Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention in Young Women with GDM and Subsequent Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
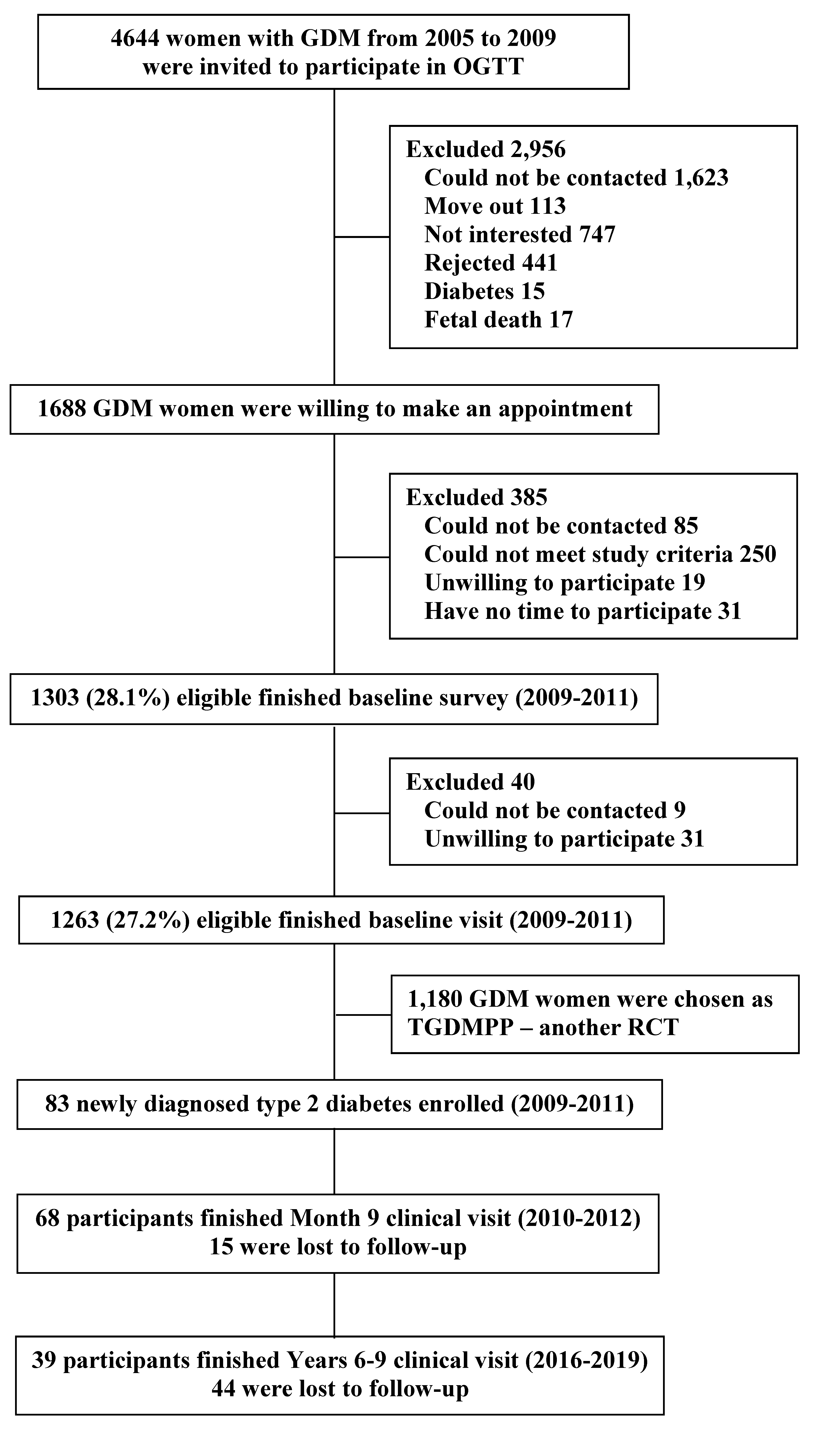
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Screening Visit
2.3. Run-In
2.4. Lifestyle Intervention
2.5. Measurement
2.6. Follow-Up and Outcome Indices
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association: 14. Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S232–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Du, S.; Sun, D.; Li, X.; Heianza, Y.; Hu, G.; Sun, L.; Pei, X.; Shang, X.; Qi, L. Prevalence and Trends in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Among Women in the United States, 2006-2017: A Population-Based Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 868094. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Dong, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Wen, J.; Gao, W.; Sun, S.; Lv, F.; Tian, H.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. Increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese women from 1999 to 2008. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Shao, P.; Zhang, C.; Tian, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.; Dong, L.; Li, L.; Yu, Z.; Chan, J.C.; et al. Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Risk Factors in Chinese Pregnant Women: A Prospective Population-Based Study in Tianjin, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vounzoulaki, E.; Khunti, K.; Abner, S.C.; Tan, B.K.; Davies, M.J.; Gillies, C.L. Progression to type 2 diabetes in women with a known history of gestational diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 369, m1361. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Ming, W.K.; Wang, Z. Incidence Rate of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 170,139 Women. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 3076463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauenborg, J.; Mathiesen, E.; Hansen, T.; Glumer, C.; Jorgensen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Hornnes, P.; Pedersen, O.; Damm, P. The prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in a danish population of women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus is three-fold higher than in the general population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4004–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.B.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Hull, R.L.; Tong, J.; Wallace, T.M.; Kodama, K.; Shofer, J.B.; Heckbert, S.R.; Boyko, E.J.; Fujimoto, W.Y.; et al. Gestational diabetes mellitus increases the risk of cardiovascular disease in women with a family history of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2078–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Shah, B.R. Mild glucose intolerance in pregnancy and risk of cardiovascular disease: A population-based cohort study. CMAJ 2009, 181, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, W.; Leng, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Tian, H.; Chen, J.; Qi, L.; et al. High risk of metabolic syndrome after delivery in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 150, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, D.K.; Stuart, J.J.; Li, S.; Chavarro, J.; Rimm, E.B.; Rich-Edwards, J.; Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Zhang, C. Association of History of Gestational Diabetes with Long-term Cardiovascular Disease Risk in a Large Prospective Cohort of US Women. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Li, W.; Leng, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Gestational diabetes with diabetes and prediabetes risks: A large observational study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, M.; Woodward, M.; Peters, S.A. Diabetes, glycated hemoglobin, and the risk of myocardial infarction in women and men: A prospective cohort study of the UK Biobank. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Jousilahti, P.; Qiao, Q.; Peltonen, M.; Katoh, S.; Tuomilehto, J. The gender-specific impact of diabetes and myocardial infarction at baseline and during follow-up on mortality from all causes and coronary heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, R.R.; Bolin, P.; Brancati, F.L.; Bray, G.A.; Clark, J.M.; Coday, M.; Crow, R.S.; Curtis, J.M.; Egan, C.M.; Espeland, M.A.; et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Tian, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X.; et al. Tianjin Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prevention Program: Study design, methods, and 1-year interim report on the feasibility of lifestyle intervention program. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 98, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Leng, J.; Li, N.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Qi, L.; Yang, X.; et al. One-year weight losses in the Tianjin Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prevention Programme: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Leng, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X.; Tian, H.; Hu, G. Different associations of diabetes with beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance among obese and nonobese Chinese women with prior gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Leng, J.; Liu, D.; Fang, H.; Li, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X.; et al. Joint effects of pre-pregnancy body mass index and weight change on postpartum diabetes risk among gestational diabetes women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014, 22, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Consultation: Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes mellitus and Its Complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes mellitus; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2005, 28 (Suppl. 1), S37–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G. More vigorous efforts are needed to fight obesity, a serious public health problem in China. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2021, 29, 1580–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; He, Y.N.; Zhai, F.Y.; Yang, X.G.; Hu, X.Q.; Zhao, W.; Ma, G. Comparison of assessment of food intakes by using 3 dietary survey methods. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2006, 40, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Luan, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, A.; Hu, X.; Cui, Z.; Zhai, F.; Yang, X. Physical activity level and its association with metabolic syndrome among an employed population in China. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9 (Suppl. 1), 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Luan, D.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; Cui, Z.; Hu, X.; Yang, X. The analysis and evaluation of a physical activity questionnaire of Chinese employed population. Nutr. Trans. 2007, 29, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Horswell, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Johnson, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ryan, D.H.; Hu, G. Body Mass Index and the Risk of All-Cause Mortality Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Circulation 2014, 130, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shi, L.; Nauman, E.