Plasma Levels of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Derived Oxylipins Are Associated with Fecal Microbiota Composition in Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Determination of Plasma Levels of Oxylipins
2.3. Fecal Collection and DNA Extraction
2.4. Anthropometry and Body Composition
2.5. Dietary Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
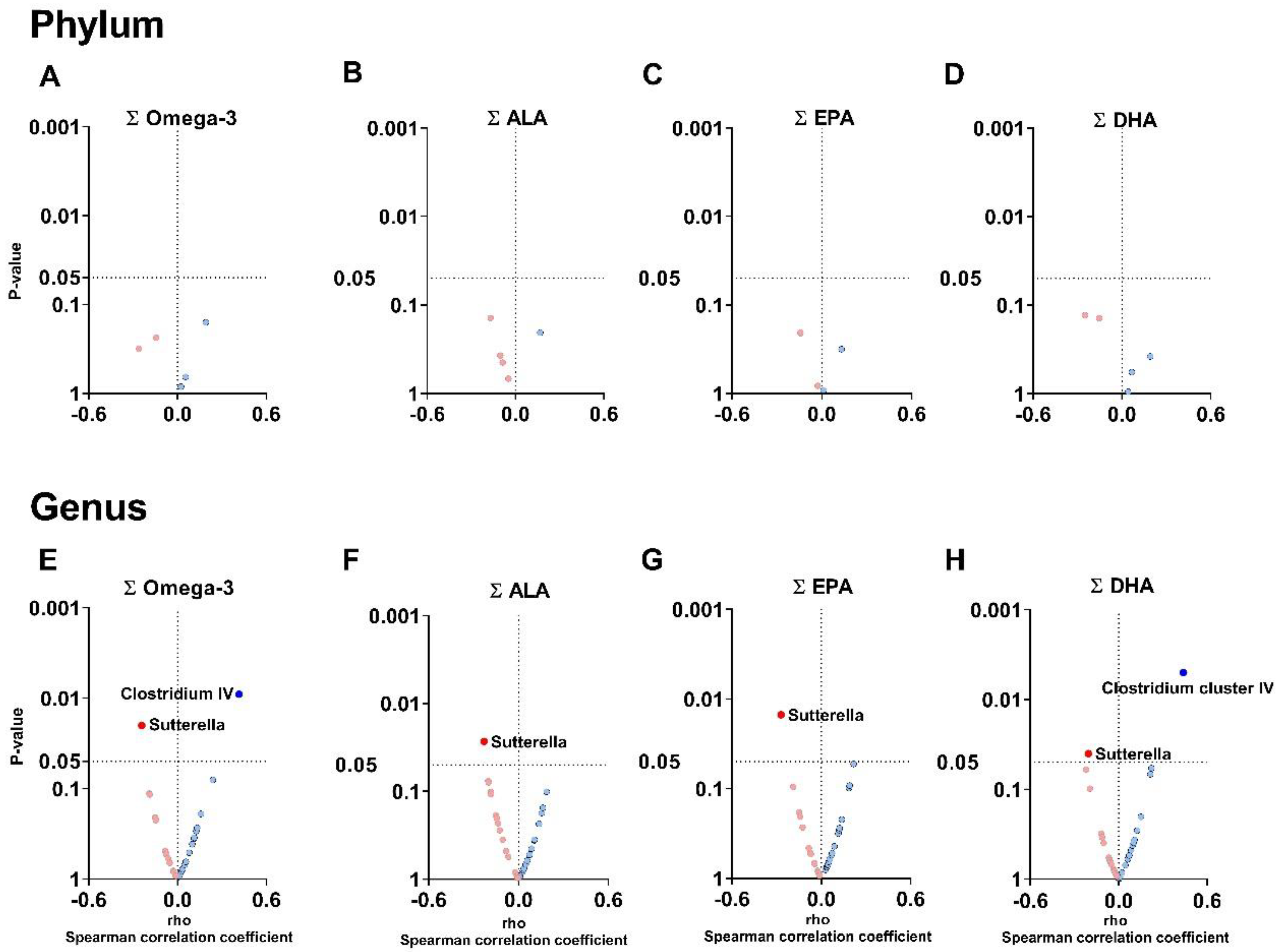
3.2. The Plasma Levels of Omega-3 Oxylipins Are Associated with the Relative Abundance of Clostridium Cluster IV and Sutterella Genera
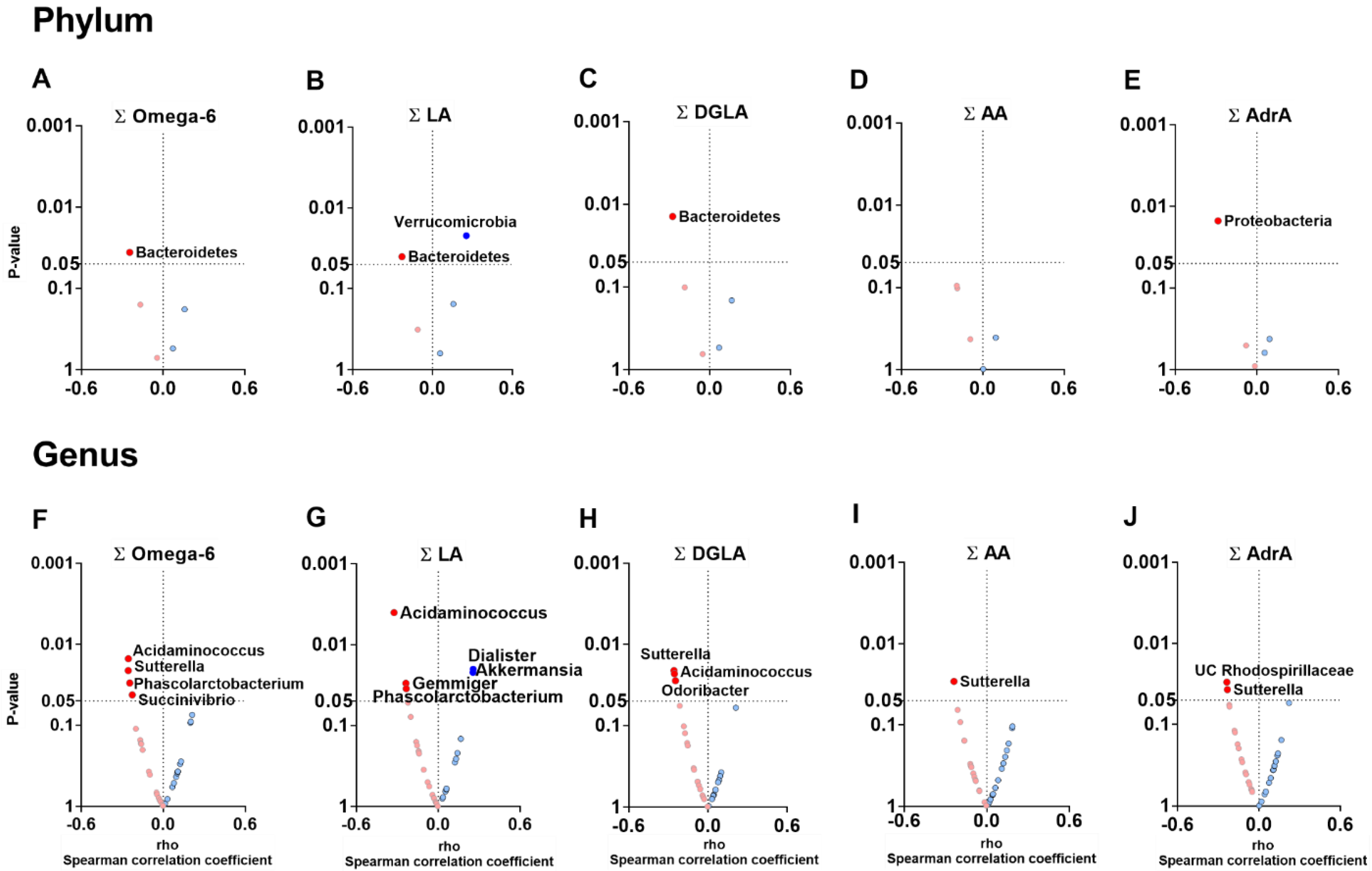
3.3. The Plasma Levels of Omega-6 Oxylipins Are Negatively Associated with the Relative Abundance of Genera Belonging to Firmicutes and Proteobacteria Phyla
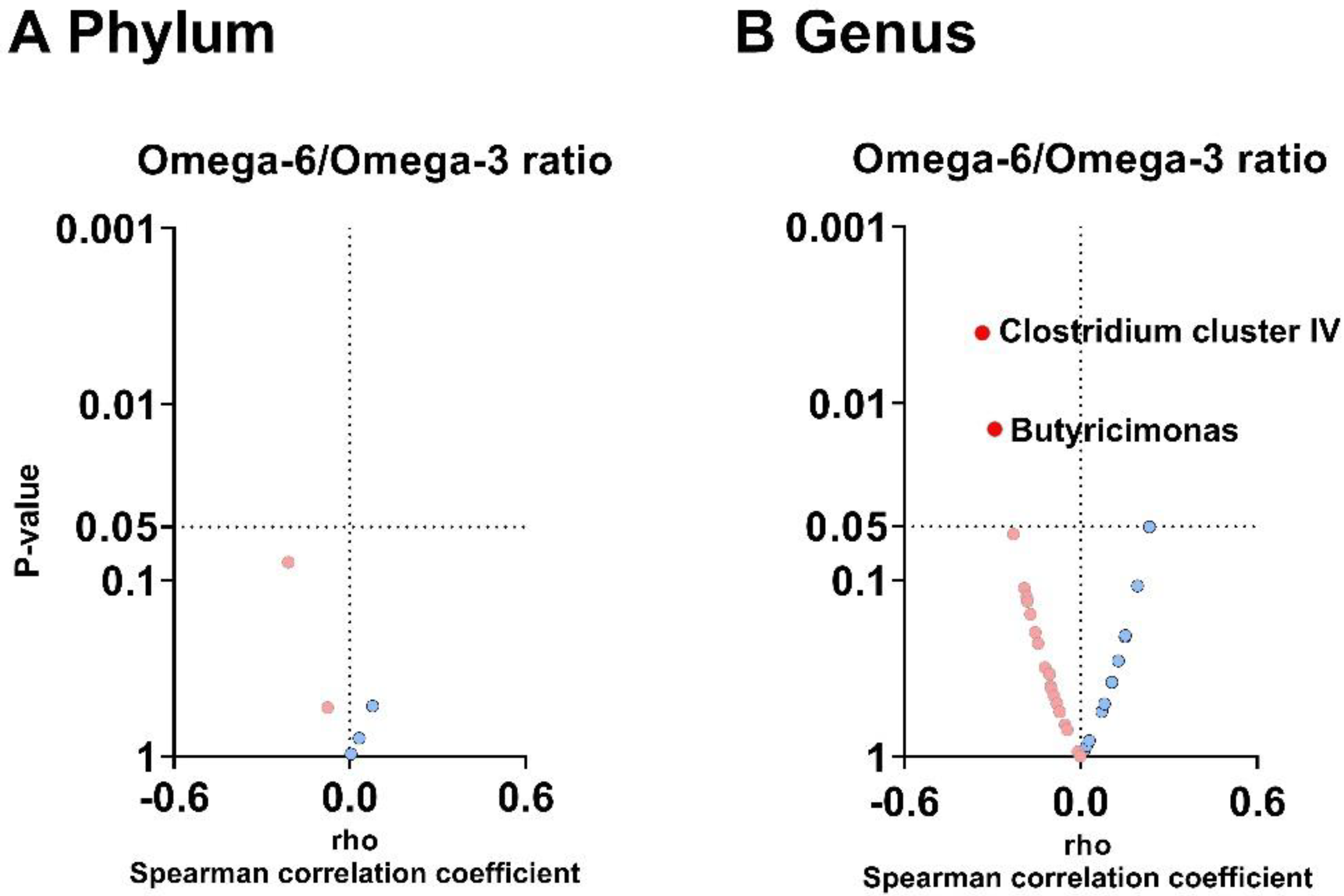
3.4. The Plasma Omega-6/Omega-3 Oxylipin Ratio Is Negatively Associated with the Relative Abundance of Clostridium Cluster IV and Butyricimonas Genera
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hotamisligil, G. Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Núñez, B.; Pruimboom, L.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Muskiet, F.A.J. Lifestyle and Nutritional Imbalances Associated with Western Diseases: Causes and Consequences of Chronic Systemic Low-Grade Inflammation in an Evolutionary Context. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1183–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A. Nonresolving Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaf, A.; Weber, P.C. A New Era for Science in Nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1987, 45, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A. The Importance of the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio in Cardiovascular Disease and Other Chronic Diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, J.; Hawley, M.; Holinstat, M. The Expansive Role of Oxylipins on Platelet Biology. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbs, M.; Leng, S.; Devassy, J.G.; Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Advances in Our Understanding of Oxylipins Derived from Dietary PUFAs 1,2. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes. Nutrients 2010, 2, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyall, S.C.; Balas, L.; Bazan, N.G.; Brenna, J.T.; Chiang, N.; da Costa Souza, F.; Dalli, J.; Durand, T.; Galano, J.-M.; Lein, P.J.; et al. