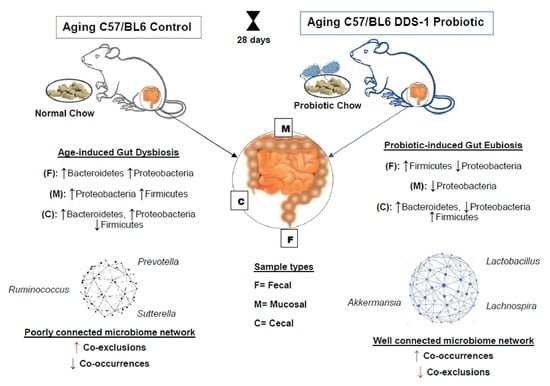
Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 Modulates the Gut Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks in Aging Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Probiotics
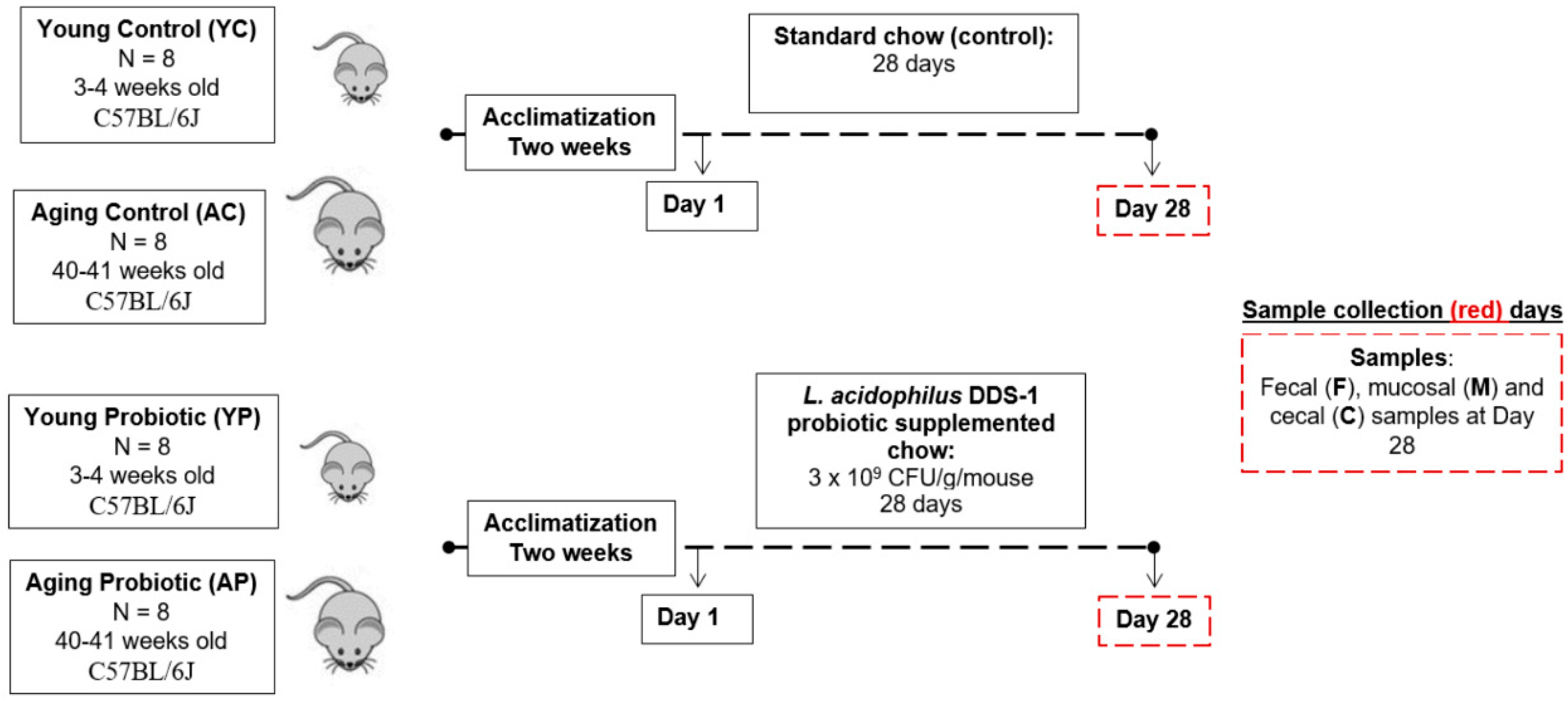
2.2. Animals
2.3. Design and Treatment
2.4. Sample Collections
2.5. 16S rRNA Sequencing and Microbiome Data Analysis
2.6. Gram Phenotype and Microbial Co-Occurrence Analyses
2.7. Multivariate and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Animal Health Characteristics
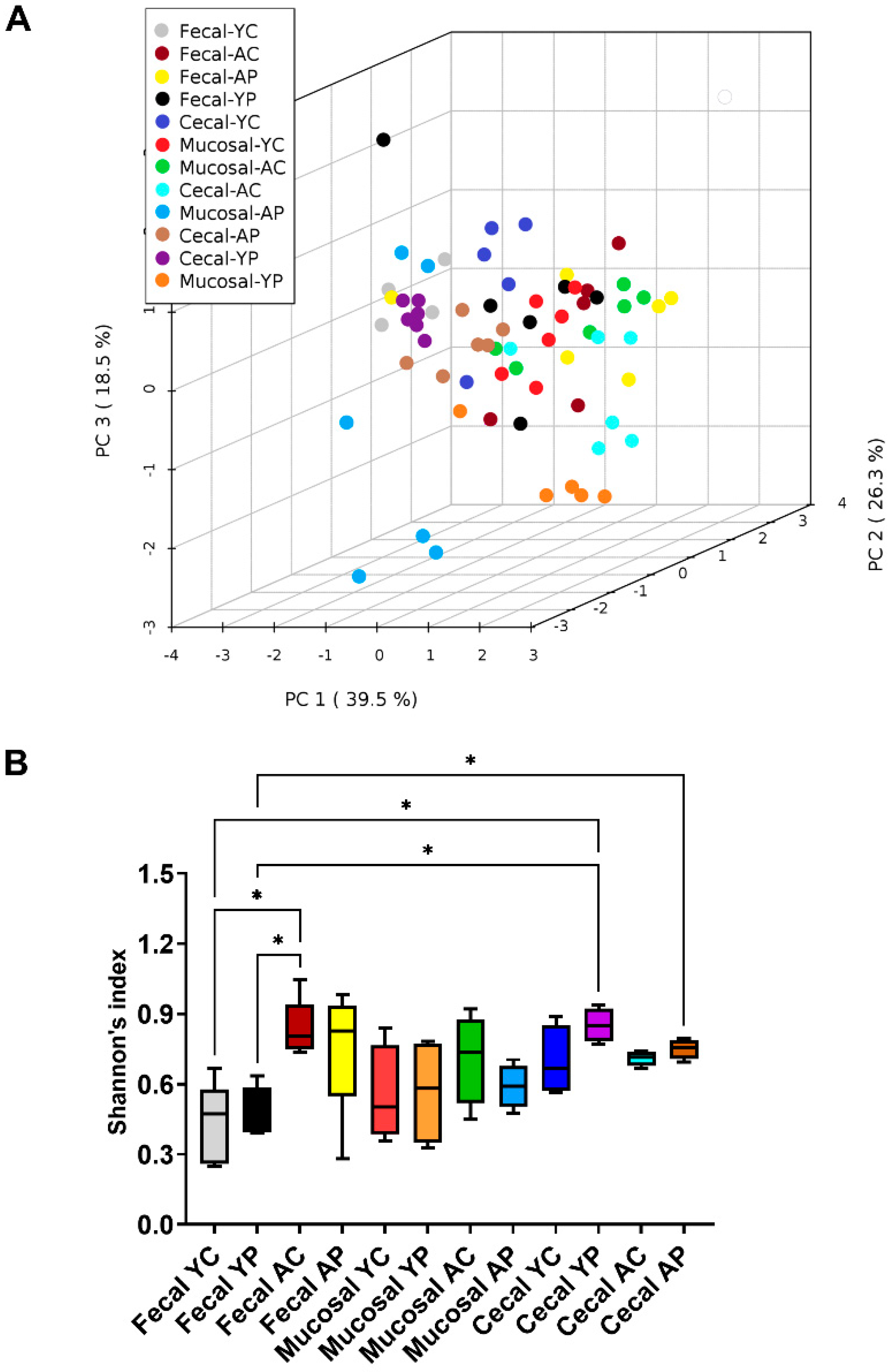
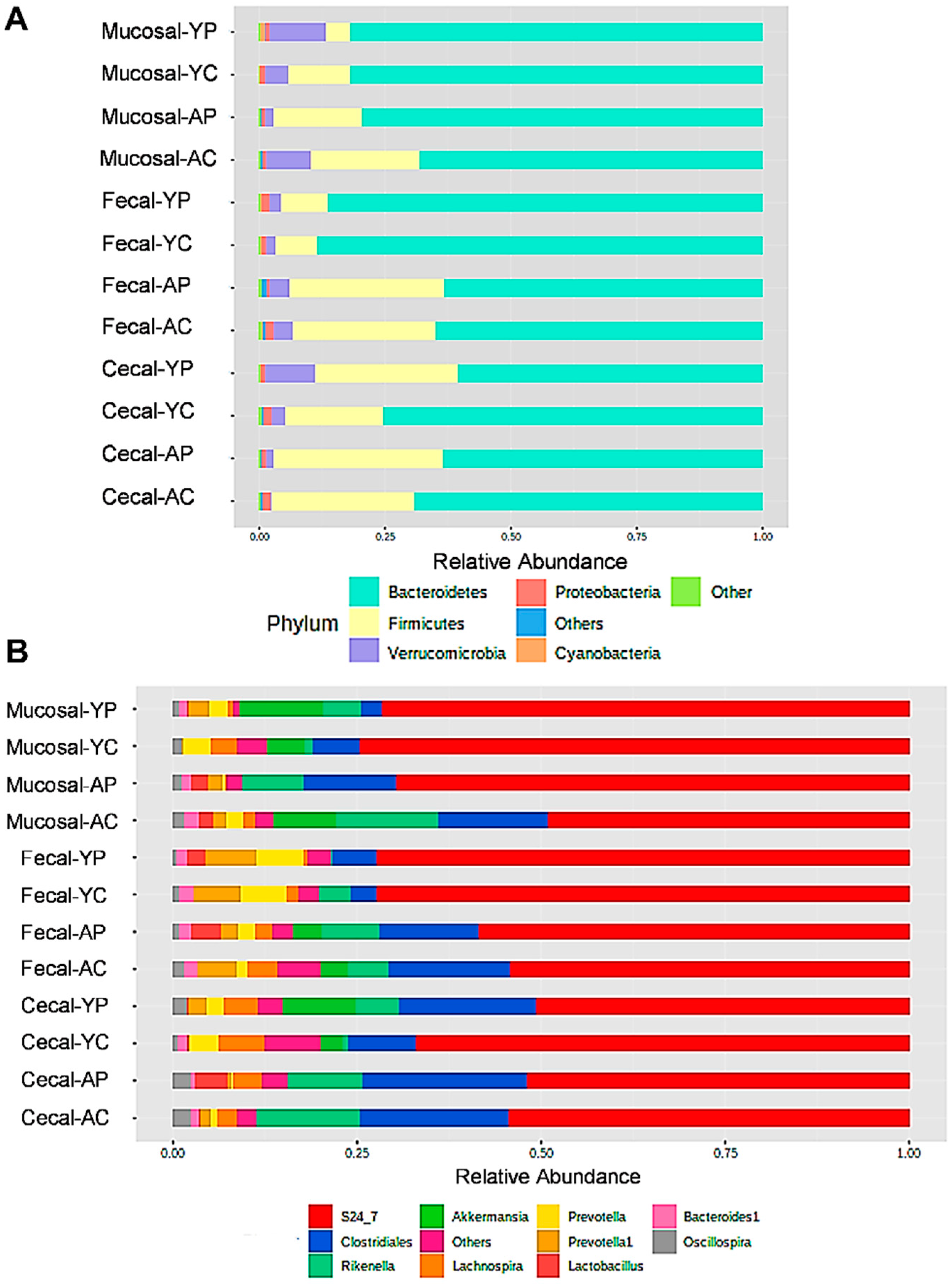
3.2. L. acidophilus DDS-1-Induced Alpha, Beta Diversity, and Taxonomic Profile Changes in Fecal, Mucosal, and Cecal Microbiomes
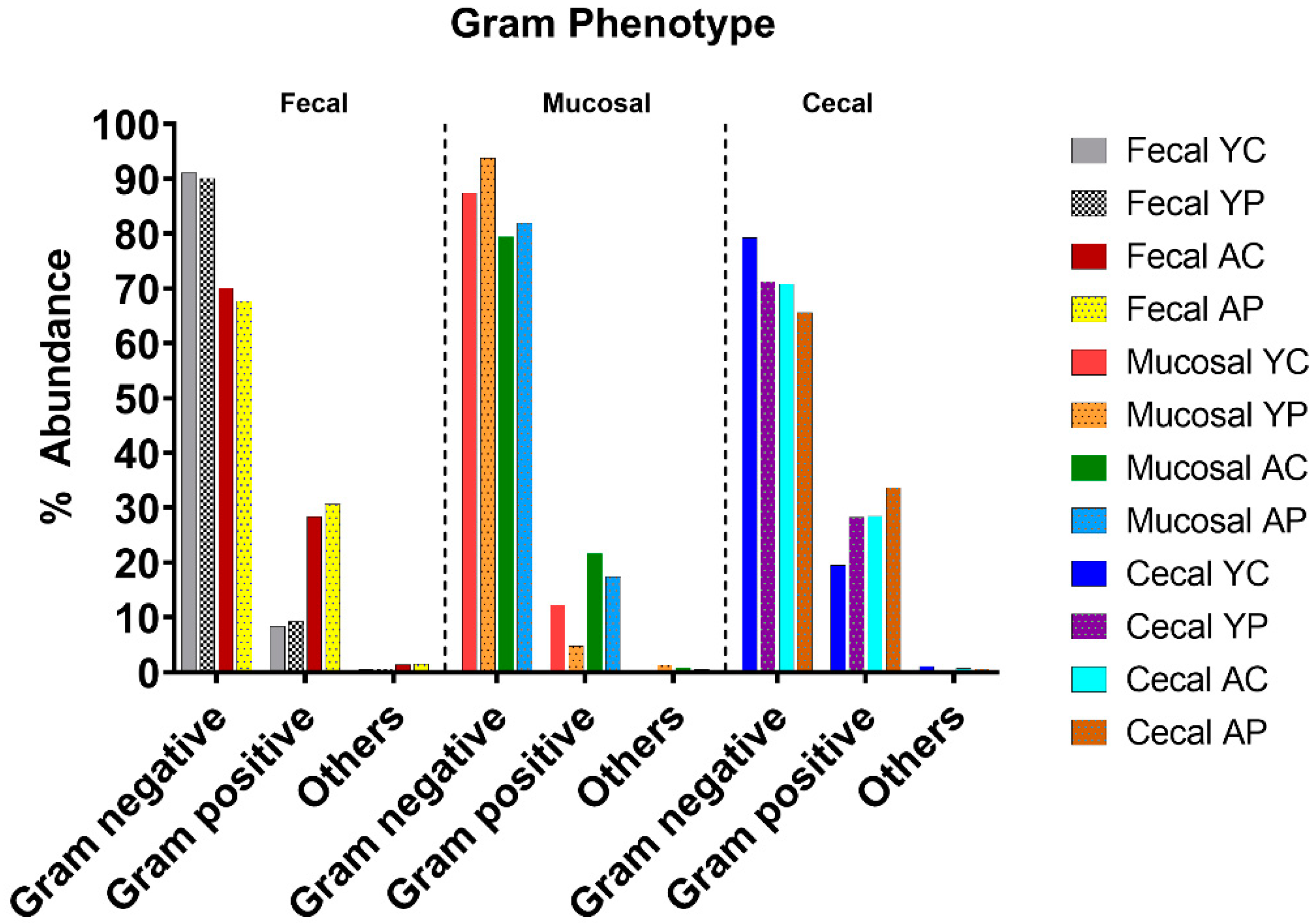
3.3. L. acidophilus DDS-1 Effect on Gram-Negative Bacteria in Aging Mice
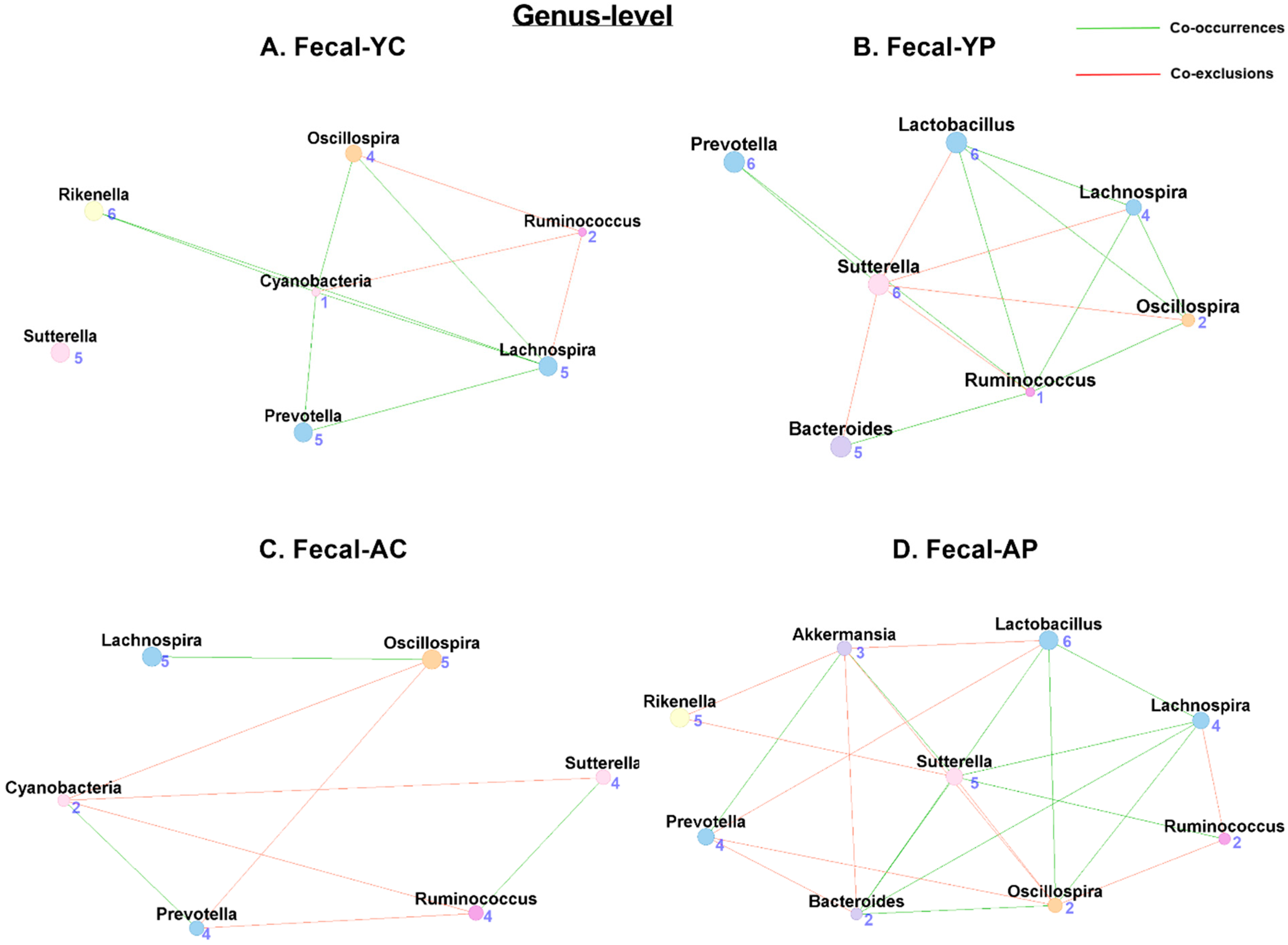
3.4. Age-Related Fecal Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Changes with L. acidophilus DDS-1
3.4.1. Phylum-Level Fecal Co-Occurrences
3.4.2. Genus-Level Fecal Co-Occurrences
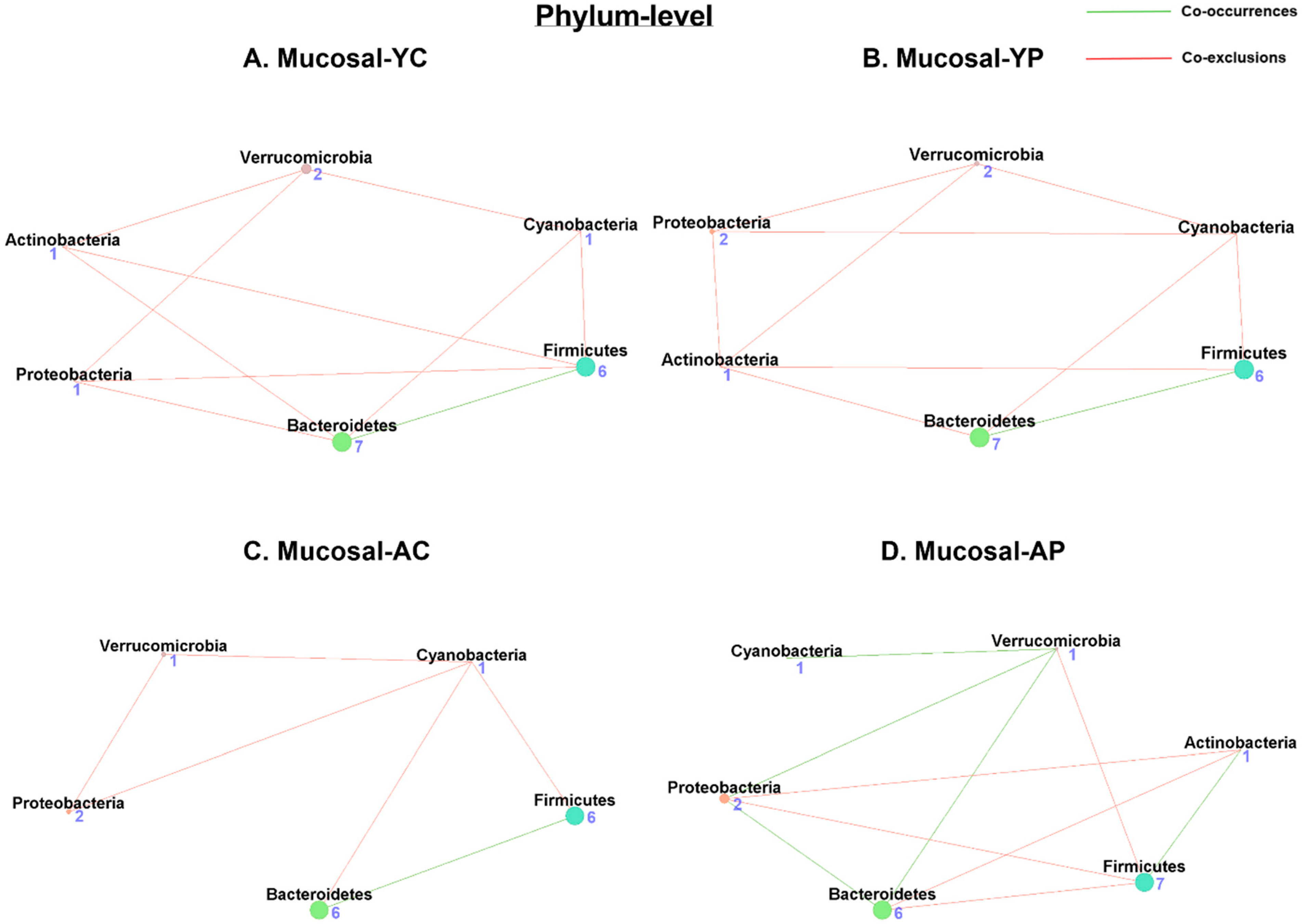
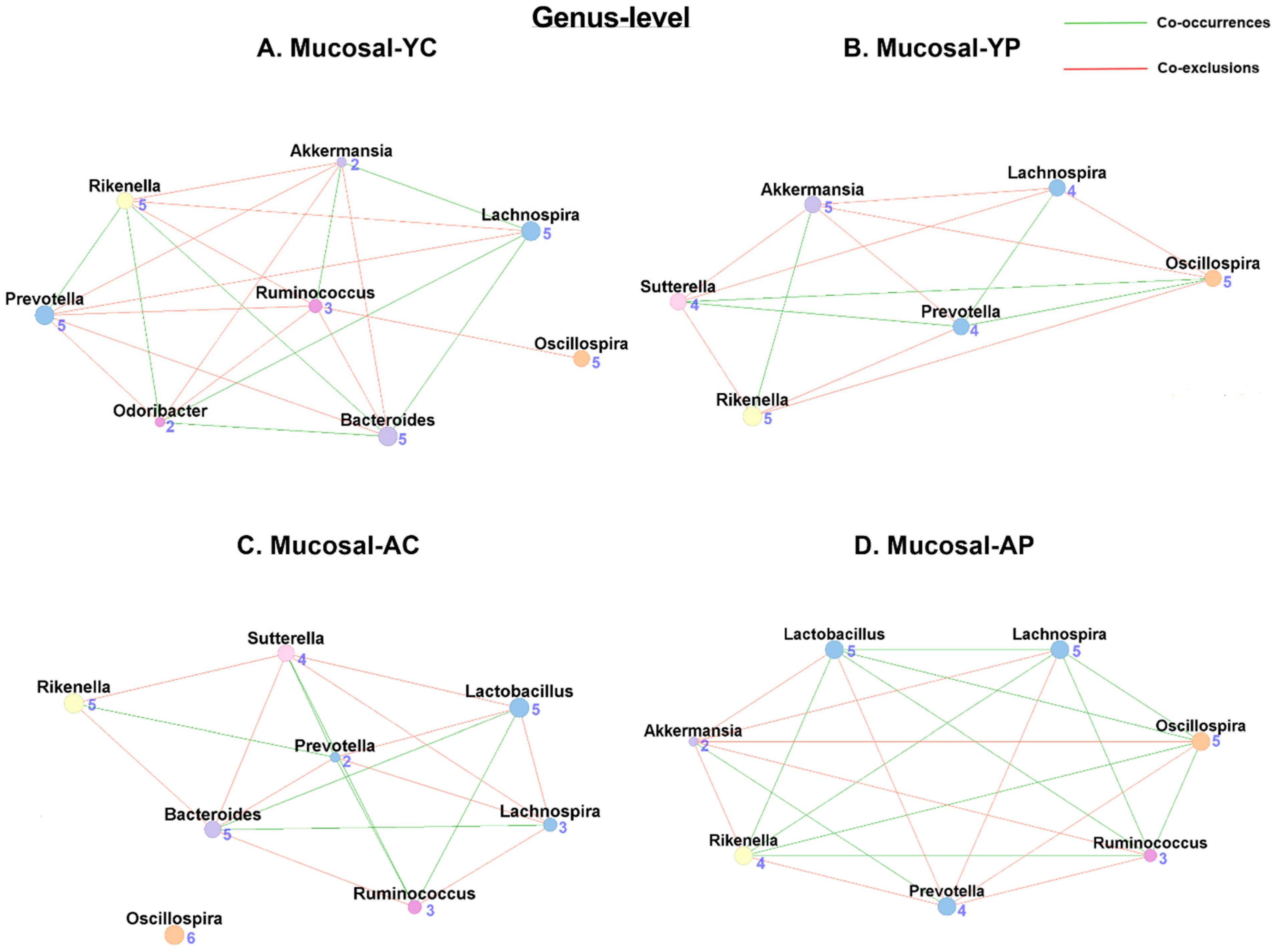
3.5. Age-Related Mucosal Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Changes with L. acidophilus DDS-1
3.5.1. Phylum-Level Mucosal Co-Occurrences
3.5.2. Genus-Level Mucosal Co-Occurrences
3.6. Age-Related Cecal Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Changes with DDS-1
3.6.1. Phylum-Level Cecal Co-Occurrences
3.6.2. Genus-Level Cecal Co-Occurrences
