Association between Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels and Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Sources
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Definition of the Primary Outcome
2.5. Study Quality Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
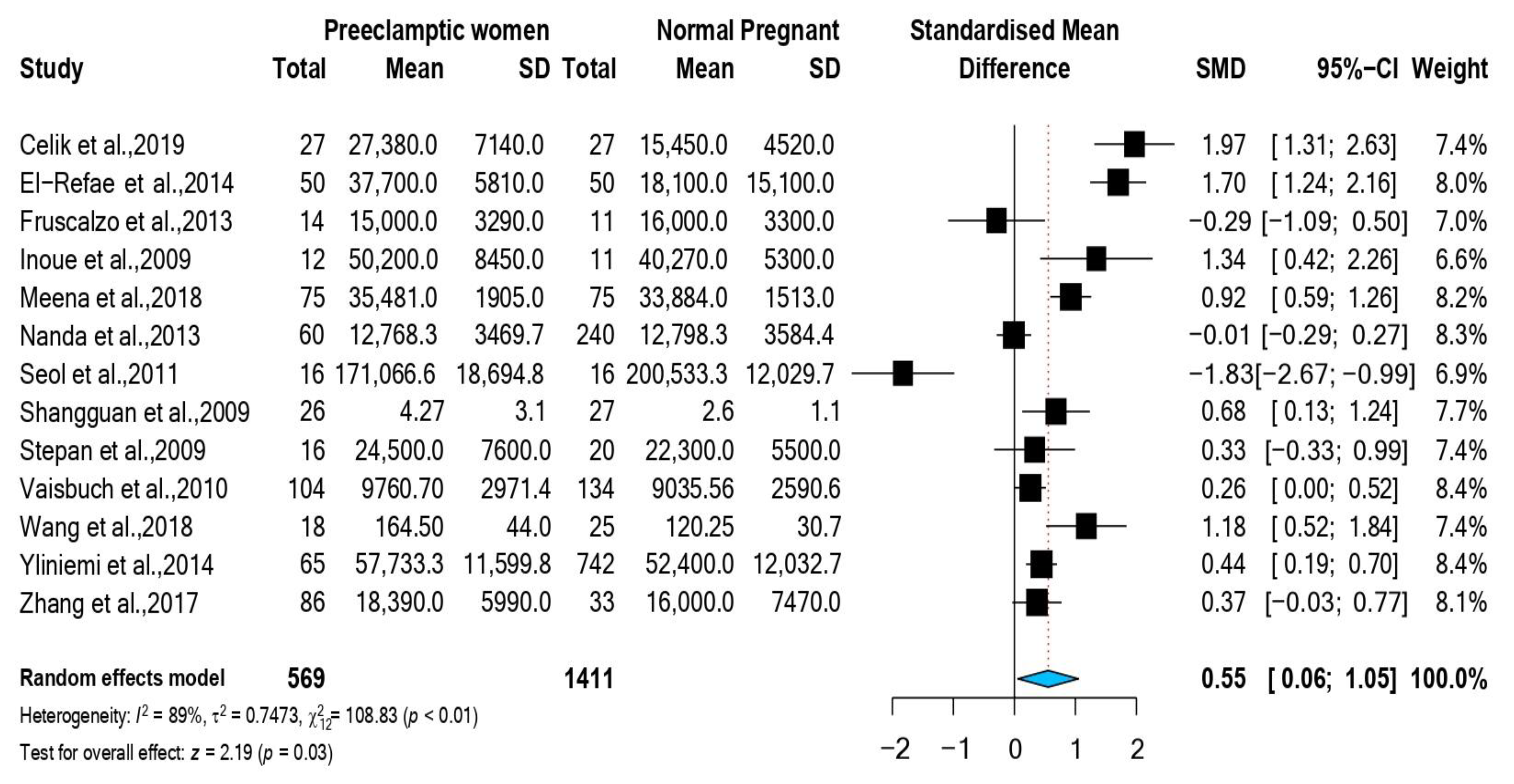
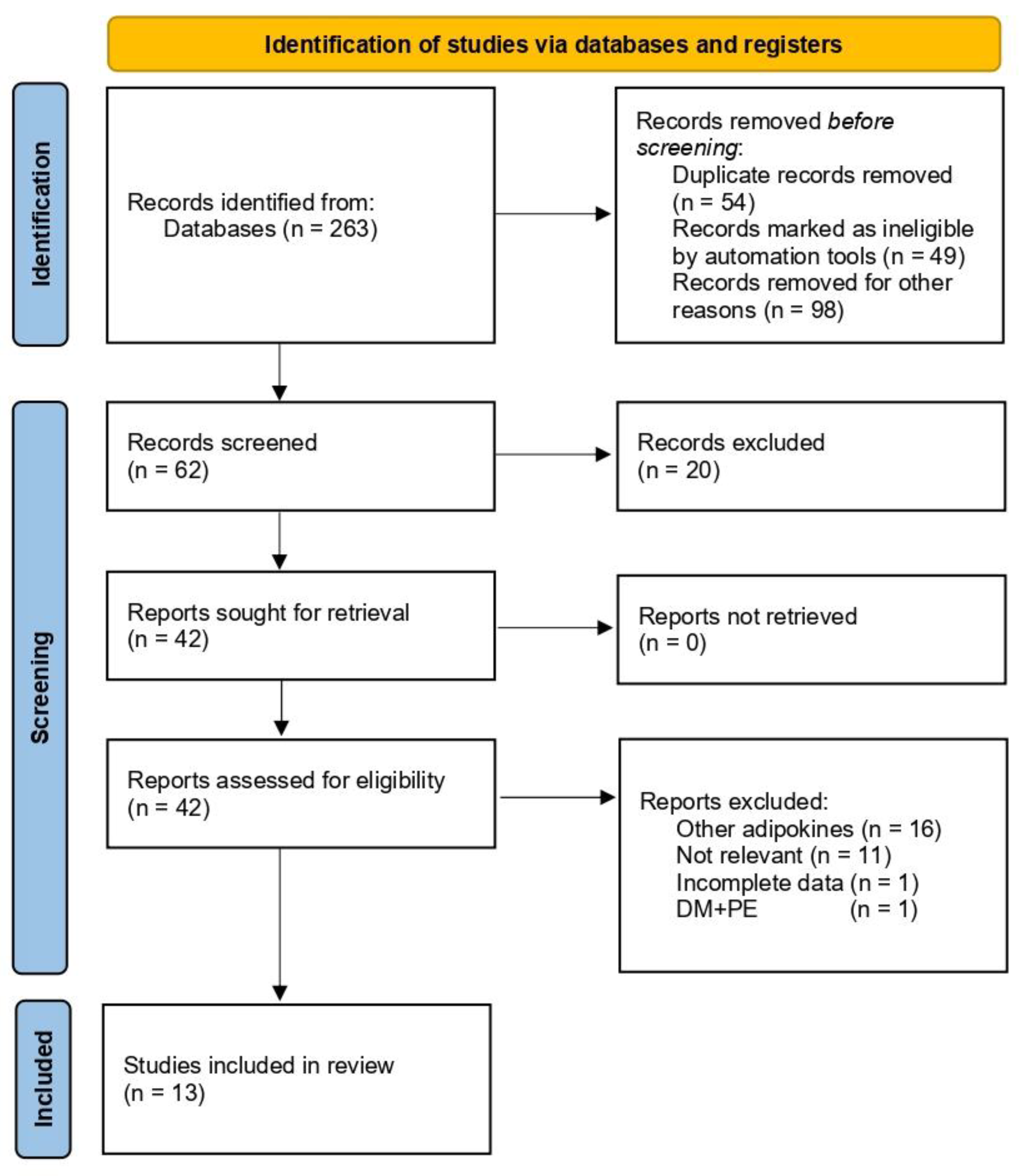
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
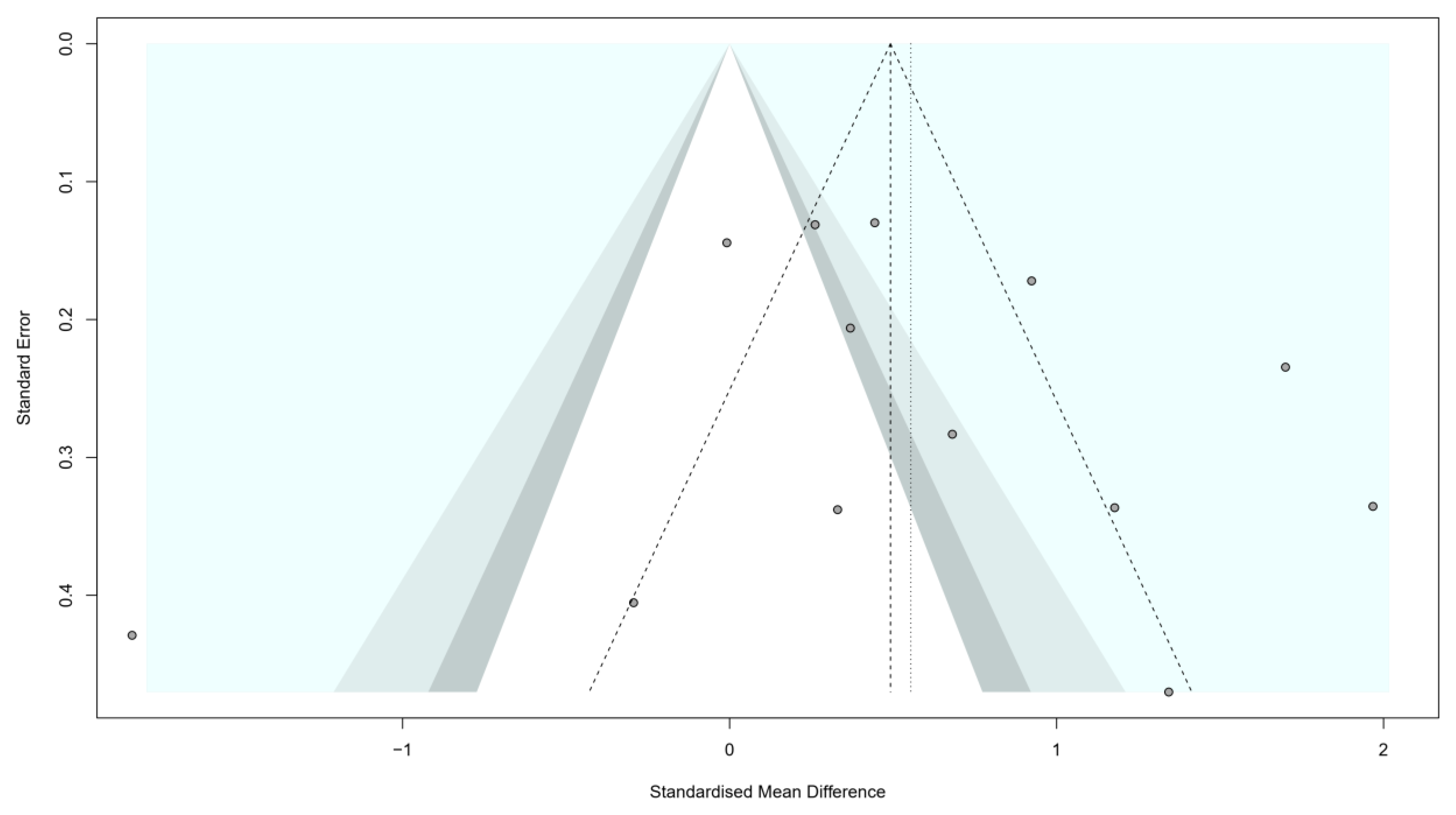
3.2. Association between RBP4 and Preeclampsia
3.3. Stratified Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abalos, E.; Cuesta, C.; Grosso, A.L.; Chou, D.; Say, L. Global and Regional Estimates of Preeclampsia and Eclampsia: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 170, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steegers, E.A.P.; Von Dadelszen, P.; Duvekot, J.J.; Pijnenborg, R. Pre-Eclampsia. Lancet 2010, 376, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meazaw, M.W.; Chojenta, C.; Muluneh, M.D.; Loxton, D. Systematic and Meta-Analysis of Factors Associated with Preeclampsia and Eclampsia in Sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, O.; Dekker Nitert, M.; Gallo, L.A.; Vejzovic, M.; Fisher, J.J.; Perkins, A.V. Review: Placental Mitochondrial Function and Structure in Gestational Disorders. Placenta 2017, 54, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellos, I.; Karageorgiou, V.; Kapnias, D.; Karamanli, K.E.; Siristatidis, C. The Role of Interleukins in Preeclampsia: A Comprehensive Review. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 80, e13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maury, E.; Brichard, S.M. Adipokine Dysregulation, Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Metabolic Syndrome. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 314, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Graham, T.E.; Mody, N.; Preitner, F.; Peroni, O.D.; Zabolotny, J.M.; Kotani, K.; Quadro, L.; Kahn, B.B. Serum Retinol Binding Protein 4 Contributes to Insulin Resistance in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Nature 2005, 436, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, S.; Kulkarni, M.J.; Malakar, D.; Joshi, S.R.; Mehendale, S.S.; Giri, A.P. Placental Proteomics Provides Insights into Pathophysiology of Pre-Eclampsia and Predicts Possible Markers in Plasma. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, B.J.; Sartoretto, J.L.; Polak, P.; Hosooka, T.; Shiroto, T.; Eskurza, I.; Lee, S.A.; Jiang, H.; Michel, T.; Kahn, B.B. Novel Role for Retinol-Binding Protein 4 in the Regulation of Blood Pressure. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Celik, S.; Celik, H.; Calışkan, C.S.; Tosun, M.; Avcı, B. Prospective Comparative Study of Third Trimester Serum Retinol Binding Protein 4 as a Potential Adipokine Marker of Pre-Eclampsia. Cumhur. Med. J. 2019, 41, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Refai, A.A.; Fatani, S.H.; Kamel, H.F.M. Association of Adipocytokines: Resistin and Retinol Binding Protein-4 with Severity of Preeclampsia and Insulin Resistance. Am. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 2, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Takamoto, N.; Akahori, Y.; Masumoto, A.; Nakatsukasa, H.; Msuyama, H.; Hiramatsu, Y. Elevated Level of Serum Retinol-Binding Protein 4 in Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2009, 35, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Dong, M. Alterations in Serum Adipocyte Fatty Acid Binding Protein and Retinol Binding Protein-4 in Normal Pregnancy and Preeclampsia. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2009, 407, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisbuch, E.; Romero, R.; Mazaki-Tovi, S.; Erez, O.; Kim, S.K.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Gotsch, F.; Than, N.G.; Dong, Z.; Pacora, P.; et al. Retinol Binding Protein 4--a Novel Association with Early-Onset Preeclampsia. J. Perinat. Med. 2010, 38, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Cao, G.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Song, M.; Zhang, Z. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Regulates the Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms of JEG-3 Cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 5877. [Google Scholar]
- Yliniemi, A.; Nurkkala, M.M.; Kopman, S.; Korpimaki, T.; Kouru, H.; Ryynanen, M.; Marttala, J. First Trimester Placental Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4) and Pregnancy-Associated Placental Protein A (PAPP-A) in the Prediction of Early-Onset Severe Pre-Eclampsia. Metabolism 2015, 64, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.J. Retinol-Binding Protein-4 Is Decreased in Patients with Preeclampsia in Comparison with Normal Pregnant Women. J. Perinat. Med. 2011, 39, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepan, H.; Ebert, T.; Schrey, S.; Reisenbüchler, C.