Time Trend of Overweight and Obesity in Adults from Rio Branco, Acre, Western Brazilian Amazon (2006–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Overweight and Obesity Prevalence
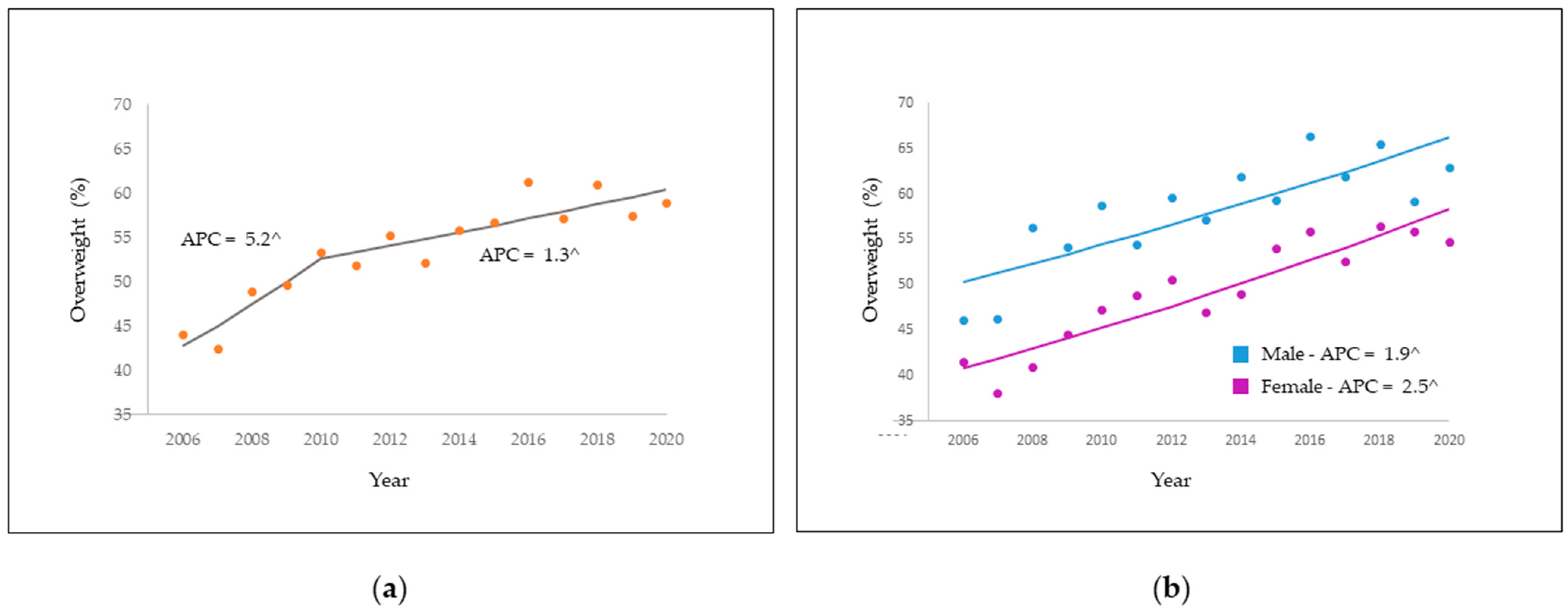
3.2. Time Trend of Overweight Prevalence
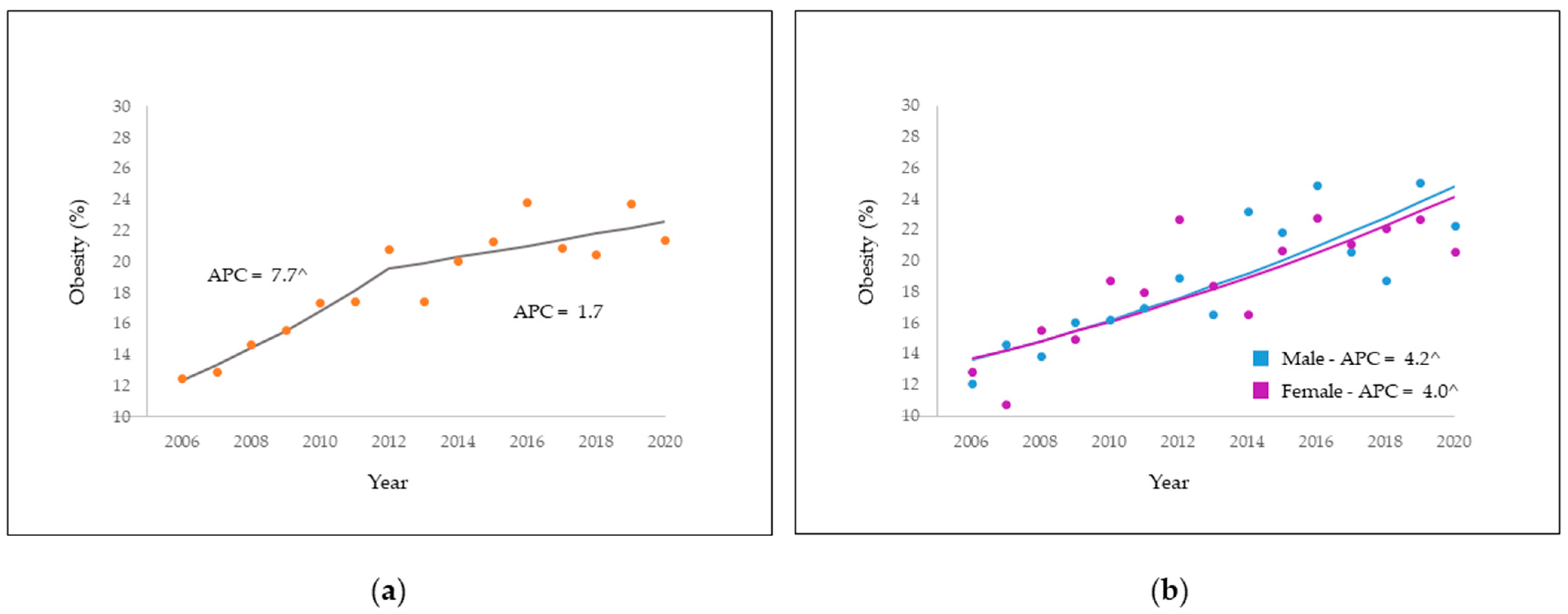
3.3. Time Trend of Obesity Prevalence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20220112232355/https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Dai, H.; Alsalhe, T.A.; Chalghaf, N.; Riccò, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Wu, J. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Pan, X.; Song, X.; Shan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, P.-F. Global Burden of Noncommunicable Disease Attributable to High Body Mass Index in 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017. Endocrine 2020, 69, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, G.; Kovalskys, I.; Leme, A.; Quesada, D.; Rigotti, A.; Cortés Sanabria, L.; Yépez García, M.; Liria-Domínguez, M.; Herrera-Cuenca, M.; Fisberg, R.; et al. Socioeconomic Status Impact on Diet Quality and Body Mass Index in Eight Latin American Countries: ELANS Study Results. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde [Ministry of Health]. VIGITEL 2017. Saúde Suplementar: Vigilância de Fatores de Risco e Proteção Para Doenças Crônicas Por Inquérito Telefônico [Supplementary Health: Surveillance of Risk and Protective Factors for Chronic Diseases by Telephone Survey]; Ministério da Saúde, Agência Nacional de Saúde Suplementar, Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brasil, 2018; pp. 38–45.
- Pinheiro, M.C.; de Moura, A.L.S.P.; Bortolini, G.A.; Coutinho, J.G.; dos Rahal, L.S.; Bandeira, L.M.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Gentil, P.C. Intersectoral approach to obesity prevention and control: The Brazilian experience from 2014 to 2018. Rev. Panam. Salud Publ. 2019, 43, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Ortiz, R.; Malta, D.C.; Velasquez-Melendez, G. Adult Body Weight Trends in 27 Urban Populations of Brazil from 2006 to 2016: A Population-Based Study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, D.C.; da Silva, A.G.; Tonaco, L.A.B.; de Fátima Freitas, M.I.; Velasquez-Melendez, G. Time trends in morbid obesity prevalence in the Brazilian adult population from 2006 to 2017. Cad. Saúde Pública 2019, 35, e00223518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde [Ministry of Health]. VIGITEL 2016. Saúde Suplementar: Vigilância de Fatores de Risco e Proteção Para Doenças Crônicas Por Inquérito Telefônico [Supplementary Health: Surveillance of Risk and Protective Factors for Chronic Diseases by Telephone Survey]; Ministério da Saúde, Agência Nacional de Saúde Suplementar, Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brasil, 2017; pp. 47–53.
