Embracing the Nutritional Assessment in Cerebral Palsy: A Toolkit for Healthcare Professionals for Daily Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Challenges While Registration Anthropometric Parameters: Questionnaire for Registers of Portuguese National Surveillance Program of Children with Cerebral Palsy
2.2. Challenges While Assessing Nutritional Status and Dealing with Feeding Problems: Meetings with Healthcare Professionals and Caregivers
2.3. Development of the Toolkit for Healthcare Professionals and Registers
3. Results
3.1. Difficulties Experienced by Registers of the Surveillance Program and Healthcare Professionals When Assessing Nutritional Status and Suggested Solutions
3.2. Difficulties Experienced by Caregivers When Dealing with Children’s Feeding Problems and Discussed Strategies to Minimize These Problems
3.3. Toolkit to Healthcare Professionals and Registers
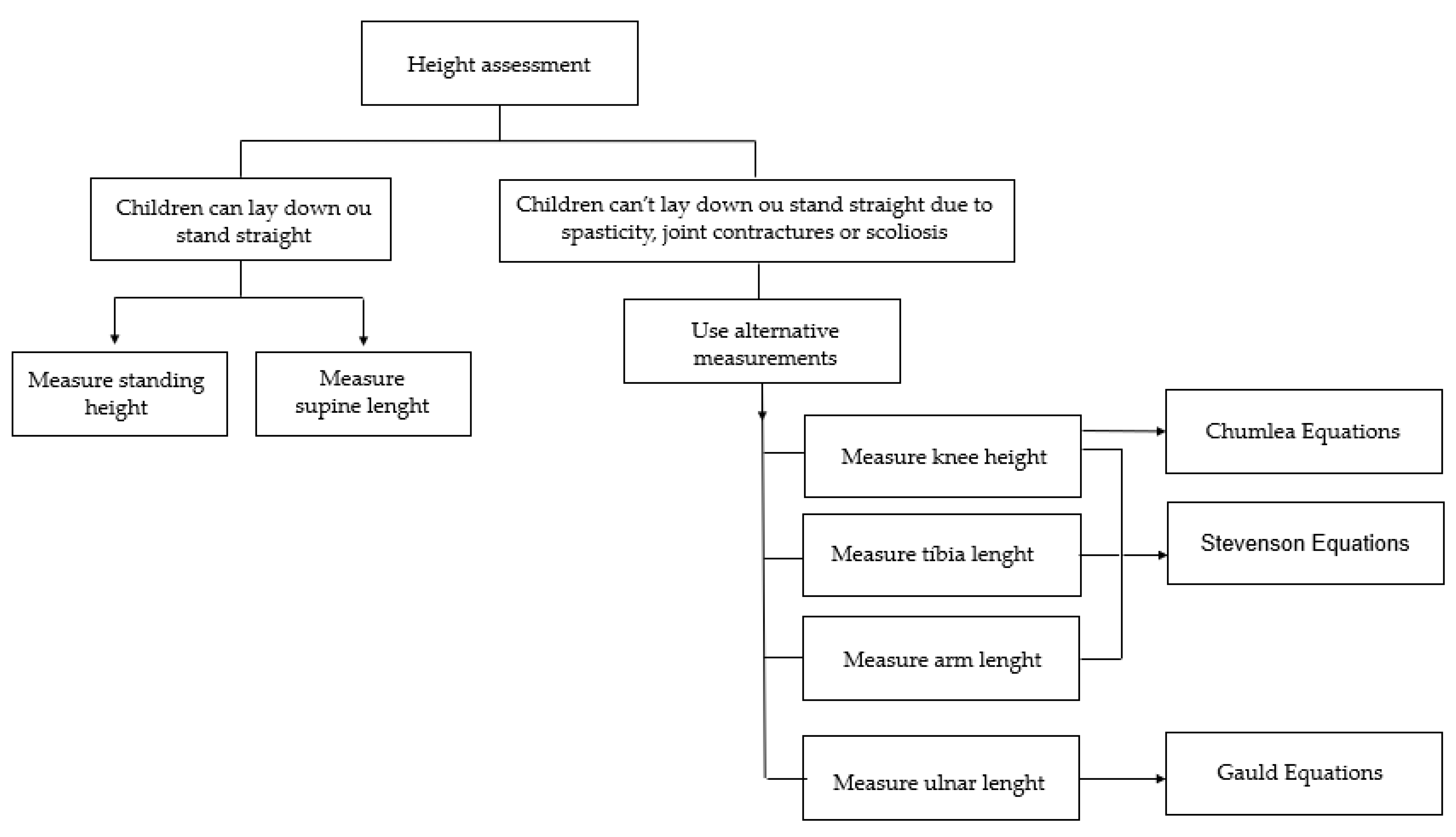
3.3.1. Weight Assessment
3.3.2. Height Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Levinton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A Report: The Definition and Classification of Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 49, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- te Velde, A.; Morgan, C.; Novak, I.; Tantsis, E.; Badawi, N. Early Diagnosis and Classification of Cerebral Palsy: An Historical Perspective and Barriers to an Early Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oftedal, S.; Davies, P.S.W.; Boyd, R.N.; Stevenson, R.D.; Ware, R.S.; Keawutan, P.; Benfer, K.A.; Bell, K.L. Longitudinal Growth, Diet, and Physical Activity in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatrics 2016, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rempel, G. The Importance of Good Nutrition in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 26, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohata, K.; Tsuboyama, T.; Haruta, T.; Ichihashi, N.; Nakamura, T. Longitudinal Change in Muscle and Fat Thickness in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2009, 51, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórska-Bednarz, J.; Perenc, L.; Drużbicki, M.; Guzik, A. Nutritional Disorders in a Group of Children and Adolescents with Syndromes or Diseases Involving Neurodysfunction. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperminc, M.N.; Gurka, M.J.; Bennis, J.A.; Busby, M.G.; Grossberg, R.I.; Henderson, R.C.; Stevenson, R.D. Anthropometric Measures: Poor Predictors of Body Fat in Children with Moderate to Severe Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barja, S.; Le Roy, C.; Sepúlveda, C.; Guzmán, M.L.; Olivarez, M.; Figueroa, M.J. Obesity and Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors among Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy. Nutr. Hosp. 2020, 37, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, E.B.; Samson-Fang, L.; Stallings, V.A.; Conaway, M.; Liptak, G.; Henderson, R.C.; Worley, G.; O’Donnell, M.; Calvert, R.; Rosenbaum, P.; et al. Feeding Dysfunction Is Associated with Poor Growth and Health Status in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2002, 102, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penagini, F.; Mameli, C.; Fabiano, V.; Brunetti, D.; Dilillo, D.; Zuccotti, G.V. Dietary Intakes and Nutritional Issues in Neurologically Impaired Children. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9400–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, I.; Muhit, M.; Karim, T.; Smithers-sheedy, H.; Novak, I.; Jones, C.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. What Makes Children with Cerebral Palsy Vulnerable to Malnutrition ? Findings from the Bangladesh Cerebral Palsy Register (BCPR). Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 41, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.L.; Bell, K.L.; Boyd, R.N.; Davies, P.S.W. Energy Requirements in Preschool-Age Children with Cerebral Palsy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvedson, J. Feeding Children with Cerebral Palsy and Swallowing Difficulties. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, S9–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, G.; Houlihan, C.M.; Herman-Giddens, M.E.; O’Donnell, M.E.; Conaway, M.; Stallings, V.A.; Chumlea, W.C.; Henderson, R.C.; Fung, E.B.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; et al. Secondary Sexual Characteristics in Children with Cerebral Palsy and Moderate to Severe Motor Impairment: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Pediatrics 2002, 110, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, S.; Adams, M.; O’banion, D.; Baltussen, M.; Asante, S.; Kerac, M.; Gladstone, M.; Zuurmond, M. Children with Cerebral Palsy in Ghana: Malnutrition, Feeding Challenges, and Caregiver Quality of Life. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huysentruyt, K.; Geeraert, F.; Allemon, H.; Prinzie, P.; Roelants, M.; Ortibus, E.; Vandenplas, Y.; De Schepper, J. Nutritional Red Flags in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snik, D.A.C.; Jongerius, P.H.; Roos, N.M.D.; Verschuren, O. Nutritional Care: The Poor Child of Clinical Care in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 12, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitadamo, P.; Thapar, N.; Staiano, A.; Borrelli, O. Gastrointestinal and Nutritional Problems in Neurologically Impaired Children. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ye, H.; Feng, Y.; Pan, L.Y.; Fu, H.H.; Liu, Y.M.; Fei, J.; Hong, L. Assessment of Nutritional Status in Paediatric Outpatients Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and Anthropometric Z-Scores. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 57, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snik, D.A.C.A.C.; de Roos, N.M.M. Criterion Validity of Assessment Methods to Estimate Body Composition in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, S.J.; Brekke, G.; Kok, K.; Sørensen, J.L.; Born, A.P.; Mølgaard, C.; Høi-Hansen, C.E. Nutritional Screening of Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: A Scoping Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivić, I.; Hojsak, I. Evaluation and Treatment of Malnutrition and Associated Gastrointestinal Complications in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, D.I.; Ricketts-Cameron, N.; Kecskemethy, H.H. Overview of Feeding and Growth in the Child with Cerebral Palsy. Cereb. Palsy 2020, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.; Day, S.; Shavelle, R.; Strauss, D. Low Weight, Morbidity, and Mortality in Children with Cerebral Palsy: New Clinical Growth Charts. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e299–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperminc, M.N.; Stevenson, R.D. Growth and Nutrition Disorders in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2008, 14, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virella, D.; Pennington, L.; Andersen, G.L.; Andrada, M.d.G.; Greitane, A.; Himmelmann, K.; Prasauskiene, A.; Rackauskaite, G.; De La Cruz, J.; Colver, A.; et al. Classification Systems of Communication for Use in Epidemiological Surveillance of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cans, C. Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe: A Collaboration of Cerebral Palsy Surveys and Registers. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 42, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, I.; Muhit, M.; Al Imam, M.H.; Ghose, R.; Chhetri, A.B.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Nutritional Status of Children with Cerebral Palsy in Gorkha, Nepal: Findings from the Nepal Cerebral Palsy Register. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virella, D.; Folha, T.; Andrada, M.d.G.; Cadete, A.; Gouveia, R.; Gaia, T.; Alvarelhão, J.; Calado, E. Paralisia Cerebral em Portugal no Século XXI–Indicadores Regionais Crianças Nascidas Entre 2001 e 2010, Registos de 2006 e 2015; Federação das Associações Portuguesas de Paralisia Cerebral: Lisboa, Portugal, 2018; ISBN 9789899828568. [Google Scholar]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A Scale for the Quality Assessment of Narrative Review Articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Brunner, M.d.l.M.; Cieri, M.E.; Butler, C.; Cuestas, E. Development of Equations and Software for Estimating Weight in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.D. Use of Segmental Measures to Estimate Stature in Children With Cerebral Palsy. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1995, 149, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumlea, W.M.C.; Guo, S.S.; Steinbaugh, M.L. Prediction of Stature from Knee Height for Black and White Adults and Children with Application to Mobility-Impaired or Handicapped Persons. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1994, 94, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauld, L.M.; Kappers, J.; Carlin, J.B.; Robertson, C.F. Height Prediction from Ulna Length. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2004, 46, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Silverman, A.H. Interdisciplinary Care for Feeding Problems in Children. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2010, 25, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.; Sá, L. Feeding a Child with Cerebral Palsy: Parents’ Difficulties. Rev. Enferm. Ref. 2016, 4, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.; Zhang, M.; Foster, J.; Novak, I.; Badawi, N. Caregivers’ Experiences of Feeding Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review Protocol of Qualitative Evidence. JBI Database Syst. Rev. Implement. Rep. 2018, 16, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwall, A.; Jewkes, R. What Is Participatory Research? Soc. Sci. Med. 1995, 41, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlou, N.; Peter, E. Participatory Action Research: Considerations for Ethical Review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2005, 60, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins Bloomberg, J.; Ii, A. A Field Guide to Designing a Health Communication Strategy. Available online: 2003http://ccp.jhu.edu/documents/A%20Field%20Guide%20to%20Designing%20Health%20Comm%20Strategy.