Gut Microbiota Composition in Relation to the Metabolism of Oral Administrated Resveratrol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bacterial Propagation
2.3. Establishment of Bacterial Colonized Germ-Free Mouse Model
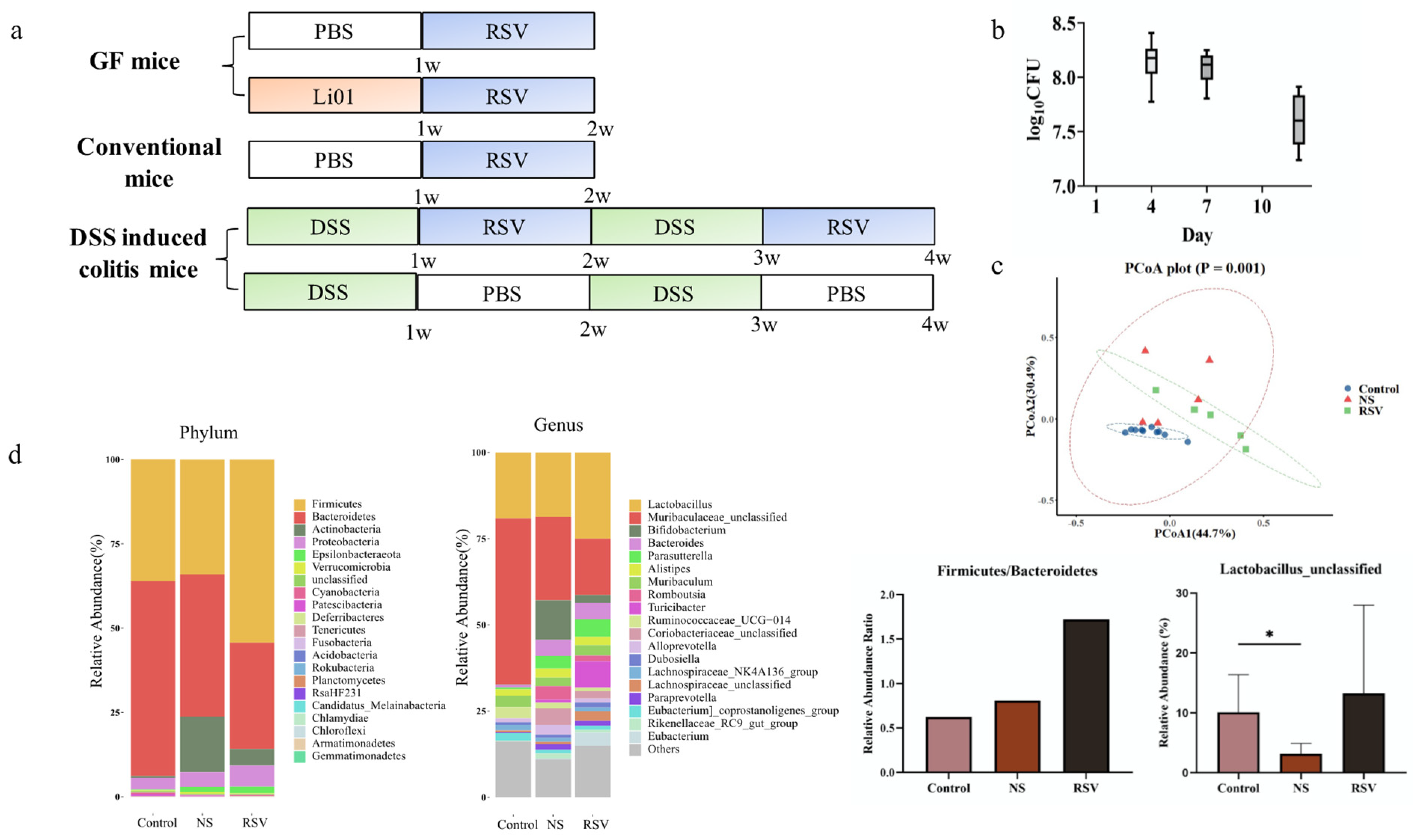
2.4. RSV Metabolism in Conventional Mice
2.5. RSV Metabolism in DSS-Induced Colitis Model
2.6. 16SrDNA Genes-Based Metagenomics
2.7. Extraction and LC-MS/MS Analysis of RSV and Its Metabolites
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
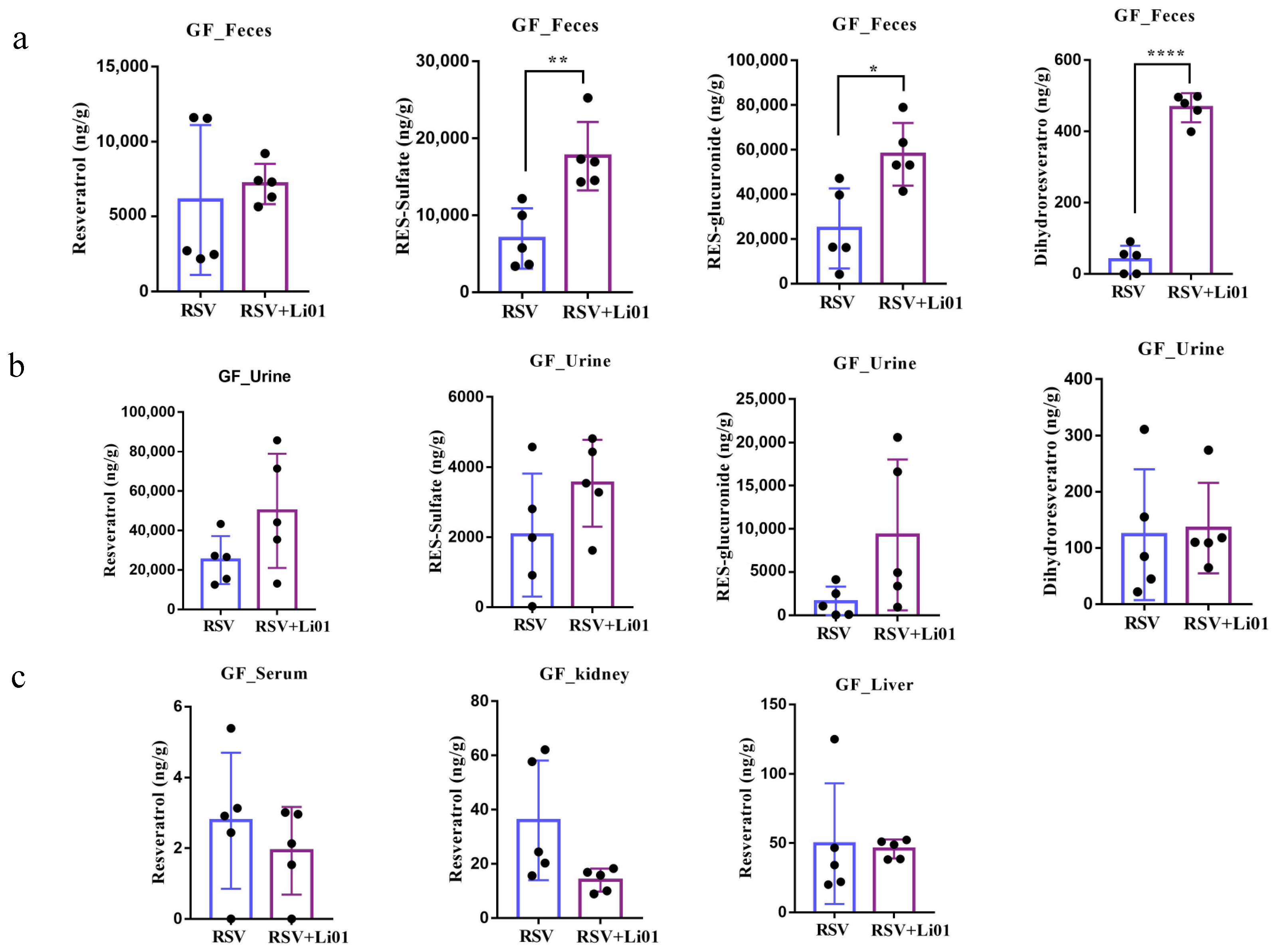
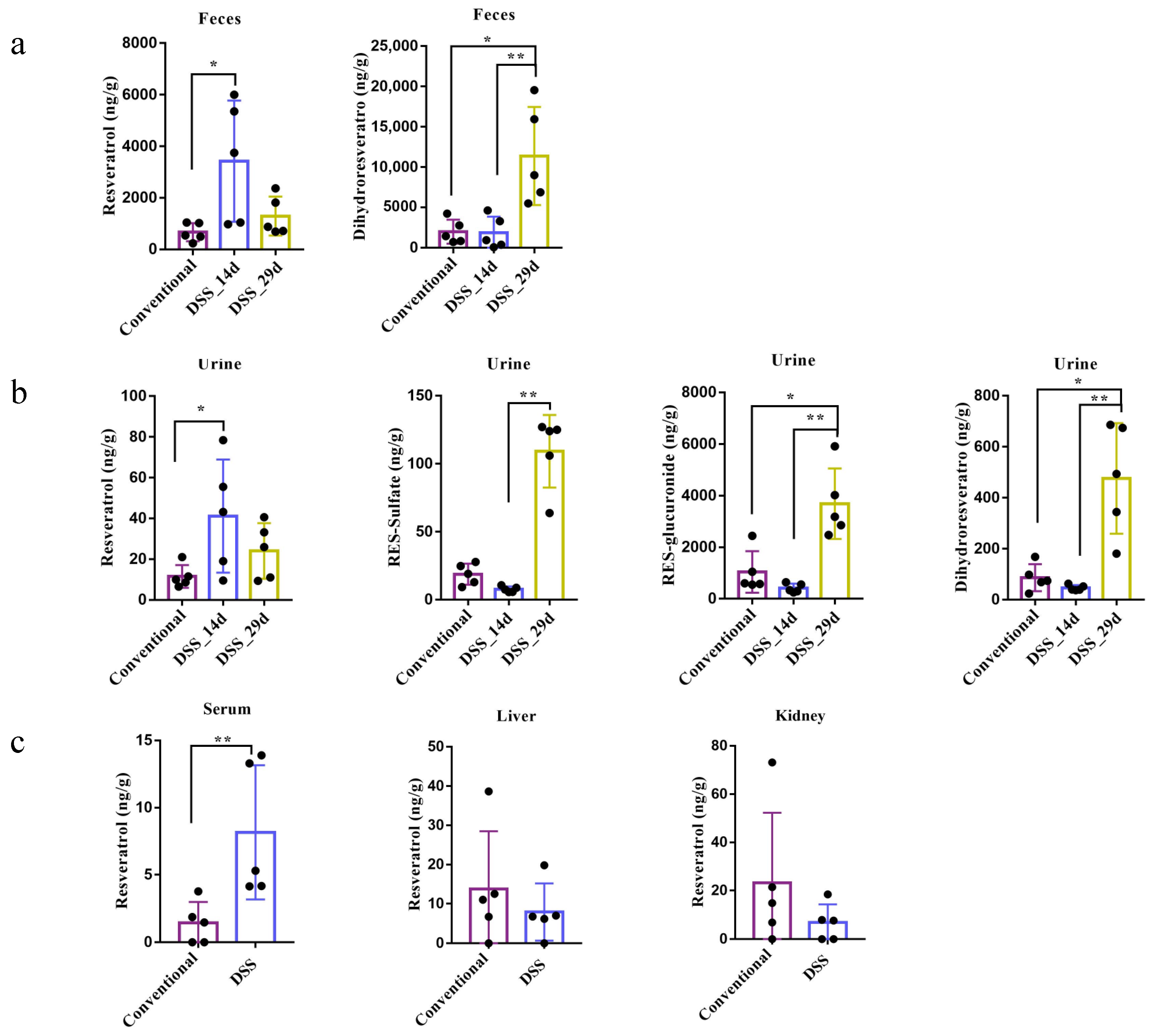
3.1. Quantification of RSV and RSV Metabolites
3.2. Gut Microbiota Composition in Different Mouse Models
3.3. RSV Metabolism in Germ-Free Mouse Model
3.4. Resveratrol Metabolism in Conventional Mice and DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dogan, A.; Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Kempińska-Kupczyk, D.; Namieśnik, J.; Kot-Wasik, A. Detection, identification and determination of chiral pharmaceutical residues in wastewater: Problems and challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.K.; Luo, J.Y.; Lau, C.W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Tian, X.Y.; Huang, Y. Pharmacological basis and new insights of resveratrol action in the cardiovascular system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1258–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.S.; Lai, P.F.; Kuo, C.H.; Day, C.H.; Chen, R.J.; Ho, T.J.; Yeh, Y.L.; Mahalakshmi, B.; Padmaviswanadha, V.; Kuo, W.W.; et al. Resveratrol enhances therapeutic effect on pancreatic regeneration in diabetes mellitus rats receiving autologous transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells. Chin. J. Physiol. 