Temporal Muscle and Stroke—A Narrative Review on Current Meaning and Clinical Applications of Temporal Muscle Thickness, Area, and Volume
Abstract
:1. Introduction
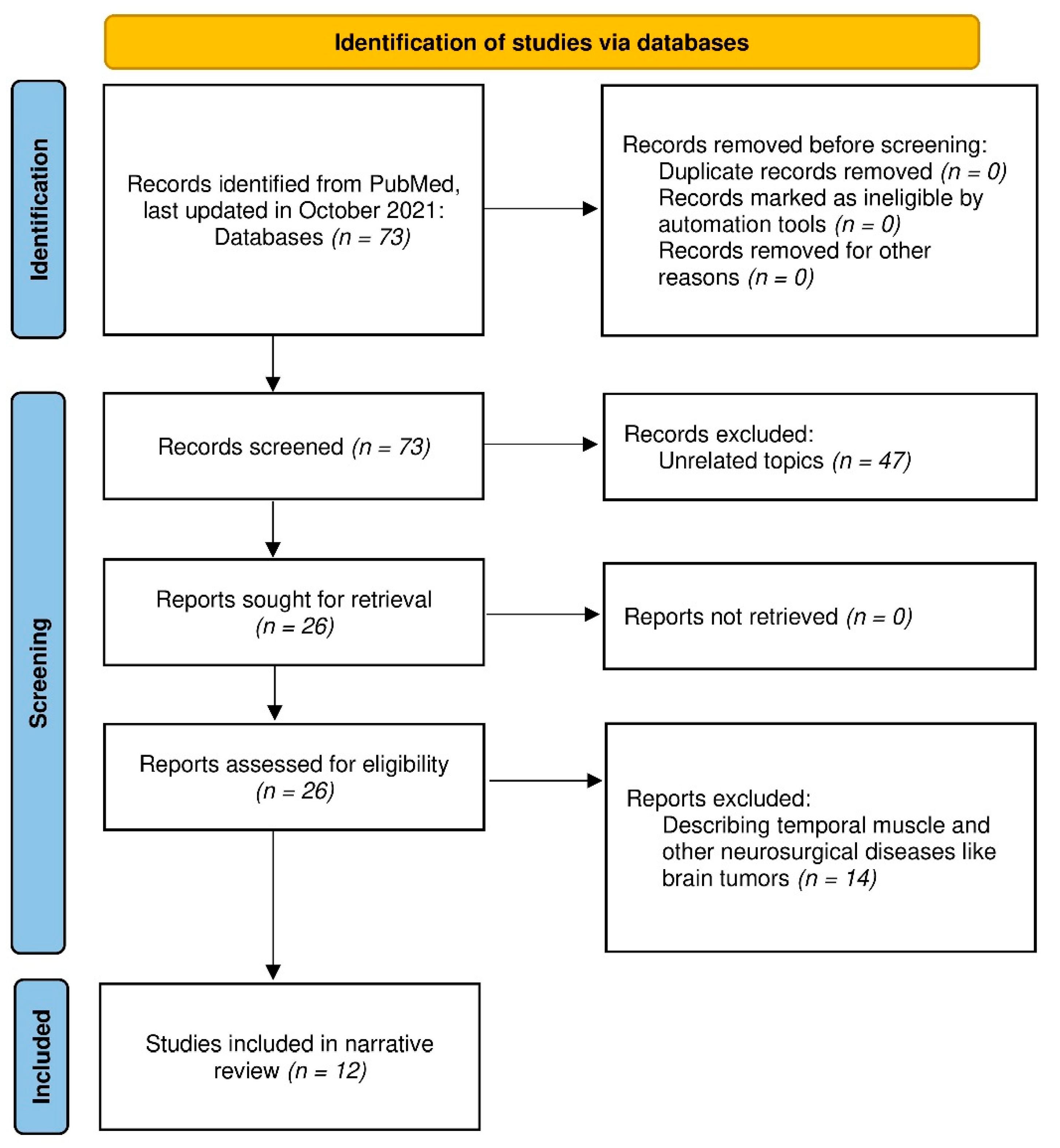
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Muscle and SAH
3.2. Temporal Muscle and ICH
3.3. Temporal Muscle and Stroke
3.4. Standard Values of TMT
3.5. TMT and Nutritional Status
4. Discussion
4.1. TMT Measurement Method
4.2. Temporal Muscle in Other Neurosurgical Practice
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toyoda, K.; Sonoda, K.; Sato, S.; Yoshimura, S. The Japan Stroke Databank -Current stroke care in Japan and ideal stroke registries. Neurol. Ther. 2018, 35, 188–192. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, A.S.; Ivey, F.M.; Serra, M.C.; Hartstein, J.; Hafer-Macko, C.E. Sarcopenia and Physical Function in Middle-Aged and Older Stroke Survivors. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2016, 98, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherbakov, N.; von Haehling, S.; Anker, S.D.; Dirnagl, U.; Doehner, W. Stroke induced Sarcopenia: Muscle wasting and disability after stroke. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 170, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Bise, T.; Nagano, F.; Shimazu, S.; Shiraishi, A.; Yamaga, M.; Koga, H. Sarcopenia is associated with worse recovery of physical function and dysphagia and a lower rate of home discharge in Japanese hospitalized adults undergoing convalescent rehabilitation. Nutrition 2019, 61, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozoe, M.; Kanai, M.; Kubo, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Shimada, S.; Mase, K. Prestroke sarcopenia and functional outcomes in elderly patients who have had an acute stroke: A prospective cohort study. Nutrition 2019, 66, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozoe, M.; Kubo, H.; Kanai, M.; Yamamoto, M. Relationships between Pre-Stroke SARC-F Scores, Disability, and Risk of Malnutrition and Functional Outcomes after Stroke—A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, N.; Okura, K.; Okamura, M.; Nawata, K.; Shinohara, A.; Tanaka, K.; Katayama, S. Measuring and Monitoring Skeletal Muscle Mass after Stroke: A Review of Current Methods and Clinical Applications. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Momosaki, R.; Nagano, F.; Bise, T.; Shimazu, S.; Shiraishi, A. Stored Energy Increases Body Weight and Skeletal Muscle Mass in Older, Underweight Patients after Stroke. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, H.; Mogamiya, T.; Matsushima, S.; Sase, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Nakamura, H.; Sakakibara, Y. High protein intake after subarachnoid hemorrhage improves oral intake and temporal muscle volume. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4187–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, H.; Mogamiya, T.; Mori, M.; Matsushima, S.; Sase, T.; Nakamura, H.; Sakakibara, Y. High protein intake after subarachnoid hemorrhage improves ingestion function and temporal muscle volume. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 40, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Yoshimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Kose, E.; Nagano, F.; Bise, T.; Kido, Y.; Shimazu, S.; Shiraishi, A. Deprescribing Leads to Improved Energy Intake among Hospitalized Older Sarcopenic Adults with Polypharmacy after Stroke. Nutrients 2022, 14, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nagano, F.; Bise, T.; Shimazu, S.; Shiraishi, A.; Kido, Y.; Matsumoto, A. Chair-Stand Exercise Improves Sarcopenia in Rehabilitation Patients after Stroke. Nutrients 2022, 14, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y. Treating sarcopenia with a hybrid of aggressive exercise therapy and nutritional therapy: Approaches at Kumamoto Rehabilitation Hospital. Mon. B Med. Rehabil. 