Lactobacillus gasseri RW2014 Ameliorates Hyperlipidemia by Modulating Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota Composition in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Screening and BSH Detection of LGA
2.3. Hypercholesterolemic Rat Model and LGA Administration
2.4. Measurement of Serum Lipids and Inflammatory Factors
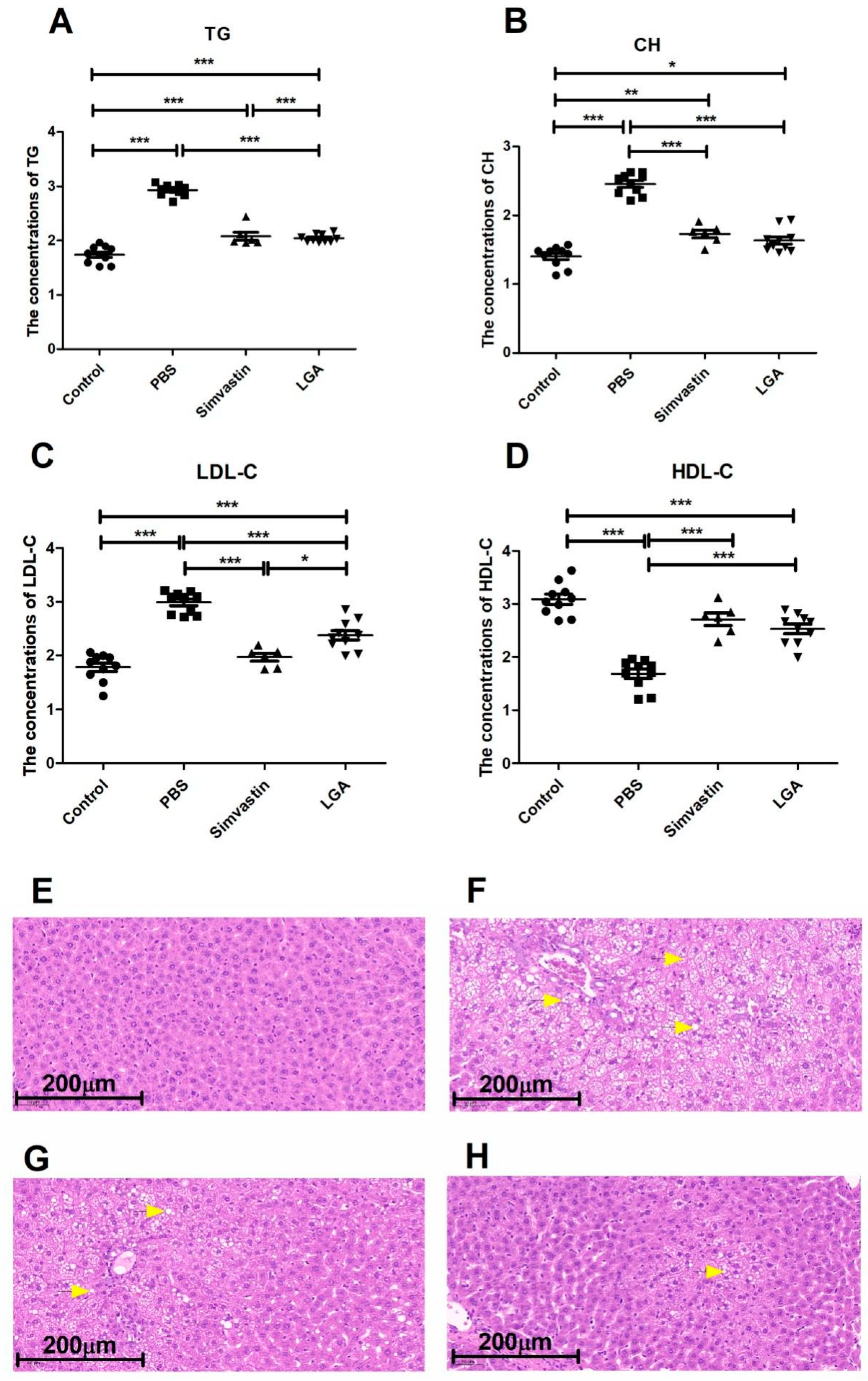
2.5. Histopathological Analysis
2.6. Measurement of Fecal SCFAs
2.7. Quantification Analysis of Bile Acids
2.8. 16S rRNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.9. Metabolomics Analysis of Serum
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. L. gasseri RW2014 Had the Character of Probiotics and Activity of Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH)
3.2. Oral Administration of L. gasseri RW2014 Significantly Improved the Hyperlipidemia in Rat Model
3.3. Oral Administration of L. gasseri RW2014 Significantly Reduced the Levels of Serum Inflammatory Factors
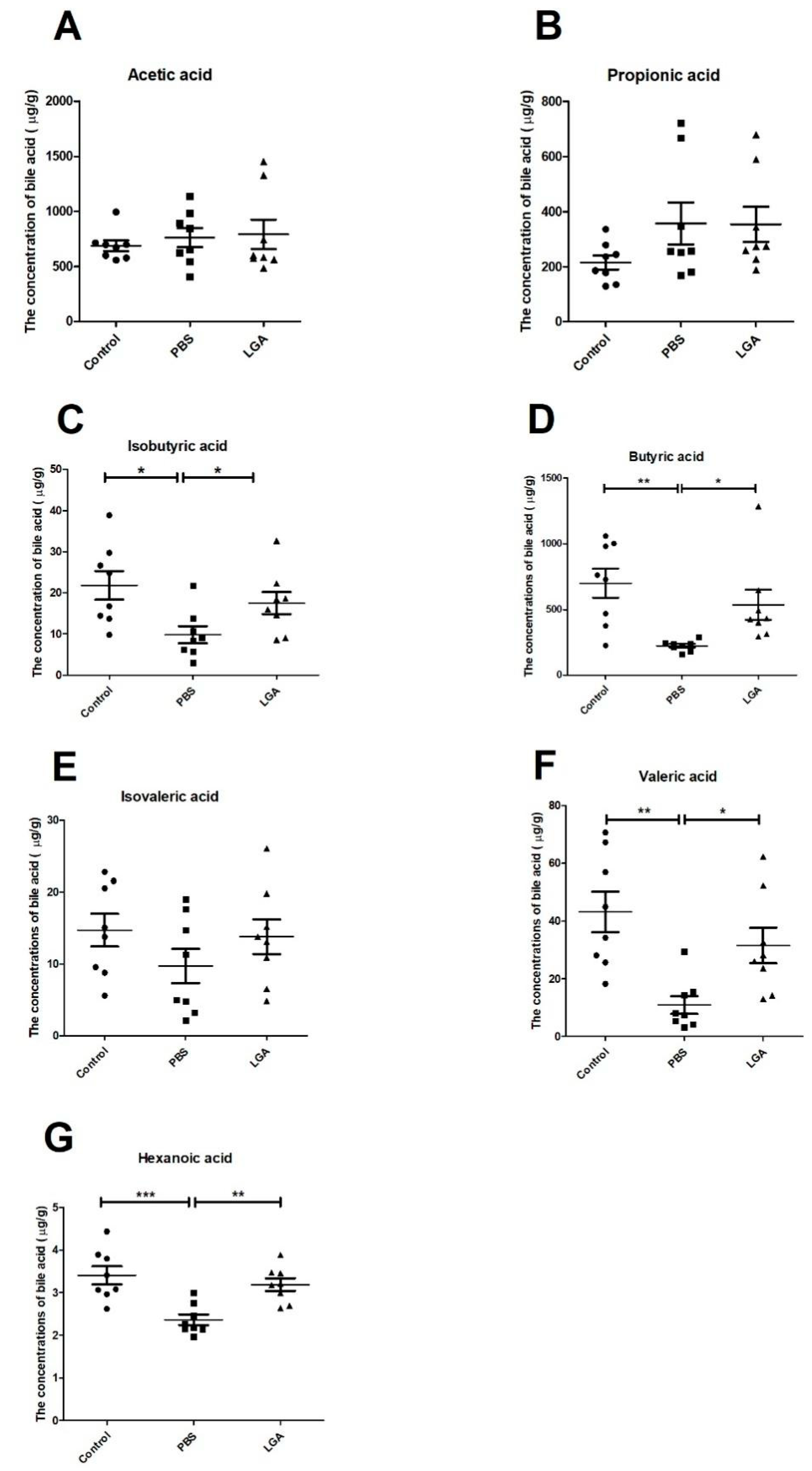
3.4. Oral Administration of L. gasseri Restored the Levels of SCFAs
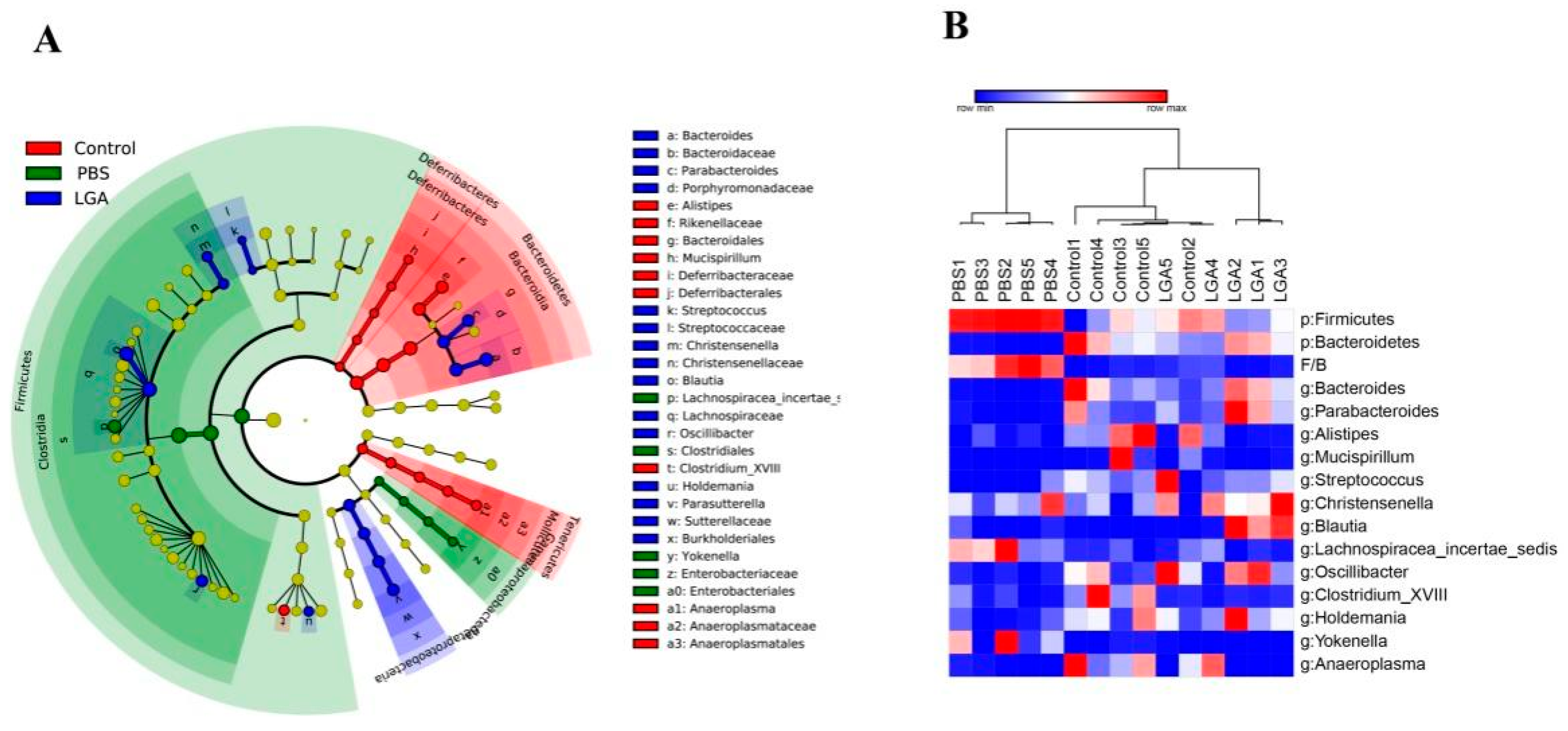
3.5. Oral Administration of L. gasseri RW2014 Altered Composition of Gut Microbiota
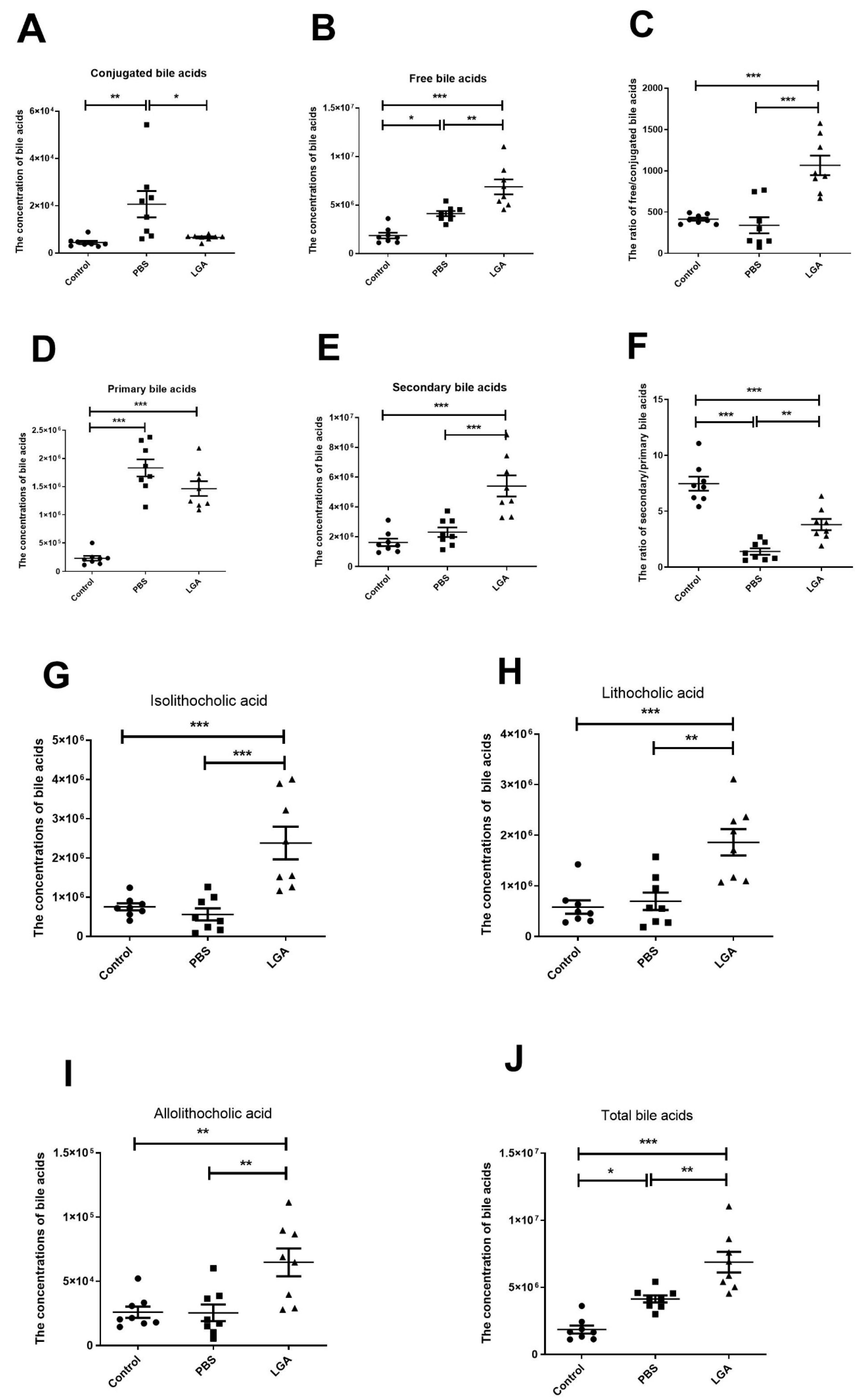
3.6. Oral Administration of L. gasseri RW2014 Increased the Concentrations of Fecal Bile Acids
3.7. The Effect of Oral Administration of L. gasseri RW2014 on Serum Metabolism
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Du, L.; Wang, S.; Kong, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, G. Differences in the prevention and control of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, T.R.; Tobert, J.A. Simvastatin: A review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2004, 5, 2583–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Includepowder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria, Cordoba, Argentina; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Song, L.; Huang, Y.; Chu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Lu, S.; Hou, L.