Dietetic-Led Nutrition Interventions in Patients with COVID-19 during Intensive Care and Ward-Based Rehabilitation: A Single-Center Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Sample
2.2. Nutritional Interventions
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
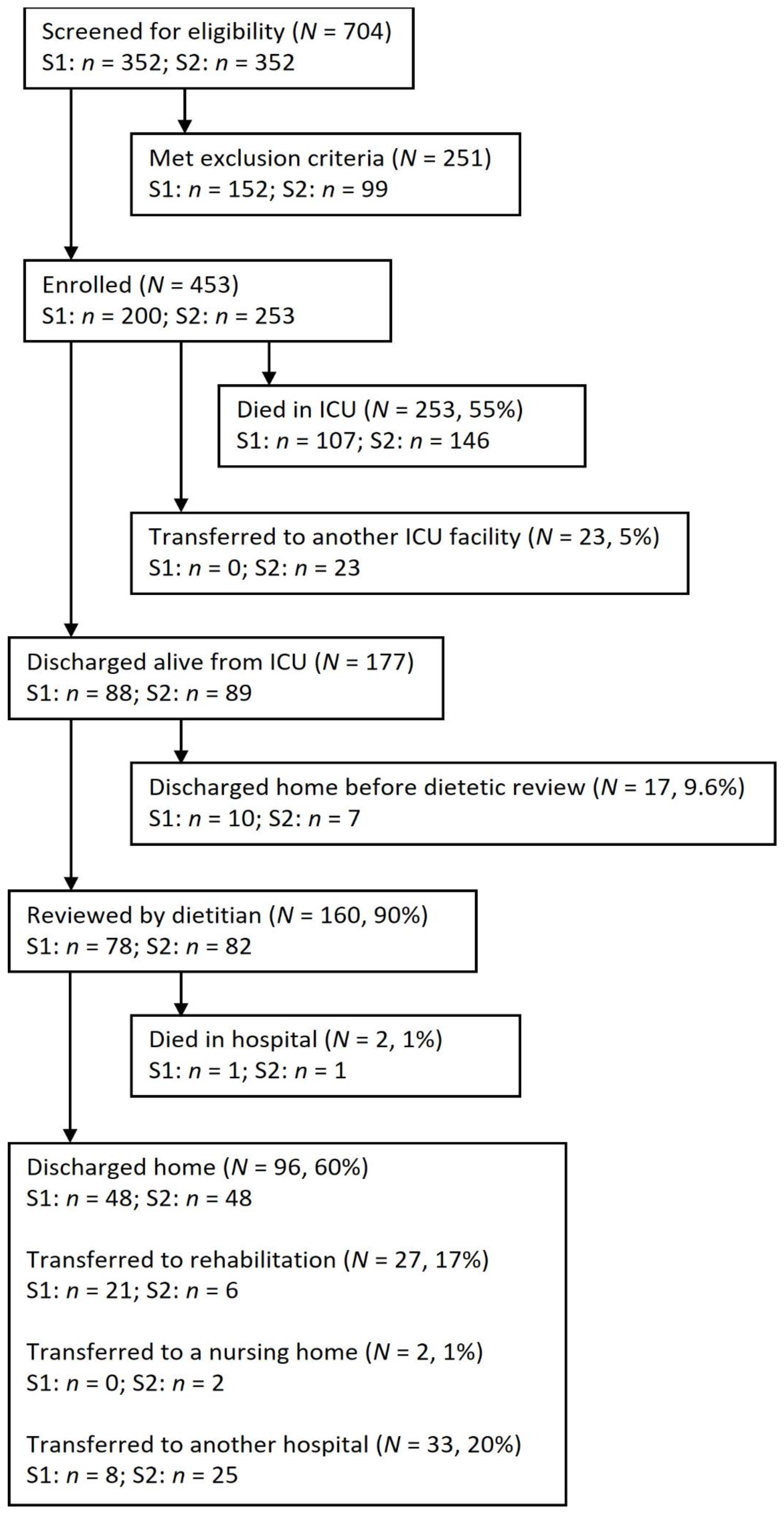
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Dietitian-Led Nutrition Interventions
3.3. Weight Loss
3.4. Dietetic-Led Nutrition Interventions after ICU Discharge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BDA. 2020. Available online: https://www.bda.uk.com/resource/critical-care-dietetics-guidance-covid-19.html (accessed on 23 October 2021).
