Short-Term Therapeutic Adherence of Hospitalized Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia after an Education Intervention: Analysis of Compliance Rates, Risk Factors and Associated Complications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
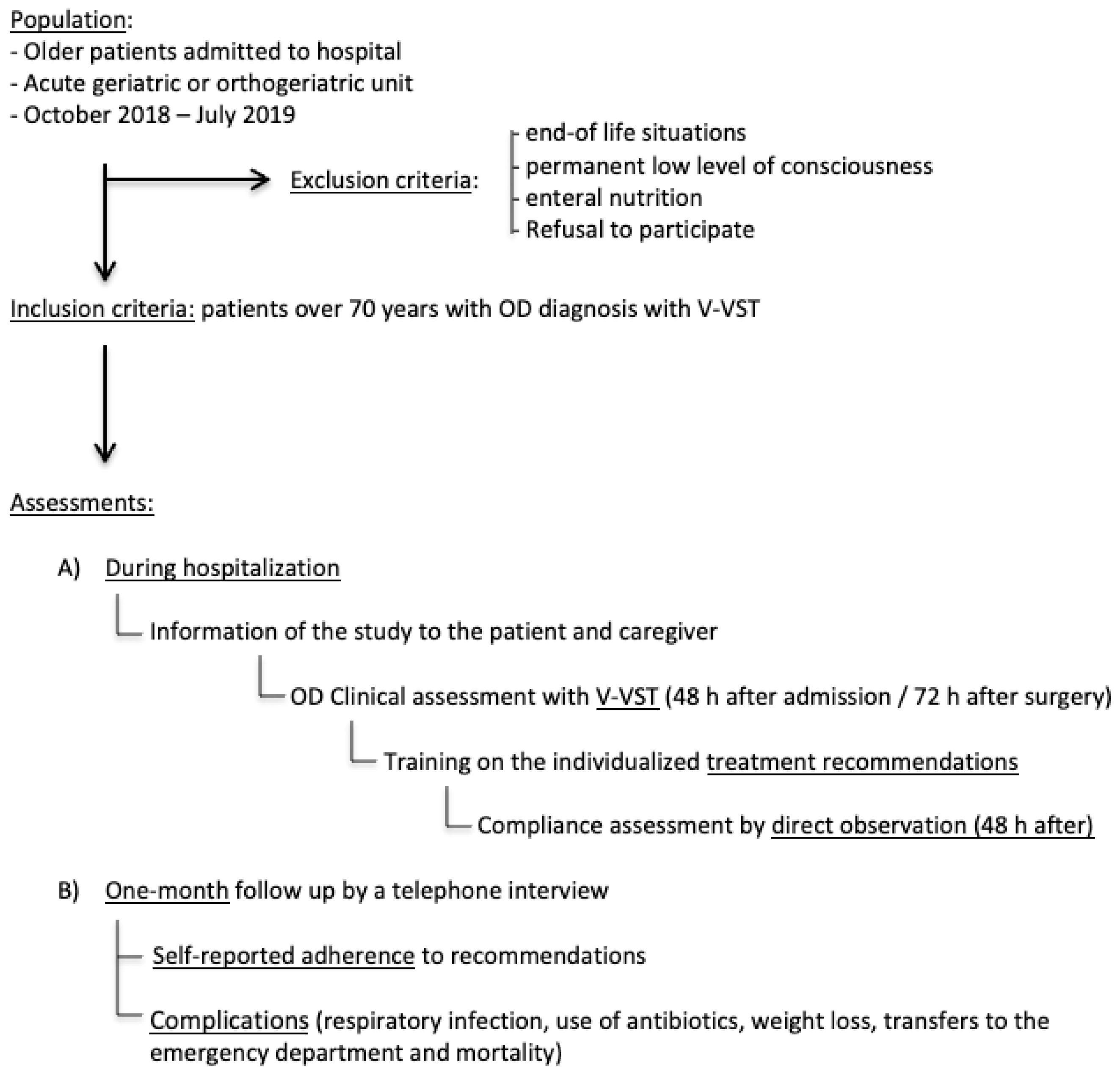
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Health Status, Comorbidity and Geriatric Assessment, and In-Hospital Evolution
2.4. OD Assessment
2.5. Dysphagia Management, Educational Intervention and In-Hospital Adherence Assessment
2.6. One-Month Self-Reported Adherence and OD-Related Complications Assessment
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. OD Management Recommendations and Post-Discharge Complications
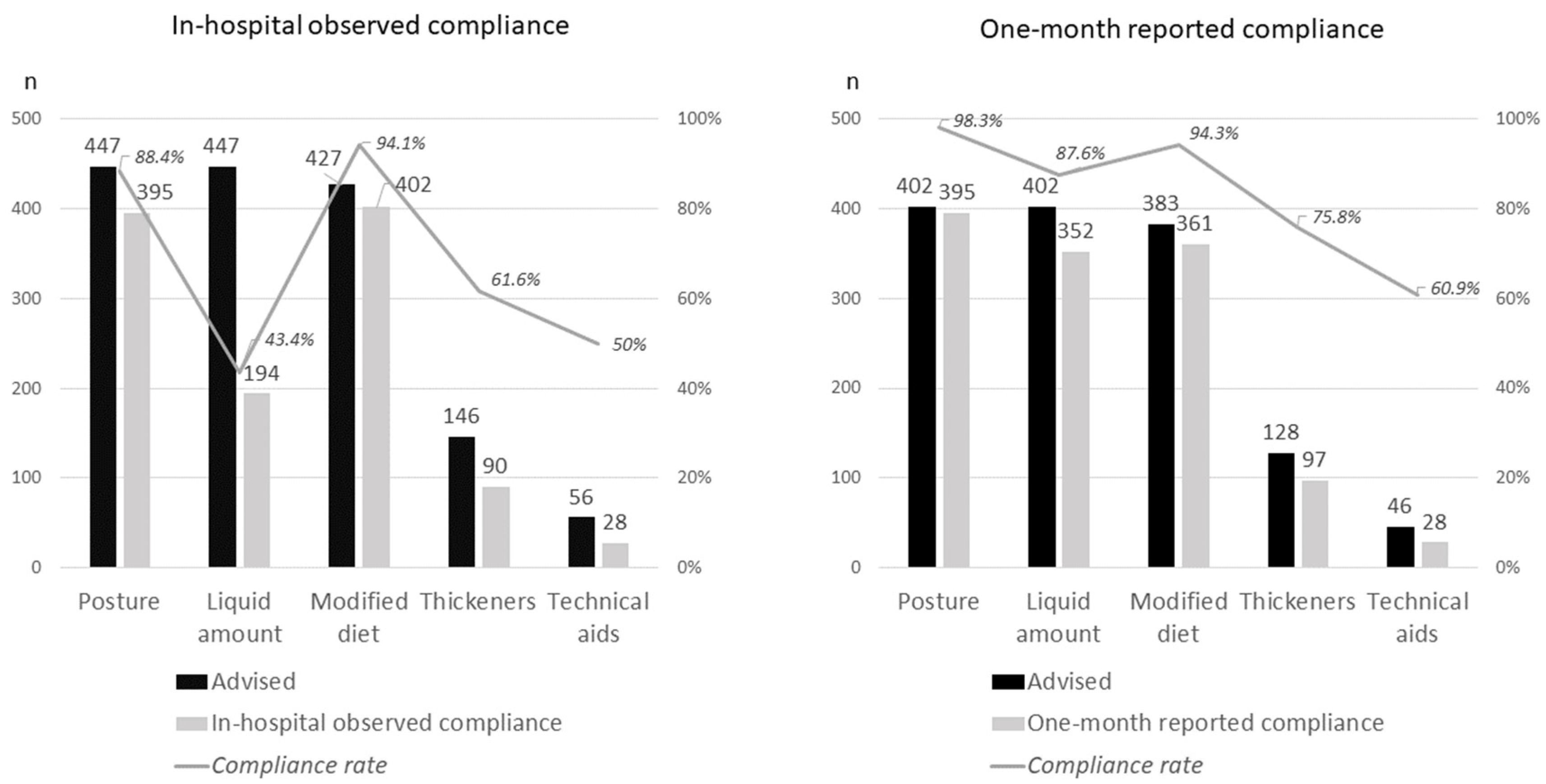
3.3. Observed Adherence to Recommendations during Hospitalization
3.4. One-Month Self-Reported Adherence to Recommendations
3.5. OD Adverse Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riera, S.A.; Marin, S.; Serra-Prat, M.; Tomsen, N.; Arreola, V.; Ortega, O.; Walshe, M.; Clavé, P. A Systematic and a Scoping Review on the Psychometrics and Clinical Utility of the Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) in the Clinical Screening and Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Foods 2021, 10, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Nozal, J.; Montero-Errasquín, B.; García, E.S.; Rodríguez, E.R.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. High Prevalence of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Acutely Hospitalized Patients Aged 80 Years and Older. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 2008–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, M.D.; Modlinski, R.M.; Poulsen, S.H.; Rosenvinge, P.M.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Holst, M. Prevalence of signs of dysphagia and associated risk factors in geriatric patients admitted to an acute medical unit. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 41, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baijens, L.W.; Clavé, P.; Cras, P.; Ekberg, O.; Forster, A.; Kolb, G.F.; Leners, J.C.; Masiero, S.; del Nozal, J.M.; Ortega, O.; et al. European Society for Swallowing Disorders European Union Geriatric Medicine Society white paper: Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a geriatric syndrome. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 1403–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrión, S.; Cabré, M.; Monteis, R.; Roca, M.