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vemuri, R.; Shankar, E.M.; Chieppa, M.; Eri, R.; Kavanagh, K. Beyond just bacteria: Functional biomes in the gut ecosystem including virome, mycobiome, archaeome and helminths. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vemuri, R.; Gundamaraju, R.; Shastri, M.D.; Shukla, S.D.; Kalpurath, K.; Ball, M.; Tristram, S.; Shankar, E.M.; Ahuja, K.; Eri, R. Gut microbial changes, interactions, and their implications on human lifecycle: An ageing perspective. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4178607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemuri, R.C.; Gundamaraju, R.; Shinde, T.; Eri, R. Therapeutic interventions for gut dysbiosis and related disorders in the elderly: Antibiotics, probiotics or faecal microbiota transplantation? Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, A.; Umeno, J.; Okamoto, Y.; Shibata, H.; Ogura, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Torisu, T.; Fujioka, S.; Fuyuno, Y.; Kawarabayasi, Y. Comparison of the microbial community structure between inflamed and non-inflamed sites in patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Nylund, L.; Candela, M.; Ostan, R.; Bucci, L.; Pini, E.; Nikkïla, J.; Monti, D.; Satokari, R.; Franceschi, C. Through ageing, and beyond: Gut microbiota and inflammatory status in seniors and centenarians. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, C.; Granata, I.; D’Argenio, V.; Tramontano, S.; Compare, D.; Guarracino, M.R.; Nardone, G.; Pilone, V.; Sacchetti, L. Characterization of the duodenal mucosal microbiome in obese adult subjects by 16S rRNA sequencing. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iljazovic, A.; Roy, U.; Gálvez, E.J.C.; Lesker, T.R.; Zhao, B.; Gronow, A.; Amend, L.; Will, S.E.; Hofmann, J.D.; Pils, M.C. Perturbation of the gut microbiome by Prevotella spp. enhances host susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Mucosal. Immunol. 