Feeding during Dialysis Increases Intradialytic Blood Pressure Variability and Reduces Dialysis Adequacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
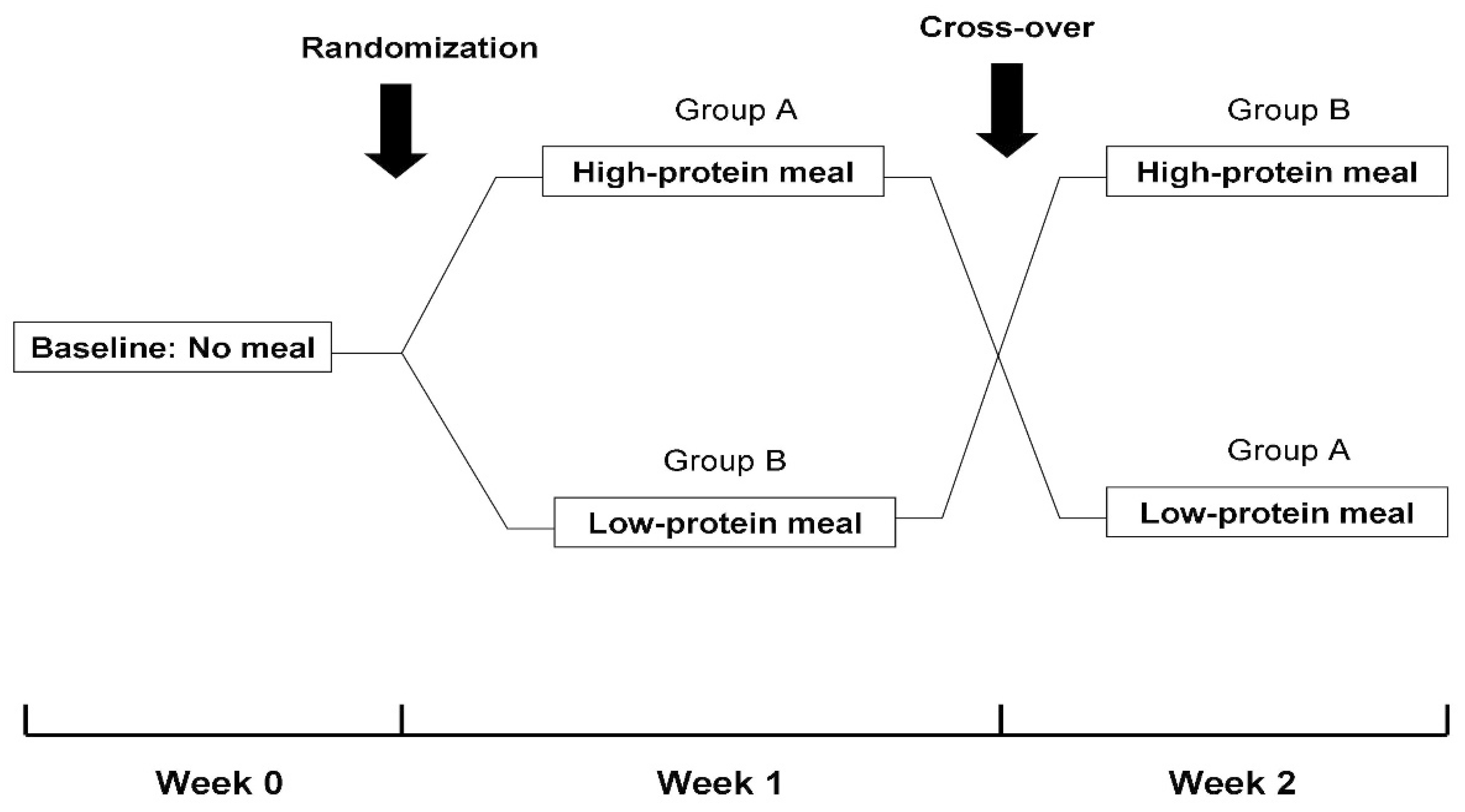
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Intradialytic BP Monitoring
2.4. Dialysis Adequacy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
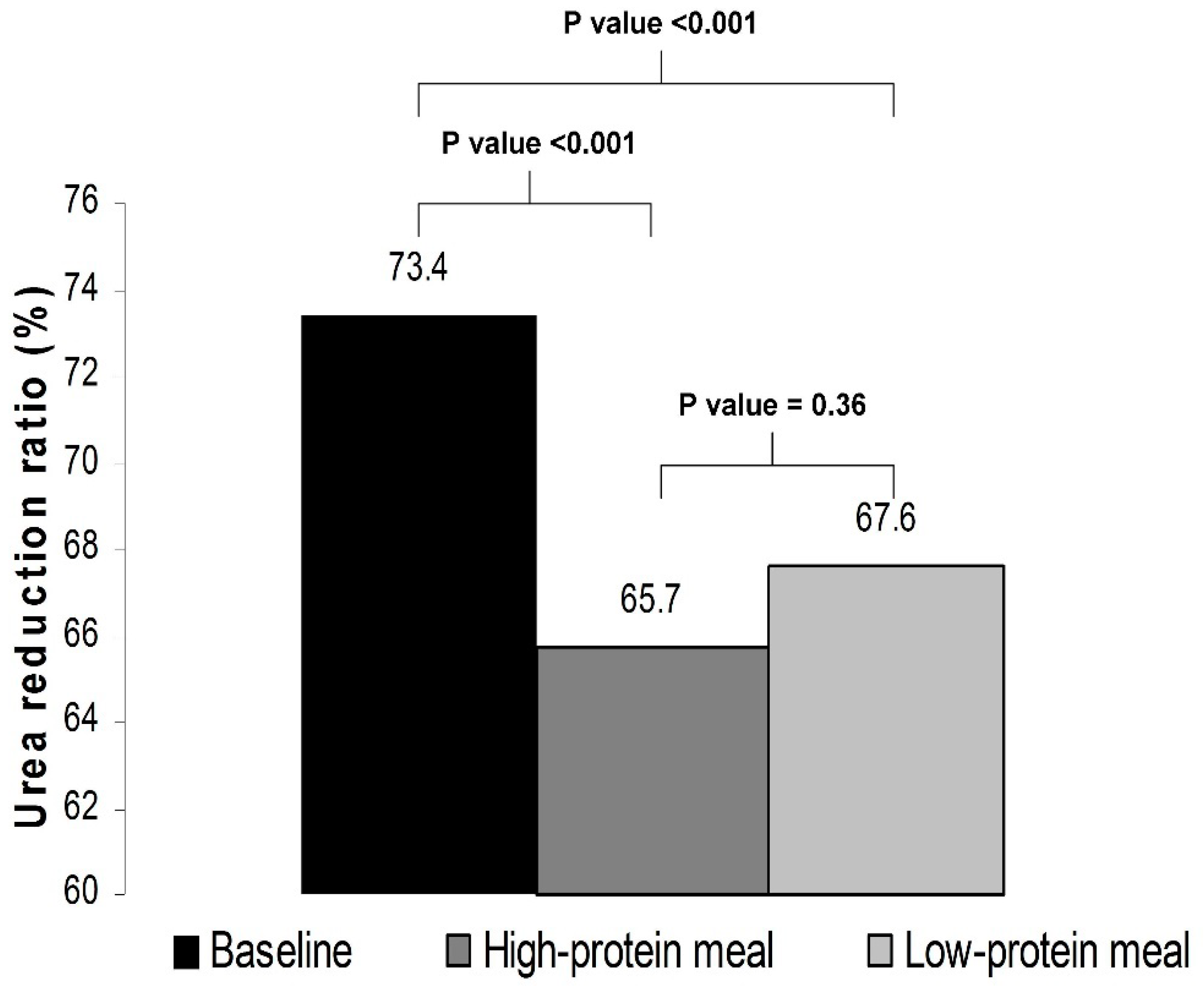
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kistler, B.M.; Benner, D.; Burrowes, J.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Fouque, D.; Garibotto, G.; Kopple, J.D.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Rhee, C.M.; Steiber, A.; et al. Eating During Hemodialysis Treatment: A Consensus Statement From the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burrowes, J.D.; Larive, B.; Cockram, D.B.; Dwyer, J.; Kusek, J.W.; McLeroy, S.; Poole, D.; Rocco, M.V. Effects of dietary intake, appetite, and eating habits on dialysis and non-dialysis treatment days in hemodialysis patients: Cross-sectional results from the HEMO study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2003, 13, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ikizler, T.A. Let them eat during dialysis: An overlooked opportunity to improve outcomes in maintenance hemodialysis patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhee, C.M.; You, A.S.; Koontz, P.T.; Tortorici, A.R.; Bross, R.; St-Jules, D.E.; Jing, J.; Lee, M.L.; Benner, D.; Kovesdy, C.P.; et al. Effect of