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Rofes, L.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a prevalent risk factor for malnutrition in a cohort of older patients admitted with an acute disease to a general hospital. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabré, M.; Serra-Prat, M.; Force, L.; Almirall, J.; Palomera, E.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia is a Risk Factor for Readmission for Pneumonia in the Very Elderly Persons: Observational Prospective Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2014, 69, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Attrill, S.; White, S.; Murray, J.; Hammond, S.; Doeltgen, S. Impact of oropharyngeal dysphagia on healthcare cost and length of stay in hospital: A systematic review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Australian and New Zealand Society for Geriatric Medicine Position Statement Abstract: Dysphagia and aspiration in older people. Australas. J. Ageing 2020, 39, 85. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, R.; Dziewas, R.; Beck, A.M.; Clave, P.; Hamdy, S.; Heppner, H.J.; Langmore, S.; Leischker, A.H.; Martino, R.; Pluschinski, P.; et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older persons from pathophysiology to adequate intervention: A review and summary of an international expert meeting. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sura, L.; Madhavan, A.; Carnaby, G.; Crary, M.A. Dysphagia in the elderly: Management and nutritional considerations. Clin. Interv. Aging 2012, 7, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Pede, C.; Mantovani, M.E.; Del Felice, A.; Masiero, S. Dysphagia in the elderly: Focus on rehabilitation strategies. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 28, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 10–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, A.M.; Kjaersgaard, A.; Hansen, T.; Poulsen, I. Systematic review and evidence based recommendations on texture modified foods and thickened liquids for adults (above 17 years) with oropharyngeal dysphagia An updated clinical guideline. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, R.; Bretón, I.; Cereda, E.; Desport, J.C.; Dziewas, R.; Genton, L.; Gomes, F.; Jésus, P.; Leischker, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; et al. ESPEN guideline clinical nutrition in neurology. