Cod Liver Oil, but Not Retinoic Acid, Treatment Restores Bone Thickness in a Vitamin A-Deficient Rat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Diet
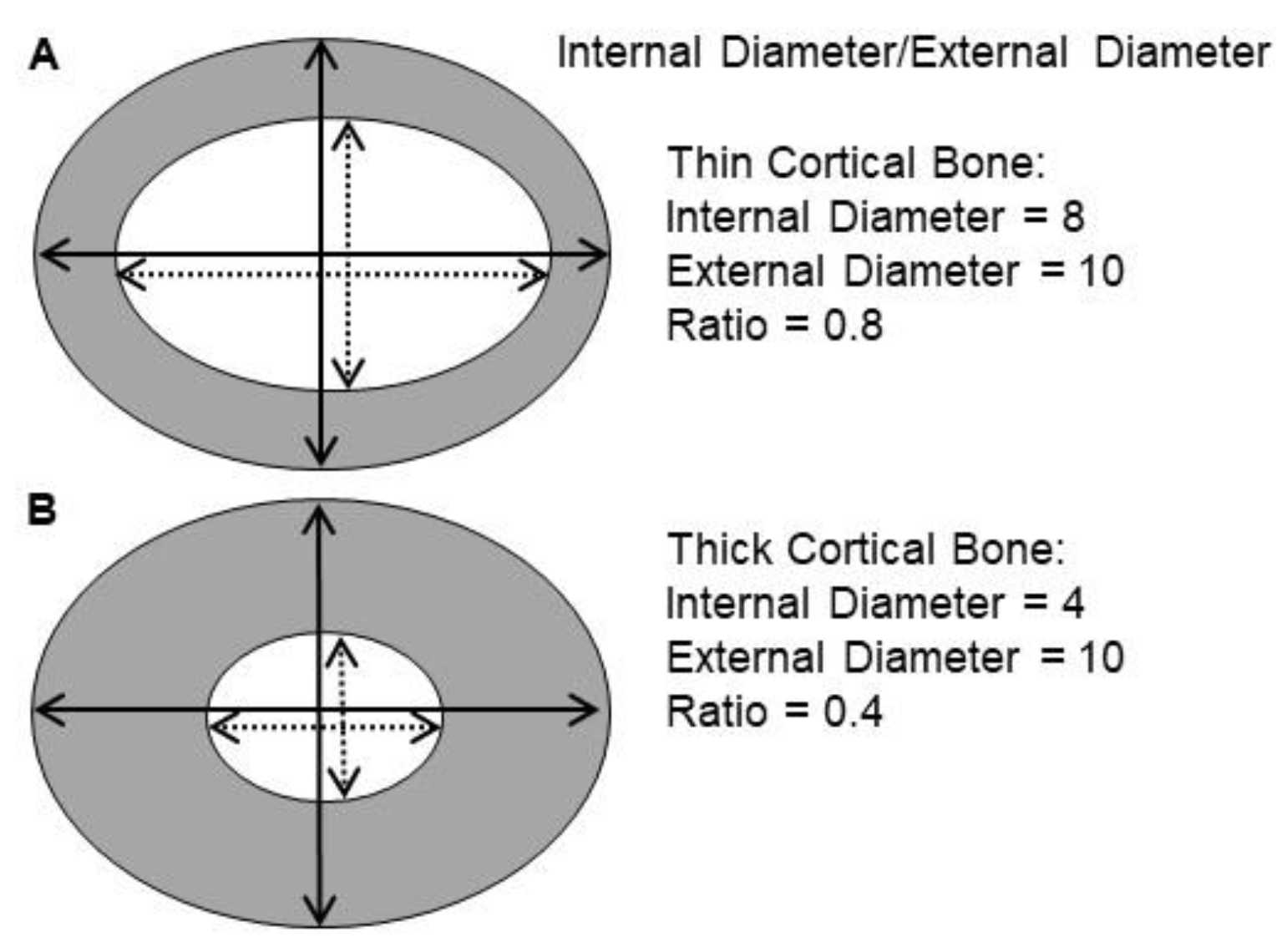
2.3. Bone Analysis
2.4. Osteoblast Cell Count & Osteoclast Cell Count
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mortality
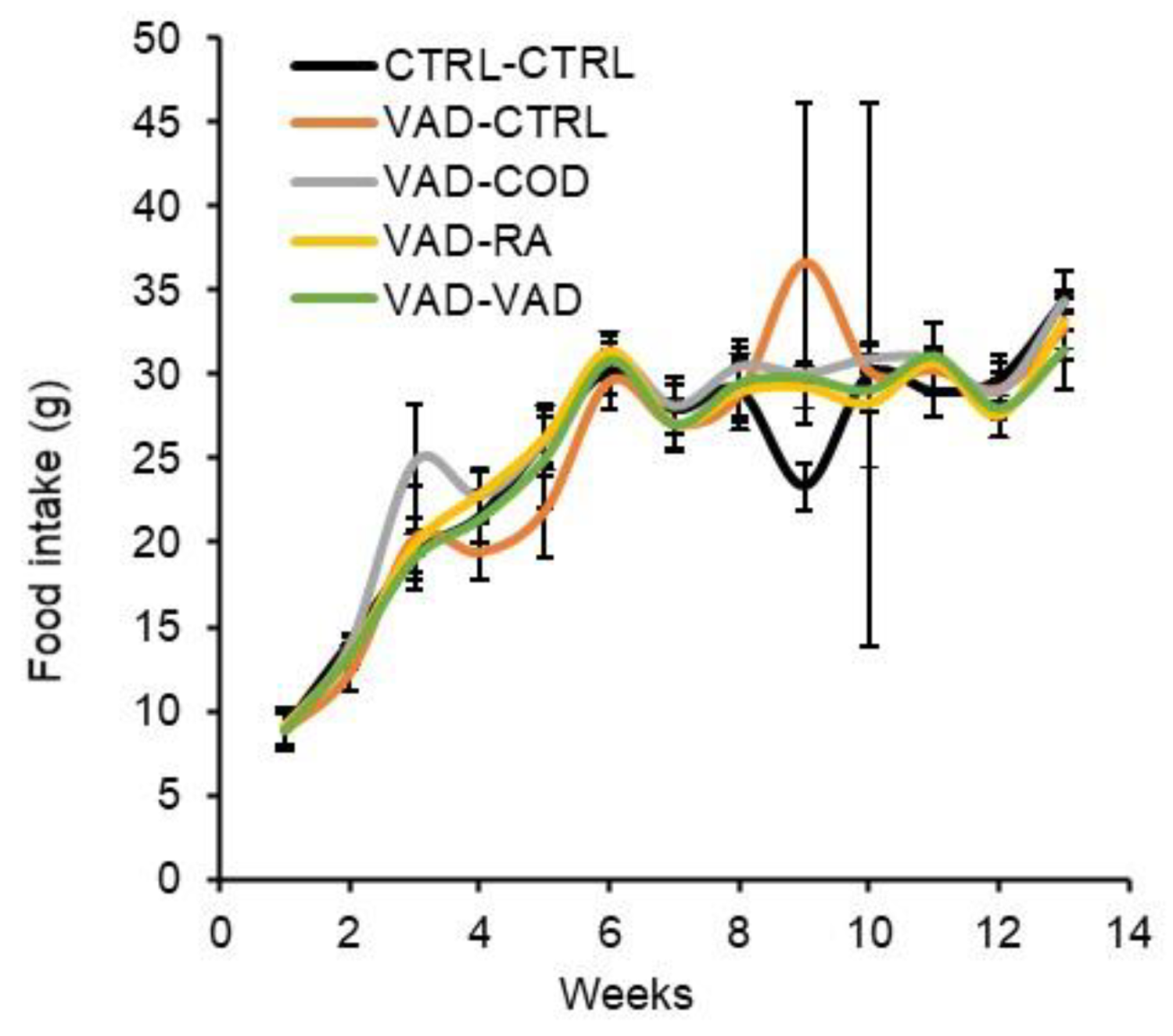
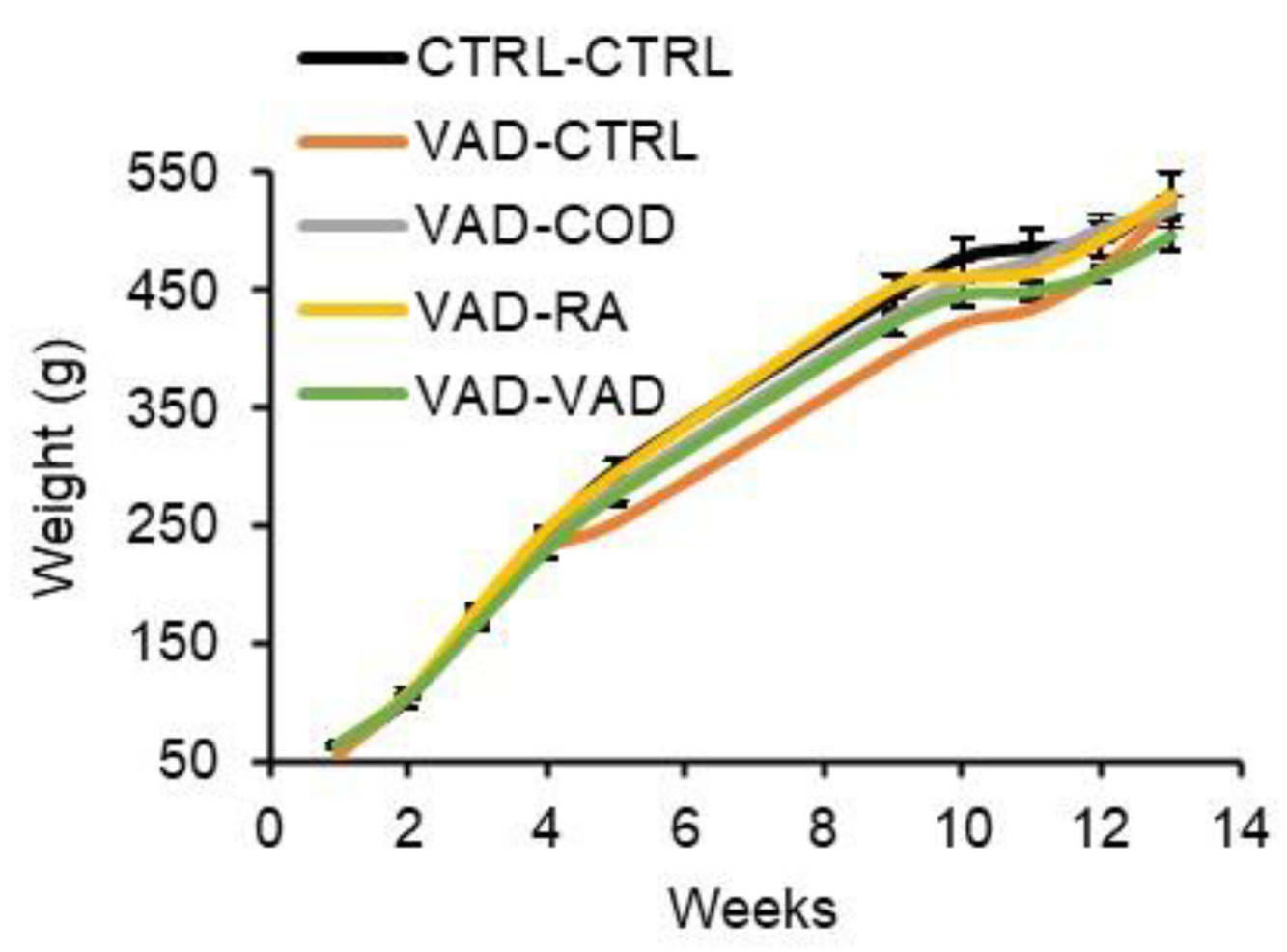
3.2. Food Intake and Body Weight Gain
3.3. DEXA
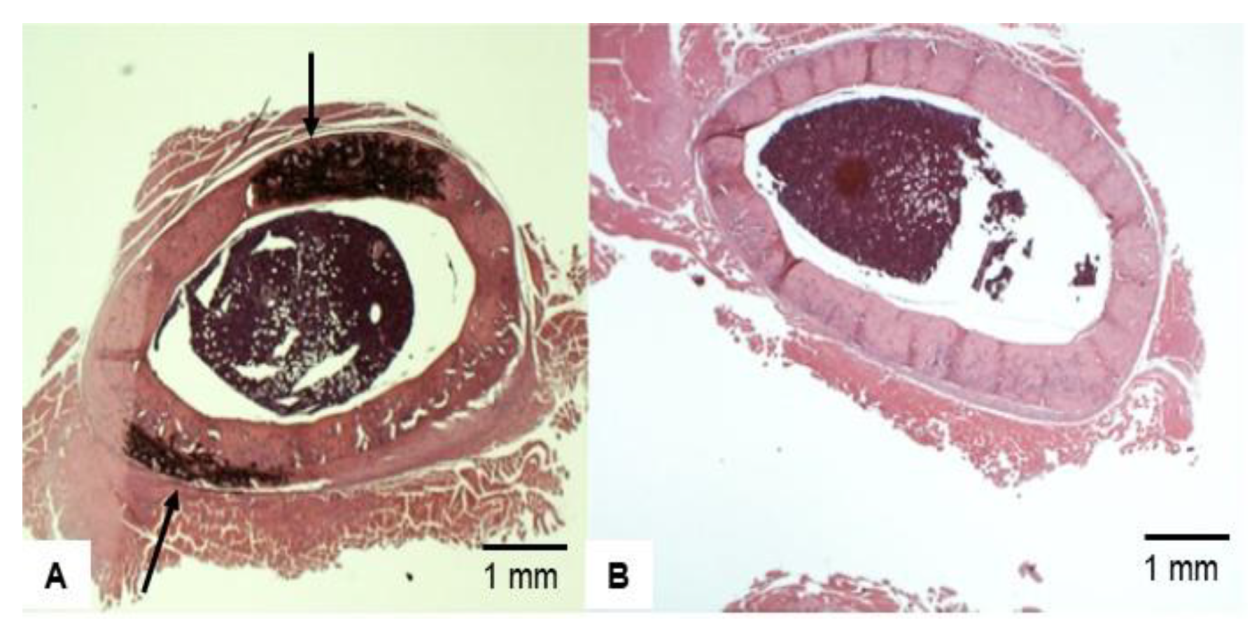
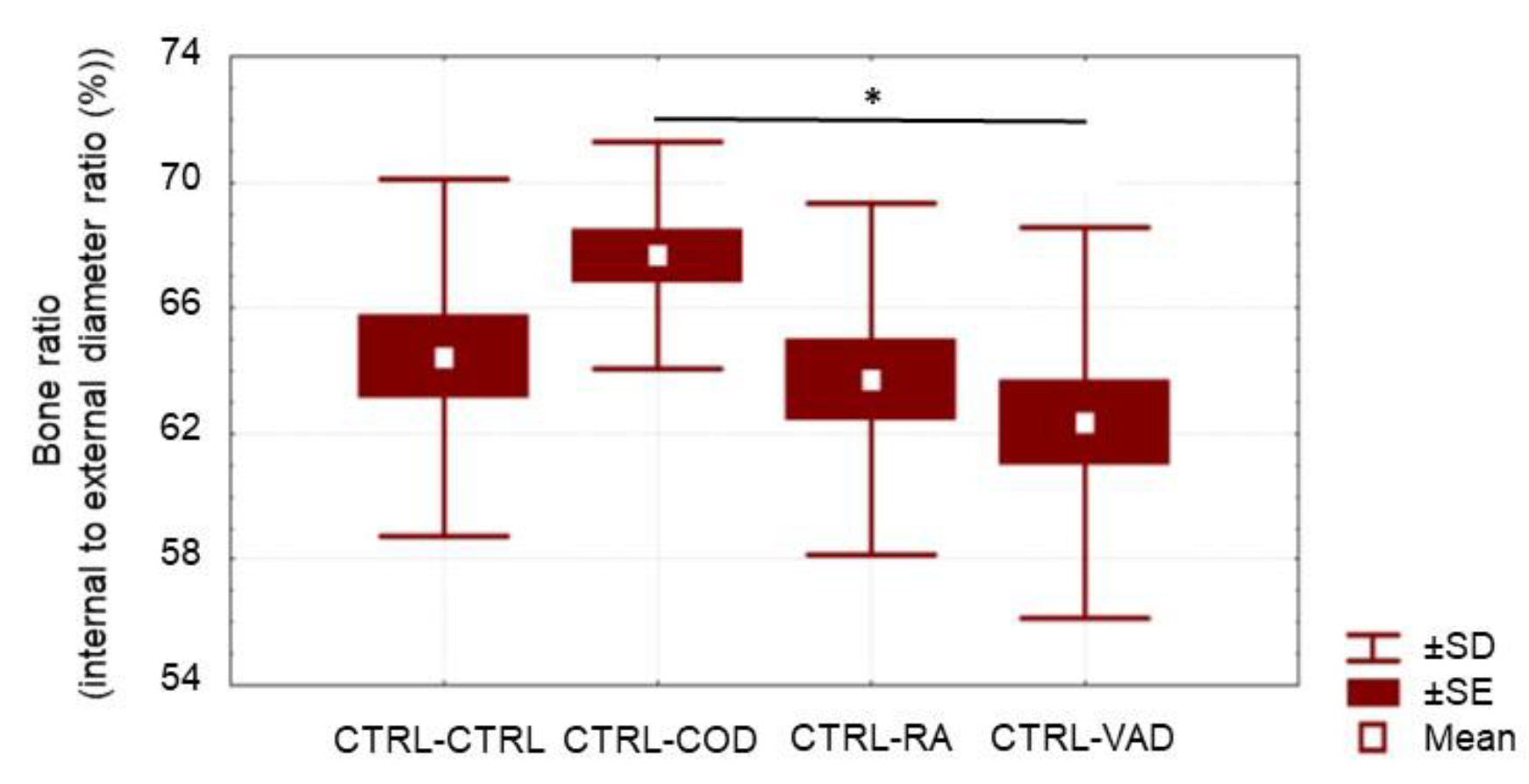
3.4. Bone Histopathology
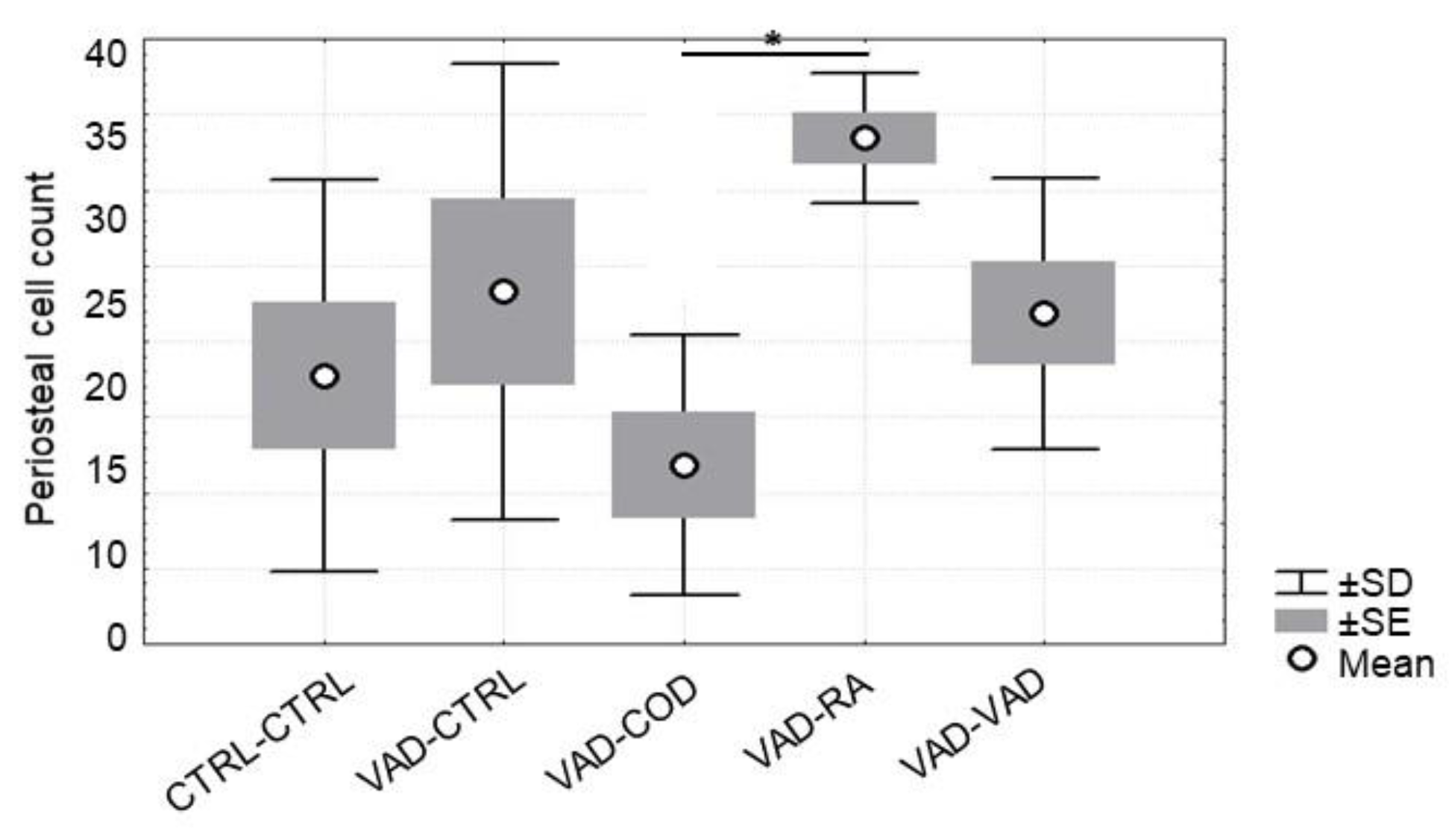
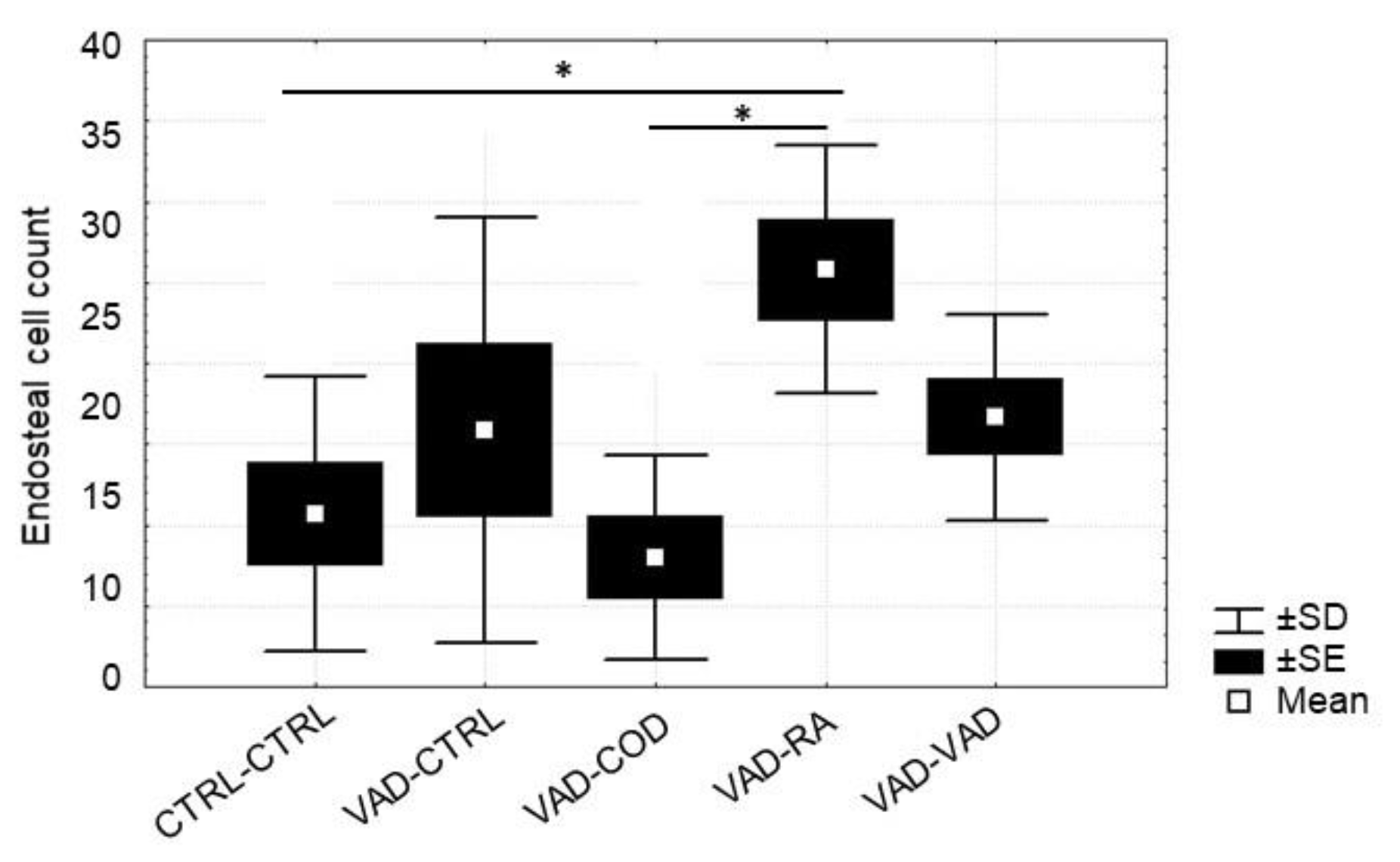
3.5. Osteoblast and Osteoclast Cell Count
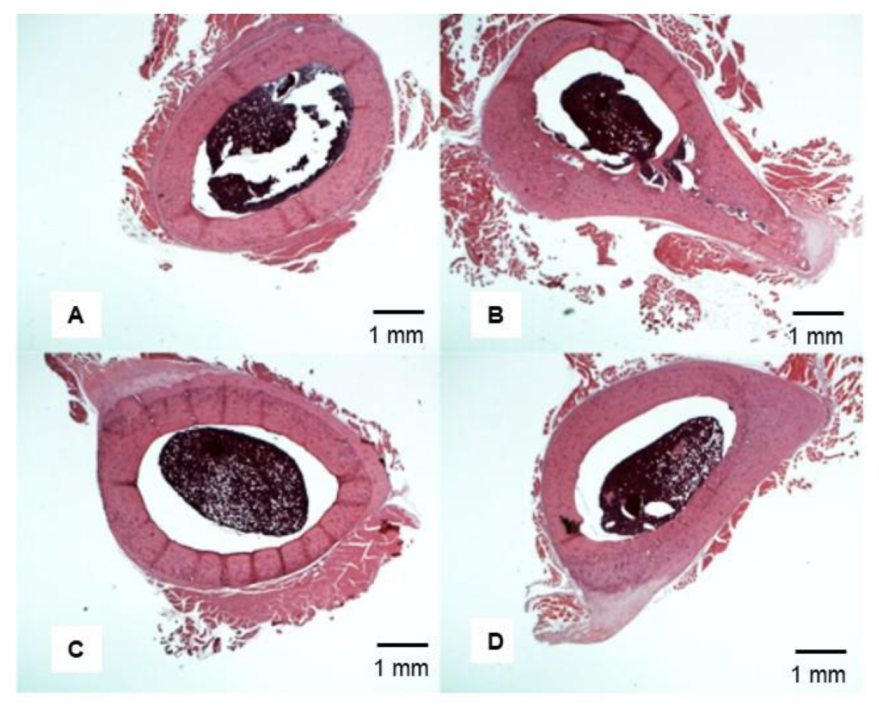
3.6. Representative Femoral Bone Cross-Section of Treated VAD Rats
4. Discussion
4.1. VAD Induces Thicker Bone
4.2. Cod Liver Oil-Containing Retinol Reduces External Bone Thickness after VAD
4.3. Osteoblast Number Increases in Response to Supplemented Retinoic Acid
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATRA | all-trans retinoic acid |
| BFR | bone formation rate |
| BMC | bone mineral content |
| BMD | bone mineral density |
| BSP | bone sialoprotein |
| COD | cod liver oil |
| COL-1 | type 1 collagen |
| CTRL | control |
| DEXA | dual-emission X-ray absorptiometry |
| OC-2 | osteoclast-2 |