- Brasil Ministério Da Saúde [Ministry of Health]. VIGITEL 2019. Saúde Suplementar: Vigilância de Fatores de Risco e Proteção Para Doenças Crônicas Por Inquérito Telefônico [Supplementary Health: Surveillance of Risk and Protective Factors for Chronic Diseases by Telephone Survey]; Ministério da Saúde, Agência Nacional de Saúde Suplementar, Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brasil, 2020; pp. 36–42.
- Wang, Y.; Beydoun, M.A.; Min, J.; Xue, H.; Kaminsky, L.A.; Cheskin, L.J. Has the Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity and Central Obesity Levelled off in the United States? Trends, Patterns, Disparities, and Future Projections for the Obesity Epidemic. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gona, P.N.; Kimokoti, R.W.; Gona, C.M.; Ballout, S.; Rao, S.R.; Mapoma, C.C.; Lo, J.; Mokdad, A.H. Changes in Body Mass Index, Obesity, and Overweight in Southern Africa Development Countries, 1990 to 2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2021, 7, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodaira, K.; Abe, F.C.; Galvão, T.F.; Silva, M.T. Time-Trend in Excess Weight in Brazilian Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.C.K.; Sichieri, R.; Junior, E.V.; Boccolini, C.S.; de Moura Souza, A.; Cunha, D.B. Trends in Obesity Prevalence among Brazilian Adults from 2002 to 2013 by Educational Level. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aprelini, C.M.O.; dos Reis, E.C.; Enríquez-Martinez, O.G.; de Jesus, T.R.; del Molina, M.C.B. Overweight and obesity prevalence trend in Espírito Santo, Brazil: An ecological study, 2009–2018. Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde 2021, 30, e2020961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canazas, V.M.A.; Faustino, C.G.; de Medeiros, M.A.A.; de Medeiros, F.A. Temporal trend of obesity prevalence in macapá. Vigitel, 2006-2018 and projection for 2030. BJD 2021, 7, 19336–19349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, N.P.; Horta, B.L.; dos Motta, J.V.S.; Valença, M.S.; Oliveira, V.; dos Santos, T.V.; Gigante, D.P.; Barros, F.C. Evolution of overweight and obesity into adulthood, Pelotas, Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil, 1982-2012. Cad. Saúde Públ. 2015, 31, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ferreira, A.P.S.; Szwarcwald, C.L.; Damacena, G.N.; de Souza Júnior, P.R.B. Increasing Trends in Obesity Prevalence from 2013 to 2019 and Associated Factors in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2021, 24, e210009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Kelifa, M.O.; Yu, B.; Herbert, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J. Gender-Specific Temporal Trends in Overweight Prevalence among Chinese Adults: A Hierarchical Age-Period-Cohort Analysis from 2008 to 2015. Glob. Health Res. Policy 2020, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State of Childhood Obesity The State of Obesity. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20220116202911/https://stateofchildhoodobesity.org/adult-obesity/ (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Tardido, P.A.; Falcao, C.M. O impacto da modernização na transição nutricional e obesidade [The impact of modernization on the nutritional transition and obesity]. Rev. Bras. Nutr. Clin. 2006, 21, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Vaz, D.V.; Hoffmann, R. Elasticidade-Renda e Concentração Das Despesas Com Alimentos No Brasil: Uma Análise Dos Dados Das POF de 2002–2003, 2008–2009 e 2017–2018 [Income Elasticity and Concentration of Food Expenditures in Brazil]. RE 2020, 41, 282–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, D.V.; Hoffmann, R. Evolução Do Padrão De Consumo Das Famílias Brasileiras Entre 2008 E 2017 [Evolution of the Consumption Pattern of Brazilian Households Between 2008 and 2017]. RE 2021, 30, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curado, M. Uma avaliação da economia brasileira no Governo Lula [An assessment of the Brazilian economy in the Lula Administration]. Ver. Econ. Tec. 2011, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde [Ministry of Health]. Política Nacional de Alimentação e Nutrição [National Food and Nutrition Policy]; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brasil, 2013; pp. 1–86. [CrossRef]
- Reis, B.S.M.T.; Machado, Í.E.; de Freitas, M.I.F.; de Jorge, A.O.; Silva, A.G.; Malta, D.C. Tendência temporal da prevalência dos fatores de risco e de proteção para doenças crônicas não transmissíveis em Belo Horizonte, MG [Time trend of the prevalence of risk and protection factors for chronic non-communicable diseases in Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil.]. REME Rev. Min. Enferm. 2020, 24, e-1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.E.S.; de Oliveira, M.M.; Stopa, S.R.; de Gouvea, E.C.D.P.; Ferreira, K.R.D.; de Santos, R.O.; da Valença Neto, P.F.; Macário, E.M.; Sardinha, L.M.V. Temporal trend of overweight and obesity prevalence among Brazilian adults, according to sociodemographic characteristics, 2006–2019. Epidemiol. Serv. Saúde 2021, 30, e2020294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.D.; César, C.C.; Malta, D.C.; de Souza Andrade, A.C.; Ramos, C.G.C.; Proietti, F.A.; Bernal, R.T.I.; Caiaffa, W.T. Validade de Estimativas Obtidas Por Inquérito Telefônico: Comparação Entre VIGITEL 2008 e Inquérito Saúde Em Beagá [Validity of Estimates from Telephone Surveys: Comparison between VIGITEL 2008 and the Health Survey in Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil]. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2011, 14, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Na | 1751 | 1768 | 1796 | 1787 | 1771 | 1768 | 1467 | 1757 | 1340 | 1707 | 1622 | 1642 | 1301 | 1576 | 869 |
| Nb | 15,472 | 17,142 | 16,150 | 16,352 | 18,539 | 19,352 | 19,519 | 20,419 | 20,255 | 20,126 | 21,681 | 21,972 | 22,103 | 21,835 | 22,123 |
