Vitamin A Concentration in Human Milk: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection and Screening
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Identification
3.2. Study Characteristics
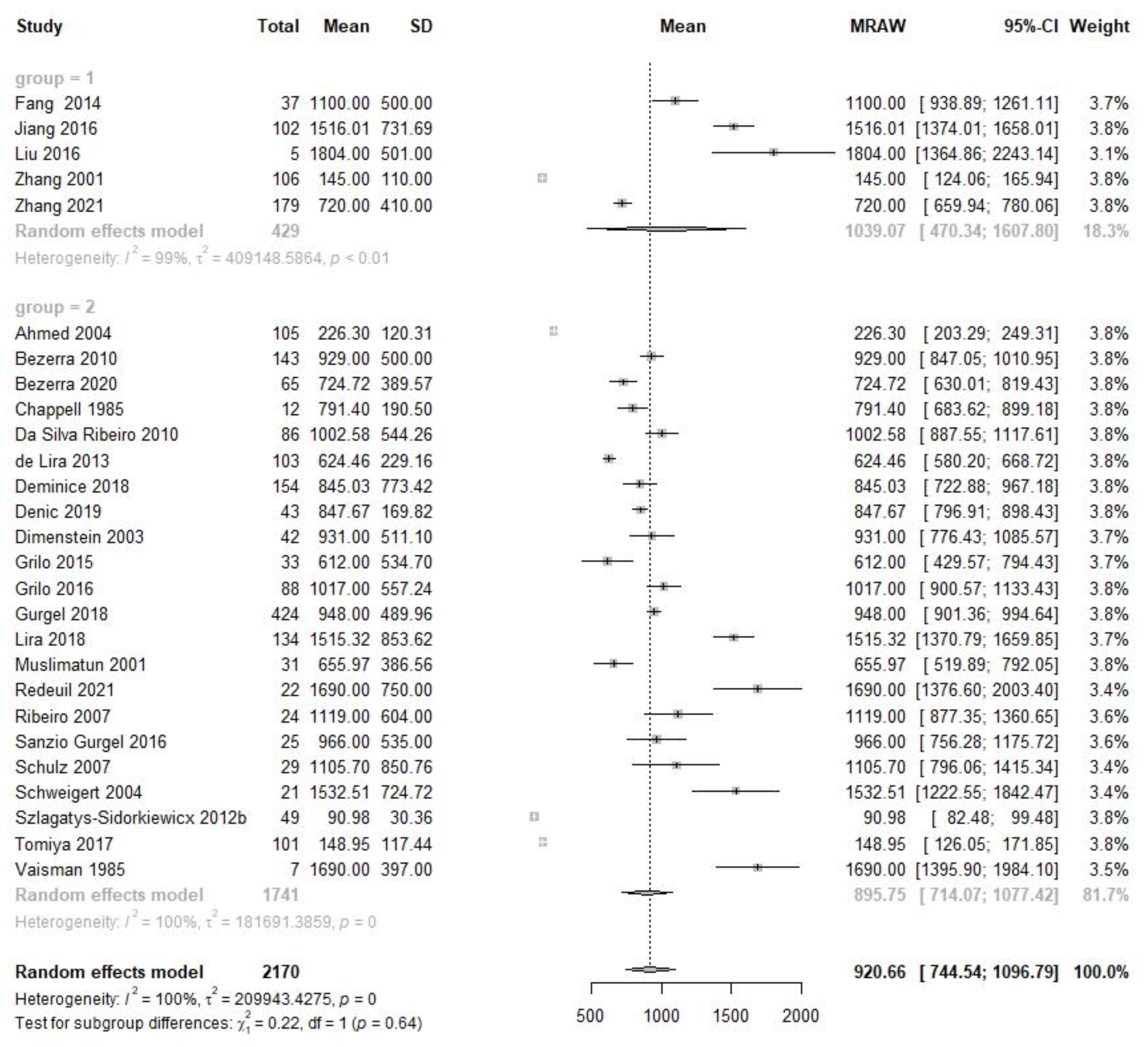
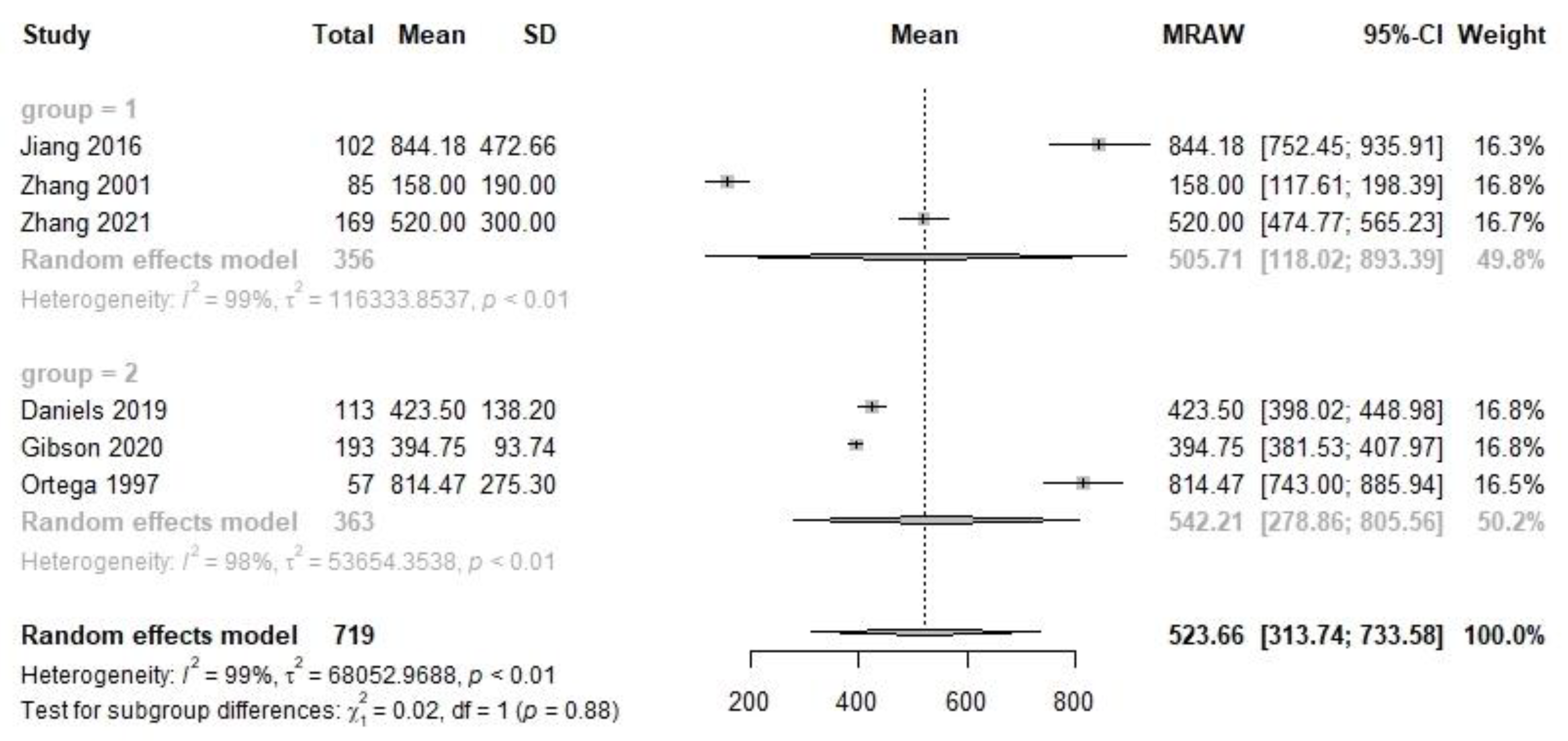
3.3. VA Concentration in Human Milk
3.4. Heterogeneity and Sensitity Analysis
3.5. Meta-Regression
4. Discussion
4.1. Data Interpretation
4.2. Implications of Our Results for DRIs Revision
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | Stage 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | R2 | p | R2 | p | R2 | p | R2 | |
| Country | 0.066 | 21.56% | 0.49 | 0.00% | <0.0001 | 54.58% | - & | - |
| Population (Chinese vs. Non-Chinese) | 0.59 | 0.00% | 0.81 | 0.00% | 0.97 | 0.00% | 0.68 | 0.00% |
| Publication year | 0.94 | 0.00% | 0.91 | 0.00% | 0.88 | 0.00% | 0.82 | 0.00% |
| Sampling time | 0.24 | 3.39% | 0.06 | 33.90% | 0.29 | 1.88% | 0.11 | 45.00% |
| Study design | 0.15 | 6.59% | 0.052 | 49.13% | 0.53 | 0.00% | 0.295 | 1.62% |
| Whether emptying breast or not | 0.23 | 2.18% | 0.49 | 0.00% | 0.37 | 0.00% | 0.12 | 36.45% |
| Maternal age (<30 years vs. ≥30 years) | 0.019 | 17.65% | - $ | - | 0.025 | 9.50% | 0.015 | 66.48% |
References
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium and Zinc; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on Dietary Reference Values for vitamin A. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinopoli, A.; Caminada, S.; Isonne, C.; Santoro, M.M.; Baccolini, V. What Are the Effects of Vitamin A Oral Supplementation in the Prevention and Management of Viral Infections? A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, B.A. Maternal vitamin A status and its importance in infancy and early childhood. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 59, 517S–522S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltzfus, R.J.; Underwood, B.A. Breast-milk vitamin A as an indicator of the vitamin A status of women and infants. Bull. World Health Organ. 1995, 73, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Human Vitamin and Mineral Requirements. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; p. 341. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA). Nutrient requirements and dietary intakes of infants and young children in the EU. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3408–3510. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.C.; Moran, N.E. Our Current Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A-Now 20 Years Old. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, nzaa096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redeuil, K.; Lévêques, A.; Oberson, J.M.; Bénet, S.; Tissot, E.; Longet, K.; de Castro, A.; Romagny, C.; Beauport, L.; Fischer Fumeaux, C.J.; et al. Vitamins and carotenoids in human milk delivering preterm and term infants: Implications for preterm nutrient requirements and human milk fortification strategies. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, L.; Nazrul Islam, S.; Khan, M.N.; Huque, S.; Ahsan, M. Antioxidant micronutrient profile (vitamin E, C, A, copper, zinc, iron) of colostrum: Association with maternal characteristics. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2004, 50, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, D.S.; de Araújo, K.F.; Azevêdo, G.M.; Dimenstein, R. A randomized trial evaluating the effect of 2 regimens of maternal vitamin a supplementation on breast milk retinol levels. J. Hum. Lact. 2010, 26, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. Understanding the Basics of Meta-Analysis and How to Read a Forest Plot: As Simple as It Gets. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2020, 81, 20f13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, Y.; Pundir, S.; McKenzie, E.; Keijer, J.; Kussmann, M. Maternal Circulating Vitamin Status and Colostrum Vitamin Composition in Healthy Lactating Women—A Systematic Approach. Nutrients 2018, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dror, D.K.; Allen, L.H. Retinol-to-Fat Ratio and Retinol Concentration in Human Milk Show Similar Time Trends and Associations with Maternal Factors at the Population Level: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 332s–346s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhon, F.S.; Ulukol, B.; Kahya, D.; Cengiz, B.; Başkan, S.; Tezcan, S. The influence of maternal smoking on maternal and newborn oxidant and antioxidant status. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisman, N.; Mogilner, B.M.; Sklan, D. Vitamin A and E content of preterm and term milk. Nutr. Res. 1985, 5, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle-Stone, R.; Haskell, M.J.; Nankap, M.; Ndjebayi, A.O.; Brown, K.H. Breast milk retinol and plasma retinol-binding protein concentrations provide similar estimates of vitamin A deficiency prevalence and identify similar risk groups among women in Cameroon but breast milk retinol underestimates the prevalence of deficiency among young children. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, H.; Su, M.; Yang, Y.; et al. Human Milk Lipid Profiles Around the World: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butte, N.F.; Calloway, D.H. Evaluation of lactational performance of Navajo women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, L.M.; Giuliano, A.R.; Neilson, E.M.; Blashil, B.M.; Graver, E.J.; Yap, H.H. Kinetics of the response of milk and serum beta-carotene to daily beta-carotene supplementation in healthy, lactating women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, L.M.; Giuliano, A.R.; Neilson, E.M.; Yap, H.H.; Graver, E.J.; Cui, H.A.; Blashill, B.M. beta-Carotene in breast milk and serum is increased after a single beta-carotene dose. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, Z.; Haki, G.D.; Schweigert, F.J.; Henkel, I.M.; Baye, K. Low human milk vitamin A concentration is prevalent in rural Ethiopia. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agne-Djigo, A.; Idohou-Dossou, N.; Kwadjode, K.M.; Tanumihardjo, S.A.; Wade, S. High prevalence of vitamin A deficiency is detected by the modified relative dose-response test in six-month-old Senegalese breast-fed infants. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, D.S.; van Raaij, J.M.; Hautvast, J.G.; Yunus, M.; Wahed, M.A.; Fuchs, G.J. Effect of dietary fat supplementation during late pregnancy and first six months of lactation on maternal and infant vitamin A status in rural Bangladesh. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2010, 28, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalhi, N.; El Hamdouchi, A.; Barkat, A.; Elkari, K.; Hamrani, A.; El Mzibri, M.; Haskell, M.J.; Mokhtar, N.; Aguenaou, H. Combined consumption of a single high-dose vitamin A supplement with provision of vitamin A fortified oil to households maintains adequate milk retinol concentrations for 6 months in lactating Moroccan women. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayah, R.A.; Mwaniki, D.L.; Magnussen, P.; Tedstone, A.E.; Marshall, T.; Alusala, D.; Luoba, A.; Kaestel, P.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Friis, H. The effects of maternal and infant vitamin A supplementation on vitamin A status: A randomised trial in Kenya. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, S.; Tarannum, S.; Nahar, L.; Mohiduzzaman, M. Retinol and alpha-tocopherol content in breast milk of Bangladeshi mothers under low socio-economic status. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1997, 48, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, D.S.; Ribeiro, K.D.S.; Lima, M.S.R.; Pires Medeiros, J.F.; da Silva, A.; Dimenstein, R.; Osório, M.M. Retinol status and associated factors in mother-newborn pairs. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 33, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, L.M.; Clandinin, M.T.; Davies, D.P.; Fernandez, M.C.; Jackson, J.; Hawkes, J.; Goldman, W.J.; Pramuk, K.; Reyes, H.; Sablan, B.; et al. Multinational study of major breast milk carotenoids of healthy mothers. Eur. J. Nutr. 2003, 42, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, L.M.; Kaminsky, R.G.; Taren, D.L.; Shaw, E.; Sander, J.K. Red palm oil in the maternal diet increases provitamin A carotenoids in human milk and serum of the mother-infant dyad. Eur. J. Nutr. 2001, 40, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, L.M.; Taren, D.L.; Kaminsky, R.G.; Mahal, Z. Short-term β-carotene supplementation of lactating mothers consuming diets low in vitamin A. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1999, 10, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, J.E.; Francis, T.; Clandinin, M.T. Vitamin A and E content of human milk at early stages of lactation. Early Hum. Dev. 1985, 11, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.G.C.L.; de Sousa Rebouças, A.; Mendonça, B.M.A.; Silva, D.C.N.E.; Dimenstein, R.; Ribeiro, K.D.D.S. Relationship between the dietary intake, serum, and breast milk concentrations of vitamin A and vitamin E in a cohort of women over the course of lactation. Mater. Child Nutr. 2019, 15, e12772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Ribeiro, K.D.; de Araújo, K.F.; de Souza, H.H.; Soares, F.B.; da Costa Pereira, M.; Dimenstein, R. Nutritional vitamin A status in northeast Brazilian lactating mothers. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2010, 23, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, L.; Gibson, R.S.; Diana, A.; Haszard, J.J.; Rahmannia, S.; Luftimas, D.E.; Hampel, D.; Shahab-Ferdows, S.; Reid, M.; Melo, L.; et al. Micronutrient intakes of lactating mothers and their association with breast milk concentrations and micronutrient adequacy of exclusively breastfed Indonesian infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lira, L.Q.; Lima, M.S.R.; de Medeiros, J.M.S.; da Silva, I.F.; Dimenstein, R. Correlation of vitamin A nutritional status on alpha-tocopherol in the colostrum of lactating women. Mater. Child Nutr. 2013, 9, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pee, S.; West, C.E.; Muhilal; Karyadi, D.; Hautvast, J.G.A.J. Lack of improvement in vitamin A status with increased consumption of dark-green leafy vegetables. Lancet 1995, 346, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pee, S.; Yuniar, Y.; West, C.E.; Muhilal. Evaluation of biochemical indicators of vitamin A status in breast- feeding and non-breast-feeding Indonesian women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deminice, T.M.M.; Ferraz, I.S.; Monteiro, J.P.; Jordão, A.A.; Ambrósio, L.M.C.S.; Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A. Vitamin A intake of Brazilian mothers and retinol concentrations in maternal blood, human milk, and the umbilical cord. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denić, M.; Sunarić, S.; Genčić, M.; Živković, J.; Jovanović, T.; Kocić, G.; Jonović, M. Maternal age has more pronounced effect on breast milk retinol and β-carotene content than maternal dietary pattern. Nutrition 2019, 65, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimenstein, R.; Simplício, J.L.; Ribeiro, K.D.S.; Melo, I.L.P. Retinol levels in human colostrum: Influence of child, maternal and socioeconomic variables. J. Pediatr. 2003, 79, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Hu, P.; Yang, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, F.; Lu, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Z. Impact of maternal daily oral low-dose vitamin a supplementation on the mother–infant pair: A randomised placebo-controlled trial in China. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.B.; So, H.J.; Shin, J.A.; Qin, Y.; Yang, J.; Lee, K.T. Different content of cholesterol, retinol, and tocopherols in human milk according to its fat content. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, G.; Nogala-Kalucka, M.; Karwowska, W.; Kupczyk, B.; Lampart-Szczapa, E. Influence of the lactating women diet on the concentration of the lipophilic vitamins in human milk. Pak. J. Nutr. 2009, 8, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ettyang, G.A.; Oloo, A.; van Marken Lichtenbelt, W.; Saris, W. Consumption of vitamin A by breastfeeding children in rural Kenya. Food Nutr. Bull. 2004, 25, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Guerra, A.; Neufeld, L.M.; Hernández-Cordero, S.; Rivera, J.; Martorell, R.; Ramakrishnan, U. Prenatal multiple micronutrient supplementation impact on biochemical indicators during pregnancy and postpartum. Salud Publica M. 2009, 51, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S.; Rahmannia, S.; Diana, A.; Leong, C.; Haszard, J.J.; Hampel, D.; Reid, M.; Erhardt, J.; Suryanto, A.H.; Sofiah, W.N.; et al. Association of maternal diet, micronutrient status, and milk volume with milk micronutrient concentrations in Indonesian mothers at 2 and 5 months postpartum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góes, H.C.A.; Torres, A.G.; Donangelo, C.M.; Trugo, N.M.F. Nutrient composition of banked human milk in Brazil and influence of processing on zinc distribution in milk fractions. Nutrition 2002, 18, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, E.C.; Lima, M.S.R.; Cunha, L.R.F.; Gurgel, C.S.S.; Clemente, H.A.; Dimenstein, R. Effect of maternal vitamin A supplementation on retinol concentration in colostrum. J. Pediatr. 