| OCN | osteocalcin |
| OPG | osteoprotegerin |
| OPN | osteopontin |
| RA | retinoic acid |
| RANK | receptor activator of nuclear Kb |
| RANKL | receptor activator of nuclear Kb ligand |
| PTH | parathyroid hormone |
| VAD | vitamin A deficient |
References
- Boyle, W.J.; Simonet, W.S.; Lacey, D.L. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 2003, 423, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducy, P.; Schinke, T.; Karsenty, G. The Osteoblast: A Sophisticated Fibroblast under Central Surveillance. Science 2000, 289, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadieh, H.; Arabi, A. Vitamins and bone health: Beyond calcium and vitamin D. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melhus, H.; Michaëlsson, K.; Kindmark, A.; Bergstrom, R.; Holmberg, L.; Mallmin, H.; Wolk, A.; Ljunghall, S. Excessive Dietary Intake of Vitamin A Is Associated with Reduced Bone Mineral Density and Increased Risk for Hip Fracture. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 129, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, S.L. Nutrition and Bone: It is More than Calcium and Vitamin D. Women’s Health 2009, 5, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, C.M.; DeLuca, H. Bone resorption activity of all-trans retinoic acid is independent of vitamin D in rats. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saneshige, S.; Mano, H.; Tezuka, K.; Kakudo, S.; Mori, Y.; Honda, Y.; Itabashi, A.; Yamada, T.; Miyata, K.; Hakeda, Y.; et al. Retinoic acid directly stimulates osteoclastic bone resorption and gene expression of cathepsin K/OC-2. Biochem. J. 1995, 309, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, T.; Lind, P.M.; Jacobson, A.; Hu, L.; Sundqvist, A.; Risteli, J.; Yebra-Rodriguez, A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.; Andersson, G.; Melhus, H. High dietary intake of retinol leads to bone marrow hypoxia and diaphyseal endosteal mineralization in rats. Bone 2011, 48, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, S.; Avioli, L.V.; Muir, H.; Gelderblom, D.; Jenkins, G.; Kurasi, H.; Slatopolsky, E.; Bergfeld, M.A.; Teitelbaum, S. Effects of Hypervitaminosis A on the Bone and Mineral Metabolism of the Rat*. Endocrinology 1988, 122, 2933–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreffo, R.O.; Teti, A.; Triffitt, J.; Francis, M.; Carano, A.; Zallone, Z.A. Effect of vitamin a on bone resorption: Evidence for direct stimulation of isolated chicken osteoclasts by retinol and retinoic acid. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 3, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.-M.; Huang, C.-Q.; Lin, Z.-K.; Tian, N.-F.; Ni, W.-F.; Wang, X.-Y.; Xu, H.