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Kratzsch, J.; Tönnessen, P.; Faber, R.; Fasshauer, M. Preliminary Report: Serum Levels of Retinol-Binding Protein 4 in Preeclampsia. Metabolism 2009, 58, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Nikoletakis, G.; Markova, D.; Poon, L.C.Y.; Nicolaides, K.H. Maternal Serum Retinol-Binding Protein-4 at 11-13 Weeks’ Gestation in Normal and Pathological Pregnancies. Metabolism 2013, 62, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.B.; Hookham, M.B.; Yu, J.Y.; Lockhart, S.M.; Du, M.; Jenkins, A.J.; Nankervis, A.; Hanssen, K.F.; Henriksen, T.; Garg, S.K.; et al. Circulating Adipokines Are Associated with Pre-Eclampsia in Women with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2514–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruscalzo, A.; Biasioli, A.; Londero, A.P.; Ceraudo, M.; Stel, G.; Bertozzi, S.; Marchesoni, D.; Driul, L.; Curcio, F. Retinol Binding Protein as Early Marker of Fetal Growth Restriction in First Trimester Maternal Serum. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2013, 29, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, U.K.; Jain, S.; Vaid, N.B.; Sharma, A.; Chawla, S.; Guleria, K.; Mehndiratta, M. Role of serum retinol binding protein 4 in preeclampsia: A case control study. Indian Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Gui, S.; Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, R.; Gong, Y. Association between Plasma Retinol Binding Protein 4 Levels and Severe Preeclampsia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 38, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E. JBI’s Systematic Reviews. AJN Am. J. Nurs. 2014, 114, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACOG. Hypertension in Pregnancy; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781934984284. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to Perform a Meta-Analysis with R: A Practical Tutorial. Evid. Based. Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V. Distribution Theory for Glass’s Estimator of Effect Size and Related Estimators. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2016, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying Heterogeneity in a Meta-Analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, M.H.; Yen, K. The Kappa Statistic Was Representative of Empirically Observed Inter-Rater Agreement for Physical Findings. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2006, 59, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.T.; Huang, Q.; Luo, W.; Li, F.; Hang, L.L.; Yu, Y.H.; Zhong, M. Circulating Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2015, 31, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Liu, Q.; Huang, X.; Tan, H. Serum Level and Polymorphisms of Retinol-Binding Protein-4 and Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2016, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, A.H.Y.; Godfrey, K.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Developmental Programming. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 76 (Suppl. 3), 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balani, J.; Hyer, S.; Syngelaki, A.; Akolekar, R.; Nicolaides, K.H.; Johnson, A.; Shehata, H. Association between Insulin Resistance and Preeclampsia in Obese Non-Diabetic Women Receiving Metformin. Obstet. Med. 2017, 10, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerczyk, M.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M.; Chudek, J. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4) as the Causative Factor and Marker of Vascular Injury Related to Insulin Resistance. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2016, 70, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qi, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y. Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Steroids 2022, 184, 108993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.E.; Yang, Q.; Blüher, M.; Hammarstedt, A.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Henry, R.R.; Wason, C.J.; Oberbach, A.; Jansson, P.-A.; Smith, U.; et al. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Insulin Resistance in Lean, Obese, and Diabetic Subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2552–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, G.; Guo, G. Association of Insulin Resistance and Autonomic Tone in Patients with Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 40, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Chen, H.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, C.H.; Chou, F.H.; Chen, I.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Jong, S.; Bin; Tsai, E.M. Increased Serum Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Concentrations in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Reprod. Sci. 2007, 14, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.A.; Kim, N.H.