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Fatty Acid-Derived Lipid Mediators: Recent Advances in the Understanding of Their Biosynthesis, Structures, and Functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022, 86, 101165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.C.; Kaliannan, K.; Strain, C.R.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Kang, J.X. Maternal Omega-3 Fatty Acids Regulate Offspring Obesity through Persistent Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Microbiome 2018, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Finlay, B.B. Human and Microbe: United We Stand. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 736–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the Human Gut Microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Haake, S.K.; Mannon, P.; Lemon, K.P.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Huttenhower, C.; Izard, J. Composition of the Adult Digestive Tract Bacterial Microbiome Based on Seven Mouth Surfaces, Tonsils, Throat and Stool Samples. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalto, M.; D’Onofrio, F.; Gallo, A.; Cazzato, A.; Gasbarrini, G. Intestinal Microbiota and Its Functions. Dig. Liver Dis. Suppl. 2009, 3, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Guchte, M.; Blottière, H.M.; Doré, J. Humans as Holobionts: Implications for Prevention and Therapy. Microbiome 2018, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.A.; Artis, D. Intestinal Bacteria and the Regulation of Immune Cell Homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 623–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Mazzola, M.; Leone, A.; Sinagra, E.; Zummo, G.; Farina, F.; Damiani, P.; Cappello, F.; Geagea, A.G.; Jurjus, A.; et al. Nutrition, Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Dysbiosis: Influence of Diet on Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Biomed. Pap. 2016, 160, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet Rapidly and Reproducibly Alters the Human Gut Microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszak, M.; Szulińska, M.; Bogdański, P. You Are What You Eat—The Relationship between Diet, Microbiota, and Metabolic Disorders—A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, D.; Jiang, R.; Ge, L.; Tong, C.; Xu, K. Associations among Dietary Omega-3 Poly-unsaturated Fatty Acids, the Gut Microbiota, and Intestinal Immunity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 8879227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliannan, K.; Wang, B.; Li, X.