2018, 224, 16–24. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Furtner, J.; Weller, M.; Weber, M.; Gorlia, T.; Nabors, B.; Reardon, D.A.; Tonn, J.-C.; Stupp, R.; Preusser, M. Temporal Muscle Thickness as a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: Translational Imaging Analysis of the CENTRIC EORTC 26071–22072 and CORE Trials. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 28, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Liu, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.-Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Hsu, P.-S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leitner, J.; Pelster, S.; Schöpf, V.; Berghoff, A.S.; Woitek, R.; Asenbaum, U.; Nenning, K.-H.; Widhalm, G.; Kiesel, B.; Gatterbauer, B.; et al. High correlation of temporal muscle thickness with lumbar skeletal muscle cross-sectional area in patients with brain metastases. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindl, A.; Leitner, J.; Schwarz, M.; Nenning, K.-H.; Asenbaum, U.; Mayer, S.; Woitek, R.; Weber, M.; Schöpf, V.; Berghoff, A.S.; et al. Sarcopenia in Neurological Patients: Standard Values for Temporal Muscle Thickness and Muscle Strength Evaluation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Sato, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Minematsu, T.; Sugama, J.; Sanada, H. A change in temporal muscle thickness is correlated with past energy adequacy in bedridden older adults: A prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Sato, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Minematsu, T.; Sugama, J.; Sanada, H. Temporal muscle thickness as a new indicator of nutritional status in older individuals. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uchiyama, T.; Wada, N.; Kakizawa, Y. Clinical characteristics of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the elderly over 75; would temporal muscle be a potential prognostic factor as an indicator of sarcopenia? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 186, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, R.C.G.; Rabelo, N.N.; Figueiredo, E.G.; Welling, L.C. Oral health and temporal muscle thickness. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Kunitoki, K.; Sato, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Mashiyama, S.; Matsuoka, R.; Allen, E.; Saimaru, H.; Sugawara, R.; et al. Temporal Muscle as an Indicator of Sarcopenia is Independently Associated with Hunt and Kosnik Grade on Admission and the Modified Rankin Scale Score at 6 Months of Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Treated by Endovascular Coiling. World Neurosurg. 2020, 137, e526–e534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, M.; Kakizawa, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uchiyama, T. Temporal muscle thickness and area are an independent prognostic factors in patients aged 75 or younger with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage treated by clipping. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, M.; Kakizawa, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uchiyama, T. Lower total protein and absence of neuronavigation are novel poor prognostic factors of endoscopic hematoma removal for intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.G.C.; Palinkas, M.; da Silva, G.P.; Gonçalves, C.R.; Lopes, R.F.T.; Verri, E.D.; Fabrin, S.C.V.; Fioco, E.M.; Siéssere, S.; Regalo, S.C.H. Bite Force, Thickness, and Thermographic Patterns of Masticatory Muscles Post-Hemorrhagic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Katayama, M.; Nakajima, J.; Inoue, S.; Koizumi, K.; Okada, S.; Suga, S.; Nomura, T.; Matsuura, N. Temporal muscle thickness is associated with the severity of dysphagia in patients with acute stroke. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2021, 96, 104439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozoe, M.; Kubo, H.; Kanai, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Okakita, M.; Suzuki, H.; Shimada, S.; Mase, K. Reliability and validity of measuring temporal muscle thickness as the evaluation of sarcopenia risk and the relationship with functional outcome in older patients with acute stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 201, 106444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, M.; Narita, N.; Sasaki, K.; Sato, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Mashiyama, S.; Tominaga, T. Standard values for temporal muscle thickness in the Japanese population who undergo brain check-up by magnetic resonance imaging. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtner, J.; Berghoff, A.S.; Albtoush, O.M.; Woitek, R.; Asenbaum, U.; Prayer, D.; Widhalm, G.; Gatterbauer, B.; Dieckmann, K.; Birner, P.; et al. Survival prediction using temporal muscle thickness measurements on cranial magnetic resonance images in patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 3167–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nooner, K.B.; Colcombe, S.J.; Tobe, R.H.; Mennes, M.; Benedict, M.M.; Moreno, A.L.; Panek, L.J.; Brown, S.; Zavitz, S.T.; Li, Q.; et al. The NKI-Rockland Sample: A Model for Accelerating the Pace of Discovery Science in Psychiatry. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullitt, E.; Zeng, D.; Gerig, G.; Aylward, S.; Joshi, S.; Smith, J.K.; Lin, W.; Ewend, M.G. Vessel Tortuosity and Brain Tumor Malignancy: A Blinded Study1. Acad. Radiol. 2005, 12, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriwaki, E.-I.; Enomoto, H.; Saito, M.; Hara, N.; Nishikawa, H.; Nishimura, T.; Iwata, Y.; Iijima, H.; Nishiguchi, S. The Anthropometric Assessment with the Bioimpedance Method Is Associated with the Prognosis of Cirrhotic Patients. Vivo 2020, 34, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranganathan, K.; Terjimanian, M.; Lisiecki, J.; Rinkinen, J.; Mukkamala, A.; Brownley, C.; Buchman, S.R.; Wang, S.C.; Levi, B. Temporalis muscle morphomics: The psoas of the craniofacial skeleton. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 186, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkinen, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Enchakalody, B.; Terjimanian, M.; Holcomb, S.; Wang, S.C.; Buchman, S.R.; Levi, B. Novel Temporalis Muscle and Fat Pad Morphomic Analyses Aids Preoperative Risk Evaluation and Outcome Assessment in Nonsyndromic Craniosynostosis. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2013, 24, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtner, J.; Nenning, K.-H.; Roetzer, T.; Gesperger, J.; Seebrecht, L.; Weber, M.; Grams, A.; Leber, S.; Marhold, F.; Sherif, C.; et al. Evaluation of the Temporal Muscle Thickness as an Independent Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtner, J.; Genbrugge, E.; Gorlia, T.; Bendszus, M.; Nowosielski, M.; Golfinopoulos, V.; Weller, M.; Bent, M.J.V.D.; Wick, W.; Preusser, M. Temporal muscle thickness is an independent prognostic marker in patients with progressive glioblastoma: Translational imaging analysis of the EORTC 26101 trial. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 21, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, K.; Hwang, M.; Estevez-Inoa, G.; Saraf, A.; Spina, C.; Smith, D.; Wu, C.; Wang, T. Temporalis Muscle Width as a Measure of Sarcopenia Independently Predicts Overall Survival in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 102, e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G.; Ahn, S.; Park, J.-S.; Jeun, S.S.; Kil Hong, Y. Association between temporal muscle thickness and clinical outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 147, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinkir, H.Y.; Er, H.C. Is temporal muscle thickness a survival predictor in newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme? Asia-Pacific J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 16, e223–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muglia, R.; Simonelli, M.; Pessina, F.; Morenghi, E.; Navarria, P.; Persico, P.; Lorenzi, E.; Dipasquale, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Scorsetti, M.; et al. Prognostic relevance of temporal muscle thickness as a marker of sarcopenia in patients with glioblastoma at diagnosis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 31, 4079–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Xing, D.; Zha, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, W.; Li, L.; Gong, W.; Hu, L. Predictive Value of Temporal Muscle Thickness Measurements on Cranial Magnetic Resonance Images in the Prognosis of Patients with Primary Glioblastoma. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 523292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, D.C.; Aksun, M.S.; Cakir, I.Y.; Kilickap, S.; Kertmen, N. The association of BMI and sarcopenia with survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 17, 4405–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, S.; Khalafallah, A.M.; Ruiz-Cardozo, M.A.; Botros, D.; Oliveira, L.A.; Dux, H.; White, T.; Jimenez, A.E.; Gujar, S.K.; Sair, H.I.; et al. A Novel Radiographic Marker of Sarcopenia with Prognostic Value in Glioblastoma. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtner, J.; Berghoff, A.S.; Schöpf, V.; Reumann, R.; Pascher, B.; Woitek, R.; Asenbaum, U.; Pelster, S.; Leitner, J.; Widhalm, G.; et al. Temporal muscle thickness is an independent prognostic marker in melanoma patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 140, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilic, I.; Faron, A.; Heimann, M.; Potthoff, A.-L.; Schäfer, N.; Bode, C.; Borger, V.; Eichhorn, L.; Giordano, F.; Güresir, E.; et al. Combined Assessment of Preoperative Frailty and Sarcopenia Allows the Prediction of Overall Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Surgically Treated Brain Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, R.; Sferruzza, G.; Calimeri, T.; Steffanoni, S.; Conte, G.; De Cobelli, F.; Falini, A.; Ferreri, A.; Anzalone, N. Quantitative muscle mass biomarkers are independent prognosis factors in primary central nervous system lymphoma: The role of L3-skeletal muscle index and temporal muscle thickness. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 143, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, E.; Mauricaite, R.; Pakzad-Shahabi, L.; Chen, J.; Ho, A.; Williams, M. Deep learning-based quantification of temporalis muscle has prognostic value in patients with glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 126, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Number of Cases | Abstract |
|---|---|---|---|
| Katsuki [21] | 2019 | 49 | High TMT was related to favorable outcomes among elderly SAH. |