high-protein meals during hemodialysis combined with lanthanum carbonate in hypoalbuminemic dialysis patients: Findings from the FrEDI randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fotiadou, E.; Georgianos, P.I.; Chourdakis, M.; Zebekakis, P.E.; Liakopoulos, V. Eating during the Hemodialysis Session: A Practice Improving Nutritional Status or a Risk Factor for Intradialytic Hypotension and Reduced Dialysis Adequacy? Nutrients 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Benaroia, M.; Iliescu, E.A. Oral intake during hemodialysis: Is there an association with intradialytic hypotension? Hemodial. Int. 2008, 12, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.S.; Kistler, B.; Wiese, G.N.; Stremke, E.R.; Wright, A.J.; Moorthi, R.N.; Moe, S.M.; Hill Gallant, K.M. Pilot Study of the Effects of High-Protein Meals During Hemodialysis on Intradialytic Hypotension in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2019, 29, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sherman, R.A.; Torres, F.; Cody, R.P. Postprandial blood pressure changes during hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney. Dis. 1988, 12, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Ciccarelli, M.; Maggiore, Q. Postprandial alterations in arterial pressure control during hemodialysis in uremic patients. Clin. Nephrol. 1989, 31, 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Franssen, P.M.; Imholz, B.P. Evaluation of the Mobil-O-Graph new generation ABPM device using the ESH criteria. Blood. Press. Monit. 2010, 15, 229–231. [Google Scholar]
- Sarafidis, P.A.; Lazaridis, A.A.; Imprialos, K.P.; Georgianos, P.I.; Avranas, K.A.; Protogerou, A.D.; Doumas, M.N.; Athyros, V.G.; Karagiannis, A.I. A comparison study of brachial blood pressure recorded with Spacelabs 90217A and Mobil-O-Graph NG devices under static and ambulatory conditions. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 742–749. [Google Scholar]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Parati, G.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Achimastos, A.; Andreadis, E.; Asmar, R.; Avolio, A.; Benetos, A.; Bilo, G.; Boubouchairopoulou, N.; et al. Methodology and technology for peripheral and central blood pressure and blood pressure variability measurement: Current status and future directions—Position statement of the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on blood pressure monitoring and cardiovascular variability. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Kooman, J.; Basci, A.; Pizzarelli, F.; Canaud, B.; Haage, P.; Fouque, D.; Konner, K.; Martin-Malo, A.; Pedrini, L.; Tattersall, J.; et al. EBPG guideline on haemodynamic instability. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22 (Suppl. 2), ii22–ii44. [Google Scholar]
- National Kidney Foundation: K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for hemodialysis adequacy 2000. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, S7–S64.
