Sodium Alginate Prevents Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the Gut–Liver Axis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment Design
2.2. Serum Biochemical and Inflammatory Markers Analysis
2.3. Histopathological Examination
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.6. Sequencing of Microbiota and Analysis
2.7. Measurement of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Cecal Contents
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SA Supplementation Reduced Body Weight
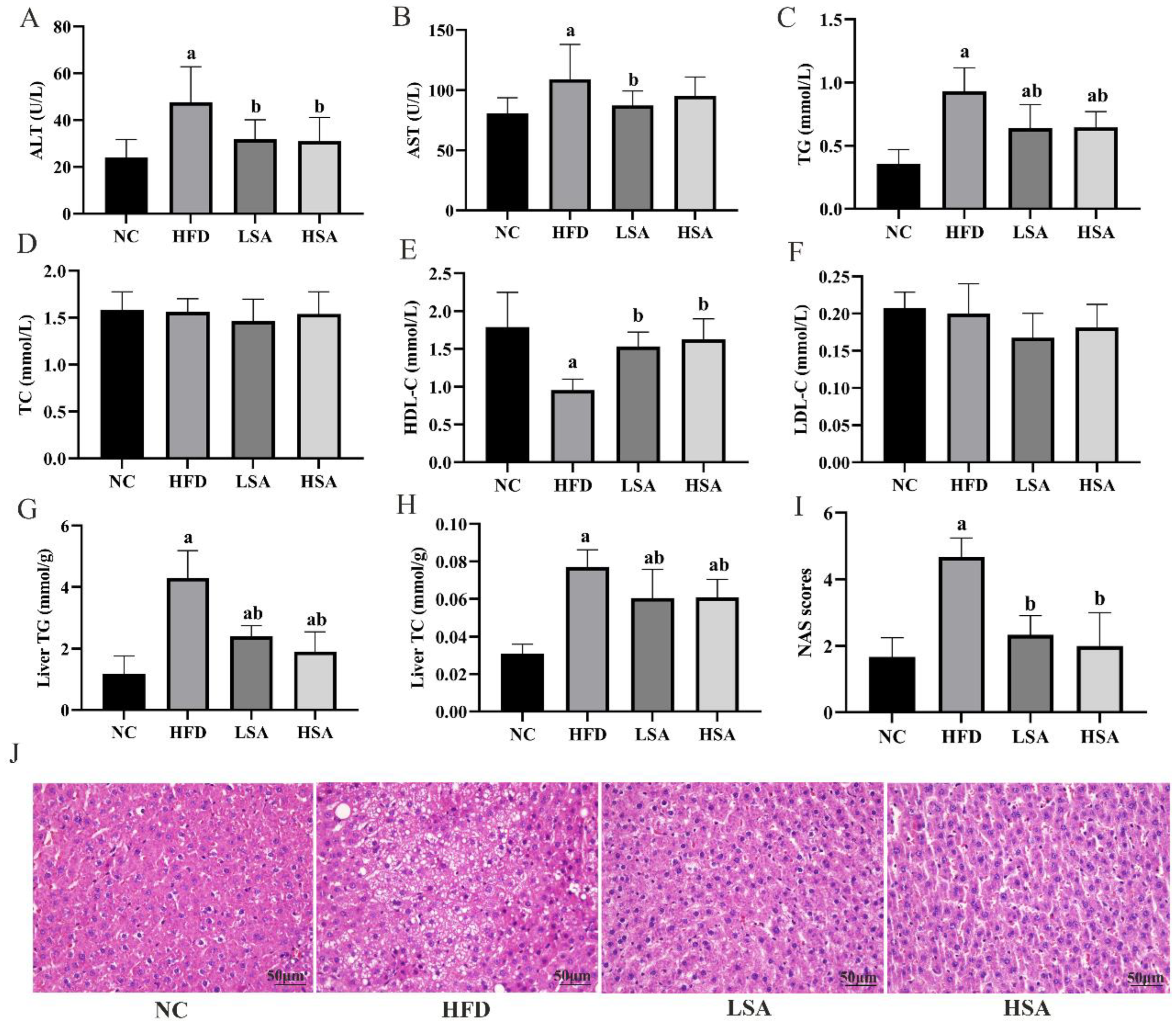
3.2. SA Supplementation Ameliorated NAFLD-Related Parameters
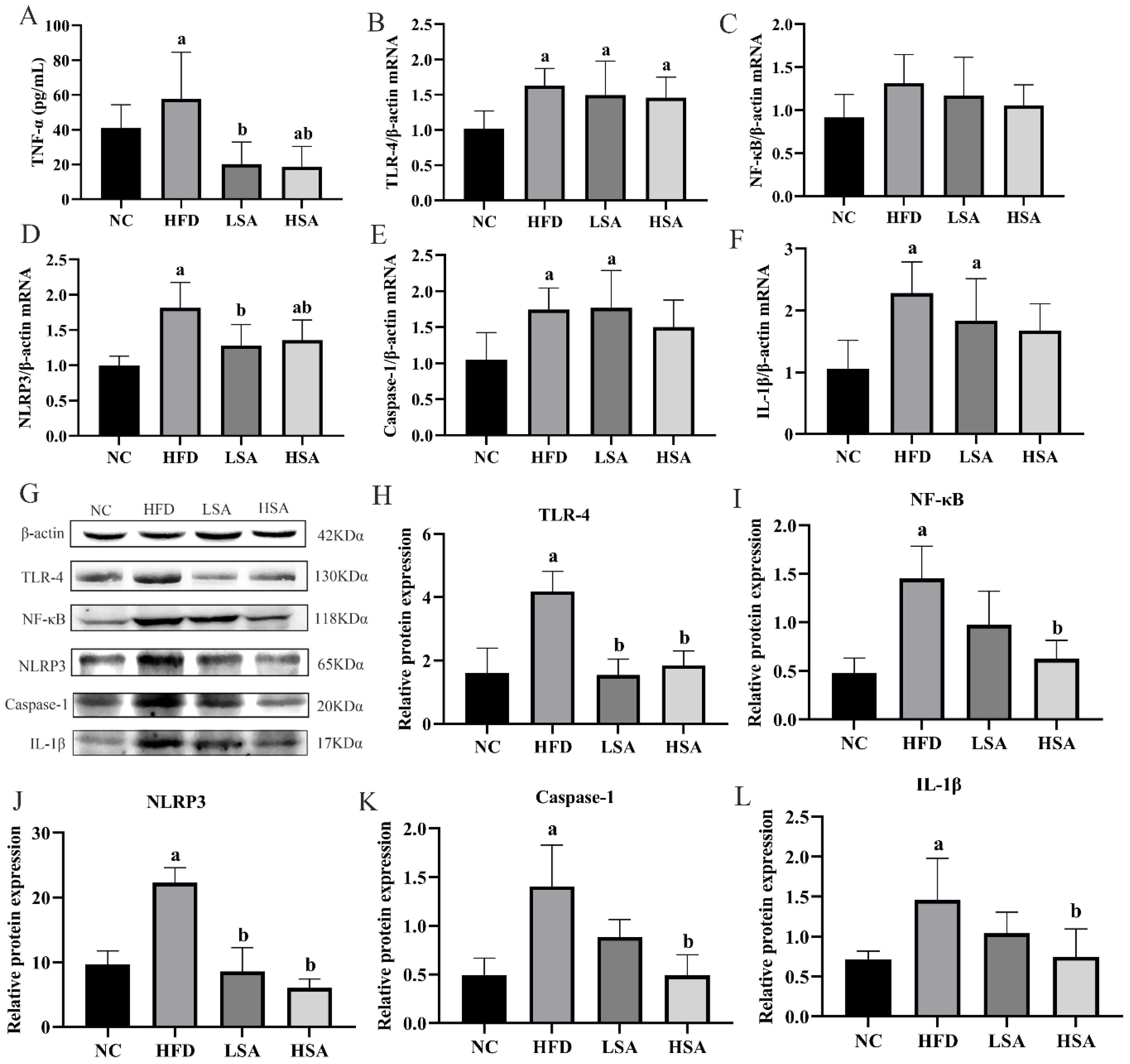
3.3. SA Supplementation Inhibited Hepatic Inflammation
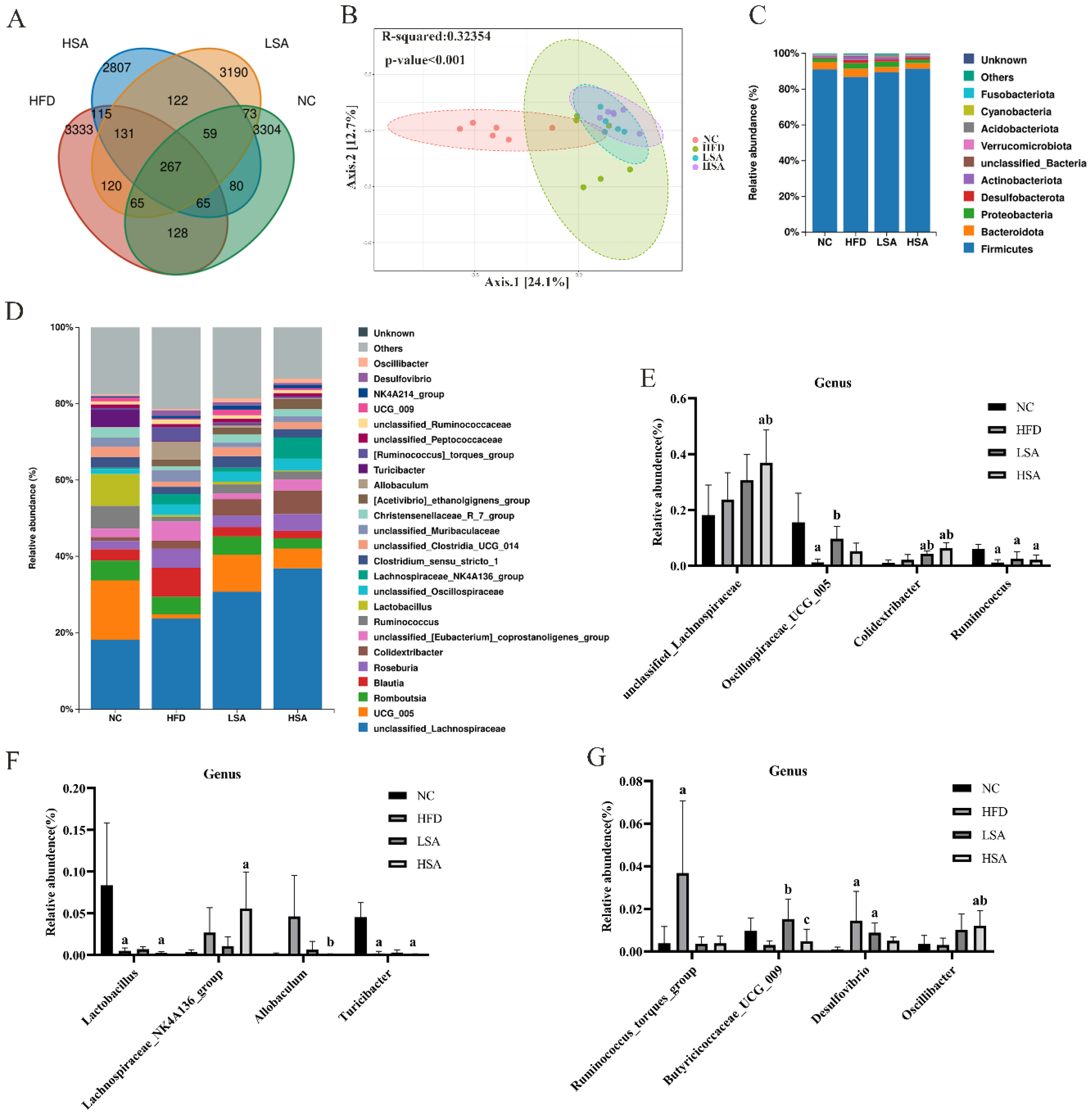
3.4. SA Supplementation Altered Overall Gut Microbial Structure
3.5. SA Supplementation Affected the Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites
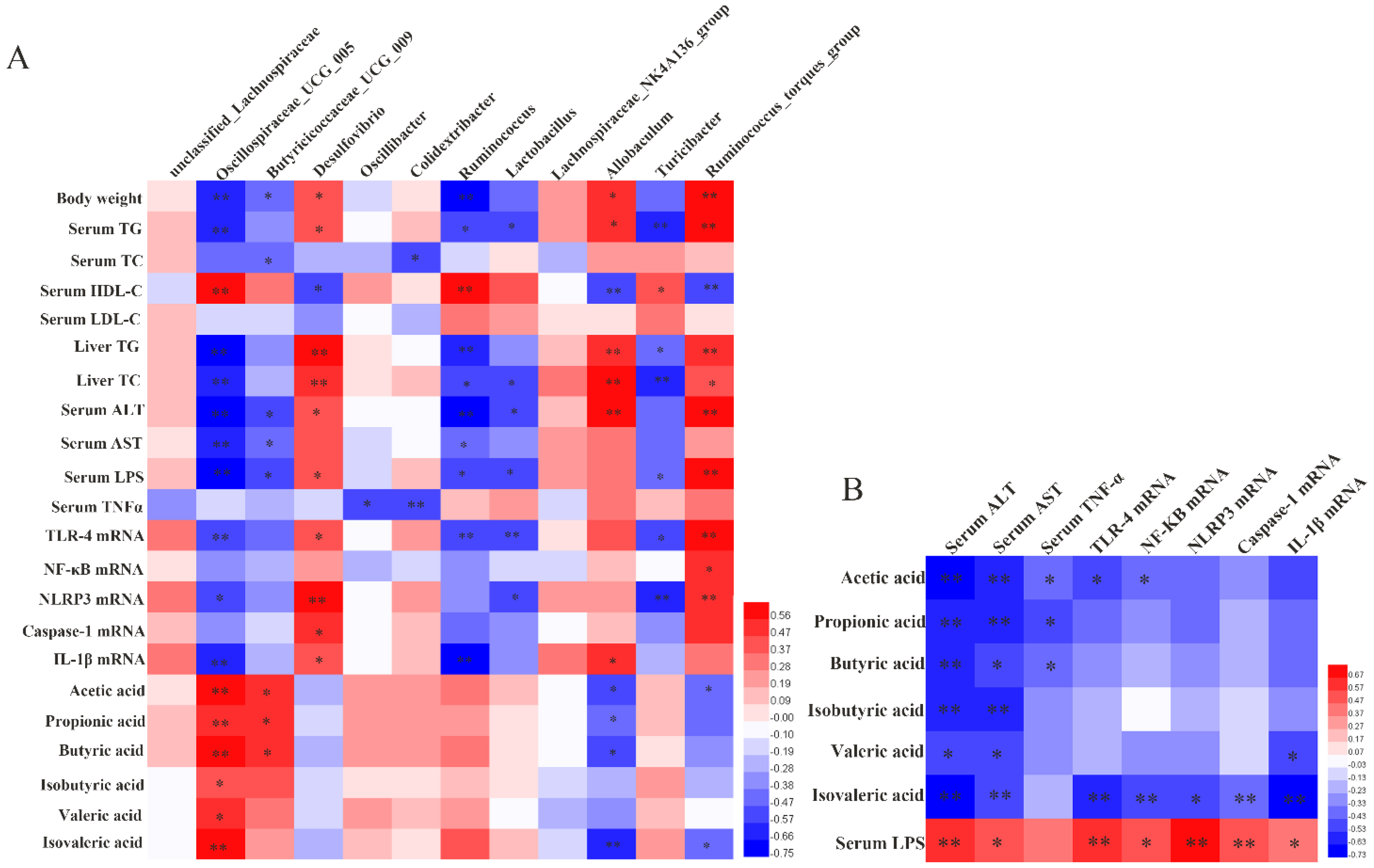
3.6. Correlation Analysis
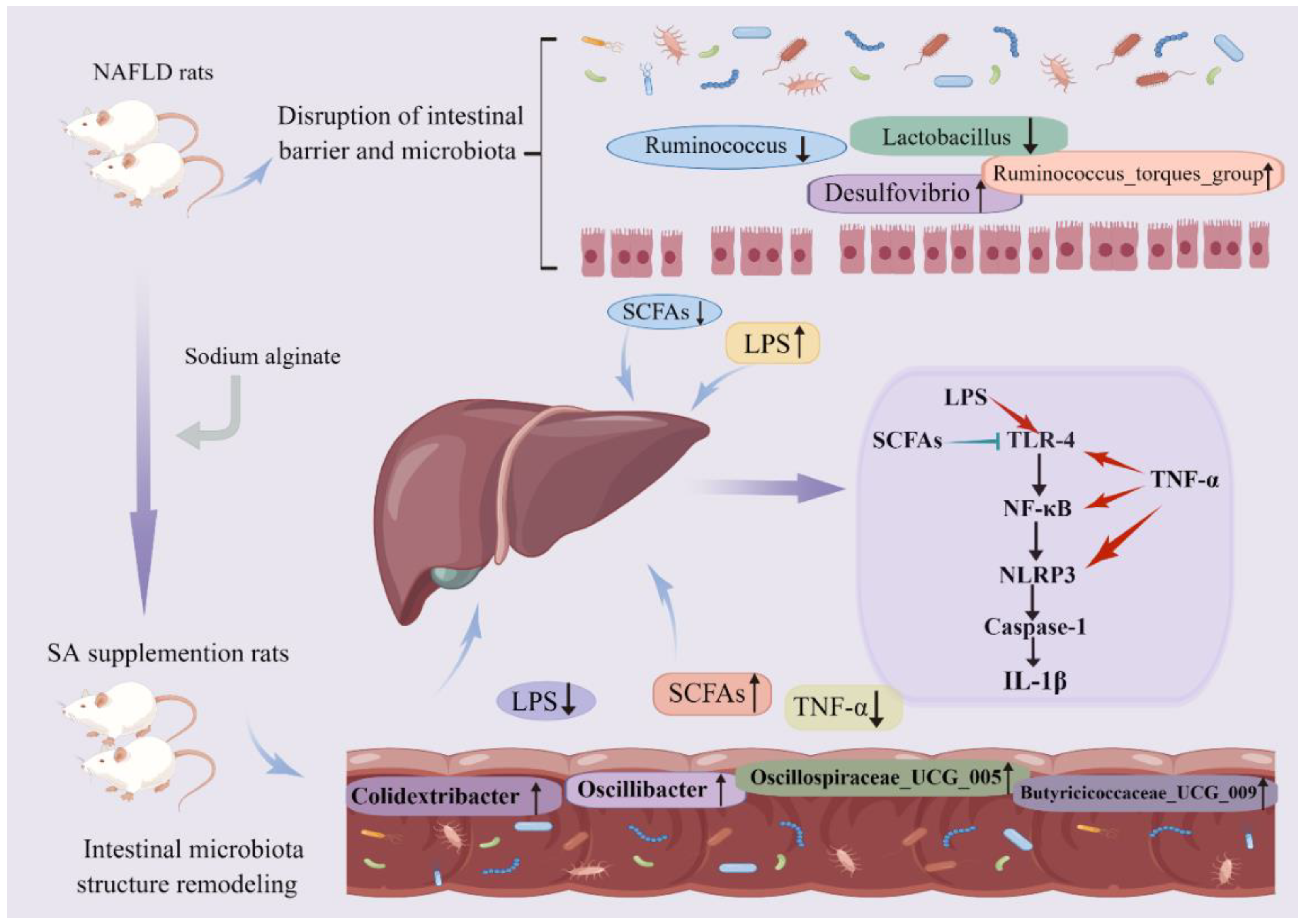
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzadilla Bertot, L.; Adams, L.A. The Natural Course of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999–2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumpail, B.J.; Khan, M.A.; Yoo, E.R.; Cholankeril, G.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 8263–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, P.; Martin, A.; Lang, S.; Kütting, F.; Goeser, T.; Demir, M.; Steffen, H.M. NAFLD and cardiovascular diseases: A clinical review. Clin. Res. Cardiol. Off. J. Ger. Card. Soc. 2021, 110, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuccilli, M.; Chonchol, M. NAFLD and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.G.; Kim, S.U.; Wong, V.W. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Gut Microbiota-Derived Components and Metabolites in the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. A High-Fat Diet Increases Gut Microbiota Biodiversity and Energy Expenditure Due to Nutrient Difference. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, S.; Thiemermann, C. Role of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Systemic Inflammation and Potential Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Ijaz, M.U.; Hussain, M.; Haq, I.U.; Zhao, D.; Li, C. High-Fat Proteins Drive Dynamic Changes in Gut Microbiota, Hepatic Metabolome, and Endotoxemia-TLR-4-NFκB-Mediated Inflammation in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11710–11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; He, X.; Yuan, X.; Hong, J.; Bhat, O.; Li, G.; Li, P.L.; Guo, J. NLRP3 Inflammasome Formation and Activation in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Therapeutic Target for Antimetabolic Syndrome Remedy FTZ. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2901871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Beneficial effects of ginger on prevention of obesity through modulation of gut microbiota in mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shang, C.; Xiang, M.; Li, L.; Cui, X. Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids: Implications for cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 900381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Qu, F.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Ren, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Ge, S.; Wu, C.; et al. SCFAs alleviated steatosis and inflammation in mice with NASH induced by MCD. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 245, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Xue, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, K.; Ling, W. Supplementation with Sodium Butyrate Modulates the Composition of the Gut Microbiota and Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, C.P.; Rosa, V.H.C.; Martins, B.C.; Soares, A.C.; Santos, I.B.; Monteiro, E.B.; Moura-Nunes, N.; da Costa, C.A.; Mulder, A.; Daleprane, J.B. Resistant starch from green banana (Musa sp.) attenuates non-alcoholic fat liver accumulation and increases