| Total | 44.0 | 42.5 | 48.9 | 49.6 | 53.3 | 51.8 | 55.2 | 52.1 | 55.8 | 56.7 | 61.3 | 57.2 | 61.0 | 57.5 | 58.9 |
| Sex | |||||||||||||||
| Male | 46.2 | 46.3 | 56.3 | 54.2 | 58.8 | 54.5 | 59.7 | 57.2 | 61.9 | 59.3 | 66.4 | 61.9 | 65.5 | 59.2 | 63.0 |
| Female | 41.6 | 38.1 | 41.0 | 44.6 | 47.3 | 48.9 | 50.6 | 47.0 | 49.0 | 54.0 | 55.9 | 52.6 | 56.5 | 55.9 | 54.8 |
| Age group (in years) | |||||||||||||||
| 18–24 | 25.4 | 20.7 | 27.2 | 30.6 | 26.6 | 30.1 | 38.8 | 37.1 | 33.6 | 29.0 | 37.9 | 31.8 | 39.8 | 39.0 | 30.3 |
| 25–34 | 42.9 | 39.9 | 44.7 | 48.0 | 59.9 | 48.0 | 57.4 | 48.4 | 57.4 | 61.2 | 59.3 | 55.7 | 63.5 | 55.1 | 63.8 |
| 35–44 | 52.1 | 54.7 | 59.4 | 59.3 | 60.4 | 67.1 | 59.7 | 58.4 | 60.5 | 63.7 | 69.9 | 67.2 | 66.6 | 64.9 | 63.2 |
| 45–54 | 58.6 | 55.6 | 72.1 | 61.5 | 60.9 | 65.3 | 66.3 | 63.0 | 67.2 | 66.6 | 78.1 | 66.6 | 70.0 | 68.2 | 68.4 |
| 55–64 | 59.0 | 62.8 | 62.5 | 51.8 | 70.1 | 60.8 | 55.8 | 60.3 | 71.3 | 65.8 | 67.6 | 66.8 | 66.6 | 64.1 | 58.5 |
| 65 or more | 50.3 | 48.9 | 52.7 | 65.2 | 55.3 | 53.2 | 54.5 | 68.7 | 53.5 | 60.7 | 63.6 | 65.3 | 62.5 | 58.5 | 65.0 |
| Skin color | |||||||||||||||
| White | 42.7 | 42.1 | 52.9 | 51.0 | 49.7 | 47.8 | 54.6 | 52.1 | 57.5 | 55.7 | 59.7 | 56.0 | 55.1 | 58.3 | 64.0 |
| Non-white | 45.0 | 57.9 | 47.3 | 49.0 | 54.7 | 53.0 | 53.8 | 51.0 | 53.8 | 56.5 | 61.7 | 57.2 | 63.4 | 57.1 | 57.3 |
| Level of schooling (by years of studying) | |||||||||||||||
| 0–8 | 50.6 | 46.8 | 58.8 | 55.5 | 61.8 | 57.6 | 61.5 | 59.0 | 62.9 | 62.1 | 69.2 | 67.8 | 65.5 | 62.7 | 57.9 |
| 9 a 11 | 38.2 | 37.9 | 38.1 | 44.7 | 47.2 | 47.0 | 50.9 | 49.9 | 53.6 | 53.3 | 59.6 | 55.1 | 60.7 | 56.7 | 59.3 |
| 12 or more | 36.1 | 38.7 | 43.7 | 44.1 | 44.6 | 48.7 | 50.8 | 44.7 | 48.0 | 54.0 | 54.5 | 49.4 | 57.7 | 54.2 | 59.1 |
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Na | 1751 | 1768 | 1796 | 1787 | 1771 | 1768 | 1467 | 1757 | 1340 | 1707 | 1622 | 1642 | 1301 | 1576 | 869 |
| Nb | 15,472 | 17,142 | 16,150 | 16,352 | 18,539 | 19,352 | 19,519 | 20,419 | 20,255 | 20,126 | 21,681 | 21,972 | 22,103 | 21,835 | 22,123 |
| Total | 12.5 | 12.9 | 14.7 | 15.6 | 17.4 | 17.5 | 20.8 | 17.5 | 20.1 | 21.3 | 23.9 | 20.9 | 20.50 | 23.8 | 21.4 |
| Sex | |||||||||||||||
| Male | 12.1 | 14.6 | 13.9 | 16.1 | 16.2 | 17.0 | 18.9 | 16.6 | 23.2 | 21.9 | 24.9 | 20.6 | 18.80 | 25.1 | 22.3 |
| Female | 12.9 | 10.8 | 15.6 | 15.0 | 18.8 | 18.0 | 22.7 | 18.4 | 16.6 | 20.7 | 22.8 | 21.1 | 22.10 | 22.7 | 20.6 |
| Age group (in years) | |||||||||||||||
| 18–24 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 4.8 | 7.1 | 5.2 | 8.8 | 12.9 | 7.9 | 5.0 | 8.3 | 12.4 | 8.3 | 4.70 | 10.3 | 13.7 |
| 25–34 | 8.7 | 10.6 | 13.4 | 11.6 | 17.6 | 13.3 | 19.1 | 15.0 | 21.7 | 22.7 | 22.3 | 13.7 | 20.00 | 24.2 | 20.4 |
| 35–44 | 15.9 | 16.0 | 22.5 | 23.2 | 21.7 | 25.2 | 23.2 | 24.5 | 25.0 | 24.4 | 27 | 31.7 | 23.40 | 31.7 | 21.4 |
