Resting Energy Expenditure in Older Inpatients: A Comparison of Prediction Equations and Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Indirect Calorimetry
2.3. Measurements and Body Composition Analysis
2.4. Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) Criteria
2.5. Predictive Equations for REE
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
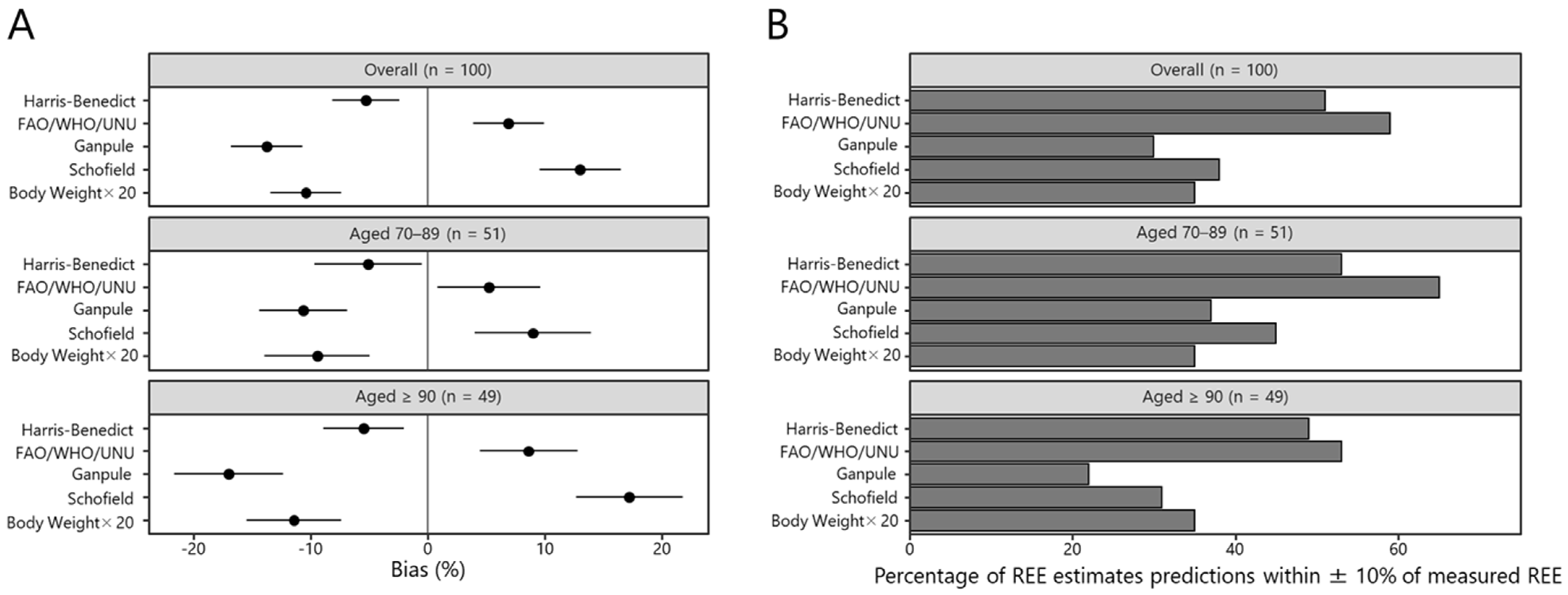
3.1. Accuracy of the REE Prediction Equations
3.2. Individual-Level Bias of the REE Prediction Equation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crichton, M.; Craven, D.; Mackay, H.; Marx, W.; de van der Schueren, M.; Marshall, S. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of the prevalence of protein-energy malnutrition: Associations with geographical region and sex. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O′Shea, E.; Trawley, S.; Manning, E.; Barrett, A.; Browne, V.; Timmons, S. Malnutrition in Hospitalised Older Adults: A Multicentre Observational Study of Prevalence, Associations and Outcomes. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Ishida, Y.; Nonogaki, T.; Mori, N. Reference body mass index values and the prevalence of malnutrition according to the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Maeda, K.; Nonogaki, T.; Shimizu, A.; Yamanaka, Y.; Matsuyama, R.; Kato, R.; Mori, N. Malnutrition at Admission Predicts In-Hospital Falls in Hospitalized Older Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalatbari-Soltani, S.; Marques-Vidal, P. The economic cost of hospital malnutrition in Europe; a narrative review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2015, 10, e89–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Fehr, R.; Baechli, V.; Geiser, M.; Deiss, M.; Gomes, F.; Kutz, A.; Tribolet, P.; Bregenzer, T.; Braun, N.; et al. Individualised nutritional support in medical inpatients at nutritional risk: A randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, D.N. Improving outcomes with a little EFFORT. Lancet 2019, 393, 2278–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zusman, O.; Theilla, M.; Cohen, J.; Kagan, I.; Bendavid, I.; Singer, P. Resting energy expenditure, calorie and protein consumption in critically ill patients: A retrospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Tamura, Y.; Yamaoka, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Umegaki, H.; Kamada, C.; Iimuro, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Ito, H.; et al. Assessing the association between optimal energy intake and all-cause mortality in older patients with diabetes mellitus using the Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, T.M. Energy expenditure and aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 10–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achamrah, N.; Delsoglio, M.; De Waele, E.; Berger, M.M.; Pichard, C. Indirect calorimetry: The 6 main issues. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Benedict, F.G. A Biometric Study of Human Basal Metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1918, 4, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendavid, I.; Lobo, D.N.; Barazzoni, R.; Cederholm, T.; Coëffier, M.; De Van Der Schueren, M.; Fontaine, E.; Hiesmayr, M.; Laviano, A.; Pichard, C.; et al. The centenary of the Harris–Benedict equations: How to assess energy requirements best? Recommendations from the ESPEN expert group. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelemaat, F.; van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren, M.A.; Thijs, A.; Seidell, J.C.; Weijs, P.J. Resting energy expenditure in malnourished older patients at hospital admission and three months after discharge: Predictive equations versus measurements. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix, E.; Berrut, G.; Boré, M.; Bouthier-Quintard, F.; Buia, J.M.; Chlala, A.; Cledat, Y.; d′Orsay, G.; Lavigne, C.; Levasseur, R.; et al. Energy requirements in hospitalized elderly people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, I.; Marra, M.; Pasanisi, F.; Scalfi, L. Prediction of resting energy expenditure in healthy older adults: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3094–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Schuetz, P.; Bounoure, L.; Austin, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.; Cederholm, T.; Fletcher, J.; Laviano, A.; Norman, K.; Poulia, K.A.