- Agarwal, R.; Georgianos, P. Feeding during dialysis-risks and uncertainties. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarafidis, P.A.; Georgianos, P.I.; Karpetas, A.; Bikos, A.; Korelidou, L.; Tersi, M.; Divanis, D.; Tzanis, G.; Mavromatidis, K.; Liakopoulos, V.; et al. Evaluation of a novel brachial cuff-based oscillometric method for estimating central systolic pressure in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shibagaki, Y.; Takaichi, K. Significant reduction of the large-vessel blood volume by food intake during hemodialysis. Clin. Nephrol. 1998, 49, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, R.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, M.; Liu, Q.; Su, B. The Association between Long- and Intra-Dialytic Blood Pressure Variability with All-Cause Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. Blood. Purif. 2019, 48, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, P.; Song, D.; Wu, J.; Jia, L. Intradialytic BP variability is associated with cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization in HD patients. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, J.; Verboom, L.M.; Ipema, K.J.R.; Paans, W.; Krijnen, W.P.; Gaillard, C.A.J.M.; Westerhuis, R.; Franssen, C.F.M. The Prevalence of Intradialytic Hypotension in Patients on Conventional Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- Shoji, T.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Fujii, M.; Imai, E. Hemodialysis-associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kara, B.; Acikel, C.H. The effect of intradialytic food intake on the urea reduction ratio and single-pool Kt/V values in patients followed-up at a hemodialysis center. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 40, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- San Juan, M.M.; Pilar, S.M.; Santos de Pablos, M.R. Reduction of Kt/V by food intake during haemodialysis. EDTNA ERCA J. 2001, 27, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
| N | 26 |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Age (years) | 60.5 ± 12.3 |
| Male gender (n, %) | 20, (76.9%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.3 ± 4.8 |
| Primary cause of ESKD (n, %) | |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 9, (34.6%) |
| Hypertensive nephrosclerosis | 4, (15.4%) |
| Glomerulonephritis | 6, (23.1%) |
| Other | 3, (11.5%) |
| Unknown | 4, (15.4%) |
| Comorbidities (n, %) | |
| Diabetes | 12, (46.2%) |
| Hypertension | 23, (88.5%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 13, (50.0%%) |
| History of CHD | 14, (53.8%) |
| History of CHF | 3, (11.5%) |
| Dialysis parameters | |
| Dialysis vintage (months) | 44 (3, 272) |
| Mode of dialysis (n, %) | |
| HD | 17, (65.4%) |
| On-line HDF | 9, (34.6%) |
| Vascular access | |
| Arteriovenous fistula | 14, (53.8%) |
| Central venous catheter | 12, (46.2% |
| Blood flow―Qb (mL/min) | 300, (250–350) |
| Dialysate flow―Qd (mL/min) | 600, (500–800) |
| Residual diuresis ≥0.5 L/24-h (n, %) | 15, (57.7%) |
| Laboratory parameters | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 11.5 ± 1.0 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 140.8 ± 35.1 |
| Urea reduction ratio (%) | 73.4 ± 4.3 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 8.1 ± 1.9 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 8.8 ± 0.7 |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 5.3 ± 1.4 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.2 ± 0.3 |
| Antihypertensive medications (n, %) | |
| β-blocker | 12, (46.2%) |
| ACEIs or ARBs | 4, (15.4%) |
| CCBs | 12, (46.2%) |
| Loop diuretics | 15, (57.7%) |
| Centrally-acting agents | 2, (7.7%) |
| Parameter | Baseline | High-Protein Meal | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average intradialytic SBP (mmHg) | 124.6 ± 17.2 | 127.1 ± 17.0 | 0.38 |