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 354–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, J.; Sklar, G.E.; Sen Oh, V.M.; Li, S.C. Factors affecting therapeutic compliance: A review from the patient´s perspective. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- DiMatteo, M.R. Patient adherence to pharmacotherapy: The importance of effective communication. Formul. (Clevel. Ohio) 1995, 30, 601. [Google Scholar]
- Krekeler, B.N.; Broadfoot, C.K.; Johnson, S.; Connor, N.P.; Rogus-Pulia, N. Patient Adherence to Dysphagia Recommendations: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia 2017, 33, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa-Val, M.C.; Martín-Martínez, A.; Graupera, M.; Arias, O.; Elvira, A.; Cabré, M.; Palomera, E.; Bolívar-Prados, M.; Clavé, P.; Ortega, O. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Complications of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older Patients with Dementia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mateos-Nozal, J.; Garcia, E.S.; Rodríguez, E.R.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older patients with hip fracture. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavé, P.; Arreola, V.; Romea, M.; Medina, L.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M. Accuracy of the volume-viscosity swallow test for clin-ical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia and aspiration. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.; Wyles, C.; Wilkinson, T.; Sainsbury, R. The Effect of Compliance on Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Dysphagia on Videofluoroscopy. Dysphagia 2001, 16, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenvinge, S.K.; Starke, I.D. Improving care for patients with dysphagia. Age Ageing 2005, 34, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, B.-M.; Han, T.R. Factors Associated With Compliance With Viscosity-Modified Diet Among Dysphagic Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 37, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, A.; Windsor, J. Compliance of geriatric dysphagic patients with safe-swallowing instructions. J. Med. Speech Lang. Pathol. 1196, 4, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Ortega, O.; Roca, M.; Arus, M.; Civit, P.C. Effect of a Minimal-Massive Intervention in Hospitalized Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: A Proof of Concept Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.; Gensler, G.; Hind, J.; Logemann, J.A.; Lindblad, A.S.; Brandt, D.; Baum, H.; Lilienfeld, D.; Kosek, S.; Lundy, D.; et al. Comparison of 2 Interventions for Liquid Aspiration on Pneumonia Incidence. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Carrión, S.; Puig-Pey, M.; Juárez, F.; Clavé, P. Triple Adaptation of the Mediterranean Diet: Design of A Meal Plan for Older People with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Based on Home Cooking. Nutrients 2019, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logemann, J.A.; Gensler, G.; Robbins, J.; Lindblad, A.S.; Brandt, D.; Hind, J.A.; Kosek, S.; Dikeman, K.; Kazandjian, M.; Gramigna, G.D.; et al. A Randomized Study of Three Interventions for Aspiration of Thin Liquids in Patients with Dementia or Parkinson’s Disease. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichero, J.A.Y.; Lam, P.; Steele, C.M.; Hanson, B.; Chen, J.; Dantas, R.O.; Duivestein, J.; Kayashita, J.; Lecko, C.; Murray, J.; et al. Development of International Terminology and Definitions for Texture-Modified Foods and Thickened Fluids Used in Dysphagia Management: The IDDSI Framework. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flynn, E.; Smith, C.; Walsh, C.D.; Walshe, M. Modifying the consistency of food and fluids for swallowing difficulties in dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD011077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Miles, A.; Braakhuis, A. Texture-Modified Diets, Nutritional Status and Mealtime Satisfaction: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazenby-Paterson, T. Thickened liquids: Do they still have a place in the dysphagia toolkit? Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 28, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keeffe, S.T. Use of modified diets to prevent aspiration in oropharyngeal dysphagia: Is current practice justified? BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, L.; Santos-Ruiz, S.; Clavé, P.; González de Paz, L.; Cabrera, E. Nursing interventions in adult patients with oropharynge-al dysphagia: A systematic review. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ESSD Position Statements: Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Adult Patients. 2012. Available online: http://www.myessd.org/docs/position_statements/ESSD_Position_Statements_on_OD_in_adult_patients_for_web.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2021).