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutritional support for polymorbid internal medicine patients. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.B. New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J. Physiol. 1949, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, L.Z.; Harker, J.O.; Salvà, A.; Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B. Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice: Developing the short-form mini-nutritional assessment (MNA-SF). J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M366–M372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition - A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint, F.A.O.; World Health Organization. Energy and Protein Requirements: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1985; Volume 724, pp. 1–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ganpule, A.A.; Tanaka, S.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Tabata, I. Interindividual variability in sleeping metabolic rate in Japanese subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, W.N. Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 39, (Suppl. S1). 5–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare of Japan. Dietary Reference Intakes for Japanese. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10904750/000586553.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Miyake, R.; Tanaka, S.; Ohkawara, K.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Hikihara, Y.; Taguri, E.; Kayashita, J.; Tabata, I. Validity of Predictive Equations for Basal Metabolic Rate in Japanese Adults. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2011, 57, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://R-project.org/ (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Siervo, M.; Bertoli, S.; Battezzati, A.; Wells, J.C.; Lara, J.; Ferraris, C.; Tagliabue, A. Accuracy of predictive equations for the measurement of resting energy expenditure in older subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, C.; Alix, E.; Sallé, A.; Berrut, G.; Ritz, P. Energy requirements in frail elderly people: A review of the literature. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocagli, H.; Lanera, C.; Azzolina, D.; Piras, G.; Soltanmohammadi, R.; Gallipoli, S.; Gafare, C.E.; Cavion, M.; Roccon, D.; Vedovelli, L.; et al. Resting Energy Expenditure in the Elderly: Systematic Review and Comparison of Equations in an Experimental Population. Nutrients 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzo, R.; Ribeiro, F.B.; Vasques, A.C.J. Accuracy of predictive equations versus indirect calorimetry for the evaluation of energy expenditure in cancer patients with solid tumors—An integrative systematic review study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 35, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.A.; Elliott, S.A.; Baracos, V.E.; Chu, Q.S.C.; Sawyer, M.B.; Mourtzakis, M.; Easaw, J.C.; Spratlin, J.L.; Siervo, M.; Prado, C.M. Accuracy of Resting Energy Expenditure Predictive Equations in Patients With Cancer. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, T.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, J. Novel equation for estimating resting energy expenditure in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katano, S.; Yano, T.; Kouzu, H.; Ohori, K.; Shimomura, K.; Honma, S.; Nagaoka, R.; Inoue, T.; Takamura, Y.; Ishigo, T.; et al. Energy intake during hospital stay predicts all-cause mortality after discharge independently of nutritional status in elderly heart failure patients. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 1202–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, A.; Fujishima, I.; Maeda, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nishioka, S.; Ohno, T.; Nomoto, A.; Kayashita, J.; Mori, N.; The Japanese Working Group On Sarcopenic Dysphagia. Nutritional Management Enhances the Recovery of Swallowing Ability in Older Patients with Sarcopenic Dysphagia. Nutrients 2021, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E. Anorexia of ageing: A key component in the pathogenesis of both sarcopenia and cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Equations | Sex | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Harris-Benedict | Male | 66.4730 + 13.7516 × W (kg) + 5.0033 × H (cm) − 6.7550 × A |
