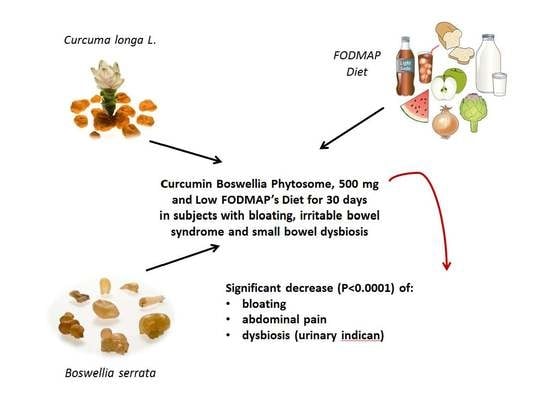
Beneficial Effects on Abdominal Bloating with an Innovative Food-Grade Formulation of Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata Extracts in Subjects with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Small Bowel Dysbiosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Population
2.3. Treatment and Concomitant Medications
2.4. Clinical Evaluation
- (1)
- The score of abdominal bloating. On the questionnaire, participants were asked whether they felt “bloating/uncomfortably full”. There were four options that participants could choose: none (symptom did not occur), mild (symptom occurred but did not interfere with usual activities), moderate (occurrence of symptom somewhat interfered with usual activities), or severe (occurrence of symptom resulted in an inability to perform usual activities) [36].
- (2)
2.5. Supplement Description
2.6. Study Endpoints
2.7. Statistical Analysis
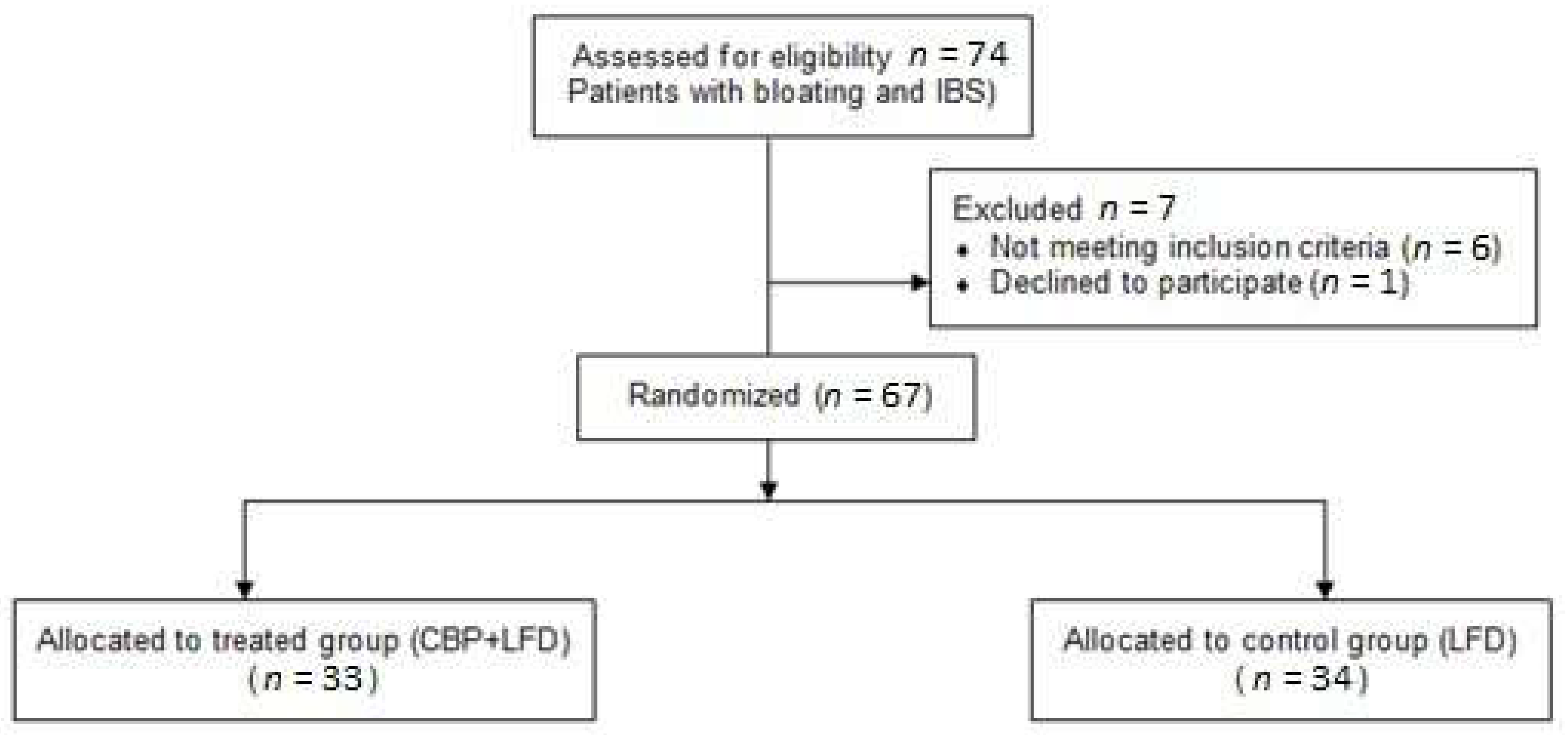
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryu, M.S.; Jung, H.-K.; Ryu, J.-I.; Kim, J.-S.; Kong, K.A. Clinical Dimensions of Bloating in Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Whorwell, P.J. Review article: Abdominal bloating and distension in functional gastrointestinal disorders—Epidemiology and exploration of possible mechanisms. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 27, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, R.S.; Stewart, W.F.; Liberman, J.N.; Ricci, J.A.; Zorich, N.L. Abdominal Pain, Bloating, and Diarrhea in the United States: Prevalence and impact. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000, 45, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, R.; Jacobsen, B.K.; Forde, O.H. Associations between symptoms of irritable colon and psychological and social conditions and lifestyle. BMJ 1986, 292, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longstreth, G.F.; Thompson, W.G.; Chey, W.D.; Houghton, L.A.; Mearin, F.; Spiller, R.C. Functional Bowel Disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringel, Y.; Williams, R.E.; Kalilani, L.; Cook, S.F. Prevalence, Characteristics, and Impact of Bloating Symptoms in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Lee, O.Y.; Naliboff, B.D.; Schmulson, M.; Mayer, E.A. Sensation of bloating and visible abdominal distension in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 3341–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Houghton, L.; Reilly, B.; Morris, J.; Whorwell, P. Bloating and Distension in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The Role of Gastrointestinal Transit. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, M.; Miwa, H.; Nakagawa, A.; Kosako, M.; Akiho, H.; Fukudo, S. Abdominal bloating is the most bothersome symptom in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C): A large population-based Internet survey in Japan. Biopsychosoc. Med. 2016, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaee, A.; Moghimi-Dehkordi, B.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Vahedi, M.; Habibi, M.; Pourhoseingholi, A.; Ghafarnejad, F. Bloating in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2011, 4, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lembo, T.; Naliboff, B.; Munakata, J.; Fullerton, S.; Saba, L.; Tung, S.; Schmulson, M.; Mayer, E.A. Symptoms and Visceral Perception in Patients With Pain-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J.; Boyce, P.; Jones, M. Identification of distinct upper and lower gastrointestinal symptom groupings in an urban population. Gut 1998, 42, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, A.K.; Talley, N.J.; Joos, S.K.; Tolman, K.G.; Hickam, D.H. Abdominal Bloating in Employed Adults: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Association With Other Bowel Disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A.; Li, Z.; Andruzzi, E.; Temple, R.D.; Talley, N.J.; Thompson, W.G.; Whitehead, W.E.; Janssens, J.; Funch-Jensen, P.; Corazziari, E.; et al. U.S. householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Alammar, N.; Singh, R.; Nanavati, J.; Song, Y.; Chaudhary, R.; Mullin, G.E. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, W.; Pimentel, M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Irritable Bowel Syndrome—An Update. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, B.E.; Gabbard, S.L.; Crowell, M.D. Pathophysiology, evaluation, and treatment of bloating: Hope, hype, or hot air? Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 729–739. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, S.M. A role for the gut microbiota in IBS. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.M. Restriction of FODMAP in the management of bloating in irritable bowel syndrome. Singap. Med. J. 2016, 57, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.S.; Gibson, P.R. Clinical Ramifications of Malabsorption of Fructose and Other Short-chain Carbohydrates. Pract. Gastroenterol. 2007, 31, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, S.J.; Parker, F.C.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Dietary Triggers of Abdominal Symptoms in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Randomized Placebo-Controlled Evidence. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunes, H.; Gulen, D.; Mutlu, R.; Gumus, A.; Tas, T.; Topkaya, A.E. Antibacterial effects of curcumin. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurenka Julie S Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: A review of preclinical and clinical research. Altern. Med. Rev. 2009, 14, 141–153.