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum HT121 on serum lipid profile, gut microbiota, and liver transcriptome and metabolomics in a high-cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia rat model. Nutrition 2020, 79–80, 110966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Cao, F.W.; Wang, W.J.; Yu, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, J.X.; Firrman, J.; Renye, J.; Ren, D.X. Probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum E680 and its effect on Hypercholesterolemic mice. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Narbad, A.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. Strain-Specific Effects of Bifidobacterium longum on Hypercholesterolemic Rats and Potential Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, L.; Caputo, M.; Bisicchia, S.; Soato, M.; Bertolino, G.; Vaccaro, S.; Inturri, R. The Role of Bifidobacteria in Predictive and Preventive Medicine: A Focus on Eczema and Hypercholesterolemia. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Derrien, M.; Rocher, E.; Van-Hylckama, V.J.; Strissel, K.; Zhao, L.; Obin, M.; et al. Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, Q.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. Bifidobacterium adolescentis Isolated from Different Hosts Modifies the Intestinal Microbiota and Displays Differential Metabolic and Immunomodulatory Properties in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yan, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Shan, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Anti-obesity effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LS-8 and Lactobacillus crustorum MN047 on high-fat and high-fructose diet mice base on inflammatory response alleviation and gut microbiota regulation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2709–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.Y.; Ahn, Y.T.; Park, S.H.; Huh, C.S.; Yoo, S.R.; Yu, R.; Sung, M.K.; McGregor, R.A.; Choi, M.S. Supplementation of Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032 in diet-induced obese mice is associated with gut microbial changes and reduction in obesity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman; Hosono, A. Effect of administration of Lactobacillus gasseri on serum lipids and fecal steroids in hypercholesterolemic rats. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toit, M.D.; Franz, C.M.; Dicks, L.M.; Schillinger, U.; Haberer, P.; Warlies, B.; Ahrens, F.; Holzapfel, W.H. Characterisation and selection of probiotic lactobacilli for a preliminary minipig feeding trial and their effect on serum cholesterol levels, faeces pH and faeces moisture content. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 40, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Song, L.; Lu, S.; Ren, Z. A strain of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron attenuates colonization of Clostridioides difficile and affects intestinal microbiota and bile acids profile in a mouse model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, P.; Ravi, S.; Krishnan, M.; Livya, C.M.; Manikandan, B.; Arunagirinathan, K.; Ramar, M. Dynamic Role of Macrophage Sub Types on Development of Atherosclerosis and Potential Use of Herbal Immunomodulators as Imminent Therapeutic Strategy. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 20, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Bharadwaj, D.; Prasad, G.; Grechko, A.V.; Sazonova, M.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Anti-Inflammatory Therapy for Atherosclerosis: Focusing on Cytokines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anto, L.; Blesso, C.N. Interplay between diet, the gut microbiome, and atherosclerosis: Role of dysbiosis and microbial metabolites on inflammation and disordered lipid metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 105, 108991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pussinen, P.J.; Kopra, E.; Pietiäinen, M.; Lehto, M.; Zaric, S.; Paju, S.; Salminen, A. Periodontitis and cardiometabolic disorders: The role of lipopolysaccharide and endotoxemia. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 89, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yi, C.X.; Katiraei, S.; Kooijman, S.; Zhou, E.; Chung, C.K.; Gao, Y.; van den Heuvel, J.K.; Meijer, O.C.; Berbée, J.; et al. Butyrate reduces appetite and activates brown adipose tissue via the gut-brain neural circuit. Gut 2018, 67, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.F.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Y.H.; Li, J.Y.; Yue, T.L. Bile Salt Hydrolase and S-Layer Protein are the Key Factors Affecting the Hypocholesterolemic Activity of Lactobacillus casei-Fermented Milk in Hamsters. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, P.; Fan, S.; Huang, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, H. Fucoidan and galactooligosaccharides ameliorate high-fat diet-induced dyslipidemia in rats by modulating the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Nutrition 2019, 65, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zheng, X.; Ma, X.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, S.; Wang, S.; Kuang, J.; et al. Theabrownin from Pu-erh tea attenuates hypercholesterolemia via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Martoni, C.J.; Parent, M.; Prakash, S. Cholesterol-lowering efficacy of a microencapsulated bile salt hydrolase-active Lactobacillus reuteri NCIMB 30242 yoghurt formulation in hypercholesterolaemic adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Martoni, C.J.; Prakash, S. Cholesterol lowering with bile salt hydrolase-active probiotic bacteria, mechanism of action, clinical evidence, and future direction for heart health applications. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liao, M.; Zhou, N.; Bao, L.