| Female | 655.0955 + 9.5634 × W (kg) + 1.8496 × H (cm) − 4.6756 × A | |
| FAO/WHO/UNU | Male | (36.8 × W (kg) + 4719.5 × (H (cm)/100) − 4481)/4.186 |
| Female | (38.5 ×W (kg) + 2665.2 × (H (cm)/100) − 1264)/4.186 | |
| Ganpule | Male | (0.0481 × W (kg) + 0.0234 × H (cm) − 0.0138 × A − 0.4235) × 1000/4.186 |
| Female | (0.0481 × W (kg) + 0.0234 × H (cm) − 0.0138 × A − 0.9708) × 1000/4.186 | |
| Schofield | Male | (0.049 ×W (kg) + 2.459) × 1000/4.186 |
| Female | (0.038 ×W (kg) + 2.755) × 1000/4.186 | |
| Body weight × 20 | W (kg) × 20 |
| Characteristics | Overall (n = 100) | Aged 70–89 (n = 51) | Aged ≥ 90 (n = 49) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 88.1 ± 6.8 | 82.9 ± 5.1 | 93.5 ± 3.0 |
| Sex, male n (%) | 34 (34%) | 23 (45%) | 11 (22%) |
| Height, cm | 146.0 ± 10.7 | 150.0 ± 11.6 | 142.0 ± 7.9 |
| Weight, kg | 42.9 ± 9.1 | 46.5 ± 8.9 | 39.2 ± 7.8 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 20.1 ± 3.5 | 20.8 ± 3.6 | 19.4 ± 3.3 |
| SMI, kg/m2 | 4.67 ± 1.47 | 4.99 ± 1.42 | 4.34 ± 1.46 |
| CC, cm | 27.3 ± 3.9 | 28.4 ± 4.1 | 26.2 ± 3.3 |
| MNA-SF, score | 7 (6–10) | 8 (6–10) | 7 (6–9) |
| CCI, score | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–2) |
| GLIM criteria | |||
| Malnutrition, n (%) | 76 (76%) | 37 (73%) | 39 (80%) |
| Moderate malnutrition, n (%) | 21 (28%) | 11 (30%) | 10 (26%) |
| Severe malnutrition, n (%) | 55 (72%) | 26 (70%) | 29 (74%) |
| REE Predictive Prediction Equation | Overall (n = 100) | Aged 70–89 (n = 51) | Aged ≥ 90 (n = 49) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (95% CI) | Mean (95% CI) | Mean (95% CI) | |
| Measured REE, kcal/day | 968.1 (931.0, 1005.3) | 1041.8 (987.5, 1096.1) | 891.4 (850.3, 932.6) |
| Harris-Benedict, kcal/day | 898.6 (873.1, 924.1) * | 964.9 (929.7, 1000.1) | 829.6 (804.3, 854.9) |
| FAO/WHO/UNU, kcal/day | 1014.3 (987.1, 1041.6) | 1074.5 (1034.9, 1114.0) | 951.8 (923.1, 980.4) |
| Ganpule, kcal/day | 830.1 (790.3, 869.9) *** | 924.2 (870.5, 977.8) ** | 732.3 (687.1, 777.5) *** |
| Schofield, kcal/day | 1066.0 (1045.8, 1086.2) *** | 1105.5 (1077.5, 1133.6) | 1024.8 (1000.3, 1049.3) *** |
| Body weight × 20, kcal/day | 857.7 (821.9, 893.5) *** | 929.0 (880.0, 978.1) ** | 783.5 (739.7, 827.2) *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawase, F.; Masaki, Y.; Ozawa, H.; Imanaka, M.; Sugiyama, A.; Wada, H.; Goto, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Tsukahara, T. Resting Energy Expenditure in Older Inpatients: A Comparison of Prediction Equations and Measurements. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245210
Kawase F, Masaki Y, Ozawa H, Imanaka M, Sugiyama A, Wada H, Goto R, Kobayashi S, Tsukahara T. Resting Energy Expenditure in Older Inpatients: A Comparison of Prediction Equations and Measurements. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245210
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawase, Fumiya, Yoshiyuki Masaki, Hiroko Ozawa, Manami Imanaka, Aoi Sugiyama, Hironari Wada, Ryokichi Goto, Shinya Kobayashi, and Takayoshi Tsukahara. 2022. "Resting Energy Expenditure in Older Inpatients: A Comparison of Prediction Equations and Measurements" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245210
APA StyleKawase, F., Masaki, Y., Ozawa, H., Imanaka, M., Sugiyama, A., Wada, H., Goto, R., Kobayashi, S., & Tsukahara, T. (2022). Resting Energy Expenditure in Older Inpatients: A Comparison of Prediction Equations and Measurements. Nutrients, 14(24), 5210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245210