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Ryu, O.H.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.L.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; et al. Serum Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels Are Elevated in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 68, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetham, R.; Dawnay, A.; Menabawy, M.; Silver, A. Urinary Excretion of Albumin and Retinol-Binding Protein during Normal Pregnancy. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.A.; Barrett, E.J.; Lindner, J.R.; Clark, M.G.; Rattigan, S. Inhibiting NOS Blocks Microvascular Recruitment and Blunts Muscle Glucose Uptake in Response to Insulin. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E123–E129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Kang, E.S.; Ahn, C.W.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, B.S. Retinol-Binding Protein-4 Is Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Adults with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2009, 204, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.C.; An, N.; Xu, H.R.; Larante, A.; Audibert, F.; Fraser, W.D. The Effects and Mechanisms of Primiparity on the Risk of Pre-Eclampsia: A Systematic Review. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2007, 21 (Suppl. 1), 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaviz-Hernandez, C.; Sosa-Macias, M.; Teran, E.; Garcia-Ortiz, J.E.; Lazalde-Ramos, B.P. Paternal Determinants in Preeclampsia. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkhtulga, L.; Nagashima, S.; Nakayama, K.; Utsumi, N.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Gotoh, T.; Omi, T.; Kumada, M.; Zolzaya, K.; Lkhagvasuren, T.; et al. Regulatory SNP in the RBP4 Gene Modified the Expression in Adipocytes and Associated With BMI. Obesity 2010, 18, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.E.; Wason, C.J.; Blüher, M.; Kahn, B.B. Shortcomings in Methodology Complicate Measurements of Serum Retinol Binding Protein (RBP4) in Insulin-Resistant Human Subjects. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1st Author, Year, Citation | Study Design | Country | NOS Score | No. Preeclampsia/ No. Controls | RBP4 Mean (SD) Preeclampsia ng/mL | RBP4 Mean (SD) Controls ng/mL | Maternal Age Cases Mean (SD): Controls Mean (SD): | Maternal BMI Cases: Mean (SD) Controls: Mean (SD) | %Nulliparous among Cases/ %Nulliparous among Controls | Assay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celik et al., 2019 [10] | Case-Control | Turkey | 5 | 27/27 | 27,380 (7140) | 15,450 (4520) | Cases: 30.59 ± 5.73 Controls: 29 ± 5.96 | Cases: 28.76 ± 2.12 Controls: 27.97 ± 2.67 | - | ELISA |