-Y.; Kim, K.-J.; Kang, J.X. A Host-Microbiome Interaction Mediates the Opposing Effects of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Metabolic Endotoxemia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliannan, K.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, B.; Pan, Q.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hao, L.; Xie, S.; Kang, J.X. Multi-Omic Analysis in Transgenic Mice Implicates Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Imbalance as a Risk Factor for Chronic Disease. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Román, J.; Arreaza-Gil, V.; Cortés-Espinar, A.J.; Soliz-Rueda, J.R.; Mulero, M.; Muguerza, B.; Arola-Arnal, A.; Arola, L.; Torres-Fuentes, C. Impact of Gut Microbiota on Plasma Oxylipins Profile under Healthy and Obesogenic Conditions. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Olza, J.; Aguilera, C.M.; Labayen, I.; Ortega, F.B.; Chillon, P.; Fernandez-Reguera, C.; Alcantara, J.M.A.A.; Martinez-Avila, W.D.; et al. Activating Brown Adipose Tissue through Exercise (ACTIBATE) in Young Adults: Rationale, Design and Methodology. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Di, X.; Kohler, I.; Osuna-Prieto, F.J.; Hankemeier, T.; Krekels, E.; Harms, A.C.; Yang, W.; Garcia-Lario, J.V.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; et al. Omega-6 and Omega-3 Oxylipins as Potential Markers of Cardiometabolic Risk in Young Adults. Obesity 2022, 30, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, v. 4.2.2; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Kuske, C.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and Tools for High Throughput RRNA Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D633–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Amaro-Gahete, F.J.; Merchan-Ramirez, E.; Labayen, I.; Ruiz, J.R. Relationships between Diet and Basal Fat Oxidation and Maximal Fat Oxidation during Exercise in Sedentary Adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Amaro-Gahete, F.J.; Arias-Tellez, M.J.; Gil, A.; Labayen, I.; Ruiz, J.R. Relationship between Dietary Factors and S-Klotho Plasma Levels in Young Sedentary Healthy Adults. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 194, 111435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Merchan-Ramirez, E.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Acosta, F.M.