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Price-Haywood, E.G.; Bazzano, A.N.; Nigam, S.; Hu, G. Association between Body Mass Index and Stroke Risk Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Leng, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.Q.; Li, N.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; et al. Obesity index and the risk of diabetes among Chinese women with prior gestational diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 8. Obesity Management for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S113–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, R.R.; Neiberg, R.H.; Bahnson, J.L.; Clark, J.M.; Espeland, M.A.; Hill, J.O.; Johnson, K.C.; Knowler, W.C.; Olson, K.; Steinburg, H.; et al. Weight Change During the Postintervention Follow-up of Look AHEAD. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, R.R.; Bray, G.A.; Cassidy-Begay, M.; Clark, J.M.; Coday, M.; Egan, C.; Evans, M.; Foreyt, J.P.; Glasser, S.; Gregg, E.W.; et al. Effects of Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on All-Cause Mortality in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes and Overweight/Obesity: Results From the Look AHEAD Study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, M.J.; Boucher, J.L.; Rutten-Ramos, S.; VanWormer, J.J. Lifestyle weight-loss intervention outcomes in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, R.O.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Luk, A.; Yang, W.Y.; Sobrepena, L.; Yoon, K.H.; Aravind, S.R.; Sheu, W.Y.; Nguyen, T.K.; Ozaki, R.; et al. Metabolic profiles and treatment gaps in young-onset type 2 diabetes in Asia (the JADE programme): A cross-sectional study of a prospective cohort. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Rawshani, A.; Franzen, S.; Rawshani, A.; Svensson, A.M.; Rosengren, A.; McGuire, D.K.; Eliasson, B.; Gudbjornsdottir, S. Age at Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Associations with Cardiovascular and Mortality Risks Findings from the Swedish National Diabetes Registry. Circulation 2019, 139, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Horswell, R.; Wang, Y.; Johnson, J.; Hu, G. HbA1c and Coronary Heart Disease Risk Among Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, L. Glycosylated hemoglobin in relationship to cardiovascular outcomes and death in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Bray, G.A.; Carey, V.J.; Smith, S.R.; Ryan, D.H.; Anton, S.D.; McManus, K.; Champagne, C.M.; Bishop, L.M.; Laranjo, N.; et al. Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, A.; Hedderson, M.M.; Brown, S.D.; Albright, C.L.; Ehrlich, S.F.; Tsai, A.L.; Caan, B.J.; Sternfeld, B.; Gordon, N.P.; Schmittdiel, J.A.; et al. The Comparative Effectiveness of Diabetes Prevention Strategies to Reduce Postpartum Weight Retention in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: The Gestational Diabetes’ Effects on Moms (GEM) Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total Samples | Month 9 visit | p-values | Year 6–9 Follow-Up Visit | p-Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attend | Absence | Attend | Absence | ||||
| No. of participants | 83 | 68 | 15 | 39 | 44 | ||
| Age at baseline (years) | 32.7 ± 3.84 | 33.2 ± 3.90 | 30.3 ± 2.47 | 0.007 | 33.7 ± 3.83 | 31.7 ± 3.64 | 0.016 |
| Baseline years after delivery (years) | 2.63 ± 0.95 | 2.73 ± 0.94 | 2.17 ± 0.88 | 0.034 | 2.69 ± 0.95 | 2.58 ± 0.96 | 0.628 |