2021, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, C.; Ciucci, S.; Palladini, A.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Zippo, A.G.; Sterbini, F.P.; Masucci, L.; Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Spuul, P. Nonlinear machine learning pattern recognition and bacteria-metabolite multilayer network analysis of perturbed gastric microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Chia, N.; O’Connor, H.M.; Wolf, P.G.; Gaskins, H.R.; Bharucha, A.E. Relationship between microbiota of the colonic mucosa vs feces and symptoms, colonic transit, and methane production in female patients with chronic constipation. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilhan, Z.E.; DiBaise, J.K.; Dautel, S.E.; Isern, N.G.; Kim, Y.-M.; Hoyt, D.W.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Brewer, H.M.; Weitz, K.K.; Metz, T.O. Temporospatial shifts in the human gut microbiome and metabolome after gastric bypass surgery. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sartor, R.B. Optimal sampling of the intestinal microbiota for research. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, Q.N.; Wells, M.; Davis, A.T.; Sherrill, C.; Tsilimigras, M.C.B.; Jones, R.B.; Fodor, A.A.; Kavanagh, K. Greater microbial translocation and vulnerability to metabolic disease in healthy aged female monkeys. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, E.L.; Davis, A.T.; Brass, K.; Dendinger, M.; Barner, R.; Gharaibeh, R.; Fodor, A.A.; Kavanagh, K. Reduced intestinal motility, mucosal barrier function, and inflammation in aged monkeys. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.J.; Jones, P.J.; Ammitzboll, H.; Barmuta, L.A.; Breed, M.F.; Chariton, A.; Charleston, M.; Dakwa, V.; Dewi, F.; Eri, R. Mainstreaming microbes across biomes. BioScience 2020, 70, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Baah-Acheamfour, M.; Carlyle, C.N.; Bissett, A.; Richardson, A.E.; Siddique, T.; Bork, E.W.; Chang, S.X. Determinants of bacterial communities in C anadian agroforestry systems. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, R.; Sherrill, C.; Davis, M.A.; Kavanagh, K. Age-Related Colonic Mucosal Microbiome Community Shifts in Monkeys. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 76, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Limenitakis, J.P.; Fuhrer, T.; Geuking, M.B.; Lawson, M.A.; Wyss, M.; Brugiroux, S.; Keller, I.; Macpherson, J.A.; Rupp, S.; et al. The outer mucus layer hosts a distinct intestinal microbial niche. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faust, K.; Sathirapongsasuti, J.F.; Izard, J.; Segata, N.; Gevers, D.; Raes, J.; Huttenhower, C. Microbial co-occurrence relationships in the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilli, J. Macroecological laws describe variation and diversity in microbial communities. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Collij, V.; Jaeger, M.; van den Munckhof, I.C.L.; Vila, A.V.; Kurilshikov, A.; Gacesa, R.; Sinha, T.; Oosting, M.; Joosten, L.A.B. Gut microbial co-abundance networks show specificity in inflammatory bowel disease and obesity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Rampelli, S.; Jeffery, I.B.; Santoro, A.; Neto, M.; Capri, M.; Giampieri, E.; Jennings, A.