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Amaro-Gahete, F.J.; Muñoz Hernandez, V.; Martinez-Avila, W.D.; Ortiz-Alvarez, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Association between Dietary Factors and Brown Adipose Tissue Volume/18F-FDG Uptake in Young Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vioque, J.; Navarrete-Muñoz, E.-M.; Gimenez-Monzó, D.; García-de-la-Hera, M.; Granado, F.; Young, I.S.; Ramón, R.; Ballester, F.; Murcia, M.; Rebagliato, M.; et al. Reproducibility and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire among Pregnant Women in a Mediterranean Area. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X.; He, P. Clostridium Species as Probiotics: Potentials and Challenges. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Becker, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Ma, X. Butyrate: A Double-Edged Sword for Health? Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, J.; Igarashi, M.; Watanabe, K.; Karaki, S.I.; Mukouyama, H.; Kishino, S.; Li, X.; Ichimura, A.; Irie, J.; Sugimoto, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Confers Host Resistance to Obesity by Metabolizing Dietary Poly-unsaturated Fatty Acids. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Sleep, S.L.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Holland, O.J.; McAinch, A.J.; Dekker Nitert, M.; Hryciw, D.H. Pregnancy and Diet-Related Changes in the Maternal Gut Microbiota Following Exposure to an Elevated Linoleic Acid Diet. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E276–E285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.; Mitra, S.; Croden, F.C.; Taylor, M.; Wood, H.M.; Perry, S.L.; Spencer, J.A.; Quirke, P.; Toogood, G.J.; Lawton, C.L.; et al. A Randomised Trial of the Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplements on the Human Intestinal Microbiota. Gut 2018, 67, 1974–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Singh, S.K.; Pal, D.; Khajuria, R.; Mandal, A.K.; Prasad, R. Implication of BBM Lipid Composition and Fluidity in Mitigated Alkaline Phosphatase Activity in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 369, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, W.F.; Seetharam, B.; Talkad, V.; Pickett, W.; Dudeja, P.; Brasitus, T.A. Effects of Dietary Fish Oil Supplementation on Membrane Fluidity and Enzyme Activity in Rat Small Intestine. Biochem. J. 1989, 263, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; DeCoffe, D.; Brown, K.; Rajendiran, E.; Estaki, M.; Dai, C.; Yip, A.; Gibson, D.L. Fish Oil Attenuates Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Induced Dysbiosis and Infectious Colitis but Impairs LPS Dephosphorylation Activity Causing Sepsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, E.L.; MacManus, C.F.; Kominsky, D.J.; Keely, S.; Glover, L.E.; Bowers, B.E.; Scully, M.; Bruyninckx, W.J.; Colgan, S.P. Resolvin E1-Induced Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase Promotes Resolution of Inflammation through LPS Detoxification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14298–14303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallès, J.-P. Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase: Multiple Biological Roles in Maintenance of Intestinal Homeostasis and Modulation by Diet. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; McCauley, M.; Villéger, S.; Jackson, C.R. Ranking the Biases: The Choice of OTUs vs. ASVs in 16S RRNA Amplicon Data Analysis Has Stronger Effects on Diversity Measures than Rarefaction and OTU Identity Threshold. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R. Taxonomy Annotation and Guide Tree Errors in 16S RRNA Databases. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Zazzo, A.; Yang, W.; Coassin, M.; Micera, A.; Antonini, M.; Piccinni, F.; De Piano, M.; Kohler, I.; Harms, A.C.; Hankemeier, T.; et al. Signaling lipids as diagnostic biomarkers for ocular surface cicatrizing conjunctivitis. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Kloet, F.M.; Bobeldijk, I.; Verheij, E.R.; Jellema, R.H. Analytical error reduction using single point calibration for accurate and precise metabolomic phenotyping. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5132–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N | Mean | ± | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (women, %) | 80 | 59 (73.8%) | ||
| Age (years) | 80 | 21.9 | ± | 2.2 |
| Body composition | ||||
| Lean mass (kg) | 80 | 41.0 | ± | 8.9 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 80 | 36.3 | ± | 7.8 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 80 | 24.7 | ± | 4.7 |
| Dietary intake | ||||
| Energy (kcal/day) | 80 | 1920 | ± | 489 |
| PUFAs (g/day) | 80 | 13 | ± | 5 |
| Fish (servings/week) | 77 | 5 | ± | 3 |
| Total plasma levels of derived-oxylipins (peak area ratio) | ||||