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Kreuter, M.W.; McClure, S.M. The Role of Culture in Health Communication. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2004, 25, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpato, E.; Staiano, A.; Molteni, M.; Terrone, G.; Mazzocchi, A.; Agostoni, C. Nutritional Assessment and Intervention in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Practical Approach. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyer, R.; Cordier, R.; Kim, J.H.; Cocks, N.; Michou, E.; Wilkes-Gillan, S. Prevalence of Drooling, Swallowing, and Feeding Problems in Cerebral Palsy across the Lifespan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeffinger, D.J.; Gurka, M.J.; Kuperminc, M.; Hassani, S.; Buhr, N.; Tylkowski, C. Accuracy of Skinfold and Bioelectrical Impedance Assessments of Body Fat Percentage in Ambulatory Individuals with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, C.; van Wynckel, M.; Hulst, J.; Broekaert, I.; Bronsky, J.; Dall’Oglio, L.; Mis, N.F.; Hojsak, I.; Orel, R.; Papadopoulou, A.; et al. European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Gastrointestinal and Nutritional Complications in Children With Neurological Impairment. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 242–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dipasquale, V.; Catena, M.A.; Cardile, S.; Romano, C. Standard Polymeric Formula Tube Feeding in Neurologically Impaired Children: A Five-Year Retrospective Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurka, M.J.; Kuperminc, M.N.; Busby, M.G.; Bennis, J.A.; Grossberg, R.I.; Houlihan, C.M.; Stevenson, R.D.; Henderson, R.C. Assessment and Correction of Skinfold Thickness Equations in Estimating Body Fat in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoum, H.Y.; Badawy, N.B.; Hassan, N.E.; Alian, K.M. Anthropometry and Body Composition Analysis in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Iñiguez, J.A.; Vásquez-Garibay, E.M.; García-Contreras, A.; Romero-Velarde, E.; Troyo-Sanroman, R.; García Iñiguez, J.A.; Vásquez-Garibay, E.M.; García Contreras, A.; Romero-Velarde, E.; Troyo Sanromán, R. Assessment of Anthropometric Indicators in Children with Cerebral Palsy According to the Type of Motor Dysfunction and Reference Standard. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 212–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHANES Anthropometry Procedures Manual. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_07_08/manual_an.pdf. (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Frisancho, A.R. New Norms of Upper Limb Fat and Muscle Areas for Assessment of Nutritional Status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.G.; Going, S.B. Body Composition Assessment for Development of an International Growth Standard for Preadolescent and Adolescent Children. Food Nutr. Bull. 2006, 27, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Difficulties Experienced | Suggested Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Registers of the Surveillance Program |