2020, 63, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Ma, F.; Wang, X.; Li, G. Combination of dihydroartemisinin and resveratrol effectively inhibits cancer cell migration via regulation of the DLC1/TCTP/Cdc42 pathway. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9573–9584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Han, Y.; Cai, X.; Gu, M.; Sun, J.; Qi, C.; Goulette, T.; Song, M.; Li, Z.; Xiao, H. Dietary resveratrol attenuated colitis and modulated gut microbiota in dextran sulfate sodium-treated mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, M.; Lu, F.; He, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, T. Dual Strategy for Improving the Oral Bioavailability of Resveratrol: Enhancing Water Solubility and Inhibiting Glucuronidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9249–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullon-Vela, V.; Abete, I.; Zulet, M.A.; Xu, Y.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Sayon-Orea, C.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Toledo, E.; Sanchez, V.M.; Estruch, R.; et al. Urinary Resveratrol Metabolites Output: Differential Associations with Cardiometabolic Markers and Liver Enzymes in House-Dwelling Subjects Featuring Metabolic Syndrome. Molecules 2020, 25, 4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shin, Y.G.; Chow, A.; Li, Y.; Kosmeder, J.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Hirschelman, W.H.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Mehta, R.G.; van Breemen, R.B. Human, rat, and mouse metabolism of resveratrol. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Andreadi, C.; Britton, R.G.; Horner-Glister, E.; Karmokar, A.; Sale, S.; Brown, V.A.; Brenner, D.E.; Singh, R.; Steward, W.P.; et al. Sulfate metabolites provide an intracellular pool for resveratrol generation and induce autophagy with senescence. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 205ra133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tome-Carneiro, J.; Larrosa, M.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Espin, J.C. Resveratrol and clinical trials: The crossroad from in vitro studies to human evidence. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6064–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, T.T.; Ye, X.L.; Li, R.R.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yong, H.J.; Pan, M.L.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Miao, H.; et al. Resveratrol Modulates the Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Protect Against Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, L.M.; Bunzel, D.; Huch, M.; Cho, G.S.; Ruhland, D.; Bunzel, M.; Bub, A.; Franz, C.M.; Kulling, S.E. In vivo and in vitro metabolism of trans-resveratrol by human gut microbiota. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.F.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J.; Li, L.J. Microencapsulation of Lactobacillus salivarious Li01 for enhanced storage viability and targeted delivery to gut microbiota. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qv, L.; Yang, Z.; Yao, M.; Mao, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Methods for Establishment and Maintenance of Germ-Free Rat Models. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.G. Components of the AIN-93 diets as improvements in the AIN-76A diet. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 838S–841S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, J.B.; Stedmon, C.A.; Kellerman, A.M.; Nielsen, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Laudon, H.; Lindström, E.S.; Kritzberg, E.S. Experimental insights into the importance of aquatic bacterial community composition to the degradation of dissolved organic matter. ISME J. 2016, 10, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shin, Y.G.; Yu, C.; Kosmeder, J.W.; Hirschelman, W.H.; Pezzuto, J.M.; van Breemen, R.B. Increasing the throughput and productivity of Caco-2 cell permeability assays using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Application to resveratrol absorption and metabolism. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 2003, 6, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.M.; Yan, J.; Soleas, G.J. Absorption of three wine-related polyphenols in three different matrices by healthy subjects. Clin. Biochem. 2003, 36, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T.; Hsieh, F.; DeLegge, M.H.; Oatis, J.E., Jr.; Walle, U.K. High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral resveratrol in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2004, 32, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarosova, V.; Vesely, O.; Doskocil, I.; Tomisova, K.; Marsik, P.; Jaimes, J.D.; Smejkal, K.; Kloucek, P.; Havlik, J. Metabolism of cis- and trans-Resveratrol and Dihydroresveratrol in an Intestinal Epithelial Model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Lv, H.; Pang, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, S. Intestinal pharmacokinetics of resveratrol and regulatory effects of resveratrol metabolites on gut barrier and gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrosa, M.; Yanez-Gascon, M.J.; Selma, M.V.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Toti, S.; Ceron, J.J.; Tomas-Barberan, F.; Dolara, P.; Espin, J.C. Effect of a low dose of dietary resveratrol on colon microbiota, inflammation and tissue damage in a DSS-induced colitis rat model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, M.E.; Alfaras, I.; Planas, J.M. Determination