| Characteristics of GDM | |||||||
| Fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L) | 6.01 ± 1.23 | 6.04 ± 1.31 | 5.88 ± 0.78 | 0.636 | 5.98 ± 1.41 | 6.04 ± 1.07 | 0.809 |
| 2-h plasma glucose (mmol/L) | 10.5 ± 1.75 | 10.6 ± 1.67 | 10.1 ± 2.06 | 0.249 | 10.7 ± 1.84 | 10.3 ± 1.67 | 0.355 |
| Gestational week at OGTT (weeks) | 28.5 ± 2.16 | 28.5 ± 2.21 | 28.5 ± 1.83 | 0.971 | 28.3 ± 2.56 | 28.7 ± 1.74 | 0.490 |
| Gestational age at delivery (weeks) | 38.5 ± 1.80 | 38.4 ± 1.88 | 38.9 ± 1.36 | 0.412 | 38.7 ± 1.71 | 38.3 ± 1.88 | 0.286 |
| Pre-pregnancy body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.6 ± 3.71 | 25.4 ± 3.77 | 26.5 ± 3.36 | 0.276 | 25.3 ± 3.05 | 25.8 ± 4.23 | 0.520 |
| Baseline survey | |||||||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 4.04 | 27.1 ± 4.23 | 28.3 ± 2.89 | 0.272 | 27.1 ± 3.74 | 27.4 ± 4.32 | 0.738 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 88.7 ± 9.62 | 88.0 ± 10.2 | 91.7 ± 5.97 | 0.170 | 88.3 ± 8.90 | 88.9 ± 10.3 | 0.775 |
| Body fat (%) | 37.8 ± 5.19 | 37.5 ± 5.46 | 39.5 ± 3.39 | 0.215 | 37.7 ± 4.84 | 38.0 ± 5.53 | 0.812 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 115 ± 15.1 | 115 ± 16.1 | 112 ± 9.57 | 0.405 | 115 ± 12.6 | 114 ± 17.2 | 0.670 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 80.7 ± 11.2 | 81.2 ± 11.8 | 78.3 ± 7.96 | 0.360 | 81.6 ± 9.96 | 79.9 ± 12.3 | 0.484 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L) | 7.64 ± 2.17 | 7.73 ± 2.27 | 7.23 ± 1.61 | 0.425 | 7.58 ± 1.85 | 7.69 ± 2.43 | 0.825 |
| 2-h plasma glucose (mmol/L) | 14.1 ± 3.01 | 14.3 ± 3.15 | 13.3 ± 2.14 | 0.250 | 14.3 ± 2.99 | 14.0 ± 3.06 | 0.702 |
| Fasting serum insulin (pmol/L) | 82.6 ± 68.0 | 82.9 ± 72.9 | 82.4 ± 45.4 | 0.985 | 88.2 ± 87.5 | 77.9 ± 46.0 | 0.492 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.91 ± 1.23 | 6.94 ± 1.29 | 6.75 ± 0.92 | 0.577 | 6.83 ± 1.16 | 6.98 ± 1.30 | 0.591 |
| Plasma total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.92 ± 0.88 | 4.91 ± 0.91 | 4.95 ± 0.75 | 0.862 | 4.74 ± 0.90 | 5.07 ± 0.84 | 0.078 |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.26 ± 0.27 | 1.28 ± 0.25 | 1.18 ± 0.32 | 0.171 | 1.28 ± 0.25 | 1.25 ± 0.28 | 0.259 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.78 ± 1.02 | 2.85 ± 0.79 | 2.47 ± 1.72 | 0.189 | 2.73 ± 0.73 | 2.83 ± 1.23 | 0.692 |
| Plasma triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.90 ± 2.31 | 1.69 ± 0.78 | 2.86 ± 5.20 | 0.077 | 1.60 ± 0.78 | 2.17 ± 3.08 | 0.656 |
| Use of glucose-lowering agents (%) | 2.4 | 2.9 | 0 | 0.527 | 2.6 | 2.3 | 0.595 |
| Leisure time physical activity (min/day) | 2.81 ± 7.96 | 3.31 ± 8.68 | 0.59 ± 2.04 | 0.234 | 2.63 ± 8.40 | 2.99 ± 7.64 | 0.839 |
| Dietary intake a | |||||||
| Energy intake (kcal/day) | 1708 ± 418 | 1720 ± 420 | 1653 ± 420 | 0.574 | 1738 ± 402 | 1681 ± 436 | 0.536 |
| Protein (% energy) | 16.0 ± 2.36 | 16.2 ± 2.37 | 15.3 ± 2.23 | 0.191 | 16.0 ± 2.36 | 16.0 ± 2.29 | 0.956 |
| Fat (% energy) | 33.3 ± 6.44 | 33.9 ± 6.21 | 30.5 ± 6.95 | 0.063 | 33.8 ± 6.85 | 32.9 ± 6.10 | 0.523 |
| Carbohydrate (% energy) | 50.7 ± 7.12 | 49.9 ± 6.75 | 54.2 ± 7.91 | 0.034 | 50.2 ± 7.82 | 51.1 ± 6.49 | 0.576 |
| Month 1 | Month 3 | Month 6 | Month 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of participants | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 |
| Change in weight | ||||
| (kg) | −1.82 ± 2.51 | −2.81 ± 3.19 | −3.21 ± 3.73 | −2.90 ± 3.77 |
| Percent reduction in initial weight | −2.54 ± 3.62 | −3.97 ± 4.61 | −4.52 ± 5.37 | −4.02 ± 5.34 |
| Change in energy intakes (kcal/day) a | −242 ± 451 | −240 ± 414 | −227 ± 416 | −61.7 ± 371 |