short-chain fatty acids production in high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; He, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, H. Inulin Exerts Beneficial Effects on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Modulating gut Microbiome and Suppressing the Lipopolysaccharide-Toll-Like Receptor 4-Mψ-Nuclear Factor-κB-Nod-Like Receptor Protein 3 Pathway via gut-Liver Axis in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 558525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, I.A.; Allen, A.; Pearson, J.P.; Dettmar, P.W.; Havler, M.E.; Atherton, M.R.; Onsøyen, E. Alginate as a source of dietary fiber. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Duan, M.; Jia, J.; Song, S.; Ai, C. Low-molecular alginate improved diet-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome through modulating the gut microbiota in BALB/c mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Gao, Y.; Xue, C.H.; Li, R.W.; Tang, Q.J. Transcriptome analysis revealed anti-obesity effects of the Sodium Alginate in high-fat diet -induced obese mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, K. Modulation of hyperglycemia by sodium alginate is associated with changes of serum metabolite and gut microbiota in mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, S.; Horibe, S.; Sasaki, N.; Tanahashi, T.; Mizuno, S.; Hamaguchi, T.; Rikitake, Y. Inhibitory Effects of Sodium Alginate on Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Induced by a Methionine- and Choline-deficient Diet. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, F.; Zhou, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, H. Sodium alginate and galactooligosaccharides ameliorate metabolic disorders and alter the composition of the gut microbiota in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, M.N.; Kuda, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Nakamura, S.; Hajime, T.; Kimura, B. Detection and isolation of low molecular weight alginate- and laminaran-susceptible gut indigenous bacteria from ICR mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Wilson, L.A.; Belt, P.