| Intradialytic SBP-SD (mmHg) | 11.7 ± 4.1 | 15.6 ± 7.6 | <0.01 |
| Intradialytic SBP-CV (%) | 9.5 ± 3.7 | 12.4 ± 6.0 | <0.01 |
| Intradialytic SBP-ARV (mmHg) | 9.4 ± 3.9 | 12.1 ± 5.2 | <0.01 |
| Average intradialytic DBP (mmHg) | 78.9 ± 10.2 | 79.0 ± 11.4 | 0.98 |
| Intradialytic DBP-SD (mmHg) | 8.3 ± 2.6 | 9.7 ± 0.9 | 0.17 |
| Intradialytic DBP-CV (%) | 10.6 ± 3.5 | 12.5 ± 5.7 | 0.14 |
| Intradialytic DBP-ARV (mmHg) | 7.2 ± 2.1 | 7.9 ± 3.1 | 0.41 |
| Average intradialytic HR (bpm) | 70.7 ± 12.1 | 72.9 ± 10.8 | 0.16 |
| Ultrafiltration volume (L) | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 0.79 |
| Ultrafiltration rate (mL/kg/h) | 6.9 ± 3.7 | 7.0 ± 3.3 | 0.97 |
| Parameter | Baseline | Low-Protein Meal | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average intradialytic SBP (mmHg) | 124.6 ± 17.2 | 129.9 ± 18.3 | 0.11 |
| Intradialytic SBP-SD (mmHg) | 11.7 ± 4.1 | 14.1 ± 4.5 | <0.05 |
| Intradialytic SBP-CV (%) | 9.5 ± 3.7 | 11.1 ± 3.8 | <0.05 |
| Intradialytic SBP-ARV (mmHg) | 9.4 ± 3.9 | 10.9 ± 3.9 | <0.05 |
| Average intradialytic DBP (mmHg) | 78.9 ± 10.2 | 80.7 ± 12.9 | 0.37 |
| Intradialytic DBP-SD (mmHg) | 8.3 ± 2.6 | 8.6 ± 2.9 | 0.66 |
| Intradialytic DBP-CV (%) | 10.6 ± 3.5 | 11.0 ± 3.8 | 0.72 |
| Intradialytic DBP-ARV (mmHg) | 7.2 ± 2.1 | 7.3 ± 2.2 | 0.92 |
| Average intradialytic HR (bpm) | 70.7 ± 12.1 | 72.2 ± 11.0 | 0.21 |
| Ultrafiltration volume (L) | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 0.61 |
| Ultrafiltration rate (mL/kg/h) | 6.9 ± 3.7 | 6.4 ± 3.3 | 0.23 |
| Parameter | High-Protein Meal | Low-Protein Meal | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average intradialytic SBP (mmHg) | 127.1 ± 17.0 | 129.9 ± 18.3 | 0.24 |
| Intradialytic SBP-SD (mmHg) | 15.6 ± 7.6 | 14.1 ± 4.5 | 0.32 |
| Intradialytic SBP-CV (%) | 12.4 ± 6.0 | 11.1 ± 3.8 | 0.26 |
| Intradialytic SBP-ARV (mmHg) | 12.1 ± 5.2 | 10.9 ± 3.9 | 0.23 |
| Average intradialytic DBP (mmHg) | 79.0 ± 11.4 | 80.7 ± 12.9 | 0.26 |
| Intradialytic DBP-SD (mmHg) | 9.7 ± 0.9 | 8.6 ± 2.9 | 0.15 |
| Intradialytic DBP-CV (%) | 12.5 ± 5.7 | 11.0 ± 3.8 | 0.12 |
| Intradialytic DBP-ARV (mmHg) | 7.9 ± 3.1 | 7.3 ± 2.2 | 0.31 |
| Average intradialytic HR (bpm) | 72.9 ± 10.8 | 72.2 ± 11.0 | 0.60 |
| Ultrafiltration volume (L) | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 0.44 |
| Ultrafiltration rate (mL/kg/h) | 7.0 ± 3.3 | 6.4 ± 3.3 | 0.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fotiadou, E.; Georgianos, P.I.; Vaios, V.; Sgouropoulou, V.; Divanis, D.; Karligkiotis, A.; Leivaditis, K.; Chourdakis, M.; Zebekakis, P.E.; Liakopoulos, V. Feeding during Dialysis Increases Intradialytic Blood Pressure Variability and Reduces Dialysis Adequacy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071357
Fotiadou E, Georgianos PI, Vaios V, Sgouropoulou V, Divanis D, Karligkiotis A, Leivaditis K, Chourdakis M, Zebekakis PE, Liakopoulos V. Feeding during Dialysis Increases Intradialytic Blood Pressure Variability and Reduces Dialysis Adequacy. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071357
Chicago/Turabian StyleFotiadou, Elena, Panagiotis I. Georgianos, Vasilios Vaios, Vasiliki Sgouropoulou, Dimitrios Divanis, Apostolos Karligkiotis, Konstantinos Leivaditis, Michail Chourdakis, Pantelis E. Zebekakis, and Vassilios Liakopoulos. 2022. "Feeding during Dialysis Increases Intradialytic Blood Pressure Variability and Reduces Dialysis Adequacy" Nutrients 14, no. 7: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071357
APA StyleFotiadou, E., Georgianos, P. I., Vaios, V., Sgouropoulou, V., Divanis, D., Karligkiotis, A., Leivaditis, K., Chourdakis, M., Zebekakis, P. E., & Liakopoulos, V. (2022). Feeding during Dialysis Increases Intradialytic Blood Pressure Variability and Reduces Dialysis Adequacy. Nutrients, 14(7), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071357