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Parabacteroides distasonis Alleviates Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunctions via Production of Succinate and Secondary Bile Acids. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, R.; Onuki, M.; Hattori, K.; Ito, M.; Yamada, T.; Kamikado, K.; Kim, Y.G.; Nakamoto, N.; Kimura, I.; Clarke, J.M.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived acetate suppresses NAFLD/NASH development via hepatic FFAR2 signalling in mice. Microbiome 2021, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mao, B.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Cui, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Blautia-a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1875796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, L.; Li, M.; Ren, Z. Lactobacillus gasseri RW2014 Ameliorates Hyperlipidemia by Modulating Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota Composition in Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234945
Li X, Xiao Y, Huang Y, Song L, Li M, Ren Z. Lactobacillus gasseri RW2014 Ameliorates Hyperlipidemia by Modulating Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota Composition in Rats. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234945
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianping, Yuchun Xiao, Yuanming Huang, Liqiong Song, Mengde Li, and Zhihong Ren. 2022. "Lactobacillus gasseri RW2014 Ameliorates Hyperlipidemia by Modulating Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota Composition in Rats" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234945
APA StyleLi, X., Xiao, Y., Huang, Y., Song, L., Li, M., & Ren, Z. (2022). Lactobacillus gasseri RW2014 Ameliorates Hyperlipidemia by Modulating Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota Composition in Rats. Nutrients, 14(23), 4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234945