2015, 91, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, E.C.; Medeiros, W.F.; Silva, A.G.; Gurgel, C.S.; Ramalho, H.M.; Dimenstein, R. Maternal supplementation with a megadose of vitamin A reduces colostrum level of α-tocopherol: A randomised controlled trial. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, R.; Hänsel, H.; Schultink, W.; Shrimpton, R.; Matulessi, P.; Gross, G.; Tagliaferri, E.; Sastroamdijojo, S. Moderate zinc and vitamin A deficiency in breast milk of mothers from East-Jakarta. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 52, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, C.S.S.; Grilo, E.C.; Lira, L.Q.; Assunção, D.G.F.; Oliveira, P.G.; Melo, L.R.M.d.; de Medeiros, S.V.; Pessanha, L.C.; Dimenstein, R.; Lyra, C.O. Vitamin A nutritional status in high- and low-income postpartum women and its effect on colostrum and the requirements of the term newborn. J. Pediatr. 2018, 94, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, D.; Shahab-Ferdows, S.; Islam, M.M.; Peerson, J.M.; Allen, L.H. Vitamin Concentrations in Human Milk Vary with Time within Feed, Circadian Rhythm, and Single-Dose Supplementation. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskell, M.J.; Young, R.; Adu-Afaruwah, S.; Lartey, A.; Okronipa, H.E.T.; Maleta, K.; Ashorn, U.; Jorgensen, J.M.; Fan, Y.M.; Arnold, C.D.; et al. Small-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements Do Not Affect Plasma or Milk Retinol Concentrations Among Malawian Mothers, or Plasma Retinol Concentrations among Young Malawian or Ghanaian Children in Two Randomized Trials. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, K.; Yu, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Li, D. Retinol and α-tocopherol in human milk and their relationship with dietary intake during lactation. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.C.; West, C.E.; de Pee, S.; Bosch, D.; Phuong, H.D.; Hulshof, P.J.; Khoi, H.H.; Verhoef, H.; Hautvast, J.G. The contribution of plant foods to the vitamin A supply of lactating women in Vietnam: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, B.N.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, J.A.; Chang, N. Retinol, α-tocopherol, and selected minerals in breast milk of lactating women with full-term infants in South Korea. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; English, C.; Reich, P.; Gerber, L.E.; Simpson, K.L. VITAMIN-A AND CAROTENOIDS IN HUMAN-MILK. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klevor, M.K.; Haskell, M.J.; Lartey, A.; Adu-Afarwuah, S.; Zeilani, M.; Dewey, K.G. Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements Providing Approximately the Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin A Do Not Increase Breast Milk Retinol Concentrations among Ghanaian Women. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, L.Q.; de Souza, A.F.; Amâncio, A.M.; Bezerra, C.G.; Pimentel, J.B.; Moia, M.N.; Dimenstein, R. Retinol and Betacarotene Status in Mother-Infant Dyads and Associations between Them. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 72, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, C.; Hettiarachchi, M.; Mangalajeewa, P.; Malawipathirana, S. Adequacy of vitamin A and fat in the breast milk of lactating women in south Sri Lanka. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Teros, V.; Limon-Miro, A.T.; Astiazaran-Garcia, H.; Tanumihardjo, S.A.; Tortoledo-Ortiz, O.; Valencia, M.E. ‘Dose-to-Mother’ Deuterium Oxide Dilution Technique: An Accurate Strategy to Measure Vitamin A Intake in Breastfed Infants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.R.; Kamp, F.; Nunes, J.C.; El-Bacha, T.; Torres, A.G. Breast Milk Content of Vitamin A and E from Early- to Mid-Lactation Is Affected by Inadequate Dietary Intake in Brazilian Adult Women. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.M.; Ferraz, I.S.; Daneluzzi, J.C.; Martinelli, C.E.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Ricco, R.G.; Jordo, A.A.; Patta, M.C.; Vannucchi, H. Impact of maternal vitamin A supplementation on the mother-Infant pair in Brazil. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamoros, N.; Visentin, S.; Ferrari, G.; Falivene, M.; Fasano, V.; González, H.F. Vitamin A content in mature breast milk and its adequacy to the nutritional recommendations for infants. Arch. Argent Pediatr. 2018, 116, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello-Neto, J.; Rondó, P.H.C.; Oshiiwa, M.; Morgano, M.A.; Zacari, C.Z.; Domingues, S. The influence of maternal factors on the concentration of vitamin A in mature breast milk. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses, F.; Trugo, N.M.F. Retinol, β-carotene, and lutein + zeaxanthin in the milk of Brazilian nursing women: Associations with plasma concentrations and influences of maternal characteristics. Nutr. Res. 2005, 25, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimatun, S.; Schmidt, M.K.; West, C.E.; Schultink, W.; Hautvast, J.G.A.J.; Karyadi, D. Weekly vitamin A and iron supplementation during pregnancy increases vitamin A concentration of breast milk but not iron status in indonesian lactating women. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2664–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsdottir, A.S.; Wagner, K.H.; Thorsdottir, I.; Elmadfa, I. Fat-soluble vitamins in the maternal diet, influence of cod liver oil supplementation and impact of the maternal diet on human milk composition. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2001, 45, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.M.; Andrés, P.; Martínez, R.M.; López-Sobaler, A.M. Vitamin A status during the third trimester of pregnancy in Spanish women: Influence on concentrations of vitamin A in breast milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palmer, A.C.; Chileshe, J.; Hall, A.G.; Barffour, M.A.; Molobeka, N.; West, K.P.; Haskell, M.J. Short-term daily consumption of provitamin a carotenoid-biofortified maize has limited impact on breast milk retinol concentrations in Zambian women enrolled in a randomized controlled feeding trial. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palmer, A.C.; Jobarteh, M.L.; Chipili, M.; Greene, M.D.; Oxley, A.; Lietz, G.; Mwanza, R.; Haskell, M.J. Biofortified and fortified maize consumption reduces prevalence of low milk retinol, but does not increase vitamin A stores of breastfeeding Zambian infants with adequate reserves: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpanich, R.; Vitsupakorn, K.; Harper, G.; Brabin, B. Serum and breast-milk vitamin A in women during lactation in rural Chiang Mai, Thailand. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2002, 22, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, K.D.; Araújo, K.F.; Pereira, M.C.; Dimenstein, R. Evaluation of retinol levels in human colostrum in two samples collected at an interval of 24 hours. J. Pediatr. 2007, 83, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.L.; Stoltzfus, R.J.; De Francisco, A.; Kjolhede, C.L. Evaluation of serum retinol, the modified-relative-dose-response ratio, and breast-milk vitamin A as indicators of response to postpartum maternal vitamin A supplementation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samano, R.; Martinez-Rojano, H.; Hernandez, R.M.; Ramirez, C.; Quijano, M.E.F.; Espindola-Polis, J.M.; Veruete, D. Retinol and alpha-Tocopherol in the Breast Milk of Women after a High-Risk Pregnancy. Nutrients 2017, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sânzio Gurgel, C.S.; Alves de Araújo Pereira, L.; de Assis Costa, A.; Adja da Silva Souza, M.; Araújo de Brito, P.; Miranda de Melo, L.R.; Dimenstein, R. Effect of routine prenatal supplementation on vitamin concentrations in maternal serum and breast milk. Nutrition 2017, 33, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Engel, U.; Kreienberg, R.; Biesalski, H.K. Vitamin A and β-carotene