-Z.; Chi, Y.-L. The Relationship Between Vitamin A and Risk of Fracture: Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Haub, M.D.; Smith, B.W.; Baybutt, R.C. Decreases in Bone Mineral Content by Dietary All-Trans Retinoic Acid Precede Decreases in Bone Mineral Density in a Weanling Rat Model of Cigarette Smoke—Induced Lung Injuries. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2011, 81, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellanby, E. Skeletal changes affecting the nervous system produced in young dogs by diets deficient in vitamin A. J. Physiol. 1941, 99, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellanby, E. Vitamin A and bone growth: The reversibility of vitamin A-deficiency changes. J. Physiol. 1947, 105, 382–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conaway, H.H.; Pirhayati, A.; Persson, E.; Pettersson, U.; Svensson, O.; Lindholm, C.; Henning, P.; Tuckermann, J.; Lerner, U.H. Retinoids Stimulate Periosteal Bone Resorption by Enhancing the Protein RANKL, a Response Inhibited by Monomeric Glucocorticoid Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31425–31436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.; Choi, Y. Biology of the RANKL–RANK–OPG system in immunity, bone and beyond. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, M.C.; Willenberg, H.S.; Schott, M.; Papewalis, C.; Stumpf, U.; Flohe, S.; Scherbaum, W.A.; Schinner, S. Adipocyte-secreted factors increase osteoblast proliferation and the OPG/RANKL ratio to influence osteoclast formation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 349, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.L.; Hankenson, K.D. Integration of BMP, Wnt, and notch signaling pathways in osteoblast differentiation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Hata, K.; Ikeda, F.; Ichida, F.; Shimoyama, A.; Matsubara, T.; Wada, M.; Amano, K.; Yoneda, T. Signal transduction and transcriptional regulation during mesenchymal cell differentiation. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, T.; Sundqvist, A.; Hu, L.; Pejler, G.; Andersson, G.; Jacobson, A.; Melhus, H. Vitamin A Is a Negative Regulator of Osteoblast Mineralization. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionikaite, V.; Gustafsson, K.L.; Westerlund, A.; Windahl, S.H.; Koskela, A.; Tuukkanen, J.; Johansson, H.; Ohlsson, C.; Conaway, H.H.; Henning, P.; et al. Clinically relevant doses of vitamin A decrease cortical bone mass in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 239, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionikaite, V.; Henning, P.; Drevinge, C.; Shah, F.A.; Palmquist, A.; Wikström, P.; Windahl, S.H.; Lerner, U.H. Vitamin A decreases the anabolic bone response to mechanical loading by suppressing bone formation. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5237–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.H. Mechanisms involved in the intestinal absorption of dietary vitamin A and provitamin A carotenoids. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, R.; Taschler, U.; Preiss-Landl, K.; Wongsiriroj, N.; Zimmermann, R.; Lass, A. Retinyl ester hydrolases and their roles in vitamin A homeostasis. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeier, A.; Niedzielska, D.; Secer, R.; Schilling, A.; Merkel, M.; Enrich, C.; Rensen, P.C.; Heeren, J. Uptake of postprandial lipoproteins into bone in vivo: Impact on osteoblast function. Bone 2008, 43, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidge, N.H.; Shiratori, T.; Ganguly, J.; Goodman, D.S. Pathways of absorption of retinal and retinoic acid in the rat. J. Lipid Res. 1968, 9, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadeddin, A.; Torres-Molina, F.; Cárcel-Trullols, J.; Araico, A.; Peris, J.-E. Pharmacokinetics of the time-dependent elimination of all-trans-retinoic acid in rats. AAPS PharmSci 2004, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muindi, J.; Frankel, S.R.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Jakubowski, A.; Scheinberg, D.A.; Young, C.W.; Dmitrovsky, E.; Warrell, R.P., Jr. Continuous treatment with all-trans retinoic acid causes a progressive reduction in plasma drug concentrations: Implications for relapse and retinoid “resistance” in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 1992, 79, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Nelson, C.; Paik, J.; Shirasaka, Y.; Amory, J.; Isoherranen, N. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model of All-trans-Retinoic Acid with Application to Cancer Populations and Drug Interactions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 361, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diet | Diet Characterization |
|---|---|
| CTRL | Rats euthanized at week 9 after fed a control diet (n = 6) |
| CTRL-CTRL | Rats were fed a control diet for 9 weeks and |
| remained on the diet for weeks 10–13 (n = 7) | |
| VAD | Rats euthanized at week 9 after fed VAD diet (n = 6) |
| After rats were fed a VAD diet for 9 weeks subsequent treatments as follows: | |
| VAD-VAD | VAD diet for weeks 10–13 (n = 7) |
| VAD-CTRL | Control diet for weeks 10–13 (n = 6) |
| VAD-COD | Control diet + cod liver oil for weeks 10–13 (n = 6) |