of dihydroresveratrol in rat plasma by HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7472–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, M.; Moco, S. Resveratrol and Its Human Metabolites-Effects on Metabolic Health and Obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
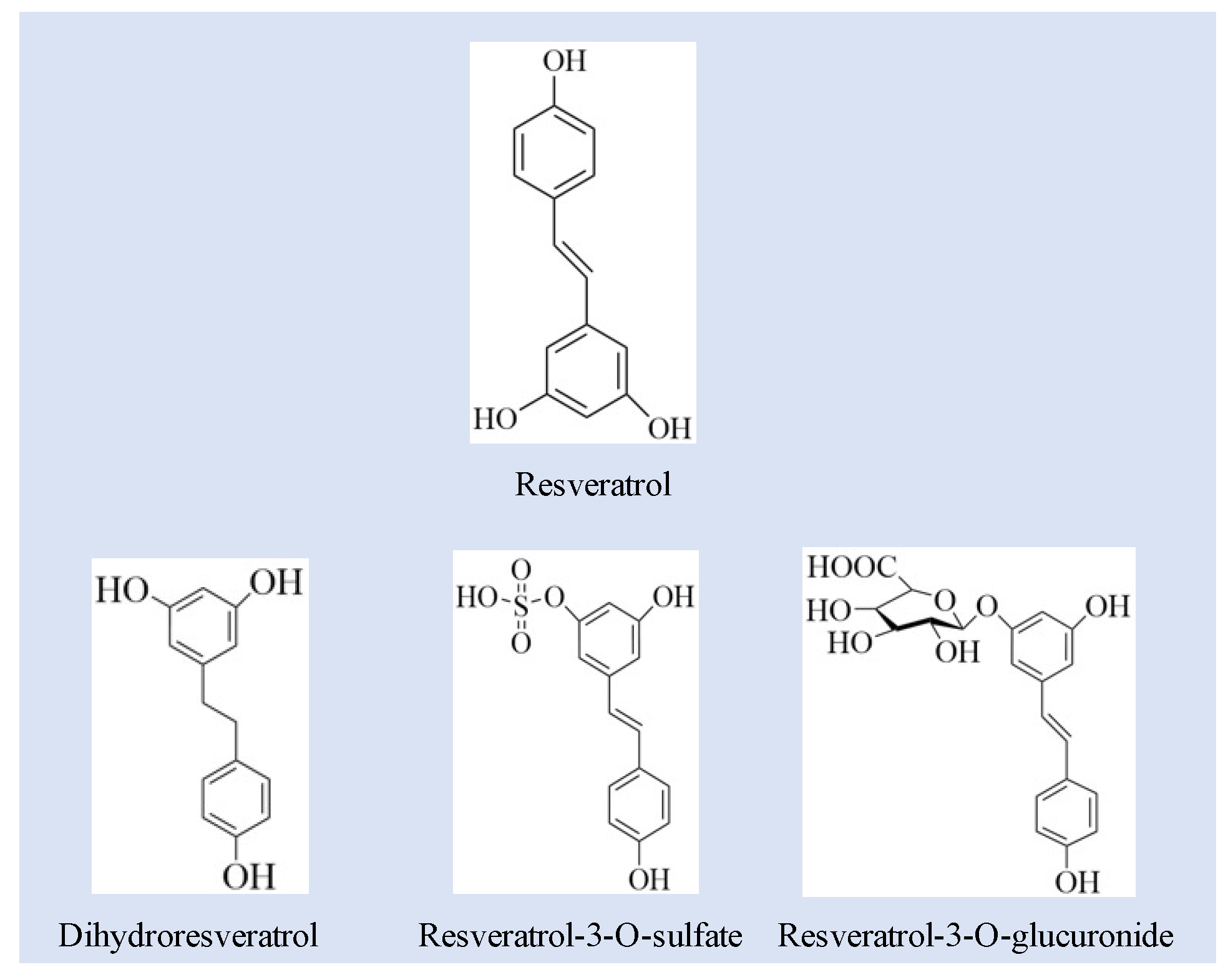
| No. | Compounds | m/z [M-H] | MS/MS Fragment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RSV | 227.0708 | 227.0702, 185.0790 |
| 2 | RES-sulfate | 307.027 | 307.0269, 185.0595 |
| 3 | RES-glucuronide | 403.1029 | 403.1029, 227.0703 |
| 4 | DHR | 229.0865 | 229.0837, 123.0442 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, M.; Fei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, B.; Zhu, L.; Li, F.; Berglund, B.; Xiao, H.; Li, L. Gut Microbiota Composition in Relation to the Metabolism of Oral Administrated Resveratrol. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051013
Yao M, Fei Y, Zhang S, Qiu B, Zhu L, Li F, Berglund B, Xiao H, Li L. Gut Microbiota Composition in Relation to the Metabolism of Oral Administrated Resveratrol. Nutrients. 2022; 14(5):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051013
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Mingfei, Yiqiu Fei, Shuobo Zhang, Bo Qiu, Lian Zhu, Fang Li, Björn Berglund, Hang Xiao, and Lanjuan Li. 2022. "Gut Microbiota Composition in Relation to the Metabolism of Oral Administrated Resveratrol" Nutrients 14, no. 5: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051013
APA StyleYao, M., Fei, Y., Zhang, S., Qiu, B., Zhu, L., Li, F., Berglund, B., Xiao, H., & Li, L. (2022). Gut Microbiota Composition in Relation to the Metabolism of Oral Administrated Resveratrol. Nutrients, 14(5), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051013