supply of women with gemini or short birth intervals: A pilot study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2007, 46, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweigert, F.J.; Bathe, K.; Chen, F.; Büscher, U.; Dudenhausen, J.W. Effect of the stage of lactation in humans on carotenoid levels in milk, blood plasma and plasma lipoprotein fractions. Eur. J. Nutr. 2004, 43, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.; Dolinsky, M.; Matos, A.; Chagas, C.; Ramalho, A. Vitamin A concentration in human milk and its relationship with liver reserve formation and compliance with the recommended daily intake of vitamin A in pre-term and term infants in exclusive breastfeeding. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 291, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz, A.; Zagierski, M.; Jankowska, A.; Łuczak, G.; Macur, K.; Baogonekczek, T.; Korzon, M.; Krzykowski, G.; Martysiak-Zurowska, D.; Kamińska, B. Longitudinal study of vitamins A, E and lipid oxidative damage in human milk throughout lactation. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz, A.; Zagierski, M.; Łuczak, G.; MacUr, K.; Bączek, T.; Kamińska, B. Maternal smoking does not influence vitamin A and e concentrations in mature human milk. Breastfeed. Med. 2012, 7, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijerina-Sáenz, A.; Innis, S.M.; Kitts, D.D. Antioxidant capacity of human milk and its association with vitamins A and E and fatty acid composition. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuşoǧlu, Ö.; Tansuǧ, N.; Akşit, S.; Dinç, G.; Kasirga, E.; Özcan, C. Retinol and α-tocopherol concentrations in breast milk of Turkish lactating mothers under different socio-economic status. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 59, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiya, M.T.O.; de Arruda, I.K.G.; da Silva Diniz, A.; Santana, R.A.; da Silveira, K.C.; Andreto, L.M. The effect of vitamin A supplementation with 400 000 IU vs 200 000 IU on retinol concentrations in the breast milk: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.; Burri, B.J.; Jamil, K.M.; Jamil, M. The effects of daily consumption of β-cryptoxanthin-rich tangerines and β-carotene-rich sweet potatoes on vitamin A and carotenoid concentrations in plasma and breast milk of Bangladeshi women with low vitamin A status in a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, K.C.; Shahab-Ferdows, S.; Kroeun, H.; Sophonneary, P.; Green, T.J.; Allen, L.H.; Hampel, D. Macro- and Micronutrients in Milk from Healthy Cambodian Mothers: Status and Interrelations. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Ye, W. vestigation of the Contents of the Fat-Soluble Vitamins A, D and E in Human Milk from Hohho. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Bao, J.; Chen, H. Determination of vitamin A of human milk from Zhoushan islands from Zhejiang Province. J. Hygiene Res. 2001, 30, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Study on the Vitamin Contents of Human Milk in Huhhot. Food Res. Dev. 2016, 37, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wan, R.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yin, S. Concentrations of vitamin A and vitamin E in breast milk at different lactation stages from urban and rural china. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2021, 43, 347–351+357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, S.; Sethom, M.M.; Kacem, S.; Ksibi, I.; Feki, M.; Jebnoun, S.; Kaabachi, N. Retinol and Alpha-tocopherol in the Colostrum of Lactating Tunisian Women Delivering Prematurely: Associations with Maternal Characteristics. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2016, 57, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montreewasuwat, N.; Olson, J.A. Serum and liver concentrations of vitamin A in Thai fetuses as a function of gestational age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1979, 32, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.A.; Gunning, D.B.; Tilton, R.A. Liver concentrations of vitamin A and carotenoids, as a function of age and other parameters, of American children who died of various causes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 39, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