| 45–54 | 19.0 | 15.1 | 22.3 | 24.7 | 22.0 | 26.7 | 29.9 | 22.4 | 21.6 | 29.5 | 31.8 | 27.9 | 27.10 | 26.4 | 22.5 |
| 55–64 | 25.8 | 27.0 | 19.7 | 15.9 | 32.3 | 21.7 | 24.4 | 20.2 | 31.1 | 22.8 | 32.6 | 29.1 | 33.80 | 26.8 | 30.3 |
| 65 or more | 13.8 | 16.1 | 10.4 | 20.9 | 17.8 | 15.9 | 20.0 | 23.6 | 23.5 | 22.6 | 25.1 | 26.2 | 23.20 | 21.7 | 29 |
| Skin color | |||||||||||||||
| White | 11.4 | 12.9 | 14.1 | 16.6 | 18.9 | 15.7 | 26.3 | 15.5 | 17.9 | 23.3 | 20.7 | 18.9 | 16.50 | 26.2 | 28.7 |
| Non-white | 12.9 | 11.3 | 14.9 | 15.3 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 16.9 | 17.5 | 20.0 | 20.8 | 24.8 | 21.2 | 21.90 | 22.7 | 19.1 |
| Level of schooling (in years of studying) | |||||||||||||||
| 0–8 | 14.5 | 15.1 | 20.0 | 20.4 | 20.8 | 22.2 | 24.7 | 22.2 | 26.3 | 25.1 | 31.1 | 26.4 | 25.2 | 32.3 | 21.9 |
| 9 a 11 | 11.3 | 9.8 | 9.0 | 11.4 | 15.7 | 15.6 | 18.7 | 14.7 | 16.9 | 18.8 | 21.4 | 19.2 | 22.8 | 22.2 | 22.4 |
| 12 or more | 8.9 | 12.2 | 11.6 | 11.4 | 12.7 | 11.5 | 17.0 | 14.1 | 15.4 | 19.7 | 18.9 | 17.4 | 14.0 | 18.7 | 20.2 |
| % | |||||
| 2006 | 2020 | APC | 95% CI | Period | |
| Total | 44.1 | 58.9 | 5.2 ^ | 1.4; 9.1 | 2006–2010 |
| 1.3 ^ | 0.4–2.2 | 2010–2020 | |||
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 46.2 | 63 | 1.9 ^ | 1.0; 2.7 | 2006–2020 |
| Female | 41.7 | 54.8 | 2.5 ^ | 1.8; 3.2 | 2006–2020 |
| Age group (in years) | |||||
| 18–24 | 25.4 | 30.3 | 2.7 ^ | 0.8; 4.8 | 2006–2020 |
| 25–34 | 42.9 | 63.8 | 2.7 ^ | 1.4; 4.0 | 2006–2020 |
| 35–44 | 52.2 | 63.2 | 1.3 ^ | 0.6; 2.0 | 2006–2020 |
| 45–54 | 58.6 | 68.4 | 1.0 ^ | 0.2; 1.8 | 2006–2020 |
| 55–64 | 59 | 58.5 | 0.5 | −0.6; 1.7 | 2006–2020 |
| 65 or more | 50.3 | 65 | 1.5 ^ | 0.4; 2.7 | 2006–2020 |
| Skin color | |||||
| White | 41.7 | 64 | 2.3 ^ | 1.4; 3.1 | 2006–2020 |
| Non-white | 45 | 57.3 | 1.4 ^ | 0.5; 2.3 | 2006–2020 |
| Level of schooling (in years of studying) | |||||
| 0–8 years | 50.7 | 57.9 | 2.6 ^ | 1.1; 4.2 | 2006–2017 |
| −4.8 | −13.5; 4.8 | 2017–2020 | |||
| 9–11 years | 38.2 | 59.3 | 5.4 ^ | 3.0; 7.8 | 2006–2012 |
| 2.1 ^ | 0.6; 3.7 | 2012–2020 | |||
| 12 years | 36.1 | 59.1 | 2.9 ^ | 2.0 a 3.7 | 2006–2020 |
| Marital status | |||||
| No partner | 33.5 | 49.6 | 2.7 ^ | 1.7; 3.7 | 2006–2020 |
| Companion | 54 | 68.7 | 2.0 ^ | 1.4 a 2.7 | 2006–2020 |
| Regular consumption of fruits and vegetables * | |||||
| No | 43.4 | 58.1 | 2.2^ | 1.4; 3.0 | 2006–2020 |
| Yes | 47 | 61.6 | 1.9^ | 1.3 a 2.4 | 2006–2020 |
| Excessive consumption of sugary drinks ** | |||||
| No | 43.7 | 59.3 | 2.0 ^ | 1.5; 2.6 | 2006–2020 |
| Yes | 45 | 56.6 | 1.9 ^ | 0.5; 3.3 | 2006–2020 |
| TV time per day on 5 days a week | |||||
| Does not watch or watches up to 3 h | 44.4 | 55.5 | 1.8^ | 1.1; 2.6 | 2006–2020 |
| Watches 3 or more hours | 43.1 | 70.4 | 3.0^ | 1.8; 4.1 | 2006–2020 |
| % | |||||
| 2006 | 2020 | APC | 95% CI | Period | |
| Total | 12.5 | 21.4 | 7.7 ^ | 4.5; 10.9 | 2006–2012 |