| Katsuki [23] | 2020 | 298 | TMT and TMA were related to Hunt and Kosnik grade and functional outcome at six months after endovascular coiling, regardless of age. |
| Katsuki [24] | 2021 | 127 | The threshold of TMT was 4.9 mm in women and 6.7 mm in men, and that of TMA was 193 mm2 in women and 333 mm2 in men, which were the cut-off values for the functional outcomes at six months among SAH patients under 75 years of age. |
| Onodera [9] | 2021 | 60 | The food intake score and the functional outcome at discharge were significantly more positive in the TMV maintenance group than the TMV atrophy group after SAH. |
| Author | Year | Number of Cases | Abstract |
|---|---|---|---|
| Katsuki [25] | 2019 | 75 | Low nutritional status, indicated by low total protein level and low TMA altogether, seemed to be associated with the poor functional outcomes at six months after endoscopic hematoma removal. |
| Gomes [26] | 2021 | 24 | TMT on the unaffected side was greater than on the affected side after a hemorrhagic stroke. |
| Author | Year | Number of Cases | Abstract |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sakai [27] | 2021 | 70 | TMT was a significant explanator of dysphagia severity following acute ischemic stroke. |
| Nozoe [28] | 2021 | 289 | Sarcopenia risk was independently associated with TMT in older patients with acute stroke, but TMT was not independently related to the functional outcome. |
| Author | Year | Number of Cases | Abstract |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steindl [18] | 2020 | 1175 | Standard values of TMT were investigated, and TMT and grip strength were correlated. |
| Katsuki [29] | 2021 | 360 | Standard values of TMT were investigated among Japanese individuals who underwent brain check-ups. |
| Author | Year | Number of Cases | Abstract |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hasegawa [20] | 2019 | 73 | TMT was strongly correlated with CC and ACM. However, there were no strong correlations with serum protein levels, nor was fat mass evaluated in the triceps skinfold thickness. |
| Hasegawa [19] | 2021 | 48 | TMT changes were directly correlated with energy adequacy in bedridden older adults. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katsuki, M.; Kakizawa, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uchiyama, T.; Agata, M.; Wada, N.; Kawamura, S.; Koh, A. Temporal Muscle and Stroke—A Narrative Review on Current Meaning and Clinical Applications of Temporal Muscle Thickness, Area, and Volume. Nutrients 2022, 14, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030687
Katsuki M, Kakizawa Y, Nishikawa A, Yamamoto Y, Uchiyama T, Agata M, Wada N, Kawamura S, Koh A. Temporal Muscle and Stroke—A Narrative Review on Current Meaning and Clinical Applications of Temporal Muscle Thickness, Area, and Volume. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030687
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatsuki, Masahito, Yukinari Kakizawa, Akihiro Nishikawa, Yasunaga Yamamoto, Toshiya Uchiyama, Masahiro Agata, Naomichi Wada, Shin Kawamura, and Akihito Koh. 2022. "Temporal Muscle and Stroke—A Narrative Review on Current Meaning and Clinical Applications of Temporal Muscle Thickness, Area, and Volume" Nutrients 14, no. 3: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030687
APA StyleKatsuki, M., Kakizawa, Y., Nishikawa, A., Yamamoto, Y., Uchiyama, T., Agata, M., Wada, N., Kawamura, S., & Koh, A. (2022). Temporal Muscle and Stroke—A Narrative Review on Current Meaning and Clinical Applications of Temporal Muscle Thickness, Area, and Volume. Nutrients, 14(3), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030687