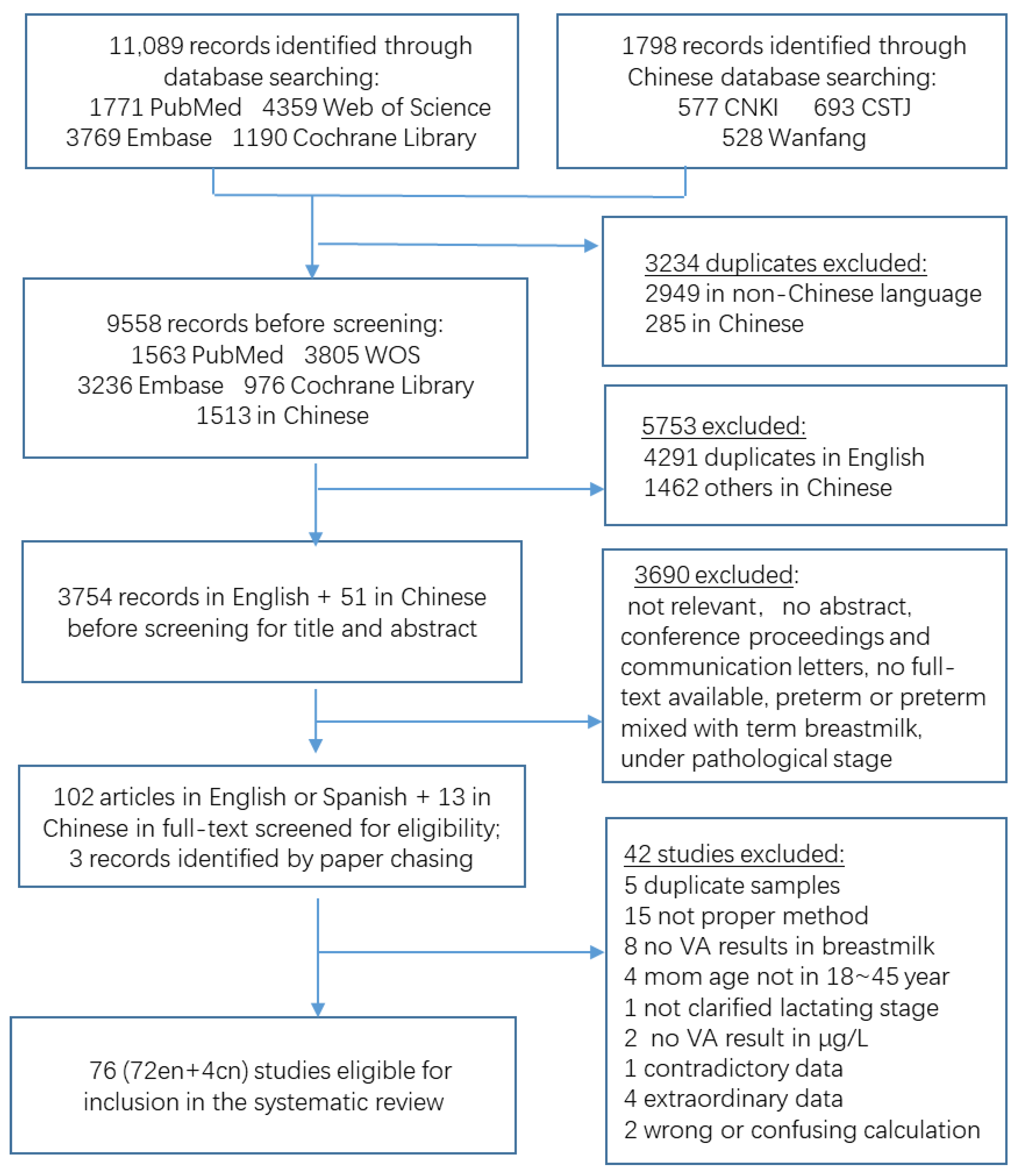


| First Author and Publication Year | Country | Study Design | Postpartum Days | Lactation Stage | Age of Mothers (y) | Subjects | Sample Size | Empty Breast or Not | Sampling Time # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abebe 2019 [22] | Ethiopia | CSS | 180 | 3 | 23.0~33.6 | 110 | 110 | No | AM |
| Agne-Djigo 2012 [23] | Senegalese | IS | 156–198 | 3 + 4 | 20.9~35.3 | 59 | 59 | Yes | AM |
| Ahmed 2004 [10] | Bangladesh | CSS | 2 | 1 | 18.7~27.5 | 105 | 105 | No | NS |
| Alam 2010 [24] | Bangladesh | RCT | 61–89 | 3 | 21~33 | 251 | 251 | No | AM + PM |
| Atalhi 2020 [25] | Morocco | IS | 15 | 3 | 19~40 | 68 | 68 | No | AM |
| Ayah 2007 [26] | Kenya | RCT | 92–98 | 3 | 18.0~30.8 | 201 | 201 | NS | NS |
| Barua1997 [27] | Bangladesh | CSS | 45–780 | 3 | 18–32 | 61 | 61 | No | AM |
| Bezerra 2010 [11] | Brazil | IS | 1 | 1 | 19.2~29.8 | 143 | 143 | No | AM |
| Bezerra 2020 [28] | Brazil | CSS | 1 | 1 | 19.4~30.2 | 65 | 65 | No | AM |
| Canfield 1997 [21] | China | IS | 75–277 | 3 + 4 * | 24.8~32.6 | 6 | 6 | Yes | PM |
| Canfield 1998 [20] | China | IS | 30~298 | 3 + 4 | 20.8~35.6 | 3 | 3 | Yes | PM |
| Canfield 1999 [31] | Honduras | IS | 30~365 | 3 + 4 | 17.3~30.1 | 36 | 36 | Yes | AM |
| Canfield 2001 [30] | Honduras | IS | 90–330 | 3 + 4 | 19.5~32.5 | 79 | 79 | no | AM |
| Canfield 2003 [29] | Multination & | CSS | 25–193 | 3, 3 + 4 | 24.6~30.4 | 471 | 471 | Yes | PM |
| Chappell 1985 [32] | Canada | CS | 1~25 | 1, 3 | NA | 12 | 24 | Yes | AM |
| da Silva 2019 [33] | Brazil | CS | 25–134 | 3 | 20.4~35.2 | 42 | 42 | No | NS |
| da Silva 2010 [34] | Brazil | CSS | 1 | 1 | 19.6~31.2 | 86 | 86 | Yes | AM |
| Daniels 2019 [35] | Indonesia | CSS | 14 | 2 | 19.7~31.9 | 113 | 113 | Yes | AM |
| de Lira 2013 [36] | Brazil | CSS | 1–3 | 1 | 17~31 | 103 | 103 | no | AM |
| de Pee 1995 [37] | Indonesia | RCT | 150–384 | 3 + 4 | 17~40 | 175 | 175 | yes | AM |
| de Pee 1997 [38] | Indonesia | CSS+ IS | 90–180, 181~548 | 3, 4 | 17~40 | 168 | 168 | Yes | AM |
| Deminice 2018 [39] | Brazil | CSS | 2~6 | 1 | 20.3~31.4 | 154 | 154 | No | NS |
| Denic 2019 [40] | Serbia | CSS | 1~30 | 1, 3 | 18~40 | 43 | 86 | Yes | AM |
| Dimenstein 2003 [41] | Brazil | CSS | 1~2 | 1 | 18~39 | 42 | 42 | No | AM + PM |
| Ding 2021 [42] | China | RCT | 30–45 | 3 | 26.0–34.9 | 294 | 294 | No | AM |
| Duan 2021 [43] | South Korea | CSS | NA | 3 + 4 | NA | 34 | 34 | NS | NS |
| Duda 2009 [44] | Poland | CSS | 30–360 | 3 + 4 | 25.7~31.7 | 30 | 30 | NS | NS |
| Ettyang 2004 [45] | Kenya | CSS | 14~450 | 3 + 4 | 23~35 | 62 | 62 | No | random |
| Fang 2014 [88] | China | CSS | 3–30 | 1, 3 | NA | 70 | 70 | NS | NS |
| Garcia-Guerra 2009 [46] | Mexico | IS | 30 | 3 | 18~28.8 | 122 | 122 | Yes | AM + PM |
| Gibson 2020 [47] | Indonesia | LS | 60–150 | 2 | 22~34.8 | 193 | 193 | Yes | AM |
| Goes 2002 [48] | Brazil | CSS | 30–180 | 3 | NA | 60 | 60 | NS | NS |
| Grilo 2015 [49] | Brazil | RCT | 1 | 1 | 18–35 | 33 | 33 | No | AM |
| Grilo 2016 [50] | Brazil | RCT | 1~30 | 1,3 | 16~31 | 88 | 132 | No | AM |
| Gross 1998 [51] | Indonesia | CSS | 30~114 | 3 | 20.2~30.6 | 81 | 81 | Yes | AM |
| Gurgel 2018 [52] | Brazil | CSS | 1–2 | 1 | 24.8~34.0 | 424 | 424 | No | AM |
| Hampel 2017 [53] | Bangladesh | IS | 60–120 | 3 | 18~22 | 17 | 17 | Yes | AM |
| Haskell 2021 [54] | Malawi | RCT | 180 | 3 | 19~31 | 103 | 103 | No | NS |
| Jiang 2016 [55] | China | CS | 1–42 | 1, 2, 3 | 20–35 | 102 | 306 | No | AM |
| Khan 2007 [56] | Vietnam | RCT | 174~342 | 4 | 21.2~31.2 | 268 | 268 | NS | AM |
| Kim 1990 [58] | USA | CSS | 30–210 | 3 + 4 | NA | 54 | 54 | NS | AM |
| Kim 2017 [57] | South Korea | CSS | 30–330 | 3, 4 | 28.6~34.8 | 334 | 334 | Yes | random |
| Klevor 2016 [59] | Ghana | RCT | 180 | 3 | 21.1~32.1 | 243 | 243 | No | NS |
| Lira 2018 [60] | Brazil | CSS | 2 | 1 | 18.3~35.5 | 134 | 134 | No | AM |
| Liu 2016 [90] | China | CSS | 3–180 | 1, 3 | NA | 43 | 43 | NS | NS |
| Liyanage 2008 [61] | Sri Lanka | CSS | 60–270 | 3 + 4 | 21.0~33.2 | 88 | 88 | NS | NS |
| Lopez-Teros 2017 [62] | Mexico | CSS | 30–150 | 3 | 22~32 | 56 | 56 | No | AM |
| Machado 2019 [63] | Brazil | LS | 85–105 | 3 | 20–40 | 19 | 19 | No | AM |
| Martin 2010 [64] | Brazil | RCT | 20–30 | 3 | 19.3~30.7 | 61 | 61 | NS | AM |