| Variable | Characteristic | Total n = 447 | Adherence during Hospitalization n = 166 | Non Adherence during Hospitalization n = 281 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | Age (years) c | 92 (88; 95) | 91 (86; 95) | 92 (89; 96) | 0.003 |
| Female b | 316 (70.7%) | 116 (69.9%) | 200 (71.2%) | 0.771 | |
| Living in nursing home b | 114 (25.5%) | 33 (19.9%) | 81 (28.9%) | 0.036 | |
| Geriatric Assessment | Barthel Index < 40 b | 147 (33.5%) | 29 (17.9%) | 118 (42.6%) | <0.001 |
| Lawton 0 b | 244 (57.2%) | 68 (42.5%) | 177 (66.0%) | <0.001 | |
| FAC ≤ 3 b | 244 (57.1%) | 69 (43.4%) | 175 (65.3%) | <0.001 | |
| GDS ≥ 4 b | 203 (54.4%) | 53 (39.3%) | 150 (63.0%) | <0.001 | |
| MNA-SF ≤ 7 b | 122 (31%) | 25 (15.1%) | 97 (39.3%) | <0.001 | |
| BMI < 22 b | 80 (18.1%) | 29 (17.5%) | 51 (18.9%) | 0.848 | |
| Professional caregiver b | 60 (13.4%) | 22 (13.3%) | 38 (13.5%) | 0.681 | |
| Comorbidities and previous treatment | Dementia b | 122 (27.3%) | 29 (17.5%) | 93 (33.1%) | <0.001 |
| Vascular disease b | 119 (26.6%) | 37 (22.3%) | 82 (29.2%) | 0.111 | |
| Stroke b | 61 (13.6%) | 15 (9.0%) | 46 (16.4%) | 0.029 | |
| Parkinson b | 30 (6.7%) | 12 (7.2%) | 18 (6.4%) | 0.737 | |
| Head and neck cancer b | 18 (4.0%) | 4 (2.4%) | 14 (5.0%) | 0.181 | |
| Malnutrition b | 10 (2.2%) | 2 (1.2%) | 8 (2.8%) | 0.335 | |
| Number of drugs c | 8 (6; 10) | 8 (5; 10) | 8 (6; 8) | 0.149 | |
| Unit of admission | Acute Geriatric Unit b | 271 (60.6%) | 79 (47.6%) | 192 (68.3%) | <0.001 |
| Main reason for admission | Respiratory infection b | 144 (32.2%) | 43 (25.9%) | 101 (35.9%) | 0.028 |
| Dysphagia assessment | Safety sign b | 286 (64.0%) | 74 (44.6%) | 212 (75.4%) | <0.001 |
| Efficacy sign b | 437 (97.8%) | 161 (97.0%) | 276 (98.2%) | 0.510 | |
| Self feeding advised b | 254 (56.8%) | 134 (80.7%) | 120 (42.7%) | <0.001 | |
| Professional caregiver present b | 20 (4.6%) | 9 (5.7%) | 11 (4.0%) | 0.437 | |
| In-hospital complications and discharge | Delirium b | 269 (60.2%) | 92 (55.4%) | 177 (63.0%) | 0.114 |
| Length of stay (days) c | 8 (5; 12) | 8 (5; 13) | 8 (5; 12) | 0.405 | |
| ONS at discharge b | 80 (19.9%) | 38 (23.8%) | 42 (17.4%) | 0.116 | |
| Nursing home b | 131 (31.8%) | 42 (28.4%) | 89 (33.7%) | 0.265 | |
| 1 month complications | Chest infection or antibiotic use b | 36 (8.9%) | 12 (7.5%) | 24 (9.9%) | 0.413 |
| Weight loss ≥ 3 Kg b | 63 (15.6%) | 28 (17.5%) | 35 (14.4%) | 0.402 | |
| Emergency department referral or hospital admission b | 71 (17.6%) | 22 (13.8%) | 49 (20.2%) | 0.098 | |
| Death b | 24 (6%) | 7 (4.4%) | 17 (7.0%) | 0.277 |
| Variables | Always/Sometimes Complied with Advice n = 308 | Never Complied with Advice n = 95 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | Age b | 92 (88; 95) | 92 (88; 95) | 0.996 |
| Female a | 228 (74.0%) | 63 (66.3%) | 0.142 | |
| Discharge to nursing home a | 103 (33.4%) | 19 (20.0%) | 0.013 | |
| Professional caregiver interviewed a | 86 (28.6%) | 14 (14.9%) | 0.008 | |
| Geriatric assessment | Barthel Index < 40 a | 92 (30.4%) | 38 (41.3%) | 0.050 |
| Lawton 0 a | 169 (57.5%) | 52 (57.8%) | 0.961 | |
| FAC ≤ 3 a | 167 (56.6%) | 51 (57.3%) | 0.908 | |
