional Study in Project Viva. Obesity 2020, 28, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.H. Emerging Perspectives on Essential Amino Acid Metabolism in Obesity and the Insulin-Resistant State. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosking, J.; Pinkney, J.; Jeffery, A.; Cominetti, O.; Silva, L.D.; Collino, S.; Kussmann, M.; Hager, J.; Martin, F. Insulin Resistance during Normal Child Growth and Development Is Associated with a Distinct Blood Metabolic Phenotype (Earlybird 72). Pediatr. Diabetes 2019, 20, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Jang, H.B.; Ra, M.; Choi, Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Park, K.-H.; Park, S.I.; Song, J. Prediction of Future Risk of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome Based on Korean Boy’s Metabolite Profiling. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangge, H.; Zelzer, S.; Prüller, F.; Schnedl, W.J.; Weghuber, D.; Enko, D.; Bergsten, P.; Haybaeck, J.; Meinitzer, A. Branched-Chain Amino Acids Are Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk Profiles Found Already in Lean, Overweight and Obese Young. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 32, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevara-Cruz, M.; Vargas-Morales, J.M.; Méndez-García, A.L.; López-Barradas, A.M.; Granados-Portillo, O.; Ordaz-Nava, G.; Rocha-Viggiano, A.K.; Gutierrez-Leyte, C.A.; Medina-Cerda, E.; Rosado, J.L.; et al. Amino Acid Profiles of Young Adults Differ by Sex, Body Mass Index and Insulin Resistance. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepcion, J.; Chen, K.; Saito, R.; Gangoiti, J.; Mendez, E.; Nikita, M.E.; Barshop, B.A.; Natarajan, L.; Sharma, K.; Kim, J.J. Identification of Pathognomonic Purine Synthesis Biomarkers by Metabolomic Profiling of Adolescents with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmuth, C.; Kirchberg, F.F.; Lass, N.; Harder, U.; Peissner, W.; Koletzko, B.; Reinehr, T. Tyrosine Is Associated with Insulin Resistance in Longitudinal Metabolomic Profiling of Obese Children. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaliszyn, S.F.; Sjaarda, L.A.; Mihalik, S.J.; Lee, S.; Bacha, F.; Chace, D.H.; Jesus, V.R.D.; Vockley, J.; Arslanian, S.A. Metabolomic Profiling of Amino Acids and β-Cell Function Relative to Insulin Sensitivity in Youth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E2119–E2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perng, W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Hivert, M.-F.; Chavarro, J.E.; Oken, E. Branched Chain Amino Acids, Androgen Hormones, and Metabolic Risk Across Early Adolescence: A Prospective Study in Project Viva: BCAA, Androgens, and Metabolic Risk in Adolescence. Obesity 2018, 26, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esko, T.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Feldman, H.A.; Hsu, Y.-H.H.; Deik, A.A.; Clish, C.B.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Ludwig, D.S. Metabolomic Profiles as Reliable Biomarkers of Dietary Composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, C.M.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Zheng, Z.; Appel, L.J.; Coresh, J. Serum Untargeted Metabolomic Profile of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Dietary Pattern. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Black, A.; Kales, S.N.; Vattem, D.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Sotos-Prieto, M. Metabolomics and Microbiomes as Potential Tools to Evaluate the Effects of the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Playdon, M.C.; Moore, S.C.; Derkach, A.; Reedy, J.; Subar, A.F.; Sampson, J.N.; Albanes, D.; Gu, F.; Kontto, J.; Lassale, C.; et al. Identifying Biomarkers of Dietary Patterns by Using Metabolomics. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, M.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Schlesinger, S.; Borggrefe, J.; Hov, J.R.; Jensen, M.K.; Pick, J.; Markus, M.R.P.; Höpfner, T.; Jacobs, G.; et al. Serum Metabolomic Profiling Highlights Pathways Associated with Liver Fat Content in a General Population Sample. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalhan, S.C.; Guo, L.; Edmison, J.; Dasarathy, S.; McCullough, A.J.; Hanson, R.W.; Milburn, M. Plasma Metabolomic Profile in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Metabolism 2011, 60, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwasa, M.; Ishihara, T.; Mifuji-Moroka, R.; Fujita, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Iwata, K.; Kaito, M.; Takei, Y. Elevation of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Levels in Diabetes and NAFL and Changes with Antidiabetic Drug Treatment. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Guirro, M.; Riera-Borrull, M.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Mariné-Casadó, R.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Sabench, F.; Hernández, M.; del Castillo, D.; et al. Mapping of the Circulating Metabolome Reveals α-Ketoglutarate as a Predictor of Morbid Obesity-Associated Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, A.D.; Novak, P.; Shipkova, P.; Aranibar, N.; Robertson, D.G.; Reily, M.D.; Lehman-McKeeman, L.D.; Vaillancourt, R.R.; Cherrington, N.J. Branched Chain Amino Acid Metabolism Profiles in Progressive Human Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wiklund, P.; Autio, R.; Borra, R.; Ojanen, X.; Xu, L.; Törmäkangas, T.; Alen, M. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Altered Systemic Amino Acid Metabolism Are Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufe, S.; Engeli, S.; Kaminski, J.; Witt, H.; Rein, D.; Kamlage, B.; Utz, W.; Fuhrmann, J.C.; Haas, V.; Mähler, A.; et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism Rather than Amino Acids Plasma Concentrations Is Associated with Diet-Induced Changes in Insulin Resistance in Overweight to Obese Individuals. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusial, R.D.; Cioffi, C.E.; Caltharp, S.A.; Krasinskas, A.M.; Alazraki, A.; Knight-Scott, J.; Cleeton, R.; Castillo-Leon, E.; Jones, D.P.; Pierpont, B.; et al. Development of a Plasma Screening Panel for Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using Metabolomics. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, R.; Banton, S.; Tran, V.T.; Konomi, J.V.; Li, S.; Jones, D.P.; Vos, M.B. Amino Acid Metabolism Is Altered in Adolescents with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease—An Untargeted, High Resolution Metabolomics Study. J. Pediatr. 2016, 172, 14–19.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.H.; Crosslin, D.R.; Haynes, C.S.; Nelson, S.; Turer, C.B.; Stevens, R.D.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Wenner, B.R.; Bain, J.R.; Laferrère, B.; et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Levels Are Associated with Improvement in Insulin Resistance with Weight Loss. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laferrère, B.; Reilly, D.; Arias, S.; Swerdlow, N.; Gorroochurn, P.; Bawa, B.; Bose, M.; Teixeira, J.; Stevens, R.D.; Wenner, B.R.; et al. Differential Metabolic Impact of Gastric Bypass Surgery Versus Dietary Intervention in Obese Diabetic Subjects Despite Identical Weight Loss. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 80re2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oberbach, A.; Bergen, M.v.; Blüher, S.; Lehmann, S.; Till, H. Combined Serum Proteomic and Metabonomic Profiling After Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy in Children and Adolescents. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2012, 22, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swierczynski, J.; Sledzinski, T.; Slominska, E.; Smolenski, R.; Sledzinski, Z. Serum Phenylalanine Concentration as a Marker of Liver Function in Obese Patients Before and After Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2009, 19, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, S.; Herzog, R.I.; Caprio, S.; Santoro, N.; Tricò, D. Glutamate–Serine–Glycine Index: A Novel Potential Biomarker in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Children 2020, 7, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polidori, N.; Grasso, E.A.; Chiarelli, F.; Giannini, C. Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature in Obese Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071454
Polidori N, Grasso EA, Chiarelli F, Giannini C. Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature in Obese Children and Adolescents. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071454
Chicago/Turabian StylePolidori, Nella, Eleonora Agata Grasso, Francesco Chiarelli, and Cosimo Giannini. 2022. "Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature in Obese Children and Adolescents" Nutrients 14, no. 7: 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071454
APA StylePolidori, N., Grasso, E. A., Chiarelli, F., & Giannini, C. (2022). Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature in Obese Children and Adolescents. Nutrients, 14(7), 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071454