| El-Refae et al., 2014 [11] | Case-Control | KSA | 5 | 50/50 | 37,700 (5810) | 18,100 (15,100) | Cases: 33.25 ± 6.1 Controls: 31.65 ± 5.47 | Cases: 28.28 ± 1.4 Controls: 27.06 ± 2.04 | - | ELISA |
| Fruscalzo et al., 2013 [21] | Case-Control | Italy | 8 | 14/11 | 15,100 (3290) | 16,100 (3300) | Cases: 34.93 ± 5.31 Controls: 32.45 ± 5.56 | Cases: 28 ± 7.4 Controls: 24 ± 2.5 | 50%/45% | ELISA |
| Inoue et al., 2009 [12] | Case-Control | Japan | 8 | 12/11 | 50,200 (8450) | 40,270 (5300) | Cases: 34.7 ± 4.9 Controls: 31.5 ± 4.7 | Cases: 21.3 ± 2.3 Controls: 20.3 ± 4 | - | DOT plot |
| Meena et al., 2018 [22] | Case-Control | India | 5 | 75/75 | 35,481 (1905) | 33,884 (1513) | - | - | - | ELISA |
| Nanda et al., 2013 [19] | Cohort | UK | 7 | 60/240 | 12,768.33 (3469.7) | 12,798.333 (3584.4) | Cases: 32.3 ± 7.5 Controls: 32 ± 6.41 | Cases: 27.7 ± 7.2 Controls: 23.9 ± 3.35 | 65%/42.5% | ELISA |
| Seol et al., 2011 [17] | Case-Control | Korea | 8 | 16/16 | 171,066.67 (18,694.8) | 200,533.33 (12,029.8) | Cases: 31.9 ± 4.8 Controls: 30.8 ± 5.4 | Cases: 23.7 ± 3.4 Controls: 21.6 ± 2 | - | ELISA |
| Shangguan et al., 2009 [13] | Case-Control | China | 7 | 26/27 | 4.27 (3.13) | 2.65 (1.16) | Cases: 27.5 ± 1.4 Controls: 29 ± 1.5 | Cases: 27.68 ± 3.28 Controls: 25.75 ± 3.03 | 100%/100% | ELISA |
| Stepan et al., 2009 [18] | Case-Control | Germany | 8 | 16/20 | 24,500 (7600) | 22,300 (5500) | Cases: 31.9 ± 5.9 Controls: 27.7 ± 6 | Cases: 22.4 ± 3.6 Controls: 20.7 ± 2.6 | - | ELISA |
| Vaisbuch et al., 2010 [14] | Cross-sectional | USA | 9 | 104/134 | 9760.7 (2971.4) | 9035.56 (2590.6) | Cases: 24.16 ± 6.74 Controls: 25 ± 6.01 | Cases: 26.7 ± 4.88 Controls: 27.3 ± 7.86 | 62.5%/27.6% | ELISA |
| Wang et al., 2018 [15] | Case-Control | China | 8 | 18/25 | 164.5 (44.07) | 120.25 (30.79) | Cases: 28.85 ± 4.72 Controls: 31.18 ± 4.05 | Cases: 21.38 ± 3.2 Controls: 22.16 ± 3.15 | - | ELISA |
| Yliniemi et al., 2014 [16] | Case-Control | Finland | 9 | 65/742 | 57,733.3 (11,599.8) | 52,400 (12,032.7) | Cases: 29.3 ± 5.3 Controls: 29.8 ± 5.86 | - | - | Immunoassay |