| GDS ≥ 4 a | 133 (51.2%) | 50 (65.8%) | 0.024 | |
| MNA-SF ≤ 7 a | 74 (27.3%) | 36 (45.0%) | 0.003 | |
| BMI < 22 a | 49 (16.1%) | 22 (23.4%) | 0.107 | |
| Comorbidities and previous treatment | Dementia a | 81 (26.3%) | 31 (32.6%) | 0.228 |
| Vascular disease a | 77 (25.0%) | 29 (30.5%) | 0.285 | |
| Stroke a | 44 (14.3%) | 10 (10.5%) | 0.347 | |
| Parkinson a | 23 (7.5%) | 5 (5.3%) | 0.460 | |
| Head and neck cancer a | 12 (3.9%) | 5 (5.3%) | 0.563 | |
| Malnutrition a | 5 (1.6%) | 3 (3.2%) | 0.399 | |
| Number of drugs b | 8 (6; 10) | 8 (6; 10) | 0.826 | |
| Current hospitalization | Acute Geriatric Unit a | 181 (58.5%) | 64 (67.4%) | 0.133 |
| Chest infection b | 98 (31.8%) | 31 (32.6%) | 0.882 | |
| Delirium a | 178 (57.7%) | 63 (66.3%) | 0.139 | |
| Length of stay b | 7 (5; 12) | 8 (5; 12) | 0.807 | |
| Dysphagia signs and indications during hospitalization | Safety sign a | 180 (58.4%) | 73 (76.8%) | 0.001 |
| Efficacy sign a | 303 (98.4%) | 90 (94.7%) | 0.060 | |
| Written indications a | 253 (82.1%) | 80 (84.2%) | 0.642 | |
| OD diagnosis in medical report a | 116 (37.7%) | 44 (46.3%) | 0.132 | |
| OD diagnosis in nurse report a | 24 (7.8%) | 7 (7.4%) | 0.892 | |
| In-hospital observed adherence a | 133 (43.2%) | 23 (28.4%) | 0.010 | |
| One-month complications | Chest infection or use of antibiotics a | 25 (8.1%) | 11 (11.6%) | 0.301 |
| Weight loss ≥ 3 kg a | 40 (13.0%) | 23 (24.2%) | 0.008 | |
| Emergency department referal or hospital admission a | 49 (15.9%) | 22 (23.2%) | 0.105 | |
| Death a | 8 (2.6%) | 16 (16.8%) | <0.001 | |
| Variables | Death | Other OD Complications | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes n = 24 | No n = 379 | p Value | Yes n = 123 | No n = 280 | p Value | ||
| Demographic | Age a | 95 (89; 98) | 92 (88; 95) | 0.029 | 92 (89; 95) | 92 (87; 95) | 0.450 |
| Female b | 62.5 | 72.8 | 0.274 | 65.0 | 75.4 | 0.033 | |
| Discharge to nursing home | 25.6 | 30.6 | 0.562 | 27.6 | 31.4 | 0.446 | |
| Geriatric assessment | Barthel Index < 40 b | 69.6 | 30.6 | <0.001 | 40.0 | 29.8 | 0.048 |
| Lawton 0 b | 78.3 | 56.2 | 0.038 | 61.7 | 55.8 | 0.278 | |
| FAC ≤ 3 b | 78.3 | 55.4 | 0.032 | 67.5 | 52.1 | 0.005 | |
| GDS ≥ 4 b | 60.9 | 54.1 | 0.608 | 57.0 | 53.4 | 0.543 | |
| MNA-SF ≤ 7 b | 47.8 | 30.2 | 0.078 | 42.1 | 26.6 | 0.004 | |
| BMI < 22 b | 41.7 | 16.3 | 0.004 | 27.0 | 13.8 | 0.001 | |
| Comorbidities | Dementia b | 25.0 | 28.0 | 0.753 | 28.5 | 27.5 | 0.844 |
| Delirium during hospitalization | 79.2 | 58.6 | 0.046 | 64.2 | 57.9 | 0.230 | |
| Vascular disease b | 16.7 | 26.9 | 0.269 | 27.6 | 25.7 | 0.686 | |
| Stroke b | 20.8 | 12.9 | 0.347 | 14.6 | 12.9 | 0.630 | |
| Parkinson b | 8.3 | 6.9 | 0.679 | 8.9 | 6.1 | 0.296 | |
| Number of drugs a | 8 (6;11) | 8 (5; 10) | 0.509 | 8 (6; 11) | 8 (5; 10) | 0.239 | |
| Dysphagia assessment | Safety sign b | 70.8 | 62.3 | 0.400 | 68.3 | 60.4 | 0.129 |
| Efficacy sign b | 95.8 | 97.6 | 0.463 | 95.9 | 98.2 | 0.181 | |
| Intrahospital adherence (observed) | Global adherence b | 29.2 | 40.4 | 0.277 | 38.2 | 40.4 | 0.685 |
| Adherence to diet b | 87.5 | 95.0 | 0.135 | 96.7 | 93.6 | 0.196 | |
| Adherence to textures of liquids b | 91. | 88.4 | 1.000 | 86.2 | 89.6 | 0.314 | |
