Trends in Prevalence, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension According to 40-Year-Old Life Expectancy at Prefectures in Japan from the National Health and Nutrition Surveys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Life Expectancy by Prefecture
2.3. Measurement and Definition of Hypertension
2.4. Statistical Analyses
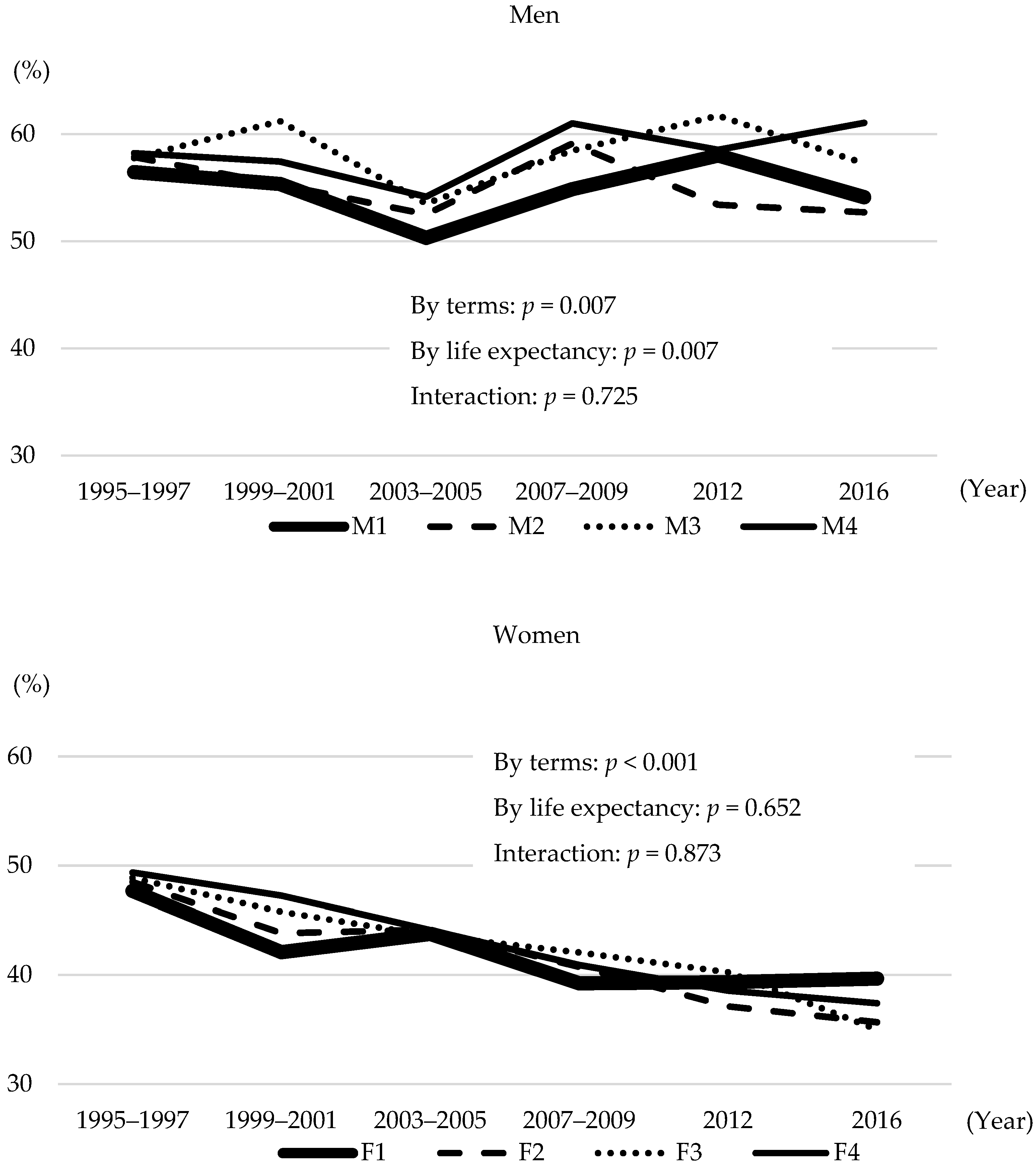
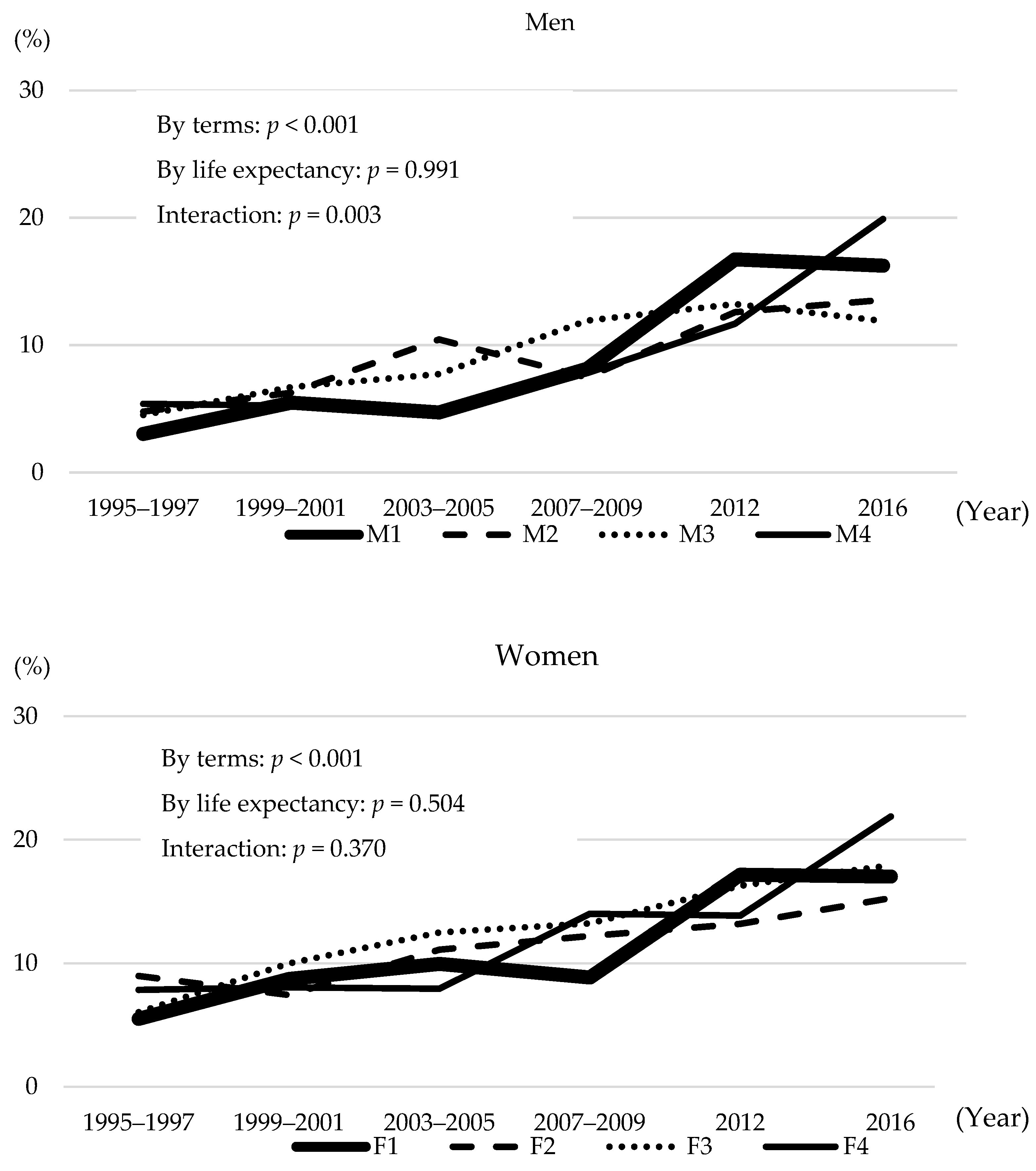
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stamler, J.; Stamler, R.; Neaton, J.D. Blood pressure, systolic and diastolic, and cardiovascular risks. US population data. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawes, C.M.; Rodgers, A.; Bennett, D.A.; Parag, V.; Suh, I.; Ueshima, H.; MacMahon, S.; Asia Pacific Cohort Studies Collaboration. Blood pressure and cardiovascular disease in the Asia Pacific region. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases Collaboration. Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes mortality burden of cardiometabolic risk factors from 1980 to 2010: A comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: A pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19·1 million participants. Lancet 2017, 389, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Nagai, M.; Ohkubo, T. Epidemiology of hypertension in Japan: Where are we now? Circ. J. 2013, 77, 2226–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan. Annual Report of the National Health and Nutrition Survey in 2020. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, Tokyo. 2020. Available online: http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/eiyou08/01.html (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). OECD Health Statistics 2021. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/health/health-data.htm (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Ikeda, N.; Inoue, M.; Iso, H.; Ikeda, S.; Satoh, T.; Noda, M.; Mizoue, T.; Imano, H.; Saito, E.; Katanoda, K.; et al. Adult mortality attributable to preventable risk factors for non-communicable diseases and injuries in Japan: A comparative risk assessment. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugane, S. Why has Japan become the world’s most long-lived country: Insights from a food and nutrition perspective. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezoe, S.; Noda, H.; Akahane, N.; Sato, O.; Hama, T.; Miyata, T.; Terahara, T.; Fujishita, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Abe, S.K.; et al. Trends in Policy on the Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases in Japan. Health Syst. Reform. 