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S. Mediterranean diet intervention alters the gut microbiome in older people reducing frailty and improving health status: The NU-AGE 1-year dietary intervention across five European countries. Gut 2020, 69, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, Z.; Wu, Z.; Glick, B.R.; He, S.; Huang, C.; Wu, L. Co-occurrence patterns of microbial communities affected by inoculants of plant growth-promoting bacteria during phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, S.; Cao, W.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ding, A.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, J. Microbial diversity and co-occurrence patterns in deep soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, R.; Shinde, T.; Gundamaraju, R.; Gondalia, S.V.; Karpe, A.V.; Beale, D.J.; Martoni, C.J.; Eri, R. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 modulates the gut microbiota and improves metabolic profiles in aging mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vemuri, R.; Gundamaraju, R.; Shinde, T.; Perera, A.P.; Basheer, W.; Southam, B.; Gondalia, S.V.; Karpe, A.V.; Beale, D.J.; Tristram, S. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 modulates intestinal-specific microbiota, short-chain fatty acid and immunological profiles in aging mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavanagh, K.; Hsu, F.-C.; Davis, A.T.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Rejeski, W.J.; Kim, S. Biomarkers of leaky gut are related to inflammation and reduced physical function in older adults with cardiometabolic disease and mobility limitations. Geroscience 2019, 41, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderman, M.; Hugenholtz, F.; Belzer, C.; Boekschoten, M.; van Beek, A.; de Haan, B.; Faas, M. Sex and strain dependent differences in mucosal immunology and microbiota composition in mice. Biol. Sex Differ. 2018, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weger, B.D.; Gobet, C.; Yeung, J.; Martin, E.; Jimenez, S.; Betrisey, B.; Gachon, F. The mouse microbiome is required for sex-specific diurnal rhythms of gene expression and metabolism. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martoni, C.J.; Srivastava, S.; Leyer, G.J. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 and Bifidobacterium lactis UABla-12 improve abdominal pain severity and symptomology in irritable bowel syndrome: Randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- West, N.P.; Hughes, L.; Ramsey, R.; Zhang, P.; Martoni, C.J.; Leyer, G.J.; Cripps, A.W.; Cox, A.J. Probiotics, Anticipation Stress, and the Acute Immune Response to Night Shift. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemuri, R.; Shinde, T.; Shastri, M.D.; Perera, A.P.; Tristram, S.; Martoni, C.J.; Gundamaraju, R.; Ahuja, K.D.K.; Ball, M.; Eri, R. A human origin strain Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 exhibits superior in vitro probiotic efficacy in comparison to plant or dairy origin probiotics. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Layeghifard, M.; Hwang, D.M.; Guttman, D.S. Disentangling interactions in the microbiome: A network perspective. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Howe, A.; Hofmockel, K.S. Demonstrating microbial co-occurrence pattern analyses within and between ecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Zheng, P.; Gao, S.; Song, C.; Yu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wan, X. Gut microbiota-mediated improvement of metabolic disorders by Qingzhuan tea in high fat diet-fed mice. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 78, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota and metabolic disease: Current understanding and future perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.B.; Yassour, M.; Sauk, J.; Garner, A.; Jiang, X.; Arthur, T.; Lagoudas, G.K.; Vatanen, T.; Fornelos, N.; Wilson, R. A novel Ruminococcus gnavus clade enriched in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Meehan, C.J.; Koenig, J.E.; Dhanani, A.S.; Rose, R.A.; Howlett, S.E.; Beiko, R.G. Microbial shifts in the aging mouse gut. Microbiome 2014, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
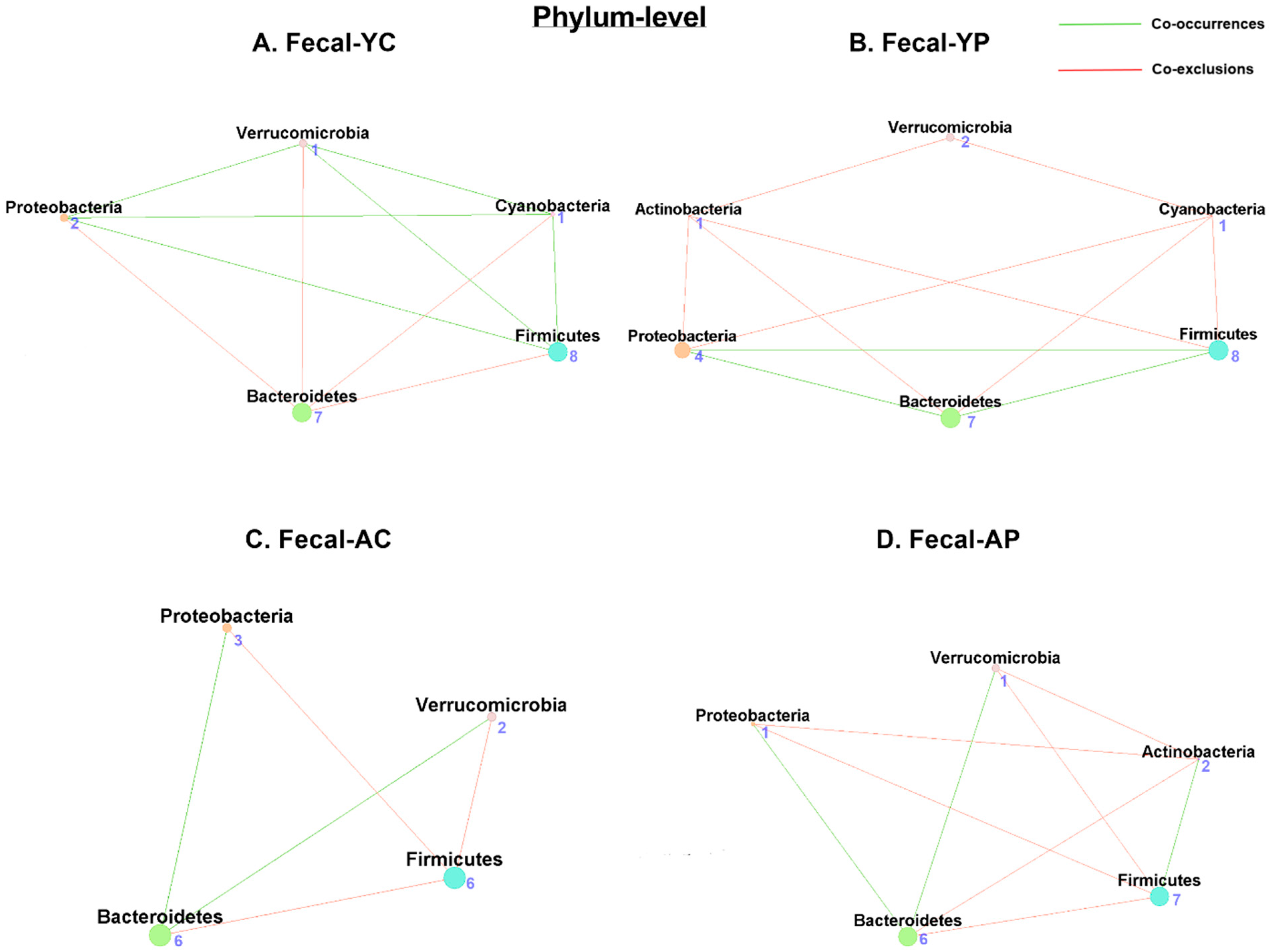



| Group | Co-Occurrences | Associations | Co-Exclusions | Associations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-YC | 0 | 0 | ||
| F-YP | 3 | Lactobacillus-Lachnospira Lactobacillus-Oscillospira Lactobacillus-Ruminococcus | 1 | Lactobacillus-Sutterella |
| F-AC | 0 | 0 | ||
| F-AP | 3 | Lactobacillus-Lachnospira Lactobacillus-Oscillospira Lactobacillus-Sutterella | 2 | Lactobacillus-Prevotella Lactobacillus-Akkermansia |
| M-YC | 0 | 0 | ||
| M-YP | 0 | 0 | ||
| M-AC | 2 | Lactobacillus-Ruminoccocus Lactobacillus-Bacteroides | 3 | Lactobacillus-Sutterella Lactobacillus-Lachnospira Lactobacillus-Prevotella |
| M-AP | 4 | Lactobacillus-Lachnospira Lactobacillus-Oscillospira Lactobacillus-Ruminococcus Lactobacillus-Rikenella | 2 | Lactobacillus-Prevotella Lactobacillus-Akkermansia |