| Adherence to liquid volumes b | 41.7 | 46.7 | 0.631 | 44.7 | 47.1 | 0.653 | |
| Adhence to posture b | 75.0 | 88.4 | 0.100 | 85.4 | 88.6 | 0.369 | |
| Adherence to technical aids b | 83.3 | 93.1 | 0.093 | 91.1 | 93.2 | 0.447 | |
| One-month reported adherence (reported) | Global adherence b | 33.3 | 79.2 | <0.001 | 65.9 | 81.1 | 0.001 |
| Adherence to diet b | 75.0 | 95.8 | 0.001 | 87.8 | 97.5 | <0.001 | |
| Adherence to textures of liquids b | 83.3 | 92.9 | 0.103 | 87.0 | 94.6 | 0.008 | |
| Adherence to liquid volumes b | 45.8 | 90.2 | <0.001 | 80.5 | 90.7 | 0.004 | |
| Adherence to posture b | 79.2 | 99.5 | <0.001 | 96.7 | 98.9 | 0.208 | |
| Adherence to delivery methods b | 87.5 | 96.0 | 0.084 | 96.7 | 95.0 | 0.430 | |
| Model | Variable | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number 1: Mortality | Age (per year) | 1.09 | 1.00–1.19 | 0.051 |
| Female | 0.47 | 0.17–1.30 | 0.146 | |
| Barthel Index < 40 | 4.37 | 1.64–11.65 | 0.003 | |
| Body Mass Index < 22 | 4.65 | 1.66–13.02 | 0.003 | |
| One-month self reported global adherence | 0.12 | 0.04–0.315 | <0.001 | |
| Model 2: Other complications associated with dysphagia | Age (per year) | 1.00 | 0.97–1.04 | 0.811 |
| Female | 0.52 | 0.32–0.85 | 0.010 | |
| Barthel Index < 40 | 1.50 | 0.93–2.41 | 0.094 | |
| Body Mass Index < 22 | 2.51 | 1.44–4.37 | 0.001 | |
| One-month self reported global adherence | 0.49 | 0.30–0.81 | 0.005 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mateos-Nozal, J.; Sánchez García, E.; Montero-Errasquín, B.; Romero Rodríguez, E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Short-Term Therapeutic Adherence of Hospitalized Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia after an Education Intervention: Analysis of Compliance Rates, Risk Factors and Associated Complications. Nutrients 2022, 14, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030413
Mateos-Nozal J, Sánchez García E, Montero-Errasquín B, Romero Rodríguez E, Cruz-Jentoft AJ. Short-Term Therapeutic Adherence of Hospitalized Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia after an Education Intervention: Analysis of Compliance Rates, Risk Factors and Associated Complications. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030413
Chicago/Turabian StyleMateos-Nozal, Jesús, Elisabeth Sánchez García, Beatriz Montero-Errasquín, Estela Romero Rodríguez, and Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft. 2022. "Short-Term Therapeutic Adherence of Hospitalized Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia after an Education Intervention: Analysis of Compliance Rates, Risk Factors and Associated Complications" Nutrients 14, no. 3: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030413
APA StyleMateos-Nozal, J., Sánchez García, E., Montero-Errasquín, B., Romero Rodríguez, E., & Cruz-Jentoft, A. J. (2022). Short-Term Therapeutic Adherence of Hospitalized Older Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia after an Education Intervention: Analysis of Compliance Rates, Risk Factors and Associated Complications. Nutrients, 14(3), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030413