- Bedock, D.; Bel Lassen, P.; Mathian, A.; Moreau, P.; Couffignal, J.; Ciangura, C.; Fadlallah, J.; Amoura, Z.; Oppert, J.-M.; Faucher, P.; et al. Prevalence and severity of malnutrition in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 40, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, T.; McAuliffe, S. Critical care nutrition and COVID-19: A cause of malnutrition not to be underestimated. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2021, 4, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, L.E.; Miller, H.; Haines, K.L.; Molinger, J.; Whittle, J.; MacLeod, D.B.; McClave, S.A.; Wischmeyer, P.E. Prolonged progressive hypermetabolism during COVID-19 hospitalization undetected by common predictive energy equations. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 45, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, J.; Molinger, J.; MacLeod, D.; Haines, K.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Group, L.-C.S. Persistent hypermetabolism and longitudinal energy expenditure in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapple, L.S.; Fetterplace, K.; Asrani, V.; Burrell, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Collins, P.; Doola, R.; Ferrie, S.; Marshall, R.N.A.P.; Ridley, E.J.; et al. Nutrition management for critically and acutely unwell hospitalised patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Australia and New Zealand. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 77, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barazzoni, R.; Bischoff, S.C.; Breda, J.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Krznaric, Z.; Nitzan, D.; Pirlich, M.; Singer, P. ESPEN expert statements and practical guidance for nutritional management of individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martindale, R.; Patel, J.J.; Taylor, B.; Arabi, Y.M.; Warren, M.; McClave, S.A. Nutrition Therapy in Critically Ill Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Watteville, A.; Montalbano, F.; Wozniak, H.; Collet, T.-H.; Jaksic, C.; Le Terrier, C.; Pugin, J.; Genton, L.; Heidegger, C.P. Impact of nutritional therapy during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in intensive care patients: A retrospective observational study. Clin. Nutr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, P.; Blaser, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Alhazzani, W.; Calder, P.C.; Casaer, M.P.; van Zanten, A.R.H.; Oczkowski, S.; Szczeklik, W.; Bischoff, S.C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 48–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.S.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition-A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- BAPEN. British Association of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (MUST). Available online: http://www.bapen.org.uk/pdfs/must/must_full.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2021).
- Rothpletz-Puglia, P.; Mena, M.D. Emergency preparedness in dietetics during a pandemic: Lessons learned from an ICU dietitian during COVID-19. Internet J. Allied Health Sci. Pract. 2021, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnelli, N.; Gibbs, L.; Larrivee, J.; Sahu, K.K. Challenges of maintaining optimal nutrition status in COVID-19 patients in intensive care settings. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Kulkarni, S.G. Evolution of COVID-19 management in critical care: Review and perspective from a hospital in the United Kingdom. Acute Crit. Care 2021, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, S.; Kozeniecki, M.; Knapp, N.; Martindale, R.G. Nutrition support during prone positioning: An old technique reawakened by COVID-19. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021, 36, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, D.; Rehm, M.; Conzen, P. Opioid-induced constipation in intensive care patients: Relief in sight? Crit. Care 2008, 12, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghorbanzadeh, K.; Ebadi, A.; Hosseini, M.; Madah, S.S.B.; Khankeh, H. Challenges of the patient transition process from the intensive care unit: A qualitative study. Acute Crit. Care 2021, 36, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient Characteristics | All Patients n = 453 | S1 n = 200 | S2 n = 253 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 61 (12.4) | 57.9 (12.7) | 62.5 (12.0) | 0.001 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 315 (70) | 135 (67) | 180 (71) | 0.44 |