| Change in leisure time physical activity (min/day) | 4.27 ± 16.8 | 4.97 ± 12.5 | 7.61 ± 20.4 | 8.46 ± 24.3 |
| Baseline | Month 9 | Changes from Baseline to Month 9 | p-Values | Years 6–9 | Changes from Baseline to Years 6–9 | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of participants | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 | ||
| Age at baseline or during follow-up (years) | 32.7 ± 3.84 | 33.8 ± 3.94 | 39.5 ± 3.98 | ||||
| Follow-up from baseline (years) | 1.12 ± 0.34 | 6.79 ± 1.13 | |||||
| Body weight (kg) | 70.2 ± 11.1 | 67.3 ± 11.0 | −2.90 ± 3.77 | < 0.001 | 66.5 ± 9.03 | −3.71 ± 6.02 | < 0.001 |
| Percent change in initial weight | −4.02 ± 5.34 | −4.62 ± 8.30 | |||||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 4.04 | 26.2 ± 4.04 | −1.12 ± 1.48 | < 0.001 | 25.7 ± 3.13 | −1.57 ± 2.35 | < 0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 88.7 ± 9.62 | 85.6 ± 9.84 | −3.12 ± 5.94 | < 0.001 | 84.1 ± 8.48 | −4.56 ± 7.41 | < 0.001 |
| Body fat (%) | 37.9 ± 5.19 | 36.1 ± 5.57 | −1.75 ± 2.28 | < 0.001 | 35.8 ± 4.51 | −2.10 ± 3.20 | < 0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 115 ± 15.1 | 116 ± 14.8 | 1.63 ± 12.7 | 0.305 | 119 ± 16.4 | 3.88 ± 14.4 | 0.072 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 80.7 ± 11.2 | 77.2 ± 11.0 | −3.49 ± 9.93 | 0.009 | 79.0 ± 10.7 | −1.64 ± 8.22 | 0.155 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L) | 7.64 ± 2.17 | 6.66 ± 1.99 | −0.98 ± 1.80 | < 0.001 | 8.28 ± 2.72 | 0.64 ± 2.81 | 0.099 |
| Fasting serum insulin (pmol/L) | 82.6 ± 68.0 | 67.0 ± 48.8 | −15.5 ± 58.3 | 0.031 | 71.8 ± 41.0 | −10.8 ± 49.3 | 0.073 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.91 ± 1.23 | 6.19 ± 1.21 | −0.72 ± 1.02 | < 0.001 | 7.13 ± 1.54 | 0.22 ± 1.76 | 0.345 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.92 ± 0.88 | 4.86 ± 0.94 | −0.06 ± 0.69 | 0.507 | 5.12 ± 1.32 | 0.20 ± 1.12 | 0.241 |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.26 ± 0.27 | 1.24 ± 0.30 | −0.02 ± 0.24 | 0.470 | 1.31 ± 0.29 | 0.05 ± 0.25 | 0.135 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.78 ± 1.02 | 2.78 ± 1.04 | 0.00 ± 0.78 | 0.968 | 2.97 ± 0.85 | 0.19 ± 0.97 | 0.136 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.90 ± 2.29 | 1.74 ± 2.54 | −0.16 ± 1.85 | 0.508 | 1.56 ± 1.74 | −0.34 ± 2.41 | 0.221 |
| Use of glucose-lowering agents (%) | 2.41 | 34.6 | 32.2 | 48.4 | 46.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, G.; Liu, H.; Leng, J.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tian, H.; Yang, S.; et al. Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention in Young Women with GDM and Subsequent Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245232
Hu G, Liu H, Leng J, Wang L, Li W, Zhang S, Li W, Liu G, Tian H, Yang S, et al. Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention in Young Women with GDM and Subsequent Diabetes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245232
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Gang, Huikun Liu, Junhong Leng, Leishen Wang, Weiqin Li, Shuang Zhang, Wei Li, Gongshu Liu, Huiguang Tian, Shengping Yang, and et al. 2022. "Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention in Young Women with GDM and Subsequent Diabetes" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245232
APA StyleHu, G., Liu, H., Leng, J., Wang, L., Li, W., Zhang, S., Li, W., Liu, G., Tian, H., Yang, S., Yu, Z., Yang, X., & Tuomilehto, J. (2022). Effects of a Lifestyle Intervention in Young Women with GDM and Subsequent Diabetes. Nutrients, 14(24), 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245232