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Harikumar, K.B. Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 40–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.F.; Ali, F.; Khan, I.A.; Shawl, A.S.; Arora, D.S.; Shah, B.A.; Taneja, S.C. Antistaphylococcal and biofilm inhibitory activities of acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid from Boswellia serrata. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.; Maraghehpour, B.; Khayamzadeh, M.; Kharazifard, M. Traditionally used herbal medicines with antibacterial effect on Aggegatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: Boswellia serrata and Nigella sativa. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2016, 20, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.Z. Boswellia Serrata, A Potential Antiinflammatory Agent: An Overview. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 73, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ku, B.; Cui, L.; Li, X.; Barish, P.A.; Foster, T.C.; Ogle, W.O. Curcumin reverses impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and increases serotonin receptor 1A mRNA and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in chronically stressed rats. Brain Res. 2007, 1162, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Xie, X.; Yu, X.; Pan, J.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, L. The effect of curcumin on the brain-gut axis in rat model of irritable bowel syndrome: Involvement of 5-HT-dependent signaling. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, B.E.; Mearin, F.; Chang, L.; Chey, W.D.; Lembo, A.J.; Simren, M.; Spiller, R. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1393–1407.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.Y.; Morris, J.; Whorwell, P. The irritable bowel severity scoring system: A simple method of monitoring irritable bowel syndrome and its progress. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikx, T.; Schnabl, B. Indoles: Metabolites produced by intestinal bacteria capable of controlling liver disease manifestation. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, R.S.; Bralley, J.A. Clinical applications of urinary organic acids. Part 2. Dysbiosis markers. Altern. Med. Rev. 2008, 13, 292–306. [Google Scholar]
- Giacosa, A.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; Allegrini, P.; Fazia, T.; Bernardinelli, L.; Gasparri, C.; Faliva, M.A.; Peroni, G.; Perna, S.; et al. Symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease management: An innovative food-grade formulation of Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata extracts. Drugs Context 2020, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.R.; Shepherd, S.J. Evidence-based dietary management of functional gastrointestinal symptoms: The FODMAP approach. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, A.; Juraschek, S.; Appel, L.J.; Miller, E.R.; Mueller, N.T. Effects of the DASH Diet and Sodium Intake on Bloating: Results From the DASH–Sodium Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sherif, F.A.; Othman, A.H.; El-Rahman, A.M.A.; Taha, O. Effect of adding intrathecal morphine to a multimodal analgesic regimen for postoperative pain management after laparoscopic bariatric surgery: A prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Br. J. Pain 2016, 10, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodribb, A. Treatment of symptomatic diverticular disease with a high-fibre diet. Lancet 1977, 309, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, F.; Fiasca, F.; Minelli, M.; Maio, D.; Mattei, A.; Vergallo, I.; Cifone, M.G.; Cinque, B.; Minelli, M. The Effects of Low-Nickel Diet Combined with Oral Administration of Selected Probiotics on Patients with Systemic Nickel Allergy Syndrome (SNAS) and Gut Dysbiosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, A.; Elisei, W.; Brandimarte, G.; Giorgetti, G.M.; Inchingolo, C.D.; Nenna, R.; Picchio, M.; Giorgio, F.; Ierardi, E. Musosal tumour necrosis factor α in diverticular disease of the colon is overexpressed with disease severity. Colorectal Dis. 2012, 14, e258–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruis, W.; Meier, E.; Schumacher, M.; Mickisch, O.; Greinwald, R.; Mueller, R. Randomised clinical trial: Mesalazine (Salofalk granules) for uncomplicated diverticular disease of the colon—A placebo-controlled study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.D.; Rahardja, D.; Qu, Y. Sample size calculation for the Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test adjusting for ties. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agresti, A. Categorical Data Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Haubo, R.; Christensen, B. Package “Ordinal” Title Regression Models for Ordinal Data; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Agresti, A. Modelling ordered categorical data: Recent advances and future challenges. Stat. Med. 1999, 18, 2191–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017.