| Matamoros 2018 [65] | Argentina | CSS | 30–90 | 3 | 18~33 | 79 | 79 | Yes | AM |
| Mello-Neto 2009 [66] | Brazil | CSS | 20–60 | 3 | 16~44 | 136 | 136 | NS | random |
| Meneses 2005 [67] | Brazil | CSS | 28–83 | 3 | 20.3~32.9 | 49 | 49 | Yes | AM |
| Muslimatun 2001 [68] | Indonesia | RCT | 4–7 | 1 | 17~35 | 31 | 31 | Yes | AM |
| Olafsdottir 2001 [69] | Iceland | CSS | 60–120 | 3 | 27~35 | 77 | 77 | No | NS |
| Ortega 1997 [70] | Spain | IS | 13–40 | 2,3 | 24.2~31.6 | 57 | 114 | No | AM |
| Palmer 2016 [71] | Zambia | RCT | 120–360 | 3 + 4 | 18~30 | 140 | 140 | Yes | AM |
| Palmer 2021 [72] | Zambia | RCT | 270 | 4 | 21~34 | 216 | 216 | Yes | AM |
| Panpanich 2002 [73] | Thailand | CSS | 120–360 | 3, 4 | 19.2~31.6 | 226 | 226 | No | NS |
| Redeuil 2021 [9] | Switzerland | CS | 1–308 | 1, 3 | 27.0~35.4 | 49 | 102 | Yes | AM |
| Ribeiro 2007 [74] | Brazil | CSS | 1 | 1 | 18–40 | 24 | 24 | No | NS |
| Rice 2000 [75] | Bangladesh | RCT | 90 | 3 | 20.9~32.3 | 35 | 35 | Yes | NS |
| Samano 2017 [76] | Mexico | CSS | 30–60 | 3 | 19.0~35.0 | 32 | 32 | Yes | AM |
| Sânzio Gurgel 2016 [77] | Brazil | CSS | 1~7 | 1 | 24.6~32.6 | 25 | 25 | No | AM |
| Schulz 2007 [78] | Germany | CSS | 2 | 1 | 24.9~32.9 | 29 | 29 | No | NS |
| Schweigert 2004 [79] | Germany | CSS | 2–21 | 1, 3 | 24~36 | 21 | 42 | Yes | NS |
| Souza 2015 [80] | Brazil | CSS | 30 | 3 | 22.4~35.0 | 80 | 80 | No | AM |
| Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz 2012 [81] | Poland | LS | 30–32 | 3 | 23.0~29.2 | 25 | 25 | Yes | AM |
| Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicx 2012 [82] | Poland | CSS | 3–32 | 1, 3 | 22.0~32.6 | 49 | 98 | Yes | AM |
| Tijerina-Saenz 2009 [83] | Canada | CSS | 30 | 3 | 20~40 | 60 | 60 | No | NS |
| Tokusoglu 2008 [84] | Turkey | CSS | 60–90 | 3 | 20–40 | 92 | 92 | No | AM |
| Tomiya 2017 [85] | Brazil | RCT | 1 | 1 | 18~31 | 101 | 101 | NS | NS |
| Turner 2013 [86] | Bangladesh | RCT | 78–267 | 3 + 4 | 20~26 | 135 | 135 | Yes | NS |
| Vaisman 1985 [16] | Israel | CSS | 7~28 | 1, 3 | NA | 7 | 14 | Yes | random |
| Whitefield 2020 [87] | Cambodian | IS | 21–187 | 3 | 21.4~30.7 | 68 | 68 | Yes | NS |
| Zhang 2001 [89] | China | CSS | 1–90 | 1, 2, 3 | 21~31 | 365 | 365 | No | NS |
| Zhang 2021 [91] | China | CSS | 1–330 | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 22.2~30.4 | 923 | 923 | Yes | AM |
| Lactation Stage | Studies Enrolling Chinese Participants | Studies Enrolling Non-Chinese Participants | X2 | p | Total Studies | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Sample Size | Mean | 95% CI | No. | Sample Size | Mean | 95% CI | No. | Sample Size | Mean | 95% CI | |||
| Colostrum | 5 | 429 | 1039.1 | 470.3, 1607.8 | 22 | 1741 | 895.8 | 714.1, 1077.4 | 0.22 | 0.64 | 27 | 2170 | 920.7 | 744.5, 1096.8 |
| Transitional | 3 | 356 | 505.7 | 118.0, 893.4 | 3 | 363 | 542.2 | 278.9, 805.6 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 6 | 719 | 523.7 | 313.7, 733.6 |
| Mature | 7 | 1268 | 386.4 | 270.6, 502.3 | 53 | 5014 | 385.2 | 335.1, 435.3 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 59 | 6282 | 385.4 | 339.4, 431.3 |
| Early | 7 | 1112 | 408.4 | 282.6, 534.1 | 38 | 3221 | 401.2 | 333.6, 468.6 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 44 | 4333 | 402.4 | 342.5, 462.3 |
| Late | 1 | 156 | 240.0 | 214.9, 265.1 | 5 | 794 | 259.3 | 220.8, 297.8 | 0.68 | 0.41 | 6 | 950 | 254.7 | 223.7, 285.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Ren, X.; Yang, Z.; Lai, J. Vitamin A Concentration in Human Milk: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224844
Zhang H, Ren X, Yang Z, Lai J. Vitamin A Concentration in Human Milk: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(22):4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224844
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huanmei, Xiangnan Ren, Zhenyu Yang, and Jianqiang Lai. 2022. "Vitamin A Concentration in Human Milk: A Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 14, no. 22: 4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224844
APA StyleZhang, H., Ren, X., Yang, Z., & Lai, J. (2022). Vitamin A Concentration in Human Milk: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 14(22), 4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224844