2017, 3, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Yamagishi, K.; Imano, H.; Kiyama, M.; Cui, R.; Ohira, T.; Umesawa, M.; Muraki, I.; Sankai, T.; Saito, I.; et al. Impact of Hypertension and Subclinical Organ Damage on the Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease Among Japanese Residents at the Population and Individual Levels—The Circulatory Risk in Communities Study (CIRCS). Circ. J. 2017, 81, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, H.; Suzuki, T.; Kojima, M.; Inoshita, E.; Lee, J.; Tanaka, S.; Fujiyoshi, A.; Hayakawa, T.; Miura, K. Factors related to life expectancy in prefectures: An ecological study using the National Database. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 2019, 66, 370–377. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, N.; Kitaoka, K.; Okami, Y.; Kondo, K.; Sata, M.; Kadota, A.; Nakamura, M.; Ojima, T.; Okamura, T.; Yoshita, K.; et al. Lifestyle trends in the National Health and Nutrition Survey according to life expectancy by prefecture. Jpn. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. Prev. 2021, 56, 258–264. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kitaoka, K.; Kadota, A.; Okami, Y.; Kondo, K.; Sata, M.; Nakamura, M.; Ojima, T.; Okamura, T.; Yoshita, K.; Nishi, N.; et al. Trends of nutrition intake in the National Health and Nutrition Survey according to life expectancy by prefecture. submitted. (In Japanese)
- Katanoda, K.; Matsumura, Y. National Nutrition Survey in Japan—Its methodological transition and current findings. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2002, 48, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, N.; Takimoto, H.; Imai, S.; Miyachi, M.; Nishi, N. Data Resource Profile: The Japan National Health and Nutrition Survey (NHNS). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Life Tables. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/seimei/list54-57-02.html (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- National Institute of Health and Nutrition. Section of the National Health and Nutrition Survey. Available online: https://www.nibiohn.go.jp/eiken/english/research/project_nhns.html (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Nishi, N.; Yoshizawa, T.; Okuda, N. Effects of rapid aging and lower participation rate among younger adults on the short-term trend of physical activity in the National Health and Nutrition Survey, Japan. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, N.; Saito, E.; Kondo, N.; Inoue, M.; Ikeda, S.; Satoh, T.; Wada, K.; Stickley, A.; Katanoda, K.; Mizoue, T.; et al. What has made the population of Japan healthy? Lancet 2011, 378, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, N.; Gakidou, E.; Hasegawa, T.; Murray, C.J. Understanding the decline of mean systolic blood pressure in Japan: An analysis of pooled data from the National Nutrition Survey, 1986–2002. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyoshi, A.; Ohkubo, T.; Miura, K.; Murakami, Y.; Nagasawa, S.Y.; Okamura, T.; Ueshima, H.; Observational Cohorts in Japan (EPOCH-JAPAN) Research Group. Blood pressure categories and long-term risk of cardiovascular disease according to age group in Japanese men and women. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Stubbs, R.W.; Morozoff, C.; Mackenbach, J.P.; van Lenthe, F.J.; Mokdad, A.H.; Murray CJL. Inequalities in Life Expectancy Among US Counties, 1980 to 2014: Temporal Trends and Key Drivers. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, R.; Emberson, J.; Fletcher, A.; Breeze, E.; Marmot, M.; Shipley, M.J. Life expectancy in relation to cardiovascular risk factors: 38 year follow-up of 19,000 men in the Whitehall study. BMJ 2009, 339, b3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hozawa, A.; Kuriyama, S.; Watanabe, I.; Kakizaki, M.; Ohmori-Matsuda, K.; Sone, T.; Nagai, M.; Sugawara, Y.; Nitta, A.; Li, Q.; et al. Participation in health check-ups and mortality using propensity score matched cohort analyses. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, T.; Sugiyama, D.; Tanaka, T.; Dohi, S. Worksite wellness for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in Japan: The current delivery system and future directions. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Statistics Office. Patient Survey, 2017. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/kanja/17/index.html (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Implementation Status of Specified Health Check-Ups and Specified Health Guidance in 2019. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/0000173202_00008.html (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Okamura, T.; Suzuki, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Terao, A.; Sato, S.; Kitamura, A.; Naito, Y.; Imano, H.; Tamura, Y.; Iida, M.; et al. Factors relate to participation in medical checkups in a rural community an analysis including social network scores. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 1999, 46, 616–623. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Miura, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Okamura, T.; Okuda, N.; Nishimura, K.; Yasumura, S.; Sakata, K.; Hidaka, H.; Okayama, A. Treated and untreated hypertension, hospitalization, and medical expenditure: An epidemiological study in 314622 beneficiaries of the medical insurance system in Japan. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliberti, M.J.R.; Szlejf, C.; Lima-Costa, M.F.; de Andrade, F.B.; Alexandre, T.S.; Ferri, C.P.; Suemoto, C.K. Frailty modifies the association of hypertension with cognition in older adults: Evidence from the ELSI-Brazil. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S. Health Labour Sciences Research: The Page of Healthy Life Expectancy. Available online: http://toukei.umin.jp/kenkoujyumyou/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).

| Men | Women | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | Year | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 |
| M1 | 38.84 | 39.65 | 40.58 | 41.34 | 42.21 | F1 | 44.96 | 46.26 | 47.23 | 47.7 | 48.12 |
| M2 | 38.47 | 39.33 | 40.27 | 40.92 | 41.96 | F2 | 44.43 | 45.76 | 46.81 | 47.31 | 47.87 |
| M3 | 38.12 | 38.97 | 39.84 | 40.62 | 41.58 | F3 | 44.29 | 45.48 | 46.53 | 47.08 | 47.62 |
| M4 | 37.68 | 38.45 | 39.3 | 40.09 | 41.17 | F4 | 43.8 | 45.14 | 46.19 | 46.73 | 47.32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sata, M.; Okamura, T.; Nishi, N.; Kadota, A.; Nakamura, M.; Kondo, K.; Okami, Y.; Kitaoka, K.; Ojima, T.; Yoshita, K.; et al. Trends in Prevalence, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension According to 40-Year-Old Life Expectancy at Prefectures in Japan from the National Health and Nutrition Surveys. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061219
Sata M, Okamura T, Nishi N, Kadota A, Nakamura M, Kondo K, Okami Y, Kitaoka K, Ojima T, Yoshita K, et al. Trends in Prevalence, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension According to 40-Year-Old Life Expectancy at Prefectures in Japan from the National Health and Nutrition Surveys. Nutrients. 2022; 14(6):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061219
Chicago/Turabian StyleSata, Mizuki, Tomonori Okamura, Nobuo Nishi, Aya Kadota, Mieko Nakamura, Keiko Kondo, Yukiko Okami, Kaori Kitaoka, Toshiyuki Ojima, Katsushi Yoshita, and et al. 2022. "Trends in Prevalence, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension According to 40-Year-Old Life Expectancy at Prefectures in Japan from the National Health and Nutrition Surveys" Nutrients 14, no. 6: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061219
APA StyleSata, M., Okamura, T., Nishi, N., Kadota, A., Nakamura, M., Kondo, K., Okami, Y., Kitaoka, K., Ojima, T., Yoshita, K., & Miura, K. (2022). Trends in Prevalence, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension According to 40-Year-Old Life Expectancy at Prefectures in Japan from the National Health and Nutrition Surveys. Nutrients, 14(6), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061219