- Gibson, P.R.; Shepherd, S.J. Personal view: Food for thought—Western lifestyle and susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. The FODMAP hypothesis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmos, E.P.; Power, V.A.; Shepherd, S.J.; Gibson, P.R.; Muir, J.G. A Diet Low in FODMAPs Reduces Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 67–75.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roest, R.H.; Dobbs, B.R.; Chapman, B.A.; Batman, B.; O’Brien, L.A.; Leeper, J.A.; Hebblethwaite, C.R.; Gearry, R.B. The low FODMAP diet improves gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A prospective study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2013, 67, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.; Andersen, N.N.; Végh, Z.; Jensen, L.; Ankersen, D.V.; Felding, M.; Simonsen, M.H.; Burisch, J.; Munkholm, P. Ehealth: Low FODMAP dietvs Lactobacillus rhamnosusGG in irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16215–16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharara, A.I.; Aoun, E.; Abdul-Baki, H.; Mounzer, R.; Sidani, S.; ElHajj, I. A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial of Rifaximin in Patients with Abdominal Bloating and Flatulence. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Park, S.; Mirocha, J.; Kane, S.V.; Kong, Y. The Effect of a Nonabsorbed Oral Antibiotic (Rifaximin) on the Symptoms of the Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Lembo, A.; Chey, W.D.; Zakko, S.; Ringel, Y.; Yu, J.; Mareya, S.M.; Shaw, A.L.; Bortey, E.; Forbes, W.P. Rifaximin Therapy for Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome without Constipation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, L.; Favari, C.; Calani, L.; Francinelli, V.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; Allegrini, P.; Mena, P.; Del Rio, D. The Effect of Formulation of Curcuminoids on Their Metabolism by Human Colonic Microbiota. Molecules 2020, 25, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treated Group (n = 33) Mean (SD) | Control Group (n = 34) Mean (SD) | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.82 (14.58) | 43.36 (15.84) | 0.88 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 26 (76.47%) | 25 (75.76) | 1 |
| Male | 8 (23.53%) | 8 (24.24) |
| Group | Mean (SD) T0 | Mean (SD) T1 | Estimate | SE | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary endpoint | ||||||
| Bloating | Treated Control | 2.94 (0.24) 2.76 (0.43) | 0.15 (0.36) 1.85 (0.74) | −6.11 | 1.18 | <0.0001 |
| Secondary endpoints | ||||||
| Abdominal Pain | Treated Control | 7.39 (2.97) 7.47 (2.38) | 1.00 (1.44) 4.71 (1.91) | −5.23 | 1.15 | <0.0001 |
| Indican (mg/L) | Treated Control | 92.39 (53.52) a 90.14 (54.82) | 52.38 (27.22) a 85.53 (54.24) | −0.52 | 0.11 | <0.0001 |
| Variable | N(%) All Sample | N(%) Control | N(%) Treated | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAE | ||||
| 1 | 17 (25.37%) | 17 (50%) | 0 (0%) | <0.0001 |
| 2 | 14 (20.89%) | 12 (35.29%) | 2 (6.1%) | |
| 3 | 17 (25.37%) | 5 (14.71%) | 12 (36.36%) | |
| 4 | 19 (28.36%) | 0 (0%) | 19 (57.58%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giacosa, A.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; Allegrini, P.; Fazia, T.; Bernardinelli, L.; Peroni, G.; Rondanelli, M. Beneficial Effects on Abdominal Bloating with an Innovative Food-Grade Formulation of Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata Extracts in Subjects with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Small Bowel Dysbiosis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030416
Giacosa A, Riva A, Petrangolini G, Allegrini P, Fazia T, Bernardinelli L, Peroni G, Rondanelli M. Beneficial Effects on Abdominal Bloating with an Innovative Food-Grade Formulation of Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata Extracts in Subjects with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Small Bowel Dysbiosis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030416
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiacosa, Attilio, Antonella Riva, Giovanna Petrangolini, Pietro Allegrini, Teresa Fazia, Luisa Bernardinelli, Gabriella Peroni, and Mariangela Rondanelli. 2022. "Beneficial Effects on Abdominal Bloating with an Innovative Food-Grade Formulation of Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata Extracts in Subjects with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Small Bowel Dysbiosis" Nutrients 14, no. 3: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030416
APA StyleGiacosa, A., Riva, A., Petrangolini, G., Allegrini, P., Fazia, T., Bernardinelli, L., Peroni, G., & Rondanelli, M. (2022). Beneficial Effects on Abdominal Bloating with an Innovative Food-Grade Formulation of Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata Extracts in Subjects with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Small Bowel Dysbiosis. Nutrients, 14(3), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030416