| C-YC | 0 | 0 | ||
| C-YP | 5 | Lactobacillus-Prevotella Lactobacillus-Bacteroides Lactobacillus-Ruminococcus Lactobacillus-Oscillospira Lactobacillus-Sutterella | 4 | Lactobacillus-Akkermansia Lactobacillus-Odoribacter Lactobacillus-Lachnospira Lactobacillus-Rikenella |
| C-AC | 0 | 0 | ||
| C-AP | 2 | Lactobacillus-Oscillospira Lactobacillus-Prevotella | 5 | Lactobacillus-Sutterella Lactobacillus-Dorea Lactobacillus-Bacteroides Lactobacillus-Ruminococcus Lactobacillus-Rikenella |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vemuri, R.; Martoni, C.J.; Kavanagh, K.; Eri, R. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 Modulates the Gut Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks in Aging Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14050977
Vemuri R, Martoni CJ, Kavanagh K, Eri R. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 Modulates the Gut Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks in Aging Mice. Nutrients. 2022; 14(5):977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14050977
Chicago/Turabian StyleVemuri, Ravichandra, Christopher J. Martoni, Kylie Kavanagh, and Rajaraman Eri. 2022. "Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 Modulates the Gut Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks in Aging Mice" Nutrients 14, no. 5: 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14050977
APA StyleVemuri, R., Martoni, C. J., Kavanagh, K., & Eri, R. (2022). Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 Modulates the Gut Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks in Aging Mice. Nutrients, 14(5), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14050977