| 1.7 | −0.2; 3.7 | 2012–2020 | |||
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 12.1 | 22.3 | 4.2 ^ | 2.7; 5.6 | 2006–2020 |
| Female | 12.9 | 20.6 | 4.0 ^ | 2.1; 5.9 | 2006–2020 |
| Age group (in years) | |||||
| 18–24 | 7.0 | 13.7 | 2.9 | −1.6; 7.5 | 2006–2020 |
| 25–34 | 8.7 | 20.4 | 5.5 ^ | 2.7; 8.4 | 2006–2020 |
| 35–44 | 15.8 | 21.4 | 2.9 ^ | 0.9; 5.0 | 2006–2020 |
| 45–54 | 19.0 | 22.5 | 2.3 ^ | 0.1; 4.5 | 2006–2020 |
| 55–64 | 25.8 | 30.3 | 2.2 | −0.5; 4.9 | 2006–2020 |
| 65 or more | 13.8 | 29.0 | 5.0 ^ | 2.6; 7.4 | 2006–2020 |
| Skin color | |||||
| White | 11.4 | 28.7 | 4.7 ^ | 2.0; 7.4 | 2006–2020 |
| Non-white | 12.9 | 19.1 | 4.0 ^ | 2.7; 5.4 | 2006–2020 |
| Level of schooling (in years of studying) | |||||
| 0–8 years | 14.4 | 21.9 | 3.8 ^ | 2.0; 5.7 | 2006–2020 |
| 9–11 years | 11.3 | 22.4 | 6.4 ^ | 4.5; 8.3 | 2006–2020 |
| 12 or more | 8.9 | 20.2 | 4.6 ^ | 2.8; 6.5 | 2006–2020 |
| Marital status | |||||
| No partner | 8.8 | 19.2 | 4.8^ | 2.6; 7.1 | 2006–2020 |
| Companion | 15.9 | 23.8 | 3.9^ | 2.5; 5.4 | 2006–2020 |
| Regular consumption of fruits and vegetables * | |||||
| No | 12.6 | −20.9 | 3.7 ^ | 2.5; 5.0 | 2006–2020 |
| Yes | 11.8 | 23.4 | 5.2 ^ | 3.1; 7.4 | 2006–2020 |
| Excessive consumption of sugary drinks ** | |||||
| No | 12.1 | 20.2 | 3.8 ^ | 2.4; 5.2 | 2006–2020 |
| Yes | 13.4 | 28.0 | 4.7 ^ | 1.6; 7.9 | 2006–2020 |
| TV time per day on 5 days a week | |||||
| Does not watch or watches up to 3 h | 13.3 | 19.3 | 3.5^ | 2.3; 4.6 | 2006–2020 |
| Watches 3 or more hours | 10.2 | 28.9 | 6.2^ | 4.0; 8.4 | 2006–2020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, F.S.B.; de Moura Magalhães Lima, Y.; Martins, F.A.; da Silva-Nunes, M.; de Andrade, A.M.; Ramalho, A.A. Time Trend of Overweight and Obesity in Adults from Rio Branco, Acre, Western Brazilian Amazon (2006–2020). Nutrients 2022, 14, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040742
Dias FSB, de Moura Magalhães Lima Y, Martins FA, da Silva-Nunes M, de Andrade AM, Ramalho AA. Time Trend of Overweight and Obesity in Adults from Rio Branco, Acre, Western Brazilian Amazon (2006–2020). Nutrients. 2022; 14(4):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040742
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Flávia Santos Batista, Yara de Moura Magalhães Lima, Fernanda Andrade Martins, Mônica da Silva-Nunes, Andréia Moreira de Andrade, and Alanderson Alves Ramalho. 2022. "Time Trend of Overweight and Obesity in Adults from Rio Branco, Acre, Western Brazilian Amazon (2006–2020)" Nutrients 14, no. 4: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040742
APA StyleDias, F. S. B., de Moura Magalhães Lima, Y., Martins, F. A., da Silva-Nunes, M., de Andrade, A. M., & Ramalho, A. A. (2022). Time Trend of Overweight and Obesity in Adults from Rio Branco, Acre, Western Brazilian Amazon (2006–2020). Nutrients, 14(4), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040742