|
|
| Healthcare professionals present in the meetings |
|
| Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Equations | Segmental Measures Needed | |
| Brunner equation [31] | If GMFCS level I–III: | Estimated Weight = 2.52 × MUAC(cm) + 1.19 × age (years) − 32 | MUAC—mid upper arm circumference |
| If GMFCS level IV–V: | Estimated Weight = 2.02 × MUAC(cm) + 0.97 × age (years) − 22.5 | ||
| Height | |||
| Stevenson [32] | Height = (4.35 × AL) + 21.8 | Arm length (AL) | |
| Height = (3.26 × TL) + 30.8 | Tibial length (TL) | ||
| Height = (2.69 × KH) + 24.2 | Knee height (KH) | ||
| Chumlea [33] | Caucasian boys | Height = 40.54 + (2.22 × KH) | Knee height |
| African-American boys | Height = 39.60 + (2.18 × KH) | ||
| Caucasian girls | Height = 43.21 + (2.15 × KH) | ||
| African-American girls | Height = 46.59 + (2.02 × KH) | ||
| Gauld [34] | Boys | Height = (4.605 × UL) + (1.308 × A) + 28.003 | Ulna lenght (UL) |
| Girls | Height = (4.459 ×UL) + (1.315 × A) + 31.485 | ||
| Slaughter’s Equations | Sum (triceps, subscapular) ≤ 35 mm | Boys | TSC * 1 e 2 TSB * 1 e 2 TSC 3 TSB 3 TSB 4 e 5 TSB 4 e 5 | % FM * = 1.21(TFS * + SUBF *) − 0.008(TFS + SUBF)2 − 1.7 % FM = 1.21(TFS + SUBF) − 0.008(TFS + SUBF)2 − 3.2 % FM = 1.21(TFS + SUBF) − 0.008(TFS + SUBF)2 − 3.4 % FM = 1.21(TFS + SUBF) − 0.008(TFS + SUBF)2 − 5.2 % FM = 1.21(TFS + SUBF) − 0.008(TFS + SUBF)2 −5.5 % FM = 1.21(TFS + SUBF) − 0.008(TFS + SUBF)2 − 6.8 |
| Girls | % FM = 1.33(TFS + SUBF) − 0.013(TFS + SUBF)2 − 2.5 | |||
| Sum (triceps, subscapular) > 35 mm | Boys | % FM = 0.783(TFS SUBF) + 1.6 | ||
| Girls | % FM = 0.546(TFS + SUBF) + 9.7 | |||
| Gurka’s Equations [47] | Additional correction for | Overall correction Males More severe GMFCS * Black race Tanner stage 3 Tanner stage 4 e 5 Sum(triceps, subscapular) > 35 mm | +12.2 −5.0 +5.1 −3.1 +2.0 −4.6 −3.2 | |
| Mid-upper arm muscle area | MMA * = (MUA C * (cm) − TFS * (mm) × 3.1416)2/(4 × 3.1416) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, C.; Borrego, R.; Eiró-Gomes, M.; Casimiro, I.; Raposo, A.; Folha, T.; Virella, D.; Moreira, A.C. Embracing the Nutritional Assessment in Cerebral Palsy: A Toolkit for Healthcare Professionals for Daily Practice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061180
Pinto C, Borrego R, Eiró-Gomes M, Casimiro I, Raposo A, Folha T, Virella D, Moreira AC. Embracing the Nutritional Assessment in Cerebral Palsy: A Toolkit for Healthcare Professionals for Daily Practice. Nutrients. 2022; 14(6):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061180
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Carolina, Rute Borrego, Mafalda Eiró-Gomes, Inês Casimiro, Ana Raposo, Teresa Folha, Daniel Virella, and Ana Catarina Moreira. 2022. "Embracing the Nutritional Assessment in Cerebral Palsy: A Toolkit for Healthcare Professionals for Daily Practice" Nutrients 14, no. 6: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061180
APA StylePinto, C., Borrego, R., Eiró-Gomes, M., Casimiro, I., Raposo, A., Folha, T., Virella, D., & Moreira, A. C. (2022). Embracing the Nutritional Assessment in Cerebral Palsy: A Toolkit for Healthcare Professionals for Daily Practice. Nutrients, 14(6), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061180