| VAD-RA | Control diet + retinoic acid for weeks 10–13 (n = 6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baybutt, R.C.; Standard, J.T.; Dim, D.; Quinn, T.; Hamdan, H.; Lin, D.; Kunz, K.; Bomstein, Z.S.; Estorge, B.J.; Herndon, B.; et al. Cod Liver Oil, but Not Retinoic Acid, Treatment Restores Bone Thickness in a Vitamin A-Deficient Rat. Nutrients 2022, 14, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030486
Baybutt RC, Standard JT, Dim D, Quinn T, Hamdan H, Lin D, Kunz K, Bomstein ZS, Estorge BJ, Herndon B, et al. Cod Liver Oil, but Not Retinoic Acid, Treatment Restores Bone Thickness in a Vitamin A-Deficient Rat. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030486
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaybutt, Richard C., Joseph T. Standard, Daniel Dim, Tim Quinn, Hana Hamdan, Dingbo Lin, Kyle Kunz, Zachary S. Bomstein, Benjamin J. Estorge, Betty Herndon, and et al. 2022. "Cod Liver Oil, but Not Retinoic Acid, Treatment Restores Bone Thickness in a Vitamin A-Deficient Rat" Nutrients 14, no. 3: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030486
APA StyleBaybutt, R. C., Standard, J. T., Dim, D., Quinn, T., Hamdan, H., Lin, D., Kunz, K., Bomstein, Z. S., Estorge, B. J., Herndon, B., Zia, H., Mansour, A., Lankachandra, M., & Molteni, A. (2022). Cod Liver Oil, but Not Retinoic Acid, Treatment Restores Bone Thickness in a Vitamin A-Deficient Rat. Nutrients, 14(3), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030486