| Weight (kg), mean (SD) | 84 (20) | 86 (21) | 84 (19.4) | 0.32 |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 29 (6.3) | 29 (6.5) | 29 (6.1) | 0.82 |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | ||||
| White | 114 (25) | 46 (23) | 68 (27) | 0.34 |
| Asian | 96 (21) | 41 (21) | 55 (21) | 0.85 |
| Black | 71 (16) | 36 (18) | 35 (14) | 0.22 |
| Other ethnic groups | 48 (11) | 23 (12) | 25 (10) | 0.57 |
| Not stated | 124 (27) | 54 (27) | 70 (28) | 0.87 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||||
| Nil or 1 | 90 (20) | 50 (25) | 40 (16) | 0.02 |
| More than 2 | 362 (80) | 150 (75) | 212 (84) | |
| APACHE II, mean (SD) | 15.1 (6.8) | 15.5 (7.3) | 14.8 (6.5) | 0.32 |
| ICU mortality, n (%) | 253 (55) | 107 (54) | 146 (57) | 0.37 |
| ICU length of stay (days), mean (SD) | 20 (18) | 18.1 (14.4) | 22.3 (21.2) | 0.02 |
| Total hospital stay (days), mean (SD) | 35.6 (21) | 33.8 (19.7) | 37.4 (22.85) | 0.2 |
| Intervention | n = 453 n (%) | S1 n = 200 n (%) | S2 n = 253 n (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed adjustment to meet energy needs for the different metabolic phases | 337 (74) | 141 (71) | 196 (78) | 0.09 |
| Feed adjustment to account for calories derived from propofol sedation > 15 mL/h (360 kCals/24 h) | 248 (55) | 144 (72) | 104 (41) | 0.001 |
| Feed adjustment for gastrointestinal dysfunction | 154 (34) | 47 (24) | 107 (42) | 0.001 |
| Transition from EN to oral diet | 146 (32) | 62 (31) | 84 (33) | 0.62 |
| Feed adjustment due to changes in renal function, fluid status, or electrolyte balance | 120 (26) | 73 (37) | 47 (19) | 0.001 |
| Feed adjustment to allow feed interruption for drug absorption of medication given via the enteral route | 18 (4) | 6 (3) | 12 (5) | 0.34 |
| All n = 160 | S1 n = 78 | S2 n = 82 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICU admission weight (kg) | 85 (20.1) | 86 (21) | 84 (19.4) | 0.32 |
| ICU admission BMI (kg/m2) | 29 (6.3) | 29 (6.5) | 29 (6.1) | 0.82 |
| ICU weight loss (kg) | 7.9 (6.8) | 7.8 (7.8) | 8.1 (5.9) | 0.80 |
| ICU weight loss % | 8.8 (6.9) | 8.5 (7.7) | 9.0 (6.3) | 0.65 |
| Percentage ICU weight loss n (%) | ||||
| <5% | 58 (35) | 30 (41) | 36 (40) | 0.22 |
| 5–10% | 57 (34) | 27 (36) | 27 (30) | |
| >10% | 53 (32) | 22 (30) | 26 (29) | |
| Total weight loss (kg) from ICU admission to hospital discharge | 7.5 (6.6) | 8.0 (7.4) | 7.3 (6.1) | 0.70 |
| Nutrition Intervention | n = 160 n (%) | S1 n =78 n (%) | S2 n = 82 n (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exclusive EN | 36 (23) | 14 (18) | 22 (27) | 0.17 |
| Supplementary EN | 70 (44) | 38 (49) | 32 (39) | 0.21 |
| Exclusive and supplementary EN combined | 106 (66) | 52 (67) | 54 (66) | 0.91 |
| ONS | 68 (43) | 34 (44) | 34 (42) | 0.78 |
| Texture modification | 34 (21) | 23 (29) | 11 (13) | 0.01 |
| Diet alone | 33 (21) | 21 (27) | 12 (14) | 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terblanche, E.; Hills, J.; Russell, E.; Lewis, R.; Rose, L. Dietetic-Led Nutrition Interventions in Patients with COVID-19 during Intensive Care and Ward-Based Rehabilitation: A Single-Center Observational Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051062
Terblanche E, Hills J, Russell E, Lewis R, Rose L. Dietetic-Led Nutrition Interventions in Patients with COVID-19 during Intensive Care and Ward-Based Rehabilitation: A Single-Center Observational Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(5):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051062
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerblanche, Ella, Jessica Hills, Edie Russell, Rhiannon Lewis, and Louise Rose. 2022. "Dietetic-Led Nutrition Interventions in Patients with COVID-19 during Intensive Care and Ward-Based Rehabilitation: A Single-Center Observational Study" Nutrients 14, no. 5: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051062
APA StyleTerblanche, E., Hills, J., Russell, E., Lewis, R., & Rose, L. (2022). Dietetic-Led Nutrition Interventions in Patients with COVID-19 during Intensive Care and Ward-Based Rehabilitation: A Single-Center Observational Study. Nutrients, 14(5), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051062