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score and the histopathologic diagnosis in NAFLD: Distinct clinicopathologic meanings. Hepatology 2011, 53, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Morelli, M.; Buzzigoli, E.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Bugianesi, E.; Gastaldelli, A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its connection with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1544–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, N.; Wang, L. Efficiently Anti-Obesity Effects of Unsaturated Alginate Oligosaccharides (UAOS) in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshazly, M.B.; Nicholls, S.J.; Nissen, S.E.; St John, J.; Martin, S.S.; Jones, S.R.; Quispe, R.; Stegman, B.; Kapadia, S.R.; Tuzcu, E.M.; et al. Implications of Total to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio Discordance with Alternative Lipid Parameters for Coronary Atheroma Progression and Cardiovascular Events. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 118, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Ribeiro, M.; Szabo, G. Role of the Inflammasome in Liver Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Hong, W.; Lu, S.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Weng, X.; Feng, Z. The NLRP3 Inflammasome in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis: Therapeutic Targets and Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 780496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Csak, T. Inflammasomes in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, J.A.; Gallego, P.; Grande, L. Role of inflammatory response in liver diseases: Therapeutic strategies. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Qiu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H. Sodium Alginate Modulates Immunity, Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function, and Gut Microbiota in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppressed BALB/c Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7064–7073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Shirakami, Y.; Kubota, M.; Ideta, T.; Kochi, T.; Sakai, H.; Tanaka, T.; Moriwaki, H.; Shimizu, M. Sodium alginate prevents progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver carcinogenesis in obese and diabetic mice. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10448–10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shanab, A.; Quigley, E.M. The role of the gut microbiota in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Dimitriadis, G.; Triantafyllou, K. Gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. HBPD INT 2015, 14, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Coker, O.O.; Chu, E.S.; Fu, K.; Lau, H.C.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Chan, A.W.H.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Dietary cholesterol drives fatty liver-associated liver cancer by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gut 2021, 70, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cai, B.Y.; Zhu, L.X.; Xin, X.; Wang, X.; An, Z.M.; Li, S.; Hu, Y.Y.; Feng, Q. Liraglutide modulates gut microbiome and attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver in db/db mice. Life Sci. 2020, 261, 118457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Pan, Q.; Xin, F.Z.; Zhang, R.N.; He, C.X.; Chen, G.Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.W.; Fan, J.G. Sodium butyrate attenuates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice by improving gut microbiota and gastrointestinal barrier. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, V.; Cighetti, R.; Peri, F. Molecular simplification of lipid A structure: TLR4-modulating cationic and anionic amphiphiles. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.F.; Nada, S.A.; Hassan, A.; El-Ansary, M.R.