| Omega-3 | 80 | 172.8 | ± | 65.6 |
| ALA | 80 | 12.0 | ± | 5.1 |
| EPA | 80 | 19.0 | ± | 10.3 |
| DHA | 80 | 141.7 | ± | 54.6 |
| Omega-6 | 80 | 99.5 | ± | 27.8 |
| LA | 80 | 28.6 | ± | 10.6 |
| DGLA | 80 | 1.0 | ± | 0.5 |
| AA | 80 | 66.4 | ± | 22.2 |
| AdrA | 80 | 1.0 | ± | 0.6 |
| Omega-6/omega-3 oxylipin ratio | 80 | 0.6 | ± | 0.1 |
| Fecal microbiota composition (phylum, %) | ||||
| Actinobacteria | 80 | 1.6 | ± | 1.6 |
| Bacteroidetes | 80 | 39.6 | ± | 9.0 |
| Firmicutes | 80 | 48.8 | ± | 9.7 |
| Proteobacteria | 80 | 6.5 | ± | 4.8 |
| Verrucomicrobia | 80 | 2.3 | ± | 4.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Ortiz-Alvarez, L.; Osuna-Prieto, F.J.; Kohler, I.; Di, X.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Link, A.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Gil, A.; et al. Plasma Levels of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Derived Oxylipins Are Associated with Fecal Microbiota Composition in Young Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4991. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234991
Xu H, Jurado-Fasoli L, Ortiz-Alvarez L, Osuna-Prieto FJ, Kohler I, Di X, Vilchez-Vargas R, Link A, Plaza-Díaz J, Gil A, et al. Plasma Levels of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Derived Oxylipins Are Associated with Fecal Microbiota Composition in Young Adults. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):4991. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234991
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Huiwen, Lucas Jurado-Fasoli, Lourdes Ortiz-Alvarez, Francisco J. Osuna-Prieto, Isabelle Kohler, Xinyu Di, Ramiro Vilchez-Vargas, Alexander Link, Julio Plaza-Díaz, Angel Gil, and et al. 2022. "Plasma Levels of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Derived Oxylipins Are Associated with Fecal Microbiota Composition in Young Adults" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 4991. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234991
APA StyleXu, H., Jurado-Fasoli, L., Ortiz-Alvarez, L., Osuna-Prieto, F. J., Kohler, I., Di, X., Vilchez-Vargas, R., Link, A., Plaza-Díaz, J., Gil, A., Rensen, P. C. N., Ruiz, J. R., & Martinez-Tellez, B. (2022). Plasma Levels of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Derived Oxylipins Are Associated with Fecal Microbiota Composition in Young Adults. Nutrients, 14(23), 4991. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234991