| Zhang et al., 2017 [23] | Case-Control | China | 6 | 86/33 | 18,390 (5990) | 16,000 (7470) | Cases: 30.28 ± 5.58 Controls: 30.49 ± 4.8 | Cases: 22.48 ± 3.02 Controls: 21.35 ± 2.13 | - | ELISA |
| Sub-Group | No. Included Studies | No. Preeclampsia | No. Normal Controls | SMD (95% CI) | Higgin’s Index I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trimester of RBP4 measurements | |||||
| 3rd trimester | 10 | 430 | 418 | 0.70 (0.081; 1.331) | 90% |
| 1st trimester | 3 | 139 | 993 | 0.14 (−0.264; 0.531) | 72% |
| Disease severity | |||||
| Severe-preeclampsia | 4 | 181 | 811 | 0.71 (0.270; 1.145) | 61% |
| All spectrum | 9 | 388 | 600 | 0.44 (−0.271; 1.143) | 92% |
| Studies Continent | |||||
| Europe & America | 6 | 286 | 1174 | 0.44 (−0.144; 1.025) | 82% |
| Asia | 7 | 283 | 237 | 0.64 (−0.180, 1.466) | 90% |
| RBP4 assay | |||||
| ELISA | 11 | 492 | 658 | 0.50 (−0.08; 1.08) | 85% |
| Other methods | 2 | 77 | 753 | 0.78 (−0.07; 1.63) | 15% |
| Covariate | Estimate Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study sample size | −0.0002 | 0.0019 | 0.9001 | (−0.0034; 0.0039) |
| Measuring RBP4 in the 3rd trimester | 0.8831 | 0.9235 | 0.339 | (−0.927; 2.6932) |
| NOS | −0.5838 | 0.3516 | 0.0969 | (−1.2729; 0.1054) |
| Disease severity: Severe-preeclampsia | 1.2851 | 0.9464 | 0.1745 | (−0.5698; 3.1401) |
| Year of publication | −0.0575 | 0.1219 | 0.6373 | (−0.2964; 0.1815) |
| Continent: Europe and America | 1.0822 | 0.8609 | 0.2087 | (−0.6051; 2.7696) |
| Study design: Non-case-control design | −0.0102 | 0.8851 | 0.9908 | (−1.745; 1.7246) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamdan, H.Z.; Ali, T.; Adam, I. Association between Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels and Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245201
Hamdan HZ, Ali T, Adam I. Association between Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels and Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245201
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamdan, Hamdan Z., Tasneem Ali, and Ishag Adam. 2022. "Association between Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels and Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245201
APA StyleHamdan, H. Z., Ali, T., & Adam, I. (2022). Association between Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels and Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 14(24), 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245201