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Abdelsalam, R.M. Saroglitazar Deactivates the Hepatic LPS/TLR4 Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates Adipocyte Dysfunction in Rats with High-Fat Emulsion/LPS Model-Induced Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Inflammation. 2019, 42, 1056–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, J.; Garber, J.J.; Khalili, H.; Dave, M.; Bale, S.S.; Jindal, R.; Motola, D.L.; Luther, S.; Bohr, S.; Jeoung, S.W.; et al. Hepatic Injury in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Contributes to Altered Intestinal Permeability. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Petrasek, J. Inflammasome activation and function in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, A.; Su, Y. Antagonization of Ghrelin Suppresses Muscle Protein Deposition by Altering Gut Microbiota and Serum Amino Acid Composition in a Pig Model. Biology 2022, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, D. Core gut microbiota in Jinhua pigs and its correlation with strain, farm and weaning age. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, N.; Ling, J.; Jie, H.; Leung, K.; Poon, E. The potential role of lactulose pharmacotherapy in the treatment and prevention of diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 956203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Yao, Q. A Holistic View of Berberine Inhibiting Intestinal Carcinogenesis in Conventional Mice Based on Microbiome-Metabolomics Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 588079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Meng, L.; Ai, D.; Hou, N.; Li, H.; Shuai, X.; Peng, X. Acetic acid alleviates the inflammatory response and liver injury in septic mice by increasing the expression of TRIM40. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 2789–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hellman, J.; Horswill, A.R.; Crosby, H.A.; Francis, K.P.; Prakash, A. Elevated Gut Microbiome-Derived Propionate Levels Are Associated with Reduced Sterile Lung Inflammation and Bacterial Immunity in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Qin, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, L.; Zou, Z.; Wang, L. Dietary butyrate suppresses inflammation through modulating gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yi, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Wan, Y.; Fu, X.; Shu, W.; et al. Gut Microbiome Signatures in the Progression of Hepatitis B Virus-Induced Liver Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 916061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Baker, S.S.; Nugent, C.A.; Tsompana, M.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Buck, M.J.; Genco, R.J.; Baker, R.D.; Zhu, R.; et al. Gut microbiome may contribute to insulin resistance and systemic inflammation in obese rodents: A meta-analysis. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y. Sodium Alginate Prevents Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the Gut–Liver Axis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224846
Zhao H, Gao X, Liu Z, Zhang L, Fang X, Sun J, Zhang Z, Sun Y. Sodium Alginate Prevents Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the Gut–Liver Axis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. Nutrients. 2022; 14(22):4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224846
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hui, Xiang Gao, Zhizuo Liu, Lei Zhang, Xuan Fang, Jianping Sun, Zhaofeng Zhang, and Yongye Sun. 2022. "Sodium Alginate Prevents Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the Gut–Liver Axis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats" Nutrients 14, no. 22: 4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224846
APA StyleZhao, H., Gao, X., Liu, Z., Zhang, L., Fang, X., Sun, J., Zhang, Z., & Sun, Y. (2022). Sodium Alginate Prevents Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the Gut–Liver Axis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. Nutrients, 14(22), 4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224846







